- Preface
- 1. Getting Started
- 2. Basic Concepts
- 2.1. Introduction
- 2.2. Basic Select
- 2.3. Basic Aggregation
- 2.4. Basic Filter
- 2.5. Basic Filter and Aggregation
- 2.6. Basic Data Window
- 2.7. Basic Data Window and Aggregation
- 2.8. Basic Filter, Data Window and Aggregation
- 2.9. Basic Where-Clause
- 2.10. Basic Time Window and Aggregation
- 2.11. Basic Partitioned Statement
- 2.12. Basic Output-Rate-Limited Statement
- 2.13. Basic Partitioned and Output-Rate-Limited Statement
- 2.14. Basic Named Windows and Tables
- 2.15. Basic Aggregated Statement Types
- 2.16. Basic Match-Recognize Patterns
- 2.17. Basic EPL Patterns
- 2.18. Basic Indexes
- 2.19. Basic Null
- 3. Event Representations
- 3.1. Event Underlying Java Objects
- 3.2. Event Properties
- 3.3. Dynamic Event Properties
- 3.4. Fragment and Fragment Type
- 3.5. Comparing Event Representations
- 3.6. Support for Generic Tuples
- 3.7. Updating, Merging and Versioning Events
- 3.8. Coarse-Grained Events
- 3.9. Event Objects Instantiated and Populated by Insert Into
- 3.10. Event Type Uniqueness
- 4. Context and Context Partitions
- 4.1. Introduction
- 4.2. Context Declaration
- 4.3. Context Nesting
- 4.4. Partitioning Without Context Declaration
- 4.5. Output When a Context Partition Starts (Non-Overlapping Context) or Initiates (Overlapping Context)
- 4.6. Output When a Context Partition Ends (Non-Overlapping Context) or Terminates (Overlapping Context)
- 4.7. Context and Named Window
- 4.8. Context and Tables
- 4.9. Context and Variables
- 4.10. Operations on Specific Context Partitions
- 5. EPL Reference: Clauses
- 5.1. EPL Introduction
- 5.2. EPL Syntax
- 5.2.1. Specifying Time Periods
- 5.2.2. Using Comments
- 5.2.3. Reserved Keywords
- 5.2.4. Escaping Strings
- 5.2.5. Data Types
- 5.2.6. Using Constants and Enum Types
- 5.2.7. Annotation
- 5.2.8. Expression Alias
- 5.2.9. Expression Declaration
- 5.2.10. Inlined-Class Declaration
- 5.2.11. Script Declaration
- 5.2.12. Referring to a Context
- 5.2.13. Composite Keys and Array Values as Keys
- 5.3. Choosing Event Properties and Events: The Select Clause
- 5.3.1. Choosing the Event Itself: Select *
- 5.3.2. Choosing Specific Event Properties
- 5.3.3. Expressions
- 5.3.4. Renaming Event Properties
- 5.3.5. Choosing Event Properties and Events in a Join
- 5.3.6. Choosing Event Properties and Events From a Pattern
- 5.3.7. Selecting Insert and Remove Stream Events
- 5.3.8. Select Distinct
- 5.3.9. Transposing an Expression Result to a Stream
- 5.3.10. Selecting EventBean Instead of Underlying Event
- 5.4. Specifying Event Streams: The From Clause
- 5.5. Specifying Search Conditions: The Where Clause
- 5.6. Aggregates and Grouping: The Group-By Clause and the Having Clause
- 5.6.1. Using Aggregate Functions
- 5.6.2. Organizing Statement Results into Groups: The Group-by Clause
- 5.6.3. Using Group-By with Rollup, Cube and Grouping Sets
- 5.6.4. Specifying Grouping for Each Aggregation Function
- 5.6.5. Specifying a Filter Expression for Each Aggregation Function
- 5.6.6. Selecting Groups of Events: The Having Clause
- 5.6.7. How the Stream Filter, Where, Group By and Having-Clauses Interact
- 5.6.8. Comparing Keyed Segmented Context, the Group By Clause and #groupwin for Data Windows
- 5.7. Stabilizing and Controlling Output: The Output Clause
- 5.8. Sorting Output: the Order By Clause
- 5.9. Limiting Row Count: the Limit Clause
- 5.10. Merging Streams and Continuous Insertion: The Insert Into Clause
- 5.10.1. Transposing a Property to a Stream
- 5.10.2. Merging Streams by Event Type
- 5.10.3. Merging Disparate Types of Events: Variant Streams
- 5.10.4. Decorated Events
- 5.10.5. Event as a Property
- 5.10.6. Instantiating and Populating an Underlying Event Object
- 5.10.7. Transposing an Expression Result
- 5.10.8. Select-Clause Expression and Inserted-Into Column Event Type
- 5.10.9. Insert Into for Event Types Without Properties
- 5.10.10. Insert Into and Event Precedence
- 5.11. Subqueries
- 5.12. Joining Event Streams
- 5.13. Accessing Relational Data via SQL
- 5.13.1. Joining SQL Query Results
- 5.13.2. SQL Query and the EPL Where Clause
- 5.13.3. Outer Joins With SQL Queries
- 5.13.4. Using Patterns to Request (Poll) Data
- 5.13.5. Polling SQL Queries via Iterator
- 5.13.6. JDBC Implementation Overview
- 5.13.7. Oracle Drivers and No-Metadata Workaround
- 5.13.8. SQL Input Parameter and Column Output Conversion
- 5.13.9. SQL Row POJO Conversion
- 5.13.10. Executing SQL Fire-and-Forget Queries Using EPFireAndForgetService
- 5.14. Accessing Non-Relational Data via Method, Script or UDF Invocation
- 5.15. Declaring an Event Type: Create Schema
- 5.16. Splitting and Duplicating Streams
- 5.17. Variables and Constants
- 5.18. Declaring Global Expressions, Aliases and Scripts: Create Expression
- 5.19. Contained-Event Selection
- 5.19.1. Select-Clause in a Contained-Event Selection
- 5.19.2. Where Clause in a Contained-Event Selection
- 5.19.3. Contained-Event Selection and Joins
- 5.19.4. Sentence and Word Example
- 5.19.5. More Examples
- 5.19.6. Contained Expression Returning an Array of Property Values
- 5.19.7. Contained Expression Returning an Array of EventBean
- 5.19.8. Contained Expression Returning a Collection of Underlying Event Objects
- 5.19.9. Generating Marker Events Such as a Begin and End Event
- 5.19.10. Contained-Event Limitations
- 5.20. Updating an Insert Stream: The Update IStream Clause
- 5.21. Controlling Event Delivery : The For Clause
- 6. EPL Reference: Named Windows and Tables
- 6.1. Overview
- 6.2. Named Window Usage
- 6.3. Table Usage
- 6.3.1. Creating Tables: The Create Table Clause
- 6.3.2. Aggregating Into Table Rows: The Into Table Clause
- 6.3.3. Table Column Keyed-Access Expressions
- 6.3.4. Inserting Into Tables
- 6.3.5. Selecting From Tables
- 6.3.6. Resetting Table Columns and Aggregation State
- 6.3.7. Initializing Table Columns and Aggregation State
- 6.4. Triggered Select: The On Select Clause
- 6.5. Triggered Select+Delete: The On Select Delete Clause
- 6.6. Updating Data: The On Update Clause
- 6.7. Deleting Data: The On Delete Clause
- 6.8. Triggered Upsert Using the On-Merge Clause
- 6.9. Explicitly Indexing Named Windows and Tables
- 6.10. Using Fire-and-Forget Queries With Named Windows and Tables
- 6.11. Events as Property
- 7. EPL Reference: Patterns
- 8. EPL Reference: Match Recognize
- 8.1. Overview
- 8.2. Comparison of Match Recognize and EPL Patterns
- 8.3. Syntax
- 8.4. Pattern and Pattern Operators
- 8.4.1. Operator Precedence
- 8.4.2. Concatenation
- 8.4.3. Alternation
- 8.4.4. Quantifiers Overview
- 8.4.5. Permutations
- 8.4.6. Variables Can Be Singleton or Group
- 8.4.7. Eliminating Duplicate Matches
- 8.4.8. Greedy or Reluctant
- 8.4.9. Quantifier - One or More (+ and +?)
- 8.4.10. Quantifier - Zero or More (* and *?)
- 8.4.11. Quantifier - Zero or One (? and ??)
- 8.4.12. Repetition - Exactly N Matches
- 8.4.13. Repetition - N or More Matches
- 8.4.14. Repetition - Between N and M Matches
- 8.4.15. Repetition - Between Zero and M Matches
- 8.4.16. Repetition Equivalence
- 8.5. Define Clause
- 8.6. Measure Clause
- 8.7. Datawindow-Bound
- 8.8. Interval
- 8.9. Interval-or-Terminated
- 8.10. Use With Different Event Types
- 8.11. Limiting Runtime-Wide State Count
- 8.12. Limitations
- 9. EPL Reference: Operators
- 9.1. Arithmetic Operators
- 9.2. Logical and Comparison Operators
- 9.3. Concatenation Operators
- 9.4. Binary Operators
- 9.5. Array Definition Operator
- 9.6. Array Element Operator
- 9.7. Dot Operator
- 9.8. The 'In' Keyword
- 9.9. The 'Between' Keyword
- 9.10. The 'Like' Keyword
- 9.11. The 'Regexp' Keyword
- 9.12. The 'Any' and 'Some' Keywords
- 9.13. The 'All' Keyword
- 9.14. The 'New' Keyword
- 10. EPL Reference: Functions
- 10.1. Single-Row Function Reference
- 10.1.1. The Case Control Flow Function
- 10.1.2. The Cast Function
- 10.1.3. The Coalesce Function
- 10.1.4. The Current_Evaluation_Context Function
- 10.1.5. The Current_Timestamp Function
- 10.1.6. The Event_Identity_Equals Function
- 10.1.7. The Exists Function
- 10.1.8. The Grouping Function
- 10.1.9. The Grouping_Id Function
- 10.1.10. The Instance-Of Function
- 10.1.11. The Istream Function
- 10.1.12. The Min and Max Functions
- 10.1.13. The Previous Function
- 10.1.14. The Previous-Tail Function
- 10.1.15. The Previous-Window Function
- 10.1.16. The Previous-Count Function
- 10.1.17. The Prior Function
- 10.1.18. The Type-Of Function
- 10.2. Aggregation Functions
- 10.3. User-Defined Functions
- 10.4. Select-Clause Transpose Function
- 11. EPL Reference: Enumeration Methods
- 11.1. Overview
- 11.2. Example Events
- 11.3. How to Use
- 11.4. Inputs
- 11.4.1. Subquery Results
- 11.4.2. Named Window
- 11.4.3. Table
- 11.4.4. Event Property and Insert-Into With @eventbean
- 11.4.5. Event Aggregation Function
- 11.4.6. Prev, Prevwindow and Prevtail Single-Row Functions as Input
- 11.4.7. Single-Row Function, User-Defined Function and Enum Types
- 11.4.8. Declared Expression
- 11.4.9. Variables
- 11.4.10. Substitution Parameters
- 11.4.11. Match-Recognize Group Variable
- 11.4.12. Pattern Repeat and Repeat-Until Operators
- 11.5. Example
- 11.6. Reference
- 11.6.1. Aggregate
- 11.6.2. AllOf
- 11.6.3. AnyOf
- 11.6.4. ArrayOf
- 11.6.5. Average
- 11.6.6. CountOf
- 11.6.7. DistinctOf
- 11.6.8. Except
- 11.6.9. FirstOf
- 11.6.10. GroupBy
- 11.6.11. Intersect
- 11.6.12. LastOf
- 11.6.13. LeastFrequent
- 11.6.14. Max
- 11.6.15. MaxBy
- 11.6.16. Min
- 11.6.17. MinBy
- 11.6.18. MostFrequent
- 11.6.19. OrderBy and OrderByDesc
- 11.6.20. Reverse
- 11.6.21. SelectFrom
- 11.6.22. SequenceEqual
- 11.6.23. SumOf
- 11.6.24. Take
- 11.6.25. TakeLast
- 11.6.26. TakeWhile
- 11.6.27. TakeWhileLast
- 11.6.28. ToMap
- 11.6.29. Union
- 11.6.30. Where
- 12. EPL Reference: Date-Time Methods
- 12.1. Overview
- 12.2. How to Use
- 12.3. Calendar and Formatting Reference
- 12.4. Interval Algebra Reference
- 12.4.1. Examples
- 12.4.2. Interval Algebra Parameters
- 12.4.3. Performance
- 12.4.4. Limitations
- 12.4.5. After
- 12.4.6. Before
- 12.4.7. Coincides
- 12.4.8. During
- 12.4.9. Finishes
- 12.4.10. Finished By
- 12.4.11. Includes
- 12.4.12. Meets
- 12.4.13. Met By
- 12.4.14. Overlaps
- 12.4.15. Overlapped By
- 12.4.16. Starts
- 12.4.17. Started By
- 13. EPL Reference: Aggregation Methods
- 13.1. Overview
- 13.2. How to Use
- 13.3. Aggregation Methods for Sorted Aggregations
- 13.3.1. Overview
- 13.3.2. Specifying Composite Keys
- 13.3.3. CeilingEvent, FloorEvent, HigherEvent, LowerEvent, GetEvent
- 13.3.4. CeilingEvents, FloorEvents, HigherEvents, LowerEvents, GetEvents
- 13.3.5. CeilingKey, FloorKey, HigherKey, LowerKey
- 13.3.6. FirstEvent, LastEvent, MinBy, MaxBy
- 13.3.7. FirstEvents, LastEvents
- 13.3.8. FirstKey, LastKey
- 13.3.9. ContainsKey
- 13.3.10. CountEvents
- 13.3.11. CountKeys
- 13.3.12. EventsBetween
- 13.3.13. Submap
- 13.3.14. NavigableMapReference
- 13.4. Aggregation Methods for Window Aggregations
- 13.5. Aggregation Methods for CountMinSketch Aggregations
- 13.6. Aggregation Methods for Custom Plug-In Multi-Function Aggregations
- 14. EPL Reference: Data Windows
- 14.1. A Note on Data Window Name and Parameters
- 14.2. A Note on Batch Windows
- 14.3. Data Windows
- 14.3.1. Length Window (length or win:length)
- 14.3.2. Length Batch Window (length_batch or win:length_batch)
- 14.3.3. Time Window (time or win:time)
- 14.3.4. Externally-timed Window (ext_timed or win:ext_timed)
- 14.3.5. Time batch Window (time_batch or win:time_batch)
- 14.3.6. Externally-timed Batch Window (ext_timed_batch or win:ext_timed_batch)
- 14.3.7. Time-Length Combination Batch Window (time_length_batch or win:time_length_batch)
- 14.3.8. Time-Accumulating Window (time_accum or win:time_accum)
- 14.3.9. Keep-All Window (keepall or win:keepall)
- 14.3.10. First Length Window(firstlength or win:firstlength)
- 14.3.11. First Time Window (firsttime or win:firsttime)
- 14.3.12. Expiry Expression Window (expr or win:expr)
- 14.3.13. Expiry Expression Batch Window (expr_batch or win:expr_batch)
- 14.3.14. Unique Window (unique or std:unique)
- 14.3.15. Grouped Data Window (groupwin or std:groupwin)
- 14.3.16. Last Event Window (std:lastevent)
- 14.3.17. First Event Window (firstevent or std:firstevent)
- 14.3.18. First Unique Window (firstunique or std:firstunique)
- 14.3.19. Sorted Window (sort or ext:sort)
- 14.3.20. Ranked Window (rank or ext:rank)
- 14.3.21. Time-Order Window (time_order or ext:time_order)
- 14.3.22. Time-To-Live Window (timetolive or ext:timetolive)
- 14.4. Special Derived-Value Windows
- 14.4.1. Size Derived-Value Window (size) or std:size)
- 14.4.2. Univariate Statistics Derived-Value Window (uni or stat:uni)
- 14.4.3. Regression Derived-Value Window (linest or stat:linest)
- 14.4.4. Correlation Derived-Value Window (correl or stat:correl)
- 14.4.5. Weighted Average Derived-Value Window (weighted_avg or stat:weighted_avg)
- 15. Compiler Reference
- 15.1. Introduction
- 15.2. Concepts
- 15.3. Compiling a Module
- 15.4. Reading and Writing a Compiled Module
- 15.5. Reading Module Content
- 15.6. Compiler Arguments
- 15.7. Statement Object Model
- 15.8. Substitution Parameters
- 15.9. OSGi, Class Loader, Class-For-Name
- 15.10. Authoring Tools
- 15.11. Testing Tools
- 15.12. Debugging
- 15.13. Ordering Multiple Modules
- 15.14. Logging
- 15.15. Debugging Generated Code
- 15.16. Compiler Version and Runtime Version
- 15.17. Compiler Byte Code Optimizations
- 15.18. Compiler Filter Expression Analysis
- 15.19. Limitations
- 16. Runtime Reference
- 16.1. Introduction
- 16.2. Obtaining a Runtime From EPRuntimeProvider
- 16.3. The EPRuntime Runtime Interface
- 16.4. Deploying and Undeploying Using EPDeploymentService
- 16.5. Obtaining Results Using EPStatement
- 16.6. Processing Events and Time Using EPEventService
- 16.7. Execute Fire-and-Forget Queries Using EPFireAndForgetService
- 16.8. Runtime Threading and Concurrency
- 16.9. Controlling Time-Keeping
- 16.10. Exception Handling
- 16.11. Condition Handling
- 16.12. Runtime and Statement Metrics Reporting
- 16.13. Monitoring and JMX
- 16.14. Event Rendering to XML and JSON
- 16.15. Plug-In Loader
- 16.16. Context Partition Selection
- 16.17. Context Partition Administration
- 16.18. Test and Assertion Support
- 16.19. OSGi, Class Loader, Class-For-Name
- 16.20. When Deploying with J2EE
- 16.21. Stages
- 17. Configuration
- 17.1. Overview
- 17.2. Programmatic Configuration
- 17.3. Configuration via XML File
- 17.4. Configuration Common
- 17.4.1. Annotation Class and Package Imports
- 17.4.2. Class and Package Imports
- 17.4.3. Events Represented by Classes
- 17.4.4. Events Represented by java.util.Map
- 17.4.5. Events Represented by Object[] (Object-array)
- 17.4.6. Events Represented by JSON
- 17.4.7. Events Represented by Avro GenericData.Record
- 17.4.8. Events Represented by org.w3c.dom.Node
- 17.4.9. Event Type Defaults
- 17.4.10. Event Type Import Package (Event Type Auto-Name)
- 17.4.11. From-Clause Method Invocation
- 17.4.12. Relational Database Access
- 17.4.13. Common Settings Related to Logging
- 17.4.14. Common Settings Related to Time Source
- 17.4.15. Variables
- 17.4.16. Variant Stream
- 17.5. Configuration Compiler
- 17.5.1. Compiler Settings Related to Byte Code Generation
- 17.5.2. Compiler Settings Related to View Resources
- 17.5.3. Compiler Settings Related to Logging
- 17.5.4. Compiler Settings Related to Stream Selection
- 17.5.5. Compiler Settings Related to Language and Locale
- 17.5.6. Compiler Settings Related to Expression Evaluation
- 17.5.7. Compiler Settings Related to Scripts
- 17.5.8. Compiler Settings Related to Execution of Statements
- 17.5.9. Compiler Settings Related to Serializers and Deserializers
- 17.6. Configuration Runtime
- 17.6.1. Runtime Settings Related to Concurrency and Threading
- 17.6.2. Runtime Settings Related to Logging
- 17.6.3. Runtime Settings Related to Variables
- 17.6.4. Runtime Settings Related to Patterns
- 17.6.5. Runtime Settings Related to Match-Recognize
- 17.6.6. Runtime Settings Related to Time Source
- 17.6.7. Runtime Settings Related to JMX Metrics
- 17.6.8. Runtime Settings Related to Metrics Reporting
- 17.6.9. Runtime Settings Related to Expression Evaluation
- 17.6.10. Runtime Settings Related to Execution of Statements
- 17.6.11. Runtime Settings Related to Exception Handling
- 17.6.12. Runtime Settings Related to Condition Handling
- 17.7. Passing Services or Transient Objects
- 17.8. Type Names
- 17.9. Logging Configuration
- 18. Inlined Classes
- 19. Script Support
- 20. EPL Reference: Spatial Methods and Indexes
- 20.1. Overview
- 20.2. Spatial Methods
- 20.3. Spatial Index - Quadtree
- 20.3.1. Overview
- 20.3.2. Declaring a Point-Region Quadtree Index
- 20.3.3. Using a Point-Region Quadtree as a Filter Index
- 20.3.4. Using a Point-Region Quadtree as an Event Index
- 20.3.5. Declaring a MX-CIF Quadtree Index
- 20.3.6. Using a MX-CIF Quadtree as a Filter Index
- 20.3.7. Using a MX-CIF Quadtree as an Event Index
- 20.4. Spatial Types, Functions and Methods from External Libraries
- 21. EPL Reference: Data Flow
- 22. Integration and Extension
- 22.1. Overview
- 22.2. Single-Row Function
- 22.2.1. Using an Inlined Class to Provide a Single-Row Function
- 22.2.2. Using an Application Class to Provide a Single-Row Function
- 22.2.3. Value Cache
- 22.2.4. Single-Row Functions in Filter Predicate Expressions
- 22.2.5. Single-Row Functions Taking Events as Parameters
- 22.2.6. Single-Row Functions Returning Events
- 22.2.7. Receiving a Context Object
- 22.2.8. Exception Handling
- 22.3. Virtual Data Window
- 22.4. Data Window View and Derived-Value View
- 22.5. Aggregation Function
- 22.6. Pattern Guard
- 22.7. Pattern Observer
- 22.8. Date-Time Method
- 22.9. Enumeration Method
- 22.9.1. Implement the EnumMethodForgeFactory Interface
- 22.9.2. Implement the EnumMethodState Interface
- 22.9.3. Implement the Static Method for Processing
- 22.9.4. Add the Enumeration Method Extension to the Compiler Configuration
- 22.9.5. Use the new Enumeration Method
- 22.9.6. Further Information to Lambda Parameters
- 23. Examples, Tutorials, Case Studies
- 23.1. Examples Overview
- 23.2. Running the Examples
- 23.3. AutoID RFID Reader
- 23.4. Runtime Configuration
- 23.5. JMS Server Shell and Client
- 23.6. Market Data Feed Monitor
- 23.7. OHLC Plug-In Data Window
- 23.8. Transaction 3-Event Challenge
- 23.9. Self-Service Terminal
- 23.10. Assets Moving Across Zones - An RFID Example
- 23.11. StockTicker
- 23.12. MatchMaker
- 23.13. Named Window Query
- 23.14. Sample Virtual Data Window
- 23.15. Sample Cycle Detection
- 23.16. Quality of Service
- 23.17. Trivia Geeks Club
- 24. Performance
- 24.1. Big O Notation
- 24.1.1. Big-O Complexity of Matching Events to Statements and Context Partitions
- 24.1.2. Big-O Complexity of Matching Time to Statements and Context Partitions
- 24.1.3. Big-O Complexity of Joins, Subqueries, On-Select, On-Merge, On-Update, On-Delete
- 24.1.4. Big-O Complexity of Enumeration Methods
- 24.1.5. Big-O Complexity of Aggregation Methods
- 24.2. Performance Tips
- 24.2.1. Understand How to Tune Your Java Virtual Machine
- 24.2.2. Input and Output Bottlenecks
- 24.2.3. Threading
- 24.2.4. Select the Underlying Event Rather Than Individual Fields
- 24.2.5. Prefer Stream-Level Filtering Over Where-Clause Filtering
- 24.2.6. Reduce the Use of Arithmetic in Expressions
- 24.2.7. Remove Unneccessary Constructs
- 24.2.8. End Pattern Sub-Expressions
- 24.2.9. Consider Using EventPropertyGetter for Fast Access to Event Properties
- 24.2.10. Consider Casting the Underlying Event
- 24.2.11. Turn Off Logging and Audit
- 24.2.12. Tune or Disable Delivery Order Guarantees
- 24.2.13. Use a Subscriber Object to Receive Events
- 24.2.14. Consider Data Flows
- 24.2.15. High-Arrival-Rate Streams and Single Statements
- 24.2.16. Subqueries Versus Joins and Where-Clause and Data Windows
- 24.2.17. Patterns and Pattern Sub-Expression Instances
- 24.2.18. Pattern Sub-Expression Instance Versus Data Window Use
- 24.2.19. The Keep-All Data Window
- 24.2.20. Statement Design for Reduced Memory Consumption - Diagnosing OutOfMemoryError
- 24.2.21. Performance, JVM, OS and Hardware
- 24.2.22. Consider Using Hints
- 24.2.23. Optimizing Stream Filter Expressions
- 24.2.24. Statement and Runtime Metric Reporting
- 24.2.25. Expression Evaluation Order and Early Exit
- 24.2.26. Large Number of Threads
- 24.2.27. Filter Evaluation Tuning
- 24.2.28. Context Partition Related Information
- 24.2.29. Prefer Constant Variables Over Non-Constant Variables
- 24.2.30. Prefer POJO Events or alternatively Object-Array Events
- 24.2.31. Notes on Query Planning
- 24.2.32. Query Planning Expression Analysis Hints
- 24.2.33. Query Planning Index Hints
- 24.2.34. Measuring Throughput
- 24.2.35. Do Not Create the Same or Similar Statement X Times
- 24.2.36. Comparing Single-Threaded and Multi-Threaded Performance
- 24.2.37. Incremental Versus Recomputed Aggregation for Named Window Events
- 24.2.38. When Does Memory Get Released
- 24.2.39. Measure Throughput of Non-Matches as Well as Watches
- 24.2.40. Options for When an Event Type has a Large Number of Event Properties i.e. Large Events
- 24.3. Using the Performance Kit
- 25. References
- A. Output Reference and Samples
- A.1. Introduction and Sample Data
- A.2. Output for Un-Aggregated and Un-Grouped Statements
- A.3. Output for Fully-Aggregated and Un-Grouped Statements
- A.4. Output for Aggregated and Un-Grouped Statements
- A.5. Output for Fully-Aggregated and Grouped Statements
- A.6. Output for Aggregated and Grouped Statements
- A.7. Output for Fully-Aggregated, Grouped Statements With Rollup
- B. Runtime Considerations for Output Rate Limiting
- C. Reserved Keywords
- D. Event Representation: Plain-Old Java Object Events
- E. Event Representation: java.util.Map Events
- F. Event Representation: Object-Array (Object[]) Events
- G. Event Representation: JSON Events
- G.1. Overview
- G.2. JSON Event Type
- G.3. JSON Object Nesting
- G.4. JSON Supported Types
- G.5. JSON Application-Provided Class
- G.6. JSON Dynamic Event Properties
- G.7. API for Parsing JSON Documents
- G.8. API for Building JSON Documents
- G.9. Customizing JSON Serializing and Deserializing
- G.10. Customizing the JSON Event Class
- G.11. Limitations
- H. Event Representation: Avro Events (org.apache.avro.generic.GenericData.Record)
- H.1. Overview
- H.2. Avro Event Type
- H.3. Avro Schema Name Requirement
- H.4. Avro Field Schema to Property Type Mapping
- H.5. Primitive Data Type and Class to Avro Schema Mapping
- H.6. Customizing Avro Schema Assignment
- H.7. Customizing Class-to-Avro Schema
- H.8. Customizing Object-to-Avro Field Value Assignment
- H.9. API Examples
- H.10. Limitations
- I. Event Representation: org.w3c.dom.Node XML Events
- J. NEsper .NET -Specific Information
- J.1. .NET General Information
- J.2. .NET and Annotations
- J.3. .NET and Locks and Concurrency
- J.4. .NET and Threading
- J.5. .NET and Timer
- J.6. .NET NEsper Configuration
- J.7. .NET Event Underlying Objects
- J.8. .NET Object Events
- J.9. .NET IDictionary Events
- J.10. .NET XML Events
- J.11. .NET Event Objects Instantiated and Populated by Insert Into
- J.12. .NET Basic Concepts
- J.13. .NET EPL Syntax - Data Types
- J.14. .NET Accessing Relational Data via SQL
- J.15. .NET API - Receiving Statement Results
- J.16. .NET API - Adding Listeners
- J.17. .NET Configurations - Relational Database Access
- J.18. .NET Configurations - Logging Configuration
- Index
Analyzing and reacting to information in real-time oftentimes requires the development of custom applications. Typically these applications must obtain the data to analyze, filter data, derive information and then indicate this information through some form of presentation or communication. Data may arrive with high frequency requiring high throughput processing. And applications may need to be flexible and react to changes in requirements while the data is processed. Esper is an event stream processor that aims to enable a short development cycle from inception to production for these types of applications.
This document is a resource for software developers who develop event driven applications. It also contains information that is useful for business analysts and system architects who are evaluating Esper.
It is assumed that the reader is familiar with the Java programming language.
For NEsper .NET the reader is is familiar with the C# programming language. For NEsper .NET, please also review Appendix J, NEsper .NET -Specific Information.
This document is relevant in all phases of your software development project: from design to deployment and support.
If you are new to Esper, please follow these steps:
Read the tutorials, case studies and solution patterns available on the Esper public web site at
http://www.espertech.com/esperRead Chapter 1, Getting Started if you are new to CEP and streaming analytics
Read Chapter 2, Basic Concepts to gain insight into EPL basic concepts
Read Chapter 3, Event Representations that explains the different ways of representing events to Esper
Read Section 5.1, “EPL Introduction” for an introduction to event stream processing via EPL
Read Section 7.1, “Event Pattern Overview” for an overview over event patterns
Read Section 8.1, “Overview” for an overview over event patterns using the match recognize syntax.
Then glance over the examples Section 23.1, “Examples Overview”
Finally to test drive Esper performance, read Chapter 24, Performance
The Esper compiler and runtime have been developed to address the requirements of applications that analyze and react to events. Some typical examples of applications are:
Business process management and automation (process monitoring, BAM, reporting exceptions)
Finance (algorithmic trading, fraud detection, risk management)
Network and application monitoring (intrusion detection, SLA monitoring)
Sensor network applications (RFID reading, scheduling and control of fabrication lines, air traffic)
What these applications have in common is the requirement to process events (or messages) in real-time or near real-time. This is sometimes referred to as complex event processing (CEP) and event series analysis. Key considerations for these types of applications are throughput, latency and the complexity of the logic required.
High throughput - applications that process large volumes of messages (between 1,000 to 100k messages per second)
Low latency - applications that react in real-time to conditions that occur (from a few milliseconds to a few seconds)
Complex computations - applications that detect patterns among events (event correlation), filter events, aggregate time or length windows of events, join event series, trigger based on absence of events etc.
The EPL compiler and runtime were designed to make it easier to build and extend CEP applications.
More information on CEP can be found at FAQ.
Esper is a language, a language compiler and a runtime environment.
The Esper language is the Event Processing Language (EPL). It is a declarative, data-oriented language for dealing with high frequency time-based event data. EPL is compliant to the SQL-92 standard and extended for analyzing series of events and in respect to time.
The Esper compiler compiles EPL source code into Java Virtual Machine (JVM) bytecode so that the resulting executable code runs on a JVM within the Esper runtime environment.
The Esper runtime runs on top of a JVM. You can run byte code produced by the Esper compiler using the Esper runtime.
The Esper architecture is similar to that of other programming languages that are compiled to JVM bytecode, such as Scala, Clojure and Kotlin for example. Esper EPL however is not an imperative (procedural) programming language.
The Esper language is the Event Processing Language (EPL) designed for Complex Event Processing and Streaming Analytics.
EPL is organized into modules. Modules are compiled into byte code by the compiler. We use the term module for an EPL source code unit.
A module consists of statements. Statements are the declarative code for performing event and time analysis. Most statements are in the form of "select ... from ...".
We use the term statement for each unit of declarative code that makes up a module.
Your application receives output from statements via callback or by iterating current results of a statement.
A statement can declare an EPL-object such as listed below:
Event types define stream type information and are added using
create schemaor by configuration.Variables are free-form value holders and are added using
create variableor by configuration.Named windows are sharable named data windows and are added using
create window.Tables are sharable organized rows with columns that are simple, aggregation and complex types, and are added using
create table.Contexts define analysis lifecycle and are added using
create context.Expressions and Scripts are reusable expressions and are added using
create expression.Indexes organize named window events and table rows for fast lookup and are added using
create index.
Use access modifiers such as private, protected and public to control access to EPL-objects.
A module can optionally have a module name. The module name has a similar use as the package name or namespace name in a programming language. A module name is used to organize EPL objects and to avoid name conflicts.
When deploying a compiled module the runtime assigns a deployment id to the deployment. The deployment id uniquely identifies a given deployment of a compiled module. A compiled module can be parameterized and deployed multiple times.
A statement always has a statement name. The statement name identifies a statement within a deployed module and is unique within a deployment. The combination of deployment id and statement name uniquely identifies a statement within a runtime.
EPL is type-safe in that EPL does not allow performing an operation on an object that is invalid for that object.
Please add the Esper compiler jar file, the common jar file and the compiler dependencies to the classpath of the program that will be compiling EPL.
The jar files listed here are not required for the runtime except for esper-common-version.jar.
Common jar file
esper-common-version.jarCompiler jar file
esper-compiler-version.jarANTLR parser jar file
antlr4-runtime-4.7.2.jarSLF4J logging library
slf4j-api-1.7.26.jarJanino Java compiler
janino-3.1.0.jarandcommons-compiler-3.1.0.jar
Optionally, for logging using Log4j, please add slf4j-log4j12-1.7.26.jar and log4j-1.2.17.jar to the classpath.
There are no additional jar files required by Esper for using Esper with JSON-formatted event documents.
Optionally, for using Apache Avro, please add esper-common-avro-version.jar to the classpath.
Optionally, for using XML XSD schemas for event types, please add esper-common-xmlxsd-version.jar to the classpath.
Your application can register an event type to instruct the compiler what the input events look like. When compiling modules the compiler checks the available event type information to determine that the module is valid.
This example assumes that there is a Java class PersonEvent and each instance of the PersonEvent class is an event.
Tip
It is not necessary to create classes for each event type.
It is not necessary to preconfigure each event type. It is not necessary to set up a Configuration object.
This step-by-step keeps it simple to get you started.
Our event class for the step-by-step is:
package com.mycompany.myapp;
public class PersonEvent {
private String name;
private int age;
public PersonEvent(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
}The different event representations are discussed at Section 3.5, “Comparing Event Representations”.
For declaring event types using EPL with create schema, see Section 5.15, “Declaring an Event Type: Create Schema”.
Your application can obtain a compiler calling the getCompiler static method of the EPCompilerProvider class:
EPCompiler compiler = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler();
The step-by-step provides a Configuration object to the compiler that adds the predefined person event:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); configuration.getCommon().addEventType(PersonEvent.class);
The sample module for this getting-started section simply has one statement that selects the name and the age of each arriving person event.
It specifies a statement name using the @name annotation and assigns a name my-statement to the statement.
@name('my-statement') select name, age from PersonEvent
Compile a module by using the compile method passing the configuration as part of the compiler arguments:
CompilerArguments args = new CompilerArguments(configuration);
EPCompiled epCompiled;
try {
epCompiled = compiler.compile("@name('my-statement') select name, age from PersonEvent", args);
}
catch (EPCompileException ex) {
// handle exception here
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
Upon compiling this module, the compiler verifies that PersonEvent exists since it is listed in the from-clause.
The compiler also verifies that the name and age properties are available for the PersonEvent since they are listed in the select-clause.
The compiler generates byte code for extracting property values and producing output events.
The compiler builds internal data structures for later use by filter indexes to ensure that when a PersonEvent comes in it will be processed fast.
More information on the compile API can be found at Chapter 15, Compiler Reference and the JavaDoc.
Please add the Esper common jar file, the runtime jar file and the runtime dependencies to the classpath of the program that will be executing compiled modules. The runtime jar file is not required for the compiler.
Common jar file
esper-common-version.jarRuntime jar file
esper-runtime-version.jarSLF4J logging library
slf4j-api-1.7.25.jar
Optionally, for logging using Log4j, please add slf4j-log4j12-1.7.25.jar and log4j-1.2.17.jar to the classpath.
There are no additional jar files required by Esper for using Esper with JSON-formatted event documents.
Optionally, for using Apache Avro, please add esper-common-avro-version.jar to the classpath.
Optionally, for using XML XSD schemas for event types, please add esper-common-xmlxsd-version.jar to the classpath.
The step-by-step provides a Configuration object to the runtime that adds the predefined person event:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); configuration.getCommon().addEventType(PersonEvent.class);
Tip
It is not necessary to preconfigure each event type. It is not necessary to set up a Configuration object.
For this example however since the compiler knows PersonEvent as a predefined type and it must this be preconfigured for the runtime as well.
Your application can obtain a runtime by calling the getDefaultRuntime static method of the EPRuntimeProvider class and passing the configuration:
EPRuntime runtime = EPRuntimeProvider.getDefaultRuntime(configuration);
More information about the runtime can be found at Chapter 16, Runtime Reference and the JavaDoc.
More information about configuration can be found at Chapter 17, Configuration and the JavaDoc.
Your application can deploy a compiled module using the deploy method of the administrative interface.
The API calls are:
EPDeployment deployment;
try {
deployment = runtime.getDeploymentService().deploy(epCompiled);
}
catch (EPDeployException ex) {
// handle exception here
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
As part of deployment, the runtime verifies that all module dependencies, such as event types, do indeed exist.
During deployment the runtime adds entries to filter indexes to ensure that when a PersonEvent comes in it will be processed fast.
Your application can attach a callback to the EPStatement to receive statement results. The following sample callback simply prints name and age:
EPStatement statement = runtime.getDeploymentService().getStatement(deployment.getDeploymentId(), "my-statement");
statement.addListener( (newData, oldData, statement, runtime) -> {
String name = (String) newData[0].get("name");
int age = (int) newData[0].get("age");
System.out.println(String.format("Name: %s, Age: %d", name, age));
});Your application can provide different kinds of callbacks, see Table 16.2, “Choices For Receiving Statement Results”.
Your application can send events into the runtime using the sendEventBean method (or other sendEvent method matching your choice of event) that is part of the runtime interface:
runtime.getEventService().sendEventBean(new PersonEvent("Peter", 10), "PersonEvent");The output you should see is:
Name: Peter, Age: 10
Upon sending the PersonEvent event object to the runtime, the runtime consults the internally-maintained shared filter index tree structure to determine if any statement is interested in PersonEvent events.
The statement that was deployed as part of this example has PersonEvent in the from-clause, thus the runtime delegates processing of such events to the statement.
The compiled bytecode obtains the name and age properties by calling the getName and getAge methods.
The compiler and runtime both require the following 3rd-party libraries:
SLF4J is a logging API that can work together with LOG4J and other logging APIs. While SLF4J is required, the LOG4J log component is not required and can be replaced with other loggers. SLF4J is licensed under Apache 2.0 license as provided in
lib/esper_3rdparties.license.
The compiler requires the following 3rd-party libraries for compiling only (and not at runtime):
ANTLR is the parser generator used for parsing and parse tree walking of the pattern and EPL syntax. Credit goes to Terence Parr at http://www.antlr.org. The ANTLR license is a BSD license and is provided in
lib/esper_3rdparties.license. Theantlr-runtimeruntime library is required for runtime.Janino is a small and fast Java compiler. The compiler generates code and compiles generated code using Janino. Janino is licensed under 3-clause New BSD License as provided in
lib/esper_3rdparties.license.
- 2.1. Introduction
- 2.2. Basic Select
- 2.3. Basic Aggregation
- 2.4. Basic Filter
- 2.5. Basic Filter and Aggregation
- 2.6. Basic Data Window
- 2.7. Basic Data Window and Aggregation
- 2.8. Basic Filter, Data Window and Aggregation
- 2.9. Basic Where-Clause
- 2.10. Basic Time Window and Aggregation
- 2.11. Basic Partitioned Statement
- 2.12. Basic Output-Rate-Limited Statement
- 2.13. Basic Partitioned and Output-Rate-Limited Statement
- 2.14. Basic Named Windows and Tables
- 2.15. Basic Aggregated Statement Types
- 2.16. Basic Match-Recognize Patterns
- 2.17. Basic EPL Patterns
- 2.18. Basic Indexes
- 2.19. Basic Null
For NEsper .NET also see Section J.12, “.NET Basic Concepts”.
Statements are continuous queries that analyze events and time and that detect situations.
You interact with Esper by compiling and deploying modules that contain statements, by sending events and advancing time and by receiving output by means of callbacks or by polling for current results.
Table 2.1. Interacting With Esper
| What | How |
|---|---|
| EPL | First, compile and deploy statements, please refer to Chapter 5, EPL Reference: Clauses,Chapter 15, Compiler Reference and Chapter 16, Runtime Reference. |
| Callbacks | Second, attach executable code that your application provides to receive output, please refer to Table 16.2, “Choices For Receiving Statement Results”. |
| Events | Next, send events using the runtime API, please refer to Section 16.6, “Processing Events and Time Using EPEventService”. |
| Time | Next, advance time using the runtime API or system time, please refer to Section 16.9, “Controlling Time-Keeping”. |
The runtime contains statements like so:
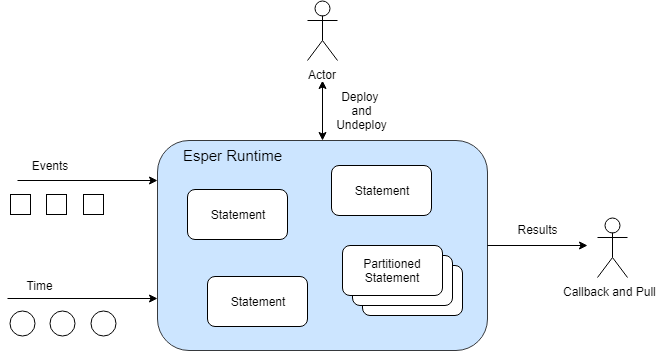
Statements can be partitioned. A partitioned statement can have multiple partitions. For example, there could be partition for each room in a building. For a building with 10 rooms you could have one statement that has 10 partitions. Please refer to Chapter 4, Context and Context Partitions.
A statement that is not partitioned implicitly has one partition. Upon deploying the un-partitioned statement the runtime allocates the single partition. Upon undeploying the un-partitioned statement the runtime destroys the partition.
A partition (or context partition) is where the runtime keeps the state. In the picture above there are three un-partitioned statement and one partitioned statement that has three partitions.
The next sections discuss various easily-understood statements.
The sections illustrate how statements behave, the information that the runtime passes to callbacks (the output) and what information the runtime remembers for statements (the state, all state lives in a partition).
The sample statements assume an event type by name Withdrawal that has account and amount properties.
This statement selects all Withdrawal events.
select * from Withdrawal
Upon a new Withdrawal event arriving, the runtime passes the arriving event, unchanged and the same object reference, to callbacks.
After that the runtime effectively forgets the current event.
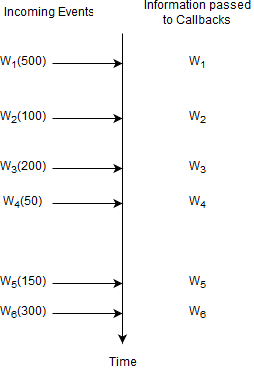
The diagram below shows a series of Withdrawal events (1 to 6) arriving over time.
In the picture the Wn stands for a specific Withdrawal event arriving. The number in parenthesis is the withdrawal amount.
For this statement, the runtime remembers no information and does not remember any events. A statement where the runtime does not need to remember any information at all is a statement without state (a stateless statement).
The term insert stream is a name for the stream of new events that are arriving. The insert stream in this example is the stream of arriving Withdrawal events.
An aggregation function is a function that groups multiple events together to form a single value. Please find more information at Section 10.2, “Aggregation Functions”.
This statement selects a count and a total amount of all Withdrawal events.
select count(*), sum(amount) from Withdrawal
Upon a new Withdrawal event arriving, the runtime increments the count and adds the amount to a running total. It passes the new count and total to callbacks.
After that the runtime effectively forgets the current event and does not remember any events at all, but does remember the current count and total.
Here, the runtime only remembers the current number of events and the total amount.
The count is a single long-type value and the total is a single double-type value (assuming amount is a double-value, the total can be BigDecimal as applicable).
This statement is not stateless and the state consists of a long-typed value and a double-typed value.
Upon a new Withdrawal event arriving, the runtime increases the count by one and adds the amount to the running total. the runtime does not re-compute the count and total because it does not remember events.
In general, the runtime does not re-compute aggregations (unless otherwise indicated). Instead, the runtime adds (increments, enters, accumulates) data to aggregation state and subtracts (decrements, removes, reduces, decreases) from aggregation state.
Place filter expressions in parenthesis after the event type name. For further information see Section 5.4.1, “Filter-Based Event Streams”.
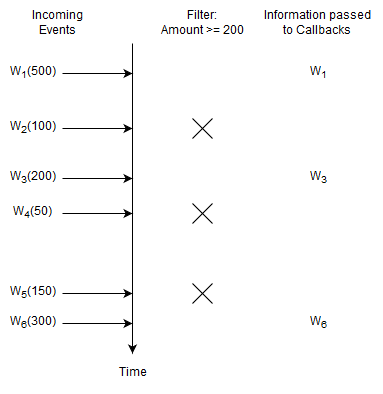
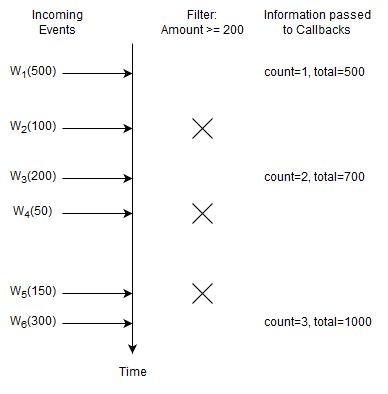
This statement selects Withdrawal events that have an amount of 200 or higher:
select * from Withdrawal(amount >= 200)
Upon a new Withdrawal event with an amount of 200 or higher arriving, the runtime passes the arriving event to callbacks.
For this statement, the runtime remembers no information and does not remember any events.
You may ask what happens for Withdrawal events with an amount of less than 200. The answer is that the statement itself does not even see such events. This is because the runtime knows to discard such events right away
and the statement does not even know about such events. The runtime discards unneeded events very fast enabled by statement analysis, planning and suitable data structures.
This statement selects the count and the total amount for Withdrawal events that have an amount of 200 or higher:
select count(*), sum(amount) from Withdrawal(amount >= 200)
Upon a new Withdrawal event with an amount of 200 or higher arriving, the runtime increments the count and adds the amount to the running total. The runtime passes the count and total to callbacks.
In this example the runtime only remembers the count and total and again does not remember events. The runtime discards Withdrawal events with an amount of less than 200.
A data window, or window for short, retains events for the purpose of aggregation, join, match-recognize patterns, subqueries, iterating via API and output-snapshot. A data window defines which subset of events to retain. For example, a length window keeps the last N events and a time window keeps the last N seconds of events. See Chapter 14, EPL Reference: Data Windows for details.
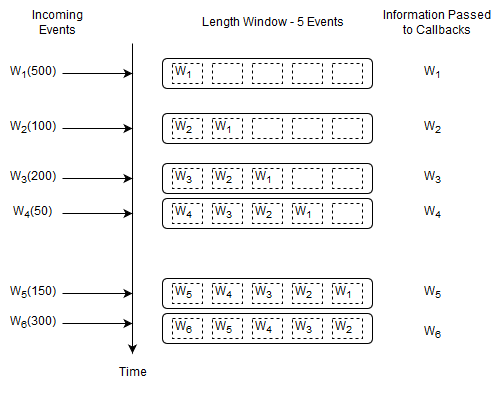
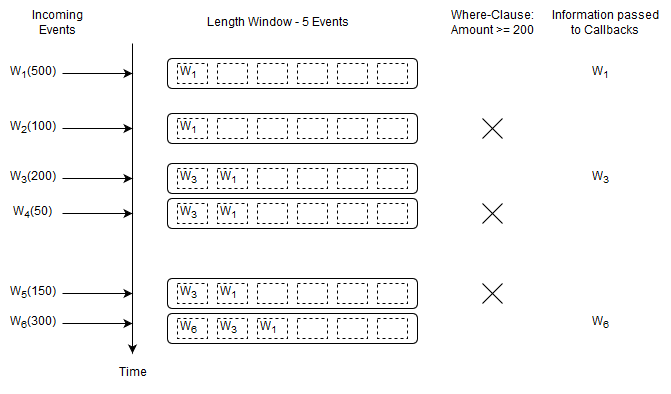
This statement selects all Withdrawal events and instructs the runtime to remember the last five events.
select * from Withdrawal#length(5)
Upon a new Withdrawal event arriving, the runtime adds the event to the length window. It also passes the same event to callbacks.
Upon arrival of event W6, event W1 leaves the length window. We use the term expires to say that an event leaves a data window. We use the term remove stream to describe the stream of events leaving a data window.
The runtime remembers up to five events in total (the last five events). At the start of the statement the data window is empty. By itself, keeping the last five events may not sound useful. But in connection with a join, subquery or match-recognize pattern for example a data window tells the runtime which events you want to query.
Note
By default the runtime only delivers the insert stream to listeners and observers. EPL supports optionalistream, irstream and rstream keywords for select- and insert-into clauses to control which streams to deliver, see Section 5.3.7, “Selecting Insert and Remove Stream Events”.
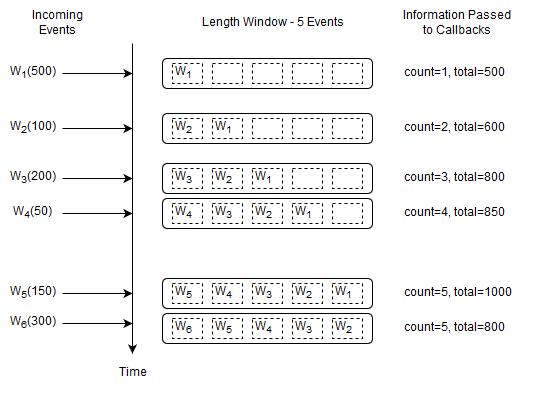
This statement outputs the count and total of the last five Withdrawal events.
select count(*), sum(amount) from Withdrawal#length(5)
Upon a new Withdrawal event arriving, the runtime adds the event to the length window, increases the count by one and adds the amount to the current total amount.
Upon a Withdrawal event leaving the data window, the runtime decreases the count by one and subtracts its amount from the current total amount.
It passes the running count and total to callbacks.
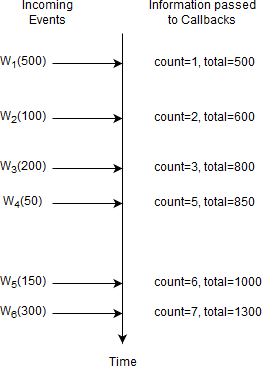
Before the arrival of event W6 the current count is five and the running total amount is 1000. Upon arrival of event W6 the following takes place:
The runtime determines that event W1 leaves the length window.
To account for the new event W6, the runtime increases the count by one and adds 300 to the running total amount.
To account for the expiring event W1, the runtime decreases the count by one and subtracts 500 from the running total amount.
The output is a count of five and a total of 800 as a result of
1000 + 300 - 500.
The runtime adds (increments, enters, accumulates) insert stream events into aggregation state and subtracts (decrements, removes, reduces, decreases) remove stream events from aggregation state. It thus maintains aggregation state in an incremental fashion.
For this statement, once the count reaches 5, the count will always remain at 5.
The information that the runtime remembers for this statement is the last five events and the current long-typed count and double-typed total.
Tip
Use the irstream keyword to receive both the current as well as the previous aggregation value for aggregating statements.
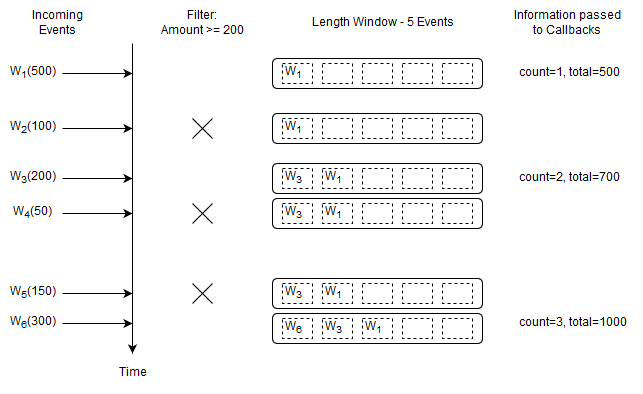
The following statement outputs the count and total of the last five Withdrawal events considering only those Withdrawal events that have an amount of at least 200:
select count(*), sum(amount) from Withdrawal(amount>=200)#length(5)
Upon a new Withdrawal event arriving, and only if that Withdrawal event has an amount of 200 or more, the runtime adds the event to the length window, increases the count by one and adds the amount to the current total amount.
Upon a Withdrawal event leaving the data window, the runtime decreases the count by one and subtracts its amount from the current total amount.
It passes the running count and total to callbacks.
For statements without a data window, the where-clause behaves the same as the filter expressions that are placed in parenthesis.
The following two statements are fully equivalent because of the absence of a data window (the .... means any select-clause expressions):
select .... from Withdrawal(amount > 200) // equivalent to select .... from Withdrawal where amount > 200
Note
In EPL, the where-clause is typically used for correlation in a join or subquery. Filter expressions should be placed right after the event type name in parenthesis.
The next statement applies a where-clause to Withdrawal events. Where-clauses are discussed in more detail in Section 5.5, “Specifying Search Conditions: The Where Clause”.
select * from Withdrawal#length(5) where amount >= 200
The where-clause applies to both new events and expiring events. Only events that pass the where-clause are passed to callbacks.
A time window is a data window that extends the specified time interval into the past. More information on time windows can be found at Section 14.3.3, “Time Window (time or win:time)”.
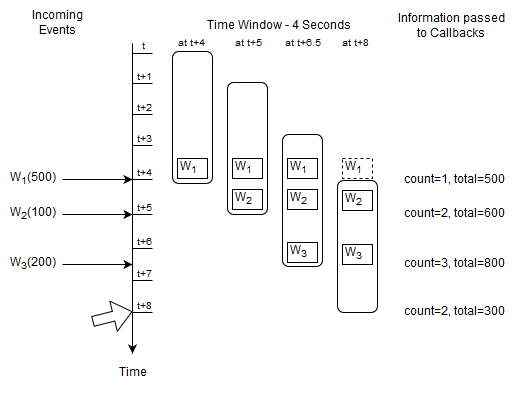
The next statement selects the count and total amount of Withdrawal events considering the last four seconds of events.
select count(*), sum(amount) as total from Withdrawal#time(4)
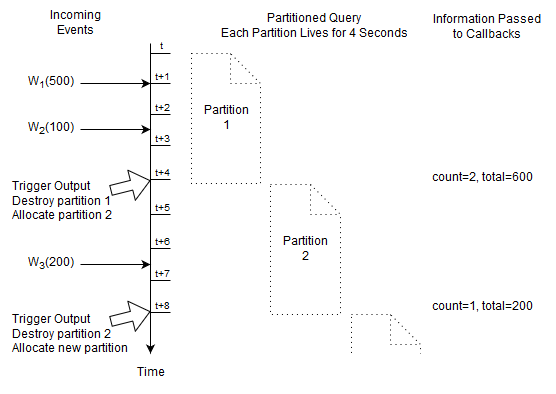
The diagram starts at a given time t and displays the contents of the time window at t + 4 and t + 5 seconds and so on.
The activity as illustrated by the diagram:
At time
t + 4 secondsan eventW1arrives and the output is a count of one and a total of 500.At time
t + 5 secondsan eventW2arrives and the output is a count of two and a total of 600.At time
t + 6.5 secondsan eventW3arrives and the output is a count of three and a total of 800.At time
t + 8 secondseventW1expires and the output is a count of two and a total of 300.
For this statement the runtime remembers the last four seconds of Withdrawal events as well as the long-typed count and the double-typed total amount.
Tip
Time can have a millisecond or microsecond resolution.
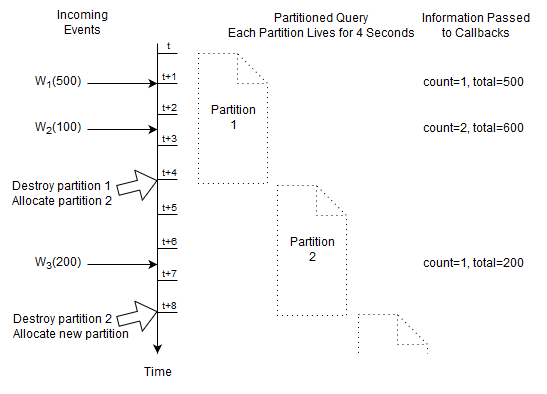
The statements discussed so far are not partitioned. A statement that is not partitioned implicitly has one partition. Upon deploying the un-partitioned statement the runtime allocates the single partition and it destroys the partition when your application undeploys the statement.
A partitioned statement is handy for batch processing, sessions, resetting and start/stop of your analysis. For partitioned statements you must specify a context. A context defines how partitions are allocated and destroyed. Additional information about partitioned statements and contexts can be found at Chapter 4, Context and Context Partitions.
We shall have a single partition that starts immediately and ends after four seconds:
create context Batch4Seconds start @now end after 4 sec
The next statement selects the count and total amount of Withdrawal events that arrived since the last reset (resets are at t, t+4, t+8 as so on), resetting each four seconds:
context Batch4Seconds select count(*), total(amount) from Withdrawal
At time t + 4 seconds and t + 8 seconds the runtime destroys the current partition. This discards the current count and running total.
The runtime immediately allocates a new partition and the count and total start fresh at zero.
For this statement the runtime only remembers the count and running total, and the fact how long a partition lives.
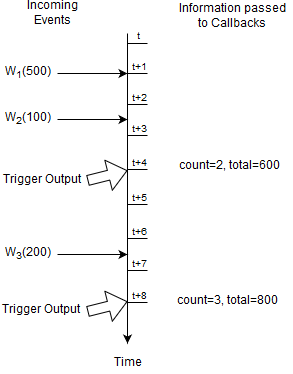
All the previous statements had continuous output. In other words, in each of previous statements output occurred as a result of a new event arriving. Use output rate limiting to output when a condition occurs, as described in Section 5.7, “Stabilizing and Controlling Output: The Output Clause”.
The next statement outputs the last count and total of all Withdrawal events every four seconds:
select count(*), total(amount) from Withdrawal output last every 4 seconds
At time t + 4 seconds and t + 8 seconds the runtime outputs the last aggregation values to callbacks.
For this statement the runtime only remembers the count and running total, and the fact when output shall occur.
Use a partitioned statement with output rate limiting to output-and-reset. This allows you to form batches, analyze a batch and then forget all such state in respect to that batch, continuing with the next batch.
The next statement selects the count and total amount of Withdrawal events that arrived within the last four seconds at the end of four seconds, resetting after output:
create context Batch4Seconds start @now end after 4 sec
context Batch4Seconds select count(*), total(amount) from Withdrawal output last when terminated
At time t + 4 seconds and t + 8 seconds the runtime outputs the last aggregation values to callbacks, and resets the current count and total.
For this statement the runtime only remembers the count and running total, and the fact when the output shall occur and how long a partition lives.
Named windows manage a subset of events for use by other statements. They can be selected-from, inserted- into, deleted-from and updated by multiple statements.
Tables are similar to named windows but are organized by primary keys and hold rows and columns. Tables can share aggregation state while named windows only share the subset of events they manage.
The documentation link for both is Chapter 6, EPL Reference: Named Windows and Tables. Named windows and tables can be queried with fire-and-forget queries through the API and also the inward-facing JDBC driver.
Named windows declare a window for holding events, and other statements that have the named window name in the from-clause implicitly aggregate or analyze the same set of events.
This removes the need to declare the same window multiple times for different EPL statements.
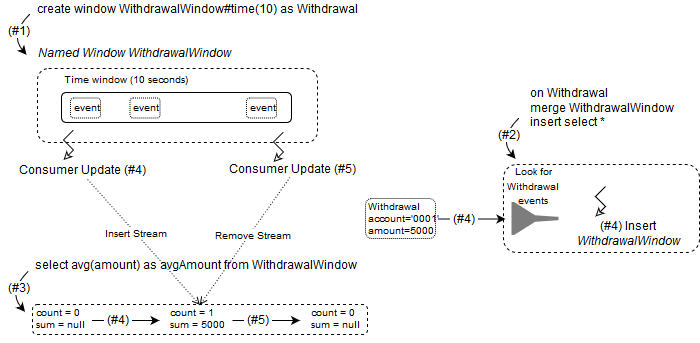
The below drawing explains how named windows work.
The step #1 creates a named window like so:
create window WithdrawalWindow#time(10) as Withdrawal
The name of the named window is WithdrawalWindow and it will be holding the last 10 seconds of Withdrawal events (#time(10) as Withdrawal).
As a result of step #1 the runtime allocates a named window to hold 10 seconds of Withdrawal events. In the drawing the named window is filled with some events. Normally a named window starts out as an empty window however it looks nicer with some boxes already inside.
The step #2 creates an EPL statement to insert into the named window:
on Withdrawal merge WithdrawalWindow insert select *
This tells the runtime that on arrival of a Withdrawal event it must merge with the WithdrawalWindow and insert the event. The runtime now waits for Withdrawal events to arrive.
The step #3 creates an EPL statement that computes the average withdrawal amount of the subset of events as controlled by the named window:
select avg(amount) as avgAmount from WithdrawalWindow
As a result of step #3 the runtime allocates state to keep a current average. The state consists of a count field and a sum field to compute a running average.
It determines that the named window is currently empty and sets the count to zero and the sum to null (if the named window was filled already it would determine the count and sum by iterating).
Internally, it also registers a consumer callback with the named window to receive inserted and removed events (the insert and remove stream). The callbacks are shown in the drawing as a dotted line.
In step #4 assume a Withdrawal event arrives that has an account number of 0001 and an amount of 5000.
The runtime executes the on Withdrawal merge WithdrawalWindow insert select * and thus adds the event to the time window.
The runtime invokes the insert stream callback for all consumers (dotted line, internally managed callback).
The consumer that computes the average amount receives the callback and the newly-inserted event. It increases the count field by one and increases the sum field by 5000.
The output of the statement is avgAmount as 5000.
In step #5, which occurs 10 seconds after step #4, the Withdrawal event for account 0001 and amount 5000 leaves the time window.
The runtime invokes the remove stream callback for all consumers (dotted line, internally managed callback).
The consumer that computes the average amount receives the callback and the newly-removed event. It decreases the count field by one and sets the sum to null and the count is zero.
The output of the statement is avgAmount as null.
Tables in EPL are not just holders of values of some type. EPL tables are also holders for aggregation state. Aggregations in EPL can be simple aggregations, such as count or average or standard deviation, but can also be much richer
aggregations. Examples of richer aggregations are list of events (window and sorted aggregation) or a count-min-sketch (a set of hash tables that store approximations). Your application can easily extend
and provide its own aggregations.
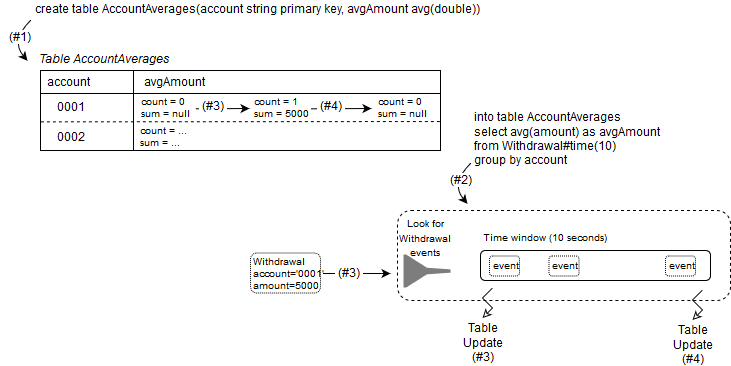
As table columns can serve as holders for aggregation state, they are a central place for updating and accessing aggregation state to be shared between statements. The below drawing explains how tables work with aggregation state.
The step #1 creates a table like so:
create table AccountAverages(account string primary key, avgAmount avg(double))
The table that has string-typed account number as the primary key. The table also has a column that contains an average of double-type values. Note how create table does not need to know how the average gets updated,
it only needs to know that the average is an average of double-type values.
As a result of step #1 the runtime allocates a table. In the drawing the table is filled with two rows for two different account numbers 0001 and 0002. Normally a table starts out as an empty table but let's assume the table has rows already.
In order to store an average of double-type values, the runtime must keep a count and a sum. Therefore in the avgAmount column of the table there are fields for count and sum.
For account 0001 let's say there are currently no values and the count is zero and the sum is null.
The step #2 creates an EPL statement that aggregates the last 10 seconds of Withdrawal events:
into table AccountAverages select avg(amount) as avgAmount from Withdrawal#time(10) group by account
The into table tells the compiler to store aggregations not locally as part of the statement, but into the AccountAverages table instead. The as avgAmount tells the compiler to use the column avgAmount in the table.
The compiler checks that aggregation type and value types match with the table column, and that the group by-clause matches the table primary key.
The runtime looks for Withdrawal events and keeps a 10-second time window. Normally a time window starts out as an empty time window but the drawing shows a few events in the time window.
In step #3 assume a Withdrawal event arrives that has an account number of 0001 and an amount of 5000. The runtime adds the event to the time window.
The runtime updates the avgAmount column of the table specifically the two fields count and sum. It increases the count field by one and increases the sum field by 5000.
In the case when a row for the account number does not exist, the runtime allocates a table row and its columns and aggregation fields.
In step #4, which occurs 10 seconds after step #3, the Withdrawal event for account 0001 and amount 5000 leaves the time window.
The runtime updates the avgAmount column of the table. It decreases the count field by one and sets the sum to null as the count is zero.
Other EPL statements may access table columns by putting the table into a from-clause, or by table-access-expression, on-action statement or fire-and-forget query.
The expressions in the select-clause, the use of aggregation functions and the group-by-clause are relevant to statement design. The overview herein is especially relevant to joins, on-trigger, output-rate-limiting and batch data windows.
If your statement only selects aggregation values, the runtime outputs one row (or zero rows in a join).
Without a group-by clause, if your statement selects non-aggregated values along with aggregation values, the runtime outputs a row per event.
With a group-by clause, if your statement selects non-aggregated values that are all in the group-by-clause, the runtime outputs a row per group.
With a group-by clause, if your statement selects non-aggregated values and not all non-aggregated values are in the group-by-clause, the runtime outputs a row per event.
EPL allows each aggregation function to specify its own grouping criteria. Please find further information in Section 5.6.4, “Specifying Grouping for Each Aggregation Function”. The documentation provides output examples for statement types in Appendix A, Output Reference and Samples, and the next sections outlines each statement type.
The examples below assume BankInformationWindow is a named window defined elsewhere.
The examples use a join to illustrate. Joins are further described in Section 5.12, “Joining Event Streams”.
An example statement for the un-aggregated and un-grouped case is as follows:
select * from Withdrawal unidirectional, BankInformationWindow
Upon a Withdrawal event coming in, the number of output rows is the number of rows in the BankInformationWindow.
The appendix provides a complete example including input and output events over time at Section A.2, “Output for Un-Aggregated and Un-Grouped Statements”.
If your statement only selects aggregation values and does not group, your statement may look as the example below:
select sum(amount) from Withdrawal unidirectional, BankInformationWindow
Upon a Withdrawal event coming in, the number of output rows is always zero or one.
The appendix provides a complete example including input and output events over time at Section A.3, “Output for Fully-Aggregated and Un-Grouped Statements”.
If any aggregation functions specify the group_by parameter and a dimension, for example sum(amount, group_by:account),
the statement executes as an aggregated and grouped statement instead.
If your statement selects non-aggregated properties and aggregation values, and does not group, your statement may be similar to this statement:
select account, sum(amount) from Withdrawal unidirectional, BankInformationWindow
Upon a Withdrawal event coming in, the number of output rows is the number of rows in the BankInformationWindow.
The appendix provides a complete example including input and output events over time at Section A.4, “Output for Aggregated and Un-Grouped Statements”.
If your statement selects aggregation values and all non-aggregated properties in the select clause are listed in the group by clause, then your statement may look similar to this example:
select account, sum(amount) from Withdrawal unidirectional, BankInformationWindow group by account
Upon a Withdrawal event coming in, the number of output rows is one row per unique account number.
The appendix provides a complete example including input and output events over time at Section A.5, “Output for Fully-Aggregated and Grouped Statements”.
If any aggregation functions specify the group_by parameter and a dimension other than group by dimension(s),
for example sum(amount, group_by:accountCategory), the statement executes as an aggregated and grouped statement instead.
If your statement selects non-aggregated properties and aggregation values, and groups only some properties using the group by clause, your statement may look as below:
select account, accountName, sum(amount) from Withdrawal unidirectional, BankInformationWindow group by account
Upon a Withdrawal event coming in, the number of output rows is the number of rows in the BankInformationWindow.
The appendix provides a complete example including input and output events over time at Section A.6, “Output for Aggregated and Grouped Statements”.
EPL offers the standardized match-recognize syntax for finding patterns among events. A match-recognize pattern is very similar to a regular-expression pattern.
The below statement is a sample match-recognize pattern. It detects a pattern that may be present in the events held by the named window as declared above. It looks for two immediately-followed events, i.e. with no events in-between for the same origin. The first of the two events must have high priority and the second of the two events must have medium priority.
select * from AlertNamedWindow
match_recognize (
partition by origin
measures a1.origin as origin, a1.alarmNumber as alarmNumber1, a2.alarmNumber as alarmNumber2
pattern (a1 a2)
define
a1 as a1.priority = 'high',
a2 as a2.priority = 'medium'
)The EPL pattern language is a versatile and expressive syntax for finding time and property relationships between events of many streams.
Event patterns match when an event or multiple events occur that match the pattern's definition, in a bottom-up fashion. Pattern expressions can consist of filter expressions combined with pattern operators. Expressions can contain further nested pattern expressions by including the nested expression(s) in parenthesis.
There are five types of operators:
Operators that control pattern finder creation and termination:
everyLogical operators:
and,or,notTemporal operators that operate on event order:
->(the followed-by operator)Guards are where-conditions that cause termination of pattern subexpressions, such as
timer:withinObservers that observe time events, such as
timer:interval(an interval observer),timer:at(a crontab-like observer)
A sample pattern that alerts on each IBM stock tick with a price greater than 80 and within the next 60 seconds:
every StockTickEvent(symbol="IBM", price>80) where timer:within(60 seconds)
A sample pattern that alerts every five minutes past the hour:
every timer:at(5, *, *, *, *)
A sample pattern that alerts when event A occurs, followed by either event B or event C:
A -> ( B or C)
A pattern where a property of a following event must match a property from the first event:
every a=EventX -> every b=EventY(objectID=a.objectID)
The compliler and runtime, depending on the statements, plan, build and maintain two kinds of indexes: filter indexes and event indexes.
The runtime builds and maintains indexes for efficiency so as to achieve good performance.
The following table compares the two kinds of indexes:
Table 2.2. Kinds of Indexes
| Filter Indexes | Event Indexes | |
|---|---|---|
| Improve the speed of | Matching incoming events to currently-active filters that shall process the event | Lookup of rows |
| Similar to | A structured registry of callbacks; or content-based routing | Database index |
| Index stores values of | Values provided by expressions | Values for certain column(s) |
| Index points to | Currently-active filters | Rows |
| Comparable to | A sieve or a switchboard | An index in a book |
Filter indexes organize filters so that they can be searched efficiently. Filter indexes link back to the statement and partition that the filter(s) come from.
We use the term filter or filter criteria to mean the selection predicate, such as symbol=“google” and price > 200 and volume > 111000.
Statements provide filter criteria in the from-clause, and/or in EPL patterns and/or in context declarations.
Please see Section 5.4.1, “Filter-Based Event Streams”, Section 7.4, “Filter Expressions in Patterns” and Section 4.2.7.1, “Filter Context Condition”.
Filter index building is a result of the compiler analyzing the filter expressions as described in Section 15.18, “Compiler Filter Expression Analysis”. The runtime uses the compiler output to build, maintain and use filter indexes.
Big-O notation scaling information can be found at Section 24.1.1, “Big-O Complexity of Matching Events to Statements and Context Partitions”.
When the runtime receives an event, it consults the filter indexes to determine which statements, if any, must process the event.
The purpose of filter indexes is to enable:
Efficient matching of events to only those statements that need them.
Efficient discarding of events that are not needed by any statement.
Efficient evaluation with best case approximately O(1) to O(log n) i.e. in the best case executes in approximately the same time regardless of the size of the input data set which is the number of active filters.
The runtime builds and maintains separate sets of filter indexes per event type, when such event type occurs in the from-clause or pattern.
Filter indexes are sharable within the same event type filter. Thus various from-clauses and patterns that refer for the same event type can contribute to the same set of filter indexes.
The runtime builds filter indexes in a nested fashion: Filter indexes may contain further filter indexes, forming a tree-like structure, a filter index tree. The nesting of indexes is beyond the introductory discussion provided here.
The from-clause in a statement and, in special cases, also the where-clause provide filter criteria that the compiler analyzes and for which it builds filter indexes.
For example, assume the WithdrawalEvent has an account field. You could create three statements like so:
@name('A') select * from WithdrawalEvent(account = 1)@name('B') select * from WithdrawalEvent(account = 1)@name('C') select * from WithdrawalEvent(account = 2)
In this example, both statement A and statement B register interest in WithdrawalEvent events that have an account value of 1.
Statement C registers interest in WithdrawalEvent events that have an account value of 2.
The below table is a sample filter index for the three statements:
Table 2.3. Sample Filter Index Multi-Statement Example
Value of account | Filter |
|---|---|
1 | Statement A, Statement B |
2 | Statement C |
When a Withdrawal event arrives, the runtime extracts the account and performs a lookup into above table.
If there are no matching rows in the table, for example when the account is 3, the runtime knows that there is no further processing for the event.
For filter index planning, we use the term lookupable-expression to mean the expression providing the filter index lookup value.
In this example there is only one lookupable-expression and that is account.
We use the term value-expression to mean the expression providing the indexed value.
Here there are three value-expressions namely 1 (from statement A), 1 (from statement B) and 2 (from statement C).
We use the term filter-index-operator to mean the type of index such as equals(=), relational (<,>,<=, >=) etc..
As part of a pattern you may specify event types and filter criteria. The compiler analyzes patterns and determines filter criteria for filter index building.
Consider the following example pattern that fires for each WithdrawalEvent that is followed by another WithdrawalEvent for the same account value:
@name('P') select * from pattern [every w1=WithdrawalEvent -> w2=WithdrawalEvent(account = w.account)]
Upon creating the above statement, the runtime starts looking for WithdrawalEvent events. At this time there is only one active filter:
A filter looking for
WithdrawalEventevents regardless of account id.
Assume a WithdrawalEvent Wa for account 1 arrives. The runtime then activates a filter looking for another WithdrawalEvent for account 1.
At this time there are two active filters:
A filter looking for
WithdrawalEventevents regardless of account id.A filter looking for
WithdrawalEvent(account=1)associated tow1=Wa.
Assume another WithdrawalEvent Wb for account 1 arrives. The runtime then activates a filter looking for another WithdrawalEvent for account 1.
At this time there are three active filters:
A filter looking for
WithdrawalEventevents regardless of account id.A filter looking for
WithdrawalEvent(account=1)associated tow1=Wa.A filter looking for
WithdrawalEvent(account=1)associated tow2=Wb.
Assume another WithdrawalEvent Wc for account 2 arrives. The runtime then activates a filter looking for another WithdrawalEvent for account 2.
At this time there are four active filters:
A filter looking for
WithdrawalEventevents regardless of account id.A filter looking for
WithdrawalEvent(account=1)associated tow1=Wa.A filter looking for
WithdrawalEvent(account=1)associated tow1=Wb.A filter looking for
WithdrawalEvent(account=2)associated tow1=Wc.
The below table is a sample filter index for the pattern after the Wa, Wband Wc events arrived:
Table 2.4. Sample Filter Index Pattern Example
Value of account | Filter |
|---|---|
1 | Statement P Pattern w1=Wa, Statement P Pattern w1=Wb |
2 | Statement P Pattern w1=Wc |
When a Withdrawal event arrives, the runtime extracts the account and performs a lookup into above table.
If a matching row is found, the runtime can hand off the event to the relevant pattern subexpressions.
This example is similar to the previous example of multiple statements, but instead it declares a context and associates a single statement to the context.
For example, assume the LoginEvent has an account field. You could declare a context initiated by a LoginEvent for a user:
@name('A') create context UserSession initiated by LoginEvent as loginEvent
By associating the statement to the context you can tell the compiler to analze per LoginEvent, for example:
@name('B') context UserSession select count(*) from WithdrawalEvent(account = context.loginEvent.account)
Upon creating the above two statements, the runtime starts looking for LoginEvent events. At this time there is only one active filter:
A filter looking for
LoginEventevents (any account id).
Assume a LoginEvent La for account 1 arrives. The runtime then activates a context partition of statement B and therefore the filter looking for WithdrawalEvent for account 1.
At this time there are two active filters:
A filter looking for
LoginEventevents (any account id).A filter looking for
WithdrawalEvent(account=1)associated tologinEvent=La.
Assume a LoginEvent Lb for account 1 arrives. The runtime then activates a context partition of statement B and therefore the filter looking for WithdrawalEvent for account 1.
At this time there are three active filters:
A filter looking for
LoginEventevents (any account id).A filter looking for
WithdrawalEvent(account=1)associated tologinEvent=La.A filter looking for
WithdrawalEvent(account=1)associated tologinEvent=Lb.
Assume a LoginEvent Lc for account 2 arrives. The runtime then activates a context partition of statement B and therefore the filter looking for WithdrawalEvent for account 2.
At this time there are four active filters:
A filter looking for
LoginEventevents (any account id).A filter looking for
WithdrawalEvent(account=1)associated tologinEvent=La.A filter looking for
WithdrawalEvent(account=1)associated tologinEvent=Lb.A filter looking for
WithdrawalEvent(account=2)associated tologinEvent=Lc.
The below table is a sample filter index for the three statement context partitions:
Table 2.5. Sample Filter Index Context Example
Value of account | Filter |
|---|---|
1 | Statement B Context Partition #0 loginEvent=La, Statement B Context Partition #1 loginEvent=Lb |
2 | Statement B Context Partition #2 loginEvent=Lc |
When a Withdrawal event arrives, the runtime extracts the account and performs a lookup into above table.
It can then hand of the event directly to the relevant statement context partitions, or ignore the event if no rows are found for a given account id.
Event indexes organize certain columns so that they can be searched efficiently. Event indexes link back to the row that the column(s) come from.
Big-O notation scaling information can be found at Section 24.1.3, “Big-O Complexity of Joins, Subqueries, On-Select, On-Merge, On-Update, On-Delete”.
As event indexes are similar to database indexes, for this discussion, we use the term column to mean a column in a EPL table or named window and to also mean an event property or field. We use the term row to mean a row in an EPL table or named window and to also mean an event.
When the runtime performs statement processing it may use event indexes to find correlated rows efficiently.
The purpose of event indexes is to enable:
Efficient evaluation of subqueries.
Efficient evaluation of joins.
Efficient evaluation of on-action statements.
Efficient evaluation of fire-and-forget queries.
Event index building is a result of the compiler analyzing the where-clause correlation criteria for joins (on-clause for outer joins), subqueries, on-action and fire-and-forget queries.
It is done automatically by the compiler. You may utilize the create index clause to explicitly index named windows and tables. You may utilize query planner hints to influence index building, use and sharing.
EPL and SQL use a three-valued logic: besides true and false, the result of expressions can also be unknown. Three-valued logic is a consequence of supporting null to mark absent data.
If a null value affects the result of a logical expression, the result is neither true nor false but unknown.
A null value basically means “could be anything”. It is therefore impossible to tell whether a comparison to null is true or false.
That’s where the third logical value, unknown, comes in. Unknown means “true or false, depending on the null values”.
The result of each of the following comparisons is therefore null (unknown):
null = 1
null <> 1
null > 1
null = null
Nothing equals null. Not even null equals null because each null could be different.
That’s why EPL has the is null predicate to test whether a value is null or not.
Credit: Above is an excerpt from an online text that can be found at http://modern-sql.com/concept/three-valued-logic.
- 3.1. Event Underlying Java Objects
- 3.2. Event Properties
- 3.3. Dynamic Event Properties
- 3.4. Fragment and Fragment Type
- 3.5. Comparing Event Representations
- 3.6. Support for Generic Tuples
- 3.7. Updating, Merging and Versioning Events
- 3.8. Coarse-Grained Events
- 3.9. Event Objects Instantiated and Populated by Insert Into
- 3.10. Event Type Uniqueness
This section outlines the different means to model and represent events.
EPL uses the term event type to describe the type information available for an event representation.
Your application may configure predefined event types using the configuration object or dynamically add event types using create schema.
The EPL create schema syntax allows declaring an event type at runtime using EPL, see Section 5.15, “Declaring an Event Type: Create Schema”.
Section 16.5.5, “Event and Event Type” explains how an event type becomes visible in statements and output events delivered by the runtime.
An event is an immutable record of a past occurrence of an action or state change. Event properties capture the state information for an event.
In EPL, an event can be represented by any of the following underlying Java objects (NEsper .NET, see Section J.7, “.NET Event Underlying Objects”):
Table 3.1. Event Underlying Java Objects
| Java Class | Description |
|---|---|
java.lang.Object | Any Java POJO (plain-old java object) with getter methods following JavaBean conventions; Legacy Java classes not following JavaBean conventions can also serve as events . |
java.util.Map | Map events are implementations of the java.util.Map interface where each map entry is a propery value. |
Object[] (array of object) | Object-array events are arrays of objects (type Object[]) where each array element is a property value. |
String (or JsonEventUnderlying) | JSON events are string-typed JSON-formatted documents. The parsed JSON document is available and implements the JsonEventUnderlying interface. |
org.apache.avro.generic.GenericData.Record | Apache Avro events are GenericData.Record objects (Avro is a data serialization system with schema support) |
org.w3c.dom.Node | XML document object model (DOM). |
EPL provides multiple choices for representing an event. There is no absolute need for you to create new Java classes to represent an event.
Event representations have the following in common:
All event representations support nested, indexed and mapped properties (aka. property expression), as explained in more detail below. There is no limitation to the nesting level.
All event representations provide event type metadata. This includes type metadata for nested properties.
All event representations allow transposing the event itself and parts or all of its property graph into new events. The term transposing refers to selecting the event itself or event properties that are themselves nestable property graphs, and then querying the event's properties or nested property graphs in further statements.
The Java object, Map, Object-array, JSON and Avro representations allow supertypes.
The API behavior for all event representations is the same, with minor exceptions noted.
The benefits of multiple event representations are:
For applications that already have events in one of the supported representations, there is no need to transform events before processing for both input and output.
Event representations are exchangeable, reducing or eliminating the need to change statements when the event representation changes, i.e. the EPL does not depend on whether events are Objects, Map(s), Object-array(s), JSON document(s), Avro record(s) or XML document(s).
Event representations are interoperable, allowing all event representations to interoperate in same or different statements.
The choice makes it possible to consciously trade-off performance, ease-of-use, the ability to evolve and effort needed to import or externalize events and use existing event type metadata.
Event properties capture the state information for an event. Event properties can be simple, indexed, mapped and nested event properties.
The table below outlines the different types of properties and their syntax in an event expression:
Table 3.2. Types of Event Properties
| Type | Description | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple | A property that has a single value that may be retrieved. | name | sensorId |
| Indexed | An indexed property stores an ordered collection of objects (all of the same type) that can be individually accessed by an integer-valued, non-negative index (or subscript). | name[index] | temperature[0] |
| Mapped | A mapped property stores a keyed collection of objects (all of the same type). | name('key') | isTurnedOn('light') |
| Nested | A nested property is a property that lives within another property of an event. | name.nestedname | sensor.value |
Combinations are also possible. For example, a valid combination could be person.address('home').street[0].
You may use any expression as a mapped property key or indexed property index by putting the expression within parenthesis after the mapped or index property name. Please find examples below.
If your application uses java.util.Map, Object[] (object-array) or JSON or XML to represent events, then event property names may themselves contain the dot ('.') character. The backslash ('\') character can be used to escape dot characters in property names, allowing a property name to contain dot characters.
For example, the EPL as shown below expects a property by name part1.part2 to exist on event type MyEvent:
select part1\.part2 from MyEvent
Sometimes your event properties may overlap with EPL language keywords or contain spaces or other special characters. In this case you may use the backwards apostrophe ` (aka. back tick) character to escape the property name.
The next example assumes a Quote event that has a property by name order, while order is also a reserved keyword:
select `order`, price as `price.for.goods` from Quote
When escaping mapped or indexed properties, make sure the back tick character appears outside of the map key or index.
The next EPL selects event properties that have names that contain spaces (e.g. candidate book), have the tick special character (e.g. children's books), are an indexed property (e.g. children's books[0]) and a mapped property
that has a reserved keyword as part of the property name (e.g. book select('isbn')):
select `candidate book` , `children's books`[0], `book select`('isbn') from MyEventType
When referring to nested properties, escape at the individual nesting level, for example (assuming MyEventType has a payload property that is itself an event):
select payload.`candidate book`, payload.`other books`? from MyEventType
Note
Avro does not support the dot-character in field names.
The key or index expression must be placed in parenthesis. When using an expression as key for a mapped property, the expression must return a String-typed value. When using an expression as index for an indexed property, the expression must return an int-typed value.
This example below uses Java classes to illustrate; The same principles apply to all event representations.
Assume a class declares these properties (getters not shown for brevity):
public class MyEventType {
String myMapKey;
int myIndexValue;
int myInnerIndexValue;
Map<String, InnerType> innerTypesMap; // mapped property
InnerType[] innerTypesArray; // indexed property
}
public class InnerType {
String name;
int[] ids;
}A sample statement demonstrating expressions as map keys or indexes is:
select innerTypesMap('somekey'), // returns map value for 'somekey'
innerTypesMap(myMapKey), // returns map value for myMapKey value (an expression)
innerTypesArray[1], // returns array value at index 1
innerTypesArray(myIndexValue) // returns array value at index myIndexValue (an expression)
from MyEventTypeThe dot-operator can be used to access methods on the value objects returned by the mapped or indexed properties. By using the dot-operator the syntax follows the chained method invocation described at Section 9.7, “Dot Operator”.
A sample statement demonstrating the dot-operator as well as expressions as map keys or indexes is:
select innerTypesMap('somekey').ids[1],
innerTypesMap(myMapKey).getIds(myIndexValue),
innerTypesArray[1].ids[2],
innerTypesArray(myIndexValue).getIds(myInnerIndexValue)
from MyEventTypePlease note the following limitations:
The square brackets-syntax for indexed properties does now allow expressions and requires a constant index value.
When using the dot-operator with mapped or indexed properties that have expressions as map keys or indexes you must follow the chained method invocation syntax.
Dynamic (unchecked) properties are event properties that need not be known at statement compilation time. Such properties are resolved during runtime: they provide duck typing functionality.
The idea behind dynamic properties is that for a given underlying event representation you don't always know all properties in advance. An underlying event may have additional properties that are not known at statement compilation time, that you want to query on. The concept is especially useful for events that represent rich, object-oriented domain models.
The syntax of dynamic properties consists of the property name and a question mark. Indexed, mapped and nested properties can also be dynamic properties:
Table 3.3. Types of Event Properties
| Type | Syntax |
|---|---|
| Dynamic Simple | name? |
| Dynamic Indexed | name[index]? |
| Dynamic Mapped | name('key')? |
| Dynamic Nested | name?.nestedPropertyName |
Dynamic properties always return the java.lang.Object type. Also, dynamic properties return a null value if the dynamic property does not exist on events processed at runtime.
As an example, consider an OrderEvent event that provides an "item" property. The "item" property is of type Object and holds a reference to an instance of either a Service or Product.
Assume that both Service and Product classes provide a property named "price". Via a dynamic property you can specify a statement that obtains the price property from either object (Service or Product):
select item.price? from OrderEvent
As a second example, assume that the Service class contains a "serviceName" property that the Product class does not possess. The following statement returns the value of the "serviceName" property for Service objects. It returns a null-value for Product objects that do not have the "serviceName" property:
select item.serviceName? from OrderEvent
Consider the case where OrderEvent has multiple implementation classes, some of which have a "timestamp" property. The next statement returns the timestamp property of those implementations of the OrderEvent interface that feature the property:
select timestamp? from OrderEvent
The statement as above returns a single column named "timestamp?" of type Object.
When dynamic properties are nested, then all properties under the dynamic property are also considered dynamic properties. In the below example the statement asks for the "direction" property of the object returned by the "detail" dynamic property:
select detail?.direction from OrderEvent
Above is equivalent to:
select detail?.direction? from OrderEvent
The functions that are often useful in conjunction with dynamic properties are:
The
castfunction casts the value of a dynamic property (or the value of an expression) to a given type.The
existsfunction checks whether a dynamic property exists. It returnstrueif the event has a property of that name, or false if the property does not exist on that event.The
instanceoffunction checks whether the value of a dynamic property (or the value of an expression) is of any of the given types.The
typeoffunction returns the string type name of a dynamic property.
Sometimes an event can have properties that are itself events. EPL uses the term fragment and fragment type for such event pieces. The best example is a pattern that matches two or more events and the output event contains the matching events as fragments. In other words, output events can be a composite event that consists of further events, the fragments.
Fragments have the same metadata available as their enclosing composite events. The metadata for enclosing composite events contains information about which properties are fragments, or have a property value that can be represented as a fragment and therefore as an event itself.
Fragments and type metadata can allow your application to navigate composite events without the need for using the Java reflection API and reducing the coupling to the underlying event representation. The API is further described in Section 16.5.5, “Event and Event Type”.
More information on event representations can be found in the appendix. The links are:
Table 3.4. Comparing Event Representations
| Event Representation | More Information and Examples |
|---|---|
| Java Object (POJO/Bean or other) | Appendix D, Event Representation: Plain-Old Java Object Events |
| Map | Appendix E, Event Representation: java.util.Map Events |
| Object-array | Appendix F, Event Representation: Object-Array (Object[]) Events |
| JSON | Appendix G, Event Representation: JSON Events |
| Avro | Appendix H, Event Representation: Avro Events (org.apache.avro.generic.GenericData.Record) |
| XML Document | Appendix I, Event Representation: org.w3c.dom.Node XML Events |
For sending incoming events into the runtime for processing, your application uses one of the send-event methods on the EPEventService interface:
Table 3.5. EPEventService Send-Event Methods
| Event Representation | Method for Processing Events |
|---|---|
| Java Object (POJO/Bean or other) | sendEventBean(Object event, String eventTypeName) |
| Map | sendEventMap(Map map, String mapEventTypeName) |
| Object-array | sendEventObjectArray(Object[] objectarray, String objectArrayEventTypeName) |
| JSON | sendEventJson(String json, String jsonEventTypeName) |
| Avro | sendEventAvro(Object avroGenericDataDotRecord, String avroEventTypeName) |
| XML Document | sendEventXMLDOM(org.w3c.dom.Node node, String eventTypeName) |
Please find an example in the respective appendix.
The StatementUpdateListener interface receives statement output. The output events can be either of the representations
Table 3.6. Annotation for Receiving Events
| Event Representation | Annotation |
|---|---|
| Java Object (POJO/Bean or other) | N/A |
| Map | @EventRepresentation(map) |
| Object-array | @EventRepresentation(objectarray) |
| JSON | @EventRepresentation(json) |
| Avro | @EventRepresentation(avro) |
| XML Document | N/A |
Please find an example in the respective appendix.
The create-schema clause can be used to define an event type and its event representation.
Table 3.7. Create-Schema
| Event Representation | Annotation |
|---|---|
| Java Object (POJO/Bean or other) | create schema name as class_name |
| Map | create map schema name as (...) |
| Object-array | create objectarray schema name as (...) |
| JSON | create json schema name as (...) |
| Avro | create avro schema name as (...) |
| XML Document | @XMLSchema(...) create xml schema name as () |
Your statements can use create schema and insert into to define an event type and to produce events of the type.
In the following example the first statement declares a schema and the second statement inserts events according to the schema:
create map schema ParkingEvent as (carId string, driverName string)
insert into ParkingEvent select carId, 'jim' as driverName from CarArrivalEvent
Please find additional examples in Section 5.15, “Declaring an Event Type: Create Schema”.
Each of the event representations of Java object, Map, Object-array, JSON, Avro and XML document has advantages and disadvantages that are summarized in the table below:
Table 3.8. Comparing Event Representations
| Java Object (POJO/Bean or other) | Map | Object-array | JSON | Avro | XML Document | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent | Good | Excellent | Excellent | Very Good | Not comparable and depending on use of XPath |
| Memory Use | Small | Medium | Small | Small | Small | Depends on DOM and XPath implementation used, can be large |
| Call Method on Event | Yes | Yes, if contains Object(s) | Yes, if contains Object(s) | No | No | No |
| Nested, Indexed, Mapped and Dynamic Properties | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Course-grained event syntax | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Insert-into that Representation | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Create-schema Syntax | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Object is Self-Descriptive | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Supertypes | Multiple | Multiple | Single | Single | Single | No |
EPL does not require a fixed tuple structure and fully supports generic tuples. Event properties can be defined, added to existing types and queried at runtime.
The facilities for support of generic tuples are:
Dynamic properties allow querying properties that are not defined, see Section 3.3, “Dynamic Event Properties”.
The
castfunction for operations that require strongly-typed data, see Section 10.1.2, “The Cast Function”.Type inheritance for adding properties to supertypes, see Section 5.15, “Declaring an Event Type: Create Schema”
The Map event representation, as it allows any map key to become an event property, see Appendix E, Event Representation: java.util.Map Events
The JSON event representation, as it allows any JSON value (JSON objects, arrays, all JSON types) to become an event property, see Appendix G, Event Representation: JSON Events
The Avro event representation, as it allows any Avro field to become an event property, see Appendix H, Event Representation: Avro Events (org.apache.avro.generic.GenericData.Record)
The POJO event representation, as getter-methods and fields can be dynamically discovered to become an event property, see Appendix D, Event Representation: Plain-Old Java Object Events
The XML event representation, as the DOM can have any attribute or nested element and there does not need to be a schema, see Appendix I, Event Representation: org.w3c.dom.Node XML Events
Event types can be deployed and undeploy at runtime using
create schemaand the deployment API
There is no need to explicitly create an event type for each tuple type. It is not necessary to create classes for tuple types at all. Events can be arbitrary objects.
The compiler uses the type information that is available: the compiler can verifies your statement against the known properties and types,
preventing you as the EPL designer from making mistakes in EPL design.
The compiler does not verify dynamic properties, which may return null at runtime.
If type information is not available then properties are assumed to return java.lang.Object-typed values.
For example, let's say you need a generic tuple and you have Map events:
create schema GenericTuple()
Create statements that use dynamic properties, as the next EPL shows, which casts the timestamp value to a long-type value and outputs the hour-minute-second string:
select cast(timestamp?, long).format('hh mm ss') from GenericTupleSend events like this:
Map<String, Object> genericEvent = new HashMap<>();
genericEvent.put("timestamp", new Date().getTime());
genericEvent.put("some_other_property", "hello");
runtime.getEventService().sendEventMap(genericEvent, "GenericTuple");To summarize, an event is an immutable record of a past occurrence of an action or state change, and event properties contain useful information about an event.
The length of time an event is of interest to the runtime (retention time) depends on your statements, and especially the data window, pattern and output rate limiting clauses of your statements.
During the retention time of an event more information about the event may become available, such as additional properties or changes to existing properties. EPL provides two concepts for handling updates to events.
The first means to handle updating events is the update istream clause as further described in Section 5.20, “Updating an Insert Stream: The Update IStream Clause”. It is useful when you need to update events as they enter a stream, before events are evaluated by any particular
consuming statement to that stream.
The second means to update events is the on-merge and on-update clauses, for use with tables and named windows only, as further described in Section 6.8, “Triggered Upsert Using the On-Merge Clause” and Section 6.6, “Updating Data: The On Update Clause”. On-merge
is similar to the SQL merge clause and provides what is known as an "Upsert" operation: Update existing events or if no existing event(s) are found then insert a new event, all in one atomic operation provided by a single statement.
On-update can be used to update individual properties of rows held in a table or named window.
Your application events may consist of fairly comprehensive, coarse-grained structures or documents. For example in business-to-business integration scenarios, XML documents or other event objects can be rich deeply-nested graphs of event properties.
To extract information from a coarse-grained event or to perform bulk operations on the rows of the property graph in an event, EPL provides a convenient syntax:
When specifying a filter expression in a pattern or in a select clause, it may contain an contained-event selection syntax, as further described in Section 5.19, “Contained-Event Selection”.
For NEsper .NET also see Section J.11, “.NET Event Objects Instantiated and Populated by Insert Into”.
The insert into clause can instantiate and populate new instances of Java object events, java.util.Map events and Object[] (object array) events directly from the results of select clause expressions. Simply use the event type name as the stream name in the insert into clause as described in Section 5.10, “Merging Streams and Continuous Insertion: The Insert Into Clause”.
If instead you have an existing instance of a Java object returned by an expression, such as a single-row function or static method invocation for example, you can transpose that expression result object to a stream. This is described further in Section 5.10.7, “Transposing an Expression Result” and Section 10.4, “Select-Clause Transpose Function”.
The column names specified in the select and insert into clause must match available writable properties in the event object to be populated (the target event type). The expression result types of any expressions in the select clause must also be compatible with the property types of the target event type.
If populating a POJO-based event type and the class provides a matching constructor, the expression result types of expressions in the select clause must be compatible with the constructor parameters in the order listed by the constructor. The insert into clause column names are not relevant in this case.
Consider the following example statement:
insert into com.mycompany.NewEmployeeEvent select fname as firstName, lname as lastName from HRSystemEvent
The above example specifies the fully-qualified class name of NewEmployeeEvent. The runtime instantianes NewEmployeeEvent for each result row and populates the firstName and lastName properties of each instance from the result of select clause expressions. The HRSystemEvent in the example is assumed to have lname and fname properties, and either setter-methods and a default constructor, or a matching constructor.
Note how the example uses the as-keyword to assign column names that match the property names of the NewEmployeeEvent target event. If the property names of the source and target events are the same, the as-keyword is not required.
The next example is an alternate form and specifies property names within the insert into clause instead. The example also assumes that NewEmployeeEvent has been defined or imported via configuration since it does not specify the event class package name:
insert into NewEmployeeEvent(firstName, lastName) select fname, lname from HRSystemEvent
Finally, this example populates HRSystemEvent events. The example populates the value of a type property where the event has the value 'NEW' and populates a new event object with the value 'HIRED', copying the fname and lname property values to the new event object:
insert into HRSystemEvent select fname, lname, 'HIRED' as type from HRSystemEvent(type='NEW')
The matching of the select or insert into-clause column names to target event type's property names is case-sensitive. You can specify a subset of all available columns in the target event type. Wildcard (*) is allowed and copies all fields of the events or multiple events in a join.
For Java object events, your event class must provide setter-methods according to JavaBean conventions or, alternatively, a matching constructor. If the event class provides setter methods the class should also provide a default constructor taking no parameters. If the event class provides a matching constructor there is no need for setter-methods. If your event class does not have a default constructor and setter methods, or a matching constructor, your application may configure a factory method via ConfigurationEventTypeLegacy. If your event class does not have a default constructor and there is no factory method provided, the runtime uses in connection with the Oracle JVM the sun.reflect.ReflectionFactory, noting that in this case member variables do not get initialized to assigned defaults.
The compiler follows Java standards in terms of widening, performing widening automatically in cases where widening type conversion is allowed without loss of precision, for both boxed and primitive types and including BigInteger and BigDecimal.
When inserting array-typed properties into a Java, Map-type, Object-array or JSON underlying event the event definition should declare the target property as an array (Avro uses Collections).
Please note the following limitations:
Event types that utilize XML
org.w3c.dom.Nodeunderlying event objects cannot be target of aninsert intoclause.
Event type names of preconfigured event types are unique within both compiler and runtime.
Event type names of event types allocated by create schema are unique within both the compiler and the runtime by the combination of the deployment id and the event type name.
At runtime for internal lookups the runtime computes a CRC32 value pair. Usually you don't need to worry about CRC32 values as a collision is very unlikely and the compiler and runtime indicate relevant collisions
by throwing a compile-time or deployment-time exception.
For preconfigured event types the CRC32 of the type name must be unique within the runtime.
For event types allocated by create schema the combination of CRC32 of the deployment id and the CRC32 of the event type name must be unique within the runtime.
- 4.1. Introduction
- 4.2. Context Declaration
- 4.3. Context Nesting
- 4.4. Partitioning Without Context Declaration
- 4.5. Output When a Context Partition Starts (Non-Overlapping Context) or Initiates (Overlapping Context)
- 4.6. Output When a Context Partition Ends (Non-Overlapping Context) or Terminates (Overlapping Context)
- 4.7. Context and Named Window
- 4.8. Context and Tables
- 4.9. Context and Variables
- 4.10. Operations on Specific Context Partitions
This section discusses the notion of context and its role in the event processing language (EPL).
When you look up the word context in a dictionary, you may find: Context is the set of circumstances or facts that surround a particular event, situation, etc.
Context-dependent event processing occurs frequently: For example, consider a requirement that monitors banking transactions. For different customers your analysis considers customer-specific aggregations, patterns or data windows. In this example the context of detection is the customer. For a given customer you may want to analyze the banking transactions of that customer by using aggregations, data windows, patterns including other EPL constructs.
In a second example, consider traffic monitoring to detect speed violations. Assume the speed limit must be enforced only between 9 am and 5 pm. The context of detection is of temporal nature.
A context takes a cloud of events and classifies them into one or more sets. These sets are called context partitions. An event processing operation that is associated with a context operates on each of these context partitions independently. (Credit: Taken from the book "Event Processing in Action" by Opher Etzion and Peter Niblett.) A basic partitioned statement was reviewed in Section 2.11, “Basic Partitioned Statement”.
A context is a declaration of dimension and may thus result in one or more context partitions. In the banking transaction example the context dimension is the customer and a context partition exists per customer. In the traffic monitoring example there is a single context partition that exists only between 9 am and 5 pm and does not exist outside of that daily time period.
In an event processing glossary you may find the term event processing agent. An statement is an event processing agent. An alternative term for context partition is event processing agent instance.
Tip
Think of context partitions as instances of a class, wherein the class is the statement.
EPL allows you to declare contexts explicitly, offering the following benefits:
Context can apply to multiple statements thereby eliminating the need to duplicate context dimensional information between statements.
Context partitions can be temporally overlapping.
Context partitions provide a fine-grained lifecycle that is independent of the lifecycle of statement lifecycle, making it easy to specify when an analysis should start and end.
Fine-grained lock granularity: The runtime locks on the level of context partitions thereby allowing very high concurrency, with a maximum (theoretical) degree of parallelism at 2^31-1 (2,147,483,647) parallel threads working to process a single statement under a hash segmented context.
EPL can become easier to read as common predicate expressions can be factored out into a context.
You may specify a nested context that is composed from two or more contexts. In particular a temporal context type is frequently used in combination with a segmentation-oriented context.
Using contexts your application can aggregate events over time periods (overlapping or non-overlapping) without retaining any events in memory.
Using contexts your application can coordinate boundaries for multiple statements.
EPL allows you to declare a context explicitly via the create context syntax introduced below.
After you have declared a context, one or more statements can refer to that context by specifying context name.
When a statement refers to a context, all EPL-statement related state such as aggregations, patterns or data windows etc. exists once per context partition.
If a statement does not declare a context, it implicitly has a single context partition. The single context partition lives as long as the statement is deployed and ends when the statement is undeployed.
You may have heard of the term session. A context partition is the same as a session.
You may have heard of the term session window to describe the duration between when a session becomes alive to when a session gets destroyed. We use the term context partition lifecycle instead.
The context declaration specifies how the runtime manages context partitions (or sessions):
For keyed segmented context there is a context partition (or session) per key or multiple keys see Section 4.2.2, “Keyed Segmented Context”.
For hash segmented context there is a context partition (or session) per hash code of one or more keys see Section 4.2.3, “Hash Segmented Context”.
For overlapping contexts there can be multiple overlapping context partitions (or sessions), see Section 4.2.6, “Overlapping Context”.
For non-overlapping contexts there is only zero or one single context partition (or session), see Section 4.2.5, “Non-Overlapping Context”.
For category segmented context there is a context partition (or session) per predefined category, see Section 4.2.4, “Category Segmented Context”.
For the API to administrate context partitions please see Section 16.17, “Context Partition Administration”. For more information on locking and threading please see Section 16.8, “Runtime Threading and Concurrency”. For performance related information please refer to Chapter 24, Performance.
The create context statement declares a context by specifying a context name and context dimension information.
A context declaration by itself does not consume any resources or perform any logic until your application starts at least one statement that refers to that context. Until then the context is inactive and not in use.
When your application deploys the first statement that refers to the context, the runtime activates the context.
As soon as your application undeploys all statements that refer to the context, the context becomes inactive again.
When your application undeploys a statement that refers to a context, the context partitions associated to that statement also end (context partitions associated to other deployed statements live on).
In order for your application to undeploy the statement that declared the context it must also undeploy any statements that refer to the context.
When your application undeploys all statements that refer to that context and undeploys the statement that declared the context then the runtime removes the context declaration entirely.
The create context statement posts no output events to listeners or subscribers and does not return any rows when iterated.
Each of the context declarations makes available a set of built-in context properties as well as initiating event or pattern properties, as applicable. You may select these context properties for output or use them in any of the statement expressions.
Refer to built-in context properties as context.property_name, wherein property_name refers to the name of the built-in context property.
Refer to initiating event or pattern match event properties as context.stream_name.property_name, wherein stream_name refers to the name assigned to the event or the tag name specified in a pattern and property_name refers to the name of the initiating event or pattern match event property.
This context assigns events to context partitions based on the values of one or more event properties, using the value of these property(s) as a key that picks a unique context partition directly. Each event thus belongs to exactly one context partition or zero context partitions (zero context partitions only if the event does not match the optional filter predicate expression(s)). Each context partition handles one key value (a key value can be a composite key).
The syntax for creating a keyed segmented context is:
create context context_name partition [by] partition_def [initiated [by] initiated_def] [terminated [by] terminating_condition]
The context_name you assign to the context can be any identifier.
Following the context name is the partition keyword and a partition_def partition definition that list event properties and event types providing the partition key value (or values for composite keys).
You may optionally declare initiating events using the initiated keyword and you may provide a termination condition for terminating partitions.
After partitioned by you can list the event properties that provide the key values that identify a unique partition. The synopsis is:
create context context_name partition [by] event_property [and event_property [and ...]] from stream_def [ [as] stream_name] [, event_property [...] from stream_def] [, ...]
The event_property is the name(s) of the event properties that provide the value(s) to pick a unique partition. Multiple event property names are separated by the and keyword or by comma. Further detail on key expressions can be found at Section 5.2.13, “Composite Keys and Array Values as Keys”.
The stream_def is a stream definition which consists of an event type name optionally followed by parenthesis that contains filter expressions. If providing filter expressions, only events matching the provided filter expressions for that event type are considered by context partitions. The name of a named window or table is not allowed.
You may list multiple event properties for each stream definition. You may list multiple stream definitions. Please refer to usage guidelines below when specifying multiple event properties and/or multiple stream definitions.
You may specify the optional as-keyword and a stream name. This instructs the runtime to make the first event of a partition available in context built-in properties and for matching in terminated by.
You may specify stream names either in partition by or in initiated by but not both.
The next statement creates a context SegmentedByCustomer that considers the value of the custId property of the BankTxn event type to pick the context partition to assign events to:
create context SegmentedByCustomer partition by custId from BankTxn
The following statement refers to the context created as above to compute a total withdrawal amount per account for each customer:
context SegmentedByCustomer select custId, account, sum(amount) from BankTxn group by account
The following statement refers to the context created as above and detects a withdrawal of more than 400 followed by a second withdrawal of more than 400 that occur within 10 minutes of the first withdrawal, all for the same customer:
context SegmentedByCustomer select * from pattern [ every a=BankTxn(amount>400) -> b=BankTxn(amount>400) where timer:within(10 minutes) ]
The statement that refers to a keyed segmented context must have at least one filter expression, at any place within the statement that looks for events of any of the event types listed in the context declaration.
For example, the following is not valid:
// Neither LoginEvent nor LogoutEvent are listed in the context declaration context SegmentedByCustomer select * from pattern [every a=LoginEvent -> b=LogoutEvent where timer:within(10 minutes)]
When provided, initiated by lists the event type and filter criteria of events that can initiate new partitions. The synopsis is:
initiated by stream_def [ [as] stream_name] [, stream_def [ [as] stream_name]] [, ...]
When initiated by is not provided, the partitioned by provides the event type and filter criteria for events that can initiate new partitions.
The stream_def is the stream definition which consists of an event type name optionally followed by parenthesis that contains filter expressions.
If providing filter expressions, only events matching the provided filter expressions for that event type initiate a new context partition. The name of a named window or table is not allowed.
You may use the as-keyword and a stream name to name the initiating event. That event becomes available in context built-in properties and for matching in terminated by.
You may specify stream names either in partition by or in initiated by but not both.
This is a sample context and statement:
create context PerCustId_TriggeredByLargeAmount partition by custId from BankTxn initiated by BankTxn(amount>100) as largeTxn
context PerCustId_TriggeredByLargeAmount select context.largeTxn, custId, sum(amount) from BankTxn
When a BankTxn event arrives with an amount value of greater than 100, the system starts the analysis (allocates a partition) for the specific custId value of the BankTxn event.
The statement totals up the amount value of all BankTxn events for that same custId value (regardless of their amount).
The sample assigns the name largeTxn to the initiating event and selects the event with context.largeTxn.
When provided, terminated by provides the condition that terminates partitions. The synopsis is:
terminated [by] terminating_conditionA list of possible conditions is provided in Section 4.2.7, “Context Conditions”. An event that causes termination does not also allocate a new partition.
Any event types that are listed in both the termination condition and partition by are implicitly correlated by key.
Note
In the case that the terminating condition and the statements that are associated to the context look for the same events, you may use @Priority to assign whether the context or the statement are processed first.
Consider the following two statements:
create context PerCustId_UntilExpired partition by custId from BankTxn terminated by BankTxn(expired=true)
context PerCustId_UntilExpired select custId, sum(amount) from BankTxn output last when terminated
When a BankTxn event arrives, the system starts the analysis (allocates a partition) for the specific custId value of the BankTxn event only.
The system stops the analysis (discards the partition) when a BankTxn event arrives, for that same custId value, that has an expired value of true.
The output occurs when the analysis stops as the statement specifies output last when terminated.
The termination condition can be correlated to the initiating event provided that initiated by provides a stream name.
A context that correlates the terminating event to the initiating event is:
create context PerCustId_TriggeredByLargeAmount_UntilExpired partition by custId from BankTxn initiated by BankTxn(amount>100) as txn terminated by BankTxn(expired=true and user=txn.user)
This example defines a context wherein the system starts the analysis when a BankTxn event arrives that has an amount value of greater than 100 (the initiating event).
The analysis for the specific custId value only. It stops the analysis when a BankTxn event arrives that has an expired value of true
and that the same custId value and that has a user value that matches the initiating event's user value.
If the context declaration lists multiple streams, each event type must be unrelated: You may not list the same event type twice and you may not list a sub- or super-type of any event type already listed.
The following is not a valid declaration since the BankTxn event type is listed twice:
// Not valid create context SegmentedByCustomer partition by custId from BankTxn, account from BankTxn
If the context declaration lists multiple streams, the number of event properties provided for each event type must also be the same. The value type returned by event properties of each event type must match within the respective position it is listed in, i.e. the first property listed for each event type must have the same type, the second property listed for each event type must have the same type, and so on.
The following is not a valid declaration since the customer id of BankTxn and login time of LoginEvent is not the same type:
// Invalid: Type mismatch between properties create context SegmentedByCustomer partition by custId from BankTxn, loginTime from LoginEvent
The next statement creates a context SegmentedByCustomer that also considers LoginEvent and LogoutEvent:
create context SegmentedByCustomer partition by custId from BankTxn, loginId from LoginEvent, loginId from LogoutEvent
As you may have noticed, the above example refers to loginId as the event property name for LoginEvent and LogoutEvent events. The assumption is that the loginId event property of the login and logout events has the same type and carries the same exact value as the custId of bank transaction events, thereby allowing all events of the three event types to apply to the same customer-specific context partition.
You may add a filter expression to each of the event types.
Filter criteria in partition by apply to all statements that refer to the context and to the same event type.
Filter criteria in initiated by apply to initiating events only.
The below statements total up the amount of all BankTxn events per custId for only those BankTxn events that have an amount greater 100.
create context PerCust_AmountGreater100 partition by custId from BankTxn(amount>100) initiated by BankTxn
context PerCust_AmountGreater100 select custId, sum(amount) from BankTxn
The below statements total up the amount of all BankTxn events per custId, but only when a first BankTxn event comes in that has an amount greater 100.
create context PerCust_TriggeredByLargeTxn partition by custId from BankTxn initiated by BankTxn(amount>100)
context PerCust_TriggeredByLargeTxn select custId, sum(amount) from BankTxn
You may assign events to context partitions based on the values of two or more event properties. The runtime thus uses the combination of values of these properties to pick a context partition.
An example context declaration follows:
create context ByCustomerAndAccount partition by custId and account from BankTxn
The next statement refers to the context and computes a total withdrawal amount, per account and customer:
context ByCustomerAndAccount select custId, account, sum(amount) from BankTxn
As you can see, the above statement does not need to specify group by clause to aggregate per customer and account, since events of each unique combination of customer id and account are assigned to separate context partitions.
The following context properties are available in your statement when it refers to a keyed segmented context:
Table 4.1. Keyed Segmented Context Properties
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
name | The string-type context name. |
id | The integer-type internal context partition id that the runtime assigns to the context partition. |
key1 | The event property value for the first key. |
keyN | The event property value for the Nth key. |
stream name from partitioned by or initiated by | The event initiating the partition. |
Assume the keyed segmented context is declared as follows:
create context ByCustomerAndAccount partition by custId and account from BankTxn
You may, for example, select the context properties as follows:
context ByCustomerAndAccount select context.name, context.id, context.key1, context.key2 from BankTxn
This section discusses the impact of contexts on joins to provide further samples of use and deepen the understanding of context partitions.
Consider a context declared as follows:
create context ByCust partition by custId from BankTxn
The following statement matches, within the same customer id, the current event with the last 30 minutes of events to determine those events that match amounts:
context ByCust select * from BankTxn as t1 unidirectional, BankTxn#time(30) t2 where t1.amount = t2.amount
Note that the where-clause in the join above does not mention customer id. Since each BankTxn applies to a specific context partition the join evaluates within that single context partition.
Consider the next statement that matches a security event with the last 30 minutes of transaction events for each customer:
context ByCust select * from SecurityEvent as t1 unidirectional, BankTxn#time(30) t2 where t1.customerName = t2.customerName
When a security event comes in, it applies to all context partitions and not any specific context partition, since the SecurityEvent event type is not part of the context declaration.
This context assigns events to context partitions based on the result of a hash function and modulo operation. Each event belongs to exactly one context partition or zero context partitions (zero context partitions only if the event does not match the optional filter predicate expression(s)). Each context partition handles exactly one result of hash value modulo granularity.
The syntax for creating a hashed segmented context is as follows:
create context context_name coalesce [by] hash_func_name(hash_func_param) from stream_def [, hash_func_name(hash_func_param) from stream_def ] [, ...] granularity granularity_value [preallocate]
The context_name you assign to the context can be any identifier.
Following the context name is one or more lists of hash function name and parameters pairs and a stream definition for each entry, separated by comma (,).
The hash_func_name can either be consistent_hash_crc32 or hash_code or a plug-in single-row function. The hash_func_param is a list of parameter expressions.
If you specify
consistent_hash_crc32the runtime computes a consistent hash code using the CRC-32 algorithm.If you specify
hash_codethe runtime uses the Java object hash code.If you specify the name of a plug-in single-row function your function must return an integer value that is the hash code. You may use the wildcard
(*)character among the parameters to pass the underlying event to the single-row function.
The stream_def is a stream definition which consists of an event type name optionally followed by parenthesis that contains filter expressions. If providing filter expressions, only events matching the provided filter expressions for that event type are considered by context partitions. The name of a named window or table is not allowed.
You may list multiple stream definitions. Please refer to usage guidelines below when specifying multiple stream definitions.
The granularity is required and is an integer number that defines the maximum number of context partitions. The runtime computes hash code modulo granularity hash(params) mod granularity to determine the context partition. When you specify the hash_code function the runtime uses the object hash code and the computation is params.hashCode() % granularity.
Since the runtime locks on the level of context partition to protect state, the granularity defines the maximum degree of parallelism. For example, a granularity of 1024 means that 1024 context partitions handle events and thus a maximum 1024 threads can process each assigned statement concurrently.
The optional preallocate keyword instructs the runtime to allocate all context partitions at once at the time a statement refers to the context. This is beneficial for performance as the runtime does not need to determine whether a context partition exists and dynamically allocate, but may require more memory.
The next statement creates a context SegmentedByCustomerHash that considers the CRC-32 hash code of the custId property of the BankTxn event type to pick the context partition to assign events to, with up to 16 different context partitions that are preallocated:
create context SegmentedByCustomerHash coalesce by consistent_hash_crc32(custId) from BankTxn granularity 16 preallocate
The following statement refers to the context created as above to compute a total withdrawal amount per account for each customer:
context SegmentedByCustomerHash select custId, account, sum(amount) from BankTxn group by custId, account
Note that the statement above groups by custId: Since the events for different customer ids can be assigned to the same context partition, it is necessary that the statement also groups by customer id.
The context declaration shown next assumes that the application provides a computeHash single-row function that accepts BankTxn as a parameter, wherein the result of this function must be an integer value that returns the context partition id for each event:
create context MyHashContext coalesce by computeHash(*) from BankTxn granularity 16 preallocate
The statement that refers to a hash segmented context must have at least one filter expression, at any place within the statement that looks for events of any of the event types listed in the context declaration.
For example, the following is not valid:
// Neither LoginEvent nor LogoutEvent are listed in the context declaration context SegmentedByCustomerHash select * from pattern [every a=LoginEvent -> b=LogoutEvent where timer:within(10 minutes)]
If the context declaration lists multiple streams, each event type must be unrelated: You may not list the same event type twice and you may not list a sub- or super-type of any event type already listed.
If the context declaration lists multiple streams, the hash code function should return the same hash code for the related keys of all streams.
The next statement creates a context HashedByCustomer that also considers LoginEvent and LogoutEvent:
create context HashedByCustomer as coalesce consistent_hash_crc32(custId) from BankTxn, consistent_hash_crc32(loginId) from LoginEvent, consistent_hash_crc32(loginId) from LogoutEvent granularity 32 preallocate
You may add a filter expression to each of the event types listed. The runtime applies the filter expression to the statement that refers to the context and to the same event type.
The next statement creates a context HashedByCustomer that does not consider login events that indicate that the login failed.
create context HashedByCustomer coalesce consistent_hash_crc32(loginId) from LoginEvent(failed = false) granularity 1024 preallocate
The following context properties are available in your statement when it refers to a keyed segmented context:
Table 4.2. Hash Segmented Context Properties
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
name | The string-type context name. |
id | The integer-type internal context partition id that the runtime assigns to the context partition. |
Assume the hashed segmented context is declared as follows:
create context ByCustomerHash coalesce consistent_hash_crc32(custId) from BankTxn granularity 1024
You may, for example, select the context properties as follows:
context ByCustomerHash select context.name, context.id from BankTxn
The hash_code function based on the Java object hash code is generally faster than the CRC32 algorithm. The CRC32 algorithm, when used with a non-String parameter or with multiple parameters, requires the runtime to serialize all expression results to a byte array to compute the CRC32 hash code.
We recommend keeping the granularity small (1k and under) when using preallocate.
When specifying a granularity greater than 65536 (64k) the runtime switches to a Map-based lookup of context partition state which can slow down statement processing.
This context assigns events to context partitions based on the values of one or more event properties, using a predicate expression(s) to define context partition membership. Each event can thus belong to zero, one or many context partitions depending on the outcome of the predicate expression(s).
The syntax for creating a category segmented context is as follows:
create context context_name group [by] group_expression as category_label [, group [by] group_expression as category_label] [, ...] from stream_def
The context_name you assign to the context can be any identifier.
Following the context name is a list of groups separated by the group keyword. The list of groups is followed by the from keyword and a stream definition.
The group_expression is an expression that categorizes events. Each group expression must be followed by the as keyword and a category label which can be any identifier.
Group expressions are predicate expressions and must return a Boolean-type true or false when applied to an event. For a given event, any number of group expressions may return true thus categories can be overlapping.
The stream_def is a stream definition which consists of an event type name optionally followed by parenthesis that contains filter expressions. If providing filter expressions, only events matching the provided filter expressions for that event type are considered by context partitions.
The next statement creates a context CategoryByTemp that consider the value of the temperature property of the SensorEvent event type to pick context partitions to assign events to:
create context CategoryByTemp group temp < 65 as cold, group temp between 65 and 85 as normal, group temp > 85 as large from SensorEvent
The following statement simply counts, for each category, the number of events and outputs the category label and count:
context CategoryByTemp select context.label, count(*) from SensorEvent
The following context properties are available in your statement when it refers to a category segmented context:
Table 4.3. Category Segmented Context Properties
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
name | The string-type context name. |
id | The integer-type internal context partition id that the runtime assigns to the context partition. |
label | The category label is the string identifier value after the as keyword that is specified for each group. |
You may, for example, select the context properties as follows:
context CategoryByTemp select context.name, context.id, context.label from SensorEvent
You may declare a non-overlapping context that exists once or that repeats in a regular fashion as controlled by a start condition and an optional end condition. The number of context partitions is always either one or zero: Context partitions do not overlap.
The syntax for creating a non-overlapping context is as follows:
create context context_name start (@now | start_condition) [ end end_condition ]
The context_name you assign to the context can be any identifier.
Following the context name is the start keyword, either @now or a start_condition. It follows the optional end keyword and an end_condition.
Both the start condition and the end condition, if specified, can be an event filter, a pattern, a crontab or a time period. The syntax of start and end conditions is described in Section 4.2.7, “Context Conditions”.
Once the start condition occurs, the runtime no longer observes the start condition and begins observing the end condition, if an end condition was provided.
Once the end condition occurs, the runtime observes the start condition again.
If you specified @now instead of a start condition, the runtime begins observing the end condition instead.
If there is no end condition the context partition remains alive and does not end.
If you specified an event filter as the start condition, then the event also counts towards the statement(s) that refer to that context. If you specified a pattern as the start condition, then the events that may constitute the pattern match can also count towards the statement(s) that refer to the context provided that @inclusive and event tags are both specified (see below).
At the time of context activation when your application creates a statement that utilizes the context, the runtime checks whether the start and end condition are crontab expressions. The runtime evaluates the start and end crontab expressions and determines whether the current time is a time between start and end. If the current time is between start and end times, the runtime allocates the context partition and waits for observing the end time. Otherwise the runtime waits to observe the start time and does not allocate a context partition.
The built-in context properties that are available are the same as described in Section 4.2.6.2, “Built-In Context Properties”.
The next statement creates a context NineToFive that declares a daily time period that starts at 9 am and ends at 5 pm:
create context NineToFive start (0, 9, *, *, *) end (0, 17, *, *, *)
The following statement outputs speed violations between 9 am and 5 pm, considering a speed of 100 or greater as a violation:
context NineToFive select * from TrafficEvent(speed >= 100)
The example that follows demonstrates the use of an event filter as the start condition and a pattern as the end condition.
The next statement creates a context PowerOutage that starts when the first PowerOutageEvent event arrives and that ends 5 seconds after a subsequent PowerOnEvent arrives:
create context PowerOutage start PowerOutageEvent end pattern [PowerOnEvent -> timer:interval(5)]
The following statement outputs the temperature during a power outage and for 5 seconds after the power comes on:
context PowerOutage select * from TemperatureEvent
To output only the last value when a context partition ends (terminates, expires), please read on to the description of output rate limiting.
The next statement creates a context Every15Minutes that starts immediately and lasts for 15 minutes, repeatedly allocating a new context partition at the end of 15 minute intervals:
create context Every15Minutes start @now end after 15 minutes
The next example declares an AlwaysOn context: It starts immediately and does not end unless the application uses the API to terminate the context partition:
create context AlwaysOn start @now
Tip
A non-overlapping context with @now is always-on: A context partition is always allocated at any given point in time. Only if @now is specified
will a context partition always exist at any point in time.
Note
If you specified an event filter or pattern as the end condition for a context partition, and statements that refer to the context specify an event filter or pattern that matches the same conditions, use @Priority to instruct the runtime whether the context management or the statement evaluation takes priority (see below for configuring prioritized execution).
For example, if your context declaration looks like this:
create context MyCtx start MyStartEvent end MyEndEvent
And a statement managed by the context is this:
context MyCtx select count(*) as cnt from MyEndEvent output when terminated
By using @Priority(1) for create-context and @Priority(0) for the counting statement the counting statement does not count the last MyEndEvent
since context partition management takes priority.
By using @Priority(0) for create-context and @Priority(1) for the counting statement the counting statement will count the last MyEndEvent
since the statement evaluation takes priority.
This context initiates a new context partition when an initiating condition occurs, and terminates one or more context partitions when the terminating condition occurs, if a terminating condition was specified. Thus multiple overlapping context partitions can be active at any point and context partitions can overlap.
The syntax for creating an overlapping context is as follows:
create context context_name initiated [by] [distinct (distinct_value_expr [,...])] [@now and] initiating_condition [ terminated [by] terminating_condition ]
The context_name you assign to the context can be any identifier.
Following the context name is the initiated keyword.
After the initiated keyword you can optionally specify the distinct keyword and, within parenthesis, list one or more distinct value expressions.
After the initiated keyword you can also specify @now and as explained below.
After the initiated keyword you must specify the initiating condition.
You may optionally use the terminated keyword followed by the terminating condition.
If no terminating condition is specified each context partition remains alive and does not terminate.
Both the initiating condition and the terminating condition, if specified, can be an event filter, a pattern, a crontab or a time period. The syntax of initiating and terminating conditions is described in Section 4.2.7, “Context Conditions”.
If you specified @now and before the initiating condition then the runtime initiates a new context partition immediately. The @now is only allowed in conjunction with initiation conditions that specify a pattern, crontab or time period and not with event filters.
If you specified an event filter for the initiating condition, then the event that initiates a new context partition also counts towards the statement(s) that refer to that context. If you specified a pattern to initiate a new context partition, then the events that may constitute the pattern match can also count towards the statement(s) that refer to the context provided that @inclusive and event tags are both specified (see below).
The next statement creates a context CtxTrainEnter that allocates a new context partition when a train enters a station, and that terminates each context partition 5 minutes after the time the context partition was allocated:
create context CtxTrainEnter initiated by TrainEnterEvent as te terminated after 5 minutes
The context declared above assigns the stream name te. Thereby the initiating event's properties can be accessed, for example, by specifying context.te.trainId.
The following statement detects when a train enters a station as indicated by a TrainEnterEvent, but does not leave the station within 5 minutes as would be indicated by a matching TrainLeaveEvent:
context CtxTrainEnter select t1 from pattern [ t1=TrainEnterEvent(trainId = context.te.trainId) -> timer:interval(5 min) and not TrainLeaveEvent(trainId = context.te.trainId) ]
Tip
Each event (incoming or inserted-into) applies to each context partition. You must provide filter expressions that indicate how events apply to context partitions.
The example above has trainId = context.te.trainId to say that the train id of events must match the train id of the initiating event of the particular context partition.
Since the TrainEnterEvent that initiates a new context partition also counts towards the statement, the first part of the pattern (the t1=TrainEnterEvent) is satisfied by that initiating event.
The next statement creates a context CtxEachMinute that allocates a new context partition immediately and every 1 minute, and that terminates each context partition 1 minute after the time the context partition was allocated:
create context CtxEachMinute initiated @now and pattern [every timer:interval(1 minute)] terminated after 1 minutes
The statement above specifies @now to instruct the runtime to allocate a new context partition immediately as well as when the pattern fires.
Without the @now the runtime would only allocate a new context partition when the pattern fires after 1 minute and every minute thereafter.
The following statement averages the temperature, starting anew every 1 minute and outputs the aggregate value continuously:
context CtxEachMinute select avg(temp) from SensorEvent
To output only the last value when a context partition ends (terminates, expires), please read on to the description of output rate limiting.
By providing no terminating condition, you can tell the runtime to allocate context partitions that never terminate, for example:
create context CtxTrainEnter initiated by TrainEnterEvent as te
Note
If you specified an event filter or pattern as the termination condition for a context partition, and statements that refer to the context specify an event filter or pattern that matches the same conditions, use @Priority to instruct the runtime whether the context management or the statement evaluation takes priority (see below for configuring prioritized execution). See the note above for more information.
If your initiating condition is a filter context condition, you may specify the distinct keyword followed by one or more distinct-value expressions.
Further detail on key expressions can be found at Section 5.2.13, “Composite Keys and Array Values as Keys”.
The following sample EPL specifies a context that initiates a context partition for distinct order id values, remembering that order id until the time the context partition terminates:
create context OrderContext initiated by distinct(orderId) NewOrderEvent as newOrder terminated by CloseOrderEvent(closeOrderId = newOrder.orderId)
The runtime allocates a new context partition only when a context partition does not already exist for a given orderId value of NewOrderEvent.
When the context partition terminates at the time a CloseOrderEvent arrives, the runtime forgets about the orderId,
allowing the next NewOrderEvent event for the same orderId to allocate a new context partition.
Please note the following limitations:
The
distinctkeyword requires the initiating condition to be an event stream (and not a crontab or pattern, for example) and a stream name must be assigned using theaskeyword.Subqueries, aggregations and the special
prevandpriorfunctions are not allowed among the distinct-value expressions.
The following context properties are available in your statement when it refers to a context:
Table 4.4. Context Properties
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
name | The string-type context name. |
startTime | The start time of the context partition. |
endTime | The end time of the context partition. This field is only available in the case that it can be computed from the crontab or time period expression that is provided. Use current_timestamp instead.
|
You may, for example, select the context properties as follows:
context NineToFive select context.name, context.startTime, context.endTime from TrafficEvent(speed >= 100)
The following statement looks for the next train leave event for the same train id and selects a few of the context properties:
context CtxTrainEnter select *, context.te.trainId, context.id, context.name from TrainLeaveEvent(trainId = context.te.trainId)
Context start/initiating and end/terminating conditions are for use with overlapping and non-overlapping contexts. Any combination of conditions may be specified.
Define the stream that starts/initiates a context partition or that ends/terminates a context partition:
event_stream_name [(filter_criteria)] [as stream_name]
The event_stream_name is either the name of an event type or name of an event stream populated by an insert into statement. The filter_criteria is optional and consists of a list of expressions filtering the events of the event stream, within parenthesis after the event stream name.
Two examples are:
// A non-overlapping context that starts when MyStartEvent arrives and ends when MyEndEvent arrives create context MyContext start MyStartEvent end MyEndEvent
// An overlapping context where each MyEvent with level greater zero // initiates a new context partition that terminates after 10 seconds create context MyContext initiated MyEvent(level > 0) terminated after 10 seconds
You may correlate the start/initiating and end/terminating streams by providing a stream name following the as keyword, and by referring to that stream name in the filter criteria of the end condition.
Two examples that correlate the start/initiating and end/terminating condition are:
// A non-overlapping context that starts when MyEvent arrives // and ends when a matching MyEvent arrives (same id) create context MyContext start MyEvent as myevent end MyEvent(id=myevent.id)
// An overlapping context where each MyInitEvent initiates a new context partition // that terminates when a matching MyTermEvent arrives create context MyContext initiated by MyInitEvent as e1 terminated by MyTermEvent(id=e1.id, level <> e1.level) as e2
When specifying a stream name for the filter the context built-in properties carry the stream name. For example (termination is output only when using output when terminated):
context MyContext select context.e1, context.e1.propertyName, context.e2, context.e2.propertyName from SomeEvent
You can define a pattern that starts/initiates a context partition or that ends/terminates a context partition:
pattern [pattern_expression] [@inclusive] [as stream_name]
The pattern_expression is a pattern at Chapter 7, EPL Reference: Patterns.
Specify @inclusive after the pattern to have those same events that constitute the pattern match also count towards any statements that are associated to the context.
You must also provide a tag for each event in a pattern that should be included.
Examples are:
// A non-overlapping context that starts when either StartEventOne or StartEventTwo arrive // and that ends after 5 seconds. // Here neither StartEventOne or StartEventTwo count towards any statements // that are referring to the context. create context MyContext start pattern [StartEventOne or StartEventTwo] end after 5 seconds
// Same as above. // Here both StartEventOne or StartEventTwo do count towards any statements // that are referring to the context. create context MyContext start pattern [a=StartEventOne or b=StartEventTwo] @inclusive end after 5 seconds
// An overlapping context where each distinct MyInitEvent initiates a new context // and each context partition terminates after 20 seconds // Use @inclusive to say that the same MyInitEvent that fires the pattern // also applies to statements that are associated to the context. create context MyContext initiated by pattern [every-distinct(a.id, 20 sec) a=MyInitEvent]@inclusive terminated after 20 sec
// An overlapping context where each pattern match initiates a new context // and all context partitions terminate when MyTermEvent arrives. // The MyInitEvent and MyOtherEvent that trigger the pattern are themselves not included // in any statements that are associated to the context. create context MyContext initiated by pattern [every MyInitEvent -> MyOtherEvent where timer:within(5)] terminated by MyTermEvent
You may correlate the start and end streams by providing tags as part of the pattern, and by referring to the tag name(s) in the filter criteria of the end condition.
An example that correlates the start and end condition is:
// A non-overlapping context that starts when either StartEventOne or StartEventTwo arrive // and that ends when either a matching EndEventOne or EndEventTwo arrive create context MyContext start pattern [a=StartEventOne or b=StartEventTwo] end pattern [EndEventOne(id=a.id) or EndEventTwo(id=b.id)]
You may correlate the start/initiating and end/terminating patterns by providing a stream name following the as keyword, and by referring to that stream name in the filter criteria of the end condition.
An example that correlates the start and end condition and that specifies a stream name for the pattern match follows:
create context MyContext start pattern [a=StartEventOne or b=StartEventTwo] as startingPattern end pattern [c=EndEventOne(id=startingPattern.a.id) or d=EndEventTwo(id=startingPattern.b.id)] as endingPattern
When specifying a stream name for the pattern the context built-in properties carry the stream name. For example (termination is output only when using output when terminated):
context MyContext select context.startingPattern, context.startingPattern.a, context.startingPattern.a.propertyName, context.endingPattern, context.endingPattern.c, context.endingPattern.c.propertyName from SomeEvent
Crontab expressions are described in Section 7.6.4, “Crontab (timer:at)”.
Multiple crontab expressions may be provided that are separated by comma. When specifying multiple crontabs, the runtime determines the earliest time according to the crontabs.
Examples are:
// A non-overlapping context started daily between 9 am to 5 pm // and not started outside of these hours: create context NineToFive start (0, 9, *, *, *) end (0, 17, *, *, *)
// An overlapping context where crontab initiates a new context every 1 minute // and each context partition terminates after 10 seconds: create context MyContext initiated (*, *, *, *, *) terminated after 10 seconds
// From 8:00am (see start) to 9am (see end) and from 10am (see start) to 12pm (see end). create context MyContext start (0, 8, *, *, *, *), (0, 10, *, *, *, *) end (0, 9, *, *, *, *), (0, 12, *, *, *, *)
// Monday to Friday from 8am to 11am, Saturday and Sunday from 8am to 8pm. create context MyContext start (0, 8, *, *, *, *) end (0, 11, *, *, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], *), (0, 20, *, *, [0, 6], *)
// Monday from 8am to 10am, Tuesday from 9am to 10am create context MyContext start (0, 8, *, *, 1, *), (0, 9, *, *, 2, *) end (0, 10, *, *, *)
You may specify a time period that the runtime observes before the condition fires. Time period expressions are described in Section 5.2.1, “Specifying Time Periods”.
The syntax is:
after time_period_expressionExamples are:
// A non-overlapping context started after 10 seconds // that ends 1 minute after it starts and that again starts 10 seconds thereafter. create context NonOverlap10SecFor1Min start after 10 seconds end after 1 minute
// An overlapping context that starts a new context partition every 5 seconds // and each context partition lasts 1 minute create context Overlap5SecFor1Min initiated after 5 seconds terminated after 1 minute
A nested context is a context that is composed from two or more contexts.
The syntax for creating a nested context is as follows:
create context context_name context nested_context_name [as] nested_context_definition , context nested_context_name [as] nested_context_definition [, ...]
The context_name you assign to the context can be any identifier.
Following the context name is a comma-separated list of nested contexts. For each nested context specify the context keyword followed a nested context name and the nested context declaration. Any of the context declarations as outlined in Section 4.2, “Context Declaration” are allowed for nested contexts.
The order of nested context declarations matters as outlined below. The nested context names have meaning only in respect to built-in properties and statements may not be assigned to nested context names.
The next statement creates a nested context NineToFiveSegmented that, between 9 am and 5 pm, allocates a new context partition for each customer id:
create context NineToFiveSegmented context NineToFive start (0, 9, *, *, *) end (0, 17, *, *, *), context SegmentedByCustomer partition by custId from BankTxn
The following statement refers to the nested context to compute a total withdrawal amount per account for each customer but only between 9 am and 5 pm:
context NineToFiveSegmented select custId, account, sum(amount) from BankTxn group by account
EPL implements nested contexts as a context tree: The context declared first controls the lifecycle of the context(s) declared thereafter. Thereby, in the above example, outside of the 9am-to-5pm time the runtime has no memory and consumes no resources in relationship to bank transactions or customer ids.
When combining segmented contexts, the set of context partitions for the nested context effectively is the Cartesian product of the partition sets of the nested segmented contexts.
When combining temporal contexts with other contexts, since temporal contexts may overlap and may terminate, it is important to understand that temporal contexts control the lifecycle of sub-contexts (contexts declared thereafter). The order of declaration of contexts in a nested context can thereby change resource usage and output result.
The next statement creates a context that allocates context partition only when a train enters a station and then for each hash of the tag id of a passenger as indicated by PassengerScanEvent events, and terminates all context partitions after 5 minutes:
create context CtxNestedTrainEnter
context InitCtx initiated by TrainEnterEvent as te terminated after 5 minutes,
context HashCtx coalesce by consistent_hash_crc32(tagId) from PassengerScanEvent
granularity 16 preallocate
In the example above the runtime does not start tracking PassengerScanEvent events or hash codes or allocate context partitions until a TrainEnterEvent arrives. Because the HashCtx declares preallocate the runtime allocates 16 partitions as soon as
a TrainEnterEvent arrives. If the HashCtx did not declare preallocate the runtime would wait for PassengerScanEvent events to arrive and only then allocate a partition, and as more PassengerScanEvent events arrive, up to 16 partitions in total depending on the tagId values.
Tip
Think of nested contexts as a parent-child relationship with the parent declared first and its child listed next.
Nested contexts are not an OR-operator and are not an intersection. Switching the parent and child changes the behavior.
This section declares a nested context with nested non-overlapping contexts and walks through a specific scenario to help you better understand nested context lifecycles.
Assume event types AStart, AEnd, BStart, BEnd and C.
The following EPL counts C-events that occur within the span of AStart and AEnd and
a span of BStart and BEnd, wherein the span of AStart-to-AEnd must contain the span of BStart-to-BEnd:
create context CtxSampleNestedContext context SpanA start AStart end AEnd, context SpanB start BStart end BEnd
context CtxSampleNestedContext select count(*) from C
Upon creating the statements above, the runtime starts looking for an AStart event only and does not yet look for AEnd, BStart, BEnd or C events.
In the scenario, assume that an AStart event arrives next. This is, logically, the beginning of the SpanA lifecycle (aka. session, interval):
The runtime stops looking for an
AStartevent.The runtime starts looking for an
AEndevent, since that would mean the end of the currentSpanAlifecycle.The runtime starts looking for a
BStartevent, in order to detect the beginning of aSpanBlifecycle.
In the scenario, assume that a BStart event arrives. This is, logically, the beginning of the SpanB lifecycle:
The runtime stops looking for further
BStartevents.The runtime starts looking for a
BEndevent, since that would mean the end of the currentSpanBlifecycle.The runtime keeps looking for an
AEndevent, since that would mean the end of the currentSpanAlifecycle.The runtime starts looking for
Cevents and now starts counting eachCthat arrives.
In the scenario, assume that a BEnd event arrives. This is, logically, the end of the SpanB lifecycle:
The runtime stops looking for a
BEndevent.The runtime stops looking for
Cevents and stops counting each.The runtime starts looking for a
BStartevent, since that would mean the beginning of anotherSpanBlifecycle.
In the scenario, assume that an AEnd event arrives. This is, logically, the end of the SpanA lifecycle:
The runtime stops looking for an
AEndevent.The runtime stops looking for a
BStartevent.The runtime starts looking for an
AStartevent, since that would mean the beginning of anotherSpanAlifecycle.
In the scenario describe above, after the AEnd arrives, the runtime is back to the same state as the runtime had after the statements were created originally.
If your use case calls for a logical OR relationships, please consider a pattern for the start condition, like for example so (not equivalent to above):
create context CtxSampleNestedContext start pattern[every a=AStart or every a=BStart] as mypattern end pattern[every AEnd or every BEnd]
Context properties of all nested contexts are available for use. Specify context.nested_context_name.property_name or if nested context declaration provided stream names or tags for patterns then context.nested_context_name.stream_name.property_name.
For example, consider the CtxNestedTrainEnter context declared earlier. The following statement selects a few of the context properties:
context CtxNestedTrainEnter select context.InitCtx.te.trainId, context.HashCtx.id, tagId, count(*) from PassengerScanEvent group by tagId
In a second example, consider the NineToFiveSegmented context declared earlier. The following statement selects a few of the context properties:
context NineToFiveSegmented select context.NineToFive.startTime, context.SegmentedByCustomer.key1 from BankTxn
The following context properties are available in your statement when it refers to a nested context:
Table 4.5. Nested Context Properties
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
name | The string-type context name. |
id | The integer-type internal context partition id that the runtime assigns to the context partition. |
This example selects the nested context name and context partition id:
context NineToFiveSegmented select context.name, context.id from BankTxn
You do not need to declare a context to partition data windows, aggregation values or patterns themselves individually. You may mix-and-match partitioning as needed.
The table below outlines other partitioning syntax supported by EPL:
Table 4.6. Partition in EPL Without the Use of Context Declarations
| Partition Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Grouped Data Window | Partitions at the level of data window, only applies to appended data window(s). Syntax: | // Length window of 2 events per customer select * from BankTxn#groupwin(custId)#length(2) |
| Grouped Aggregation | Partitions at the level of aggregation, only applies to any aggregations. Syntax: | select avg(price), window(*) from BankTxn group by custId |
| Pattern | Partitions pattern subexpressions. Syntax: | select * from pattern [ every a=BankTxn -> BankTxn(custId = a.custId)...] |
| Match-Recognize | Partitions match-recognize patterns. Syntax: | select * from match_recognize ... partition by custId |
| Join and Subquery | Partitions join and subqueries. Syntax: | select * from ... where a.custId = b.custId |
The from-clause is optional in EPL statements and you may simply select the relevant context properties. The links to the respective sections are Section 4.2.2.7, “Built-In Context Properties”, Section 4.2.3.3, “Built-In Context Properties”, Section 4.2.4.1, “Built-In Context Properties”, Section 4.2.6.2, “Built-In Context Properties” and Section 4.3.2, “Built-In Nested Context Properties”.
The following example CtxPerOrder context initiates a new context partition for each OrderEvent and each context partition expires after 5 minutes:
create context CtxPerOrderFiveMinutes initiated by OrderEvent as orderEvent terminated after 5 minutes
This EPL fires when the runtime initiates a context partition due to an OrderEvent arriving:
context CtxPerOrderFiveMinutes select context.orderEvent as orderEvent
Use insert into to trigger additional activity. Use the fire-and-forget API to query context partitions. An example can be found at Section 16.7.4, “The From-Clause is Optional”. Use the iterator API on the EPStatement instance of the above EPL to iterate the context partition information. More information can be found at Section 16.5.4, “Using Iterators”.
You may use output rate limiting to trigger output when a context partition ends or terminates using output when terminated.
This concept was introduced to you in Section 2.13, “Basic Partitioned and Output-Rate-Limited Statement”.
For more information on output rate limiting please see Section 5.7, “Stabilizing and Controlling Output: The Output Clause”.
The context CtxEachMinute initiates a new context partition every 1 minute, and each context partition expires after 5 minutes:
create context CtxEachMinute initiated by pattern [every timer:interval(1 min)] terminated after 5 minutes
The from-clause is optional in EPL statements and you may simply select the relevant context properties and use output when terminated:
context CtxEachMinute select current_timestamp as endtime, context.id as contextId output when terminated
The following statement computes an ongoing average temperature however only outputs the last value of the average temperature, together with the context partition id and the current runtime time, after 5 minutes when a context partition ends:
context CtxEachMinute select current_timestamp as endtime, context.id, avg(temp) from SensorEvent output last when terminated
The when terminated syntax can be combined with other output rates.
The next example outputs every 1 minute and also when the context partition ends:
context CtxEachMinute select context.id, avg(temp) from SensorEvent output last every 1 minute and when terminated
In the case that the end/terminating condition of the context partition is an event or pattern, the context properties contain the information of the tagged events in the pattern or the single event that ended/terminated the context partition.
For example, consider the following context wherein the runtime initializes a new context partition for each arriving MyStartEvent event and that terminates a context partition when a matching MyEndEvent arrives:
create context CtxSample initiated by MyStartEvent as startevent terminated by MyEndEvent(id = startevent.id) as endevent
The following statement outputs the id property of the initiating and terminating event and only outputs when a context partition ends:
context CtxSample select context.startevent.id, context.endevent.id, count(*) from MyEvent output last when terminated
You may in addition specify a termination expression that the runtime evaluates when a context partition terminates. Only when the termination expression evaluates to true does output occur. The expression may refer to built-in properties as described in Section 5.7.1.1, “Controlling Output Using an Expression”. The syntax is as follows:
...output when terminated and termination_expressionThe next example statement outputs when a context partition ends but only if at least two events are available for output:
context CtxEachMinute select * from SensorEvent output when terminated and count_insert >= 2
The final example EPL outputs when a context partition ends and sets the variable myvar to a new value:
context CtxEachMinute select * from SensorEvent output when terminated then set myvar=3
Named windows are globally-visible data windows that may be referred to by multiple statements. You may refer to named windows in statements that declare a context without any special considerations, with the exception of on-action statements (latter must refer to the same context associated with the named window).
You may also create a named window and declare a context for the named window. In this case the runtime in effect manages separate named windows, one for each context partition.
For example, consider the 9 am to 5 pm non-overlapping context as shown earlier:
create context NineToFive start (0, 9, *, *, *) end (0, 17, *, *, *)
You may create a named window that only exists between 9 am and 5 pm:
context NineToFive create window SpeedingEvents1Hour#time(30 min) as TrafficEvent
You can insert into the named window:
context NineToFive on TrafficEvent(speed > 100) merge SpeedingEvents1Hour insert select *
Any on-merge, on-select, on-update and on-delete statements must declare the same context, in order to operate on partitioned named windows or tables for the same partition.
The following is not a valid statement as it does not declare the same context that was used to declare the named window:
// You must declare the same context for on-trigger statements on TruncateEvent delete from SpeedingEvents1Hour
The following is valid:
context NineToFive on TruncateEvent delete from SpeedingEvents1Hour
For context declarations that require specifying event types, such as the hash segmented context and keyed segmented context, please provide the named window underlying event type.
The following sample statements define a type for the named window, declare a context and associate the named window to the context:
create schema ScoreCycle (userId string, keyword string, productId string, score long)
create context HashByUserCtx as coalesce by consistent_hash_crc32(userId) from ScoreCycle granularity 64
context HashByUserCtx create window ScoreCycleWindow#unique(productId, keyword) as ScoreCycle
Note
Use on-merge to insert events into a specific partition.
Insert Into produces an event that is visible to all partitions.
Tables are globally-visible data structures that hold rows organized by primary key(s) and that may be referred to by multiple statements. You may refer to tables in statements that declare a context without any special considerations, with the exception of on-action statements (latter must refer to the same context associated with the table).
You may also create a table and declare a context for the table. In this case the runtime in effect manages separate tables, one for each context partition.
For example, consider the 9 am to 5 pm non-overlapping context as shown earlier:
create context NineToFive start (0, 9, *, *, *) end (0, 17, *, *, *)
You may create a table that only exists between 9 am and 5 pm:
context NineToFive create table AverageSpeedTable ( carId string primary key, avgSpeed avg(double))
You can aggregate-into the table only if the aggregating statement declares the same context:
// declare the same context as for the table context NineToFive into table AverageSpeedTable select avg(speed) as avgSpeed from TrafficEvent group by carId
When you declare a context for a table, any select, on-merge, on-select, on-update and on-delete statements as well as statements that subquery the table must declare the same context.
For example, this EPL truncates the AverageSpeedTable:
context NineToFive on TruncateEvent delete from AverageSpeedTable
Note
Use on-merge or into-table to insert events into a specific partition.
Insert Into produces an event that is visible to all partitions.
A variable is a scalar, object or event value that is available for use in all statements. Variables can be either global variables or context variables.
The value of a global variable is the same for all context partitions. The next example declares a global threshold variable:
create variable integer var_global_threshold = 100
For context variables, there is a variable value per context partition. The next example declares a context and a context variable:
create context ParkingLotContext initiated by CarArrivalEvent as cae terminated by CarDepartureEvent(lot = cae.lot)
context ParkingLotContext create variable integer var_parkinglot_threshold = 100
The variable var_parkinglot_threshold is a context variable. Each context partition can have its own value for the variable.
For more information on variables, please refer to Section 5.17, “Variables and Constants”.
Context variables can only be used in statements that associated to the same context.
The API to read and manage content partitions themselves is Section 16.17, “Context Partition Administration”.
Selecting specific context partitions and interrogating context partition state is useful for:
Iterating a specific context partition or a specific set of context partitions. Iterating a statement is described in Section 16.5.4, “Using Iterators”.
Executing a fire-and-forget (on-demand) query against specific context partition(s). Fire-and-forget queries are described in Section 16.7, “Execute Fire-and-Forget Queries Using EPFireAndForgetService”.
The runtime provides APIs to identify, filter and select context partitions for statement iteration and fire-and-forget queries. The APIs are described in detail at Section 16.16, “Context Partition Selection”.
For statement iteration, your application can provide context selector objects to the iterate and safeIterate methods on EPStatement. If your code does not provide context selectors
the iteration considers all context partitions. At the time of iteration, the runtime obtains the current set of context partitions and iterates each independently. If your statement has an order-by clause, the order-by clause orders within the context partition and does not order across context partitions.
For fire-and-forget queries, your application can provide context selector objects to the executeQuery method on EPFireAndForgetService and to the execute method on EPFireAndForgetPreparedQuery. If your code does not provide context selectors the fire-and-forget query considers all context partitions. At the time of fire-and-forget query execution, the runtime obtains the current set of context partitions and queries each independently. If the fire-and-forget query has an order-by clause, the order-by clause orders within the context partition and does not order across context partitions.
- 5.1. EPL Introduction
- 5.2. EPL Syntax
- 5.2.1. Specifying Time Periods
- 5.2.2. Using Comments
- 5.2.3. Reserved Keywords
- 5.2.4. Escaping Strings
- 5.2.5. Data Types
- 5.2.6. Using Constants and Enum Types
- 5.2.7. Annotation
- 5.2.8. Expression Alias
- 5.2.9. Expression Declaration
- 5.2.10. Inlined-Class Declaration
- 5.2.11. Script Declaration
- 5.2.12. Referring to a Context
- 5.2.13. Composite Keys and Array Values as Keys
- 5.3. Choosing Event Properties and Events: The Select Clause
- 5.3.1. Choosing the Event Itself: Select *
- 5.3.2. Choosing Specific Event Properties
- 5.3.3. Expressions
- 5.3.4. Renaming Event Properties
- 5.3.5. Choosing Event Properties and Events in a Join
- 5.3.6. Choosing Event Properties and Events From a Pattern
- 5.3.7. Selecting Insert and Remove Stream Events
- 5.3.8. Select Distinct
- 5.3.9. Transposing an Expression Result to a Stream
- 5.3.10. Selecting EventBean Instead of Underlying Event
- 5.4. Specifying Event Streams: The From Clause
- 5.5. Specifying Search Conditions: The Where Clause
- 5.6. Aggregates and Grouping: The Group-By Clause and the Having Clause
- 5.6.1. Using Aggregate Functions
- 5.6.2. Organizing Statement Results into Groups: The Group-by Clause
- 5.6.3. Using Group-By with Rollup, Cube and Grouping Sets
- 5.6.4. Specifying Grouping for Each Aggregation Function
- 5.6.5. Specifying a Filter Expression for Each Aggregation Function
- 5.6.6. Selecting Groups of Events: The Having Clause
- 5.6.7. How the Stream Filter, Where, Group By and Having-Clauses Interact
- 5.6.8. Comparing Keyed Segmented Context, the Group By Clause and #groupwin for Data Windows
- 5.7. Stabilizing and Controlling Output: The Output Clause
- 5.8. Sorting Output: the Order By Clause
- 5.9. Limiting Row Count: the Limit Clause
- 5.10. Merging Streams and Continuous Insertion: The Insert Into Clause
- 5.10.1. Transposing a Property to a Stream
- 5.10.2. Merging Streams by Event Type
- 5.10.3. Merging Disparate Types of Events: Variant Streams
- 5.10.4. Decorated Events
- 5.10.5. Event as a Property
- 5.10.6. Instantiating and Populating an Underlying Event Object
- 5.10.7. Transposing an Expression Result
- 5.10.8. Select-Clause Expression and Inserted-Into Column Event Type
- 5.10.9. Insert Into for Event Types Without Properties
- 5.10.10. Insert Into and Event Precedence
- 5.11. Subqueries
- 5.12. Joining Event Streams
- 5.13. Accessing Relational Data via SQL
- 5.13.1. Joining SQL Query Results
- 5.13.2. SQL Query and the EPL Where Clause
- 5.13.3. Outer Joins With SQL Queries
- 5.13.4. Using Patterns to Request (Poll) Data
- 5.13.5. Polling SQL Queries via Iterator
- 5.13.6. JDBC Implementation Overview
- 5.13.7. Oracle Drivers and No-Metadata Workaround
- 5.13.8. SQL Input Parameter and Column Output Conversion
- 5.13.9. SQL Row POJO Conversion
- 5.13.10. Executing SQL Fire-and-Forget Queries Using EPFireAndForgetService
- 5.14. Accessing Non-Relational Data via Method, Script or UDF Invocation
- 5.15. Declaring an Event Type: Create Schema
- 5.16. Splitting and Duplicating Streams
- 5.17. Variables and Constants
- 5.18. Declaring Global Expressions, Aliases and Scripts: Create Expression
- 5.19. Contained-Event Selection
- 5.19.1. Select-Clause in a Contained-Event Selection
- 5.19.2. Where Clause in a Contained-Event Selection
- 5.19.3. Contained-Event Selection and Joins
- 5.19.4. Sentence and Word Example
- 5.19.5. More Examples
- 5.19.6. Contained Expression Returning an Array of Property Values
- 5.19.7. Contained Expression Returning an Array of EventBean
- 5.19.8. Contained Expression Returning a Collection of Underlying Event Objects
- 5.19.9. Generating Marker Events Such as a Begin and End Event
- 5.19.10. Contained-Event Limitations
- 5.20. Updating an Insert Stream: The Update IStream Clause
- 5.21. Controlling Event Delivery : The For Clause
The Event Processing Language (EPL) is a SQL-standard language with extensions, offering SELECT, FROM, WHERE, GROUP BY, HAVING and ORDER BY clauses. Streams replace tables as the source of data with events replacing rows as the basic unit of data. Since events are composed of data, the SQL concepts of correlation through joins, subqueries and aggregation through grouping can be effectively leveraged.
The INSERT INTO clause is recast as a means of forwarding events to other streams for further processing. External data may be queried and joined with the stream data. Additional clauses such as the PATTERN and OUTPUT clauses are available to provide the missing SQL language constructs specific to event processing.
Statements can specify data windows. Similar to tables in a SQL statement, data windows define the subset of events to be analyzed.
Data windows can be combined to an intersection or union of sets of events.
Some of the often-used data windows are #length, #time, #unique, #lastevent, #firstevent and #keepall.
EPL provides the concept of named window. Named windows are data windows that can be used by multiple statements.
The name of a named window can occur in a statement's FROM clause to query the named window or to include the named window in a join or subquery.
EPL provides the concept of table. Tables are globally-visible data structures that typically have primary key columns and that can hold aggregation state. An overview of named windows and tables, and a comparison between them, can be found at Section 6.1, “Overview”.
EPL allows execution of fire-and-forget (on-demand, non-continuous, triggered by API) queries against named windows and tables through the runtime API. The statement compiler automatically indexes named window data for fast access by ON SELECT/MERGE/UPDATE/INSERT/DELETE without the need to create an index explicitly, or can access explicit (secondary) table indexes for operations on tables. For fast fire-and-forget query execution via runtime API use the CREATE INDEX syntax to create an explicit index for the named window or table in question.
Use CREATE SCHEMA to declare an event type.
Variables can come in handy to parameterize statements and change parameters on-the-fly and in response to events. Variables can be used in an expression anywhere in a statement as well as in the output clause for dynamic control of output rates.
The compiler and runtime can be extended by plugging-in custom developed data windows, aggregation functions, and more.
Statement are compiled and deployed into the runtime, and publish results to listeners as events are received by the runtime or time advances that match the criteria specified in the statement. Events can also be obtained from polling statement via the safeIterator and iterator methods that provide a pull-data API.
The select clause in a statement specifies the event properties or events to retrieve. The from clause in a statement specifies the event stream definitions and stream names to use. The where clause in n statement specifies search conditions that specify which event or event combination to search for. For example, the following statement returns the average price for IBM stock ticks in the last 30 seconds.
select avg(price) from StockTick#time(30 sec) where symbol='IBM'
Statements follow the below syntax. Statements can be simple queries or more complex queries. A simple select contains only a select clause and a single stream definition. Complex statements can be build that feature a more elaborate select list utilizing expressions, may join multiple streams, may contain a where clause with search conditions and so on.
[annotations] [expression_declarations] [context context_name] [into table table_name] [insert into insert_into_def] select select_list from stream_def [as name] [, stream_def [as name]] [,...] [where search_conditions] [group by grouping_expression_list] [having grouping_search_conditions] [output output_specification] [order by order_by_expression_list] [limit num_rows]
Time-based windows as well as pattern observers and guards take a time period as a parameter. Time periods follow the syntax below.
time-period : [year-part] [month-part] [week-part] [day-part] [hour-part] [minute-part] [seconds-part] [milliseconds-part] [microseconds-part] year-part : (number|variable_name) ("years" | "year") month-part : (number|variable_name) ("months" | "month") week-part : (number|variable_name) ("weeks" | "week") day-part : (number|variable_name) ("days" | "day") hour-part : (number|variable_name) ("hours" | "hour") minute-part : (number|variable_name) ("minutes" | "minute" | "min") seconds-part : (number|variable_name) ("seconds" | "second" | "sec") milliseconds-part : (number|variable_name) ("milliseconds" | "millisecond" | "msec") microseconds-part : (number|variable_name) ("microseconds" | "microsecond" | "usec")
Some examples of time periods are:
10 seconds 10 minutes 30 seconds 20 sec 100 msec 1 day 2 hours 20 minutes 15 seconds 110 milliseconds 5 microseconds 0.5 minutes 1 year 1 year 1 month
Variable names and substitution parameters '?' for prepared statements are also allowed as part of a time period expression.
Note
When the time period has a month or year part, all values must be integer-type values.
Comments can appear anywhere in the module and statement text where whitespace is allowed. Comments can be written in two ways: slash-slash (// ...) comments and slash-star (/* ... */) comments.
Slash-slash comments extend to the end of the line:
// This comment extends to the end of the line. // Two forward slashes with no whitespace between them begin such comments. select * from MyEvent // this is a slash-slash comment // All of this text together is a valid statement.
Slash-star comments can span multiple lines:
/* This comment is a "slash-star" comment that spans multiple lines. * It begins with the slash-star sequence with no space between the '/' and '*' characters. * By convention, subsequent lines can begin with a star and are aligned, but this is * not required. */ select * from MyEvent /* this also works */
Comments styles can also be mixed:
select field1, // first comment /* second comment*/ field2 from MyEvent
Certain words such as select, delete or set are reserved and may not be used as identifiers. Please consult Appendix C, Reserved Keywords for the list of reserved keywords and permitted keywords.
Names of built-in functions and certain auxiliary keywords are permitted as event property names and in the rename syntax of the select clause. For example, count is acceptable.
Consider the example below, which assumes that 'last' is an event property of MyEvent:
// valid select last, count(*) as count from MyEvent
This example shows an incorrect use of a reserved keyword:
// invalid select insert from MyEvent
EPL offers an escape syntax for reserved keywords: Event properties as well as event or stream names may be escaped via the backwards apostrophe ` (ASCII 96) character.
The next example queries an event type by name Order (a reserved keyword) that provides a property by name insert (a reserved keyword):
// valid select `insert` from `Order`
You may surround string values by either double-quotes (") or single-quotes ('). When your string constant in a statement itself contains double quotes or single quotes,
you must escape the quotes.
Double and single quotes may be escaped by the backslash (\) character or by unicode notation. Unicode 0027 is a single quote (') and 0022 is a double quote (").
Escaping event property names is described in Section 3.2.1, “Escape Characters”.
The sample EPL below escapes the single quote in the string constant John's, and filters out order events where the name value matches:
select * from OrderEvent(name='John\'s') // ...equivalent to... select * from OrderEvent(name='John\u0027s')
The next EPL escapes the string constant Quote "Hello":
select * from OrderEvent(description like "Quote \"Hello\"") // is equivalent to select * from OrderEvent(description like "Quote \u0022Hello\u0022")
When building an escape string via the API, escape the backslash, as shown in below code snippet:
compiler.compile("select * from OrderEvent(name='John\\'s')", ...);
// ... and for double quotes...
compiler.compile("select * from OrderEvent(description like \"Quote \\\"Hello\\\"\")", ...);For NEsper .NET also see Section J.13, “.NET EPL Syntax - Data Types”.
EPL honors all Java built-in primitive and boxed types, including java.math.BigInteger and java.math.BigDecimal.
EPL also follows Java standards in terms of widening, performing widening automatically in cases where widening type conversion is allowed without loss of precision, for both boxed and primitive types and including BigInteger and BigDecimal:
byte to short, int, long, float, double, BigInteger or BigDecimal
short to int, long, float, or double, BigInteger or BigDecimal
char to int, long, float, or double, BigInteger or BigDecimal
int to long, float, or double, BigInteger or BigDecimal
long to float or double, BigInteger or BigDecimal
float to double or BigDecimal
double to BigDecimal
In cases where loss of precision is possible because of narrowing requirements, EPL compilation outputs a compilation error.
EPL supports casting via the cast function.
EPL returns double-type values for division regardless of operand type. EPL can also be configured to follow Java rules for integer arithmetic instead as described in Section 17.5.6, “Compiler Settings Related to Expression Evaluation”.
Division by zero returns positive or negative infinity. Division by zero can be configured to return null instead.
An EPL constant is a number or a character string that indicates a fixed value. Constants can be used as expressions in many statements, including variable assignment and case-when statements. They can also be used as parameter values for many built-in objects and clauses. Constants are also called literals.
EPL supports the standard SQL constant notation as well as Java data type literals.
The following are types of EPL constants:
Table 5.1. Types of EPL constants
| Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| string | A single character to an unlimited number of characters. Valid delimiters are the single quote (') or double quote ("). | select 'volume' as field1, "sleep" as field2, "\u0041" as unicodeA |
| boolean | A boolean value. | select true as field1, false as field2 |
| integer | An integer value (4 byte). | select 1 as field1, -1 as field2, 1e2 as field3 |
| long | A long value (8 byte). Use the "L" or "l" (lowercase L) suffix. | select 1L as field1, 1l as field2 |
| double | A double-precision 64-bit IEEE 754 floating point. | select 1.67 as field1, 167e-2 as field2, 1.67d as field3 |
| float | A single-precision 32-bit IEEE 754 floating point. Use the "f" suffix. | select 1.2f as field1, 1.2F as field2 |
| byte | A 8-bit signed two's complement integer. | select 0x10 as field1 |
EPL does not have a single-byte character data type for its literals. Single character literals are treated as string.
Internal byte representation and boundary values of constants follow the Java standard.
EPL automatically performs widening of numbers to BigInteger and BigDecimal as required, and employs the respective equals, compareTo and arithmetic methods provided by BigInteger and BigDecimal.
To explicitly create BigInteger and BigDecimal constants in EPL, please use the cast syntax : cast(value, BigInteger).
Note that since BigDecimal.valueOf(1.0) is not the same as BigDecimal.valueOf(1) (in terms of equality through equals), care should be taken towards the consistent use of scale.
When using aggregation functions for BigInteger and BigDecimal values, please note these limitations:
The
median,stddevandavedevaggregation functions operate on the double value of the object and return a double value.All other aggregation functions return
BigDecimalorBigIntegervalues (exceptcount).
For BigDecimal precision and rounding, please see Section 17.5.6.5, “Math Context”. For division operations with BigDecimal number we recommend
configuring a math context.
This chapter is about Java language constants and enum types and their use in EPL expressions.
Java language constants are public static final fields in Java that may participate in expressions of all kinds, as this example shows:
select * from MyEvent where property = MyConstantClass.FIELD_VALUE
Event properties that are enumeration values can be compared by their enum type value:
select * from MyEvent where enumProp = EnumClass.ENUM_VALUE_1
Event properties can also be passed to enum type functions or compared to an enum type method result:
select * from MyEvent where somevalue = EnumClass.ENUM_VALUE_1.getSomeValue() or EnumClass.ENUM_VALUE_2.analyze(someothervalue)
Enum types have a valueOf method that returns the enum type value:
select * from MyEvent where enumProp = EnumClass.valueOf('ENUM_VALUE_1')
If your application does not import, through configuration, the package that contains the enumeration class, then it must also specify the package name of the class. Enum types that are inner classes must be qualified with $ following Java conventions.
For example, the Color enum type as an inner class to MyEvent in package org.myorg can be referenced as shown:
select * from MyEvent(enumProp=org.myorg.MyEvent$Color.GREEN)#firstevent
Instance methods may also be invoked on event instances by specifying a stream name, as shown below:
select myevent.computeSomething() as result from MyEvent as myevent
Chaining instance methods is supported as this example shows:
select myevent.getComputerFor('books', 'movies').calculate() as result
from MyEvent as myeventAn annotation is an addition made to information in a statement. EPL provides certain built-in annotations for defining statement name, adding a statement description or for tagging statements such as for managing statements or directing statement output. Other than the built-in annotations, applications can provide their own annotation classes that the EPL compiler can populate.
An annotation is part of the statement text and precedes the statement. Annotations are therefore part of the EPL grammar. The syntax for annotations follows the host language (Java, .NET) annotation syntax:
@annotation_name [(annotation_parameters)]
An annotation consists of the annotation name and optional annotation parameters. The annotation_name is the simple class name or fully-qualified class name of the annotation class. The optional annotation_parameters are a list of key-value pairs following the syntax:
@annotation_name (attribute_name = attribute_value, [name=value, ...])
The attribute_name is an identifier that must match the attributes defined by the annotation class. An attribute_value is a constant of any of the primitive types or string, an array, an enum type value or another (nested) annotation. Null values are not allowed as annotation attribute values. Enumeration values are supported in statements and not support in statements created via the createPattern method.
Use the getAnnotations method of EPStatement to obtain annotations.
Your application may provide its own annotation classes. The compiler detects and populates annotation instances for application annotation classes.
The name of application-provided annotations is case-sensitive.
To enable the compiler to recognize application annotation classes, your annotation name must include the package name (i.e. be fully-qualified) or your compiler configuration must import the annotation class or package via the configuration API.
For example, assume that your application defines an annotation in its application code as follows:
public @interface ProcessMonitor {
String processName();
boolean isLongRunning default false;
int[] subProcessIds;
}Shown next is a statement that utilizes the annotation class defined earlier:
@ProcessMonitor(processName='CreditApproval',
isLongRunning=true, subProcessIds = {1, 2, 3} )
select count(*) from ProcessEvent(processId in (1, 2, 3)#time(30)
Above example assumes the ProcessMonitor annotation class is imported via configuration XML or API.
If ProcessMonitor should only be visible for use in annotations, use addAnnotationImport (or the auto-import-annotations XML tag).
If ProcessMonitor should be visible in all of EPL including annotations, use addImport (or the auto-import XML tag).
Here is an example API call to import for annotation-only all classes in package com.mycompany.app.myannotations:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addAnnotationImport("com.mycompany.app.myannotations.*");
The next example imports the ProcessMonitor class only and only for annotation use:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addAnnotationImport("com.mycompany.myannotations.ProcessMonitor");For annotations that accept an enumeration value, the enumeration name does not need to be specified and matching is not case-sensitive.
For example, assume the enum is:
public enum MyEnum {
ENUM_VALUE_1,
ENUM_VALUE_2;
}Assume the annotation is:
public @interface MyAnnotationWithEnum {
MyEnum myEnum();
}The statement can specify:
@MyAnnotationWithEnum(myEnum = enum_value_1) select * from MyEvent
The name of built-in annotations is not case-sensitive, allowing both @NAME or @name, for example.
The list of built-in statement-level annotations is:
Table 5.2. Built-In Statement Annotations
| Name | Purpose and Attributes | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Name |
Provides a statement name. Attributes are: value : Statement name. | @Name("MyStatementName") |
| Description |
Provides a statement description. Attributes are: value : Statement description. | @Description("Place statement
description here.") |
| Tag |
For tagging a statement with additional information. Attributes are: name : Tag name. value : Tag value. | @Tag(name="MyTagName", value="MyTagValue") |
| Priority |
Applicable when an event (or schedule) matches filter criteria for multiple statements: Defines the order of statement processing (requires an runtime-level setting). Attributes are: value : priority value. | @Priority(10) |
| Drop |
Applicable when an event (or schedule) matches filter criteria for multiple statements, drops the event after processing the statement (requires a runtime-level setting). No attributes. | @Drop |
| Hint |
For providing one or more hints towards how the runtime should execute a statement. Attributes are: value : A comma-separated list of one or more case-insensitive keywords. | @Hint('iterate_only') |
| Hook |
Use this annotation to register one or more statement-specific hooks providing a hook type for each individual hook, such as for SQL parameter, column or row conversion. Attributes are the hook | @Hook(type=HookType.SQLCOL, hook='MyDBTypeConvertor') |
| Audit |
Causes the runtime to output detailed processing information for a statement. optional value : A comma-separated list of one or more case-insensitive keywords. | @Audit |
| EventRepresentation |
Causes the compiler to use a specific event representation for output and internal event types. |
For Object-Array: @EventRepresentation(objectarray) For JSON: @EventRepresentation(json) For Map: @EventRepresentation(map) For Avro: @EventRepresentation(avro) |
| IterableUnbound |
For use when iterating statements with unbound streams, instructs the compiler to retain the last event for iterating. | @IterableUnbound |
The following example statement specifies some of the built-in annotations in combination:
@Name("RevenuePerCustomer")
@Description("Outputs revenue per customer considering all events encountered so far.")
@Tag(name="grouping", value="customer")
select customerId, sum(revenue) from CustomerRevenueEventUse the @Name EPL annotation to specify a statement name within the statement itself, as an alternative to specifying the statement name via API.
If your application is also providing a statement name through the API, the statement name provided through the API overrides the annotation-provided statement name.
Example:
@Name("SecurityFilter1") select * from SecurityFilter(ip="127.0.0.1")Use the @Description annotation to add a description text.
Example:
@Description('This statement filters localhost.') select * from SecurityFilter(ip="127.0.0.1")
Use the @Tag EPL annotation to tag statements with name-value pairs, effectively adding a property to the statement. The attributes name and value are of type string.
Example:
@Tag(name='ip_sensitive', value='Y') @Tag(name='author', value='Jim') select * from SecurityFilter(ip="127.0.0.1")
This annotation only takes effect if the runtime-level setting for prioritized execution is set via configuration, as described in Section 17.6.10, “Runtime Settings Related to Execution of Statements”.
Use the @Priority EPL annotation to tag statements with a priority value. The default priority value is zero (0) for all statements. When an event (or single timer execution) requires processing the event for multiple statements, processing begins with the highest priority statement and ends with the lowest-priority statement.
Example:
@Priority(10) select * from SecurityFilter(ip="127.0.0.1")
This annotation only takes effect if the runtime-level setting for prioritized execution is set via configuration, as described in Section 17.6.10, “Runtime Settings Related to Execution of Statements”.
Use the @Drop EPL annotation to tag statements that preempt all other same or lower-priority statements. When an event (or single timer execution) requires processing the event for multiple statements, processing begins with the highest priority statement and ends with the first statement marked with @Drop, which becomes the last statement to process that event.
Unless a different priority is specified, the statement with the @Drop EPL annotation executes at priority 1. Thereby @Drop alone is an effective means to remove events from a stream.
Example:
@Drop select * from SecurityFilter(ip="127.0.0.1")
A hint can be used to provide tips for the runtime to affect statement execution. Hints change performance or memory-use of a statement but generally do not change its output.
The string value of a Hint annotation contains a keyword or a comma-separated list of multiple keywords. Hint keywords are case-insensitive. A list of hints is available in Section 24.2.22, “Consider Using Hints”.
Example:
@Hint('disable_reclaim_group')
select ipaddress, count(*) from SecurityFilter#time(60 sec) group by ipaddressA hook is for attaching a callback to a statement.
The type value of a @Hook annotation defines the type of hook and the hook value is an imported or fully-qualified class name providing the callback implementation.
Causes the runtime to output detailed information about the statements processing. Described in more detail at Section 15.12.1, “@Audit Annotation”.
Use the @EventRepresentation annotation with create schema and create window statements to instruct the compiler to use a specific event representation for the schema or named window.
Use the @EventRepresentation annotation with select statements to instruct the compiler to use a specific event representation for output events.
When no @EventRepresentation annotation is specified, the compiler uses the default event representation as configured, see Section 17.4.9.1, “Default Event Representation”.
Use @EventRepresentation(objectarray) to instruct the compiler to use object-array events.
Use @EventRepresentation(json) to instruct the compiler to use JSON events.
Use @EventRepresentation(avro) to instruct the compiler to use Avro events.
Use @EventRepresentation(map) to instruct the compiler to use Map events.
Causes the compiler, for statements with unbound streams, to retain the last event for the purpose of iterating using the iterator API. A compiler configuration is also available as described in Section 17.5.2.1, “Iterator Behavior For Unbound Streams”.
An expression alias simply assigns a name to an expression. The alias name can be used in other expressions to refer to that expression, without the need to duplicate the expression.
The expression alias obtains its scope from where it is used. Parameters cannot be provided. A second means to sharing expressions is the expression declaration as described next, which allows passing parameters and is more tightly scoped.
A statement can contain and refer to any number of expression aliases.
For expressions aliases that are visible across multiple statements please consult Section 5.18.1, “Global Expression Aliases”
that explains the create expression clause.
The syntax for an expression alias is:
expression expression_namealias for {expression}
An expression alias consists of the expression name and an expression in curly braces. The return type of the expression is determined by the compiler and need not be specified. The scope is automatic and determined by where the alias name is used therefore parameters cannot be specified.
This example declares an expression alias twoPI that substitutes Math.PI * 2:
expression twoPI alias for { Math.PI * 2 }
select twoPI from SampleEvent
The next example specifies an alias countPeople and uses the alias in the select-clause and the having-clause:
expression countPeople alias for { count(*) }
select countPeople from EnterRoomEvent#time(10 seconds) having countPeople > 10
When using the expression alias in an expression, empty parentheses can optionally be specified. In the above example, countPeople() can be used instead and equivalently.
The following scope rules apply for expression aliases:
Expression aliases do not remove implicit limitations: For example, aggregation functions cannot be used in a filter expression even if assigned an alias.
A statement can contain expression declarations. Expressions that are common to multiple places in the same statement can be moved to a named expression declaration and reused within the same statement without duplicating the expression itself.
For declaring expressions that are visible across multiple statements i.e. globally visible expressions please consult Section 5.18.2, “Global Expression Declarations”
that explains the create expression clause.
The runtime may cache declared expression result values and reuse cache values, see Section 17.6.10.6, “Declared Expression Value Cache Size”.
An expression declaration follows the lambda-style expression syntax. This syntax was chosen as it typically allows for a shorter and more concise expression body that can be easier to read then most procedural code.
The syntax for an expression declaration is:
expression expression_name { expression_body }
An expression declaration consists of the expression name and an expression body. The expression_name is any identifier. The expression_body contains optional parameters and the expression. The parameter types and the return type of the expression is determined by the compiler and do not need to be specified.
Parameters to a declared expression can be:
Any expression. For example
expression E {(v1,v2) => max(v1,v2)} select E(1, 2) from OrderItemEvent.A stream name defined in the
from-clause. For exampleexpression E {e => max(e.price,e.quote)} select E(o) from OrderItemEvent as o.A pattern tag name. For example
expression E {e => max(e.price,e.quote)} select E(o) from pattern[timer:interval(10) or o=OrderItemEvent].A wildcard (
*). For exampleexpression E {e => max(e.price,e.quote)} select E(*) from OrderItemEvent.
Use wildcard to pass the event itself to the expression. In a join or subquery, or more generally in an expression where multiple streams or pattern tags are available, the EPL must specify the stream name or pattern tag name and cannot use wildcard.
In the expression body the => lambda operator reads as "goes to" (-> may be used and is equivalent). The left side of the lambda operator specifies the input parameters (if any) and the right side holds the expression. The lambda expression x => x * x is read "x goes to x times x".
In the expression body, if your expression takes no parameters, you may simply specify the expression and do not need the => lambda operator.
If your expression takes one parameters, specify the input parameter name followed by the => lambda operator and followed by the expression. The synopsis for use with a single input parameter is:
expression_body: input_param_name => expression
If your expression takes two or more parameters, specify the input parameter names in parenthesis followed by the => lambda operator followed by the expression. The synopsis for use with a multiple input parameter is:
expression_body: (input_param [,input_param [,...]]) => expression
The following example declares an expression that returns two times PI (ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter) and demonstrates its use in a select-clause:
expression twoPI { Math.PI * 2} select twoPI() from SampleEventThe parentheses are optional when the expression accepts no parameters. The below is equivalent to the previous example:
expression twoPI { Math.PI * 2} select twoPI from SampleEventThe next example declares an expression that accepts one parameter: a MarketData event. The expression computes a new "mid" price based on the buy and sell price:
expression midPrice { x => (x.buy + x.sell) / 2 }
select midPrice(md) from MarketDataEvent as mdThe variable name can be left off if event property names resolve without ambiguity.
This example EPL removes the variable name x:
expression midPrice { x => (buy + sell) / 2 }
select midPrice(md) from MarketDataEvent as mdThe next example EPL specifies wildcard instead:
expression midPrice { x => (buy + sell) / 2 }
select midPrice(*) from MarketDataEventA further example that demonstrates two parameters is listed next. The example joins two streams and uses the price value from MarketDataEvent and the sentiment value of NewsEvent to compute a weighted sentiment:
expression weightedSentiment { (x, y) => x.price * y.sentiment }
select weightedSentiment(md, news)
from MarketDataEvent#lastevent as md, NewsEvent#lastevent news
Any expression can be used in the expression body including aggregations, variables, subqueries or further declared or alias expressions. Sub-queries, when used without in or exists, must be placed within parenthesis.
An example subquery within an expression declaration is shown next:
expression newsSubq { md ->
(select sentiment from NewsEvent#unique(symbol) where symbol = md.symbol)
}
select newsSubq(mdstream)
from MarketDataEvent mdstreamWhen using expression declarations please note these limitations:
Parameters to a declared expression can only be a stream name, pattern tag name or wildcard (
*).Expression declarations do not remove implicit limitations: For example, aggregation functions cannot be used in a filter expression even if using an expression declaration.
The following scope rules apply for declared expressions:
The scope of the expression body of a declared expression only includes the parameters explicitly listed. Consider using an expression alias instead.
EPL allows adding Java-language (C# for NEsper) class code directly into the EPL. Please see Chapter 18, Inlined Classes for more information.
EPL allows the use of scripting languages. Any scripting language that supports JSR 223 and also the MVEL scripting language can be specified in EPL.
Please see Chapter 19, Script Support for more information.
You may refer to a context in the EPL text by specifying the context keyword followed by a context name. Context are described in more detail at Chapter 4, Context and Context Partitions
The effect of referring to a context is that your statement operates according to the context dimensional information as declared for the context.
The synopsis is:
... context context_name ...You may refer to a context in all statements except for the following types of statements:
create schemafor declaring event types.create variablefor declaring a variable.create indexfor creating an index on a named window or table.update istreamfor updating insert stream events.
EPL allows composite keys that consist of two or more expressions (or fields or columns or more generally expressions) that identify an occurrence. EPL also allows keys to be of type array.
This is applicable in each place there is an opportunity to provide key expressions. It is thus applicable to the group-by clause including rollup, data windows with keys (such as #unique, #firstunique, #groupwin, #rank), partition-by for keyed segmented contexts, contexts with distinct, the select-clause distinct keyword, the query planner when planning implicit and explicit indexes, create index, every-distinct, the partition-by clause for match-recognize, table column keyed-access expressions, the for-clause for grouped delivery and the distinctOf enumeration method as well as the distinct keyword for aggregation functions.
For expressions returning array of primitive the compiler uses Arrays.hashCode and Arrays.equals.
For expressions returning array of object the compiler uses Arrays.deepHashCode and Arrays.deepEquals.
The select clause is required in all statements. The select clause can be used to select all properties via the wildcard *, or to specify a list of event properties and expressions. The select clause defines the event type (event property names and types) of the resulting events published by the statement, or pulled from the statement via the iterator methods.
The select clause also offers optional istream, irstream and rstream keywords to control whether input stream, remove stream or input and remove stream events are posted to UpdateListener instances and observers to a statement. By default, the runtime provides only the insert stream to listener and observers. See Section 17.5.4, “Compiler Settings Related to Stream Selection” on how to change the default.
The syntax for the select clause is summarized below.
select [istream | irstream | rstream] [distinct] * | expression_list ...
The istream keyword is the default, and indicates that the runtime only delivers insert stream events to listeners and observers. The irstream keyword indicates that the runtime delivers both insert and remove stream. Finally, the rstream keyword tells the runtime to deliver only the remove stream.
The distinct keyword outputs only unique rows depending on the column list you have specified after it. It must occur after the select and after the optional stream keywords, as described in more detail below.
The syntax for selecting the event itself is:
select * from stream_defThe following statement selects StockTick events for the last 30 seconds of IBM stock ticks.
select * from StockTick(symbol='IBM')#time(30 sec)
You may well be asking: Why does the statement specify a time window here? First, the statement is meant to demonstrate the use of * wildcard.
When the runtime pushes statement results to your listener and as the statement does not select remove stream events via rstream keyword, the listener receives only new events and the time window could be left off.
By adding the time window the pull API (iterator API or JDBC driver) returns the last 30 seconds of events.
The * wildcard and expressions can also be combined in a select clause. The combination selects all event properties and in addition the computed values
as specified by any additional expressions that are part of the select clause. Here is an example that selects all properties of stock tick events plus a computed product of price and volume that the
statement names 'pricevolume':
select *, price * volume as pricevolume from StockTick
When using wildcard (*), the runtime does not actually read or copy your event properties out of your event or events, neither does it copy the event object.
It simply wraps your native type in an EventBean interface. Your application has access to
the underlying event object through the getUnderlying method and has access to the property values through the get method.
In a join statement, using the select * syntax selects one event property per stream to hold the event for that stream. The property name is the stream name in the from clause.
To choose the particular event properties to return:
select event_property [, event_property] [, ...] from stream_def
The following statement simply selects the symbol and price properties of stock ticks, and the total volume for stock tick events in a 60-second time window.
select symbol, price, sum(volume) from StockTick(symbol='IBM')#time(60 sec)
The select clause can contain one or more expressions.
select expression [, expression] [, ...] from stream_def
The following statement selects the volume multiplied by price for a time batch of the last 30 seconds of stock tick events.
select volume * price from StockTick#time_batch(30 sec)
Event properties and expressions can be renamed using below syntax.
select [event_property | expression] [as] identifier [, ...]
The following statement selects volume multiplied by price and specifies the name volPrice for the resulting column.
select volume * price as volPrice from StockTick
Identifiers cannot contain the "." (dot) character, i.e. "vol.price" is not a valid identifier for the rename syntax.
The as keyword is optional. The following EPL is therefore equivalent to above:
select volume * price volPrice from StockTick
If your statement is joining multiple streams, your may specify property names that are unique among the joined streams, or use wildcard (*) as explained earlier.
In case the property name in your select or other clauses is not unique considering all joined streams, you will need to use the name of the stream as a prefix to the property.
This example is a join between the two streams StockTick and News, respectively named as 'tick' and 'news'. The example selects from the StockTick event the symbol value using the 'tick' stream name as a prefix:
select tick.symbol from StockTick#time(10) as tick, News#time(10) as news where news.symbol = tick.symbol
Use the wildcard (*) selector in a join to generate a property for each stream, with the property value being the event itself. The output events of the statement below have two properties: the 'tick' property holds the StockTick event and the 'news' property holds the News event:
select * from StockTick#time(10) as tick, News#time(10) as news
The following syntax can also be used to specify what stream's properties to select:
select stream_name.* [as name] from ...
The selection of tick.* selects the StockTick stream events only:
select tick.* from StockTick#time(10) as tick, News#time(10) as news where tick.symbol = news.symbol
The next example uses the as keyword to name each stream's joined events. This instructs the compiler to create a property for each named event:
select tick.* as stocktick, news.* as news from StockTick#time(10) as tick, News#time(10) as news where stock.symbol = news.symbol
The output events of the above example have two properties 'stocktick' and 'news' that are the StockTick and News events.
The stream name itself, as further described in Section 5.4.5, “Using the Stream Name”, may be used within expressions or alone.
This example passes events to a user-defined function named compute and also shows insert-into to populate an event stream of combined events:
insert into TickNewStream select tick, news, MyLib.compute(news, tick) as result from StockTick#time(10) as tick, News#time(10) as news where tick.symbol = news.symbol
// second statement that uses the TickNewStream stream select tick.price, news.text, result from TickNewStream
In summary, the stream_name.* streamname wildcard syntax can be used to select a stream as the underlying event or as a property, but cannot appear within an expression. While the stream_name syntax (without wildcard) always selects a property (and not as an underlying event), and can occur anywhere within an expression.
If your statement employs pattern expressions, then your pattern expression tags events with a tag name. Each tag name becomes available for use as a property in the select clause and all other clauses.
For example, here is a very simple pattern that matches on every StockTick event received within 30 seconds after start of the statement. The sample selects the symbol and price properties of the matching events:
select tick.symbol as symbol, tick.price as price from pattern[every tick=StockTick where timer:within(10 sec)]
The use of the wildcard selector, as shown in the next statement, creates a property for each tagged event in the output. The next statement outputs events that hold a single 'tick' property whose value is the event itself:
select * from pattern[every tick=StockTick where timer:within(10 sec)]
You may also select the matching event itself using the tick.* syntax. The runtime outputs the StockTick event itself to listeners:
select tick.* from pattern[every tick=StockTick where timer:within(10 sec)]
A tag name as specified in a pattern is a valid expression itself. This example uses the insert into clause to make available the events matched by a pattern to further statements:
// make a new stream of ticks and news available insert into StockTickAndNews select tick, news from pattern [every tick=StockTick -> news=News(symbol=tick.symbol)]
// second statement to select from the stream of ticks and news select tick.symbol, tick.price, news.text from StockTickAndNews
The optional istream, irstream and rstream keywords in the select clause control the event streams posted to listeners and observers to a statement.
If neither keyword is specified, and in the default configuration, the runtime posts only
insert stream events via the newEvents parameter to the update method of UpdateListener instances listening to
the statement. The runtime does not post remove stream events, by default.
The insert stream consists of the events entering the respective window(s) or stream(s) or aggregations, while the remove stream consists of the events leaving the respective window(s) or the changed aggregation result. See Chapter 2, Basic Concepts for more information on insert and remove streams.
The runtime posts remove stream events to the oldEvents parameter of the update method only if the irstream keyword
occurs in the select clause. This behavior can be changed via configuration as described in Section 17.5.4, “Compiler Settings Related to Stream Selection”.
By specifying the istream keyword you can instruct the runtime to only post insert stream events via the newEvents parameter to the update method on listeners. The runtime will then not post any remove stream events, and the oldEvents parameter is always a null value.
By specifying the irstream keyword you can instruct the runtime to post both insert stream and remove stream events.
By specifying the rstream keyword you can instruct the runtime to only post remove stream events via the newEvents parameter to the update method on listeners. The runtime will then not post any insert stream events, and the oldEvents parameter is also always a null value.
The following statement selects only the events that are leaving the 30 second time window.
select rstream * from StockTick#time(30 sec)
The istream and rstream keywords in the select clause are matched by same-name keywords available in the insert into clause. While the keywords in the select clause control the event stream posted to listeners to the statement, the same keywords in the insert into clause specify the event stream that the runtime makes available to other statements.
The optional distinct keyword removes duplicate output events from output. The keyword must occur after the select keyword and after the optional irstream keyword.
The distinct keyword in your select instructs the runtime to consolidate, at time of output, the output event(s) and remove output events with identical property values.
Duplicate removal only takes place when two or more events are output together at any one time, therefore distinct is typically used with a batch data window, output rate limiting, fire-and-forget queries, on-select or iterator pull API.
If two or more output event objects have same property values for all properties of the event, the distinct removes all but one duplicated event before outputting events to listeners. Indexed, nested and mapped properties
are considered in the comparison, if present in the output event. Further detail on key expressions can be found at Section 5.2.13, “Composite Keys and Array Values as Keys”.
The next example outputs sensor ids of temperature sensor events, but only every 10 seconds and only unique sensor id values during the 10 seconds:
select distinct sensorId from TemperatureSensorEvent output every 10 seconds
Use distinct with wildcard (*) to remove duplicate output events considering all properties of an event.
This example statement outputs all distinct events either when 100 events arrive or when 10 seconds passed, whichever occurs first:
select distinct * from TemperatureSensorEvent#time_length_batch(10, 100)
When selecting nested, indexed, mapped or dynamic properties in a select clause with distinct, it is relevant to know that the comparison uses hash code and the Java equals semantics.
For transposing an instance of a Java object returned by an expression to a stream use the transpose function as described in Section 10.4, “Select-Clause Transpose Function”.
By default, for certain select-clause expressions that output events or a collection of events, the runtime outputs the underlying event objects. The term outputs means the data passed to listeners, subscribers and inserted-into into another stream via insert-into.
The select-clause expressions for which underlying event objects are output by default are:
- Event Aggregation Functions (including extension API)
-
The
previousfamily of single-row functions - Subselects that select events
- Declared expressions and enumeration methods that operate on any of the above
To have the runtime output EventBean instance(s) instead, add @eventbean
to the relevant expressions of the select-clause.
The sample EPL shown below outputs current data window contents as EventBean instances
into the stream OutStream, thereby statements consuming the stream may operate on such instances:
insert into OutStream select prevwindow(s0) @eventbean as win from MyEvent#length(2) as s0
The next EPL consumes the stream and selects the last event:
select win.lastOf() from OutStream
It is not necessary to use @eventbean if an event type by the same name (OutStream in the example) is already declared
and a property exist on the type by the same name (win in this example) and the type of the property is the event type (MyEvent in the example)
returned by the expression. This is further described in Section 5.10.8, “Select-Clause Expression and Inserted-Into Column Event Type”.
The from clause is required in all statements. It specifies one or more event streams, named windows or tables. Each event stream, named window or table can optionally be given a name by means of the as keyword.
from stream_def [as name] [unidirectional] [retain-union | retain-intersection] [, stream_def [as stream_name]] [, ...]
The event stream definition stream_def as shown in the syntax above can consists of either a filter-based event stream definition or a pattern-based event stream definition.
For joins and outer joins, specify two or more event streams. Joins and the unidirectional keyword are described in more detail in Section 5.12, “Joining Event Streams”.
Joins are handy when multiple streams or patterns can trigger output and outer joins can be used to union and connect streams via or.
EPL supports joins against relational databases for access to historical or reference data as explained in Section 5.13, “Accessing Relational Data via SQL”. EPL can also join results returned by an arbitrary invocation, as discussed in Section 5.14, “Accessing Non-Relational Data via Method, Script or UDF Invocation”.
The stream_name is an optional identifier assigned to the stream. The stream name can itself occur in any expression and provides access to the event itself from the named stream. Also, a stream name may be combined with a method name to invoke instance methods on events of that stream.
For all streams with the exception of historical sources your statement may employ data windows as outlined below. The retain-intersection (the default) and retain-union keywords build a union or intersection of two or more data windows as described in Section 5.4.4, “Multiple Data Windows”.
The stream_def syntax for a filter-based event stream is as below:
event_stream_name [(filter_criteria)] [contained_selection] [#window_spec] [#window_spec] [...]
The event_stream_name is either the name of an event type or name of an event stream populated by an insert into statement
or the name of a named window or table.
The filter_criteria is optional and consists of a list of expressions filtering the events of the event stream, within parenthesis after the event stream name. Filter criteria cannot be specified for tables.
The contained_selection is optional and is for use with coarse-grained events that have properties that are themselves one or more events, see Section 5.19, “Contained-Event Selection” for the synopsis and examples. Contained-event cannot be specified for tables.
The window_spec specify one or more data windows.
Data windows cannot be specified for named windows and tables. Instead of the # hash character the . dot character can also be used, however the dot character requires the data window namespace.
The following statement shows event type, filter criteria and data windows combined in one statement. It selects all event properties for the last 100 events of IBM stock ticks for volume. In the example, the event type is StockTick. The expression filters for events where the property symbol has a value of "IBM". This statement specifies a length window and thus computes the total volume of the last 100 events.
select sum(volume) from StockTick(symbol='IBM')#length(100)
The runtime filters out events in an event stream as defined by filter criteria that are placed in parenthesis, before it sends events to the data window(s) (if any). Thus, compared to search conditions in a where clause, filter criteria remove unneeded events early. In the above example, events with a symbol other than IBM do not enter the length window.
The simplest form of filter is a filter for events of a given type without any conditions on the event property values. This filter matches any event of that type regardless of the event's properties. The example below is such a filter.
select * from RfidEvent
Instead of the fully-qualified Java class name any other event name can be mapped via Configuration to a Java class, making the resulting statement more readable:
select * from RfidEvent
Interfaces and superclasses are also supported as event types. In the below example IRfidReadable is an interface class.
select * from org.myorg.rfid.IRfidReadable
The filtering criteria to filter for events with certain event property values are placed within parenthesis after the event type name:
select * from RfidEvent(category="Perishable")
All expressions can be used in filters, including static methods that return a boolean value:
select * from RfidEvent(MyRFIDLib.isInRange(x, y) or (x < 0 and y < 0))
Filter expressions can be separated via a single comma ','. The comma represents a logical AND between filter expressions:
select * from RfidEvent(zone=1, category=10) ...is equivalent to... select * from RfidEvent(zone=1 and category=10)
The compiler analyzes the filter expressions and determines the filter indexes. This process is futher described at Section 15.18, “Compiler Filter Expression Analysis”. The runtime uses the compiler output to build, maintain and use filter indexes, please see Section 2.18.2, “Filter Indexes”. The compiler can translate the following operators, including combinations of these operators connected via and and or, into filter indexes:
equals
=not equals
!=comparison operators
< , > , >=, <=ranges
use the
betweenkeyword for a closed range where both endpoints are includeduse the
inkeyword and round()or square brackets[]to control how endpoints are includedfor inverted ranges use the
notkeyword and thebetweenorinkeywords
list-of-values checks using the
inkeyword or thenot inkeywords followed by a comma-separated list of valuessingle-row functions that have been registered and are invoked via function name (see user-defined functions) and that either return a boolean value or that have their return value compared to a constant
the
andandorlogical operators
At compile time the compiler scans filter expressions for sub-expressions that can be placed into filter indexes. Indexing filter values to match event properties of incoming events enables the runtime to match incoming events faster, especially if your application creates a large number of statements or context partitions or requires many similar filters. The use of comma or logical and in filter expressions is fully equivalent.
Ranges come in the following 4 varieties. The use of round ()
or square [] bracket dictates whether an endpoint is included or excluded. The low point and the high-point of the range are separated by the colon : character.
Open ranges that contain neither endpoint
(low:high)Closed ranges that contain both endpoints
[low:high]. The equivalent 'between' keyword also defines a closed range.Half-open ranges that contain the low endpoint but not the high endpoint
[low:high)Half-closed ranges that contain the high endpoint but not the low endpoint
(low:high]
The next statement shows a filter specifying a range for x and y values of RFID events. The range includes both endpoints therefore uses [] hard brackets.
mypackage.RfidEvent(x in [100:200], y in [0:100])
The between keyword is equivalent for closed ranges. The same filter using the between keyword is:
mypackage.RfidEvent(x between 100 and 200, y between 0 and 50)
The not keyword can be used to determine if a value falls outside a given range:
mypackage.RfidEvent(x not in [0:100])
The equivalent statement using the between keyword is:
mypackage.RfidEvent(x not between 0 and 100)
The in keyword for filter criteria determines if a given value matches any value in a list of values.
In this example you are interested in RFID events where the category matches any of the given values:
mypackage.RfidEvent(category in ('Perishable', 'Container'))
By using the not in keywords you can filter events with a property value that does not match any of the values in a list of values:
mypackage.RfidEvent(category not in ('Household', 'Electrical'))The following restrictions apply to filter criteria:
Range and comparison operators require the event property to be of a numeric or string type.
Aggregation functions are not allowed within filter expressions.
The
prevprevious event function and thepriorprior event function cannot be used in filter expressions.
Event pattern expressions can also be used to specify one or more event streams in a statement.
For pattern-based event streams, the event stream definition stream_def consists of the keyword pattern and a pattern expression in brackets []. The syntax for an event stream definition using a pattern expression is below. As in filter-based event streams you can specify data windows.
pattern [pattern_expression] [#window_spec] [#window_spec] [...]
The next statement specifies an event stream that consists of both stock tick events and trade events. The example tags stock tick events with the name "tick" and trade events with the name "trade".
select * from pattern [every tick=StockTickEvent or every trade=TradeEvent]
This statement generates an event every time the runtime receives either one of the event types. The generated events resemble a map with "tick" and "trade" keys. For stock tick events, the "tick" key value is the underlying stock tick event, and the "trade" key value is a null value. For trade events, the "trade" key value is the underlying trade event, and the "tick" key value is a null value.
Lets further refine this statement adding a data window the gives us the last 30 seconds of either stock tick or trade events. Lets also select prices and a price total.
select tick.price as tickPrice, trade.price as tradePrice,
sum(tick.price) + sum(trade.price) as total
from pattern [every tick=StockTickEvent or every trade=TradeEvent]#time(30 sec)
Note that in the statement above tickPrice and tradePrice can each be null values depending on the event processed. Therefore, an aggregation function such as sum(tick.price + trade.price)) would always return null values as either of the two price properties are always a null value for any event matching the pattern. Use the coalesce function to handle null values, for example: sum(coalesce(tick.price, 0) + coalesce(trade.price, 0)).
Note
When used with patterns, specifying a data window defines what pattern matches to retain in memory for the purpose of joins or for using the iterator API.
When used with patterns, specifying a data window does not limit pattern matches to events in the window. The match_recognize pattern matching however does limit matches to events retained by a data window.
Data windows retain a subset of events. They provide an retain/expiry policy for events and the runtime automatically removes events according to the retain/expiry policy. Data windows can be grouped and data windows can be intersected or unioned. See the section Chapter 14, EPL Reference: Data Windows on the data windows available. Data windows can take parameters. Any expressions can be a parameter, with limitations.
The example statement below outputs a count per expressway for car location events (contains information about the location of a car on a highway) of the last 60 seconds:
select expressway, count(*) from CarLocEvent#time(60) group by expressway
The next example declares #groupwin and a #length window to indicate that there is a separate length window per car id:
select cardId, expressway, direction, segment, count(*) from CarLocEvent#groupwin(carId)#length(4) group by carId, expressway, direction, segment
The #groupwin(carId) groups car location events by car id. The #length(4) keeps a length window of the 4 last events, with one separate length window for each car id.
The example reports the number of events per car id and per expressway, direction and segment considering the last 4 events for each car id only.
The special keep-all window keeps all events: It does not expire events and does not provide a remove stream, i.e. events are not removed from the keep-all window unless by means of on-delete or on-merge or fire-and-forget delete.
Data windows provide an expiry policy that indicates when to remove events from the data window, with the exception of the keep-all data window which has no expiry policy and the #groupwin grouped-window for allocating a new data window per group.
EPL allows the freedom to use multiple data windows onto a stream and thus combine expiry policies. Combining data windows into an intersection (the default) or a union can achieve a useful strategy for retaining events and expiring events that are no longer of interest. Named windows, tables and on-merge and on-delete provide an additional degree of freedom.
In order to combine two or more data windows there is no keyword required. The retain-intersection keyword is the default and the retain-union keyword may instead be provided for a stream.
The concept of union and intersection come from Set mathematics. In the language of Set mathematics, two sets A and B can be "added" together: The intersection of A and B is the set of all things which are members of both A and B, i.e. the members two sets have "in common". The union of A and B is the set of all things which are members of either A or B.
Use the retain-intersection (the default) keyword to retain an intersection of all events as defined by two or more data windows. All events removed from any of the intersected data windows are entered into the remove stream. This is the default behavior if neither retain keyword is specified.
Use the retain-union keyword to retain a union of all events as defined by two or more data windows. Only events removed from all data windows are entered into the remove stream.
The next example statement totals the price of OrderEvent events in a union of the last 30 seconds and unique by product name:
select sum(price) from OrderEvent#time(30 sec)#unique(productName) retain-union
In the above statement, all OrderEvent events that are either less then 30 seconds old or that are the last event for the product name are considered.
Here is an example statement totals the price of OrderEvent events in an intersection of the last 30 seconds and unique by product name:
select sum(price) from OrderEvent#time(30 sec)#unique(productName) retain-intersection
In the above statement, only those OrderEvent events that are both less then 30 seconds old and are the last event for the product name are considered. The number of events that the runtime retains is the number of unique events per product name in the last 30 seconds (and not the number of events in the last 30 seconds).
For an intersection the runtime retains the minimal number of events representing that intersection. Thus when combining a time window of 30 seconds and a last-event window, for example, the number of events retained at any time is zero or one event (and not 30 seconds of events).
When combining a batch window into an intersection with another data window the combined data window gains batching semantics: Only when the batch criteria is fulfilled does the runtime provide the batch of intersecting insert stream events. Multiple batch data windows may not be combined into an intersection.
The table below provides additional examples for data window intersections:
Table 5.3. Intersection Data Window Examples
| Example | Description |
|---|---|
#time(30)#firstunique(keys) | Retains 30 seconds of events unique per keys value (first event per value). |
#firstlength(3)#firstunique(keys) | Retains the first 3 events that are also unique per keys value. |
#time_batch(N seconds)#unique(keys) | Posts a batch every N seconds that contains the last of each unique event per keys value. |
#time_batch(N seconds)#firstunique(keys) | Posts a batch every N seconds that contains the first of each unique event per keys value. |
#length_batch(N)#unique(keys) | Posts a batch of unique events (last event per value) when N unique events per keys value are encountered. |
#length_batch(N)#firstunique(keys) | Posts a batch of unique events (first event per value) when N unique events per keys value are encountered. |
Your from clause may assign a name to each stream. This assigned stream name can serve any of the following purposes.
First, the stream name can be used to disambiguate property names. The stream_name.property_name syntax uniquely identifies which property to select if property names overlap between streams. Here is an example:
select prod.productId, ord.productId from ProductEvent as prod, OrderEvent as ord
Second, the stream name can be used with a wildcard (*) character to select events in a join, or assign new names to the streams in a join:
// Select ProductEvent only select prod.* from ProductEvent as prod, OrderEvent
// Assign column names 'product' and 'order' to each event select prod.* as product, ord.* as order from ProductEvent as prod, OrderEvent as ord
Further, the stream name by itself can occur in any expression: The runtime passes the event itself to that expression. For example, the runtime passes the ProductEvent and the OrderEvent to the user-defined function 'checkOrder':
select prod.productId, MyFunc.checkOrder(prod, ord) from ProductEvent as prod, OrderEvent as ord
Last, you may invoke an instance method on each event of a stream, and pass parameters to the instance method as well. Instance method calls are allowed anywhere in an expression.
The next statement demonstrates this capability by invoking a method 'computeTotal' on OrderEvent events and a method 'getMultiplier' on ProductEvent events:
select ord.computeTotal(prod.getMultiplier()) from ProductEvent as prod, OrderEvent as ord
Instance methods may also be chained: Your EPL may invoke a method on the result returned by a method invocation.
Assume that your product event exposes a method getZone which returns a zone object. Assume that the Zone class declares a method checkZone.
This example statement invokes a method chain:
select prod.getZone().checkZone("zone 1") from ProductEvent as prod
Use the backwards apostrophe ` (aka. back tick) character to escape stream names in the from-clause and in on-trigger statements (e.g. from MyEvent as `order`...).
The from-clause in EPL is optional and is only required for subqueries. You may compile and deploy EPL statements without a from-clause. For example:
select 1 as value
Such an EPL statement does not output events to listeners or subscribers. However your application may call iterate to iterate statement results. See Section 16.5.4, “Using Iterators”.
The where clause is an optional clause in statements. Via the where clause event streams can be joined and correlated.
Tip
For filtering events in order to remove unwanted events, use filters as part of the from clause as described in Section 5.4.1, “Filter-Based Event Streams”
or for patterns in Section 7.4, “Filter Expressions in Patterns”.
Place expressions that remove unwanted events into parenthesis right after the event type, like ... from OrderEvent(fraud.severity = 5 and amount > 500) ....
There is related information at Section 2.18.2, “Filter Indexes” and Section 24.2.5, “Prefer Stream-Level Filtering Over Where-Clause Filtering”.
Any expression can be placed in the where clause. Typically you would use comparison operators =, < , > , >=, <=, !=, <>, is null, is not null and logical combinations via and and or for joining, correlating or comparing events.
The where clause introduces join conditions as outlined in Section 5.12, “Joining Event Streams”.
Some examples are listed below.
...where settlement.orderId = order.orderId
...where exists (select orderId from Settlement#time(1 min) where settlement.orderId = order.orderId)
The following two statements are equivalent since both query filter events by the amount property value and both statements do not specify a data window.
// preferable: specify filter criteria with the "eventtype(...filters...)" notation
@name('first') select * from Withdrawal(amount > 200)// equivalent only when there is no data window
@name('second') select * from Withdrawal where amount > 200
You can control whether the compiler rewrites the second statement to the form of the first statement. If you specify @Hint('disable_whereexpr_moveto_filter') you can instruct the compiler to not move the where-clause expression into the filter.
The aggregate functions are further documented in Section 10.2, “Aggregation Functions”. You can use aggregate functions to calculate and summarize data from event properties.
For example, to find out the total price for all stock tick events in the last 30 seconds, type:
select sum(price) from StockTickEvent#time(30 sec)
Aggregation functions do not require the use of data windows. The examples herein specify data windows for the purpose of example. An alternative means to instruct the runtime when to start and stop aggregating and on what level to aggregate is via context declarations.
For example, to find out the total price for all stock tick events since statement start, type:
select sum(price) from StockTickEvent
Here is the syntax for aggregate functions:
aggregate_function( [all | distinct] expression [,expression [,...]] [, group_by:local_group_by] [, filter:filter_expression] )
You can apply aggregate functions to all events in an event stream window or to one or more groups of events (i.e. group by). From each set of events to which an aggregate function is applied the runtime generates a single value.
Expression is usually an event property name. However it can also be a constant, function, or any combination of event property names, constants,
and functions connected by arithmetic operators.
You can provide a grouping dimension for each aggregation function by providing the optional group_by parameter as part of aggregation function parameters.
Please refer to Section 5.6.4, “Specifying Grouping for Each Aggregation Function”.
You can provide a filter expression for each aggregation function by providing the optional filter parameter as part of aggregation function parameters.
Please refer to Section 5.6.5, “Specifying a Filter Expression for Each Aggregation Function”.
For example, to find out the average price for all stock tick events in the last 30 seconds if the price was doubled:
select avg(price * 2) from StockTickEvent#time(30 seconds)
You can use the optional keyword distinct with all aggregate functions to eliminate duplicate values before the aggregate function is applied. The optional
keyword all which performs the operation on all events is the default.
You can use aggregation functions in a select clause and in a having clause. You cannot use aggregate functions in a where clause, but you can use the where clause to restrict the events to which the aggregate is applied. The next statement computes the average and sum of the price of stock tick events for the symbol IBM only, for the last 10 stock tick events regardless of their symbol.
select 'IBM stats' as title, avg(price) as avgPrice, sum(price) as sumPrice from StockTickEvent#length(10) where symbol='IBM'
In the above example the length window of 10 elements is not affected by the where clause, i.e. all events enter and leave the length window regardless of their symbol. If you only care about the last 10 IBM events, you need to add filter criteria as below.
select 'IBM stats' as title, avg(price) as avgPrice, sum(price) as sumPrice from StockTickEvent(symbol='IBM')#length(10) where symbol='IBM'
You can use aggregate functions with any type of event property or expression, with the following exceptions:
You can use
sum, avg, median, stddev, avedevwith numeric event properties only
The runtime ignores any null values returned by the event property or expression on which the aggregate function is operating, except for the count(*) function, which counts null values as well. All aggregate functions return null if the data set contains no events, or if all events in the data set contain only null values for the aggregated expression.
The group by clause is optional in all statements. The group by clause divides the output of a statement into groups. You can group by one or more event property names, or by the result of computed expressions. When used with aggregate functions, group by retrieves the calculations in each subgroup. You can use group by without aggregate functions, but generally that can produce confusing results.
For example, the below statement returns the total price per symbol for all stock tick events in the last 30 seconds:
select symbol, sum(price) from StockTickEvent#time(30 sec) group by symbol
The syntax of the group by clause is:
group by aggregate_free_expression [, aggregate_free_expression] [, ...]
The compiler places the following restrictions on expressions in the group by clause:
Expressions in the
group bycannot contain aggregate functions.When grouping an unbound stream, i.e. no data window is specified onto the stream providing groups, or when using output rate limiting with the ALL keyword, you should ensure your group-by expression does not return an unlimited number of values. If, for example, your group-by expression is a fine-grained timestamp, group state that accumulates for an unlimited number of groups potentially reduces available memory significantly. Use a @Hint as described below to instruct the runtime when to discard group state.
You can list more then one expression in the group by clause to nest groups. Once the sets are established with group by the aggregation
functions are applied. Further detail on key expressions can be found at Section 5.2.13, “Composite Keys and Array Values as Keys”.
This statement posts the median volume for all stock tick events in the last 30 seconds per symbol and tick data feed. The runtime posts one event for each group to statement listeners:
select symbol, tickDataFeed, median(volume) from StockTickEvent#time(30 sec) group by symbol, tickDataFeed
In the statement above the event properties in the select list (symbol, tickDataFeed) are also listed in the group by clause.
The statement thus follows the SQL standard which prescribes that non-aggregated event properties in the select list must match the
group by columns.
EPL also supports statements in which one or more event properties in the select list are not listed in the group by clause.
The statement below demonstrates this case. It calculates the standard deviation since statement start over stock ticks aggregating by symbol and posting for
each event the symbol, tickDataFeed and the standard deviation on price.
select symbol, tickDataFeed, stddev(price) from StockTickEvent group by symbol
The above example still aggregates the price event property based on the symbol, but produces one event per incoming event, not one
event per group.
Additionally, EPL supports statements in which one or more event properties in the group by clause are not listed in the select list.
This is an example that calculates the mean deviation per symbol and tickDataFeed and posts one event per group with symbol and mean deviation of price in the generated events. Since tickDataFeed is not in the posted results, this can potentially be confusing.
select symbol, avedev(price) from StockTickEvent#time(30 sec) group by symbol, tickDataFeed
Expressions are also allowed in the group by list:
select symbol * price, count(*) from StockTickEvent#time(30 sec) group by symbol * price
If the group by expression resulted in a null value, the null value becomes its own group. All null values are aggregated into the same group. If you are using the count(expression) aggregate function which does not count null values, the count returns zero if only null values are encountered.
You can use a where clause in a statement with group by. Events that do not satisfy the conditions in the where clause are eliminated before any grouping is done. For example, the statement below posts the number of stock ticks in the last 30 seconds with a volume larger then 100, posting one event per group (symbol).
select symbol, count(*) from StockTickEvent#time(30 sec) where volume > 100 group by symbol
The runtime reclaims aggregation state agressively when it determines that a group has no data points, based on the data in the data windows. When your application data creates a large number of groups with a small or zero number of data points then performance may suffer as state is reclaimed and created anew. EPL provides the @Hint('disable_reclaim_group') hint that you can specify as part of a statement to avoid group reclaim.
When aggregating values over an unbound stream (i.e. no data window is specified onto the stream) and when your group-by expression returns an unlimited number of values, for example when a timestamp expression is used, then please note the next hint.
A sample statement that aggregates stock tick events by timestamp, assuming the event type offers a property by name timestamp that, reflects time in high resolution, for example arrival or system time:
// Note the below statement could lead to an out-of-memory problem: select symbol, sum(price) from StockTickEvent group by timestamp
As the runtime has no means of detecting when aggregation state (sums per symbol) can be discarded, you may use the following hints to control aggregation state lifetime.
The @Hint("reclaim_group_aged=age_in_seconds") hint instructs the runtime to discard aggregation state that has not been
updated for age_in_seconds seconds.
The optional @Hint("reclaim_group_freq=sweep_frequency_in_seconds") can be used in addition to control the frequency at which the runtime sweeps aggregation
state to determine aggregation state age and remove state that is older then age_in_seconds seconds.
If the hint is not specified, the frequency defaults to the same value as age_in_seconds.
The updated sample statement with both hints:
// Instruct runtime to remove state older then 10 seconds and sweep every 5 seconds
@Hint('reclaim_group_aged=10,reclaim_group_freq=5')
select symbol, sum(price) from StockTickEvent group by timestampVariables may also be used to provide values for age_in_seconds and sweep_frequency_in_seconds.
This example statement uses a variable named varAge to control how long aggregation state remains in memory, and the runtime defaults the sweep frequency to the same value as the variable provides:
@Hint('reclaim_group_aged=varAge')
select symbol, sum(price) from StockTickEvent group by timestamp
EPL supports the SQL-standard rollup, cube and grouping sets keywords. These keywords are available only in the group-by clause and instruct the runtime to compute higher-level (or super-aggregate) aggregation values, i.e. to perform multiple levels of analysis (groupings) at the same time.
EPL also supports the SQL-standard grouping and grouping_id functions. These functions can be used in the select-clause, having-clause or order by-clause to obtain information about the current row's grouping level in expressions. Please see Section 10.1.8, “The Grouping Function”.
Detailed examples and information in respect to output rate limiting can be found in Section A.7, “Output for Fully-Aggregated, Grouped Statements With Rollup”.
Use the rollup keyword in the group-by lists of expressions to compute the equivalent of an OLAP dimension or hierarchy.
For example, the following statement outputs for each incoming event three rows. The first row contains the total volume per symbol and feed, the second row contains the total volume per symbol and the third row contains the total volume overall. This example aggregates across all events for each aggregation level (3 groupings) since it declares no data window:
select symbol, tickDataFeed, sum(volume) from StockTickEvent group by rollup(symbol, tickDataFeed)
The value of tickDataFeed is null for the output row that contains the total per symbol and the output row that contains the total volume overall.
The value of both symbol and tickDataFeed is null for the output row that contains the overall total.
Use the cube keyword in the group-by lists of expressions to compute a cross-tabulation.
The following statement outputs for each incoming event four rows. The first row contains the total volume per symbol and feed, the second row contains the total volume per symbol, the third row contains the total volume per feed and the forth row contains the total volume overall (4 groupings):
select symbol, tickDataFeed, sum(volume) from StockTickEvent group by cube(symbol, tickDataFeed)
The grouping sets keywords allows you to specify only the groupings you want. It can thus be used to generate the same groupings that simple group-by expressions, rollup or cube would produce.
In this example each incoming event causes the runtime to compute two output rows: The first row contains the total volume per symbol and the second row contains the total volume per feed (2 groupings):
select symbol, tickDataFeed, sum(volume) from StockTickEvent group by grouping sets(symbol, feed)
Your group-by expression can list grouping expressions and use rollup, cube and grouping sets keywords in addition or in combination.
This statement outputs the total per combination of symbol and feed and the total per symbol (2 groupings):
select symbol, tickDataFeed, sum(volume) from StockTickEvent group by symbol, rollup(tickDataFeed)
You can specify combinations of expressions by using parenthesis.
The next statement is equivalent and also outputs the total per symbol and feed and the total per symbol (2 groupings, note the parenthesis):
select symbol, tickDataFeed, sum(volume) from StockTickEvent group by grouping sets ((symbol, tickDataFeed), symbol)
Use empty parenthesis to aggregate across all dimensions.
This statement outputs the total per symbol, the total per feed and the total overall (3 groupings):
select symbol, tickDataFeed, sum(volume) from StockTickEvent group by grouping sets (symbol, tickDataFeed, ())
The order of any output events for both insert and remove stream data is well-defined and exactly as indicated before. For example, specifying grouping sets ((), symbol, tickDataFeed) outputs a total overall, a total by symbol and a total by feed in that order. If the statement has an order-by-clause then the ordering criteria of the order-by-clause take precedence.
You can use rollup and cube within grouping sets.
This statement outputs the total per symbol and feed, the total per symbol, the total overall and the total by feed (4 groupings):
select symbol, tickDataFeed, sum(volume) from StockTickEvent group by grouping sets (rollup(symbol, tickDataFeed), tickDataFeed)
Note
In order to use any of the rollup, cube and grouping sets keywords the statement must be fully-aggregated.
All non-aggregated properties in the select-clause, having-clause or order-by-clause must also be listed in the group by clause.
This section provides additional examples of group-by-clauses and groupings or dimensions.
The examples use event properties a, b, c, d, e to keep the examples easy to read.
Empty parenthesis () stand for aggregation overall (across all dimensions).
If a statement provides no order-by clause, its order of output events is exactly as indicated below. Otherwise order-by takes precedence
and within the same ordering criteria the order of output events is as indicated below.
Table 5.4.
Group-By Clause | Grouping |
|---|---|
group by a, b, c | a, b, c |
group by rollup(a, b, c) | a, b, c a, b a () |
group by a, rollup(b, c) | a, b, c a, b a |
group by rollup(a, b), rollup(c, d) | a,b,c,d a,b,c a,b a,c,d a,c a c,d c () |
group by cube(a, b, c) | a, b, c a, b a, c a b, c b c () |
group by cube(a, b, c, d) | a,b,c,d a,b,c a,b,d a,b a,c,d a,c a,d a b,c,d b,c b,d b c,d c d () |
group by grouping sets(a, b, c) | a b c |
group by grouping sets((a, b), rollup(c, d)) | a,b c,d c () |
The following table outlines sample equivalent group-by-clauses.
Table 5.5. Equivalent Group-By-Clause Expressions
| Expression | Equivalent |
|---|---|
| group by a, b | group by grouping sets((a, b)) |
| group by rollup(a, b) | group by grouping sets((a, b), a, ()) |
| group by cube(a, b) | group by grouping sets((a, b), a, b, ()) |
| group by a, b, rollup(c, d) | group by grouping sets((a, b, c, d), (a, b, c), (a, b)) |
| group by rollup((a, b), c) | group by grouping sets((a, b, c), (a, b), ()) |
| group by grouping sets((a)) | group by grouping sets(a) |
The prev and prior functions returns the previous event's property values and since they are not aggregation functions
return the same value for each grouping. Declared or alias expressions and correlated subqueries also receive the same value for each grouping.
Context partitions operate on a higher level then rollups, i.e. rollups are never across context partitions.
EPL allows each aggregation function to specify its own grouping criteria. This is useful for aggregating across multiple dimensions.
The syntax for the group_by parameter for use with aggregation functions is:
group_by: ( [expression [,expression [,...]]] )
The group_by identifier can occur at any place within the aggregation function parameters. It follows a colon and within parenthesis an
optional list of grouping expressions. The parenthesis are not required when providing a single expression.
For grouping on the top level (overall aggregation) please use () empty parenthesis.
Further detail on key expressions can be found at Section 5.2.13, “Composite Keys and Array Values as Keys”.
The presence of group_by aggregation function parameters, the grouping expressions as well as the group-by clause
determine the number of output rows for statements as further described in Section 2.15, “Basic Aggregated Statement Types”.
For un-grouped statements (without a group by clause), if any aggregation function specifies a group_by other than the () overall group, the statement executes
as aggregated and un-grouped.
For example, the next statement is an aggregated (but not fully aggregated) and ungrouped statement and outputs various totals for each arriving event:
select sum(price, group_by:()) as totalPriceOverall, sum(price, group_by:account) as totalPricePerAccount, sum(price, group_by:(account, feed)) as totalPricePerAccountAndFeed from Orders
For grouped statements (with a group by clause), if all aggregation functions specifiy either no group_by or group_by criteria that subsume the criteria in the group by clause, the statement executes as a fully-aggregated and grouped statement. Otherwise the statement executes as an aggregated and grouped statement.
The next example is fully-aggregated and grouped and it computes, for the last one minute of orders, the ratio of orders per account compared to all orders:
select count(*)/count(*, group_by:()) as ratio from Orders#time(1 min) group by account
The next example is an aggregated (and not fully-aggregated) and grouped statement that in addition outputs a count per order category:
select count(*) as cnt, count(*, group_by:()) as cntOverall, count(*, group_by:(category)) as cntPerCategory from Orders#time(1 min) group by account
Please note the following restrictions:
Expressions in the
group_bycannot contain aggregate functions.Hints pertaining to group-by are not available when a statement specifies aggregation functions with
group_by.The
group_byaggregation function parameters are not available in subqueries, match-recognize, statements that aggregate into tables usinginto tableor in combination withrollupandgrouping sets.
EPL allows each aggregation function to specify its own filter expression. This is useful for conditionally aggregating.
The syntax for the filter parameter for use with aggregation functions is:
filter:expression
The filter identifier can occur at any place within the aggregation function parameters. It follows a colon and the filter expression.
The filter expression must return a boolean-type value.
If a filter expression is present, the runtime evaluates the filter expression to determine whether to update the aggregation.
For example, the next statement returns the total price of small orders (price less 100), the total price of large orders (price >= 100), as well as the events themselves of each category, considering the last 10 seconds of orders:
select
sum(price, filter: price < 100) as smallOrderTotal,
sum(price, filter: price >= 100) as largeOrderTotal,
window(*, filter: price < 100) as smallOrderEvents,
window(*, filter: price >= 100) as largeOrderEvents
from Orders#time(10)Note
Filter expression that are parameters to aggregation functions must return reproducible results: When the expression is evaluated against the same input values it should return the same result. Aggregation functions and subqueries are not allowed therein.
Use the having clause to pass or reject events defined by the group-by clause. The having clause sets conditions for the group by clause in the same way where sets conditions for the select clause, except where cannot include aggregate functions, while having often does.
This statement is an example of a having clause with an aggregate function. It posts the total price per symbol for the last 30 seconds of stock tick events for only those symbols in which the total price exceeds 1000. The having clause eliminates all symbols where the total price is equal or less then 1000.
select symbol, sum(price) from StockTickEvent#time(30 sec) group by symbol having sum(price) > 1000
To include more then one condition in the having clause combine the conditions with and, or or not.
This is shown in the statement below which selects only groups with a total price greater then 1000 and an average volume less then 500.
select symbol, sum(price), avg(volume) from StockTickEvent#time(30 sec) group by symbol having sum(price) > 1000 and avg(volume) < 500
A statement with the having clause should also have a group by clause. If you omit group-by, all the events not excluded
by the where clause return as a single group. In that case having acts like a where except that having can have aggregate functions.
The having clause can also be used without group by clause as the below example shows. The example below posts events where the price is less then the current running average price of all stock tick events in the last 30 seconds.
select symbol, price, avg(price) from StockTickEvent#time(30 sec) having price < avg(price)
When you include filters, the where condition, the group by clause and the having condition in a statement
the sequence in which each clause affects events determines the final result:
The event stream's filter condition, if present, dictates which events enter a window (if one is used). The filter discards any events not meeting filter criteria.
The
whereclause excludes events that do not meet its search condition.Aggregate functions in the select list calculate summary values for each group.
The
havingclause excludes events from the final results that do not meet its search condition.
The following statement illustrates the use of filter, where, group by and having clauses in one statement with
a select clause containing an aggregate function.
select tickDataFeed, stddev(price) from StockTickEvent(symbol='IBM')#length(10) where volume > 1000 group by tickDataFeed having stddev(price) > 0.8
The runtime filters events using the filter criteria for the event stream StockTickEvent. In the example above only events with symbol IBM enter the length window over the last 10 events, all other events are simply discarded. The where clause removes any events posted by the length window (events entering the window and event leaving the window) that do not match the condition of volume greater then 1000. Remaining events are applied to the stddev standard deviation aggregate function for each tick data feed as specified in the group by clause. Each tickDataFeed value generates one event. The runtime applies the having clause and only lets events pass for tickDataFeed groups with a standard deviation of price greater then 0.8.
The keyed segmented context create context ... partition by and the group by clause as well as the built-in #groupwin are similar in their ability to group events but very different in their semantics. This section explains the key differences in their behavior and use.
The keyed segmented context as declared with create context ... partition by and context .... select ... creates a new context partition per key value(s). The runtime maintains separate data windows as well as separate aggregations per context partition; thereby the keyed segmented context applies to both. See Section 4.2.2, “Keyed Segmented Context” for additional examples.
The group by clause works together with aggregation functions in your statement to produce an aggregation result per group. In greater detail, this means that when a new event arrives, the runtime applies the expressions in the group by clause to determine a grouping key. If the runtime has not encountered that grouping key before (a new group), the runtime creates a set of new aggregation results for that grouping key and performs the aggregation changing that new set of aggregation results. If the grouping key points to an existing set of prior aggregation results (an existing group), the runtime performs the aggregation changing the prior set of aggregation results for that group.
The #groupwin instructs the system to have a separate data window per group, see Section 14.3.15, “Grouped Data Window (groupwin or std:groupwin)”. It causes allocation of separate data window(s) for each grouping key encountered.
The table below summarizes the point:
Table 5.6. Grouping Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Keyed Segmented Context |
Separate context partition per key value. Affects all of data windows, aggregations, patterns, etc. (except variables which are global). |
| Grouped Data Window (#groupwin) |
Separate data window per key value. Affects only the data window that is declared next to it. |
| Group By Clause (group by) |
Separate aggregation values per key value. Affects only aggregation values. |
Please review the performance section for advice related to performance or memory-use.
The next example shows statements that produce equivalent results. The statement using the group by clause is generally preferable as is easier to read. The second form introduces the #uni special data window which computes univariate statistics for a given property:
select symbol, avg(price) from StockTickEvent group by symbol // ... is equivalent to ... select symbol, average from StockTickEvent#groupwin(symbol)#uni(price)
The next example shows two statements that are NOT equivalent as the length window is ungrouped in the first statement, and grouped in the second statement:
select symbol, sum(price) from StockTickEvent#length(10) group by symbol // ... NOT equivalent to ... select symbol, sum(price) from StockTickEvent#groupwin(symbol)#length(10)
The key difference between the two statements is that in the first statement the length window is ungrouped and applies to all events regardless of group. While in the second statement each group gets its own length window. For example, in the second statement events arriving for symbol "ABC" get a length window of 10 events, and events arriving for symbol "DEF" get their own length window of 10 events.
The output clause is optional in EPL and is used to control or stabilize the rate at which events are output and to suppress output events. The EPL language provides for several different ways to control output rate.
Here is the syntax for the output clause that specifies a rate in time interval or number of events:
output [after suppression_def] [[all | first | last | snapshot] every output_rate [seconds | events]] [and when terminated]
An alternate syntax specifies the time period between output as outlined in Section 5.2.1, “Specifying Time Periods” :
output [after suppression_def] [[all | first | last | snapshot] every time_period] [and when terminated]
A crontab-like schedule can also be specified. The schedule parameters follow the pattern observer parameters and are further described in Section 7.6.4, “Crontab (timer:at)” :
output [after suppression_def] [[all | first | last | snapshot] at (minutes, hours, days of month, months, days of week [, seconds])] [and when terminated]
For use with contexts, in order to trigger output only when a context partition terminates, specify when terminated as further described in Section 4.6, “Output When a Context Partition Ends (Non-Overlapping Context) or Terminates (Overlapping Context)”:
output [after suppression_def] [[all | first | last | snapshot] when terminated [and termination_expression] [then set variable_name = assign_expression [, variable_name = assign_expression [,...]]] ]
Last, output can be controlled by an expression that may contain variables, user-defined functions and information about the number of collected events. Output that is controlled by an expression is discussed in detail below.
The after keyword and suppression_def can appear alone or together with further output conditions and suppresses output events.
For example, the following statement outputs, every 60 seconds, the total price for all orders in the 30-minute time window:
select sum(price) from OrderEvent#time(30 min) output snapshot every 60 seconds
The all keyword is the default and specifies that all events in a batch should be output, each incoming row in the batch producing an output row.
Note that for statements that group via the group by clause, the all keyword provides special behavior as below.
The first keyword specifies that only the first event in an output batch is to be output.
Using the first keyword instructs the runtime to output the first matching event as soon as it arrives, and then ignores matching events for the time interval or number of events specified.
After the time interval elapsed, or the number of matching events has been reached, the next first matching event is output again and the following interval the runtime again ignores matching events.
For statements that group via the group by clause, the first keywords provides special behavior as below.
The last keyword specifies to only output the last event at the end of the given time interval or after the given number of matching events
have been accumulated. Again, for statements that group via the group by clause the last keyword provides special behavior as below.
The snapshot keyword is often used with unbound streams and/or aggregation to output current aggregation results. While the other keywords control how a batch of events between output intervals is being considered, the snapshot keyword outputs current state of a statement independent of the last batch. Its output is comparable to the iterator method provided by a statement. More information on output snapshot can be found in Section 5.7.1.3, “Output Snapshot”.
The output_rate is the frequency at which the runtime outputs events. It can be specified in terms of time or number of events. The value can be a number to denote a fixed output rate, or the name of a variable whose value is the output rate. By means of a variable the output rate can be controlled externally and changed dynamically at runtime.
Please consult the Appendix A, Output Reference and Samples for detailed information on insert and remove stream output for the various output clause keywords.
For use with contexts you may append the keywords and when terminated to trigger output at the rate defined and in addition trigger output when the context partition terminates. Please see Section 4.6, “Output When a Context Partition Ends (Non-Overlapping Context) or Terminates (Overlapping Context)” for details.
Note
Please see Appendix B, Runtime Considerations for Output Rate Limiting for information on how the system retains input events and computes output events according to the specified output rate.
The time interval can also be specified in terms of minutes; the following statement is identical to the first one.
select * from StockTickEvent output every 1.5 minutes
A second way that output can be stabilized is by batching events until a certain number of events have been collected:
select * from StockTickEvent output every 5 events
Additionally, event output can be further modified by the optional last keyword, which causes output of only the last event to arrive into an output batch.
select * from StockTickEvent output last every 5 events
Using the first keyword you can be notified at the start of the interval. The allows to watch for situations such as a rate falling below a threshold
and only be informed every now and again after the specified output interval, but be informed the moment it first happens.
select * from TickRate where rate<100 output first every 60 seconds
A sample statement using the Unix "crontab"-command schedule is shown next. See Section 7.6.4, “Crontab (timer:at)” for details on schedule syntax. Here, output occurs every 15 minutes from 8am to 5:45pm (hours 8 to 17 at 0, 15, 30 and 45 minutes past the hour):
select symbol, sum(price) from StockTickEvent group by symbol output at (*/15, 8:17, *, *, *)
Output can also be controlled by an expression that may check variable values, use user-defined functions and statement built-in properties that provide additional information. The synopsis is as follows:
output [after suppression_def] [[all | first | last | snapshot] when trigger_expression [then set variable_name = assign_expression [, variable_name = assign_expression [,...]]] [and when terminated [and termination_expression] [then set variable_name = assign_expression [, variable_name = assign_expression [,...]]] ]
The when keyword must be followed by a trigger expression returning a boolean value of true or false, indicating whether to output.
Use the optional then keyword to change variable values after the trigger expression evaluates to true. An assignment expression assigns a new value to variable(s).
For use with contexts you may append the keywords and when terminated to also trigger output when the context partition terminates. Please see Section 4.6, “Output When a Context Partition Ends (Non-Overlapping Context) or Terminates (Overlapping Context)” for details. You may optionally specify a termination expression. If that expression is provided the
runtime evaluates the expression when the context partition terminates: The evaluation result of true means output occurs when the context partition terminates, false means no output occurs when the context partition terminates.
You may specify then set followed by a list of assignments to assign variables. Assignments are executed on context partition termination regardless of the termination expression, if present.
Lets consider an example. The next statement assumes that your application has defined a variable by name OutputTriggerVar of boolean type. The statement outputs rows only when the OutputTriggerVar variable has a boolean value of true:
select sum(price) from StockTickEvent output when OutputTriggerVar = true
The runtime evaluates the trigger expression when streams and data windows (if any) post one or more insert or remove stream events after considering the where clause, if present. It also evaluates the trigger expression when any of the variables used in the trigger expression, if any, changes value. Thus output occurs as follows:
When there are insert or remove stream events and the
whentrigger expression evaluates to true, the runtime outputs the resulting rows.When any of the variables in the
whentrigger expression changes value, the runtime evaluates the expression and outputs results. Result output occurs within the minimum time interval of timer resolution.
By adding a then part to the EPL, you can reset any variables after the trigger expression evaluated to true:
select sum(price) from StockTickEvent output when OutputTriggerVar = true then set OutputTriggerVar = false
Expressions in the when and then may, for example, use variables, user defined functions or any of the built-in named properties that are described in the below list.
The following built-in properties are available for use:
Table 5.7. Built-In Properties for Use With Output When
| Built-In Property Name | Description |
|---|---|
last_output_timestamp | Timestamp when the last output occurred for the statement; Initially set to time of statement deployment |
count_insert | Number of insert stream events |
count_insert_total | Number of insert stream events in total (not reset when output occurs). |
count_remove | Number of remove stream events |
count_remove_total | Number of remove stream events in total (not reset when output occurs). |
The values provided by count_insert and count_remove are non-continues: The number returned for these properties may 'jump' up rather then count up by 1.
The counts reset to zero upon output.
The following restrictions apply to expressions used in the output rate clause:
Event property names cannot be used in the output clause.
Aggregation functions cannot be used in the output clause.
The
prevprevious event function and thepriorprior event function cannot be used in the output clause.
The after keyword and its time period or number of events parameters is optional and can occur after the output keyword, either alone or with output conditions as listed above.
The synopsis of after is as follows:
output after time_period | number events [...]
When using after either alone or together with further output conditions, the runtime discards all output events until the time period passed as measured from the start of the statement, or until the
number of output events are reached. The discarded events are not output and do not count towards any further output conditions if any are specified.
For example, the following statement outputs every minute the total price for all orders in the 30-minute time window but only after 30 minutes have passed:
select sum(price) from OrderEvent#time(30 min) output after 30 min snapshot every 1 min
An example in which after occur alone is below, in a statement that outputs total price for all orders in the last minute but only after 1 minute passed, each time an event arrives or leaves the data window:
select sum(price) from OrderEvent#time(1 min) output after 1 min
To demonstrate after when used with an event count, this statement find pairs of orders with the same id but suppresses output for the first 5 pairs:
select * from pattern[every o=OrderEvent->p=OrderEvent(id=o.id)] output after 5 events
For fully aggregated and un-grouped statements, output snapshot outputs a single row with current aggregation value(s).
For aggregated ungrouped and grouped statements, as well as for unaggregated statements,
output snapshot considers events held by the data window and outputs a row for each event.
If the statement specifies no data window or a join results in no rows, the output is no rows.
For fully aggregated and grouped statements that select from a single stream (or pattern, non-joining) and that do not specify a data window, the runtime outputs current aggregation results for all groups. For fully aggregated and grouped statements with a join and/or data windows the output consists of aggregation values according to events held in the data window (single stream) or that are join results (join).
When the from-clause lists only tables, use output snapshot to output table contents.
Remove stream events can also be useful in conjunction with aggregation and the output clause: When the runtime posts remove stream events for fully-aggregated statements, it presents the aggregation state before the expiring event leaves the data window. Your application can thus easily obtain a delta between the new aggregation value and the prior aggregation value.
The runtime evaluates the having-clause at the granularity of the data posted by data windows (if any) or when an event arrives (without a data windows). That is, if you utilize a time window and output every 10 events, the having clause applies to each individual event or events entering and leaving the time window (and not once per batch of 10 events).
The output clause interacts in two ways with the group by and having clauses. First, in the output every n events case, the number n refers to the number of events arriving into the group by clause. That is, if the group by clause outputs only 1 event per group, or if the arriving events don't satisfy the having clause, then the actual number of events output by the statement could be fewer than n.
Second, the last, all and first keywords have special meanings when used in a statement with aggregate functions and the group by clause:
When no keyword is specified, the runtime produces an output row for each row in the batch or when using group-by then an output per group only for those groups present in the batch, following Section 2.15, “Basic Aggregated Statement Types”.
The
allkeyword (the default) specifies that the most recent data for all groups seen so far should be output, whether or not these groups' aggregate values have just been updatedThe
lastkeyword specifies that only groups whose aggregate values have been updated with the most recent batch of events should be output.The
firstkeyword specifies that only groups whose aggregate values have been updated with the most recent batch of events should be output following the defined frequency, keeping frequency state for each group.The
snapshotkeyword does not consider the recent batch and has special behavior as discussed in Section 5.7.1.3, “Output Snapshot”.
Please consult the Appendix A, Output Reference and Samples for detailed information on insert and remove stream output for aggregation and group-by.
By adding an output rate limiting clause to a statement that contains a group by clause you can control output of groups to obtain one row for each group, generating an event per group at the given output frequency.
The next statement outputs total price per symbol cumulatively (no data window was used here). As it specifies the all keyword, the statement outputs the current value for all groups seen so far, regardless of whether the group was updated in the last interval. Output occurs after an interval of 5 seconds passed and at the end of each subsequent interval:
select symbol, sum(price) from StockTickEvent group by symbol output all every 5 seconds
The below statement outputs total price per symbol considering events in the last 3 minutes. When events leave the 3-minute data window output also occurs as new aggregation values are computed. The last keyword instructs the runtime to output only those groups that had changes. Output occurs after an interval of 10 seconds passed and at the end of each subsequent interval:
select symbol, sum(price) from StockTickEvent#time(3 min) group by symbol output last every 10 seconds
This statement also outputs total price per symbol considering events in the last 3 minutes. The first keyword instructs the runtime to output as soon as there is a new value for a group. After output for a given group the runtime suppresses output for the same group for 10 seconds and does not suppress output for other groups. Output occurs again for that group after the interval when the group has new value(s):
select symbol, sum(price) from StockTickEvent#time(3 min) group by symbol output first every 10 seconds
The order by clause is optional. It is used for ordering output events by their properties, or by expressions involving those properties. .
For example, the following statement outputs batches of 5 or more stock tick events that are sorted first by price ascending and then by volume ascending:
select symbol from StockTickEvent#time(60 sec) output every 5 events order by price, volume
Here is the syntax for the order by clause:
order by expression [asc | desc] [, expression [asc | desc]] [, ...]
If the order by clause is absent then the runtime still makes certain guarantees about the ordering of output:
If the statement is not a join, does not group via
group byclause and does not declare grouped data windows via#groupwin, the order in which events are delivered to listeners and through theiteratorpull API is the order of event arrival.If the statement is a join or outer join, or groups, then the order in which events are delivered to listeners and through the
iteratorpull API is not well-defined. Use theorder byclause if your application requires events to be delivered in a well-defined order.
The compiler places the following restrictions on the expressions in the order by clause:
All aggregate functions that appear in the
order byclause must also appear in theselectexpression.
Otherwise, any kind of expression that can appear in the select clause,
as well as any name defined in the select clause, is also valid in the order by clause.
By default all sort operations on string values are performed via the compare method and are thus not locale dependent. To account for differences in language or locale, see Section 17.5.5, “Compiler Settings Related to Language and Locale” to change this setting.
The limit clause is typically used together with the order by and output clause to limit your statement results to those that fall within a specified range. You can use it to receive the first given number of result rows, or to receive a range of result rows.
There are two syntaxes for the limit clause, each can be parameterized by integer constants or by variable names. The first syntax is shown below:
limit row_count [offset offset_count]
The required row_count parameter specifies the number of rows to output. The row_count can be an integer constant and can also be the name of the integer-type variable to evaluate at runtime.
The optional offset_count parameter specifies the number of rows that should be skipped (offset) at the beginning of the result set. A variable can also be used for this parameter.
The next sample statement outputs the top 10 counts per property 'uri' every 1 minute.
select uri, count(*) from WebEvent group by uri output snapshot every 1 minute order by count(*) desc limit 10
The next statement demonstrates the use of the offset keyword. It outputs ranks 3 to 10 per property 'uri' every 1 minute:
select uri, count(*) from WebEvent group by uri output snapshot every 1 minute order by count(*) desc limit 8 offset 2
The second syntax for the limit clause is for SQL standard compatibility and specifies the offset first, followed by the row count:
limit offset_count[, row_count]
The following are equivalent:
limit 8 offset 2 // ...equivalent to limit 2, 8
A negative value for row_count returns an unlimited number or rows, and a zero value returns no rows. If variables are used, then the current variable value at the time of output dictates the row count and offset. A variable returning a null value for row_count also returns an unlimited number or rows.
A negative value for offset is not allowed. If your variable returns a negative or null value for offset then the value is assumed to be zero (i.e. no offset).
The iterator pull API also honors the limit clause, if present.
The insert into clause is optional in EPL. The clause can be specified to make the results of a statement available as an event stream for use
in further statements, or to insert events into a named window or table. The clause can also be used to merge multiple event streams to form a single stream of events.
The syntax for the insert into clause is as follows:
insert [istream | irstream | rstream] into event_stream_name [ ( [property_name [, property_name]] ) ] [ event-precedence (precedence-expression) ]
The istream (default) and rstream keywords are optional. If no keyword or the istream keyword is specified, the runtime supplies the insert stream events generated by the statement. The insert stream consists of the events entering the respective window(s) or stream(s). If the rstream keyword is specified, the runtime supplies the remove stream events generated by the statement. The remove stream consists of the events leaving the respective window(s).
If your application specifies irstream, the runtime inserts into the new stream both the insert and remove stream. This is often useful in connection with the istream built-in function that returns an inserted/removed boolean indicator for each event, see Section 10.1.11, “The Istream Function”.
The event_stream_name is an identifier that names the event stream (and also implicitly names the types of events in the stream) generated by the compiler.
It may also specify a named window name or a table name.
The identifier can be used in further statements to filter and process events of that event stream, unless inserting into a table.
The insert into clause can consist of just an event stream name, or an event stream name and one or more property names.
The event-precedence keyword and the precedence-expression expression are for control over the order of processing of events that the insert into-clause produces. It is further explained in Section 5.10.10, “Insert Into and Event Precedence”.
The runtime also allows listeners to be attached to a statement that contain an insert into clause. Listeners receive all events posted to the event stream.
To merge event streams, simply use the same event_stream_name identifier in all statements that merge their result event streams. Make sure to use the
same number and names of event properties and event property types match up.
The compiler places the following restrictions on the insert into clause:
The number of elements in the
selectclause must match the number of elements in theinsert intoclause if the clause specifies a list of event property namesIf the event stream name has already been defined by a prior statement or configuration, and the event property names and/or event types do not match, an exception is thrown at statement compile time.
The following sample inserts into an event stream by name CombinedEvent:
insert into CombinedEvent select A.customerId as custId, A.timestamp - B.timestamp as latency from EventA#time(30 min) A, EventB#time(30 min) B where A.txnId = B.txnId
Each event in the CombinedEvent event stream has two event properties named "custId" and "latency". The events generated by the above statement can be used in further statements, such as shown in the next statement:
select custId, sum(latency) from CombinedEvent#time(30 min) group by custId
The example statement below shows the alternative form of the insert into clause that explicitly defines the property names to use.
insert into CombinedEvent (custId, latency) select A.customerId, A.timestamp - B.timestamp ...
The rstream keyword can be useful to indicate to the runtime to generate only remove stream events. This can be useful if you want to trigger
actions when events leave a window rather then when events enter a window. The statement below generates CombinedEvent events when
EventA and EventB leave the window after 30 minutes.
insert rstream into CombinedEvent select A.customerId as custId, A.timestamp - B.timestamp as latency from EventA#time(30 min) A, EventB#time(30 min) B where A.txnId = B.txnId
The insert into clause can be used in connection with patterns to provide pattern results to further statements for analysis:
insert into ReUpEvent select linkUp.ip as ip from pattern [every linkDown=LinkDownEvent -> linkUp=LinkUpEvent(ip=linkDown.ip)]
Sometimes your events may carry properties that are themselves event objects. Therefore EPL offers a special syntax to insert the value of a property itself as an event into a stream:
insert into stream_name select property_name.* from ...
This feature is only supported for JavaBean events and for Map and Object-array (Object[]) event types that associate an event type name with the property type. It is not supported for XML events. Nested property names are also not supported.
In this example, the class Summary with properties bid and ask that are of type Quote is:
public class Summary {
private Quote bid;
private Quote ask;
...
The statement to populate a stream of Quote events is thus:
insert into MyBidStream select bid.* from Summary
The insert into clause allows to merge multiple event streams into a event single stream.
The clause names an event stream to insert into by specifing an event_stream_name. The first statement that inserts into the named stream defines the stream's event types. Further statements that
insert into the same event stream must match the type of events inserted into the stream as declared by the first statement.
One approach to merging event streams specifies individual colum names either in the select clause or in the insert into clause of the statement. This approach has been shown in earlier examples.
Another approach to merging event streams specifies the wildcard (*) in the select clause (or the stream wildcard) to select the underlying event. The events in the event stream must then
have the same event type as generated by the from clause.
Assume a statement creates an event stream named MergedStream by selecting OrderEvent events:
insert into MergedStream select * from OrderEvent
A statement can use the stream wildcard selector to select only OrderEvent events in a join:
insert into MergedStream select ord.* from ItemScanEvent, OrderEvent as ord
And a statement may also use an application-supplied user-defined function to convert events to OrderEvent instances:
insert into MergedStream select MyLib.convert(item) from ItemScanEvent as item
The compiler specifically recognizes a conversion function as follows: A conversion function must be the only selected column, and it must return either a Java object or java.util.Map or Object[] (object array).
Your EPL should not use the as keyword to assign a column name.
A variant stream is a predefined stream into which events of multiple disparate event types can be inserted.
A variant stream name may appear anywhere in a pattern or from clause. In a pattern, a filter against a variant stream matches any events of any of the event types inserted into the variant stream.
In a from clause including for named windows, data windows may hold events of any of the event types inserted into the variant stream.
A variant stream is thus useful in problems that require different types of event to be treated the same.
Variant streams can be declared by means of create variant schema or can be predefined via runtime or initialization-time configuration as described in Section 17.4.16, “Variant Stream”. Your application may declare or predefine variant streams to carry events of a limited set of event types, or you may choose the variant stream to carry any and all types of events. This choice affects what event properties are available for consuming statements or patterns of the variant stream.
Assume that an application predefined a variant stream named OrderStream to carry only ServiceOrder and ProductOrder events. An insert into clause inserts events into
the variant stream:
insert into OrderStream select * from ServiceOrder
insert into OrderStream select * from ProductOrder
Here is a sample statement that consumes the variant stream and outputs a total price per customer id for the last 30 seconds of ServiceOrder and ProductOrder events:
select customerId, sum(price) from OrderStream#time(30 sec) group by customerId
If your application predefines the variant stream to hold specific type of events, as the sample above did, then all event properties that are common to all specified types are visible on the variant stream, including nested, indexed and mapped properties. For access to properties that are only available on one of the types, the dynamic property syntax must be used. In the example above, the customerId and price were properties common to both ServiceOrder and ProductOrder events.
For example, here is a consuming statement that selects a service duraction property that only ServiceOrder events have, and that must therefore be casted to double and null values removed in order to aggregate:
select customerId, sum(coalesce(cast(serviceDuraction?, double), 0)) from OrderStream#time(30 sec) group by customerId
If your application predefines a variant stream to hold any type of events (the any type variance), then all event properties of the variant stream are effectively dynamic properties.
For example, an application may define an OutgoingEvents variant stream to hold any type of event. The next statement is a sample consumer of the OutgoingEvents variant stream that looks for the destination property and fires for each event in which the property exists with a value of 'email':
select * from OutgoingEvents(destination = 'email')
Your select clause may use the '*' wildcard together with further expressions to populate a stream of events. A sample statement is:
insert into OrderStream select *, price*units as linePrice from PurchaseOrder
When using wildcard and selecting additional expression results, the runtime produces what is called decorating events for the resulting stream. Decorating events add additional property values to an underlying event.
In the above example the resulting OrderStream consists of underlying PurchaseOrder events decorated by a linePrice property that is a result of the price*units expression.
In order to use insert into to insert into an existing stream of decorated events, your underlying event type must match, and all additional decorating property names and types of the select clause must also match.
Your select clause may use the stream name to populate a stream of events in which each event has properties that are itself an event. A sample statement is:
insert into CompositeStream select order, service, order.price+service.price as totalPrice from PurchaseOrder#lastevent as order, ServiceEvent#lastevent as service
When using the stream name (or tag in patterns) in the select-clause, the runtime produces composite events: One or more of the properties of the composite event are events themselves.
In the above example the resulting CompositeStream consists of 3 columns: the PurchaseOrder event, the ServiceEvent event and the totalPrice property that is a result of the order.price+service.price expression.
In order to use insert into to insert into an existing stream of events in which properties are themselves events, each event column's event type must match, and all additional property names and types of the select clause must also match.
Your insert into clause may also directly instantiate and populate application underlying event objects or Map or Object[] event objects. This is described in greater detail in Section 3.9, “Event Objects Instantiated and Populated by Insert Into”.
If instead you have an expression that returns an event object, please read on to the next section.
You can transpose an object returned as an expression result into a stream using the transpose function as described further in Section 10.4, “Select-Clause Transpose Function”.
When you declare the inserted-into event type in advance to the statement that inserts, the runtime compares the inserted-into event type information to the return type of expressions in the select-clause.
The comparison uses the column alias assigned to each select-clause expression using the as keyword.
When the inserted-into column type is an event type and when using a subquery or the new operator,
the runtime compares column names assigned to subquery columns or new operator columns.
For example, assume a PurchaseOrder event type that has a property called items that consists of Item rows:
create schema Item(name string, price double)
create schema PurchaseOrder(orderId string, items Item[])
Declare a statement that inserts into the PurchaseOrder stream:
insert into PurchaseOrder
select '001' as orderId, new {name='i1', price=10} as items
from TriggerEvent
The alias assigned to the first and second expression in the select-clause, namely orderId and items,
both match the event property names of the Purchase Order event type. The column names provided to the new operator
also both match the event property names of the Item event type.
When the event type declares the column as a single value (and not an array) and when the select-clause expression produces a multiple rows, the runtime only populate the first row.
Consider a PurchaseOrder event type that has a property called item that consists of a single Item event:
create schema PurchaseOrder(orderId string, items Item)
The sample subquery below populates only the very first event, discarding remaining subquery result events, since the items property above is declared as holding a single Item-typed event only (versus Item[] to hold multiple Item-typed events).
insert into PurchaseOrder select (select 'i1' as name, 10 as price from HistoryEvent#length(2)) as items from TriggerEvent
Consider using a subquery with filter, or one of the enumeration methods to select a specific subquery result row.
When using insert-into and the type information for the inserted-into stream exists and the type has no properties, specify a select-clause that selects a single column of value null and that provides no column name.
For example, the next EPL declares a TriggerStream type that has no event properties:
create schema TriggerStream ()
To populate events of type TriggerStream, let the select-clause simply select null, like this:
insert into TriggerStream select null from ...
This example uses a pattern to populate a TrggerStream event every 10 seconds:
insert into TriggerStream select null from pattern[every timer:interval(10 sec)]
As part of the insert into clause the optional event-precedence keyword allows specifying an expression that returns an
event precedence value that applies to the inserted event. The value controls the order in which the runtime processes the inserted event as compared to other inserted events
that are yet to be processed.
Warning
In order to use event precedence you must set the precedence-enabled flag in the runtime configuration. Please refer to Section 17.6.10.2, “Event-Precedence Execution”.
The event precedence expression must return an integer-type value. The expression may return negative values.
The default precedence is zero (0) and applies when there is no event-precedence-clause or when the event-precedence expression returns a null-value.
Note
The event precedence expression can use properties of the insert-into generated event and may use wildcard to mean the inserted event.
The expression cannot use properties of from-clause or on-clause events.
To illustrate the concept of event precedence, consider two example event types InputEvent and FurtherEvent:
@public @buseventtype create schema InputEvent(name string); @public create schema FurtherEvent(id string);
Here is a statement that, upon an InputEvent, produces two events of type FurtherEvent:
on InputEvent insert into FurtherEvent select 'id-1' as id insert into FurtherEvent select 'id-2' as id output all;
The above statement does not specify an event-precedence and therefore the runtime processes the FurtherEvent events in the order they are generated.
So the runtime first processes the InputEvent, and then the FurtherEvent={id='id-1'} and then the FurtherEvent={id='id-2'}, in that order.
The next example assigns a precedence value of 1 to FurtherEvent={id='id-1'} and a precedence value of 2 to FurtherEvent={id='id-2'}:
on InputEvent insert into FurtherEvent event-precedence(1) select 'id-1' as id insert into FurtherEvent event-precedence(2) select 'id-2' as id output all
The precedence values instruct the runtime to process FurtherEvent={id='id-2'} first, and then FurtherEvent={id='id-1'} (higher precedence value first).
The precedence can be computed. The below statement determines the precedence value based on the value of the name property of the inserted event.
insert into FurtherEvent event-precedence(case when name = 'Joe' then 1 else 2 end) select name, 'id-a' as id from InputEvent;
For further information on runtime event processing order, please read Section 16.8.2.2, “Processing Principles of Events and Listener Updates”.
A subquery is a select within another statement. The compiler supports subqueries in the select clause, where clause, having clause and in stream and pattern filter expressions. Subqueries provide an alternative way to perform operations that would otherwise require complex joins. Subqueries can also make statements more readable then complex joins.
EPL supports both simple subqueries as well as correlated subqueries. In a simple subquery, the inner query is not correlated to the outer query. Here is an example simple subquery within a select clause:
select assetId, (select zone from ZoneClosed#lastevent) as lastClosed from RFIDEvent
If the inner query is dependent on the outer query, you will have a correlated subquery. An example of a correlated subquery is shown below. Notice the where clause in the inner query, where the condition involves a stream from the outer query:
select * from RfidEvent as RFID where 'Dock 1' = (select name from Zones#unique(zoneId) where zoneId = RFID.zoneId)
The example above shows a subquery in the where clause. The statement selects RFID events in which the zone name matches a string constant based on zone id. The statement sets #unique to guarantee that only the last event per zone id is retained for processing by the subquery.
The next example is a correlated subquery within a select clause. In this statement the select clause retrieves the zone name by means of a subquery against the Zones set of events correlated by zone id:
select zoneId, (select name from Zones#unique(zoneId) where zoneId = RFID.zoneId) as name from RFIDEvent
Note that when a simple or correlated subquery returns multiple rows, the runtime returns a null value as the subquery result. To limit the number of events returned by a subquery consider using one of the #lastevent, #unique data windows or aggregation functions or the multi-row and multi-column-select as described below.
The select clause of a subquery also allows wildcard selects, which return as an event property the underlying event object of the event type as defined in the from clause. An example:
select (select * from MarketData#lastevent) as md from pattern [every timer:interval(10 sec)]
The output events to the statement above contain the underlying MarketData event in a property named "md". The statement populates the last MarketData event into a property named "md" every 10 seconds following the pattern definition, or populates a null value if no MarketData event has been encountered so far.
Aggregation functions may be used in the select clause of the subselect as this example outlines:
select * from MarketData where price > (select max(price) from MarketData(symbol='GOOG')#lastevent)
As the sub-select expression is evaluated first (by default), the query above actually never fires for the GOOG symbol, only for other symbols that have a price higher then the current maximum for GOOG. As a sidenote, the insert into clause can also be handy to compute aggregation results for use in multiple subqueries.
When using aggregation functions in a correlated subselect the runtime computes the aggregation based on data window (if provided), named window or table contents matching the where-clause (correlated subquery aggregations are not incrementally computed).
The following example compares the quantity value provided by the current order event against the total quantity of all order events in the last 1 hour for the same client.
select * from OrderEvent oe where qty > (select sum(qty) from OrderEvent#time(1 hour) pd where pd.client = oe.client)
Filter expressions in a pattern or stream may also employ subqueries. Subqueries can be uncorrelated or can be correlated to properties of the stream or to properties of tagged events in a pattern. Subqueries may reference named windows and tables as well.
The following example filters BarData events that have a close price less then the last moving average (field movAgv) as provided by stream SMA20Stream (an uncorrelated subquery):
select * from BarData(ticker='MSFT', closePrice <
(select movAgv from SMA20Stream(ticker='MSFT')#lastevent))
A few generic examples follow to demonstrate the point. The examples use short event and property names so they are easy to read. Assume A and B are streams and DNamedWindow is a named window, and ETable is a table and properties a_id, b_id, d_id, e_id, a_val, b_val, d_val, e_val respectively:
// Sample correlated subquery as part of stream filter criteria select * from A(a_val in (select b_val from B#unique(b_val) as b where a.a_id = b.b_id)) as a
// Sample correlated subquery against a named window select * from A(a_val in (select d_val from DNamedWindow as d where a.a_id = d.d_id)) as a
// Sample correlated subquery in the filter criteria as part of a pattern, querying a named window
select * from pattern [
a=A -> b=B(bvalue =
(select d_val from DNamedWindow as d where d.d_id = b.b_id and d.d_id = a.a_id))
]// Sample correlated subquery against a table select * from A(a_val in (select e_val from ETable as e where a.a_id = e.e_id)) as a
Subquery state starts to accumulate as soon as a statement starts (and not only when a pattern-subexpression activates).
The following restrictions apply to subqueries:
Subqueries can only consist of a
selectclause, afromclause, awhereclause, agroup byclause and ahavingclause. Joins, outer-joins and output rate limiting are not permitted within subqueries.If using aggregation functions in a subquery, note these limitations:
None of the properties of the correlated stream(s) can be used within aggregation functions.
The properties of the subselect stream must all be within aggregation functions.
With the exception of subqueries against named windows and tables and subqueries that are both uncorrelated and fully-aggregated, the subquery stream definition must define a data window to limit subquery results, for the purpose of identifying the events held for subquery execution.
The
having-clause, if present, requires that properties of the selected stream are aggregated and does not allow un-aggregated properties of the selected stream. You may use thefirstaggregation function to obtain properties of the selected stream instead.
The order of evaluation of subqueries relative to the containing statement is guaranteed: If the containing statement and its subqueries are reacting to the same type of event, the subquery will receive the event first before the containing statement's clauses are evaluated. This behavior can be changed via configuration. The order of evaluation of subqueries is not guaranteed between subqueries.
Performance of your statement containing one or more subqueries principally depends on two parameters. First, if your subquery correlates one or more columns in the subquery stream with the enclosing statement's streams, the compiler determines and the runtime automatically builds the appropriate indexes for fast row retrieval based on the key values correlated (joined). The second parameter is the number of rows found in the subquery stream and the complexity of the filter criteria (where clause), as each row in the subquery stream must evaluate against the where clause filter.
The exists condition is considered "to be met" if the subquery returns at least one row. The not exists condition is considered true if the subquery returns no rows.
The synopsis for the exists keyword is as follows:
exists (subquery)
Let's take a look at a simple example. The following is a statement that uses the exists condition:
select assetId from RFIDEvent as RFID where exists (select * from Asset#unique(assetId) where assetId = RFID.assetId)
This select statement will return all RFID events where there is at least one event in Assets unique by asset id with the same asset id.
The in subquery condition is true if the value of an expression matches one or more of the values returned by the subquery. Consequently, the not in condition is true if the value of an expression matches none of the values returned by the subquery.
The synopsis for the in keyword is as follows:
expression in (subquery)
The right-hand side subquery must return exactly one column.
The next statement demonstrates the use of the in subquery condition:
select assetId from RFIDEvent where zone in (select zone from ZoneUpdate(status = 'closed')#time(10 min))
The above statement demonstrated the in subquery to select RFID events for which the zone status is in a closed state.
Note that if the left-hand expression yields null, or if there are no equal right-hand values and at least one right-hand row yields null, the result of the in construct will be null, not false (or true for not-in). This is in accordance with SQL's normal rules for Boolean combinations of null values.
The any subquery condition is true if the expression returns true for one or more of the values returned by the subquery.
The synopsis for the any keyword is as follows:
expression operator any (subquery) expression operator some (subquery)
The left-hand expression is evaluated and compared to each row of the subquery result using the given operator, which must yield a Boolean result. The result of any is "true" if any true result is obtained. The result is "false" if no true result is found (including the special case where the subquery returns no rows).
The operator can be any of the following values: =, !=, <>, <, <=, >, >=.
The some keyword is a synonym for any. The in construct is equivalent to = any.
The right-hand side subquery must return exactly one column.
The next statement demonstrates the use of the any subquery condition:
select * from ProductOrder as ord
where quantity < any
(select minimumQuantity from MinimumQuantity#keepall)The above statement compares ProductOrder event's quantity value with all rows from the MinimumQuantity stream of events and returns only those ProductOrder events that have a quantity that is less then any of the minimum quantity values of the MinimumQuantity events.
Note that if there are no successes and at least one right-hand row yields null for the operator's result, the result of the any construct will be null, not false. This is in accordance with SQL's normal rules for Boolean combinations of null values.
The all subquery condition is true if the expression returns true for all of the values returned by the subquery.
The synopsis for the all keyword is as follows:
expression operator all (subquery)
The left-hand expression is evaluated and compared to each row of the subquery result using the given operator, which must yield a Boolean result. The result of all is "true" if all rows yield true (including the special case where the subquery returns no rows). The result is "false" if any false result is found. The result is null if the comparison does not return false for any row, and it returns null for at least one row.
The operator can be any of the following values: =, !=, <>, <, <=, >, >=.
The not in construct is equivalent to != all.
The right-hand side subquery must return exactly one column.
The next statement demonstrates the use of the all subquery condition:
select * from ProductOrder as ord
where quantity < all
(select minimumQuantity from MinimumQuantity#keepall)The above statement compares ProductOrder event's quantity value with all rows from the MinimumQuantity stream of events and returns only those ProductOrder events that have a quantity that is less then all of the minimum quantity values of the MinimumQuantity events.
The optional group by clause in subqueries works the same way as the group-by clause outside of subqueries,
except that it impacts only those aggregations within the subquery.
The following restrictions apply:
Expressions in the group-by clause cannot contain aggregate functions, subqueries or the
prevandpriorfunctions.Subqueries only support the fully-aggregated case when using group-by: All non-aggregated properties in the select clause must be listed in the group by clause.
The group-by expressions cannot be correlated. All properties in the
group bymust be provided by the subselect stream.
Your subquery may select multiple columns in the select clause including multiple aggregated values from a data window or named window or table.
The following example is a correlated subquery that selects wildcard and in addition selects the bid and offer properties of the last MarketData event for the same symbol as the arriving OrderEvent:
select *, (select bid, offer from MarketData#unique(symbol) as md where md.symbol = oe.symbol) as bidoffer from OrderEvent oe
Output events for the above statement contain all properties of the original OrderEvent event. In addition each output event contains a bidoffer nested property that itself contains the bid and offer properties. You may retrieve the bid and offer from output events directly via the bidoffer.bid property name syntax for nested properties.
The next example is similar to the above statement but instead selects aggregations and selects from a named window by name OrderNamedWindow (creation not shown here). For each arriving OrderEvent it selects the total quantity and count of all order events for the same client, as currently held by the named window:
select *, (select sum(qty) as sumPrice, count(*) as countRows from OrderNamedWindow as onw where onw.client = oe.client) as pastOrderTotals from OrderEvent as oe
The next statement computes a prorated quantity considering the maximum and minimum quantity for the last 1 minute of order events:
expression subq {
(select max(quantity) as maxq, min(quantity) as minq from OrderEvent#time(1 min))
}
select (quantity - minq) / (subq().maxq - subq().minq) as prorated
from OrderEvent
Output events for the above statement contain all properties of the original OrderEvent event. In addition each output event contains a pastOrderTotals nested property that itself contains the sumPrice and countRows properties.
While a subquery cannot change the cardinality of the selected stream, a subquery can return multiple values from the selected data window or named window or table. This section shows examples of the window aggregation function as well as the use of enumeration methods with subselects.
Consider using an inner join, outer join or unidirectional join instead to achieve a 1-to-many cardinality in the number of output events.
The next example is an uncorrelated subquery that selects all current ZoneEvent events considering the last ZoneEvent per zone for each arriving RFIDEvent.
select assetId, (select window(z.*) as winzones from ZoneEvent#unique(zone) as z) as zones from RFIDEvent
Output events for the above statement contain two properties: the assetId property and the zones property. The latter property is a nested property that contains the winzones property. You may retrieve the zones from output events directly via the zones.winzones property name syntax for nested properties.
In this example for a correlated subquery against a named window, assume that the OrderNamedWindow has been created and contains order events. The statement returns for each MarketData event
the list of order ids for orders with the same symbol:
select price, (select window(orderId) as winorders from OrderNamedWindow onw where onw.symbol = md.symbol) as orderIds from MarketData md
Output events for the above statement contain two properties: the price property and the orderIds property. The latter property is a nested property that contains the winorders property of type array.
Another option to reduce selected rows to a single value is through the use of enumeration methods.
select price, (select * from OrderNamedWindow onw where onw.symbol = md.symbol).selectFrom(v => v) as ordersSymbol from MarketData md
Output events for the above statement also contain a Collection of underlying events in the ordersSymbol property.
The following hints are available to tune performance and memory use of subqueries.
Use the @Hint('set_noindex') hint for a statement that utilizes one or more subqueries. It instructs the runtime to always perform a full scan. The runtime does not build an implicit index or use an explicitly-created index when this hint is provided. Use of the hint may result in reduced memory use but poor statement performance.
The following hints are available to tune performance and memory use of subqueries that select from named windows (does not apply to tables).
Named windows are globally-visible data windows. As such an application may create explicit indexes as discussed in Section 6.9, “Explicitly Indexing Named Windows and Tables”. The runtime may also elect to create implicit indexes (no create-index EPL required) for index-based lookup of rows when executing on-select, on-merge, on-update and on-delete statements and for statements that subquery a named window.
By default and without specifying a hint, each statement that subqueries a named window also maintains its own index for looking up events held by the named window. The runtime maintains the index by consuming the named window insert and remove stream. When the statement is undeployed it releases that index.
Specify the @Hint('enable_window_subquery_indexshare') hint to enable subquery index sharing for named windows. When using this hint, indexes for subqueries are maintained by the named window itself (and not each statement context partition).
However only indexes explictly created with create index are used in this case. Specify the hint once as part of the create window statement.
This sample statement creates a named window with subquery index sharing enabled:
@Hint('enable_window_subquery_indexshare')
create window OrdersNamedWindow#keepall as OrderMapEventTypeWhen subquery index sharing is enabled, performance may increase as named window stream consumption is no longer needed for correlated subqueries. You may also expect reduced memory use especially if a large number of statements perform similar subqueries against a named window. Subquery index sharing may require additional short-lived object creation and may slightly increase lock held time for named windows.
The following statement performs a correlated subquery against the named window above. When a settlement event arrives it select the order detail for the same order id as provided by the settlement event:
select
(select * from OrdersNamedWindow as onw
where onw.orderId = se.orderId) as orderDetail
from SettlementEvent as seWith subquery index sharing enabled and only when a suitable index exists the query planner uses the index. A sample index is:
create index MyIndex on OrdersNamedWindow(orderId)
You may disable subquery index sharing for a specific statement by specifying the @Hint('disable_window_subquery_indexshare') hint, as this example shows, causing the statement to maintain its own index:
@Hint('disable_window_subquery_indexshare')
select
(select * from OrdersNamedWindow as onw
where onw.orderId = se.orderId) as orderDetail
from SettlementEvent as se
Two or more event streams can be part of the from-clause and thus both (all) streams determine the resulting events. This section summarizes the important concepts. The sections that follow present more detail on each topic.
The default join is an inner join which produces output events only when there is at least one match in all streams.
Consider the sample statement shown next:
select * from TickEvent#lastevent, NewsEvent#lastevent
The above statement outputs the last TickEvent and the last NewsEvent in one output event when either a TickEvent or a NewsEvent arrives. If no TickEvent was received before a NewsEvent arrives, no output occurs. Similarly when no NewsEvent was received before a TickEvent arrives, no output occurs.
The where-clause lists the join conditions that the compiler uses to relate events in the two or more streams.
The next example statement retains the last TickEvent and last NewsEvent per symbol, and joins the two streams based on their symbol value:
select * from TickEvent#unique(symbol) as t, NewsEvent#unique(symbol) as n where t.symbol = n.symbol
As before, when a TickEvent arrives for a symbol that has no matching NewsEvent then there is no output event.
An outer join does not require each event in either stream to have a matching event. The full outer join is useful when output is desired when no match is found. The different outer join types (full, left, right) are explained in more detail below.
This example statement is an outer-join and also returns the last TickEvent and last NewsEvent per symbol:
select * from TickEvent#unique(symbol) as t full outer join NewsEvent#unique(symbol) as n on t.symbol = n.symbol
In the sample statement above, when a TickEvent arrives for a symbol that has no matching NewsEvent, or when a NewsEvent arrives for a symbol that has no matching TickEvent, the statement still produces an output event with a null column value for the missing event.
Note that each of the sample statements above defines a data window. The sample statements above use the last-event data window (#lastevent) or the unique data window (#unique). A data window serves to indicate the subset of events to join from each stream and may be required depending on the join.
In above statements, when either a TickEvent arrives or when a NewsEvent arrives then the statement evaluates and there is output. The same holds true if additional streams are added to the from-clause: Each of the streams in the from-clause trigger the join to evaluate.
The unidirectional keyword instructs the runtime to evaluate the join only when an event arrives from the single stream that was marked with the unidirectional keyword. In this case no data window should be specified for the stream marked as unidirectional since the keyword implies that the current event of that stream triggers the join.
Here is the sample statement above with unidirectional keyword, so that output occurs only when a TickEvent arrives and not when a NewsEvent arrives:
select * from TickEvent as t unidirectional, NewsEvent#unique(symbol) as n where t.symbol = n.symbol
It is oftentimes the case that an aggregation (count, sum, average) only needs to be calculated in the context of an arriving event or timer. Consider using the unidirectional keyword when aggregating over joined streams.
An EPL pattern is a normal citizen also providing a stream of data consisting of pattern matches. A time pattern, for example, can be useful to evaluate a join and produce output upon each interval.
This sample statement includes a pattern that fires every 5 seconds and thus triggers the join to evaluate and produce output, computing an aggregated total quantity per symbol every 5 seconds:
select symbol, sum(qty) from pattern[every timer:interval(5 sec)] unidirectional, TickEvent#unique(symbol) t, NewsEvent#unique(symbol) as n where t.symbol = n.symbol group by symbol
Named windows as well as reference and historical data such as stored in your relational database, and data returned by a method/script/UDF invocation, can also be included in joins as discussed in Section 5.13, “Accessing Relational Data via SQL” and Section 5.14, “Accessing Non-Relational Data via Method, Script or UDF Invocation”.
Related to joins are subqueries: A subquery is a select within another statement, see Section 5.11, “Subqueries”
The compiler performs extensive statement analysis and planning, building internal indexes and strategies as required to allow fast evaluation of many types of statements.
Each point in time that an event arrives to one of the event streams, the two event streams are joined and output events are produced according to the where clause when matching events are found for all joined streams.
This example joins 2 event streams. The first event stream consists of fraud warning events for which it keep the last 30 minutes. The second stream is withdrawal events for which it considers the last 30 seconds. The streams are joined on account number.
select fraud.accountNumber as accntNum, fraud.warning as warn, withdraw.amount as amount,
max(fraud.timestamp, withdraw.timestamp) as timestamp, 'withdrawlFraud' as desc
from FraudWarningEvent#time(30 min) as fraud, WithdrawalEvent#time(30 sec) as withdraw
where fraud.accountNumber = withdraw.accountNumberJoins can also include one or more pattern statements as the next example shows:
select * from FraudWarningEvent#time(30 min) as fraud,
pattern [every w=WithdrawalEvent -> PINChangeEvent(acct=w.acct)]#lastevent as withdraw
where fraud.accountNumber = withdraw.w.accountNumberThe statement above joins the last 30 minutes of fraud warnings with a pattern. The pattern consists of every withdrawal event that is followed by a PIN change event for the same account number. It joins the two event streams on account number. The last-event window instucts the join to only consider the last pattern match.
In a join and outer join, your statement must declare a data window onto each stream. Streams that are marked as unidirectional and named windows and tables as well as database or methods in a join are an exception and do not require a data window. If you are joining an event to itself via contained-event selection, data windows also do not need to be specified. The reason that a data window must be declared is that a data window specifies which events are considered for the join (i.e. last event, last 10 events, all events, last 1 second of events etc.).
The next example joins all FraudWarningEvent events that arrived since the statement was started, with the last 20 seconds of PINChangeEvent events:
select * from FraudWarningEvent#keepall as fraud, PINChangeEvent#time(20 sec) as pin where fraud.accountNumber = pin.accountNumber
The above example employed the special keep-all window that retains all events.
EPL supports left outer joins, right outer joins, full outer joins and inner joins in any combination between an unlimited number of event streams. Outer and inner joins can also join reference and historical data as explained in Section 5.13, “Accessing Relational Data via SQL”, as well as join data returned by a method, script or UDF invocation as outlined in Section 5.14, “Accessing Non-Relational Data via Method, Script or UDF Invocation”.
The keywords left, right, full and inner control the type of the join between two streams. The optional on clause specifies one or more properties that join each stream. The synopsis is as follows:
...from stream_def [as name] ((left|right|full outer) | inner) join stream_def [on property = property [and property = property ...] ] [ ((left|right|full outer) | inner) join stream_def [on ...]]...
If the outer join is a left outer join, there will be at least one output event for each event of the stream on the left-hand side of the clause. For example, in the left outer join shown below you get output for each event in the stream RfidEvent, even if the event does not match any event in the event stream OrderList.
select * from RfidEvent#time(30 sec) as rfid
left outer join
OrderList#length(10000) as orderlist
on rfid.itemId = orderList.itemIdSimilarly, if the join is a Right Outer Join, then there will be at least one output event for each event of the stream on the right-hand side of the clause. For example, in the right outer join shown below you get output for each event in the stream OrderList, even if the event does not match any event in the event stream RfidEvent.
select * from RfidEvent#time(30 sec) as rfid
right outer join
OrderList#length(10000) as orderlist
on rfid.itemId = orderList.itemIdFor all types of outer joins, if the join condition is not met, the select list is computed with the event properties of the arrived event while all other event properties are considered to be null.
The next type of outer join is a full outer join. In a full outer join, each point in time that an event arrives to one of the event streams, one or more output events are produced. In the example below, when either an RfidEvent or an OrderList event arrive, one or more output event is produced. The next example shows a full outer join that joins on multiple properties:
select * from RfidEvent#time(30 sec) as rfid
full outer join
OrderList#length(10000) as orderlist
on rfid.itemId = orderList.itemId and rfid.assetId = orderList.assetIdThe last type of join is an inner join. In an inner join, the runtime produces at least one output event for each event of the stream on the left-hand side that matches at least one event on the right hand side considering the join properties. For example, in the inner join shown below you get output for each event in the RfidEvent stream that matches one or more events in the OrderList data window:
select * from RfidEvent#time(30 sec) as rfid
inner join
OrderList#length(10000) as orderlist
on rfid.itemId = orderList.itemId and rfid.assetId = orderList.assetId
Patterns as streams in a join follow this rule: If your statement does not specify a data window for the pattern then the pattern stream retains the last match. Thus a pattern must have matched at least once for the last match to become available in a join. Multiple rows from a pattern stream may be retained by declaring a data window onto a pattern using the pattern [...]#window_spec syntax.
This example outer joins multiple streams. Here the RfidEvent stream is outer joined to both ProductName and LocationDescription via left outer join:
select * from RfidEvent#time(30 sec) as rfid
left outer join ProductName#keepall as refprod
on rfid.productId = refprod.prodId
left outer join LocationDescription#keepall as refdesc
on rfid.location = refdesc.locId
If the optional on clause is specified, it may only employ the = equals operator and property names. Any other operators must be placed in the where-clause.
The stream names that appear in the on clause may refer to any stream in the from-clause.
Your EPL may also provide no on clause. This is useful when the streams that are joined do not provide any properties to join on, for example when joining with a time-based pattern.
The next example employs a unidirectional left outer join such that the runtime, every 10 seconds, outputs a count of the number of RfidEvent events in the 60-second time window.
select count(*) from pattern[every timer:interval(1)] unidirectional left outer join RfidEvent#time(60 sec)
In a join or outer join your statement lists multiple event streams, data windows and/or patterns in the from clause. As events arrive into the runtime, each of the streams (data windows, patterns) provides insert and remove stream events. The runtime evaluates each insert and remove stream event provided by each stream, and joins or outer joins each event against data window contents of each stream, and thus generates insert and remove stream join results.
The direction of the join execution depends on which stream or streams are currently providing an insert or remove stream event for executing the join. A join is thus multidirectional, or bidirectional when only two streams are joined. A join can be made unidirectional if your application does not want new results when events arrive on a given stream or streams.
The unidirectional keyword can be used in the from clause to identify streams that provide the events to execute the join. If the keyword is present for a stream, all other streams in the from clause become passive streams. When events arrive or leave a data window of a passive stream then the join does not generate join results.
For example, consider a use case that requires us to join stock tick events (TickEvent) and news events (NewsEvent). The unidirectional keyword allows to generate results only when TickEvent events arrive, and not when NewsEvent arrive or leave the 10-second time window:
select * from TickEvent unidirectional, NewsEvent#time(10 sec) where tick.symbol = news.symbol
Aggregation functions in a unidirectional join aggregate within the context of each unidirectional event evaluation and are not cumulative. Thereby aggregation functions when used with unidirectional may evaluate faster as they do not need to consider a remove stream (data removed from data windows or named windows).
The count function in the next statement returns, for each TickEvent, the number of matching NewEvent events:
select count(*) from TickEvent unidirectional, NewsEvent#time(10 sec) where tick.symbol = news.symbol
The following restrictions apply to unidirectional joins:
The
unidirectionalkeyword can only be specified for a single stream in thefromclause, unless all streams are in a full outer join and all streams declareunidirectional.Receiving data from a unidirectional join via the pull API (
iteratormethod) is not allowed. This is because the runtime holds no state for the single stream that provides the events to execute the join.The stream that declares the
unidirectionalkeyword cannot declare a data window for that stream, since remove stream events are not processed for the single stream.
In a full outer join all streams can be marked as unidirectional.
This is useful for declaring multiple triggering events and for performing a union or merge of streams.
When marking more than one stream as unidirectional, all streams must be unidirectional and inner, left and right joins are not allowed. This is because unidirectional streams have an undefined depth and cannot be looked-up against.
For example, consider a use case where output should occur when either a tick event or a news event arrives:
select * from TickEvent as te unidirectional, full outer join NewsEvent as ne unidirectional
Place filter criteria for a given stream into parenthesis, for example:
select * from TickEvent(symbol='IBM') unidirectional, full outer join TradeEvent(symbol='IBM') unidirectional full outer join SettlementEvent(symbol='IBM') unidirectional where coalesce(TickEvent.price,TradeEvent.price) > 100 // place common critera into a where-clause that may use coalesce
When joining 3 or more streams (including any relational or non-relational sources as below) it can sometimes help to provide the query planner instructions how to best execute the join. The compiler compiles a query plan for the statement. You can output the query plan to logging (see configuration).
An outer join that specifies only inner keywords for all streams is equivalent to an default (inner) join. The following two statements are equivalent:
select * from TickEvent#lastevent,
NewsEvent#lastevent where tick.symbol = news.symbolEquivalent to:
select * from TickEvent#lastevent inner join NewsEvent#lastevent on tick.symbol = news.symbol
For all types of joins, the query planner determines a query graph: The term is used here for all the information regarding what properties or expressions are used to join the streams. The query graph thus includes the where-clause expressions as well as outer-join on-clauses if this statement is an outer join. The query planner also computes a dependency graph which includes information about all historical data streams (relational and non-relational as below) and their input needs.
For default (inner) joins the query planner first attempts to find a path of execution as a nested iteration. For each stream the query planner selects the best order of streams available for the nested iteration considering the query graph and dependency graph. If the full depth of the join is achievable via nested iteration for all streams without full table scan then the query planner uses that nested iteration plan. If not, then the query planner re-plans considering a merge join (Cartesian) approach instead.
Specify the @Hint('prefer_merge_join') to instruct the query planner to prefer a merge join plan instead of a nested iteration plan. Specify the @Hint('force_nested_iter') to instruct the query planner to always use a nested iteration plan.
For example, consider the below statement. Depending on the number of matching rows in OrderBookOne and OrderBookTwo (named windows in this example, and assumed to be defined elsewhere) the performance of the join may be better using the merge join plan.
@Hint('prefer_merge_join')
select * from TickEvent#lastevent t,
OrderBookOne ob1, OrderBookOne ob2
where ob1.symbol = t.symbol and ob2.symbol = t.symbol
and ob1.price between t.buy and t.sell and ob2.price between t.buy and t.sellFor outer joins the query planner considers nested iteration and merge join (Cartesian) equally and above hints don't apply.
For NEsper .NET also see Section J.14, “.NET Accessing Relational Data via SQL”.
This chapter outlines how reference data and historical data that are stored in a relational database can be queried via SQL within statements.
EPL can access via join and outer join as well as via iterator (poll) API all types of event streams to stored data. In order for such data sources to become accessible to EPL, some configuration is required. The Section 17.4.12, “Relational Database Access” explains the required configuration for database access in greater detail, and includes information on configuring a query result cache.
The compiler does not parse or otherwise inspect your SQL query. Therefore your SQL can make use of any database-specific SQL language extensions or features that your database provides.
If you have enabled SQL query result caching in your database configuration, the runtime retains SQL query results in cache following the configured cache eviction policy.
Also if you have enabled SQL query result caching in your database configuration and provide EPL where clause and/or on clause (outer join) expressions, then
the runtime builds indexes on the SQL query results to enable fast lookup. This is especially useful if your SQL queries return a large number of rows. For building the proper indexes, the compiler inspects the expression found in your statement where clause, if present. For outer joins, the compiler also inspects your statement on clause. The compiler analyzes the EPL on clause and where clause expressions, if present, looking for property comparison with or without logical AND-relationships between properties. When a SQL query returns rows for caching, the runtime builds and caches the appropriate index and lookup strategies for fast row matching against indexes.
Joins or outer joins in which only SQL statements or method, script and UDF invocations are listed in the from clause and no other event streams are termed passive joins. A passive join does not produce an insert or remove stream and therefore does not invoke statement listeners with results. A passive join can be iterated on (polled) using a statement's safeIterator and iterator methods.
There are no restrictions to the number of SQL statements or types of streams joined. The following restrictions currently apply:
An SQL query cannot declare data windows; That is, you cannot create a time or length window on an SQL query. Instead, use
insert intoto make join results available for further processing.Your database software must support JDBC prepared statements that provide statement meta data at compilation time. Most major databases provide this function. A workaround is available for databases that do not provide this function.
JDBC drivers must support the getMetadata feature. A workaround is available as below for JDBC drivers that don't support getting metadata.
The next sections assume basic knowledge of SQL (Structured Query Language).
To join an event stream against stored data, specify the sql keyword followed by the name of the database and a parameterized SQL query. The syntax to use in the from clause of a statement is:
sql:database_name [" parameterized_sql_query "]
The runtime uses the database_name identifier to obtain configuration information in order to establish a database connection, as well as settings that control connection creation and removal. Please see Section 17.4.12, “Relational Database Access” to configure an runtime for database access.
Following the database name is the SQL query to execute. The SQL query can contain one or more substitution parameters. The SQL query string is placed in single brackets [ and ]. The SQL query can be placed in either single quotes (') or double quotes ("). The SQL query grammer is passed to your database software unchanged, allowing you to write any SQL query syntax that your database understands, including stored procedure calls.
Substitution parameters in the SQL query string take the form ${expression}. The compiler resolves expression at statement execution time to the actual expression result by evaluating the events in the joined event stream or current variable values, if any event property references or variables occur in the expression. An expression may not contain EPL substitution parameters.
The compiler determines the type of the SQL query output columns by means of the result set metadata that your database software returns for the statement. The actual
SQL query results are obtained via the getObject on java.sql.ResultSet.
The sample statement below joins an event stream consisting of CustomerCallEvent events with the results of an SQL query against the database named MyCustomerDB and table Customer:
select custId, cust_name from CustomerCallEvent,
sql:MyCustomerDB [' select cust_name from Customer where cust_id = ${custId} ']
The example above assumes that CustomerCallEvent supplies an event property named custId. The SQL query selects the customer name from the Customer table. The where clause in the SQL matches the Customer table column cust_id with the value of custId in each CustomerCallEvent event. The runtime executes the SQL query for each new CustomerCallEvent encountered.
If the SQL query returns no rows for a given customer id, the runtime generates no output event. Else the runtime generates one output event for each row returned by the SQL query. An outer join as described in the next section can be used to control whether the runtime should generate output events even when the SQL query returns no rows.
The next example adds a time window of 30 seconds to the event stream CustomerCallEvent. It also renames the selected properties to customerName and customerId to demonstrate how the naming of columns in an SQL query can be used in the select clause in the statement. And the example uses explicit stream names via the as keyword.
select customerId, customerName from
CustomerCallEvent#time(30 sec) as cce,
sql:MyCustomerDB ["select cust_id as customerId, cust_name as customerName from Customer
where cust_id = ${cce.custId}"] as cq
Any window, such as the time window, generates insert stream (istream) events as events enter the window, and remove stream (rstream) events as events leave the window. The runtime executes the given SQL query for each CustomerCallEvent in both the insert stream and the remove stream. As a performance optimization, the istream or rstream keywords in the select clause can be used to instruct the runtime to only join insert stream or remove stream events, reducing the number of SQL query executions.
Since any expression may be placed within the ${...} syntax, you may use variables or user-defined functions as well.
The next example assumes that a variable by name varLowerLimit is defined and that a user-defined function getLimit exists on the MyLib imported class that takes a LimitEvent as a parameter:
select * from LimitEvent le,
sql:MyCustomerDB [' select cust_name from Customer where
amount > ${max(varLowerLimit, MyLib.getLimit(le))} ']The example above takes the higher of the current variable value or the value returned by the user-defined function to return only those customer names where the amount exceeds the computed limit.
Consider using the EPL where clause to join the SQL query result to your event stream. Similar to EPL joins and outer-joins that join event streams or patterns, the EPL where clause provides join criteria between the SQL query results and the event stream (as a side note, an SQL where clause is a filter of rows executed by your database on your database server before returning SQL query results).
The compiler analyzes the expression in the EPL where clause and outer-join on clause, if present, and builds the appropriate indexes from that information at runtime, to ensure fast matching of event stream events to SQL query results, even if your SQL query returns a large number of rows. Your applications must ensure to configure a cache for your database using configuration, as such indexes are held with regular data in a cache. If your application does not enable caching of SQL query results, the runtime does not build indexes on cached data.
The sample statement below joins an event stream consisting of OrderEvent events with the results of an SQL query against the database named MyRefDB and table SymbolReference:
select symbol, symbolDesc from OrderEvent as orders, sql:MyRefDB ['select symbolDesc from SymbolReference'] as reference where reference.symbol = orders.symbol
Notice how the EPL where clause joins the OrderEvent stream to the SymbolReference table. In this example, the SQL query itself does not have a SQL where clause
and therefore returns all rows from table SymbolReference.
If your application enables caching, the SQL query fires only at the arrival of the first OrderEvent event. When the second OrderEvent arrives, the join execution uses the cached SQL query result. If the caching policy that you specified in the database configuration evicts the SQL query result from cache, then the runtime fires the SQL query again to obtain a new result and places the result in cache.
If SQL result caching is enabled and your EPL where clause, as show in the above example, provides the properties to join, then the runtime indexes the SQL query results in cache and retains the index together with the SQL query result in cache. Thus your application can benefit from high performance index-based lookups as long as the SQL query results are found in cache.
The SQL result caches operate on the level of all result rows for a given parameter set. For example, if your SQL query returns 10 rows for a certain set of parameter values then the cache treats all 10 rows as a single entry keyed by the parameter values, and the expiry policy applies to all 10 rows and not to each individual row.
It is also possible to join multiple autonomous database systems in a single statement, for example:
select symbol, symbolDesc from OrderEvent as orders, sql:My_Oracle_DB ['select symbolDesc from SymbolReference'] as reference, sql:My_MySQL_DB ['select orderList from orderHistory'] as history where reference.symbol = orders.symbol and history.symbol = orders.symbol
You can use outer joins to join data obtained from an SQL query and control when an event is produced. Use a left outer join, such as in the next statement, if you need an output event for each event regardless of whether or not the SQL query returns rows. If the SQL query returns no rows, the join result populates null values into the selected properties.
select custId, custName from
CustomerCallEvent as cce
left outer join
sql:MyCustomerDB ["select cust_id, cust_name as custName
from Customer where cust_id = ${cce.custId}"] as cq
on cce.custId = cq.cust_id
The statement above always generates at least one output event for each CustomerCallEvent, containing all columns selected by the SQL query, even if the SQL query does not return any rows. Note the on expression that is required for outer joins. The on acts as an additional filter to rows returned by the SQL query.
Pattern statements and SQL queries can also be applied together in useful ways. One such use is to poll or request data from a database at regular intervals or following the schedule of the crontab-like timer:at.
The next statement is an example that shows a pattern that fires every 5 seconds to query the NewOrder table for new orders:
insert into NewOrders select orderId, orderAmount from pattern [every timer:interval(5 sec)], sql:MyCustomerDB ['select orderId, orderAmount from NewOrders']
Usually your SQL query will take part in a join and thus be triggered by an event or pattern occurrence. Instead, your application may need to poll a SQL query and thus use runtime statement execution and caching facilities and obtain event data and metadata.
Your statement can specify an SQL statement without a join. Such a stand-alone SQL statement does not post new events, and may only be queried via the iterator poll API. Your EPL and SQL statement may still use variables.
The next statement assumes that a price_var variable has been declared. It selects from the relational database table named NewOrder all rows in which the price column is greater
then the current value of the price_var EPL variable:
select * from sql:MyCustomerDB ['select * from NewOrder where ${price_var} > price']
Use the iterator and safeIterator methods on EPStatement to obtain results. The statement does not post events to listeners, it is strictly passive in that sense.
The runtime translates SQL queries into JDBC java.sql.PreparedStatement statements by replacing ${name} parameters with '?' placeholders. It obtains name and type of result columns from the compiled PreparedStatement meta data when the statement gets compiled.
The runtime supplies parameters to the compiled statement via the setObject method on PreparedStatement. The runtime uses the getObject method on the compiled statement PreparedStatement to obtain column values.
Certain JDBC database drivers are known to not return metadata for precompiled prepared SQL statements. This can be a problem as metadata is required by the compiler. The compiler obtains SQL result set metadata to validate a statement and to provide column types for output events. JDBC drivers that do not provide metadata for precompiled SQL statements require a workaround. Such drivers do generally provide metadata for executed SQL statements, however do not provide the metadata for precompiled SQL statements.
Please consult the Chapter 17, Configuration for the configuration options available in relation to metadata retrieval.
To obtain metadata for an SQL statement, the compiler can alternatively fire a SQL statement which returns the same column names and types as the actual SQL statement but without returning any rows. This kind of SQL statement is referred to as a sample statement in below workaround description. The compiler can then use the sample SQL statement to retrieve metadata for the column names and types returned by the actual SQL statement.
Applications can provide a sample SQL statement to retrieve metadata via the metadatasql keyword:
sql:database_name ["parameterized_sql_query" metadatasql "sql_meta_query"]
The sql_meta_query must be an SQL statement that returns the same number of columns, the same type of columns and the same column names as the parameterized_sql_query, and does not return any rows.
Alternatively, applications can choose not to provide an explicit sample SQL statement. If the statement does not use the metadatasql syntax, the compiler applies lexical analysis to the SQL statement. From the lexical analysis the compiler generates a sample SQL statement adding a restrictive clause "where 1=0" to the SQL statement.
Alternatively, you can add the following tag to the SQL statement: ${$ESPER-SAMPLE-WHERE}. If the tag exists in the SQL statement, the compiler does not perform lexical analysis and simply replaces the
tag with the SQL where clause "where 1=0". Therefore this workaround is applicable to SQL statements that cannot be correctly lexically analyzed. The SQL text after the placeholder is not part of the sample SQL query. For example:
select mycol from sql:myDB [
'select mycol from mytesttable ${$ESPER-SAMPLE-WHERE} where ....'], ...If your parameterized_sql_query SQL query contains vendor-specific SQL syntax, generation of the metadata query may fail to produce a valid SQL statement. If you experience an SQL error while fetching metadata, use any of the above workarounds with the Oracle JDBC driver.
As part of database access configuration you may optionally specify SQL type mappings. These mappings apply to all SQL queries against the same database identified by name.
If your application must perform SQL-query-specific or EPL-statement-specific mapping or conversion between types, the facility to register a conversion callback exists as follows.
Use the @Hook instruction and HookType.SQLCOL as part of your statement to register a statement SQL parameter or column conversion hook.
Implement the interface com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.type.SQLColumnTypeConversion to perform the input parameter or column value conversion.
A sample statement with annotation is shown:
@Hook(type=HookType.SQLCOL, hook='MyDBTypeConvertor') select * from sql:MyDB ['select * from MyEventTable]
The compiler expects MyDBTypeConvertor to resolve to a class (considering imports) and instantiates one instance of MyDBTypeConvertor for each statement.
Your application may also directly convert a SQL result row into a Java class which is an opportunity for your application to interrogate and transform the SQL row result data freely before packing the data into a Java class. Your application can additionally indicate to skip SQL result rows.
Use the @Hook instruction and HookType.SQLROW as part of your statement to register a statement SQL output row conversion hook.
Implement the interface com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.type.SQLOutputRowConversion to perform the output row conversion.
A sample statement with annotation is shown:
@Hook(type=HookType.SQLROW, hook='MyDBRowConvertor') select * from sql:MyDB ['select * from MyEventTable]
The compiler expects MyDBRowConvertor to resolve to a class (considering imports) and instantiates one MyDBRowConvertor instance for each statement.
The Esper fire-and-forget query API provides a facility to execute on-demand one-time queries and such queries can query a relational database. The Esper runtime executes SQL queries and returns the results as events - thereby an application can avoid using the JDBC API. For further information please refer to Section 16.7.5, “The From-Clause can Access Relational Data via SQL”.
Your application may need to join data that originates from a web service, a distributed cache, an object-oriented database or simply data held in memory by your application.
One way to join in external data is by means of method, script or user-defined function invocation (or procedure call or function) in the from clause of a statement.
The results of such a method, script or UDF invocation in the from clause plays the same role as a relational database table in an inner and outer join in SQL.
EPL can join and outer join an unlimited number and all types of event streams to the data returned by your invocation. In addition, the runtime can be configured to cache the data returned by your method, script or UDF invocations.
Joins or outer joins in which only SQL statements or method, script or UDF invocations are listed in the from clause and no other event streams are termed passive joins. A passive join does not produce an insert or remove stream and therefore does not invoke statement listeners with results. A passive join can be iterated on (polled) using a statement's safeIterator and iterator methods.
The following restrictions currently apply:
A invocation cannot declare data windows; That is, you cannot create a time or length window on an invocation. Instead, use
insert intoto make join results available for further processing.
The syntax for a method, script or UDF invocation in the from clause of a statement is:
method: [class_or_variable_name.]method_script_udf_name[(parameter_expressions)] [@type(eventtype_name)]
The method keyword denotes a method, script or UDF invocation. It is followed by an optional class or variable name.
The method_script_udf_name is the name of the method, script or user-defined function.
If you have parameters to your method, script or UDF invocation, these are placed in
parentheses after the method or script name. Any expression is allowed as a parameter, and individual parameter expressions are separated by a comma.
Expressions may also use event properties of the joined stream.
In case the return type of the method is EventBean instances, you must provide the @type annotation to name the event type of events returned.
Otherwise @type is not allowed.
In the sample join statement shown next, the method lookupAsset provided by class (or variable) MyLookupLib returns one or more rows based on the asset id (a property of the AssetMoveEvent) that is passed to the method:
select * from AssetMoveEvent, method:MyLookupLib.lookupAsset(assetId)
The following statement demonstrates the use of the where clause to join events to the rows returned by an invocation, which in this example does not take parameters:
select assetId, assetDesc from AssetMoveEvent as asset,
method:MyLookupLib.getAssetDescriptions() as desc
where asset.assetid = desc.assetid
Your method, scipt or UDF invocation may return zero, one or many rows for each invocation. If you have caching enabled through configuration, then the runtime can avoid the invocation and instead use cached results. Similar to SQL joins, the runtime also indexes cached result rows such that join operations based on the where clause or outer-join on clause can be very efficient, especially if your invocation returns a large number of rows.
If the time taken by method, script or UDF invocations is critical to your application, you may configure local caches as Section 17.4.11, “From-Clause Method Invocation” describes.
The compiler analyzes the expression in the EPL where clause and outer-join on clause, if present, and builds the appropriate indexes from that information at runtime, to ensure fast matching of event stream events to invocation results, even if your invocation returns a large number of rows. Your applications must ensure to configure a cache for your invocation using configuration, as such indexes are held with regular data in a cache. If your application does not enable caching of invocation results, the runtime does not build indexes on cached data.
Usually your invocation will take part in a join and thus be triggered by an event or pattern occurrence. Instead, your application may need to poll an invocation and thus use SQL query execution and caching facilities and obtain event data and metadata.
Your statement can specify an invocation in the from clause without a join. Such a stand-alone invocation does not post new events, and may only be queried via the iterator poll API. Your statement may still use variables.
The next statement assumes that a category_var variable has been declared. It polls the getAssetDescriptions method passing the current value of the category_var EPL variable:
select * from method:MyLookupLib.getAssetDescriptions(category_var)]
Use the iterator and safeIterator methods on EPStatement to obtain results. The statement does not post events to listeners, it is strictly passive in that sense.
Your application can provide a public static method or can provide an instance method of an existing object. The declaring class must be public as well. The method must accept the same number and type of parameters as listed in the parameter expression list.
The examples herein mostly use public static methods. For a detail description of instance methods please see Section 5.17.5, “Class and Event-Type Variables” and below example.
If your invocation returns either no row or only one row, then the return type of the method can be a Java class, java.util.Map or Object[] (object-array). If your invocation can return more then one row, then the return type of the method must be an array of Java class, array of Map, Object[][] (object-array 2-dimensional) or
Collection or Iterator (or subtypes thereof).
If you are using a Java class, an array of Java class or a Collection<Class> or an Iterator<Class> as the return type, then the class must adhere to JavaBean conventions: it must expose properties through getter methods.
If you are using java.util.Map or an array of Map or a Collection<Map> or an Iterator<Map> as the return type, please note the following:
- Your application must provide a second method that returns event property metadata, as the next section outlines.
-
Each map instance returned by your method should have
String-type keys and object values (Map<String, Object>).
If you are using Object[] (object-array) or Object[][] (object-array 2-dimensional) or Collection<Object[]> or Iterator<Object[]> as the return type, please note the following:
- Your application must provide a second method that returns event property metadata, as the next section outlines.
- Each object-array instance returned by your method should have the exact same array position for values as the property metadata indicates and the array length must be the same as the number of properties.
Your application method must return either of the following:
A
nullvalue or an empty array to indicate an empty result (no rows).A Java object or
MaporObject[]to indicate a zero (null) or one-row result.Return multiple result rows by returning either:
- An array of Java objects.
-
An array of
Mapinstances. -
An array of
Object[]instances. -
An array of
EventBean[]instances (requires@type). -
A
Collectionof Java objects. -
A
CollectionofMapinstances. -
A
CollectionofObject[]instances. -
An
CollectionofEventBean[]instances (requires@type). -
An
Iteratorof Java objects. -
An
IteratorofMapinstances. -
An
IteratorofObject[]instances. -
An
IteratorofEventBean[]instances (requires@type).
As an example, consider the method 'getAssetDescriptions' provided by class 'MyLookupLib' as discussed earlier:
select assetId, assetDesc from AssetMoveEvent as asset,
method:com.mypackage.MyLookupLib.getAssetDescriptions() as desc
where asset.assetid = desc.assetidThe 'getAssetDescriptions' method may return multiple rows and is therefore declared to return an array of the class 'AssetDesc'. The class AssetDesc is a POJO class (not shown here):
public class MyLookupLib {
...
public static AssetDesc[] getAssetDescriptions() {
...
return new AssetDesc[] {...};
}The example above specifies the full Java class name of the class 'MyLookupLib' class in the statement. The package name does not need to be part of the EPL if your application imports the package using the auto-import configuration through the API or XML, as outlined in Section 17.4.2, “Class and Package Imports”.
Alternatively the example above could return a Collection wherein the method declares as public static Collection<AssetDesc> getAssetDescriptions() {...} or an Iterator wherein the method declares as public static Iterator<AssetDesc> getAssetDescriptions() {...}.
Method overloading is allowed as long as overloaded methods return the same result type.
If your application has an existing object instance such as a service or a dependency injected bean then it must make the instance available as a variable. Please see Section 5.17.5, “Class and Event-Type Variables” for more information.
For example, assuming you provided a stateChecker variable that points to an object instance that provides a public getMatchingAssets instance method
and that returns property assetIds, you may use the state checker service in the from-clause as follows:
select assetIds from AssetMoveEvent, method:stateChecker.getMatchingAssets(assetDesc)
Your application may return java.util.Map or an array of Map from invocations. If doing so, your application must provide metadata about each row: it must declare the property name and property type of each Map entry of a row. This information allows the compiler to perform type checking of expressions used within the statement.
You declare the property names and types of each row by providing a method that returns property metadata. The metadata method must follow these conventions:
The method name providing the property metadata must have same method name appended by the literal
Metadata.The method must have an empty parameter list and must be declared public and static.
The method providing the metadata must return a
MapofStringproperty name keys andjava.lang.Classproperty name types (Map<String, Class>).
In the following example, a class 'MyLookupLib' provides a method to return historical data based on asset id and asset code:
select assetId, location, x_coord, y_coord from AssetMoveEvent as asset,
method:com.mypackage.MyLookupLib.getAssetHistory(assetId, assetCode) as historyA sample implementation of the class 'MyLookupLib' is shown below.
public class MyLookupLib {
...
// For each column in a row, provide the property name and type
//
public static Map<String, Class> getAssetHistoryMetadata() {
Map<String, Class> propertyNames = new HashMap<String, Class>();
propertyNames.put("location", String.class);
propertyNames.put("x_coord", Integer.class);
propertyNames.put("y_coord", Integer.class);
return propertyNames;
}
...
// Lookup rows based on assetId and assetCode
//
public static Map<String, Object>[] getAssetHistory(String assetId, String assetCode) {
Map rows = new Map[2]; // this sample returns 2 rows
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
rows[i] = new HashMap();
rows[i].put("location", "somevalue");
rows[i].put("x_coord", 100);
// ... set more values for each row
}
return rows;
}In the example above, the 'getAssetHistoryMetadata' method provides the property metadata: the names and types of properties in each row. The compiler calls this method once per statement to determine event typing information.
The 'getAssetHistory' method returns an array of Map objects that are two rows. The implementation shown above is a simple example. The parameters to the method are the assetId and assetCode properties of the AssetMoveEvent joined to the method. The runtime calls this method for each insert and remove stream event in AssetMoveEvent.
To indicate that no rows are found in a join, your application method may return either a null value or an array of size zero.
Alternatively the example above could return a Collection wherein the method declares as public static Collection<Map> getAssetHistory() {...} or an Iterator wherein the method declares as public static Iterator<Map> getAssetHistory() {...}.
Your application may return Object[] (object-array) or an array of Object[] (object-array 2-dimensional) from invocations. If doing so, your application must provide metadata about each row: it must declare the property name and property type of each array entry of a row in the exact same order as provided by value rows. This information allows the runtime to perform type checking of expressions used within the statement.
You declare the property names and types of each row by providing a method that returns property metadata. The metadata method must follow these conventions:
The method name providing the property metadata must have same method name appended by the literal
Metadata.The method must have an empty parameter list and must be declared public and static.
The method providing the metadata must return a
LinkedHashMapofStringproperty name keys andjava.lang.Classproperty name types (Map<String, Class>).
In the following example, a class 'MyLookupLib' provides a method to return historical data based on asset id and asset code:
select assetId, location, x_coord, y_coord from AssetMoveEvent as asset,
method:com.mypackage.MyLookupLib.getAssetHistory(assetId, assetCode) as historyA sample implementation of the class 'MyLookupLib' is shown below.
public class MyLookupLib {
...
// For each column in a row, provide the property name and type
//
public static LinkedHashMap<String, Class> getAssetHistoryMetadata() {
LinkedHashMap<String, Class> propertyNames = new LinkedHashMap<String, Class>();
propertyNames.put("location", String.class);
propertyNames.put("x_coord", Integer.class);
propertyNames.put("y_coord", Integer.class);
return propertyNames;
}
...
// Lookup rows based on assetId and assetCode
//
public static Object[][] getAssetHistory(String assetId, String assetCode) {
Object[][] rows = new Object[5][]; // this sample returns 5 rows
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
rows[i] = new Object[2]; // single row has 2 fields
rows[i][0] = "somevalue";
rows[i][1] = 100;
// ... set more values for each row
}
return rows;
}In the example above, the 'getAssetHistoryMetadata' method provides the property metadata: the names and types of properties in each row. The compiler calls this method once per statement to determine event typing information.
The 'getAssetHistory' method returns an Object[][] that represents five rows. The implementation shown above is a simple example. The parameters to the method are the assetId and assetCode properties of the AssetMoveEvent joined to the method. The runtime calls this method for each insert and remove stream event in AssetMoveEvent.
To indicate that no rows are found in a join, your application method may return either a null value or an array of size zero.
Alternatively the example above could return a Collection wherein the method declares as public static Collection<Object[]> getAssetHistory() {...} or an Iterator wherein the method declares as public static Iterator<Object[]> getAssetHistory() {...}.
When the return type is EventBean[], Collection<EventBean> or Iterator<EventBean>, you must specify the event type name using @type.
For example assuming the event type ItemEvent is declared as create schema ItemEvent(p0 string):
select * from MyEvent, method:MyLib.myFunc() @type(ItemEvent)
public static EventBean[] myFunc(EPLMethodInvocationContext context) {
EventBean[1] events = new EventBean[1];
events[0] = context.getEventBeanService().adapterForMap(Collections.singletonMap("p0", "hello"), "ItemEvent");
return events;
}
Your script must declare the return type as EventBean[]. In the @type annotation you must provide an event type name.
For example assuming the event type ItemEvent is declared as create schema ItemEvent(id string):
select id from MyEvent, method:myItemProducerScript()
The example JavaScript script is:
create expression EventBean[] @type(ItemEvent) js:myItemProducerScript() [
myItemProducerScript()
function myItemProducerScript() {
var EventBeanArray = Java.type(\"com.espertech.esper.common.client.EventBean[]\");
var events = new EventBeanArray(1);
events[0] = epl.getEventBeanService().adapterForMap(java.util.Collections.singletonMap(\"id\", \"id1\"), \"ItemEvent\");
return events;
}]
Your script must declare the return type of the UDF as EventBean[]. In the @type annotation you must provide an event type name.
For example assuming you have registered a user-defined function myUserDefinedFunction:
select id from MyEvent, method:myUserDefinedFunction() @type(ItemEvent)
EPL allows declaring an event type via the create schema clause and also by configuring predefined types. The term schema and event type has the same meaning in EPL.
When using the create schema syntax to declare an event type, the runtime automatically removes the event type on undeploy.
The synopsis of the create schema syntax providing property names and types is:
create [map | objectarray | json | avro | xml] schema schema_name [as] (property_name property_type [,property_name property_type [,...]) [inherits inherited_event_type[, inherited_event_type] [,...]] [starttimestamp timestamp_property_name] [endtimestamp timestamp_property_name] [copyfrom copy_type_name [, copy_type_name] [,...]]
The create keyword can be followed by map to instruct the compiler to represent events of that type by the Map event representation, or objectarray to denote an Object-array event type, or json to denote a JSON event type, or avro to denote an Avro event type, or xml to denote an XML event type. If neither the map or objectarray or json or avro or xml keywords are provided, the compiler default event representation applies.
After create schema follows a schema_name. The schema name is the event type name.
The property_name is an identifier providing the event property name. The property_type is also required for each property. Valid property types are listed in Section 5.17.1, “Creating Variables: The Create Variable Clause” and in addition include:
Any Java class name, fully-qualified or the simple class name if imports are configured. Parameterized types such as
java.util.Collection<String>are supported as well.Add left and right square brackets
[]to any type to denote an array-type event property, and[][]for two-dimensional arrays.Use an event type name as a property type.
The
nullkeyword for a null-typed property.
For XML event types please check Section I.5, “Using XML-Schema Annotations with create xml schema” for information on how to declare properties.
The optional inherits keywords is followed by a comma-separated list of event type names that are the supertypes to the declared type.
The optional starttimestamp keyword is followed by a property name. Use this to tell the compiler that your event has a timestamp. The compiler checks that the property name exists on the declared type and returns a date-time value.
Declare a timestamp property if you want your events to implicitly carry a timestamp value for convenient use with interval algebra methods as a start timestamp.
The optional endtimestamp keyword is followed by a property name. Use this together with starttimestamp to tell the compiler that your event has a duration. The compiler checks that the property name exists on the declared type and returns a date-time value.
Declare an endtimestamp property if you want your events to implicitly carry a duration value for convenient use with interval algebra methods.
The optional copyfrom keyword is followed by a comma-separate list of event type names. For each event type listed, the compiler looks up that type and adds all event property definitions to the newly-defined type, in addition to those listed explicitly (if any). The resulting order of properties is that copied-from properties are first (in the order of event types and their property order) and explicitly-listed properties last.
A few example event type declarations follow:
// Declare type SecurityEvent create schema SecurityEvent as (ipAddress string, userId String, numAttempts int) // Declare type AuthorizationEvent with the roles property being an array of String // and the hostinfo property being a POJO object create schema AuthorizationEvent(group String, roles String[], hostinfo com.mycompany.HostNameInfo) // Declare type CompositeEvent in which the innerEvents property is an array of SecurityEvent create schema CompositeEvent(group String, innerEvents SecurityEvent[]) // Declare type WebPageVisitEvent that inherits all properties from PageHitEvent create schema WebPageVisitEvent(userId String) inherits PageHitEvent // Declare a type with start and end timestamp (i.e. event with duration). create schema RoboticArmMovement (robotId string, startts long, endts long) starttimestamp startts endtimestamp endts // Create a type that has all properties of SecurityEvent plus a userName property create schema ExtendedSecurityEvent (userName string) copyfrom SecurityEvent // Create a type that has all properties of SecurityEvent create schema SimilarSecurityEvent () copyfrom SecurityEvent // Create a type that has all properties of SecurityEvent and WebPageVisitEvent plus a userName property create schema WebSecurityEvent (userName string) copyfrom SecurityEvent, WebPageVisitEvent
To elaborate on the inherits keyword, consider the following two schema definitions:
create schema Foo as (prop1 string)
create schema Bar() inherits Foo
Following above schema, Foo is a supertype or Bar and therefore any Bar event also fulfills Foo and matches where Foo matches. A statement such as select * from Foo
returns any Foo event as well as any event that is a subtype of Foo such as all Bar events. When your statements don't use any Foo events there is no cost, thus inherits is
generally an effective way to share properties between types. The start and end timestamp are also inherited from any supertype that has the timestamp property names defined.
The optional copyfrom keyword is for defining a schema based on another schema. This keyword causes the compiler to copy property definitions: There is no inherits, extends, supertype or subtype relationship between the types listed.
To define an event type Bar that has the same properties as Foo:
create schema Foo as (prop1 string)
create schema Bar() copyfrom Foo
To define an event type Bar that has the same properties as Foo and that adds its own property prop2:
create schema Foo as (prop1 string)
create schema Bar(prop2 string) copyfrom Foo
If neither the map or objectarray or json or avro keywords are provided, the following rule applies:
If the create-schema statement provides the
@EventRepresentation(objectarray)annotation the runtime expects object array events.If the statement provides the
@EventRepresentation(json)annotation the runtime expects JSON strings as events.If the statement provides the
@EventRepresentation(avro)annotation the runtime expects Avro objects as events.If the statement provides the
@EventRepresentation(map)annotation the runtime expects Map objects as events.If neither annotation is provided, the runtime uses the configured default event representation as discussed in Section 17.4.9.1, “Default Event Representation”.
The following two statements both instructs the compiler to represent Foo events as object arrays. When sending Foo events into the runtime use the sendEventObjectArray(Object[] data, String typeName) footprint.
create objectarray schema Foo as (prop1 string)
@EventRepresentation(objectarray) create schema Foo as (prop1 string)
The next two statements both instructs the compiler to represent Foo events as Maps. When sending Foo events into the runtime use the sendEventMap(Map data, String typeName) footprint.
create map schema Foo as (prop1 string)
@EventRepresentation(map) create schema Foo as (prop1 string)
The following two statements both instructs the compiler to represent Foo events as JSON. When sending Foo events into the runtime use the sendEventJson(String json, String typeName) footprint.
create json schema Foo as (prop1 string)
@EventRepresentation(json) create schema Foo as (prop1 string)
The following two statements both instructs the compiler to represent Foo events as Avro GenericData.Record. When sending Foo events into the runtime use the sendEventAvro(Object genericDataDotRecord, String typeName) footprint.
create avro schema Foo as (prop1 string)
@EventRepresentation(avro) create schema Foo as (prop1 string)
When using Java classes as the underlying event representation your application may simply provide the class name:
create schema schema_name [as] class_name [starttimestamp timestamp_property_name] [endtimestamp timestamp_property_name]
The class_name must be a fully-qualified class name (including the package name) if imports are not configured. If your application configures imports then the simple class name suffices without package name.
Parameterized types such as java.util.MyEvent<String> are supported as well.
The optional starttimestamp and endtimestamp keywords have a meaning as defined earlier.
The next example statements declare an event type based on a class:
// Shows the use of a fully-qualified class name to declare the LoginEvent event type create schema LoginEvent as com.mycompany.LoginValue // When the configuration includes imports, the declaration does not need a package name create schema LogoutEvent as SignoffValue
A variant stream is a predefined stream into which events of multiple disparate event types can be inserted. Please see Section 5.10.3, “Merging Disparate Types of Events: Variant Streams” for rules regarding property visibility and additional information.
The synopsis is:
create variant schema schema_name [as] eventtype_name|* [, eventtype_name|*] [,...]
Provide the variant keyword to declare a variant stream.
The '*' wildcard character declares a variant stream that accepts any type of event inserted into the variant stream.
Provide eventtype_name if the variant stream should hold events of the given type only. When using insert into to
insert into the variant stream the compiler checks to ensure the inserted event type or its supertypes match the required event type.
A few examples are shown below:
// Create a variant stream that accepts only LoginEvent and LogoutEvent event types create variant schema SecurityVariant as LoginEvent, LogoutEvent // Create a variant stream that accepts any event type create variant schema AnyEvent as *
EPL offers a convenient syntax to splitting, routing or duplicating events into multiple streams, and for receiving unmatched events among a set of filter criteria.
For splitting a single event that acts as a container and expose child events as a property of itself consider the contained-event syntax as described in Section 5.19, “Contained-Event Selection”. For generating marker events for contained-events please see below.
You may define a triggering event or pattern in the on-part of the statement followed by multiple insert into, select and where clauses.
The synopsis is:
[context context_name] on event_type[(filter_criteria)] [as stream_name] insert into insert_into_def select select_list [where condition] [insert into insert_into_def select select_list [from contained-event-selection] [where condition]] [insert into insert_into_def select select_list [from contained-event-selection] [where condition]] [insert into...] [output first | all]
The event_type is the name of the type of events that trigger the split stream. It is optionally
followed by filter_criteria which are filter expressions to apply to arriving events. The optional as keyword
can be used to assign a stream name. Patterns and named windows can also be specified in the on clause.
Following the on-clause is one or more insert into clauses as described in Section 5.10, “Merging Streams and Continuous Insertion: The Insert Into Clause” and select clauses as described in Section 5.3, “Choosing Event Properties and Events: The Select Clause”.
The second and subsequent insert into and select clause pair can have a from clause for contained-event-selection.
This is useful when your trigger events themselves contain events that must be processed individually and that may be delimited by marker events that you can define.
Each select clause may be followed by a where clause containing a condition. If the condition is true for the event, the runtime transforms the event according to the select clause and inserts it into the corresponding stream.
At the end of the statement can be an optional output clause. By default the runtime inserts into the first stream for which the where clause condition matches if one was specified, starting from the top. If you specify the output all keywords, then the runtime inserts into each stream (not only the first stream) for which the where clause condition matches or that do not have a where clause.
If, for a given event, none of the where clause conditions match, the statement listener receives the unmatched event. The statement listener only receives unmatched events and does not receive any transformed or inserted events. The iterator method to the statement returns no events.
You may specify an optional context name to the effect that the split-stream operates according to the context dimensional information as declared for the context. See Chapter 4, Context and Context Partitions for more information.
In the below sample statement, the runtime inserts each OrderEvent into the LargeOrders stream if the order quantity is 100 or larger, or into the SmallOrders stream if the order quantity is smaller then 100:
on OrderEvent insert into LargeOrders select * where orderQty >= 100 insert into SmallOrders select *
The next example statement adds a new stream for medium-sized orders. The new stream receives orders that have an order quantity between 20 and 100:
on OrderEvent insert into LargeOrders select orderId, customer where orderQty >= 100 insert into MediumOrders select orderId, customer where orderQty between 20 and 100 insert into SmallOrders select orderId, customer where orderQty > 0
As you may have noticed in the above statement, orders that have an order quantity of zero don't match any of the conditions. The runtime does not insert such order events into any stream and the listener to the statement receives these unmatched events.
By default the runtime inserts into the first insert into stream without a where clause or for which the where clause condition matches. To change the default behavior and insert into all matching streams instead (including those without a where clause), add the output all keywords.
The sample statement below shows the use of the output all keywords. The statement populates both the LargeOrders stream with large orders as well as the VIPCustomerOrders stream with orders for certain customers based on customer id:
on OrderEvent insert into LargeOrders select * where orderQty >= 100 insert into VIPCustomerOrders select * where customerId in (1001, 1002) output all
Since the output all keywords are present, the above statement inserts each order event into either both streams or only one stream or none of the streams, depending on order quantity and customer id of the order event. The statement delivers order events not inserted into any of the streams to the listeners and/or subscriber to the statement.
The following limitations apply to split-stream statements:
Aggregation functions and the
prevandprioroperators are not available in conditions and theselect-clause.
When a trigger event contains properties that are themselves events, or more generally when your application needs to split the trigger event into multiple events,
or to generate marker events (begin, end etc.) or process contained events in a defined order, you may specify a from clause.
The from clause is only allowed for the second and subsequent insert into and select clause pair.
It specifies how the trigger event should get unpacked into individual events and is based on the
Section 5.19, “Contained-Event Selection”.
For example, assume there is an order event that contains order items:
create schema OrderItem(itemId string)
create schema OrderEvent(orderId string, items OrderItem[])
We can tell the runtime that, for each order event, it should process in the following order:
Process a single
OrderBeginEventthat holds just the order id.Process all order items contained in an order event.
Process a single
OrderEndEventthat holds just the order id.
The EPL is:
on OrderEvent insert into OrderBeginEvent select orderId insert into OrderItemEvent select * from [select orderId, * from items] insert into OrderEndEvent select orderId output all
When an OrderEvent comes in, the runtime first processes an OrderBeginEvent. The runtime unpacks the order event and for each
order item processes an OrderItemEvent containing the respective item. The runtime last processes an OrderEndEvent.
Such begin and end marker events are useful to initiate and terminate an analysis using context declaration, for example. The next two statements declare a context and perform a simple count of order items per order:
create context OrderContext initiated by OrderBeginEvent as obe terminated by OrderEndEvent(orderId = obe.orderId)
context OrderContext select count(*) as orderItemCount from OrderItemEvent output when terminated
The @priority annotation and the @drop annotation can split streams. Note that annotations require setting prioritized execution in the runtime configuration.
For example:
insert into AllOrders select * from OrderEvent; @priority(1) @drop insert into LargeOrders select * from AllOrders(orderQty > 100); insert into SmallOrders select * from AllOrders;
The first statement inserts all OrderEvent events into the AllOrders stream. The runtime processes the second statement before it processes the third statement
since the second statement has @priority(1). For the second statement, if the order quantity is greater than 100, the runtime inserts the event into the
LargeOrders stream and the runtime stop processing that AllOrders event since the second statement also has the @drop annotation.
If the order quantity is 100 or less, the runtime processes the third statement and inserts the event into the SmallOrders stream.
A variable is a scalar, object, event or set of aggregation values that is available for use in all statements including patterns. Variables can be used in an expression anywhere in a statement as well as in the output clause for output rate limiting.
Variables must first be declared or configured before use, by defining each variable's type and name. Variables can be created via the create variable syntax or declared by runtime or static configuration. Variables can be assigned new values by using the on set syntax or via the setVariableValue methods on EPVariableService. The EPVariableService also provides method to read variable values.
A variable can be declared constant. A constant variable always has the initial value and cannot be assigned a new value. A constant variable can be used like any other variable and can be used wherever a constant is required. By declaring a variable constant you enable the runtime to optimize and perform query planning knowing that the variable value cannot change.
When declaring a class-typed, event-typed or aggregation-typed variable you may read or set individual properties within the same variable.
The runtime guarantees consistency and atomicity of variable reads and writes on the level of context partition (this is a soft guarantee, see below). Variables are optimized for fast read access and are also multithread-safe.
When you associate a context to the variable then each context partition maintains its own variable value. See Section 4.9, “Context and Variables” for more information.
Your application can only undeploy the statement that created the variable after all statements using the variables are also undeployed.
The create variable syntax creates a new variable by defining the variable type and name. In alternative to the syntax, variables can also be declared in the configuration object.
The synopsis for creating a variable is as follows:
create [constant] variable variable_type [[]] variable_name [ = assignment_expression ]
Specify the optional constant keyword when the variable is a constant whose associated value cannot be altered. Your EPL design should prefer constant variables over non-constant variables.
The variable_type can be any of the following:
variable_type : string | char | character | bool | boolean | byte | short | int | integer | long | double | float | object | enum_class | class_name | event_type_name
Variable types can accept null values. The object type is for an untyped variable that can be assigned any value. You can provide a class name (use imports) or a fully-qualified class name to declare a variable of that Java class type including an enumeration class. You can also supply the name of an event type to declare a variable that holds an event of that type. Parameterized types such as java.util.Collection<String> are supported as well.
Append [] to the variable type to declare an array variable. A limitation is that if your variable type is an event type then array is not allowed (applies to variables only and not to named windows or tables). For arrays of primitives, specify [primitive], for example int[primitive].
The variable_name is an identifier that names the variable. The variable name should not already be in use by another variable.
The assignment_expression is optional. Without an assignment expression the initial value for the variable is null. If present, it supplies the initial value for the variable.
Note
When specifying a class_name or enum_class class name the class must have public visibility.
The EPStatement object of the create variable statement provides access to variable values.
The pull API methods iterator and safeIterator return the current variable value.
Listeners to the create variable statement subscribe to changes in variable value: the runtime posts new and old value of the variable to all listeners when the variable value is updated by an on set statement.
The example below creates a variable that provides a threshold value. The name of the variable is var_threshold and its type is long. The variable's initial value is null as no other value has been assigned:
create variable long var_threshold
This statement creates an integer-type variable named var_output_rate and initializes it to the value ten (10):
create variable integer var_output_rate = 10
The next statement declares a constant string-type variable:
create constant variable string const_filter_symbol = 'GE'
In addition to creating a variable via the create variable syntax, the configuration also allows adding variables. The next code snippet illustrates the
use of the configuration API to declare a string-typed variable:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon()..addVariable("myVar", String.class, "init value");The following example declares a constant that is an array of string:
create constant variable string[] const_filters = {'GE', 'MSFT'}
The next example declares a constant that is an array of enumeration values. It assumes the Color enumeration class was imported:
create constant variable Color[] const_colors = {Color.RED, Color.BLUE}
For an array of primitive-type bytes, specify the primitive keyword in square brackets, as the next example shows:
create variable byte[primitive] mybytes = SomeClass.getBytes()
Use the new keyword to initialize object instances (the example assumes the package or class was imported):
create constant variable AtomicInteger cnt = new AtomicInteger(1)
The runtime removes the variable if the deployment that created the variable is undeployed.
The on set statement assigns a new value to one or more variables when a triggering event arrives or a triggering pattern occurs. Use the setVariableValue methods on EPVariableService to assign variable values programmatically.
The synopsis for setting variable values is:
on event_type[(filter_criteria)] [as stream_name] set mutation_expression [, mutation_expression [,...]]
The event_type is the name of the type of events that trigger the variable assignments. It is optionally followed by filter_criteria which are filter expressions to apply to arriving events. The optional as keyword can be used to assign an stream name. Patterns and named windows can also be specified in the on clause.
After the set keyword follow one or more mutation expressions with variable names on the left hande side.
The mutation expressions set the value of one or more variables. Subqueries may by part of expressions however aggregation functions and the prev or prior function may not be used in expressions.
The below table lists the available mutation expessions:
Table 5.8. Mutation Expressions in Update-Set for Use With Variables
| Description | Syntax and Examples |
|---|---|
| Assignment |
variable_name = value_expression price = 10, side = 'BUY' |
| Array Element Assignment |
arrayvariable_name[array_index_expression] = value_expression values[position] = 10 |
| Event Property Assignment |
eventvariable_name.subproperty_name = value_expression myevent.price = 10 |
| Any Expression, For Example: User-Defined Function Call |
functionname(..., variable_name, ...) clearQuantities(variable) Requires the use of a single variable as part of each mutation expression. |
All new variable values are applied atomically: the changes to variable values by the on set statement
become visible to other statements all at the same time. No changes are visible to other processing threads until the on set statement completed processing, and at that time all changes become visible at once.
The EPStatement object provides access to variable values. The pull API methods iterator and safeIterator return the current variable values for each of the variables set by the statement.
Listeners to the statement subscribe to changes in variable values: the runtime posts new variable values of all variables to any listeners.
In the following example, a variable by name var_output_rate has been declared previously. When a NewOutputRateEvent event arrives, the variable is updated to a new value supplied by the event property 'rate':
on NewOutputRateEvent set var_output_rate = rate
The next example shows two variables that are updated when a ThresholdUpdateEvent arrives:
on ThresholdUpdateEvent as t
set var_threshold_lower = t.lower,
var_threshold_higher = t.higherThe sample statement shown next counts the number of pattern matches using a variable. The pattern looks for OrderEvent events that are followed by CancelEvent events for the same order id within 10 seconds of the OrderEvent:
on pattern[every a=OrderEvent -> (CancelEvent(orderId=a.orderId) where timer:within(10 sec))] set var_counter = var_counter + 1
A variable name can be used in any expression and can also occur in an output rate limiting clause. This section presents examples and discusses performance, consistency and atomicity attributes of variables.
The next statement assumes that a variable named 'var_threshold' was created to hold a total price threshold value. The statement outputs an event when the total price for a symbol is greater then the current threshold value:
select symbol, sum(price) from TickEvent group by symbol having sum(price) > var_threshold
This example uses a variable to dynamically change the output rate on-the-fly. The variable 'var_output_rate' holds the current rate at which the statement posts a current count to listeners:
select count(*) from TickEvent output every var_output_rate seconds
Variables are optimized towards high read frequency and lower write frequency. Variable reads do not incur locking overhead (99% of the time) while variable writes do incur locking overhead.
The runtime softly guarantees consistency and atomicity of variables when your statement executes in response to an event or timer invocation. Variables acquire a stable value (implemented by versioning) when your statement starts executing in response to an event or timer invocation, and variables do not change value during execution. When one or more variable values are updated via on set statements, the changes to all updated variables become visible to statements as one unit and only when the on set statement completes successfully.
The atomicity and consistency guarantee is a soft guarantee. If any of your application statements, in response to an event or timer invocation, execute for a time interval longer then 15 seconds (default interval length), then the runtime may use current variable values after 15 seconds passed, rather then then-current variable values at the time the statement started executing in response to an event or timer invocation.
The length of the time interval that variable values are held stable for the duration of execution of a given statement is by default 15 seconds, but can be configured via runtime settings.
A variable of type object (or java.lang.Object via the API) can be assigned any value including null. When using an object-type variable in an expression, your statement may need to cast the
value to the desired type.
The following sample EPL creates a variable by name varobj of type object:
create variable object varobj
The create variable syntax and the API accept a fully-qualified class name or alternatively the name of an event type. This is useful when you want a single variable to have multiple property values to read or set.
The next statement assumes that the event type PageHitEvent is declared:
create variable PageHitEvent varPageHitZero
These example statements show two ways of assigning to the variable:
// You may assign the complete event on PageHitEvent(ip='0.0.0.0') pagehit set varPageHitZero = pagehit
// Or assign individual properties of the event on PageHitEvent(ip='0.0.0.0') pagehit set varPageHitZero.userId = pagehit.userId
Similarly statements may use properties of class or event-type variables as this example shows:
select * from FirewallEvent(userId=varPageHitZero.userId)
Instance method can also be invoked:
create variable com.example.StateCheckerService stateChecker
select * from TestEvent as e where stateChecker.checkState(e)
A variable that represents a service for calling instance methods could be initialized by calling a factory method. This example assumes the classes were added to imports:
create constant variable StateCheckerService stateChecker = StateCheckerServiceFactory.makeService()
You can add a variable via the configuration API; an example code snippet is next:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addVariable("stateChecker", StateCheckerService.class, StateCheckerServiceFactory.makeService(), true);Application objects can also be passed via transient configuration information as described in Section 17.7, “Passing Services or Transient Objects”.
Note
When using non-constant class or event-type variables and when your EPL intends to set property values on the variable itself (i.e.set varPageHitZero.userId), please note the following requirements. In order for the runtime to assign property values, the underlying event type must allow writing property values. If using JavaBean event classes the class must have setter methods and a default constructor. The underlying event type must also be copy-able i.e. implement Serializable or configure a copy method (only for non-constant variables and when setting property values).
Your application can declare an expression or script using the create expression clause. Such expressions or scripts become available
globally to any statement.
The synopsis of the create expression syntax is:
create expression expression_or_script
Use the create expression keywords and append the expression or scripts.
Expression aliases are the simplest means of sharing expressions and do not accept parameters. Expression declarations limit the expression scope to the parameters that are passed.
The runtime may cache declared expression result values and reuse cache values, see Section 17.6.10.6, “Declared Expression Value Cache Size”.
The syntax and additional examples for declaring an expression is outlined in Section 5.2.8, “Expression Alias”, which discusses expression aliases that are visible within the same statement i.e. visible locally only.
When using the create expression syntax to declare an expression the runtime remembers the expression alias and expression
and allows the alias to be referenced in all other statements.
The below EPL declares a globally visible expression alias for an expression that computes the total of the mid-price which is the buy and sell price divided by two:
create expression totalMidPrice alias for { sum((buy + sell) / 2) }The next EPL returns mid-price for events for which the mid-price per symbol stays below 10:
select symbol, midPrice from MarketDataEvent group by symbol having midPrice < 10
The expression name must be unique among all other expression aliases and expression declarations.
Your application can provide an expression alias of the same name local to a given statement as well as globally using create expression.
The locally-provided expression alias overrides the global expression alias.
The compiler validates global expression aliases at the time your application creates a statement that references the alias. When a statement references a global alias, the compiler uses the that statement's local expression scope to validate the expression. Expression aliases can therefore be dynamically typed and type information does not need to be the same for all statements that reference the expression alias.
The syntax and additional examples for declaring an expression is outlined in Section 5.2.9, “Expression Declaration”, which discusses declaring expressions that are visible within the same statement i.e. visible locally only.
When using the create expression syntax to declare an expression the compiler remembers the expression
and allows the expression to be referenced in all other statements.
The below EPL declares a globally visible expression that computes a mid-price and that requires a single parameter:
create expression midPrice { in => (buy + sell) / 2 }The next EPL returns mid-price for each event:
select midPrice(md) from MarketDataEvent as md
The expression name must be unique for global expressions. It is not possible to declare the same global expression twice with the same name.
Your application can declare an expression of the same name local to a given statement as well as globally using create expression.
The locally-declared expression overrides the globally declared expression.
The compiler validates globally declared expressions at the time your application creates a statement that references the global expression. When a statement references a global expression, the compiler uses that statement's type information to validate the global expressions. Global expressions can therefore be dynamically typed and type information does not need to be the same for all statements that reference the global expression.
This example shows a sequence of EPL, that can be created in the order shown, and that demonstrates expression validation at time of referral:
create expression minPrice {(select min(price) from OrderWindow)}create window OrderWindow#time(30) as OrderEvent
insert into OrderWindow select * from OrderEvent
// Validates and incorporates the declared global expression select minPrice() as minprice from MarketData
The syntax and additional examples for declaring scripts is outlined in Chapter 19, Script Support, which discusses declaring scripts that are visible within the same statement i.e. visible locally only.
When using the create expression syntax to declare a script the compiler remembers the script
and allows the script to be referenced in all other statements.
The below EPL declares a globally visible script in the JavaScript dialect that computes a mid-price:
create expression midPrice(buy, sell) [ (buy + sell) / 2 ]
The next EPL returns mid-price for each event:
select midPrice(buy, sell) from MarketDataEvent
The compiler validates globally declared scripts at the time your application creates a statement that references the global script. When a statement references a global script, the compiler uses that statement's type information to determine parameter types. Global scripts can therefore be dynamically typed and type information does not need to be the same for all statements that reference the global script.
The script name in combination with the number of parameters must be unique for global scripts. It is not possible to declare the same global script twice with the same name and number of parameters.
Your application can declare a script of the same name and number of parameters that is local to a given statement as well as globally using create expression.
The locally-declared script overrides the globally declared script.
Contained-event selection is for use when an event contains properties that are themselves events, or more generally when your application needs to split or explode an event into multiple events. One example is when application events are coarse-grained structures and you need to perform bulk operations on the rows of the property graph in an event.
Use the contained-event selection syntax in a filter expression such as in a pattern, from clause, subselect, on-select and on-delete. This section provides the synopsis and examples.
To review, in the from clause a contained_selection may appear after the event stream name and filter criteria, and before any data windows.
The synopsis for contained_selection is as follows:
[select select_expressions from] contained_expression [@type(eventtype_name)] [as alias_name] [where filter_expression]
The select clause and select_expressions are optional and may be used to select specific properties of contained events.
The contained_expression is required and returns individual events. The expression can, for example, be an event property name that returns an event fragment, i.e. a property that can itself be represented as an event by the underlying event representation. The expression can also be any other expression such as a single-row function or a script that returns either an array or a java.util.Collection of events. Simple values such as integer or string are not fragments but can be used as well as described below.
Provide the @type(name) annotation after the contained expression to name the event type of events returned by the expression. The annotation is optional and not needed when the contained-expression is an event property that returns a class or other event fragment.
The alias_name can be provided to assign a name to the expression result value rows.
The where clause and filter_expression is optional and may be used to filter out properties.
As an example event, consider a media order. A media order consists of order items as well as product descriptions. A media order event can be represented as an object graph (POJO event representation), or a structure of nested Maps (Map event representation) or a XML document (XML DOM or Axiom event representation) or other custom plug-in event representation.
To illustrate, a sample media order event in XML event representation is shown below. Also, a XML event type can optionally be strongly-typed with an explicit XML XSD schema that is not shown here. Note that Map and POJO representation can be considered equivalent for the purpose of this example.
Let us now assume the event type MediaOrder as being represented by the root node <mediaorder> of such XML snip:
<mediaorder>
<orderId>PO200901</orderId>
<items>
<item>
<itemId>100001</itemId>
<productId>B001</productId>
<amount>10</amount>
<price>11.95</price>
</item>
</items>
<books>
<book>
<bookId>B001</bookId>
<author>Heinlein</author>
<review>
<reviewId>1</reviewId>
<comment>best book ever</comment>
</review>
</book>
<book>
<bookId>B002</bookId>
<author>Isaac Asimov</author>
</book>
</books>
</mediaorder>The next statement utilizes the contained-event selection syntax to return each book:
select * from MediaOrder[books.book]
The result of the above statement is one event per book. Output events contain only the book properties and not any of the mediaorder-level properties.
Note that, when using listeners, the runtime delivers multiple results in one invocation of each listener. Therefore listeners to the above statement can expect a single invocation passing all book events within one media order event as an array.
To better illustrate the position of the contained-event selection syntax in a statement, consider the next two statements:
select * from MediaOrder(orderId='PO200901')[books.book]
The above statement the returns each book only for media orders with a given order id. This statement illustrates a contained-event selection and a data window:
select count(*) from MediaOrder[books.book]#unique(bookId)
The sample above counts each book unique by book id.
Contained-event selection can be staggered. When staggering multiple contained-event selections the staggered contained-event selection is relative to its parent.
This example demonstrates staggering contained-event selections by selecting each review of each book:
select * from MediaOrder[books.book][review]
Listeners to the statement above receive a row for each review of each book. Output events contain only the review properties and not the book or media order properties.
The following is not valid:
// not valid select * from MediaOrder[books.book.review]
The book property in an indexed property (an array or collection) and thereby requires an index in order to determine which book to use. The expression books.book[1].review is valid and means all reviews of the second (index 1) book.
The contained-event selection syntax is part of the filter expression and may therefore occur in patterns and anywhere a filter expression is valid.
A pattern example is below. The example assumes that a Cancel event type has been defined that also has an orderId property:
select * from pattern [c=Cancel -> books=MediaOrder(orderId = c.orderId)[books.book] ]
When used in a pattern, a filter with a contained-event selection returns an array of events, similar to the match-until clause in patterns. The above statement returns, in the books property, an
array of book events.
The optional select clause provides control over which fields are available in output events. The expressions in the select-clause apply only to the properties available underneath the property in the from clause, and the properties of the enclosing event.
When no select is specified, only the properties underneath the selected property are available in output events.
In summary, the select clause may contain:
Any expressions, wherein properties are resolved relative to the property in the
fromclause.Use the wildcard (
*) to provide all properties that exist under the property in thefromclause.Use the alias_name
.*syntax to provide all properties that exist under a property in thefromclause.
The next statement's select clause selects each review for each book, and the order id as well as the book id of each book:
select * from MediaOrder[select orderId, bookId from books.book][select * from review] // ... equivalent to ... select * from MediaOrder[select orderId, bookId from books.book][review]]
Listeners to the statement above receive an event for each review of each book. Each output event has all properties of the review row, and in addition the bookId of each book and the orderId of the order.
Thus bookId and orderId are found in each result event, duplicated when there are multiple reviews per book and order.
The above statement uses wildcard (*) to select all properties from reviews. As has been discussed as part of the select clause, the wildcard (*) and property_alias.* do not copy properties for performance reasons. The wildcard syntax instead specifies the underlying type, and additional properties are added onto that underlying type if required. Only one wildcard (*) and property_alias.* (unless used with a column rename) may therefore occur in the select clause list of expressions.
All the following statements produce an output event for each review of each book. The next sample statements illustrate the options available to control the fields of output events.
The output events produced by the next statement have all properties of each review and no other properties available:
select * from MediaOrder[books.book][review]
The following statement is not a valid statement, since the order id and book id are not part of the contained-event selection:
// Invalid select-clause: orderId and bookId not produced. select orderId, bookId from MediaOrder[books.book][review]
This statement is valid. Note that output events carry only the orderId and bookId properties and no other data:
select orderId, bookId from MediaOrder[books.book][select orderId, bookId from review] //... equivalent to ... select * from MediaOrder[select orderId, bookId from books.book][review]
This variation produces output events that have all properties of each book and only reviewId and comment for each review:
select * from MediaOrder[select * from books.book][select reviewId, comment from review] // ... equivalent to ... select * from MediaOrder[books.book as book][select book.*, reviewId, comment from review]
The output events of the next EPL have all properties of the order and only bookId and reviewId for each review:
select * from MediaOrder[books.book as book]
[select mediaOrder.*, bookId, reviewId from review] as mediaOrder
This EPL produces output events with 3 columns: a column named mediaOrder that is the order itself, a column named book for each book and a column named review that holds each review:
insert into ReviewStream select * from MediaOrder[books.book as book] [select mo.* as mediaOrder, book.* as book, review.* as review from review as review] as mo
// .. and a sample consumer of ReviewStream... select mediaOrder.orderId, book.bookId, review.reviewId from ReviewStream
Please note these limitations:
Sub-selects, aggregation functions and the
prevandprioroperators are not available in contained-event selection.Expressions in the
selectandwhereclause of a contained-event selection can only reference properties relative to the current event and property.
The optional where clause may be used to filter out properties at the same level that the where-clause occurs.
The properties in the filter expression must be relative to the property in the from clause or the enclosing event.
This statement outputs all books with a given author:
select * from MediaOrder[books.book where author = 'Heinlein']
This statement outputs each review of each book where a review comment contains the word 'good':
select * from MediaOrder[books.book][review where comment like 'good']
This section discusses contained-event selection in joins.
When joining within the same event it is not required to specify a data window. Recall, in a join or outer join there must be a data window specified that defines the subset of events available to be joined. For self-joins, no data window is required and the join executes against the data returned by the same event.
This statement inner-joins items to books where book id matches the product id:
select book.bookId, item.itemId
from MediaOrder[books.book] as book,
MediaOrder[items.item] as item
where productId = bookIdStatement results for the above statement when sending the media order event as shown earlier are:
| book.bookId | item.itemId |
|---|---|
| B001 | 100001 |
The next example statement is a left outer join. It returns all books and their items, and for books without item it returns the book and a null value:
select book.bookId, item.itemId
from MediaOrder[books.book] as book
left outer join
MediaOrder[items.item] as item
on productId = bookIdStatement results for the above statement when sending the media order event as shown earlier are:
| book.bookId | item.itemId |
|---|---|
| B001 | 100001 |
| B002 | null |
A full outer join combines the results of both left and right outer joins. The joined table will contain all records from both tables, and fill in null values for missing matches on either side.
This example statement is a full outer join, returning all books as well as all items, and filling in null values for book id or item id if no match is found:
select orderId, book.bookId,item.itemId
from MediaOrder[books.book] as book
full outer join
MediaOrder[select orderId, * from items.item] as item
on productId = bookId
order by bookId, item.itemId asc
As in all other statements, aggregation results are cumulative from the time the statement was created.
The following statement counts the cumulative number of items in which the product id matches a book id:
select count(*)
from MediaOrder[books.book] as book,
MediaOrder[items.item] as item
where productId = bookId
The unidirectional keyword in a join indicates to the runtime that aggregation state is not cumulative. The next statement counts the number of items in which the product id matches a book id for each event:
select count(*)
from MediaOrder[books.book] as book unidirectional,
MediaOrder[items.item] as item
where productId = bookIdThe next example splits an event representing a sentence into multiple events in which each event represents a word. It represents all events and the logic to split events into contained events as Java code. The next chapter has additional examples that use Map-type events and put contained-event logic into a separate expression or script.
The sentence event in this example is represented by a class declared as follows:
public class SentenceEvent {
private final String sentence;
public SentenceEvent(String sentence) {
this.sentence = sentence;
}
public WordEvent[] getWords() {
String[] split = sentence.split(" ");
WordEvent[] words = new WordEvent[split.length];
for (int i = 0; i < split.length; i++) {
words[i] = new WordEvent(split[i]);
}
return words;
}
}
The sentence event as above provides an event property words that returns each word event.
The declaration of word event is also a class:
public class WordEvent {
private final String word;
public WordEvent(String word) {
this.word = word;
}
public String getWord() {
return word;
}
}The statement to populate a stream of words from a sentence event is:
insert into WordStream select * from SentenceEvent[words]
Finally, the API call to send a sentence event to the runtime is shown here:
runtime.getEventService().sendEventBean(new SentenceEvent("Hello Word Contained Events"), "SentenceEvent");
The examples herein are not based on the POJO events of the prior example. They are meant to demonstrate different types of contained-event expressions and the use of @type(type_name) to identify the event type of the return values of the contained-event expression.
The example first defines a few sample event types:
create schema SentenceEvent(sentence String)
create schema WordEvent(word String)
create schema CharacterEvent(char String)
The following EPL assumes that your application defined a plug-in single-row function by name splitSentence that returns an array of Map, producting output events that are WordEvent events:
insert into WordStream select * from SentenceEvent[splitSentence(sentence)@type(WordEvent)]
The example EPL shown next invokes a JavaScript function which returns some events of type WordEvent:
expression Collection js:splitSentenceJS(sentence) [
var CollectionsClazz = Java.type('java.util.Collections');
var words = new java.util.ArrayList();
words.add(CollectionsClazz.singletonMap('word', 'wordOne'));
words.add(CollectionsClazz.singletonMap('word', 'wordTwo'));
words;
]
select * from SentenceEvent[splitSentenceJS(sentence)@type(WordEvent)]
In the next example the sentence event first gets split into words and then each word event gets split into character events via an additional splitWord single-row function,
producing events of type CharacterEvent:
select * from SentenceEvent [splitSentence(sentence)@type(WordEvent)] [splitWord(word)@type(CharacterEvent)]
Your contained_expression may return an array of property values such as an array of integer or string values.
In this case you must specify a @type(name) annotation and provide an event type name that declares a single column with a type that matches the array component type.
create schema IdContainer(id int)
create schema MyEvent(ids int[])
select * from MyEvent[ids@type(IdContainer)]
This example declares a named window and uses on-delete:
create window MyWindow#keepall (id int)
on MyEvent[ids@type(IdContainer)] as my_ids delete from MyWindow my_window where my_ids.id = my_window.id
Your contained_expression may return an array of EventBean instances.
This is handy when the expression itself must decide the type of each event to return.
For example:
create schema BaseEvent();
create schema AEvent(pa string) inherits BaseEvent;
create schema BEvent(pb string) inherits BaseEvent;
create schema ValueEvent(value string);
select * from ValueEvent[mySplitFunction(value) @type(BaseEvent)]
Then declare mySplitFunction returning an array of events, such as:
public static EventBean[] mySplitFunction(String value, EPLMethodInvocationContext context) {
EventBean[] events = new EventBean[1];
if (value.startsWith("A")) {
events[0] = context.getEventBeanService().adapterForMap(Collections.singletonMap("pa", value), "AEvent");
}
else {
events[0] = context.getEventBeanService().adapterForMap(Collections.singletonMap("pb", value), "BEvent");
}
return events;
}Your contained_expression may return a collection of underlying event instances.
In this example the selectFrom enumeration method formats subquery results and returns a collection of Map instances.
Since Map is the underlying event object for Map-type event types, each Map with the room id can be processed as an event by the contained event syntax.
// Declare Person and Room event types, represented as java.util.Map events (the default)
@public @buseventtype create schema Person(personId string);
@public @buseventtype create schema Room(roomId string);
// Have a window that holds all rooms
create window RoomWindow#keepall as Room;
insert into RoomWindow select * from Room;
// Output all rooms ids as a collection of maps into the "rooms" column
insert into PersonAndRooms select personId, (select roomId from RoomWindow).selectFrom(v => new {roomId = v}) as rooms from Person;
// Select each combination of person and room
@Name('s0') select personId, roomId from PersonAndRooms[select personId, roomId from rooms@type(Room)];The syntax for splitting and duplicating streams can be used to generate marker events. Please see Section 5.16.1, “Generating Marker Events for Contained Events” for more information.
The update istream statement allows declarative modification of event properties of events entering a stream. Update is a pre-processing step to each new event, modifying an event before the event applies to any statements.
The synopsis of update istream is as follows:
update istream event_type [as stream_name] set mutation_expression [, mutation_expression] [,...] [where where_expression]
The event_type is the name of the type of events that the update applies to.
The optional as keyword can be used to assign a name to the event type for use with subqueries, for example.
After the set keyword follow one or more mutation expressions. The below table lists the available mutation expessions:
Table 5.9. Mutation Expressions in Update IStream
| Description | Syntax and Examples |
|---|---|
| Assignment |
property_name = value_expression price = 10, side = 'BUY' |
| Array Element Assignment |
arrayproperty_name[array_index_expression] = value_expression values[position] = 10 |
| Any Expression, For Example: User-Defined Function Call |
functionname(alias)
clearQuantities(myevent) |
The optional where clause and expression can be used to filter out events to which to apply updates.
Listeners to an update statement receive the updated event in the insert stream (new data) and the event prior to the update in the remove stream (old data). Note that if there are multiple update statements that all apply to the same event then the runtime will ensure that the output events delivered to listeners or subscribers are consistent with the then-current updated properties of the event (if necessary making event copies, as described below, in the case that listeners are attached to update statements). Iterating over an update statement returns no events.
As an example, the below statement assumes an AlertEvent event type that has properties named severity and reason:
update istream AlertEvent set severity = 'High' where severity = 'Medium' and reason like '%withdrawal limit%'
The statement above changes the value of the severity property to "High" for AlertEvent events that have a medium severity and contain a specific reason text.
Update statements apply the changes to event properties before other statements receive the event(s) for processing, e.g. "select * from AlertEvent" receives the updated AlertEvent. This is true regardless of the order in which your application creates statements.
When multiple update statements apply to the same event, the runtime executes updates in the order in which update statements were deployed. We recommend the @Priority EPL annotation to define a deterministic order of processing updates, especially in the case where update statements get deployed and undeployed dynamically or multiple update statements update the same fields. The update statement with the highest @Priority value applies last.
The update clause can be used on streams populated via insert into, as this example utilizing a pattern demonstrates:
insert into DoubleWithdrawalStream select a.id, b.id, a.account as account, 0 as minimum from pattern [a=Withdrawal -> b=Withdrawal(id = a.id)]
update istream DoubleWithdrawalStream set minimum = 1000 where account in (10002, 10003)
When using update istream with named windows, any changes to event properties apply before an event enters the named window.
The update istream is not available for tables.
Consider the next example (shown here with statement names in @Name EPL annotation, multiple statements):
@Name("CreateWindow") create window MyWindow#time(30 sec) as AlertEvent
@Name("UpdateStream") update istream MyWindow set severity = 'Low' where reason = '%out of paper%'
@Name("InsertWindow") insert into MyWindow select * from AlertEvent
@Name("SelectWindow") select * from MyWindow
The UpdateStream statement specifies an update clause that applies to all events entering the named window. Note that update does not apply to events already in the named window at the time an application creates the UpdateStream statement, it only applies to new events entering the named window (after an application created the update statement).
Therefore, in the above example listeners to the SelectWindow statement as well as the CreateWindow statement receive the updated event,
while listeners to the InsertWindow statement receive the original AlertEvent event (and not the updated event).
Subqueries can also be used in all expressions including the optional where clause.
This example demonstrates a correlated subquery in an assignment expression and also demonstrates the optional as keyword. It assigns the phone property of an AlertEvent event a new value based on the lookup within all unique PhoneEvent events (according to an empid property) correlating the AlertEvent property reporter with the empid property of PhoneEvent:
update istream AlertEvent as ae
set phone =
(select phone from PhoneEvent#unique(empid) where empid = ae.reporter)
When updating indexed properties use the syntax propertyName[index] = value with the index value being an integer number.
When updating mapped properties use the syntax propertyName(key) = value with the key being a string value.
When using update, please note these limitations:
Expressions may not use aggregation functions.
The
prevandpriorfunctions may not be used.For underlying event representations that are Java objects, a event object class must implement the
java.io.Serializableinterface as discussed below.When using an XML underlying event type, event properties in the XML document representation are not available for update.
Nested properties are not supported for update. Variant streams may also not be updated.
update istreamis a pre-processing step and updates take place before other statements see the event; Therefore, when using@priority, the priority assigned to theupdate istreamstatement only prioritizes the statement among otherupdate istreamstatements.
When updating event objects the runtime maintains consistency across statements. The runtime ensures that an update to an event does not impact the results of statements that look for or retain the original un-updated event. As a result the runtime may need to copy an event object to maintain consistency.
In the case your application utilizes Java objects as the underlying event representation and an update statement updates properties on an object, then in order to maintain consistency across statements
it is necessary for the runtime to copy the object before changing properties (and thus not change the original object).
For Java application objects, the copy operation is implemented by serialization. Your event object must therefore implement the java.io.Serializable interface to become eligible for update. As an alternative to serialization, you may instead configure a copy method as part of the event type configuration via ConfigurationEventTypeLegacy.
The runtime delivers all result events of a given statement to the statement's listeners and subscriber (if any) in a single invocation of each listener and subscriber's update method passing an array of result events. For example, a statement using a time-batch window may provide many result events after a time period passes, a pattern may provide multiple matching events or in a join the join cardinality could be multiple rows.
For statements that typically post multiple result events to listeners the for keyword controls the number of invocations of the runtime to listeners and subscribers and the subset of all result events delivered by each invocation.
This can be useful when your application listener or subscriber code expects multiple invocations or expects that invocations only receive events that belong together by some additional criteria.
The for keyword is a reserved keyword. It is followed by either the grouped_delivery keyword for grouped delivery or the discrete_delivery keyword for discrete delivery. The for clause is valid after any EPL select statement.
The synopsis for grouped delivery is as follows:
... for grouped_delivery (group_expression [, group_expression] [,...])
The group_expression expression list provides one or more expressions to apply to result events. The runtime invokes listeners and subscribers once for each distinct set of values returned by group_expression expressions passing only the events for that group. Further detail on key expressions can be found at Section 5.2.13, “Composite Keys and Array Values as Keys”.
The synopsis for discrete delivery is as follows:
... for discrete_delivery
With discrete delivery the runtime invokes listeners and subscribers once for each result event passing a single result event in each invocation.
Consider the following example without for-clause. The time batch data window collects RFIDEvent events for 10 seconds and posts an array of result events:
select * from RFIDEvent#time_batch(10 sec)
Let's consider an example event sequence as follows:
Table 5.10. Sample Sequence of Events for For Keyword
| Event |
|---|
| RFIDEvent(id:1, zone:'A') |
| RFIDEvent(id:2, zone:'B') |
| RFIDEvent(id:3, zone:'A') |
Without for-clause and after the 10-second time period passes, the runtime delivers an array of 3 events in a single invocation to listeners and the subscriber.
The next example specifies the for-clause and grouped delivery by zone:
select * from RFIDEvent#time_batch(10 sec) for grouped_delivery (zone)
With grouped delivery and after the 10-second time period passes, the above statement delivers result events in two invocations to listeners and the subscriber: The first invocation delivers an array of two events that contains zone A events with id 1 and 3. The second invocation delivers an array of 1 event that contains a zone B event with id 2.
The next example specifies the for-clause and discrete delivery:
select * from RFIDEvent#time_batch(10 sec) for discrete_delivery
With discrete delivery and after the 10-second time period passes, the above statement delivers result events in three invocations to listeners and the subscriber: The first invocation delivers an array of 1 event that contains the event with id 1, the second invocation delivers an array of 1 event that contains the event with id 2 and the third invocation delivers an array of 1 event that contains the event with id 3.
Remove stream events are also delivered in multiple invocations, one for each group, if your statement selects remove stream events explicitly via irstream or rstream keywords.
The insert into for inserting events into a stream is not affected by the for-clause.
The delivery order respects the natural sort order or the explicit sort order as provided by the order by clause, if present.
The following are known limitations:
The compiler validates group_expression expressions against the output event type, therefore all properties specified in group_expression expressions must occur in the
selectclause.
- 6.1. Overview
- 6.2. Named Window Usage
- 6.3. Table Usage
- 6.3.1. Creating Tables: The Create Table Clause
- 6.3.2. Aggregating Into Table Rows: The Into Table Clause
- 6.3.3. Table Column Keyed-Access Expressions
- 6.3.4. Inserting Into Tables
- 6.3.5. Selecting From Tables
- 6.3.6. Resetting Table Columns and Aggregation State
- 6.3.7. Initializing Table Columns and Aggregation State
- 6.4. Triggered Select: The On Select Clause
- 6.5. Triggered Select+Delete: The On Select Delete Clause
- 6.6. Updating Data: The On Update Clause
- 6.7. Deleting Data: The On Delete Clause
- 6.8. Triggered Upsert Using the On-Merge Clause
- 6.9. Explicitly Indexing Named Windows and Tables
- 6.10. Using Fire-and-Forget Queries With Named Windows and Tables
- 6.11. Events as Property
A named window is a globally-visible data window. A table is a globally-visible data structure organized by primary key or keys.
Named windows and tables both offer a way to share state between statements and are stateful. Named windows and tables have differing capabilities and semantics.
To query a named window or table, simply use the named window name or table name in the from clause of your statement,
including statements that contain subqueries, joins and outer-joins.
Certain clauses operate on either a named window or a table, namely the
on-merge, on-update, on-delete and on-select clauses.
The fire-and-forget queries also operate on both named windows and tables.
Both named windows and tables can have columns that hold events as column values, as further described in Section 6.11, “Events as Property”.
Named Windows are introduced in Section 2.14.1, “Named Windows”.
A named window is a global data window that can take part in many statements and that can be inserted-into and deleted-from by multiple statements. A named window holds events of the same type or supertype, unless used with a variant stream.
The create window clause declares a new named window. The named window starts up empty unless populated from an existing named window at time of deployment. Events must be inserted into the named window using the insert into clause. Events can also be deleted from a named window via the on delete clause.
Events enter the named window by means of insert into clause of a select statement. Events leave a named window either because the expiry policy of the declared data window removes events from the named window, or through statements that use the on delete clause to explicitly delete from a named window.
A named window may also decorate an event to preserve original events as described in Section 5.10.4, “Decorated Events” and Section 6.2.2.1, “Named Windows Holding Decorated Events”.
To tune subquery performance when the subquery selects from a named window, consider the hints discussed in Section 5.11.8, “Hints Related to Subqueries”.
Tables are introduced in Section 2.14.2, “Tables”.
A table is a data structure that is globally visible and that holds state.
The columns of a table can store aggregation state, allowing for co-location of event data with aggregation state. Other statements can directly create and update the shared aggregation state. Statements can also query the aggregation state conveniently. Aggregation state can include comprehensive state such as for example a large matrix of long-type values for use in a Count-min sketch approximation. Common aggregation state can be updated by multiple statements.
Use the create table clause to declare a new table.
The atomicity guarantees under multi-threaded evaluation are as follows. For a given statement, a table row or rows either exists or do not exist, consistently, for the duration of the evaluation of an event or timer against a context partition of a statement. The same is true for updates in that for a given context partition of a statement, each table row is either completely updated or not updated at all for the duration of an evaluation. Stream-level filter expressions against tables are not part of statement evaluation and the same atomicity applies to stream-level filter expressions.
As a general rule-of-thumb, if you need to share a data window between statements, the named window is the right approach. If however rows are organized by primary key or hold aggregation state, a table may be preferable. Statements allow the combined use of both.
In summary the difference comes from named windows holding immutable events, versus tables which hold update-in-place rows and columns that can hold plain values and complex aggregation state side-by-side.
One important difference between named windows and tables is in the data that a row holds: While named windows hold events, tables can hold additional derived state.
For example, a table column can hold rich derived state such as a distinct values set and rich aggregation state such as the state of a Count-min sketch approximation aggregation (a large matrix of long-type values).
// Declare a table to hold a Count-min sketch approximate count per feed create table AppoximateCountPerWord (feed string, approx countMinSketch())
A second difference between named windows and tables is the organization of rows. For named windows, the organization of rows follows the data window declaration. Tables, on the other hand, can be organized by a primary key or by multiple primary keys that make up a compound key.
For example, if your declaration specifies a sliding time window to hold 10 seconds of stock tick events then the rows are held in a sliding time window, i.e. a list or queue according to arrival order.
// Declare a named window to hold 10 seconds of stock tick events create window TenSecOfTicksWindow#time(10 sec) as StockTickEvent
An iterator for a named window returns rows in the order as provided by the data window(s) declared for the named window. An iterator for a table returns rows in an unpredictable order.
Only named windows provide an insert and remove stream to other statements. Tables do not provide an insert and remove stream.
For example, considering the TenSecOfTicksWindow named window declared above,
the following statement outputs the current count each time events enter or leave the named window.
select count(*) from TenSecOfTicksWindow
Also for example, considering the AppoximateCountPerWord table declared above, the following EPL does not output any rows
when table rows gets inserted, updated or deleted and only outputs rows when the statement is iterated:
// does not continously output for table changes select * from AppoximateCountPerWord
As named windows hold events and events are immutable, when an update statement updates events held in a named window, the runtime performs a logical copy operation (copy-on-write, as configured for the type) of each updated event, and only modifies the newly created event, preserving the immutable original event.
Data in tables are updated in-place. There is no copy operation for table rows.
For named windows, the data window declared for the named window instructs the runtime to expire and remove events from the named window.
Events can also be removed via on-merge, on-delete and fire-and-forget delete.
For tables, row can only be removed via on-merge, on-delete, on-select-and-delete and fire-and-forget delete.
The create window statement creates a named window by specifying a window name and one or more data windows, as well as the type of event to hold in the named window.
There are two syntaxes for creating a named window: The first syntax allows modeling a named window after an existing event type or an existing named window. The second syntax is similar to the SQL create-table syntax and provides a list of column names and column types.
A new named window starts up empty. It must be explicitly inserted into by one or more statements, as discussed below. A named window can also be populated at time of creation from an existing named window.
Your application can only undeploy the statement that created the named window after all other statements that use the named window are also undeployed.
The create window statement posts to listeners any events that are inserted into the named window as new data. The statement posts all deleted events or events that expire out of the data window to listeners as the remove stream (old data). The named window contents can also be iterated on via the pull API to obtain the current contents of a named window.
The benefit of modeling a named window after an existing event type is that event properties can be nested, indexed, mapped or other types that your event objects may provide as properties, including the type of the underlying event itself. Also, using the wildcard (*) operator means your EPL does not need to list each individual property explicitly.
The syntax for creating a named window by modeling the named window after an existing event type, is as follows:
[context context_name] create window window_name.window_spec [as] [select list_of_properties from] event_type_or_windowname [insert [where filter_expression]]
The window_name you assign to the named window can be any identifier. The name should not already be in use as an event type or stream name or table name.
The window_spec are one or more data windows that define the expiry policy for removing events from the named window. Named windows must explicitly declare a data window. This is required to ensure that the policy for retaining events in the data window is well defined. To keep all events, use the keep-all window: It indicates that the named window should keep all events and only remove events from the named window that are deleted by on delete, on merge or fire-and-forget delete. Data windows are listed in Chapter 14, EPL Reference: Data Windows.
The select clause and list_of_properties are optional. If present, they specify the column names and, implicitly by definition of the event type, the column types of events held by the named window. Expressions other than column names are not allowed in the select list of properties. Wildcards (*) and wildcards with additional properties can also be used.
The event_type_or_windowname is required if using the model-after syntax. It provides the name of the event type of events held in the data window, unless column names and types have been explicitly selected via select. The name of an (existing) other named window is also allowed here. Please find more details in Section 6.2.1.4, “Populating a Named Window From an Existing Named Window”.
Finally, the insert clause and optional filter_expression are used if the new named window is modelled after an existing named window, and the data of the new named window is to be populated from the existing named window upon deployment. The optional filter_expression can be used to exclude events.
You may refer to a context by specifying the context keyword followed by a context name. Contexts are described in more detail at Chapter 4, Context and Context Partitions. The effect of referring to a context is that your named window operates according to the context dimensional information as declared for the context. For usage and limitations please see the respective chapter.
The next statement creates a named window OrdersNamedWindow for which the expiry policy is simply to keep all events. Assume that the event type 'OrderMapEventType' has been configured. The named window is to hold events of type 'OrderMapEventType':
create window OrdersNamedWindow#keepall as OrderMapEventType
The below sample statement demonstrates the select syntax. It defines a named window in which each row has the three properties 'symbol', 'volume' and 'price'. This named window actively removes events from the window that are older than 30 seconds.
create window OrdersTimeWindow#time(30 sec) as select symbol, volume, price from OrderEvent
In an alternate form, the as keyword can be used to rename columns, and constants may occur in the select-clause as well:
create window OrdersTimeWindow#time(30 sec) as select symbol as sym, volume as vol, price, 1 as alertId from OrderEvent
Note
The select-clause when used with create window provides types information only. You must still use on-merge or insert-into to insert events.
The second syntax for creating a named window is by supplying column names and types:
[context context_name] create window window_name.window_spec [as] (column_name column_type [,column_name column_type [,...])
The column_name is an identifier providing the event property name. The column_type is also required for each column. Valid column types are listed in Section 5.17.1, “Creating Variables: The Create Variable Clause” and are the same as for variable types.
For attributes that are array-type append [] (left and right brackets).
The next statement creates a named window:
create window SecurityEvent#time(30 sec) (ipAddress string, userId String, numAttempts int, properties String[])
Named window columns can hold events by declaring the column type as the event type name. Array-type in combination with event-type is also supported.
The next two statements declare an event type and create a named window with a column of the defined event type:
create schema SecurityData (name String, roles String[])
create window SecurityEvent#time(30 sec)
(ipAddress string, userId String, secData SecurityData, historySecData SecurityData[])
Whether the named window uses a Map, Object-array, JSON or Avro event representation for the rows can be specified as follows. If the create-window statement provides the @EventRepresentation(objectarray) annotation the runtime maintains named window rows as object array, for example.If no annotation is provided, the runtime uses the configured default event representation as discussed in Section 17.4.9.1, “Default Event Representation”.
The following statement instructs the runtime to represent FooWindow rows as object arrays:
@EventRepresentation(objectarray) create window FooWindow#time(5 sec) as (string prop1)
There is no syntax to drop or remove a named window.
Undeploying the deployment that created the named window also removes the named window.
Your statement may specify the name of an existing named window when creating a new named window, and may use the insert keyword to indicate that the new named window is to be populated from
the events currently held by the existing named window.
For example, and assuming the named window OrdersNamedWindow already exists, this statement creates a new named window ScratchOrders and populates all orders in OrdersNamedWindow into the new named window:
create window ScratchOrders#keepall as OrdersNamedWindow insert
The where keyword is also available to perform filtering, for example:
create window ScratchBuyOrders#time(10) as OrdersNamedWindow insert where side = 'buy'
The insert into clause inserts events into named windows. Your application must ensure that the column names and types match the declared column names and types of the named window to be inserted into.
For inserting into a named window and for simultaneously checking if the inserted row already exists in the named window or for atomic update-insert operation on a named window, or for targeting a specific partition, you must use on-merge as described in Section 6.8, “Triggered Upsert Using the On-Merge Clause”. On-merge
is similar to the SQL merge clause and provides what is known as an "Upsert" operation: Update existing events or if no existing event(s) are found then insert a new event, all in one atomic operation provided by a single statement.
This example first creates a named window using some of the columns of an OrderEvent event type:
create window OrdersWindow#keepall as select symbol, volume, price from OrderEvent
The insert into the named window selects individual columns to be inserted:
insert into OrdersWindow(symbol, volume, price) select name, count, price from FXOrderEvent
An alternative form is shown next:
insert into OrdersWindow select name as symbol, vol as volume, price from FXOrderEvent
Following above statement, the runtime enters every FXOrderEvent arriving into the runtime into the named window 'OrdersWindow'.
The following statements create a named window for an event type backed by a Java class and insert into the window any 'OrderEvent' where the symbol value is IBM:
create window OrdersWindow#time(30) as com.mycompany.OrderEvent
insert into OrdersWindow select * from com.mycompany.OrderEvent(symbol='IBM')
The last example adds one column named 'derivedPrice' to the 'OrderEvent' type by specifying a wildcard, and uses a user-defined function to populate the column:
create window OrdersWindow#time(30) as select *, price as derivedPrice from OrderEvent
insert into OrdersWindow select *, MyFunc.func(price, percent) as derivedPrice from OrderEvent
Event representations based on Java base classes or interfaces, and subclasses or implementing classes, are compatible as these statements show:
// create a named window for the base class create window OrdersWindow#unique(name) as select * from ProductBaseEvent
// The ServiceProductEvent class subclasses the ProductBaseEvent class insert into OrdersWindow select * from ServiceProductEvent
// The MerchandiseProductEvent class subclasses the ProductBaseEvent class insert into OrdersWindow select * from MerchandiseProductEvent
To avoid duplicate events inserted in a named window and atomically check if a row already exists, use on-merge as outlined in Section 6.8, “Triggered Upsert Using the On-Merge Clause”. An example:
on ServiceProductEvent as spe merge OrdersWindow as win where win.id = spe.id when not matched then insert select *
Decorated events hold an underlying event and add additional properties to the underlying event, as described further in Section 5.10.4, “Decorated Events”.
This sample statement creates a named window that decorates OrderEvent events by adding an additional property named priceTotal to each OrderEvent. A matching insert into statement is also part of the sample:
create window OrdersWindow#time(30) as select *, price as priceTotal from OrderEvent
insert into OrdersWindow select *, price * unit as priceTotal from ServiceOrderEvent
The property type of the additional priceTotal column is the property type of the existing price property of OrderEvent.
A named window can be referred to by any statement in the from clause of the statement. Filter criteria can also be specified. Data windows cannot be specified when selecting from a named window (the special derived-value windows are allowed however).
A statement selecting all events from a named window OrdersNamedWindow is shown next. The named window must first be created via the create window clause before use.
select * from OrdersNamedWindow
The statement as above simply receives the unfiltered insert stream of the named window and reports that stream to its listeners. The iterator method returns all events in the named window, if any.
If your application desires to obtain the events removed from the named window, use the rstream keyword as this statement shows:
select rstream * from OrdersNamedWindow
The next statement derives an average price per symbol for the events held by the named window:
select symbol, avg(price) from OrdersNamedWindow group by symbol
A statement that consumes from a named window, like the one above,
receives the insert and remove stream of the named window. The insert stream represents the events inserted into the named window. The remove stream represents the events expired from
the named window data window and the events explicitly deleted via on-delete for fire-and-forget (on-demand) delete.
Your application may create a consuming statement such as above on an empty named window, or your application may create the above statement on an already filled named window. The runtime provides correct results in either case: At the time of deployment the runtime internally initializes the consuming statement from the current named window, also taking your declared filters into consideration. Thus, your statement deriving data from a named window does not start empty if the named window already holds one or more events. A consuming statement also sees the remove stream of an already populated named window, if any.
If you require a subset of the data in the named window, you can specify one or more filter expressions onto the named window as shown here:
select symbol, avg(price) from OrdersNamedWindow(sector='energy') group by symbol
By adding a filter to the named window, the aggregation and grouping receive a filtered insert and remove stream. The above statement thus outputs, continuously, the average price per symbol for all orders in the named window that belong to a certain sector.
A side note on variables in filters filtering events from named windows: The runtime initializes consuming statements at statement deployment time and changes aggregation state continuously as events arrive. If the filter criteria contain variables and variable values changes, then the runtime does not re-evaluate or re-build aggregation state. In such a case you may want to place variables in the having clause which evaluates on already-built aggregation state.
The following example further declares a custom derived-value window named myplugindatawindow.
select * from OrdersNamedWindow(volume>0, price>0)#myplugindatawindow()
Data windows cannot be used onto named windows since named windows post insert and remove streams for the events entering and leaving the named window, thus the expiry policy and batch behavior are well defined by the data window declared for the named window. For example, the following is not allowed and fails at time of statement compilation:
// not a valid statement select * from OrdersNamedWindow#time(30 sec)
The create table statement creates a table.
A new table starts up empty. It must be explicitly aggregated-into using into table, or populated by an on-merge statement, or populated by insert into.
The syntax for creating a table provides the table name, lists column names and types and designates primary key columns:
[context context_name] create table table_name [as] (column_name column_type [primary key] [,column_name column_type [primary key] [,...]])
The table_name you assign to the table can be any identifier. The name should not already be in use as an event type or named window name.
You may refer to a context by specifying the context keyword followed by a context name. Contexts are described in more detail at Chapter 4, Context and Context Partitions. The effect of referring to a context is that your table operates according to the context dimensional information as declared for the context. For usage and limitations please see the respective chapter.
The column_name is an identifier providing the column name.
The column_type is required for each column. There are two categories of column types:
Non-aggregating column types: Valid column types are listed in Section 5.17.1, “Creating Variables: The Create Variable Clause” and are the same as for variable types. For attributes that are array-type append
[](left and right brackets). Table columns can hold events by declaring the column type as the event type name. Array-type in combination with event-type is also supported.Aggregation column types: These instruct the runtime to retain aggregation state.
After each column type you may add the primary key keywords. This keyword designates the column as a primary key.
When multiple columns are designated as primary key columns the combination of column values builds a compound primary key.
The order in which the primary key columns are listed is important.
Further detail on key expressions can be found at Section 5.2.13, “Composite Keys and Array Values as Keys”.
The next statement creates a table to hold a numAttempts count aggregation state and a column named active of type boolean, per ipAddress and userId:
create table SecuritySummaryTable ( ipAddress string primary key, userId String primary key, numAttempts count(*), active boolean)
The example above specifies ipAddress and userId as primary keys. This instructs the runtime that the table holds a single row
for each distinct combination of ipAddress and userId. The two values make up the compound key and there is a single row per compound key value.
If you do not designate any columns of the table as a primary key column, the table holds only one row (or no rows).
The create table statement does not provide output to its listeners. The table contents can be iterated on via the pull API to obtain the current contents of a table.
All aggregation functions can be used as column types for tables. Please simply list the aggregation function name as the column type and provide type information, when required. See Section 10.2.1, “SQL-Standard Functions” for a list of the functions and required parameter expressions for which you must provide type information.
Consider the next example that declares a table with columns for different aggregation functions (not a comprehensive example of all possible aggregation functions):
create table MyStats ( myKey string primary key, myAvedev avedev(int), // column holds a mean deviation of int-typed values myAvg avg(double), // column holds an average of double-typed values myCount count(*), // column holds a count myMax max(int), // column holds a highest int-typed value myMedian median(float), // column holds the median of float-typed values myStddev stddev(java.math.BigDecimal), // column holds a standard deviation of BigDecimal values mySum sum(long), // column holds a sum of long values myFirstEver firstever(string), // column holds a first-ever value of type string myCountEver countever(*) // column holds the count-ever (regardless of data windows) )
Additional keywords such as distinct can be used as well. If your aggregation will be associated with a filter expression, you must add boolean to
the parameters in the column type declaration.
For example, the next EPL declares a table with aggregation-type columns that hold an average of filtered double-typed values and an average of distinct double-typed values:
create table MyStatsMore (
myKey string primary key,
myAvgFiltered avg(double, boolean), // column holds an average of double-typed values
// and filtered by a boolean expression to be provided
myAvgDistinct avg(distinct double) // column holds an average of distinct double-typed values
)
The event aggregation functions can be used as column types for tables.
For event aggregation functions you must specify the event type using the @type(name) annotation.
The window event aggregation function requires the * wildcard.
The first and last cannot be used in a declaration, please use window instead and access
as described in Section 6.3.3.2, “Using Aggregation Methods to Access Aggregation State with the Dot Operator”.
The sorted, maxbyever and minbyever event aggregation functions require the criteria expression as a parameter.
The criteria expression must only use properties of the provided event type.
The maxby and minby cannot be used in a declaration, please use sorted instead and access
as described in Section 6.3.3.2, “Using Aggregation Methods to Access Aggregation State with the Dot Operator”.
In this example the table declares sample event aggregations (not a comprehensive example of all possible aggregations):
create table MyEventAggregationTable (
myKey string primary key,
myWindow window(*) @type(MyEvent), // column holds a window of MyEvent events
mySorted sorted(mySortValue) @type(MyEvent), // column holds MyEvent events sorted by mySortValue
myMaxByEver maxbyever(mySortValue) @type(MyEvent) // column holds the single MyEvent event that
// provided the highest value of mySortValue ever
)Any custom single-function and multi-function aggregation can be used as a table column type. If the aggregation has multiple different return values and aggregations share common state, the multi-function aggregation is the preferred API.
For example, the next EPL declares a table with a single column that holds the state of the aggregation function myAggregation:
create table MyStatsCustom (myCustom myAggregation('some code', 100))
The above example passes the values some code and 100 to show how to pass constants to your custom aggregation function at declaration time.
Use the into table keywords to instruct the runtime to aggregate into table columns. A given statement can only aggregate into a single table.
For example, consider a table that holds the count of intrusion events keyed by the combination of from-address and to-address:
create table IntrusionCountTable ( fromAddress string primary key, toAddress string primary key, countIntrusion10Sec count(*), countIntrusion60Sec count(*) )
The next sample statement updates the count considering the last 10 seconds of events:
into table IntrusionCountTable select count(*) as countIntrusion10Sec from IntrusionEvent#time(10) group by fromAddress, toAddress
For statements that have a data window, like the example above, the into table instructs the runtime to update the aggregations that reside in the table column for events entering the data window and for events expiring from the data window.
For statements that don't have a data window the into table instructs the runtime to update the aggregation for arriving events.
In the example above, when an IntrusionEvent enters the 10-second time window the runtime increments the count aggregation by one.
When an IntrusionEvent gets removed from (expires from) the 10-second time window the runtime decrements the count aggregation by one.
Multiple statements can aggregate into the same table columns or different table columns. The co-aggregating ability allows you to co-locate aggregation state conveniently.
The sample shown below is very similar to the previous statement except that it updates the count considering the last 60 seconds of events:
into table IntrusionCountTable select count(*) as countIntrusion60Sec from IntrusionEvent#time(60) group by fromAddress, toAddress
Considering the example above, when an intrusion event arrives and a row for the group-by key values (from and to-address) does not exists, the runtime creates a new row and updates the aggregation-type columns. If the row for the group-by key values exists, the runtime updates the aggregation-type columns of the existing row.
Tables can have no primary key columns. In this case a table either has a single row or is empty.
The next two statements demonstrate table use without a primary key column:
create table TotalIntrusionCountTable (totalIntrusions count(*))
into table TotalIntrusionCountTable select count(*) as totalIntrusions from IntrusionEvent
In conjunction with into table the unidirectional keyword is not supported.
The use of the into table clause requires that the group by clause must list group-by expressions
that match the table's primary key declarations in terms of the number, return type and order of group-by expressions.
It is not necessary that table column names match group-by expression texts.
For example consider a table with a single long-type primary key column:
create table MyTable (theKey long primary key, theCount count(*))
The following EPL are all not valid:
// Invalid: No group-by clause however the table declares a primary key into table MyTable select count(*) as theCount from MyEvent
// Invalid: Two expressions in the group-by clause however the table declares a single primary key into table MyTable select count(*) as theCount from MyEvent group by longPropertyOne, longPropertyTwo
// Invalid: The group-by clause expression returns a string-typed value however the table expects a long-type primary key into table MyTable select count(*) as theCount from MyEvent group by stringProperty
You may use the rollup, cube and grouping sets keywords in conjunction with tables.
The use of the into table clause requires that all aggregation state of the statement resides in table columns.
For example consider a simple table as follows:
create table MyTable (theKey long primary key, theCount count(*))
The following EPL is not valid:
// Invalid: the sum aggregation state is not available in a table column into table MyTable select count(*) as theCount, sum(intProperty) from MyEvent group by longProperty
The use of the into table clause requires that all aggregation functions that are listed in the statement are compatible with table column types,
and that the statement has at least one aggregation function.
For example consider a simple table as follows:
create table MyTable (theKey long primary key, theCount count(*))
The following EPL is not valid:
// Invalid: the sum aggregation state is not compatible with count(*) that was declared for the table column's type into table MyTable select sum(intProperty) as theCount from MyEvent group by longProperty
If declared, the distinct keyword and filter expressions must also match. The event type information must match for event aggregation functions.
The use of the into table clause requires that the aggregation functions are named.
You can name an expression two ways.
First, you can name the aggregation function expression by adding it to the select-clause and by providing the
as-keyword followed by the table column name. The examples earlier use this technique.Second, you can name the aggregation function by placing it into a declared expression that carries the same name as the table column.
This example demonstrates the second method of naming an aggregation function:
expression alias totalIntrusions {count(*)}
select totalIntrusions from IntrusionEventFor accessing table columns by primary key, EPL provides a convenient syntax that allows you to read table column values simply by providing the table name, primary key value expressions (if required by the table) and the column name.
The synopsis for table-column access expressions is:
table-name[primary_key_expr [, primary_key_expr] [,...]][.column-name]
The expression starts with the table name.
If the table declares primary keys you must provide the primary_key_expr value expressions for each primary key within square brackets.
To access a specific column, add the (.) dot character and the column name.
For example, consider a table that holds the count of intrusion events keyed by the combination of from-address and to-address:
create table IntrusionCountTable ( fromAddress string primary key, toAddress string primary key, countIntrusion10Sec count(*) )
Assuming that a FireWallEvent has string-type properties named from and to, the next
statement outputs the current 10-second intrusion count as held by the IntrusionCountTable row for the matching combination of keys:
select IntrusionCountTable[from, to].countIntrusion10Sec from FirewallEvent
The number of primary key expressions, the return type of the primary key expressions and the order in which they are provided must match the primary key columns that were declared for the table. If the table does not have any primary keys declared, you cannot provide any primary key expressions.
If a row for the primary key (or compound key) cannot be found, the runtime returns a null value.
An example table without primary key columns is shown next:
create table TotalIntrusionCountTable (totalIntrusions count(*))
A sample statement that outputs the current total count every 60 seconds is:
select TotalIntrusionCountTable.totalIntrusions from pattern[every timer:interval(60 sec)]
Table access expressions can be used anywhere in statements except as parameter expressions for data windows, the update istream,
context declarations, output limit expressions, pattern observer and guard parameters, pattern every-distinct, pattern match-until bounds, pattern followed-by max
and create window insert or select expression and as a create variable assignment expression.
If your keyed-access expression emits the column name, the runtime returns all current column values.
An example EPL:
select IntrusionCountTable[from, to] from FirewallEvent
The runtime returns each column value, or null if no row is found. For aggregation-type columns it returns the current aggregation value.
Certain aggregation functions allow accessing aggregation state using the (.) dot operator.
The methods that operate on aggregation state are called aggregation methods.
Aggregation methods are explained further in Chapter 13, EPL Reference: Aggregation Methods.
The EPL shown below declares a table that keeps an unsorted set of events and a sorted set of events. This sample table has no primary key columns:
create table MyTable ( theWindow window(*) @type(MyEvent), theSorted sorted(mySortValue) @type(MyEvent) )
This statement uses the first and the maxBy aggregation methods to return the first (oldest) event and the greatest event according to the sort value:
select MyTable.theWindow.first(), MyTable.theSorted.maxBy() from SomeOtherEvent
Tables provide the keys method that returns all table keys. The synopsis is:
tablename.keys()The return type of the method is object-array. Each element of the array is a table key. For composite table keys, each element of the array is itself of type object-array and each array element is the primary key value.
An example EPL:
select IntrusionCountTable.keys() from FirewallEvent
The runtime returns an array of primary keys.
The insert into clause inserts rows into a table.
Your application must ensure that the column names and types match the declared column names and types of the table to be inserted into, when provided.
For inserting into a table and for simultaneously checking if the inserted row already exists in the table or for atomic update-insert operation on a table, or for targeting a specific partition, you must use
on-merge as described in Section 6.8, “Triggered Upsert Using the On-Merge Clause”. On-merge
is similar to the SQL merge clause and provides what is known as an "Upsert" operation: Update existing rows or if no existing rows(s) are found then insert a new row,
all in one atomic operation provided by a single statement.
The following statement populates the example table declared earlier:
insert into IntrusionCountTable select fromAddress, toAddress from FirewallEvent
Note that when a row with the same primary key values already exists, your statement may encounter a unique index violation at runtime.
If the inserted-into table does not have primary key columns, the table holds a maximum of one row and your statement may also encounter a unique index violation upon
attempting to insert a second row.
Use on-merge to prevent inserts of duplicate rows.
Table columns that are aggregation functions cannot be inserted-into and must be updated using into table instead.
You may also explicitly list column names as discussed earlier in Section 6.2.2, “Inserting Into Named Windows”.
For insert-into, the context name must be the same context name as declared for the create table statement or the context name must be absent for both.
A table can be referred to by any statement in the from-clause of the statement.
Tables do not provide an insert and remove stream. When a table appears alone in the from-clause (other than as part of a subquery),
the statement produces output only when iterated (see pull API) or when executing a fire-and-forget (on-demand) query.
Assuming you have declared a table by name IntrusionCountTable as shown earlier,
the following statement only returns rows when iterated or when executing the EPL as a fire-and-forget (on-demand) query or when adding an output snapshot:
select * from IntrusionCountTable
For tables, the contained-event syntax and specifying a data window is not supported.
In a join, a table in the from-clause cannot be marked as unidirectional. You may not specify any of the retain-flags.
Tables cannot be used in the from-clause of match-recognize statements, in context declarations, in pattern filter atoms and update istream.
The following are examples of invalid statements:
// invalid statement examples select * from IntrusionCountTable#time(30 sec) // data window not allowed select * from IntrusionCountTable unidirectional, MyEvent // tables cannot be marked as unidirectional
Tables can be used in subqueries and joins.
It follows a sample subselect and join against the table:
select (select * from IntrusionCountTable as intr where intr.fromAddress = firewall.fromAddress and intr.toAddress = firewall.toAddress) from IntrusionEvent as firewall
select * from IntrusionCountTable as intr, IntrusionEvent as firewall where intr.fromAddress = firewall.fromAddress and intr.toAddress = firewall.toAddress
If the subselect or join specifies all of a table's primary key columns, please consider using the table-access expression instead. It offers a more concise syntax.
Note that for a subquery against a table that may return multiple rows, the information about subquery multi-row selection applies. For subselects, consider using @eventbean
to preserve table type information in the output event.
Note that for joins against tables the compiler does not allow specifying table filter expressions in parenthesis, in the from clause.
Filter expressions must instead be placed into the where-clause.
You may access aggregation state the same way as in table-access expressions, using the dot (.) operator.
The EPL shown below declares a table that keeps a set of events, and shows a join that selects window aggregation state:
create table MyWindowTable (theWindow window(*) @type(MyEvent))
select theWindow.first(), theWindow.last(), theWindow.window() from MyEvent, MyWindowTable
For resetting plain table columns, you may simple assign a value using set name = value within an on-merge update- action to set new values.
You may also use fire-and-forget queries.
For resetting aggregation-typed table columns, as they represent aggregation state, it is not possible to use a straight assignment. Instead, the runtime provides a reset method.
The syntax for the reset method is column-name.reset() and is only available as part of on-merge and the update-action.
You may also reset all aggregations of a table row by specifying table-alias.reset().
For example, consider a table that holds the count of intrusion events keyed by the combination of from-address and to-address:
create table IntrusionCountTable ( fromAddress string primary key, toAddress string primary key, countIntrusion10Sec count(*), countIntrusion60Sec count(*) )
Assume there is an event that triggers the reset of the countIntrusion10Sec and countIntrusion60Sec counts:
create schema IntrusionReset(fromAddress string, toAddress string)
Use on-merge to reset the count columns like so:
on IntrusionReset as resetEvent merge IntrusionCountTable as tableRow where resetEvent.fromAddress = tableRow.fromAddress and resetEvent.toAddress = tableRow.toAddress when matched then update set countIntrusion10Sec.reset(), countIntrusion60Sec.reset()
Alternatively you may specify the table alias to reset all of a table row's aggregation state:
on IntrusionReset as resetEvent merge IntrusionCountTable as tableRow where resetEvent.fromAddress = tableRow.fromAddress and resetEvent.toAddress = tableRow.toAddress when matched then update set tableRow.reset()
For initializing plain table columns, you may simple assign a value using set name = value within an on-merge update- action to set new values.
You may also use fire-and-forget queries.
For initializing aggregation-typed table columns, as they represent aggregation state, it is not possible to use a straight assignment. Instead, you must use into table since aggregation state is complex state and requires adding and removing values or events and therefore cannot be assigned to.
If the aggregation-typed column is a count, please declare the column as a sum instead and use sum(initial value) to initialize the value or sum(1) to increment the sum.
The on select clause performs a one-time, non-continuous query on a named window or table every time a triggering event arrives or a triggering pattern matches. The statement can consider all rows, or only rows that match certain criteria, or rows that correlate with an arriving event or a pattern of arriving events.
The syntax for the on select clause is as follows:
on event_type[(filter_criteria)] [as stream_name] [insert into insert_into_def] select select_list from window_or_table_name [as stream_name] [where criteria_expression] [group by grouping_expression_list] [having grouping_search_conditions] [order by order_by_expression_list]
The event_type is the name of the type of events that trigger the query against the named window or table. It is optionally followed by filter_criteria which are filter expressions to apply to arriving events. The optional as keyword can be used to assign a stream name. Patterns or named windows can also be specified in the on clause, see the samples in Section 6.7.1, “Using Patterns in the On-Delete Clause” (for a named window as a trigger only insert stream events trigger actions) (tables cannot be triggers).
The insert into clause works as described in Section 5.10, “Merging Streams and Continuous Insertion: The Insert Into Clause”. The select clause is described in Section 5.3, “Choosing Event Properties and Events: The Select Clause”. For all clauses the semantics are equivalent to a join operation: The properties of the triggering event or events are available in the select clause and all other clauses.
The window_or_table_name in the from clause is the name of the named window or table to select rows from. The as keyword is also available to assign a stream name to the table or named window. The as keyword is helpful in conjunction with wildcard in the select clause to select rows via the syntax select streamname.* .
The optional where clause contains a criteria_expression that correlates the arriving (triggering) event to the rows to be considered from the table or named window. The criteria_expression may also simply filter for rows to be considered by the statement.
The group by clause, the having clause and the order by clause are all optional and work as described in earlier chapters.
Statements that use tables and named windows work the same. The examples herein use the OrdersNamedWindow named window and the SecuritySummaryTable table to provide examples for each.
The sample statement below outputs, when a trigger event arrives, the count of all rows held by the SecuritySummaryTable table:
on QueryEvent select count(*) from SecuritySummaryTable
This sample statement outputs the total volume per symbol ordered by symbol ascending and only non-zero volumes of all rows held by the OrdersNamedWindow named window:
on QueryEvent select symbol, sum(volume) from OrdersNamedWindow group by symbol having volume > 0 order by symbol
When using wildcard (*) to select from streams in an on-select clause, each stream, that is the triggering stream and the selected-upon table or named window, are selected, similar to a join. Therefore your wildcard select returns two columns: the triggering event and the selection result row, for each row.
on QueryEvent as queryEvent select * from OrdersNamedWindow as win
The statement above returns a queryEvent column and a win column for each event.
If only a single stream's event is desired in the result, use select win.* instead.
Upon arrival of a QueryEvent event, this statement selects all rows in the OrdersNamedWindow named window:
on QueryEvent select win.* from OrdersNamedWindow as win
The runtime executes the statement on arrival of a triggering event, in this case a QueryEvent. It posts the statement results to any listeners to the statement, in a single invocation, as the new data array.
The where clause filters and correlates rows in the table or named window with the triggering event, as shown next:
on QueryEvent(volume>0) as query select query.symbol, query.volume, win.symbol from OrdersNamedWindow as win where win.symbol = query.symbol
Upon arrival of a QueryEvent, if that event has a value for the volume property that is greater than zero, the runtime executes the statement. The statement considers all events currently held by the OrdersNamedWindow that match the symbol property value of the triggering QueryEvent event.
For correlated statements that correlate triggering events with rows held by a named window, the runtime internally creates efficient indexes to enable high performance querying of rows.
It analyzes the where clause to build one or more indexes for fast lookup in the named window based on the properties of the triggering event.
To trigger an on-select when an update to the selected named window occurs or when the triggering event is the same event that is being inserted into the named window, specify the named window name as the event type.
The next statement fires the select for every change to the named window OrdersNamedWindow:
on OrdersNamedWindow as trig select onw.symbol, sum(onw.volume) from OrdersNamedWindow as onw where onw.symbol = trig.symbol
For named windows, the iterator of the EPStatement object representing the on select clause returns the last batch of selected events in response to the last triggering event, or null if the last triggering event did not select any rows.
For tables, the iterator of the EPStatement object representing the on select clause returns no events.
For correlated statements that correlate triggering events with rows held by a table, the runtime utilizes either primary key columns or
secondary explicitly-created indexes to enable high performance querying of rows, based on an analysis of the where clause.
The similarities and differences between an on select clause and a regular or outer join (and not unidirectional) are as follows:
A join is evaluated when any of the streams participating in the join have new events (insert stream) or events leaving data windows (remove stream). A join is therefore bi-directional or multi-directional. However, the
on selectstatement has one triggering event or pattern that causes the statement to be evaluated and is thus uni-directional.The query within the
on selectstatement is not continuous: It executes only when a triggering event or pattern occurs. Aggregation and groups are computed anew considering the contents of the table or named window at the time the triggering event arrives.
On-select and the unidirectional join can be compared as follows.
On-select, on-merge, on-insert, on-delete, on-update and on-select-and-delete
operate only on named windows or tables. Unidirectional joins however can operate on any stream.
If the unidirectional join is between a single named window or table and a triggering event or pattern and that triggering event or pattern is marked unidirectional, the unidirectional join is equivalent to on-select.
A unidirectional join does not execute under a named window context partition lock and instead is a consumer relationship to the named window.
The on select delete clause performs a one-time, non-continuous query on a table or named window every time a triggering event arrives or a triggering pattern matches, similar to on-select as described in the previous section. In addition, any selected rows are also deleted.
The syntax for the on select delete clause is as follows:
on trigger
select [and] delete select_list...
... (please see on-select for insert into, from, group by, having, order by)...
The syntax follows the syntax of on-select as described earlier. The select clause follows the optional and keyword and the delete keyword. The from-clause can list either a table or a named window.
The example statement below selects and deletes all rows from OrdersNamedWindow named window when a QueryEvent arrives:
on QueryEvent select and delete window(win.*) as rows from OrdersNamedWindow as win
The sample EPL above also shows the use of the window aggregation function. It specifies the window aggregation function
to instruct the runtime to output a single event, regardless of the number of rows in the named window, and that contains a column rows that contains a collection of the selected event's underlying objects.
Note
On Select Delete deletes all rows that match the where-clause. When there is no where-clause it deletes all rows regardless of what the output looks like. The having-clause is relevant to output only and does not narrow down the rows that are deleted.
An on update clause updates rows held by a table or named window. The clause can be used to update all rows, or only rows that match certain criteria, or rows that correlate with an arriving event or a pattern of arriving events.
For updating a table or named window and for simultaneously checking if the updated row exists or for atomic update-insert operation on a named window or table, consider using on-merge as described in Section 6.8, “Triggered Upsert Using the On-Merge Clause”.
On-merge is similar to the SQL merge clause and provides what is known as an "Upsert" operation:
Update existing events or if no existing event(s) are found then insert a new event, all in one atomic operation provided by a single statement.
The syntax for the on update clause is as follows:
on event_type[(filter_criteria)] [as stream_name] update window_or_table_name [as stream_name] set mutation_expression [, mutation_expression [,...]] [where criteria_expression]
The event_type is the name of the type of events that trigger an update of rows in a named window. It is optionally followed by filter_criteria which are filter expressions to apply to arriving events. The optional as keyword can be used to assign a name for use in expressions and the where clause. Patterns and named windows can also be specified in the on clause.
The window_or_table_name is the name of the table or named window to update rows.
The as keyword is also available to assign a name to the named window or table.
After the set keyword follows a list of comma-separated mutation_expression expressions. A mutation expression is any valid EPL expression and including the below.
Subqueries may by part of expressions however aggregation functions and the prev or prior function may not be used in expressions.
The below table shows some typical mutation expessions:
Table 6.1. Mutation Expressions in Update and Merge
| Description | Syntax and Examples |
|---|---|
| Assignment |
property_name = value_expression price = 10, side = 'BUY' |
| Array Element Assignment |
arrayproperty_name[array_index_expression] = value_expression values[position] = 10 |
| Event Method Invocation (not available for tables) |
alias_or_windowname.methodname(...) orderWindow.clear() |
| Property Method Invocation |
property_name.methodname(...) accountMap.clear() |
| Any Expression, For Example: User-Defined Function Call |
functionname(...)
clearQuantities(orderRow) |
The optional where clause contains a criteria_expression that correlates the arriving (triggering) event to the rows to be updated in the table or named window. The criteria_expression may also simply filter for rows to be updated.
Statements that use tables and named windows work the same. We use the term property and column interchangeably. The examples herein use the OrdersNamedWindow named window and the SecuritySummaryTable table to provide examples for each. Let's look at a couple of examples.
In the simplest form, this statement updates all rows in the named window OrdersNamedWindow when any UpdateOrderEvent event arrives, setting the price property to zero for all rows currently held by the named window:
on UpdateOrderEvent update OrdersNamedWindow set price = 0
This example demonstrates the use of a where clause and updates the SecuritySummaryTable table.
Upon arrival of a triggering ResetEvent it updates the active column value to false for all table rows that have an active column value of true:
on ResetEvent update SecuritySummaryTable set active = false where active = true
The next example shows a more complete use of the syntax, and correlates the triggering event with rows held by the OrdersNamedWindow named window:
on NewOrderEvent(volume>0) as myNewOrders update OrdersNamedWindow as myNamedWindow set price = myNewOrders.price where myNamedWindow.symbol = myNewOrders.symbol
In the above sample statement, only if a NewOrderEvent event with a volume greater then zero arrives does the statement trigger. Upon triggering, all rows in the named window that have the same value for the symbol property as the triggering NewOrderEvent event are then updated (their price property is set to that of the arriving event). The statement also showcases the as keyword to assign a name for use in the where expression.
Your application can subscribe a listener to your on update statements to determine update events. The statement post any rows that are updated to all listeners attached to the statement as new data, and the events prior to the update as old data.
The following example shows the use of tags and a pattern. It sets the price value of orders to that of either a FlushOrderEvent or OrderUpdateEvent depending on which arrived:
on pattern [every ord=OrderUpdateEvent(volume>0) or every flush=FlushOrderEvent] update OrdersNamedWindow as win set price = case when ord.price is null then flush.price else ord.price end where ord.id = win.id or flush.id = win.id
When updating indexed properties use the syntax propertyName[index] = value with the index value being an integer number.
When updating mapped properties use the syntax propertyName(key) = value with the key being a string value.
The runtime executes assignments in the order they are listed. When performing multiple assignments, the runtime takes the most recent column value according to the last assignment, if any. To instruct the runtime to use the initial value before update, prefix the column name with the literal initial. The initial prefix is only available for use with named windows and not for use with tables.
The following statement illustrates:
on UpdateEvent as upd update MyWindow as win set field_a = 1, field_b = win.field_a, // assigns the value 1 field_c = initial.field_a // assigns the field_a original value before update
The next example assumes that your application provides a user-defined function copyFields that receives 3 parameters:
The update event, the new row and the initial state before-update row.
on UpdateEvent as upd update MyWindow as win set copyFields(win, upd, initial)
You may invoke a method on a value object, for those properties that hold value objects, as follows:
on UpdateEvent update MyWindow as win set someproperty.clear()
For named windows only, you may also invoke a method on the named window event type.
The following example assumes that your event type provides a method by name populateFrom that receives the update event as a parameter:
on UpdateEvent as upd update MyWindow as win set win.populateFrom(upd)
The following restrictions apply:
Each property to be updated via assignment must be writable. For tables, all columns are always writable.
For underlying event representations that are Java objects, a event object class must implement the java.io.Serializable interface as discussed in Section 5.20.1, “Immutability and Updates” and must provide setter methods for updated properties.
When using an XML underlying event type, event properties in the XML document representation are not available for update.
Nested properties are not supported for update. Variant streams may also not be updated.
Statements that reference the named window receive the new event in the insert stream and the event prior to the update in the remove stream.
For correlated statements (as above) that correlate triggering events with events held by a named window, the runtime internally creates efficient indexes to enable high performance update of events.
The iterator of the EPStatement object representing the on update clause does not return any rows.
On-Update may not update primary key columns.
For correlated statements that correlate triggering events with rows held by a table, the runtime utilizes either primary key columns or
secondary explicitly-created indexes to enable high performance querying of rows, based on an analysis of the where clause.
The iterator of the EPStatement object representing the on update clause does not return any rows.
An on delete clause removes rows from a named window or table. The clause can be used to remove all rows, or only rows that match certain criteria, or rows that correlate with an arriving event or a pattern of arriving events.
The syntax for the on delete clause is as follows:
on event_type[(filter_criteria)] [as stream_name] delete from window_or_table_name [as stream_name] [where criteria_expression]
The event_type is the name of the type of events that trigger removal from the table or named window. It is optionally followed by filter_criteria which are filter expressions to apply to arriving events. The optional as keyword can be used to assign a name for use in the where clause. Patterns and named windows can also be specified in the on clause as described in the next section.
The window_or_table_name is the name of the named window or table to delete rows from.
The as keyword is also available to assign a name to the table or named window.
The optional where clause contains a criteria_expression that correlates the arriving (triggering) event to the rows to be removed. The criteria_expression may also simply filter for rows without correlating.
On-delete can be used against tables and named windows. The examples herein use the OrdersNamedWindow named window and the SecuritySummaryTable table to provide examples for each.
In the simplest form, this statement deletes all rows from the SecuritySummaryTable table when any ClearEvent arrives:
on ClearEvent delete from SecuritySummaryTable
The next example shows a more complete use of the syntax, and correlates the triggering event with events held by the OrdersNamedWindow named window:
on NewOrderEvent(volume>0) as myNewOrders delete from OrdersNamedWindow as myNamedWindow where myNamedWindow.symbol = myNewOrders.symbol
In the above sample statement, only if a NewOrderEvent event with a volume greater then zero arrives does the statement trigger. Upon triggering, all rows in the named window that have the same value for the symbol property as the triggering NewOrderEvent event are removed. The statement also showcases the as keyword to assign a name for use in the where expression.
By means of patterns the on delete clause and on select clause (described below) can look for more complex conditions to occur, possibly involving multiple events or the passing of time. The syntax for on delete with a pattern expression is show next:
on pattern [pattern_expression] [as stream_name] delete from window_or_table_name [as stream_name] [where criteria_expression]
The pattern_expression is any pattern that matches zero or more arriving events. Tags can be used to name events in the pattern and can occur in the optional where clause to correlate to events to be removed from a named window.
In the next example the triggering pattern fires every 10 seconds. The effect is that every 10 seconds the statement removes all rows from the SecuritySummaryTable table:
on pattern [every timer:interval(10 sec)] delete from SecuritySummaryTable
The following example shows the use of tags in a pattern and executes against the OrdersNamedWindow named window instead:
on pattern [every ord=OrderEvent(volume>0) or every flush=FlushOrderEvent] delete from OrdersNamedWindow as win where ord.id = win.id or flush.id = win.id
The pattern above looks for OrderEvent events with a volume value greater then zero and tags such events as 'ord'.
The pattern also looks for FlushOrderEvent events and tags such events as 'flush'. The where clause deletes from the OrdersNamedWindow named window any rows that match in the value of the 'id' property either of the arriving events.
When using on-delete with named windows you may specify @hint('silent_delete') to suppress output of the deleted events to listeners of the statement that declares the named window.
This is useful when listeners need to receive only expired events and not explicitly deleted events.
The @hint('silent_delete') instruction for use with on-delete removes the dispatches for all listeners of the statement that declares the named window in respect to the deleted events,
thereby listeners of the statement that declares the named window don't receive the deleted events.
Statements that reference the named window receive the deleted event as part of the remove stream.
For correlated statements (as above) that correlate triggering events with rows held by a named window, the runtime internally creates efficient indexes to enable high performance deletion of rows.
The iterator of the EPStatement object representing the on delete clause does not return any rows.
For correlated statements that correlate triggering events with rows held by a table, the runtime utilizes either primary key columns or
secondary explicitly-created indexes to enable high performance querying of rows, based on an analysis of the where clause.
The iterator of the EPStatement object representing the on delete clause does not return any rows.
The on merge clause is similar to the SQL merge clause. It provides what is known as an "Upsert" operation: Update existing rows or if no existing row(s) are found then insert a new row, all in an atomic operation provided by a single statement.
The syntax for the on merge clause has two forms.
Use on merge with insert to inserts one row. This syntax is:
on event_type[(filter_criteria)] [as stream_name] merge [into] window_or_table_name [as stream_name] insert [ (property_name [, property_name] [,...]) ] select select_expression [, select_expression[,...]]
The event_type is the name of the type of events that trigger the merge. It is optionally followed by filter_criteria which are filter expressions to apply to arriving events. The optional as keyword can be used to assign a name for use in the where clause. Patterns and named windows can also be specified in the on clause as described in prior sections.
The window_or_table_name is the name of the named window to insert a row into.
The as keyword is also available to assign a name to the named window or table.
It follows the insert keyword and optionally the into keyword. Optionally you can provide a list of property names in parenthesis.
It follows the required select keyword and one or more select-clause expressions. The wildcard (*) is available in the select-clause as well.
On-merge can be used with tables and named windows. This examples uses the SecuritySummaryTable table that was defined earlier.
This example statement inserts a row into the SecuritySummaryTable table when a SecuritySummary arrives:
on SecuritySummary merge SecuritySummaryTable insert select ipAddress, userId
The following EPL is equivalent to the statement above and uses the upsert syntax instead, described next.
on SecuritySummary merge SecuritySummaryTable where 1=2 when not matched then insert select ipAddress, userId
The syntax for on merge for update-insert (upsert) is as follows:
on event_type[(filter_criteria)] [as stream_name] merge [into] window_or_table_name [as stream_name] [where criteria_expression] when [not] matched [and search_condition] then [ insert [into streamname] [ (property_name [, property_name] [,...]) ] select select_expression [, select_expression[,...]] [where filter_expression] | update set mutation_expression [, mutation_expression [,...]] [where filter_expression] | delete [where filter_expression] ] [then [insert|update|delete]] [,then ...] [when ... then ... [...]]
The event_type is the name of the type of events that trigger the merge. It is optionally followed by filter_criteria which are filter expressions to apply to arriving events. The optional as keyword can be used to assign a name for use in the where clause. Patterns and named windows can also be specified in the on clause as described in prior sections.
The window_or_table_name is the name of the named window or table to insert, update or delete rows.
The as keyword is also available to assign a name to the named window or table.
The optional where clause contains a criteria_expression that correlates the arriving (triggering) event to the rows to be considered of the table or named window.
We recommend specifying a criteria expression that is as specific as possible.
Following the where clause is one or more when matched or when not matched clauses in any order. Each may have an additional search condition associated.
After each when [not] matched follow one or more then clauses that each contains the action to take: Either an insert, update or delete keyword.
After when not matched only insert action(s) are available. After when matched any insert, update and delete action(s) are available.
After insert follows, optionally, the into keyword followed by the stream name or named window to insert-into. If no into and stream name is specified, the insert applies to the current table or named window. It follows an optional list of columns inserted. It follows the required select keyword and one or more select-clause expressions. The wildcard (*) is available in the select-clause as well. It follows an optional where-clause that may return Boolean false to indicate that the action should not be applied.
After update follows the set keyword and one or more mutation expressions. For mutation expressions please see Section 6.6, “Updating Data: The On Update Clause”.
It follows an optional where-clause that may return Boolean false to indicate that the action should not be applied.
After delete follows an optional where-clause that may return Boolean false to indicate that the action should not be applied.
When according to the where-clause criteria_expression the runtime finds no rows in the named window or table that match the condition, the runtime evaluates each when not matched clause. If the optional search condition returns true or no search condition was provided then the runtime performs all of the actions listed after each then.
When according to the where-clause criteria_expression the runtime finds one or more rows in the named window or table that match the condition, the runtime evaluates each when matched clause. If the optional search condition returns true or no search condition was provided the runtime performs all of the actions listed after each then.
The runtime executes when matched and when not matched in the order specified. If the optional search condition returns true or no search condition was specified then the runtime takes the associated action (or multiple actions for multiple then keywords). When the block of actions completed the runtime proceeds to the next matching row, if any. After completing all matching rows the runtime continues to the next triggering event if any.
On-merge can be used with tables and named windows. The examples herein declare a ProductWindow named window and also use the SecuritySummaryTable table to provide examples for each.
This example statement updates the SecuritySummaryTable table when a ResetEvent arrives setting the active column's value to false:
on ResetEvent merge SecuritySummaryTable when matched and active = true then update set active = false
A longer example utilizing a named window follows. You start by declaring a schema that provides a product id and that holds a total price:
create schema ProductTotalRec as (productId string, totalPrice double)
We create a named window that holds a row for each unique product:
create window ProductWindow#unique(productId) as ProductTotalRec
The events for this example are order events that hold an order id, product id, price, quantity and deleted-flag declared by the next schema:
create schema OrderEvent as (orderId string, productId string, price double,
quantity int, deletedFlag boolean)
The following statement utilizes on-merge to total up the price for each product based on arriving order events:
on OrderEvent oe
merge ProductWindow pw
where pw.productId = oe.productId
when matched
then update set totalPrice = totalPrice + oe.price
when not matched
then insert select productId, price as totalPrice
In the above example, when an order event arrives, the runtime looks up in the product named window the matching row or rows for the same product id as the arriving event. In this example the runtime always finds no row or one row as the product named window is declared with a unique data window based on product id.
If the runtime finds a row in the named window, it performs the update action adding up the price as defined under when matched. If the runtime does not find a row in the named window it performs the insert action as defined under when not matched, inserting a new row.
The insert keyword may be followed by a list of columns as shown in this EPL snippet:
// equivalent to the insert shown in the last 2 lines in above EPL
...when not matched
then insert(productId, totalPrice) select productId, price
The second example demonstrates the use of a select-clause with wildcard, a search condition and the delete keyword. It creates a named window that holds order events and employs on-merge to insert order events for which no corresponding order id was found, update quantity to the quantity provided by the last arriving event and delete order events that are marked as deleted:
create window OrderWindow#keepall as OrderEvent
on OrderEvent oe
merge OrderWindow pw
where pw.orderId = oe.orderId
when not matched
then insert select *
when matched and oe.deletedFlag=true
then delete
when matched
then update set pw.quantity = oe.quantity, pw.price = oe.price
In the above example the oe.deletedFlag=true search condition instructs the runtime to take the delete action only if the deleted-flag is set.
You may specify multiple actions by providing multiple then keywords each followed by an action. Each of the insert, update and delete actions can itself have a where-clause as well.
If a where-clause exists for an action, the runtime evaluates the where-clause and applies the action only if the where-clause returns Boolean true.
This example specifies two update actions and uses the where-clause to trigger different update behavior depending on whether the order event price is less than zero.
This example assumes that the host application defined a clearorder user-defined function, to demonstrate calling a user-defined function as part of the update mutation expressions:
on OrderEvent oe
merge OrderWindow pw
where pw.orderId = oe.orderId
when matched
then update set clearorder(pw) where oe.price < 0
then update set pw.quantity = oe.quantity, pw.price = oe.price where oe.price >= 0
To insert events into another stream and not the named window, use insert into streamname.
In the next example each matched-clause contains two actions, one action to insert a log event and a second action to insert, delete or update:
on OrderEvent oe
merge OrderWindow pw
where pw.orderId = oe.orderId
when not matched
then insert into LogEvent select 'this is an insert' as name
then insert select *
when matched and oe.deletedFlag=true
then insert into LogEvent select 'this is a delete' as name
then delete
when matched
then insert into LogEvent select 'this is a update' as name
then update set pw.quantity = oe.quantity, pw.price = oe.priceWhile the runtime evaluates and executes all actions listed under the same matched-clause in order, you may not rely on updated field values of an earlier action to trigger the where-clause of a later action. Similarly you should avoid simultaneous update and delete actions for the same match: the runtime does not guarantee whether the update or the delete take final affect.
Your application can subscribe a listener to on merge statements to determine inserted, updated and removed events. Statements post any events that are inserted to, updated or deleted from a named window to all listeners attached to the statement as new data and removed data.
The following limitations apply to on-merge statements:
Aggregation functions and the
prevandprioroperators are not available in conditions and theselect-clause.
Statements that reference the named window receive an insert and remove stream represening the insertions, changes and deletions to named window rows.
For correlated statements (as above) that correlate triggering events with rows held by a named window, the runtime internally creates efficient indexes to enable high performance update and removal of events especially from named windows that hold large numbers of events.
The iterator of the EPStatement object representing the on merge clause does not return any rows.
On-Merge may not update primary key columns.
For correlated statements that correlate triggering events with rows held by a table, the runtime utilizes either primary key columns or
secondary explicitly-created indexes to enable high performance querying of rows, based on an analysis of the where clause.
The iterator of the EPStatement object representing the on merge clause does not return any rows.
You may explicitly create an index on a table or a named window. The runtime considers explicitly-created as well as implicitly-allocated indexes (named windows only) in query planning and execution of the following types of usages of tables and named windows:
Fire-and-forget (on-demand, non-continuous) queries as described in Section 16.7, “Execute Fire-and-Forget Queries Using EPFireAndForgetService”.
On-select,on-merge,on-update,on-deleteandon-insert.Subqueries against tables and named windows.
For joins (including outer joins) with named windows the runtime considers the filter criteria listed in parenthesis using the syntax
name_window_name(filter_criteria)
for index access.
For joins with tables the runtime considers the primary key columns (if any) as well as any table indexes.
The syntax to create an explicit index on a named window or table is:
create [unique] index index_name on window_or_table_name ( column_expression [hash|btree|index_type_expression] [, column_expression] [hash|btree|index_type_expression] [,...] )
The optional unique keyboard indicates that the column expressions uniquely identify rows. If unique is not specified the index allows duplicate rows.
The index_name is the name assigned to the index. The name uniquely identifies the index and is used in compiler query plan logging.
The window_or_table_name is the name of an existing table or named window. If the named window or table has rows already, the runtime builds an index for the rows.
After the table name or named window name follows a list of pairs of column_expression column expression and index type.
A column expression is the expression that is subject to index building. Typically a column expression is an event property or column name. For special application-provided or spatial indexes other column expressions are allowed and such indexes may allow multiple columns to be combined. Further detail on key expressions can be found at Section 5.2.13, “Composite Keys and Array Values as Keys”.
Following each column expression you may specify the index type by providing the optional hash or btree keywords or an index_type_expression.
For special application-provided or spatial indexes please use the index_type_expression.
If you specify no keyword or the hash keyword for a property, the index will be a hash-based (unsorted) index in respect to that property. If you specify the btree keyword, the index will be a binary-tree-based sorted index in respect to that property.
You may combine hash and btree properties for the same index.
Specify btree for a property if you expect to perform numerical or string comparison using relational operators (<, >, >=, <=), the between or the in keyword for ranges and inverted ranges. Use hash (the default) instead of btree if you expect to perform exact comparison using =.
For hash and btree index types the column expression must be an event property or column name. Expressions such as col+1 are not currently supported for
hash and btree index types but are supported for other index types.
The create table syntax is the same for tables and named windows. The examples herein create a new UserProfileWindow named window and also use the SecuritySummaryTable table.
This sample EPL creates an non-unique index on the active column of table SecuritySummaryTable:
create index MyIndex on SecuritySummaryTable(active)
We list a few example statements next that create a named window and create a single index:
// create a named window create window UserProfileWindow#time(1 hour) select * from UserProfile
// create a non-unique index (duplicates allowed) for the user id property only create index UserProfileIndex on UserProfileWindow(userId)
Next, execute a fire-and-forget query as shown below; this sample uses the prepared version to demonstrate:
String query = "select * from UserProfileWindow where userId='Joe'"; EPFireAndForgetPreparedQuery prepared = epRuntime.getFireAndForgetService().prepareQuery(query); // query performance excellent in the face of large number of rows EPFireAndForgetQueryResult result = prepared.execute(); // ...later ... prepared.execute(); // execute a second time
A unique index is generally preferable over non-unique indexes. For named windows, if your data window declares a unique data window (#unique, #firstunique, including intersections and grouped unique data windows) it is not necessary to create a unique index unless index sharing is enabled, since the compiler and runtime considers the unique data window declaration in query planning.
The runtime enforces uniqueness (e.g. unique constraint) for unique indexes. If your application inserts a duplicate row the runtime raises a runtime exception when processing the statement and discards the row. The default error handler logs such an exception and continues.
For example, if the user id together with the profile id uniquely identifies an entry into the named window, your application can create a unique index as shown below:
// create a unique index on user id and profile id create unique index UserProfileIndex on UserProfileWindow(userId, profileId)
By default, the runtime builds a hash code -based index useful for direct comparison via equals (=). Filter expressions that look for ranges or use in, between do not benefit from the hash-based index and should use the btree keyword. For direct comparison via equals (=) then compiler does not use btree indexes.
The next example creates a composite index over two fields symbol and buyPrice:
// create a named window create window TickEventWindow#time(1 hour) as (symbol string, buyPrice double)
// create a non-unique index create index idx1 on TickEventWindow(symbol hash, buyPrice btree)
A sample fire-and-forget query is shown below (this time the API calls are not shown):
// query performance excellent in the face of large number of rows select * from TickEventWindow where symbol='GE' and buyPrice between 10 and 20
Note
A table that does not declare one or more primary key columns cannot have a secondary index, as the table holds a maximum of one row.
Fire-and-Forget queries can be run against both tables and named windows. We use the term property and column interchangeably.
For selecting from named windows and tables, please see the examples in Section 16.7, “Execute Fire-and-Forget Queries Using EPFireAndForgetService”.
For data manipulation (insert, update, delete) queries, the fire-and-forget query API returns the inserted, updated or deleted rows when the query executes against a named window.
Your application can insert rows into a table or named window using fire-and-forget (on-demand, non-continuous) queries as described in Section 16.7, “Execute Fire-and-Forget Queries Using EPFireAndForgetService”.
The compiler allows the standard SQL syntax and values keyword and also supports using select to provide values.
The values keyword allows inserting multiple rows in a single query.
The syntax using the values keyword is:
insert into window_or_table_name [(property_names)] values (value_expressions) [, (value_expressions) ...]
The syntax using select is as follows:
insert into window_or_table_name [(property_names)] select value_expressions
The window_or_table_name is the name of the table or named window to insert rows into.
After the named window or table name you can optionally provide a comma-separated list of property names.
When providing property names, the order of value expressions in the values list or select clause must match the order of property names specified. Column names provided in the select-clause, if specified, are ignored.
When not providing property names and when specifying the values keyword, the order of values must match the order of properties
declared for the named window or table.
When not providing property names and when specifying the select-clause, expressions must name the properties to be inserted into
by assigning a column name using the as keyword.
The example code snippet inserts a new order row into the OrdersWindow named window:
String query =
"insert into OrdersWindow(orderId, symbol, price) values ('001', 'GE', 100)";
runtime.getFireAndForgetService().executeQuery(query);
After the values keyword there can be multiple comma-separated lists of values for insertion. A maximum of up to 1000 rows can be inserted per query.
The sample query below inserts two order rows:
insert into OrdersWindow(orderId, symbol, price) values ('001', 'GE', 100), ('002', 'IBM', 75)
Instead of the values keyword you may specify a select-clause as this example shows:
String query = "insert into OrdersWindow(orderId, symbol, price) select '001', 'GE', 100"; runtime.getFireAndForgetService().executeQuery(query);
The following EPL inserts the same values as above but specifies property names as part of the select-clause expressions:
insert into OrdersWindow select '001' as orderId, 'GE' as symbol, 100 as price
The next EPL inserts the same values as above and does not specify property names thereby populating the first 3 properties of the type of the named window:
insert into OrdersWindow values ('001', 'GE', 100)Your application can update table and named window rows using fire-and-forget (on-demand, non-continuous) queries as described in Section 16.7, “Execute Fire-and-Forget Queries Using EPFireAndForgetService”.
The syntax for the update clause is as follows:
update window_or_table_name [as stream_name] set mutation_expression [, mutation_expression [,...]] [where criteria_expression]
The window_or_table_name is the name of the table or named window to remove rows from.
The as keyword is also available to assign a name to the table or named window.
After the set keyword follows a comma-separated list of mutation expressions. For fire-and-forget queries the following restriction applies: Aggregation functions and the prev or prior function may not be used in expressions. Mutation expressions are detailed in Section 6.6, “Updating Data: The On Update Clause”.
The optional where clause contains a criteria_expression that identifies rows to be updated.
The example code snippet updates those rows of the named window that have a negative value for volume:
String query = "update OrdersNamedWindow set volume = 0 where volumne = 0"; runtime.getFireAndForgetService().executeQuery(query);
To instruct the runtime to use the initial property value before update, prefix the property name with the literal initial.
Your application can delete rows from a named window or table using fire-and-forget (on-demand, non-continuous) queries as described in Section 16.7, “Execute Fire-and-Forget Queries Using EPFireAndForgetService”.
The syntax for the delete clause is as follows:
delete from window_or_table_name [as stream_name] [where criteria_expression]
The window_or_table_name is the name of the named window or table to delete rows from.
The as keyword is also available to assign a name to the named window or table.
The optional where clause contains a criteria_expression that identifies rows to be removed from the named window or table.
The example code snippet deletes from a named window all rows that have a negative value for volume:
String query = "delete from OrdersNamedWindow where volume <= 0"; runtime.getFireAndForgetService().executeQuery(query);
Columns in a named window and table may also hold an event or multiple events. More information on the insert into clause providing event columns is in Section 5.10.5, “Event as a Property”.
A sample declaration for a named window and a table is:
create schema InnerData (value string)
create table ContainerTable (innerdata InnerData)
create window ContainerWindow#time(30) as (innerdataArray InnerData[]) // array of events
The second sample creates a named window that specifies two columns: A column that holds an OrderEvent, and a column by name priceTotal. A matching insert into statement is also part of the sample:
create window OrdersWindow#time(30) as select this, price as priceTotal from OrderEvent
insert into OrdersWindow select order, price * unit as priceTotal from ServiceOrderEvent as order
Note that the this proprerty must exist on the event and must return the event class itself (JavaBean events only). The property type of the additional priceTotal column is the property type of the existing price property.
Event patterns match when an event or multiple events occur that match the pattern's definition. Patterns can also be time-based.
Pattern expressions consist of pattern atoms and pattern operators:
Pattern atoms are the basic building blocks of patterns. Atoms are filter expressions, observers for time-based events and plug-in custom observers that observe external events not under the control of the runtime.
Pattern operators control expression lifecycle and combine atoms logically or temporally.
The below table outlines the different pattern atoms available:
Table 7.1. Pattern Atoms
| Pattern Atom | Example |
|---|---|
| Filter expressions specify an event to look for. | StockTick(symbol='ABC', price > 100) |
| Time-based event observers specify time intervals or time schedules. | timer:interval(10 seconds) timer:at(*, 16, *, *, *) timer:schedule(....) |
| Custom plug-in observers can add pattern language syntax for observing application-specific events. | myapplication:myobserver("http://someResource")
|
There are 4 types of pattern operators:
Operators that control pattern sub-expression repetition:
every,every-distinct,[num]anduntilLogical operators:
and,or,notTemporal operators that operate on event order:
->(followed-by)Guards are where-conditions that control the lifecycle of subexpressions. Examples are
timer:within,timer:withinmaxandwhile-expression. Custom plug-in guards may also be used.
Pattern expressions can be nested arbitrarily deep by including the nested expression(s) in () round parenthesis.
Underlying the pattern matching is a hierarchical finite state machine and behavior tree that allocates, transitions and destroys branch and leaf nodes of state based on arriving events and based on time advancing. A single event or advancing time may cause a reaction in multiple parts of your active pattern state. Patterns are stateful as the runtime maintains pattern state. There is a walkthrough of how a sample pattern behaves in Section 7.7, “Event Pattern Walkthrough”.
This is an example pattern expression that matches on every ServiceMeasurement events in which the
value of the latency event property is over 20 seconds, and on every ServiceMeasurement event in which the
success property is false. Either one or the other condition must be true for this pattern to match.
every spike=ServiceMeasurement(latency>20000) or every error=ServiceMeasurement(success=false)
In the example above, the pattern expression or operator indicates that the pattern should fire when either of the
filter expressions fire. The every operator indicates to fire for every matching event and not just the first
matching event.
The left hand of the or operator filters for events with a high latency value.
The right hand of the or operator filters for events with error status.
Filter expressions are explained in Section 7.4, “Filter Expressions in Patterns”.
The example above assigned the tags spike and error to the events in the pattern. The tags are important since the
runtime only places tagged events into the output event(s) that a pattern generates, and that the runtime supplies to listeners of the pattern statement. The tags can
further be selected in the select-clause of a statement as discussed in Section 5.4.2, “Pattern-Based Event Streams”.
Patterns can also contain comments within the pattern as outlined in Section 5.2.2, “Using Comments”.
A pattern may appear anywhere in the from clause of a statement including joins and subqueries. Patterns may therefore be used in combination with the where clause, group by clause, having clause as well as output rate limiting and insert into.
In addition, you may use data window with a pattern. A data window declared for a pattern only serves to retain pattern matches, for use in joins or for iterating via the iterator API. A data window declared onto a pattern does not limit, cancel, remove or delete intermediate pattern matches of the pattern when pattern matches leave the data window.
This example statement demonstrates the idea by selecting a total price per customer over pairs of events (ServiceOrder followed by a ProductOrder event for the same customer id within 1 minute), occurring in the last 2 hours, in which the sum of price is greater than 100, and using a where clause to filter on name:
select a.custId, sum(a.price + b.price)
from pattern [every a=ServiceOrder ->
b=ProductOrder(custId = a.custId) where timer:within(1 min)]#time(2 hour)
where a.name in ('Repair', b.name)
group by a.custId
having sum(a.price + b.price) > 100
When a pattern fires it publishes one or more events to any listeners to the pattern statement.
The listener interface is the com.espertech.esper.runtime.client.UpdateListener interface.
The example below shows an anonymous implementation of the UpdateListener interface.
The example adds the anonymous listener implementation to the myPattern statement created earlier.
The listener code simply extracts the underlying event class.
myPattern.addListener(new UpdateListener() {
public void update(EventBean[] newEvents, EventBean[] oldEvents, EPStatement statement, EPRuntime runtime) {
ServiceMeasurement spike = (ServiceMeasurement) newEvents[0].get("spike");
ServiceMeasurement error = (ServiceMeasurement) newEvents[0].get("error");
... // either spike or error can be null, depending on which occurred
... // add more logic here
}
});
Listeners receive an array of EventBean instances in the newEvents parameter.
There is one EventBean instance passed to the listener for each combination of events that matches
the pattern expression. At least one EventBean instance is always passed to the listener.
The properties of each EventBean instance contain the underlying events that caused the
pattern to fire, if events have been named in the filter expression via the name=eventType syntax.
The property name is thus the name supplied in the pattern expression, while the property type is the type of the underlying class,
in this example ServiceMeasurement.
Data can also be obtained from pattern statements via the safeIterator() and iterator() methods on EPStatement (the pull API)
If the pattern had fired at least once and the @IterableUnbound annotation is declared for the statement, then the iterator returns the last event for which it fired.
The hasNext() method can then be used to determine if the pattern had fired.
if (myPattern.iterator().hasNext()) {
ServiceMeasurement event = (ServiceMeasurement) statement.iterator().next().get("alert");
... // some more code here to process the event
}
else {
... // no matching events at this time
}Further, if a data window is defined onto a pattern, the iterator returns the pattern matches according to the data window expiry policy.
This pattern specifies a length window of 10 elements that retains the last 10 matches of A and B events, for use via iterator or for use in a join or subquery:
select * from pattern [every (A or B)]#length(10)
While the pattern compiler analyzes your pattern and verifies its integrity, it may not detect certain pattern errors that may occur at runtime. Sections of this pattern documentation point out common cases where the pattern runtime will log a runtime error. We recommend turning on the log warning level at project development time to inspect and report on warnings logged. If a statement name is assigned to a statement then the statement name is logged as well.
Any given event can contribute to multiple matches.
For example, consider the following pattern:
every a=A -> B
Given this sequence of events:
A1 A2 B1
When event B1 arrives the pattern matches for both the combination {A1, B1} and the combination {A2, B1}. The runtime indicates both matches to the listener or subscriber by delivering an array containing both matches in a single listener or subscriber invocation.
Use the @SuppressOverlappingMatches pattern-level annotation to instruct the runtime to discard all but the first match among multiple overlapping matches.
The same example with the pattern-level annotation is:
select * from pattern @SuppressOverlappingMatches [every a=A -> b=B]
When event B1 arrives the pattern outputs only the first combination that matches, namely the combination {A1, B1}. The runtime discards the second combination ({A2, B1}) that matches as it detects that event B1 overlaps between the first and the second match.
Note
- The runtime only considers tagged events for detecting overlap.
- Suppression takes place among multiple simultaneously occurring matches as a result of a single event arriving or time advancing.
- Partially completed patterns are not impacted and existing pattern state does not change as a result of suppression.
- Limitation: The annotation cannot be used with patterns in joins.
Partially-completed patterns are incomplete matches that are not yet indicated by the runtime because the complete pattern condition is not satisfied. Any given event can be part of multiple partially-completed patterns.
For example, consider the following pattern:
every a=A -> B and C(id=a.id)
Given this sequence of events:
A1{id='id1'} A2{id='id2'} B1
According to the sequence above there are no matches. The pattern is partially completed waiting for C events. The combination {A1, B1} is waiting for a C{id='id1'} event before the pattern match is complete for that combination. The combination {A2, B1} is waiting for a C{id='id2'} event before the pattern match is complete for that combination.
Assuming event C1{id='id1') arrives the pattern outputs the combination {A1, B1, C1}. Assuming event C2{id='id2') arrives the pattern outputs the combination {A2, B1, C2}. Note that event B1 is part of both partially-completed patterns.
Use the @DiscardPartialsOnMatch pattern-level annotation to instruct the runtime that when any matches occur to discard partially completed patterns that overlap in terms of the events that
make up the match (or matches if there are multiple matches).
The same example using the @DiscardPartialsOnMatch pattern-level annotation is:
select * from pattern @DiscardPartialsOnMatch [every a=A -> B and C(id=a.id)]
When event C1{id='id1') arrives the pattern outputs the match combination {A1, B1, C1}. Upon indication of the match the runtime discards all partially-completed patterns that refer to either of the A1, B1 and C1 events. Since event B1 is part of a partially-completed pattern waiting for C{id='id2'}, the runtime discards that partially-completed pattern. Therefore when C2{id='id2'} arrives the runtime outputs no matches.
When specifying both @DiscardPartialsOnMatch and @SuppressOverlappingMatches the runtime discards the partially-completed patterns that overlap all matches including suppressed matches.
Note
- The runtime only considers tagged events for detecting overlap.
- Only partially completed patterns are impacted.
- Limitation: The annotation cannot be used with patterns in joins.
- Limitation: Removing partially completed patterns is not an undo operation.
There is no reversal in truth-value, i.e. past matches are not retracted or indicated as a remove stream.
The
notoperator can change truth value to permanently false. The change in truth-value does not get reversed when a match removes the event that caused thenotoperator to become permanently false.
The operators at the top of this table take precedence over operators lower on the table.
Table 7.2. Pattern Operator Precedence
| Precedence | Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | guard postfix | where timer:within and while (expression) (incl. withinmax and plug-in pattern guard) | MyEvent where timer:within(1 sec) a=MyEvent while (a.price between 1 and 10) |
| 2 | unary | every, not, every-distinct | every MyEvent timer:interval(5 min) and not MyEvent |
| 3 | repeat | [num], until | [5] MyEvent [1..3] MyEvent until MyOtherEvent |
| 4 | and | and | every (MyEvent and MyOtherEvent) |
| 5 | or | or | every (MyEvent or MyOtherEvent) |
| 6 | followed-by | -> | every (MyEvent -> MyOtherEvent) |
If you are not sure about the precedence, please consider placing parenthesis () around your subexpressions. Parenthesis can also help make
expressions easier to read and understand.
The following table outlines sample equivalent expressions, with and without the use of parenthesis for subexpressions.
Table 7.3. Equivalent Pattern Expressions
| Expression | Equivalent | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| every A or B | (every A) or B | The every operator has higher precedence then the or operator. |
| every A -> B or C | (every A) -> (B or C) | The or operator has higher precedence then the followed-by operator. |
| A -> B or B -> A | A -> (B or B) -> A | The or operator has higher precedence then the followed-by operator,
specify as (A -> B) or (B -> A) instead.
|
| A and B or C | (A and B) or C | The and operator has higher precedence then the or operator. |
| A -> B until C -> D | A -> (B until C) -> D | The until operator has higher precedence then the followed-by operator. |
| [5] A or B | ([5] A) or B | The [num] repeat operator has higher precedence then the or operator. |
| every A where timer:within(10) | every (A where timer:within(10)) | The where postfix has higher precedence then the every operator. |
The simplest form of filter is a filter for events of a given type without any conditions on the event property values. This filter matches any event of that type regardless of the event's properties. The example below is such a filter. Note that this event pattern would stop firing as soon as the first RfidEvent is encountered.
com.mypackage.myevents.RfidEvent
To make the event pattern fire for every RfidEvent and not just the first event, use the every keyword.
every com.mypackage.myevents.RfidEvent
The example above specifies the fully-qualified Java class name as the event type. Via configuration, the event pattern above can be simplified by using the name that has been defined for the event type.
every RfidEvent
Interfaces and superclasses are also supported as event types. In the below example IRfidReadable is an interface class, and the statement matches any event that implements this interface:
every org.myorg.rfid.IRfidReadable
The filtering criteria to filter for events with certain event property values are placed within parenthesis after the event type name:
RfidEvent(category="Perishable")
All expressions can be used in filters, including static method invocations that return a boolean value:
RfidEvent(com.mycompany.MyRFIDLib.isInRange(x, y) or (x<0 and y < 0))
Filter expressions can be separated via a single comma ','. The comma represents a logical AND between expressions:
RfidEvent(zone=1, category=10) ...is equivalent to... RfidEvent(zone=1 and category=10)
For more information on filters please see Section 5.4.1, “Filter-Based Event Streams”. Contained-event selection on filters in patterns is further described in Section 5.19, “Contained-Event Selection”.
Filter criteria can also refer to events matching prior named events in the same expression. Below pattern is an example in which the pattern matches once for every RfidEvent that is preceded by an RfidEvent with the same asset id.
every e1=RfidEvent -> e2=RfidEvent(assetId=e1.assetId)
The syntax shown above allows filter criteria to reference prior results by specifying the event name tag of the prior event, and the event property name. The tag names in the above example were e1 and e2. This syntax can be used in all filter operators or expressions including ranges and the in set-of-values check:
every e1=RfidEvent -> e2=RfidEvent(MyLib.isInRadius(e1.x, e1.y, x, y) and zone in (1, e1.zone))
An arriving event changes the truth value of all expressions that look for the event. Consider the pattern as follows:
every (RfidEvent(zone > 1) and RfidEvent(zone < 10))
The pattern above is satisfied as soon as only one event with zone in the interval [2, 9] is received.
Important
A detailed description of how filters become active and are indexed is provided at Section 2.18.2.2, “Filter Index Pattern Example”.
An expression such as a=A -> B(id=a.id) (A followed-by B with the same id as A) is not just a state change, in fact the runtime registers new B-filter instances dynamically and in runtime-wide shared filter indexes.
This means that while such a pattern seems to be slow if you are sending A-events, the runtime can filter, match or discard B-events very fast as for B-events it only needs to perform a lookup in filter indexes.
If you are looking for best performance and don't expect to need filter indexes, or if you compare to another technology that doesn't have the concept of filter indexes, please use match-recognize instead.
The runtime analyzes all filter expressions within a pattern and determines the filter indexes to use or to create. Indexing filter values to match event properties of incoming events enables the runtime to match incoming events faster to pattern subexpressions.
More information on filter indexes in general can be found at Section 2.18.2, “Filter Indexes”.
More information on the operators relevant to filter indexes can be found at Section 5.4.1.2, “Specifying Filter Criteria”.
An arriving event applies to all filter expressions for which the event matches. In other words, an arriving event is not consumed by any specify filter expression(s) but applies to all active filter expressions of all pattern sub-expressions.
You may provide the @consume annotation as part of a filter expression to control consumption of an arriving event. If an arriving event matches the filter expression marked with @consume it
is no longer available to other filter expressions of the same pattern that also match the arriving event.
The @consume can include a level number in parenthesis. A higher level number consumes the event first. The default level number is 1. Multiple filter expressions with the same level number for @consume all match the event.
Consider the next sample pattern:
a=RfidEvent(zone='Z1') and b=RfidEvent(assetId='0001')
This pattern fires when a single RfidEvent event arrives that has zone 'Z1' and assetId '0001'. The pattern also matches when two RfidEvent events arrive, in any order, wherein one has zone 'Z1' and the other has assetId '0001'.
Mark a filter expression with @consume to indicate that if an arriving event matches multiple filter expressions that the runtime prefers the marked filter expression and does not match any other filter expression.
This updated pattern statement uses @consume to indicate that a match against zone is preferred:
a=RfidEvent(zone='Z1')@consume and b=RfidEvent(assetId='0001')
This pattern no longer fires when a single RfidEvent arrives that has zone 'Z1' and assetId '0001', because when the first filter expression matches the pattern runtime consumes the event. The pattern only matches when two RfidEvent events arrive in any order. One event must have zone 'Z1' and the other event must have a zone other than 'Z1' and an assetId '0001'.
The next sample pattern provides a level number for each @consume:
a=RfidEvent(zone='Z1')@consume(2) or b=RfidEvent(assetId='0001')@consume(1) or c=RfidEvent(category='perishable'))
The pattern fires when an RfidEvent arrives with zone 'Z1'. In this case the output event populates property 'a' but not properties 'b' and 'c'. The pattern also fires when an RfidEvent arrives with a zone other than 'Z1' and an asset id of '0001'. In this case the output event populates property 'b' but not properties 'a' and 'c'. The pattern also fires when an RfidEvent arrives with a zone other than 'Z1' and an asset id other than '0001' and a category of 'perishable'. In this case the output event populates property 'c' but not properties 'a' and 'b'.
When your filter expression provides the name of a named window then the filter expression matches each time an event is inserted into the named window that matches the filter conditions.
For example, assume a named window that holds the last order event per order id:
create window LastOrderWindow#unique(orderId) as OrderEvent
Assume that all order events are inserted into the named window using insert-into:
insert into LastOrderWindow select * from OrderEvent
This sample pattern fires 10 seconds after an order event with a price greater then 100 was inserted:
select * from pattern [every o=LastOrderWindow(price >= 100) -> timer:interval(10 sec)]
The pattern above fires only for events inserted-into the LastOrderWindow named window and does not fire when an order event was updated using on-update or merged using on-merge.
If your application would like to have the pattern fire for any change to the named window events including updates and merges, you must select from the named window as follows:
insert into OrderWindowChangeStream select * from LastOrderWindow
select * from pattern [every o=OrderWindowChangeStream(price >= 100) -> timer:interval(10 sec)]
A table cannot be listed as part of a pattern filter, however any filter EPL expressions can have tables access expressions and subqueries against tables.
Assuming that MyTable is a table, the following is not allowed:
// not allowed select * from pattern [every MyTable -> timer:interval(10 sec)]
The every operator indicates that the pattern sub-expression should restart when the subexpression qualified by the every keyword evaluates to true or false.
Without the every operator the pattern sub-expression stops when the pattern sub-expression evaluates to true or false.
As a side note, please be aware that a single invocation to the UpdateListener interface may deliver multiple events in one invocation, since the interface accepts an array of values.
Thus the every operator works like a factory for the pattern sub-expression contained within. When the pattern sub-expression within it fires and thus quits checking for events, the every causes the start of a new pattern sub-expression listening for more occurrences of the same
event or set of events.
Every time a pattern sub-expression within an every operator turns true the runtime starts a new active subexpression looking
for more event(s) or timing conditions that match the pattern sub-expression. If the every operator is not specified for a subexpression,
the subexpression stops after the first match was found.
This pattern fires when encountering an A event and then stops looking.
A
This pattern keeps firing when encountering A events, and doesn't stop looking.
every A
When using every operator with the -> followed-by operator, each time the every operator restarts it also starts a new subexpression instance looking for events in the followed-by subexpression.
Let's consider an example event sequence as follows.
A1 B1 C1 B2 A2 D1 A3 B3 E1 A4 F1 B4
Table 7.4. Every Operator Examples
| Example | Description |
|---|---|
every ( A -> B ) |
Detect an A event followed by a B event. At the time when B occurs the pattern matches, then the pattern matcher restarts and looks for the next A event.
|
every A -> B |
The pattern fires for every A event followed by a B event.
|
A -> every B |
The pattern fires for an A event followed by every B event.
|
every A -> every B |
The pattern fires for every A event followed by every B event.
|
The examples show that it is possible that a pattern fires for multiple combinations of events that match a pattern expression.
Each combination is posted as an EventBean instance to the update method in the UpdateListener implementation.
Let's consider the every operator in conjunction with a subexpression that matches 3 events that follow each other:
every (A -> B -> C)
The pattern first looks for A events. When an A event arrives, it looks for a B event. After the B event arrives, the pattern looks for a C event. Finally, when the C event arrives the pattern fires. The runtime then starts looking for an A event again.
Assume that between the B event and the C event a second A2 event arrives. The pattern would ignore the A2 event entirely since it's then looking for a C event.
As observed in the prior example, the every operator restarts the subexpression A -> B -> C only when the subexpression fires.
In the next statement the every operator applies only to the A event, not the whole subexpression:
every A -> B -> C
This pattern now matches for each A event that is followed by a B event and then a C event, regardless of when the A event arrives. Note that for each A event that arrives the pattern runtime starts a new subexpression looking for a B event and then a C event, outputting each combination of matching events.
A pattern that only has the every operator and a single filter expression is equivalent to selecting the same filter in the from clause:
select * from StockTickEvent(symbol='GE') // Prefer this // ... equivalent to ... select * from pattern[every StockTickEvent(symbol='GE')]
As the introduction of the every operator states, the operator starts new subexpression instances and can cause multiple matches to occur for a single arriving event.
New subexpressions also take a very small amount of system resources and thereby your application should carefully consider when subexpressions must end when designing patterns. Use the timer:within construct and the and not constructs to end active subexpressions. The data window onto a pattern stream does not serve to limit pattern sub-expression lifetime.
Lets look at a concrete example. Consider the following sequence of events arriving:
A1 A2 B1
This pattern matches on arrival of B1 and outputs two events (an array of length 2 if using a listener). The two events are the combinations {A1, B1} and {A2, B1}:
every a=A -> b=B
The and not operators are used to end an active subexpression.
The next pattern matches on arrival of B1 and outputs only the last A event which is the combination {A2, B1}:
every a=A -> (b=B and not A)
The and not operators cause the subexpression looking for {A1, B?} to end when A2 arrives.
Similarly, in the pattern below the runtime starts a new subexpression looking for a B event every 1 second. After 5 seconds there are 5 subexpressions active looking for a B event and 5 matches occur at once if a B event arrives after 5 seconds.
every timer:interval(1 sec) -> b=B
Again the and not operators can end subexpressions that are not intended to match any longer:
every timer:interval(1 sec) -> (b=B and not timer:interval(1 sec)) // equivalent to every timer:interval(1 sec) -> (b=B where timer:within(1 sec))
This example considers a generic pattern in which the pattern must match for each A event followed by a B event and followed by a C event, in which both the B event and the C event must arrive within 1 hour of the A event. The first approach to the pattern is as follows:
every A -> (B -> C) where timer:within(1 hour)
Consider the following sequence of events arriving:
A1 A2 B1 C1 B2 C2
First, the pattern as above never stops looking for A events since the every operator instructs the pattern to keep looking for A events.
When A1 arrives, the pattern starts a new subexpression that keeps A1 in memory and looks for any B event. At the same time, it also keeps looking for more A events.
When A2 arrives, the pattern starts a new subexpression that keeps A2 in memory and looks for any B event. At the same time, it also keeps looking for more A events.
After the arrival of A2, there are 3 subexpressions active:
The first active subexpression with A1 in memory, looking for any B event.
The second active subexpression with A2 in memory, looking for any B event.
A third active subexpression, looking for the next A event.
In the pattern above, there is a 1-hour lifetime for subexpressions looking for B and C events. Thus, if no B and no C event arrive within 1 hour after A1, the first subexpression goes away. If no B and no C event arrive within 1 hour after A2, the second subexpression goes away. The third subexpression however stays around looking for more A events.
The pattern as shown above thus matches on arrival of C1 for combination {A1, B1, C1} and for combination {A2, B1, C1}, provided that B1 and C1 arrive within an hour of A1 and A2.
You may now ask how to match on {A1, B1, C1} and {A2, B2, C2} instead, since you may need to correlate on a given property.
The pattern as discussed above matches every A event followed by the first B event followed by the next C event, and doesn't specifically qualify the B or C events to look for based on the A event. To look for specific B and C events in relation to a given A event, specify correlating properties of the A event, for example:
every a=A -> (B(id=a.id) -> C(id=a.id)) where timer:within(1 hour)
The pattern as shown above thus matches on arrival of C1 for combination {A1, B1, C1} and on arrival of C2 for combination {A2, B2, C2}.
This example looks at temperature sensor events named Sample. The pattern detects when 3 sensor events indicate a temperature of more then 50 degrees uninterrupted within 90 seconds of the first event, considering events for the same sensor only.
every sample=Sample(temp > 50) -> ( (Sample(sensor=sample.sensor, temp > 50) and not Sample(sensor=sample.sensor, temp <= 50)) -> (Sample(sensor=sample.sensor, temp > 50) and not Sample(sensor=sample.sensor, temp <= 50)) ) where timer:within(90 seconds))
The pattern starts a new subexpression in the round braces after the first followed-by operator for each time a sensor indicated more then 50 degrees. Each subexpression then lives a maximum of 90 seconds. Each subexpression ends if a temperature of 50 degress or less is encountered for the same sensor. Only if 3 temperature events in a row indicate more then 50 degrees, and within 90 seconds of the first event, and for the same sensor, does this pattern fire.
Similar to the every operator in most aspects, the every-distinct operator indicates that the pattern sub-expression should restart when the subexpression qualified by the every-distinct keyword evaluates to true or false. In addition, the every-distinct eliminates duplicate results received from an active subexpression according to its distinct-value expressions.
The synopsis for the every-distinct pattern operator is:
every-distinct(distinct_value_expr [, distinct_value_exp[...][, expiry_time_period])
Within parenthesis are one or more distinct_value_expr expressions that return the values by which to remove duplicates. Further detail on key expressions can be found at Section 5.2.13, “Composite Keys and Array Values as Keys”.
You may optionally specify an expiry_time_period time period. If present, the pattern runtime expires and removes distinct key values that are older then the time period, removing their associated memory and allowing such distinct values to match again. When your distinct value expressions return an unlimited number of values, for example when your distinct value is a timestamp or auto-increment column, you should always specify an expiry time period.
When specifying properties in the distinct-value expression list, you must ensure that the event types providing properties are tagged. Only properties of event types within filter expressions that are sub-expressions to the every-distinct may be specified.
For example, this pattern keeps firing for every A event with a distinct value for its aprop property:
every-distinct(a.aprop) a=A
Note that the pattern above assigns the a tag to the A event and uses a.prop to identify the prop property as a value of the a event A.
A pattern that returns the first Sample event for each sensor, assuming sensor is a field that returns a unique id identifying the sensor that originated the Sample event, is:
every-distinct(s.sensor) s=Sample
The next pattern looks for pairs of A and B events and returns only the first pair for each combination of aprop of an A event and bprop of a B event:
every-distinct(a.aprop, b.bprop) (a=A and b=B)
The following pattern looks for A events followed by B events for which the value of the aprop of an A event is the same value of the bprop of a B event but only for each distinct value of aprop of an A event:
every-distinct(a.aprop) a=A -> b=B(bprop = a.aprop)
When specifying properties as part of distinct-value expressions, properties must be available from tagged event types in sub-expressions to the every-distinct.
The following patterns are not valid:
// Invalid: event type in filter not tagged every-distinct(aprop) A // Invalid: property not from a sub-expression of every-distinct a=A -> every-distinct(a.aprop) b=B
When an active subexpression to every-distinct becomes permanently false, the distinct-values seen from the active subexpression are removed and the sub-expression within is restarted.
For example, the below pattern detects each A event distinct by the value of aprop.
every-distinct(a.aprop) (a=A and not B)
In the pattern above, when a B event arrives, the subexpression becomes permanently false and is restarted anew, detecting each A event distinct by the value of aprop without considering prior values.
When your distinct key is a timestamp or other non-unique property, specify an expiry time period.
The following example returns every distinct A event according to the timestamp property on the A event, retaining each timestamp value for 10 seconds:
every-distinct(a.timestamp, 10 seconds) a=A
In the example above, if for a given A event and its timestamp value the same timestamp value occurs again for another A event before 10 seconds passed, the A event is not a match. If 10 seconds passed the pattern indicates a second match.
You may not use every-distinct with a timer-within guard to expire keys: The expiry time notation as above is the recommended means to expire keys.
// This is not the same as above; It does not expire transaction ids and is not recommended every-distinct(a.timestamp) a=A where timer:within(10 sec)
The repeat operator fires when a pattern sub-expression evaluates to true a given number of times. The synopsis is as follows:
[match_count] repeating_subexpr
The repeat operator is very similar to the every operator in that it restarts the repeating_subexpr pattern sub-expression up to a given number of times.
match_count is a positive number that specifies how often the repeating_subexpr pattern sub-expression must evaluate to true before the repeat expression itself evaluates to true, after which the runtime may indicate a match.
For example, this pattern fires when the last of five A events arrives:
[5] A
Parenthesis must be used for nested pattern sub-expressions. This pattern fires when the last of a total of any five A or B events arrives:
[5] (A or B)
Without parenthesis the pattern semantics change, according to the operator precedence described earlier. This pattern fires when the last of a total of five A events arrives or a single B event arrives, whichever happens first:
[5] A or B
Tags can be used to name events in filter expression of pattern sub-expressions. The next pattern looks for an A event followed by a B event, and a second A event followed by a second B event. The output event provides indexed and array properties of the same name:
[2] (a=A -> b=B)
Using tags with repeat is further described in Section 7.5.4.6, “Tags and the Repeat Operator”.
Consider the following pattern that demonstrates the behavior when a pattern sub-expression becomes permanently false:
[2] (a=A and not C)
In the case where a C event arrives before 2 A events arrive, the pattern above becomes permanently false.
Lets add an every operator to restart the pattern and thus keep matching for all pairs of A events that arrive without a C event in between each pair:
every [2] (a=A and not C)
Since pattern matches return multiple A events, your select clause should use tag a as an array, for example:
select a[0].id, a[1].id from pattern [every [2] (a=A and not C)]
The repeat until operator provides additional control over repeated matching.
The repeat until operator takes an optional range, a pattern sub-expression to repeat, the until keyword and a second pattern sub-expression that ends the repetition. The synopsis is as follows:
[range] repeated_pattern_expr until end_pattern_expr
Without a range, the runtime matches the repeated_pattern_expr pattern sub-expression until the end_pattern_expr evaluates to true, at which time the expression turns true.
An optional range can be used to indicate the minimum number of times that the repeated_pattern_expr pattern sub-expression must become true.
The optional range can also specify a maximum number of times that repeated_pattern_expr pattern sub-expression evaluates to true and retains tagged events. When this number is reached, the runtime stops the repeated_pattern_expr pattern sub-expression.
The until keyword is always required when specifying a range and is not required if specifying a fixed number of repeat as discussed in the section before.
In the unbound repeat, without a range, the runtime matches the repeated_pattern_expr pattern sub-expression until the end_pattern_expr evaluates to true, at which time the expression turns true. The synopsis is:
repeated_pattern_expr until end_pattern_expr
This is a pattern that keeps looking for A events until a B event arrives:
A until B
Nested pattern sub-expressions must be placed in parenthesis since the until operator has precedence over most operators. This example collects all A or B events for 10 seconds and places events received in indexed properties 'a' and 'b':
(a=A or b=B) until timer:interval(10 sec)
The synopsis for the optional range qualifier is:
[ [low_endpoint] : [high_endpoint] ]
low_endpoint is an optional number that appears on the left of a colon (:), after which follows an optional high_endpoint number.
A range thus consists of a low_endpoint and a high_endpoint in square brackets and separated by a colon (:) characters. Both endpoint values are optional but either one or both must be supplied. The low_endpoint can be omitted to denote a range that starts at zero. The high_endpoint can be omitted to denote an open-ended range.
Some examples for valid ranges might be:
[3 : 10] [:3] // range starts at zero [2:] // open-ended range
The low_endpoint, if specified, defines the minimum number of times that the repeated_pattern_expr pattern sub-expression must become true in order for the expression to become true.
The high_endpoint, if specified, is the maximum number of times that the repeated_pattern_expr pattern sub-expression becomes true. If the number is reached, the runtime stops the repeated_pattern_expr pattern sub-expression.
In all cases, only at the time that the end_pattern_expr pattern sub-expression evaluates to true does the expression become true. If end_pattern_expr pattern sub-expression evaluates to false, then the expression evaluates to false.
An open-ended range specifies only a low endpoint and not a high endpoint.
Consider the following pattern which requires at least three A events to match:
[3:] A until B
In the pattern above, if a B event arrives before 3 A events occurred, the expression ends and evaluates to false.
A high-endpoint range specifies only a high endpoint and not a low endpoint.
In this sample pattern the runtime will be looking for a maximum of 3 A events. The expression turns true as soon as a single B event arrives regardless of the number of A events received:
[:3] A until B
The next pattern matches when a C or D event arrives, regardless of the number of A or B events that occurred:
[:3] (a=A or b=B) until (c=C or d=D)
In the pattern above, if more then 3 A or B events arrive, the pattern stops looking for additional A or B events. The 'a' and 'b' tags retain only the first 3 (combined) matches among A and B events. The output event contains these tagged events as indexed properties.
A bounded range specifies a low endpoint and a high endpoint.
The next pattern matches after at least one A event arrives upon the arrival of a single B event:
[1:3] a=A until B
If a B event arrives before the first A event, then the pattern does not match. Only the first 3 A events are returned by the pattern.
The tags assigned to events in filter subexpressions within a repeat operator are available for use in filter expressions and also in any EPL clause.
This sample pattern matches 2 A events followed by a B event. Note the filter on B events: only a B event that has a value for the "beta" property that equals any of the "id" property values of the two A events is considered:
[2] A -> B(beta in (a[0].id, a[1].id))
The next statement returns pairs of A events:
select a, a[0], a[0].id, a[1], a[1].id from pattern [ every [2] a=A ]
The select clause of the statement above showcases different ways of accessing tagged events:
The tag itself can be used to select an array of underlying events. For example, the 'a' expression above returns an array of underlying events of event type A.
The tag as an indexed property returns the underlying event at that index. For instance, the 'a[0]' expression returns the first underlying A event, or null if no such A event was matched by the repeat operator.
The tag as a nested, indexed property returns a property of the underlying event at that index. For example, the 'a[1].id' expression returns the 'id' property value of the second A event, or null if no such second A event was matched by the repeat operator.
You may not use indexed tags defined in the sub-expression to the repeat operator in the same subexpression. For example, in the following pattern the subexpression to the repeat operator is (a=A() -> b=B(id=a[0].id)) and the tag a cannot be used in its indexed form in the filter for event B:
// invalid every [2] (a=A() -> b=B(id=a[0].id))
You can use tags without an index:
// valid every [2] (a=A() -> b=B(id=a.id))
Similar to the Java && operator the and operator requires both nested pattern expressions to turn
true before the whole expression turns true (a join pattern).
This pattern matches when both an A event and a B event arrive, at the time the last of the two events arrive:
A and B
This pattern matches on any sequence of an A event followed by a B event and then a C event followed by a D event, or a C event followed by a D and an A event followed by a B event:
(A -> B) and (C -> D)
Note that in an and pattern expression it is not possible to correlate events based on event property values. For example, this is an invalid pattern:
// This is NOT valid a=A and B(id = a.id)
The above expression is invalid as it relies on the order of arrival of events, however in an and expression the order of events is not specified and events fulfill an and condition in any order. The above expression can be changed to use the followed-by operator:
// This is valid a=A -> B(id = a.id) // another example using 'and'... a=A -> (B(id = a.id) and C(id = a.id))
Consider a pattern that looks for the same event:
A and A
The pattern above fires when a single A event arrives. The first arriving A event triggers a state transition in both the left and the right hand side expression.
In order to match after two A events arrive in any order, there are two options to express this pattern. The followed-by operator is one option and the repeat operator is the second option, as the next two patterns show:
A -> A // ... or ... [2] A
Similar to the Java “||” operator the or operator requires either one of the expressions
to turn true before the whole expression turns true.
Look for either an A event or a B event. As always, A and B can itself be nested expressions as well.
A or B
The next EPL outputs all A and B events:
every A or every B
Elaborating further, the expression every A or every B is equivalent to every (A or B).
Prefer every A or every B as the every keyword lets the runtime know that filters for A and B can remain active.
Consider the expression every A or every timer:interval(10 sec) which is not equivalent to every (A or timer:interval(10 sec)).
This is because in the latter expression when an A event arrives the interval restarts.
The not operator negates the truth value of an expression. Pattern expressions prefixed with not are automatically
defaulted to true upon start, and turn permanently false when the expression within turns true.
The not operator is generally used in conjunction with the and operator or subexpressions as the below examples show.
This pattern matches only when an A event is encountered followed by a B event but only if no C event was encountered before either an A event and a B event, counting from the time the pattern is started:
(A -> B) and not C
Assume we'd like to detect when an A event is followed by a D event, without any B or C events between the A and D events:
A -> (D and not (B or C))
It may help your understanding to discuss a pattern that uses the or operator and the not operator together:
a=A -> (b=B or not C)
In the pattern above, when an A event arrives then the runtime starts the subexpression B or not C. As soon as the subexpression starts, the not operator turns to true. The or expression turns true and thus your listener receives an invocation providing the A event in the property 'a'. The subexpression does not end and continues listening for B and C events. Upon arrival of a B event your listener receives a second invocation. If instead a C event arrives, the not turns permanently false however that does not affect the or operator (but would end an and operator).
To test for absence of an event, use timer:interval together with and not operators. The sample statement reports each 10-second interval during which no A event occurred:
every (timer:interval(10 sec) and not A)
In many cases the not operator, when used alone, does not make sense. The following example is invalid and will log a warning when the runtime is started:
// not a sensible pattern (not a=A) -> B(id=a.id)
The followed by -> operator specifies that first the left hand expression must turn true and only
then is the right hand expression evaluated for matching events.
Look for an A event and if encountered, look for a B event. As always, A and B can itself be nested event pattern expressions.
A -> B
This is a pattern that fires when 2 status events indicating an error occur one after the other.
StatusEvent(status='ERROR') -> StatusEvent(status='ERROR')
A pattern that takes all A events that are not followed by a B event within 5 minutes:
every A -> (timer:interval(5 min) and not B)
A pattern that takes all A events that are not preceded by B within 5 minutes:
every (timer:interval(5 min) and not B -> A)
The followed-by -> operator can optionally be provided with an expression that limits the number of sub-expression instances of the right-hand side pattern sub-expression.
The synopsis for the followed-by operator with limiting expression is:
lhs_expression -[limit_expression]> rhs_expression
Each time the lhs_expression pattern sub-expression turns true the pattern runtime starts a new rhs_expression pattern sub-expression. The limit_expression returns an integer value that defines a maximum number of pattern sub-expression instances that can simultaneously be present for the same rhs_expression.
When the limit is reached the pattern runtime issues a com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.condition.ConditionPatternSubexpressionMax notification object to any condition handlers registered with the runtime as described in Section 16.11, “Condition Handling” and does not start a new pattern sub-expression instance for the right-hand side pattern sub-expression.
For example, consider the following pattern which returns for every A event the first B event that matches the id field value of the A event:
every a=A -> b=B(id = a.id)
In the above pattern, every time an A event arrives (lhs) the pattern runtime starts a new pattern sub-expression (rhs) consisting of a filter for the first B event that has the same value for the id field as the A event.
In some cases your application may want to limit the number of right-hand side sub-expressions because of memory concerns or to reduce output. You may add a limit expression returning an integer value as part of the operator.
This example employs the followed-by operator with a limit expression to indicate that maximally 2 filters for B events (the right-hand side pattern sub-expression) may be active at the same time:
every a=A -[2]> b=B(id = a.id)
Note that the limit expression in the example above is not a limit per value of id field, but a limit counting all right-hand side pattern sub-expression instances that are managed by that followed-by sub-expression instance.
If your followed-by operator lists multiple sub-expressions with limits, each limit applies to the immediate right-hand side. For example, the pattern below limits the number of filters for B events to 2 and the number of filters for C events to 3:
every a=A -[2]> b=B(id = a.id) -[3]> c=C(id = a.id)
The runtime allows setting a maximum number of pattern sub-expressions in the configuration, applicable to all followed-by operators of all statements.
If your application has patterns in multiple statements and all such patterns should count towards a total number of pattern sub-expression counts, you may consider setting a maximum number of pattern sub-expression instances, runtime-wide, via the configuration described in Section 17.6.4.1, “Followed-By Operator Maximum Subexpression Count”.
When the limit is reached the pattern runtime issues a notification object to any condition handlers registered with the runtime as described in Section 16.11, “Condition Handling”. Depending on your configuration the runtime can prevent the start of a new pattern sub-expression instance for the right-hand side pattern sub-expression, until pattern sub-expression instances end or statements are undeployed.
The notification object issued to condition handlers is an instance of com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.condition.ConditionPatternRuntimeSubexpressionMax. The notification object contains information which statement triggered the limit and the pattern counts per statement for all statements.
For information on configuration please consult Section 17.6.4.1, “Followed-By Operator Maximum Subexpression Count”.
Guards are where-conditions that control the lifecycle of subexpressions. Custom guard functions can also be used. The section Chapter 22, Integration and Extension outlines guard plug-in development in greater detail.
The pattern guard where-condition has no relationship to the EPL where clause that filters sets of events.
Take as an example the following pattern expression:
MyEvent where timer:within(10 sec)
In this pattern the timer:within guard controls the subexpression that is looking for MyEvent events. The guard terminates the subexpression looking for MyEvent events after 10 seconds after start of the pattern. Thus the pattern alerts only once when the first MyEvent event arrives within 10 seconds after start of the pattern.
The every keyword requires additional discussion since it also controls subexpression lifecycle. Let's add the every keyword to the example pattern:
every MyEvent where timer:within(10 sec)
The difference to the pattern without every is that each MyEvent event that arrives now starts a new subexpression, including a new guard, looking for a further MyEvent event. The result is that, when a MyEvent arrives within 10 seconds after pattern start, the pattern execution will look for the next MyEvent event to arrive within 10 seconds after the previous one.
By placing parentheses around the every keyword and its subexpression, you can have the every under the control of the guard:
(every MyEvent) where timer:within(10 sec)
In the pattern above, the guard terminates the subexpression looking for all MyEvent events after 10 seconds after start of the pattern. This pattern alerts for all MyEvent events arriving within 10 seconds after pattern start, and then stops.
Guards do not change the truth value of the subexpression of which the guard controls the lifecycle, and therefore do not cause a restart of the subexpression when used with the every operator. For example, the next pattern stops returning matches after 10 seconds unless a match occurred within 10 seconds after pattern start:
every ( (A and B) where timer:within(10 sec) )
The timer:within guard acts like a stopwatch.
If the associated pattern expression does not turn true within the specified time period it is stopped and permanently false.
The synopsis for timer:within is as follows:
timer:within(time_period_expression)The time_period_expression is a time period (see Section 5.2.1, “Specifying Time Periods”) or an expression providing a number of seconds as a parameter. The interval expression may contain references to properties of prior events in the same pattern as well as variables and substitution parameters.
This pattern fires if an A event arrives within 5 seconds after statement deployment.
A where timer:within (5 seconds)
This pattern fires for all A events that arrive within 5 seconds. After 5 seconds, this pattern stops matching even if more A events arrive.
(every A) where timer:within (5 seconds)
This pattern matches for any one A or B event in the next 5 seconds.
( A or B ) where timer:within (5 sec)
This pattern matches for any 2 errors that happen 10 seconds within each other.
every (StatusEvent(status='ERROR') -> StatusEvent(status='ERROR') where timer:within (10 sec))
The following guards are equivalent:
timer:within(2 minutes 5 seconds) timer:within(125 sec) timer:within(125)
The timer:withinmax guard is similar to the timer:within guard and acts as a stopwatch that additionally has a counter that counts the number of matches. It ends the subexpression when either the stopwatch ends or the match counter maximum value is reached.
The synopsis for timer:withinmax is as follows:
timer:withinmax(time_period_expression, max_count_expression)
The time_period_expression is a time period (see Section 5.2.1, “Specifying Time Periods”) or an expression providing a number of seconds.
The max_count_expression provides the maximum number of matches before the guard ends the subexpression.
Each parameter expression may also contain references to properties of prior events in the same pattern as well as variables and substitution parameters.
This pattern fires for every A event that arrives within 5 seconds after statement deployment but only up to the first two A events:
(every A) where timer:withinmax (5 seconds, 2)
If the result of the max_count_expression is 1, the guard ends the subexpression after the first match and indicates the first match.
This pattern fires for the first A event that arrives within 5 seconds after statement deployment:
(every A) where timer:withinmax (5 seconds, 1)
If the result of the max_count_expression is zero, the guard ends the subexpression upon the first match and does no indicate any matches.
This example receives every A event followed by every B event (as each B event arrives) until the 5-second subexpression timer ends or X number of B events have arrived (assume X was declared as a variable):
every A -> (every B) where timer:withinmax (5 seconds, X)
The while guard is followed by an expression that the runtime evaluates for every match reported by the guard pattern sub-expression. When the expression returns false the pattern sub-expression ends.
The synopsis for while is as follows:
while (guard_expression)The guard_expression is any expression that returns a boolean true or false. The expression may contain references to properties of prior events in the same pattern as well as variables and substitution parameters.
Each time the subexpression indicates a match, the runtime evaluates guard_expression and if true, passes the match and when false, ends the subexpression.
This pattern fires for every A event until an A event arrives that has a value of zero or less for its size property (assuming A events have an integer size property).
(every a=A) while (a.size > 0)
Note the parenthesis around the every subexpression. They ensure that, following precedence rules, the guard applies to the every operator as well.
The timer:within and timer:withinmax guards may be parameterized by an expression that contains one or more references to properties of prior events in the same pattern.
As a simple example, this pattern matches every A event followed by a B event that arrives within delta seconds after the A event:
every a=A -> b=B where timer:within (a.delta seconds)
Herein A event is assumed to have a delta property that provides the number of seconds to wait for B events. Each arriving A event may have a different value for delta
and the guard is therefore parameterized dynamically based on the prior A event received.
When multiple events accumulate, for example when using the match-until or repeat pattern elements, an index must be provided:
[2] a=A -> b=B where timer:within (a[0].delta + a[1].delta)
The above pattern matches after 2 A events arrive followed by a B event within a time interval after the A event that is defined by the sum of the delta properties of both A events.
You can combine guard expression by using parenthesis around each subexpression.
The below pattern matches for each A event while A events of size greater then zero arrive and only within the first 20 seconds:
((every a=A) while (a.size > 0)) where timer:within(20)
Filter atoms have been described in section Section 7.4, “Filter Expressions in Patterns”.
Observers observe time-based events for which the thread-of-control originates by the runtime timer or external timer event. Custom observers can also be developed that observe timer events or other runtime-external application events such as a file-exists check. The section Chapter 22, Integration and Extension outlines observer plug-in development in greater detail.
The timer:interval pattern observer waits for the defined time before the truth value of the observer turns true.
The observer takes a time period (see Section 5.2.1, “Specifying Time Periods”) as a parameter, or an expression that returns the number of seconds.
The observer may be parameterized by an expression that contains one or more references to properties of prior events in the same pattern, or may also reference variables, substitution parameters or any other expression returning a numeric value.
After an A event arrived wait 10 seconds then indicate that the pattern matches.
A -> timer:interval(10 seconds)
The pattern below fires every 20 seconds.
every timer:interval(20 sec)
The next example pattern fires for every A event that is not followed by a B event within 60 seconds after the A event arrived. The B event must have the same "id" property value as the A event.
every a=A -> (timer:interval(60 sec) and not B(id=a.id))
Consider the next example, which assumes that the A event has a property waittime:
every a=A -> (timer:interval(a.waittime + 2) and not B(id=a.id))
In the above pattern the logic waits for 2 seconds plus the number of seconds provided by the value of the waittime property of the A event.
The timer:at pattern observer is similar in function to the Unix “crontab” command. At a specified time the
expression turns true. The at operator can also be made to pattern match at regular intervals by using an every operator
in front of the timer:at operator.
The syntax is:
timer:at (minutes, hours, days of month, months, days of week [, seconds [, time zone [, milliseconds [, microseconds]]]])
The value for seconds, time zone, milliseconds and microseconds is optional. Each element allows wildcard * values. Ranges can be specified
by means of lower bounds then a colon ‘:’ then the upper bound. The division operator */x can be used to
specify that every xth value is valid. Combinations of these operators can be used by placing these into square brackets ([]).
The timer:at observer may also be parameterized by an expression that contains one or more references to properties of prior events in the same pattern, or may also reference variables, substitution parameters or any other expression returning a numeric value. The frequency division operator */x and parameters lists within brackets ([]) are an exception: they may only contain variables, substitution parameters or numeric values.
This expression pattern matches every 5 minutes past the hour.
every timer:at(5, *, *, *, *)
The below timer:at pattern matches every 15 minutes from 8am to 5:45pm (hours 8 to 17 at 0, 15, 30 and 45 minutes past the hour) on even numbered days of the month as well as on the
first day of the month.
timer:at (*/15, 8:17, [*/2, 1], *, *)
The below table outlines the fields, valid values and keywords available for each field:
Table 7.5. Crontab Fields
| Field Name | Mandatory? | Allowed Values | Additional Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minutes | yes | 0 - 59 | |
| Hours | yes | 0 - 23 | |
| Days Of Month | yes | 1 - 31 | last, weekday, lastweekday |
| Months | yes | 1 - 12 | |
| Days Of Week | yes | 0 (Sunday) - 6 (Saturday) | last |
| Seconds | no (required if specifying a time zone, milliseconds or microseconds) | 0 - 59 | |
| Time Zone | no (required if specifying milliseconds or microseconds) | any string (not validated, see TimeZone javadoc; use * for any value) | |
| Milliseconds | no (required if specifying microseconds) | 0 - 999 | |
| Microseconds | no | 0 - 999 (only relevant when using microseconds as the runtime time unit) |
The keyword last used in the days-of-month field means the last day of the month (current month). To specify the last day of another month, you must provide a value for the month field. For example: timer:at(*, *, last,2,*) is the last day of February.
The last keyword in the day-of-week field by itself simply means Saturday. If used in the day-of-week field after another value, it means "the last xxx day of the month" - for example "5 last" means "the last Friday of the month".
So the last Friday of the current month will be: timer:at(*, *, *, *, 5 last). And the last Friday of June: timer:at(*, *, *, 6, 5 last).
The keyword weekday is used to specify the weekday (Monday-Friday) nearest the given day. Variant could include month like in: timer:at(*, *, 30 weekday, 9, *) which for year 2007 is Friday September 28th (no jump over month).
The keyword lastweekday is a combination of two parameters, the last and the weekday keywords. A typical example could be: timer:at(*, *, *, lastweekday, 9, *) which will define Friday September 28th (example year is 2007).
The time zone is a string-type value that specifies the time zone of the schedule. You must specify a value for seconds when specifying a time zone. The runtime relies on the java.util.TimeZone to interpret the time zone value. Note that TimeZone does not validate time zone strings.
The following timer:at pattern matches at 5:00 pm Pacific Standard Time (PST):
timer:at (0, 17, *, *, *, *, 'PST')
Any expression may occur among the parameters. This example invokes a user-defined function computeHour to return an hour:
timer:at (0, computeHour(), *, *, *, *)
The following restrictions apply to crontab parameters:
It is not possible to specify both Days Of Month and Days Of Week.
The return value for method that returns a crontab wildcard is WildcardParameter and for a crontab range is RangeParameter.
When using timer:at with the every operator the crontab-like timer computes the next time at which the timer should fire based on the specification and the current time. When using every, the current time is the time the timer fired or the statement start time if the timer has not fired once.
For example, this pattern fires every 1 minute starting at 1:00pm and ending at 1:59pm, every day:
every timer:at(*, 13, *, *, *)
Assume the above statement gets started at 1:05pm and 20 seconds. In such case the above pattern fires every 1 minute starting at 1:06pm and ending at 1:59pm for that day and 1:00pm to 1:59pm every following day.
To get the pattern to fire only once at 1pm every day, explicitly specify the minute to start. The pattern below fires every day at 1:00pm:
every timer:at(0, 13, *, *, *)
By specifying a second resolution the timer can be made to fire every second, for instance:
every timer:at(*, *, *, *, *, *)
The timer:schedule observer is a flexible observer for scheduling.
The observer implements relevant parts of the ISO 8601 specification however it is not necessary to use ISO 8601 formats. The ISO 8601 standard is an international standard covering the exchange of date and time-related data. The standard specifies a date format, a format for time periods and a format for specifying the number of repetitions. Please find more information on ISO 8601 at Wikipedia.
The observer takes the following named parameters:
Table 7.6. Timer Schedule Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
iso | An expression returning a string-type ISO 8601 formatted date, time period and/or number of repetitions. |
repetitions | An expression returning a numeric value that specifies a number of repetitions. Provide a value of -1 for an unlimited number of repetitions.
If unspecified, the number of repetitions is one. |
date | An expression returning a string-type ISO 8601 formatted date, or an expression that returns any of these types:
long, Date, Calendar, LocalDateTime, ZonedDateTime. |
period | An expression returning a time period, see Section 5.2.1, “Specifying Time Periods” |
In summary, for example, the below pattern schedules two callbacks: The first callback 2008-03-01 at 13:00:00 UTC and the second callback on 2009-05-11 at 15:30:00 UTC.
select * from pattern[every timer:schedule(iso: 'R2/2008-03-01T13:00:00Z/P1Y2M10DT2H30M')]
The number of repetitions, date and period can be separated and do not have to be ISO 8601 strings, allowing each part to be an own expression.
This example specifies separate expressions. The equivalent schedule to the above example is:
select * from pattern[every timer:schedule(repetitions: 2, date: '2008-03-01T13:00:00Z', period: 1 year 2 month 10 days 2 hours 30 minutes)]
When providing the iso parameter, it must be the only parameter. The repetitions parameter is only allowed in conjunction with other parameters.
The complete document for ISO 8601, the international standard for the representation of dates and times, can be found at http://www.w3.org/TR/NOTE-datetime.
The supported ISO 8601 date formats are:
Table 7.7. ISO 8601 Period Examples
| Description | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Complete date plus hours, minutes and seconds (zero milliseconds, zero microseconds): | YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ssTZD |
(i.e. GMT+00:00, UTC)
(i.e. GMT+01:00)
(i.e. local time zone) |
| Complete date plus hours, minutes, seconds and a decimal fraction of a second (zero microseconds) | YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ss.sTZD |
(i.e. GMT+00:00, UTC)
(i.e. GMT+01:00)
(i.e. local time zone) |
In ISO 8601, periods are specified by a P and an optional year, month, week and day count. If there is a time part, add T and optionally provide the hour, minute and seconds. The format does not have any whitespace. The synopsis is:
P [nY] [nM] [nW] [nD] [T [nH [nM] [nS] ]
The Y stands for years, the M for month as well as minutes, the W for weeks and the D for days.
The H stands for hours and the S means seconds.
Table 7.8. ISO 8601 Period Examples
| Example | Description |
|---|---|
| P10M | 10 months |
| PT10M | 10 minutes |
| P1Y3M12D | 1 year, 3 month and 12 days |
| P10DT5M | 10 days and 5 minutes |
| P1Y2M3DT4H5M6S | 1 year, 2 month, 3 days, 4 hours, 5 minutes, 6 seconds |
To instruct the runtime to observe a date, provide a date to the observer. When time advances to the specified date, the pattern subexpression fires.
For example, this pattern fires once when time reaches 2012-10-01 at 5:52:00 (UTC):
timer:schedule(iso:'2012-10-01T05:52:00Z')
This equivalent pattern specifies separate expressions:
every timer:schedule(date: '2012-10-01T05:52:00Z')
When the observer fires, the pattern subexpression becomes permanently false and the runtime does not restart the observer.
If the provided date is a past date as compared to runtime time, the pattern subexpression becomes permanently false on start.
To instruct the runtime to observe a period starting from the current runtime time, provide a period. When time advances to the current runtime time plus the specified period, the pattern subexpression fires.
Assuming the current runtime time is 2012-10-01 at 5:52:00 (UTC), this pattern fires once when time reaches 5:53:00:
timer:schedule(iso:'PT1M')
This equivalent pattern specifies separate expressions:
every timer:schedule(period: 1 minute)
When the observer fires, the pattern subexpression becomes permanently false and the runtime does not restart the observer.
To instruct the runtime to observe a period starting from a given date, provide a date and a period. When time advances to the date plus the specified period, the pattern subexpression fires.
Assuming the current runtime time is 5:52:00 (UTC), this pattern fires once when time reaches 2012-10-01 at 5:53:00:
timer:schedule(iso:'2012-10-01T05:52:00Z/PT1M')
This equivalent pattern specifies separate expressions:
every timer:schedule(date: '2012-10-01T05:52:00Z', period: 1 minute)
When the observer fires, the pattern subexpression becomes permanently false and the runtime does not restart the observer.
To instruct the runtime to observe a period starting from the current runtime time and repeatedly thereafter anchored to current runtime time, provide a number of repetitions and a period (see synopsis provided earlier), like this:
repetitions/period
timer:schedule(iso: 'R2/PT1M')
When time advances to the current runtime time plus the specified period, the pattern subexpression fires for the first time. Repeatedly when time advances to the current runtime time plus a multiple of the specified period, the pattern subexpression fires, up to the number of repetitions specified (if any).
This pattern specifies a repetition of two. Assuming the current runtime time is 2012-10-01 at 5:52:00 (UTC), it fires when time reaches 5:53:00 and again when time reaches 5:54:00:
every timer:schedule(iso: 'R2/PT1M')
This equivalent pattern specifies separate expressions:
every timer:schedule(repetitions: 2, period: 1 minute)
All schedule computations are relative to (i.e. anchored to) current runtime time at observer start. Once the number of repetitions is reached relative to the current runtime time at observer start, the pattern subexpression becomes permanently false and the runtime does not restart the observer.
Note
Please specify the every operator for repeating schedules.
To instruct the runtime to observe a period starting from a given date and repeatedly thereafter anchored to the provide date, provide a number of repetitions and a date and a period (see synopsis provided earlier), like this:
repetitions/date/period
When time advances to the date, the pattern subexpression fires for the first time. You may specify a date older than current runtime time as an anchor. Repeatedly when time advances to the date plus a multiple of the specified period, the pattern subexpression fires, up to the number of repetitions specified (if any).
This pattern specifies a repetition of two. The pattern fires when time reaches 2012-10-01 at 5:52:00 (UTC) and again when time reaches 5:53:00.
every timer:schedule(iso: 'R2/2012-10-01T05:52:00Z/PT1M')
This equivalent pattern specifies separate expressions:
every timer:schedule(repetitions: 2, date:'2012-10-01T05:52:00Z', period: 1 minute)
All schedule computations are relative to (i.e. anchored to) the provided date. Once the number of repetitions is reached relative to the provided date, the pattern subexpression becomes permanently false and the runtime does not restart the observer.
Note
Please specify the every operator for repeating schedules.
The pattern below outputs every MyEvent event after the MyEvent arrived and upon the next round 15 seconds:
select * from pattern[every e=MyEvent -> timer:schedule(iso: 'R/1980-01-01T00:00:00Z/PT15S']
Assuming a MyEvent event arrives on 2012-10-01 at 5:51:07 the output for that event occurs at 5:51:15.
All parameters can be expressions. The date parameter could, for example, be used with current_timestamp
to compute a schedule:
select * from pattern[date: current_timestamp.withTime(9, 0, 0, 0)]
The above statement fires only at 9am and not after 9am on the same day (one repetition).
The following EPL is equivalent:
select * from pattern[every timer:schedule(iso: 'R2/2008-03-01T13:00:00Z/P1Y2M10DT2H30M')]
select * from pattern[every (timer:schedule(iso: '2008-03-01T13:00:00Z') or timer:schedule(iso: '2009-05-11T15:30:00Z'))]
select * from pattern[every (timer:schedule(iso: '2008-03-01T13:00:00Z') or timer:schedule(iso: '2008-03-01T13:00:00Z/P1Y2M10DT2H30M'))]
This walkthrough discusses the following pattern:
every a=LoginEvent -> (timer:interval(1 min) and not LogoutEvent(userId=a.userId))]
This pattern detects when a LoginEvent is not followed by a LogoutEvent arriving within 1 minute of the LoginEvent.
The runtime parses the pattern expression and builds a expression tree. At the root of the expression tree, for this specific pattern, is the followed-by (->) operator as followed-by has the lowest precedence (see precedence).
The pattern expression tree looks like this.
Followed-by operator (->)
|
| ---- Every
| |
| | ---- a=LoginEvent
|
| ---- And
|
| ---- timer:interval(1 min)
|
| ---- Not
|
| ---- LogoutEvent(userId=a.userId)
The followed-by (->) operator has two subexpressions that it manages, the Every expression that itself has the a=LoginEvent subexpression as a child, and the And expression that itself has two subexpressions as children.
When the runtime activates a pattern or pattern subexpression, it activates it from a top-down direction. In this example the runtime activates the followed-by (->) expression.
The followed-by expression activates only its own left-most subexpression, which is the Every expression. The Every expression in turn activates the a=LoginEvent subexpression which registers a filter looking for a LoginEvent in the global filter index (see Section 2.18.2, “Filter Indexes”).
In this example, the And subexpression and its subexpressions do not get activated. Therefore after this pattern initially activates there is no
filter active time looking for LogoutEvent event and there is no time tracking of any kind at this point.
Let time t0 be the time of statement deployment. As discussed, upon deployment of the statement the runtime activates the pattern subexpression every a=LoginEvent only. At this time there is 1 active subexpression:
every a=LoginEvent
As you can see, the tree of active subexpressions (the tree of states) is not the same as the tree of expressions. After the pattern activated there are no active subexpressions (no states) for the And-part of the example expression tree.
Let's assume that at time t1 a LoginEvent with user id 10 arrives.
This causes the a=LoginEvent subexpression to become true. In turn, this causes the Every subexpression to become true. This causes the left-hand-side of the followed-by subexpression to become true. This in turn causes activation of the And subexpression.
The activation of the And-subexpression causes activation of both timer:interval(1 min) (from t1) and the Not-subexpression.
The activation of the And-subexpression registers a filter looking for a LogoutEvent that has a user id value of 10 in the global filter index
and registers a timer callback for t1+1 minute.
The runtime does not terminate the subexpression a=LoginEvent as it lives under an Every operator which means it should keep looking for
more LoginEvent events.
There now are 2 active subexpressions:
every a=LoginEventtimer:interval(t1+1 min) and not LogoutEvent(userId=10)
Let's assume that at time t2 another LoginEvent with user id 20 arrives (assume t2 – t1 < 1 min).
This again causes the a=LoginEvent subexpression to become true. In turn, this causes the Every subexpression to become true. This causes the left-hand-side of the followed-by subexpression to become true. This in turn causes activation of the And subexpression.
The activation of the And-subexpression causes activation of both timer:interval(1 min) (from t2) and the Not-subexpression.
The activation of the And-subexpression registers a filter looking for a LogoutEvent that has a user id value of 20 in the global filter index
and registers a timer callback for t2+1 minute.
There now are 3 active subexpressions:
every a=LoginEventtimer:interval(t1+1 min) and not LogoutEvent(userId=10)timer:interval(t2+1 min) and not LogoutEvent(userId=20)
In this scenario at time t3 one minute has passed since t1 and a matching LogoutEvent was not received.
The subexpression timer:interval(t1+1 min) becomes true. In turn, this causes the And-subexpression to become true as the Not-subexpression is already true on start. In turn, this causes the followed-by subexpression to become true. In turn, this causes an output of the pattern match.
The runtime terminates the subexpression not LogoutEvent(userId=10) which unregisters the filter looking for a LogoutEvent that has a user id value of 10 from the global filter index.
There now are 2 active subexpressions:
every a=LoginEventtimer:interval(t2+1 min) and not LogoutEvent(userId=20)
Let's assume that at time t4 a LogoutEvent with user id 20 arrives (assume t4 – t2 < 1 min).
This again causes the LogoutEvent(userId=20) subexpression to become true. In turn, this causes the Not subexpression to become permanently false (as Not reverses the truth value). This causes the And-subexpression to become permanently false.
This causes the pattern subexpression timer:interval(t2+1 min) and not LogoutEvent(userId=20) to terminate which causes the timer callback t2+1 minute to unregister.
Finally there is 1 active subexpression remaining:
every a=LoginEvent
- 8.1. Overview
- 8.2. Comparison of Match Recognize and EPL Patterns
- 8.3. Syntax
- 8.4. Pattern and Pattern Operators
- 8.4.1. Operator Precedence
- 8.4.2. Concatenation
- 8.4.3. Alternation
- 8.4.4. Quantifiers Overview
- 8.4.5. Permutations
- 8.4.6. Variables Can Be Singleton or Group
- 8.4.7. Eliminating Duplicate Matches
- 8.4.8. Greedy or Reluctant
- 8.4.9. Quantifier - One or More (+ and +?)
- 8.4.10. Quantifier - Zero or More (* and *?)
- 8.4.11. Quantifier - Zero or One (? and ??)
- 8.4.12. Repetition - Exactly N Matches
- 8.4.13. Repetition - N or More Matches
- 8.4.14. Repetition - Between N and M Matches
- 8.4.15. Repetition - Between Zero and M Matches
- 8.4.16. Repetition Equivalence
- 8.5. Define Clause
- 8.6. Measure Clause
- 8.7. Datawindow-Bound
- 8.8. Interval
- 8.9. Interval-or-Terminated
- 8.10. Use With Different Event Types
- 8.11. Limiting Runtime-Wide State Count
- 8.12. Limitations
Using match recognize patterns are defined in the familiar syntax of regular expressions.
The match recognize syntax presents an alternative way to specify pattern detection as compared to the EPL pattern language described in the previous chapter. A comparison of match recognize and EPL patterns is below.
The match recognize syntax is a proposal for incorporation into the SQL standard. It is thus subject to change as the standard evolves and finalizes (it has not finalized yet). Please consult "row-pattern-recogniton-11-public.pdf" for further information.
You may be familiar with regular expressions in the context of finding text of interest in a string, such as particular characters, words, or patterns of characters. Instead of matching characters, match recognize matches sequences of events of interest.
EPL can apply match-recognize patterns in real-time upon arrival of new events in a stream of events (also termed incrementally, streaming or continuous). EPL can also match patterns on-demand via the iterator pull-API, if specifying a named window or data window on a stream (tables cannot be used in the from-clause with match-recognize). The runtime maintains state for partial pattern matches and match-recognize patterns are therefore stateful constructs.
This section compares pattern detection via match recognize and via the EPL pattern language.
Table 8.1. Comparison Match Recognize to EPL Patterns
| Category | EPL Patterns | Match Recognize |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Pattern detection in sequences of events. | Same. |
| Standards | Not standardized, similar to Rapide pattern language. | Proposal for incorporation into the SQL standard. |
| Real-time Processing | Yes. | Yes. |
| On-Demand query via Iterator | No. | Yes. |
| Language | Nestable expressions consisting of boolean AND, OR, NOT and time or arrival-based constructs such as -> (followed-by), timer:within and timer:interval. | Regular expression consisting of variables each representing conditions on events. |
| Event Types | An EPL pattern may react to multiple different types of events. | The input is a single type of event (unless used with variant streams). |
| Data Window Interaction | Disconnected, i.e. an event leaving a data window does not change pattern state. | Connected, i.e. an event leaving a data window removes the event from match selection. |
| Semantic Evaluation | Truth-value based: A EPL pattern such as (A and B) can fire when a single event arrives that satisfies both A and B conditions. | Sequence-based: A regular expression (A B) requires at least two events to match. |
| Time Relationship Between Events | The timer:within, timer:interval and NOT operator can expressively search for absence of events or other more complex timing relationships. | Some support for detecting absence of events using the interval clause. |
| Extensibility | Custom pattern objects, user-defined functions. | User-defined functions, custom aggregation functions. |
| Memory Use | Likely between 500 bytes to 2k per open sequence, depends on pattern. | Likely between 100 bytes to 1k per open sequence, depends on pattern. |
The synopsis is as follows:
match_recognize ( [ partition by partition_expression [, partition_expression] [,...] ] measures measure_expressionascol_name [, measure_expressionascol_name ] [,...] [ all matches ] [ after match skip (past last row | to next row | to current row) ] pattern ( variable_regular_expr [, variable_regular_expr] [,...] ) [ interval time_period [or terminated] ] [ define variable as variable_condition [, variable as variable_condition] [,...] ] )
The match_recognize keyword starts the match recognize definition and occurs right after the from clause in an EPL select statement. It is followed by parenthesis that surround the match recognize definition.
Partition by is optional and may be used to specify that events are to be partitioned by one or more event properties or expressions. If there is no Partition by then all rows of the table constitute a single partition. The regular expression applies to events in the same partition and not across partitions.
Further detail on key expressions can be found at Section 5.2.13, “Composite Keys and Array Values as Keys”.
The measures clause defines columns that contain expressions over the pattern variables. The expressions can reference partition columns, singleton variables, aggregates as well as indexed properties on the group variables. Each measure_expression expression must be followed by the as keyword and a col_name column name.
The all matches keywords are optional and instructs the runtime to find all possible matches. By default matches are ranked and the runtime returns a single match following an algorithm to eliminate duplicate matches, as described below. When specifying all matches, matches may overlap and may start at the same row.
The after match skip keywords are optional and serve to determine the resumption point of pattern matching after a match has been found. By default the behavior is after match skip past last row. This means that after eliminating duplicate matches, the logic skips to resume pattern matching at the next event after the last event of the current match.
The pattern component is used to specify a regular expression. The regular expression is built from variable names, and may use quantifiers such as *, +, ?, *?, +?, ??, {repetition} and | alteration (concatenation is indicated by the absence of any operator sign between two successive items in a pattern).
With the optional interval keyword, time period and or terminated you can control how long the runtime should wait for further events to arrive that may be part of a matching event sequence, before indicating a match (or matches) (not applicable to on-demand pattern matching).
Define is optional and is used to specify the boolean condition(s) that define some or all variable names that are declared in the pattern. A variable name does not require a definition and if there is no definition, the default is a predicate that is always true. Such a variable name can be used to match any row.
For illustration, the examples in this chapter use the TemperatureSensorEvent event. Each event has 3 properties: the id property is a unique event id, the device is a sensor device number and the temp property is a temperature reading. An event described as "id=E1, device=1, temp=100" is a TemperatureSensorEvent event with id "E1" for device 1 with a reading of 100.
This example statement looks for two TemperatureSensorEvent events from the same device, directly following each other, that indicate a jump in temperature of 10 or more between the two events:
select * from TemperatureSensorEvent
match_recognize (
partition by device
measures A.id as a_id, B.id as b_id, A.temp as a_temp, B.temp as b_temp
pattern (A B)
define
B as Math.abs(B.temp - A.temp) >= 10
)
The partition by ensures that the regular expression applies to sequences of events from the same device.
The measures clause provides a list of properties or expressions to be selected from matching events. Each property name must be prefixed by the variable name.
In the pattern component the statement declares two variables: A and B. As a matter of convention, variable names are uppercase characters.
The define clause specifies no condition for variable A. This means that A defaults to true and any event matches A. Therefore, the pattern can start at any event.
The pattern A B indicates to look for a pattern in which an event that fulfills the condition for variable A is immediately followed by an event that fulfills the condition for variable B.
A pattern thus defines the sequence (or sequences) of conditions that must be met for the pattern to fire.
Below table is an example sequence of events and output of the pattern:
Table 8.2. Example
| Arrival Time | Tuple | Output Event (if any) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | id=E1, device=1, temp=50 | |
| 2000 | id=E2, device=1, temp=55 | |
| 3000 | id=E3, device=1, temp=60 | |
| 4000 | id=E4, device=1, temp=70 | a_id = E3, b_id = E4, a_temp = 60, b_temp = 70 |
| 5000 | id=E5, device=1, temp=85 | |
| 6000 | id=E6, device=1, temp=85 | |
| 7000 | id=E7, device=2, temp=100 |
At time 4000 when event with id E4 (or event E4 or just E4 for short) arrives the pattern matches and produces an output event. Matching then skips past the last event of the current match (E4) and begins at event E5 (the default skip clause is past last row). Therefore events E4 and E5 do not constitute a match.
At time 3000, events E1 and E3 do not constitute a match as E3 does not immediately follow E, since there is E2 in between.
At time 7000, event E7 does not constitute a match as it is from device 2 and thereby not in the same partition as prior events.
The pattern specifies the pattern to be recognized in the ordered sequence of events in a partition using regular expression syntax. Each variable name in a pattern corresponds to a boolean condition, which is specified later
using the define component of the syntax. Thus the pattern can be regarded as implicitly declaring one or more variable names; the definition of those variable names appears later in the
syntax. If a variable is not defined the variable defaults to true.
It is permitted for a variable name to occur more than once in a pattern, for example pattern (A B A).
The operators at the top of this table take precedence over operators lower on the table.
Table 8.3. Match Recognize Regular Expression Operator Precedence
| Precedence | Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Grouping | () | (A B) |
| 2 | Quantifiers | * + ? {repetition} | A* B+ C? |
| 3 | Concatenation | (no operator) | A B |
| 4 | Alternation | | | A | B |
If you are not sure about the precedence, please consider placing parenthesis () around your groups. Parenthesis can also help make
expressions easier to read and understand.
The concatenation is indicated by the absence of any operator sign between two successive items in a pattern.
In below pattern the two items A and B have no operator between them. The pattern matches for any event immediately followed by an event from the same device that indicates a jump in temperature over 10:
select * from TemperatureSensorEvent
match_recognize (
partition by device
measures A.id as a_id, B.id as b_id, A.temp as a_temp, B.temp as b_temp
pattern (A B)
define
B as Math.abs(B.temp - A.temp) >= 10
)Please see the Section 8.3.1, “Syntax Example” for a sample event sequence.
The alternation operator is a vertical bar ( | ).
The alternation operator has the lowest precedence of all operators. It tells the runtime to match either everything to the left of the vertical bar, or everything to the right of the vertical bar. If you want to limit the reach of the alternation, you will need to use parentheses for grouping.
This example pattern looks for a sequence of an event with a temperature over 50 followed immediately by either an event with a temperature less than 45 or an event that indicates the temperature jumped by 10 (all for the same device):
select * from TemperatureSensorEvent
match_recognize (
partition by device
measures A.id as a_id, B.id as b_id, C.id as c.id
pattern (A (B | C))
define
A as A.temp >= 50,
B as B.temp <= 45,
C as Math.abs(C.temp - A.temp) >= 10)Below table is an example sequence of events and output of the pattern:
Table 8.4. Example
| Arrival Time | Tuple | Output Event (if any) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | id=E1, device=1, temp=50 | |
| 2000 | id=E2, device=1, temp=45 | a_id=E1, b_id=E2, c_id=null |
| 3000 | id=E3, device=1, temp=46 | |
| 4000 | id=E4, device=1, temp=48 | |
| 5000 | id=E5, device=1, temp=50 | |
| 6000 | id=E6, device=1, temp=60 | a_id = E5, b_id = null, c_id=E6 |
Quantifiers are postfix operators with the following choices:
Table 8.5. Quantifiers
| Quantifier | Meaning |
|---|---|
| * | Zero or more matches (greedy). |
| + | One or more matches (greedy). |
| ? | Zero or one match (greedy). |
| *? | Zero or more matches (reluctant). |
| +? | One or more matches (reluctant). |
| ?? | Zero or one match (reluctant). |
Quantifiers that control the number of repetitions are:
Table 8.6. Quantifiers
| Quantifier | Meaning |
|---|---|
| {n} | Exactly n matches. |
| {n, } | n or more matches. |
| {n, m} | Between n and m matches (inclusive). |
| { ,m} | Between zero and m matches (inclusive). |
Repetition quantifiers can be combined with other quantifiers and grouping. For example A?{2} or (A B){2} are valid.
To detect patterns that consist of a permutation of variables you may use match_recognize_permute.
It is possible to express a permutation as alternations but it becomes clumsy when many variables are involved.
For example, if all permutations of three variables A B C are needed you could express it as: (A B C | A C B | B A C | B C A | C A B | C B A).
You may use match_recognize_permute followed by a comma-separated list of variables, grouping, alternations or concatenations.
The following table outlines sample equivalent permutations.
Table 8.7. Equivalent Pattern Expressions
| Pattern | Equivalent |
|---|---|
| match_recognize_permute(A) | A |
| match_recognize_permute(A,B) | (A B|B A) |
| match_recognize_permute(A,B,C) | A B C|A C B|B A C|B C A|C A B|C B A |
| match_recognize_permute((A B), C) | (A B) C|C (A B) |
| A match_recognize_permute(B,C) D | A (B C|C B) D |
| match_recognize_permute(A, match_recognize_permute(B, C)) | A (B C|C B)|(B C|C B) A |
This sample pattern looks for either an event with temperature less than 100 and then an event with temperature greater or equal to 100, or an event with temperature greater or equal to 100 and then an event with temperature less than 100.
select * from TemperatureSensorEvent
match_recognize (
partition by device
measures A.id as a_id, B.id as b_id
pattern (match_recognize_permute(A, B))
define
A as A.temp < 100,
B as B.temp >= 100)An example sequence of events that matches the pattern above is:
Table 8.8. Example
| Arrival Time | Tuple | Output Event (if any) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | id=E1, device=1, temp=99 | |
| 2000 | id=E2, device=1, temp=100 | a_id = E1, b_id = E2 |
| 3000 | id=E3, device=1, temp=100 | |
| 4000 | id=E4, device=1, temp=99 | a_id = E4, b_id = E3 |
| 5000 | id=E5, device=1, temp=98 |
A singleton variable is a variable in a pattern that does not have a quantifier or has a zero-or-one quantifier (? or ??) and occurs only once in the pattern (except with alteration).
In the measures clause a singleton variable can be selected as:
variableName.propertyName
Variables with a zero-or-more or one-or-more quantifier, or variables that occur multiple places in a pattern (except when using alteration), may match multiple events and are group variables.
In the measures clause a group variable must be selected either by providing an index or via any of the aggregation functions, such as first, last, count and sum:
variableName[index].propertyNamelast(variableName.propertyName)
Enumeration methods can also be applied to group variables. An example is provided in Section 11.4.11, “Match-Recognize Group Variable”.
Please find examples of singleton and group variables and example measures and define clauses below.
For group variables all existing aggregation functions can be used and in addition the following aggregation functions may be used (measures-clause only):
Table 8.9. Syntax and Results of Aggregate Functions
| Aggregate Function | Result |
|---|---|
| first([all|distinct] expression) |
Returns the first value. |
| last([all|distinct] expression) |
Returns the last value. |
The execution of match recognize is continuous and real-time by default. This means that every arriving event, or batch of events if using batching, evaluates against the pattern and matches are immediately indicated. Elimination of duplicate matches occurs between all matches of the arriving events (or batch of events) at a given time.
As an alternative, and if your application does not require continuous pattern evaluation, you may use the iterator API to perform on-demand matching of the pattern. For the purpose of indicating to the runtime to not
generate continuous results, specify the @Hint('iterate_only') hint.
When using one-or-more, zero-or-more or zero-or-one quantifiers (?, +, *, ??, +?, *?), the output of statement can differ from the output of the on-demand iterator execution: The statement will output a match (or multiple matches) as soon as matches are detected at a given time upon arrival of events (not knowing what further events may arrive). The on-demand execution, since it knows all possible events in advance, can determine the longest match(es). Thus elimination of duplicate matches can lead to different results between real-time and on-demand use.
If the all matches keywords are specified, then all matches are returned as the result and no elimination of duplicate matches as below occurs.
Otherwise matches to a pattern in a partition are ordered by preferment. Preferment is given to matches based on the following priorities:
A match that begins at an earlier row is preferred over a match that begins at a later row.
Of two matches matching a greedy quantifier, the longer match is preferred.
Of two matches matching a reluctant quantifier, the shorter match is preferred.
After ranking matches by preferment, matches are chosen as follows:
The first match by preferment is taken.
The pool of matches is reduced as follows based on the SKIP TO clause: If SKIP PAST LAST ROW is specified, all matches that overlap the first match are discarded from the pool. If SKIP TO NEXT ROW is specified, then all matches that overlap the first row of the first match are discarded. If SKIP TO CURRENT ROW is specified, then no matches are discarded.
The first match by preferment of the ones remaining is taken.
Step 2 is repeated to remove more matches from the pool.
Steps 3 and 4 are repeated until there are no remaining matches in the pool.
Reluctant quantifiers are indicated by an additional question mark (*?, +?, ??,). Reluctant quantifiers try to match as few rows as possible, whereas non-reluctant quantifiers are greedy and try to match as many rows
as possible.
Greedy and reluctant come into play only for match selection among multiple possible matches. When specifying all matches there is no difference between greedy and reluctant quantifiers.
Consider the below example. The conditions may overlap: an event with a temperature reading of 105 and over matches both A and B conditions:
select * from TemperatureSensorEvent
match_recognize (
partition by device
measures A.id as a_id, B.id as b_id
pattern (A?? B?)
define
A as A.temp >= 100
B as B.temp >= 105)A sample sequence of events and pattern matches:
Table 8.10. Example
| Arrival Time | Tuple | Output Event (if any) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | id=E1, device=1, temp=99 | |
| 2000 | id=E2, device=2, temp=106 | a_id=null, b_id=E2 |
| 3000 | id=E3, device=1, temp=100 | a_id=E3, b_id=null |
As the ? qualifier on condition B is greedy, event E2 matches the pattern and is indicated as a B event by the measure clause (and not as an A event therefore a_id is null).
The one-or-more quantifier (+) must be matched one or more times by events. The operator is greedy and the reluctant version is +?.
In the below example with pattern (A+ B+) the pattern consists of two variable names, A and B, each of which is quantified with +, indicating that they must be matched one or more times.
The pattern looks for one or more events in which the temperature is over 100 followed by one or more events indicating a higher temperature:
select * from TemperatureSensorEvent match_recognize ( partition by device measures first(A.id) as first_a, last(A.id) as last_a, B[0].id as b0_id, B[1].id as b1_id pattern (A+ B+) define A as A.temp >= 100, B as B.temp > A.temp)
An example sequence of events that matches the pattern above is:
Table 8.11. Example
| Arrival Time | Tuple | Output Event (if any) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | id=E1, device=1, temp=99 | |
| 2000 | id=E2, device=1, temp=100 | |
| 3000 | id=E3, device=1, temp=100 | |
| 4000 | id=E4, device=1, temp=101 | first_a = E2, last_a = E3, b0_id = E4, b1_id = null |
| 5000 | id=E5, device=1, temp=102 |
Note that for statements there is no match that includes event E5 since after the pattern matches for E4 the pattern skips to start fresh at E5 (by default skip clause). When performing on-demand matching via iterator, event E5 gets included in the match
and the output is first_a = E2, last_a = E3, b0_id = E4, b1_id = E5.
The zero-or-more quantifier (*) must be matched zero or more times by events. The operator is greedy and the reluctant version is *?.
The pattern looks for a sequence of events in which the temperature starts out below 50 and then stays between 50 and 60 and finally comes over 60:
select * from TemperatureSensorEvent match_recognize ( partition by device measures A.id as a_id, count(B.id) as count_b, C.id as c_id pattern (A B* C) define A as A.temp < 50, B as B.temp between 50 and 60, C as C.temp > 60)
An example sequence of events that matches the pattern above is:
Table 8.12. Example
| Arrival Time | Tuple | Output Event (if any) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | id=E1, device=1, temp=55 | |
| 2000 | id=E2, device=1, temp=52 | |
| 3000 | id=E3, device=1, temp=49 | |
| 4000 | id=E4, device=1, temp=51 | |
| 5000 | id=E5, device=1, temp=55 | |
| 6000 | id=E5, device=1, temp=61 | a_id=E3, count_b=2, c_id=E6 |
The zero-or-one quantifier (?) must be matched zero or one time by events. The operator is greedy and the reluctant version is ??.
The pattern looks for a sequence of events in which the temperature is below 50 and then dips to over 50 and then to under 50 before indicating a value over 55:
select * from TemperatureSensorEvent match_recognize ( partition by device measures A.id as a_id, B.id as b_id, C.id as c_id, D.id as d_id pattern (A B? C? D) define A as A.temp < 50, B as B.temp > 50, C as C.temp < 50, D as D.temp > 55)
An example sequence of events that matches the pattern above is:
Table 8.13. Example
| Arrival Time | Tuple | Output Event (if any) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | id=E1, device=1, temp=44 | |
| 2000 | id=E2, device=1, temp=49 | |
| 3000 | id=E3, device=1, temp=51 | |
| 4000 | id=E4, device=1, temp=49 | |
| 5000 | id=E5, device=1, temp=56 | a_id=E2, b_id=E3, c_id=E4, d_id=E5 |
| 6000 | id=E5, device=1, temp=61 |
The exactly-n quantifier ({n}) must be matched exactly N times. The repetition quantifier can be combined with other non-repetition quantifiers and can be used with grouping.
In the below example the pattern (A{2}) consists of one variable names, A, quantified with {2}, indicating that the condition must match exactly two times.
This sample pattern looks for two events in which the temperature is over 100:
select * from TemperatureSensorEvent
match_recognize (
partition by device
measures A[0].id as a0_id, A[1].id as a1_id
pattern (A{2})
define
A as A.temp >= 100)An example sequence of events that matches the pattern above is:
Table 8.14. Example
| Arrival Time | Tuple | Output Event (if any) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | id=E1, device=1, temp=99 | |
| 2000 | id=E2, device=1, temp=100 | |
| 3000 | id=E3, device=1, temp=100 | a0_id = E2, a1_id = E3 |
| 4000 | id=E4, device=1, temp=101 | |
| 5000 | id=E5, device=1, temp=102 | a0_id = E4, a1_id = E5 |
The next sample applies the quantifier to a group. This sample pattern looks for a four events in which the temperature is, in sequence, 100, 101, 100 and 101:
select * from TemperatureSensorEvent
match_recognize (
partition by device
measures A[0].id as a0_id, A[1].id as a1_id
pattern (A B){2}
define
A as A.temp = 100,
B as B.temp = 101)
The quantifier {n, } must be matched N or more times. The repetition quantifier can be combined with other non-repetition quantifiers and can be used with grouping.
In the below example the pattern (A{2,} B) consists of two variable names, A and B. The condition A must match two or more times and the B condition must match once.
This sample pattern looks for two or more events in which the temperature is over 100 and thereafter an event with a temperature over 102:
select * from TemperatureSensorEvent
match_recognize (
partition by device
measures A[0].id as a0_id, A[1].id as a1_id, A[2].id as a2_id, B.id as b_id
pattern (A{2,} B)
define
A as A.temp >= 100,
B as B.temp >= 102)An example sequence of events that matches the pattern above is:
Table 8.15. Example
| Arrival Time | Tuple | Output Event (if any) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | id=E1, device=1, temp=99 | |
| 2000 | id=E2, device=1, temp=100 | |
| 3000 | id=E3, device=1, temp=100 | |
| 4000 | id=E4, device=1, temp=101 | |
| 5000 | id=E5, device=1, temp=102 | a0_id = E2, a1_id = E3, a2_id = E4, b_id = E5 |
The quantifier {n, m} must be matched between N and M times. The repetition quantifier can be combined with other non-repetition quantifiers and can be used with grouping.
In the below example the pattern (A{2,3} B) consists of two variable names, A and B. The condition A must match two or three times and the B condition must match once.
This sample pattern looks for two or three events in which the temperature is over 100 and thereafter an event with a temperature over 102:
select * from TemperatureSensorEvent
match_recognize (
partition by device
measures A[0].id as a0_id, A[1].id as a1_id, A[2].id as a2_id, B.id as b_id
pattern (A{2,3} B)
define
A as A.temp >= 100,
B as B.temp >= 102)An example sequence of events that matches the pattern above is:
Table 8.16. Example
| Arrival Time | Tuple | Output Event (if any) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | id=E1, device=1, temp=99 | |
| 2000 | id=E2, device=1, temp=100 | |
| 3000 | id=E3, device=1, temp=100 | |
| 4000 | id=E4, device=1, temp=101 | |
| 5000 | id=E5, device=1, temp=102 | a0_id = E2, a1_id = E3, a2_id = E4, b_id = E5 |
The quantifier {, m} must be matched between zero and M times. The repetition quantifier can be combined with other non-repetition quantifiers and can be used with grouping.
In the below example the pattern (A{, 2} B) consists of two variable names, A and B. The condition A must match zero, once or twice and the B condition must match once.
This sample pattern looks for between zero and two events in which the temperature is over 100 and thereafter an event with a temperature over 102:
select * from TemperatureSensorEvent
match_recognize (
partition by device
measures A[0].id as a0_id, A[1].id as a1_id, B.id as b_id
pattern (A{,2} B)
define
A as A.temp >= 100,
B as B.temp >= 102)An example sequence of events that matches the pattern above is:
Table 8.17. Example
| Arrival Time | Tuple | Output Event (if any) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | id=E1, device=1, temp=99 | |
| 2000 | id=E2, device=1, temp=100 | |
| 3000 | id=E3, device=1, temp=100 | |
| 4000 | id=E4, device=1, temp=101 | |
| 5000 | id=E5, device=1, temp=102 | a0_id = E3, a1_id = E4, b_id = E5 |
The following table outlines sample equivalent patterns.
Table 8.18. Equivalent Pattern Expressions
| Expression | Equivalent |
|---|---|
| Atom Examples | |
| A{2} | A A |
| A{2, } | A A A* |
| A{2, 4} | A A A? A? |
| A{, 2} | A? A? |
| Group Examples | |
| (A B){2} | (A B) (A B) |
| (A B){2, } | (A B) (A B) (A B)* |
| (A B){2, 4} | (A B) (A B) (A B)? (A B)? |
| (A B){, 2} | (A B)? (A B)? |
| Quantifier Examples | |
| A+{2, } | A+ A+ A* |
| A?{2, } | A? A? A* |
| A+{2, 4} | A+ A+ A* A* |
| A+{, 2} | A* A* |
Within define are listed the boolean conditions that defines a variable name that is declared in the pattern.
A variable name does not require a definition and if there is no definition, the default is a predicate that is always true. Such a variable name can be used to match any row.
The definitions of variable names may reference the same or other variable names as prior examples have shown.
If a variable in your condition expression is a singleton variable, then only individual columns may be referenced. If the variable is not matched by an event, a null value is returned.
If a variable in your condition expression is a group variable, then only indexed columns may be referenced. If the variable is not matched by an event, a null value is returned.
Aggregation functions are not allowed within expressions of the define clause. However define-clause expressions can utilize enumeration methods.
The prev function may be used in a define expression to access columns of the previous row of a variable name. If there is no previous row, the null value is returned.
The prev function can accept an optional non-negative integer argument indicating the offset to the previous rows. That argument must be a constant. In this case, the runtime returns the property from the
N-th row preceding the current row, and if the row doesn’t exist, it returns null.
This function can access variables currently defined, for example:
Y as Y.price < prev(Y.price, 2)
It is not legal to use prev with another variable then the one being defined:
// not allowed Y as Y.price < prev(X.price, 2)
The prev function returns properties of events in the same partition. Also, it returns properties of events according to event order-of-arrival. When using data windows or deleting events from a named window, the remove stream does not remove events from the prev function.
The pattern looks for an event in which the temperature is greater or equal 100 and that, relative to that event, has an event preceding it by 2 events that also had a temperature greater or equal 100:
select * from TemperatureSensorEvent match_recognize ( partition by device measures A.id as a_id pattern (A) define A as A.temp > 100 and prev(A.temp, 2) > 100)
An example sequence of events that matches the pattern above is:
Table 8.19. Example
| Arrival Time | Tuple | Output Event (if any) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | id=E1, device=1, temp=98 | |
| 2000 | id=E2, device=1, temp=101 | |
| 3000 | id=E3, device=1, temp=101 | |
| 4000 | id=E4, device=1, temp=99 | |
| 5000 | id=E5, device=1, temp=101 | a_id=E5 |
The measures clause defines exported columns that contain expressions over the pattern variables. The expressions can reference partition columns, singleton variables and
any aggregation functions including last and first on the group variables.
Expressions in the measures clause must use the as keyword to assign a column name.
If a variable is a singleton variable then only individual columns may be referenced, not aggregates. If the variable is not matched by an event, a null value is returned.
If a variable is a group variable and used in an aggregate, then the aggregate is performed over all rows that have matched the variable. If a group variable is not in an aggregate function, its variable name must be post-fixed with an index. See Section 8.4.6, “Variables Can Be Singleton or Group” for more information.
When using match recognize with a named window or stream bound by a data window, all events removed from the named window or data window also removed the match-in-progress that includes the event(s) removed.
The next example looks for four sensor events from the same device immediately following each other and indicating a rising temperature, but only events that arrived in the last 10 seconds are considered:
select * from TemperatureSensorEvent#time(10 sec) match_recognize ( partition by device measures A.id as a_id pattern (A B C D) define B as B.temp > A.temp, C as C.temp > B.temp, D as D.temp > C.temp)
An example sequence of events that matches the pattern above is:
Table 8.20. Example
| Arrival Time | Tuple | Output Event (if any) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | id=E1, device=1, temp=80 | |
| 2000 | id=E2, device=1, temp=81 | |
| 3000 | id=E3, device=1, temp=82 | |
| 4000 | id=E4, device=1, temp=81 | |
| 7000 | id=E5, device=1, temp=82 | |
| 9000 | id=E6, device=1, temp=83 | |
| 13000 | id=E7, device=1, temp=84 | a_id=E4, a_id=E5, a_id=E6, a_id=E7 |
| 15000 | id=E8, device=1, temp=84 | |
| 20000 | id=E9, device=1, temp=85 | |
| 21000 | id=E10, device=1, temp=86 | |
| 26000 | id=E11, device=1, temp=87 |
Note that E8, E9, E10 and E11 doe not constitute a match since E8 leaves the data window at 25000.
With the optional interval keyword and time period you can control how long the runtime should wait for further events to arrive that may be part of a matching event sequence, before indicating a match (or matches). This is not applicable to on-demand pattern matching.
The interval timer starts are the arrival of the first event matching a sequence for a partition. When the time interval passes and an event sequence matches, duplicate matches are eliminated and output occurs.
The next example looks for sensor events indicating a temperature of over 100 waiting for any number of additional events with a temperature of over 100 for 5 seconds before indicating a match:
select * from TemperatureSensorEvent match_recognize ( partition by device measures A.id as a_id, count(B.id) as count_b, first(B.id) as first_b, last(B.id) as last_b pattern (A B*) interval 5 seconds define A as A.temp > 100, B as B.temp > 100)
An example sequence of events that matches the pattern above is:
Table 8.21. Example
| Arrival Time | Tuple | Output Event (if any) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | id=E1, device=1, temp=98 | |
| 2000 | id=E2, device=1, temp=101 | |
| 3000 | id=E3, device=1, temp=102 | |
| 4000 | id=E4, device=1, temp=104 | |
| 5000 | id=E5, device=1, temp=104 | |
| 7000 | a_id=E2, count_b=3, first_b=E3, last_b=E5 |
Notice that the runtime waits 5 seconds (5000 milliseconds) after the arrival time of the first event E2 of the match at 2000, to indicate the match at 7000.
The interval keyword and time period can be followed by or terminated keywords. When or-terminated is specified, the runtime detects when a pattern state cannot match further and outputs matching event sequences collected so far that are otherwise only output at the end of the interval. This is not applicable to on-demand pattern matching.
Same as for interval alone, the interval timer starts are the arrival of the first event matching a sequence for a partition.
Event arrival can terminate the interval and lead to immediate output as follows:
- When an event arrives in the sequence that causes pattern state to terminate because no further match is possible, the event sequence matches, duplicate matches are eliminated and output occurs immediately (and not at the end of the interval), for the affected event sequence(s).
- Otherwise, when the time interval passes and an event sequence matches, duplicate matches are eliminated and output occurs.
The next example looks for sensor events indicating a temperature of over 100, waiting for any number of additional events with a temperature of over 100 for 5 seconds or when the temperature falls to equal or below 100, whichever happens first:
select * from TemperatureSensorEvent match_recognize ( partition by device measures A.id as a_id, count(B.id) as count_b, first(B.id) as first_b, last(B.id) as last_b pattern (A B*) interval 5 seconds or terminated define A as A.temp > 100, B as B.temp > 100)
An example sequence of events that matches the pattern above is:
Table 8.22. Example
| Arrival Time | Tuple | Output Event (if any) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | id=E1, device=1, temp=98 | |
| 2000 | id=E2, device=1, temp=101 | |
| 3000 | id=E3, device=1, temp=102 | |
| 4000 | id=E4, device=1, temp=101 | |
| 5000 | id=E5, device=1, temp=100 | a_id=E2, count_b=2, first_b=E3, last_b=E4 |
| 7000 | (no further output) |
Note
Interval and Interval with or terminated make most sense for open-ended patterns such as,
for example, pattern (A B*) or pattern (A B C+).
For patterns that terminate when a given event arrives, for example, pattern (A B), an Interval in combination with or terminated should not be specified
and if specified have no effect on matching.
You may match different types of events using match-recognize by following any of these strategies:
Declare a variant stream.
Declare a supertype for your event types in the
create schemasyntax.Have you event classes implement a common interface or extend a common base class.
A short example that demonstrates variant streams and match-recognize is listed below:
// Declare one sample type create schema S0 as (col string)
// Declare second sample type create schema S1 as (col string)
// Declare variant stream holding either type create variant schema MyVariantStream as S0, S1
// Populate variant stream insert into MyVariantStream select * from S0
// Populate variant stream insert into MyVariantStream select * from S1
// Simple pattern to match S0 S1 pairs
select * from MyVariantType#time(1 min)
match_recognize (
measures A.id? as a, B.id? as b
pattern (A B)
define
A as typeof(A) = 'S0',
B as typeof(B) = 'S1'
)The runtime allows setting a maximum number of states in the configuration, applicable to all match-recognize constructs of all statements.
If your application uses match-recognize in multiple statements and all such match-recognize constructs should count towards a total number of states counts, you may consider setting a maximum number of states, runtime-wide, via the configuration described in Section 17.6.5.1, “Maximum State Count”.
When the limit is reached the match-recognize runtime issues a notification object to any condition handlers registered with the runtime as described in Section 16.11, “Condition Handling”. Depending on your configuration the runtime can prevent the allocation of a new state instance, until states are discarded or statements are undeployed or context partitions are terminated.
The notification object issued to condition handlers is an instance of com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.condition.ConditionMatchRecognizeStatesMax. The notification object contains information which statement triggered the limit and the state counts per statement for all statements.
For information on configuration please consult Section 17.6.5.1, “Maximum State Count”.
Please note the following limitations:
Subqueries are not allowed in expressions within
match_recognize.Joins and outer joins are not allowed in the same statement as
match_recognize.match_recognizemay not be used withinon-selectoron-insertstatements.When using
match_recognizeon unbound streams (no data window provided) theiteratorpull API returns no rows.
- 9.1. Arithmetic Operators
- 9.2. Logical and Comparison Operators
- 9.3. Concatenation Operators
- 9.4. Binary Operators
- 9.5. Array Definition Operator
- 9.6. Array Element Operator
- 9.7. Dot Operator
- 9.8. The 'In' Keyword
- 9.9. The 'Between' Keyword
- 9.10. The 'Like' Keyword
- 9.11. The 'Regexp' Keyword
- 9.12. The 'Any' and 'Some' Keywords
- 9.13. The 'All' Keyword
- 9.14. The 'New' Keyword
Arithmetic and logical operator precedence follows Java standard arithmetic and logical operator precedence.
The below table outlines the arithmetic operators available.
Table 9.1. Syntax and Results of Arithmetic Operators
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| +, - |
As unary operators they denote a positive or negative expression. As binary operators they add or subtract. |
| *, / |
Multiplication and division are binary operators. |
| % |
Modulo binary operator. |
The below table outlines the logical and comparison operators available.
Table 9.2. Syntax and Results of Logical and Comparison Operators
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| NOT |
Returns true if the following condition is false, returns false if it is true. |
| OR |
Returns true if either component condition is true, returns false if both are false. |
| AND |
Returns true if both component conditions are true, returns false if either is false. |
| =, !=, <, > <=, >=, is, is not |
Comparison. |
The null value is a special value, see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Null_(SQL) (source:Wikipedia) for more information.
Thereby the following expressions all return null:
2 != null
null = null
2 != null or 1 = 2
2 != null and 2 = 2
Use the is and is not operators for comparing values that can be null.
The following expressions all return true:
2 is not null
null is not 2
null is null
2 is 2
The compiler allows is and is not with any expression, not only in connection with the null constant.
The below table outlines the concatenation operators available.
Table 9.3. Syntax and Results of Concatenation Operators
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| || |
Concatenates character strings |
The below table outlines the binary operators available.
Table 9.4. Syntax and Results of Binary Operators
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| & |
Bitwise AND if both operands are numbers; conditional AND if both operands are boolean. |
| | |
Bitwise OR if both operands are numbers; conditional OR if both operands are boolean. |
| ^ |
Bitwise exclusive OR (XOR). |
The { and } curly braces are array definition operators following the Java array initialization syntax. Arrays can be useful to pass to user-defined functions or to select array data in a select clause.
Array definitions consist of zero or more expressions within curly braces. Any type of expression is allowed within array definitions including constants, arithmetic expressions or event properties. This is the syntax of an array definition:
{ [expression [,expression...]] }
Consider the next statement that returns an event property named actions. The runtime populates the actions property as an array of java.lang.String values with a length of 2 elements. The first element of the array contains the observation property value and the second element the command property value of RFIDEvent events.
select {observation, command} as actions from RFIDEvent
The compiler determines the array type based on the types returned by the expressions in the array definiton. For example, if all expressions in the array definition return integer values then the type of the array is java.lang.Integer[]. If the types returned by all expressions are compatible number types, such as integer and double values, the runtime coerces the array element values and returns a suitable type, java.lang.Double[] in this example.
The type of the array returned is Object[] if the types of expressions cannot be coerced or return object values. Null values can also be used in an array definition.
Arrays can come in handy for use as parameters to user-defined functions:
select * from RFIDEvent where Filter.myFilter(zone, {1,2,3})
The [ and ] brackets are array element access operators following the Java syntax for accessing array elements. They can be used with any expression returning an array including with event types that have array inner events.
There must be a single expression returning an Integer or int-typed value within square brackets. Any type of expression is allowed as the index expression. The syntax is:
[index-expression]
Use size() to obtain array length (the identifier length cannot be used to obtain array length).
This example assumes the RFIDEvent has an array-type property called actions and an Integer-type property called actionIndex.
The expression returns the value of the actions array at index actionIndex and array length:
select actions[actionIndex], actions.size() from RFIDEvent
Array element operators can be chained and can be used with the Dot-Operator in a chain.
Here is an example of a user-defined function returning an array:
@name('s0') inlined_class """
public class Helper {
public static int[] toArray(int a, int b) {
return new int[] {a, b};
}
}
"""
select Helper.toArray(1,2)[actionIndex] from RFIDEvent
If the array input value or the result of the index expression is null the operator returns null.
If the index expression returns an index value greater than the array size the operator raises an exception.
You can use the dot operator to invoke a method on the result of an expression. The dot operator uses the dot (.) or period character.
The dot-operator is relevant with enumeration methods: Enumeration methods perform tasks such as transformation, filtering, aggregation, sequence-matching, sorting and others on subquery results, named windows, tables, event properties or inputs that are or can be projected to a collection of events, scalar values or objects. See Chapter 11, EPL Reference: Enumeration Methods
Further the dot-operator is relevant to date-time methods. Date-time methods work on date-time values to add or subtract time periods, set or round calendar fields or query fields, among other tasks. See Chapter 12, EPL Reference: Date-Time Methods.
The dot-operator is also relevant to spatial methods and the use of spatial indexes. See Chapter 20, EPL Reference: Spatial Methods and Indexes.
This section only describes the dot-operator in relation to property instance methods, the special get and size indexed-property methods and duck typing.
The synopsis for the dot operator is as follows
expression.method([parameter [,...]])[.method(...)][...]
The expression to evaluate by the dot operator is in parenthesis. After the dot character follows the method name and method parameters in parenthesis.
You may use the dot operator when your expression returns an object that you want to invoke a method on. The dot operator allows duck typing and convenient array and collection access methods.
This example statement invokes the getZones method of the RFID event class by referring to the stream name assigned in the from-clause:
select rfid.getZones() from RFIDEvent as rfid
The size() method can be used to return the array length or collection size. Use the get method to return the value at a given index for an array or collection.
The next statement selects array size and returns the last array element:
select arrayproperty.size() as arraySize, arrayproperty.get((arrayproperty).size - 1) as lastInArray from ProductEvent
The dot-operator allows a property name, for use when the object returned by the expression exposes a getter-method that matches the property name (only a simple name is supported; not allowing all event property expressions; not applicable when using duck typing).
For instance, assume that productLookup is a user-defined function that returns an object that has a getPrice() method. The dot-operator returns the result of the call to getPrice():
select productLookup(e).price from ProductEvent as e
Duck typing is when the compiler checks for the existence of a method regardless of object class inheritance hierarchies. This can be useful, for example, when a dynamic property returns an object which may or may not provide a method to return the desired value.
Duck typing is disabled in the default configuration to consistently enforce strong typing. Please enable duck typing via compiler expression settings as described in Section 17.5.6, “Compiler Settings Related to Expression Evaluation”.
The statement below selects a dynamic property by name productDesc and invokes the getCounter() method if that method exists on the property value, or returns the null value if the method does not exist for the dynamic property value of if the dynamic property value itself is null:
select (productDesc?).getCounter() as arraySize from ProductEvent
The in keyword determines if a given value matches any value in a list. The syntax of the keyword is:
test_expression [not] in (expression [,expression...] )
The test_expression is any valid expression. The keyword is followed by a list of expressions to test for a match. The optional not keyword specifies that the result of the predicate be negated.
The result of an in expression is of type Boolean. If the value of test_expression is equal to any expression from the comma-separated list, the result value is true. Otherwise, the result value is false.
The next example shows how the in keyword can be applied to select certain command types of RFID events:
select * from RFIDEvent where command in ('OBSERVATION', 'SIGNAL')The statement is equivalent to:
select * from RFIDEvent where command = 'OBSERVATION' or command = 'SIGNAL'
Expression may also return an array, a java.util.Collection or a java.util.Map. Thus event properties that are lists, sets or maps may provide values to compare against test_expression.
All expressions must be of the same type or a compatible type to test_expression. The in keyword may coerce number values to compatible types. If expression returns an array, then the component type of the array must be compatible, unless the component type of the array is Object.
If expression returns an array of component type Object, the operation compares each element of the array, applying equals semantics.
If expression returns a Collection, the operation determines if the collection contains the value returned by test_expression, applying contains semantics.
If expression returns a Map, the operation determines if the map contains the key value returned by test_expression, applying containsKey semantics.
Constants, arrays, Collection and Map expressions or event properties can be used combined.
For example, and assuming a property named 'mySpecialCmdList' exists that contains a list of command strings:
select * from RFIDEvent where command in ( 'OBSERVATION', 'SIGNAL', mySpecialCmdList)
When using prepared statements and substitution parameters with the in keyword, make sure to retain the parenthesis. Substitution values may also be arrays, Collection and Map values:
test_expression [not] in (? [,?...] )Note that if there are no successes and at least one right-hand row yields null for the operator's result, the result of the any construct will be null, not false. This is in accordance with SQL's normal rules for Boolean combinations of null values.
The in keyword can be used to specify ranges, including open, half-closed, half-open and inverted ranges.
Ranges come in the following 4 varieties. The round () or square [] bracket indicate whether an endpoint is included or excluded. The low point and the high-point of the range are separated by the colon : character.
Open ranges that contain neither endpoint
(low:high)Closed ranges that contain both endpoints
[low:high]. The equivalent 'between' keyword also defines a closed range.Half-open ranges that contain the low endpoint but not the high endpoint
[low:high)Half-closed ranges that contain the high endpoint but not the low endpoint
(low:high]
The following statement two statements are equivalent: Both statements select orders where the price is in the range of zero and 10000 (endpoints inclusive):
select * from OrderEvent where price in [0:10000]
select * from OrderEvent where price between 0 and 10000
The next statement selects order events where the price is greater then 100 and less-or-equal to 2000:
select * from OrderEvent where price in (100:2000]
Use the not in keywords to specify an inverted range.
The following statement selects an inverted range by selecting all order events where the price is less then zero or the price is greater or equal to 10000:
select * from OrderEvent where price not in (0:10000]
In case the value of low endpoint is less then the value of high endpoint the in operator reverses the range.
The following two statements are also equivalent:
select * from OrderEvent where price in [10000:0]
select * from OrderEvent where price >= 0 and price <= 1000
The between keyword specifies a range to test. The syntax of the keyword is:
test_expression [not] between begin_expression and end_expression
The test_expression is any valid expression and is the expression to test for in the range defined by begin_expression and end_expression. The not keyword specifies that the result of the predicate be negated.
The result of a between expression is of type Boolean. If the value of test_expression is greater then or equal to the value of begin_expression and less than or equal to the value of end_expression, the result is true.
The next example shows how the between keyword can be used to select events with a price between 55 and 60 (endpoints inclusive).
select * from StockTickEvent where price between 55 and 60
The equivalent expression without between is:
select * from StockTickEvent where price >= 55 and price <= 60
And also equivalent to:
select * from StockTickEvent where price between 60 and 55
While the between keyword always includes the endpoints of the range, the in operator allows finer control of endpoint inclusion.
In case the value of begin_expression is less then the value of end_expression the between operator reverses the range.
The following two statements are also equivalent:
select * from StockTickEvent where price between 60 and 55
select * from StockTickEvent where price >= 55 and price <= 60
The like keyword provides standard SQL pattern matching. SQL pattern matching allows you to use '_' to match any single character and '%' to match an arbitrary number of characters (including zero characters). SQL patterns are case-sensitive by default. The syntax of like is:
test_expression [not] like pattern_expression [escape string_literal]
The test_expression is any valid expression yielding a String-type or a numeric result. The optional not keyword specifies that the result of the predicate be negated. The like keyword is followed by any valid standard SQL pattern_expression yielding a String-typed result. The optional escape keyword signals the escape character to escape '_' and '%' values in the pattern. The default escape character is backslash (\).
The result of a like expression is of type Boolean. If the value of test_expression matches the pattern_expression, the result value is true. Otherwise, the result value is false.
An example for the like keyword is below.
select * from PersonLocationEvent where name like '%Jack%'
The escape character can be defined as follows. In this example the where-clause matches events where the suffix property is a single '_' character.
select * from PersonLocationEvent where suffix like '!_' escape '!'
The regexp keyword is a form of pattern matching based on regular expressions implemented through the Java java.util.regex package. The syntax of regexp is:
test_expression [not] regexp pattern_expression
The test_expression is any valid expression yielding a String-type or a numeric result. The optional not keyword specifies that the result of the predicate be negated. The regexp keyword is followed by any valid regular expression pattern_expression yielding a String-typed result.
The result of a regexp expression is of type Boolean. If the value of test_expression matches the regular expression pattern_expression, the result value is true. Otherwise, the result value is false.
An example for the regexp keyword is below.
select * from PersonLocationEvent where name regexp '.*Jack.*'
The rexexp function matches the entire region against the pattern via java.util.regex.Matcher.matches() method. Please consult the Java API documentation for more information or refer to Regular Expression Flavors.
The any operator is true if the expression returns true for one or more of the values returned by a list of expressions including array, Collection and Map values.
The synopsis for the any keyword is as follows:
expression operator any (expression [,expression...] )
The left-hand expression is evaluated and compared to each expression result using the given operator, which must yield a Boolean result. The result of any is "true" if any true result is obtained. The result is "false" if no true result is found (including the special case where the expressions are collections that return no rows).
The operator can be any of the following values: =, !=, <>, <, <=, >, >=.
The some keyword is a synonym for any. The in construct is equivalent to = any.
Expression may also return an array, a java.util.Collection or a java.util.Map. Thus event properties that are lists, sets or maps may provide values to compare against.
All expressions must be of the same type or a compatible type. The any keyword coerces number values to compatible types. If expression returns an array, then the component type of the array must be compatible, unless the component type of the array is Object.
If expression returns an array, the operation compares each element of the array.
If expression returns a Collection, the operation determines if the collection contains the value returned by the left-hand expression, applying contains semantics.
When using relationship operators <, <=, >, >= the operator applies to each element in the collection, and non-numeric elements are ignored.
If expression returns a Map, the operation determines if the map contains the key value returned by the left-hand expression, applying containsKey semantics.
When using relationship operators <, <=, >, >= the operator applies to each key in the map, and non-numeric map keys are ignored.
Constants, arrays, Collection and Map expressions or event properties can be used combined.
The next statement demonstrates the use of the any operator:
select * from ProductOrder where category != any (categoryArray)
The above statement selects ProductOrder event that have a category field and a category array, and returns only those events in which the category value is not in the array.
Note that if there are no successes and at least one right-hand row yields null for the operator's result, the result of the any construct will be null, not false. This is in accordance with SQL's normal rules for Boolean combinations of null values.
The all operator is true if the expression returns true for all of the values returned by a list of expressions including array, Collection and Map values.
The synopsis for the all keyword is as follows:
expression operator all (expression [,expression...] )
The left-hand expression is evaluated and compared to each expression result using the given operator, which must yield a Boolean result. The result of all is "true" if all rows yield true (including the special case where the expressions are collections that returns no rows). The result is "false" if any false result is found. The result is null if the comparison does not return false for any row, and it returns null for at least one row.
The operator can be any of the following values: =, !=, <>, <, <=, >, >=.
The not in construct is equivalent to != all.
Expression may also return an array, a java.util.Collection or a java.util.Map. Thus event properties that are lists, sets or maps may provide values to compare against.
All expressions must be of the same type or a compatible type. The all keyword coerces number values to compatible types. If expression returns an array, then the component type of the array must be compatible, unless the component type of the array is Object.
If expression returns an array, the operation compares each element of the array.
If expression returns a Collection, the operation determines if the collection contains the value returned by the left-hand expression, applying contains semantics.
When using relationship operators <, <=, >, >= the operator applies to each element in the collection, and non-numeric elements are ignored.
If expression returns a Map, the operation determines if the map contains the key value returned by the left-hand expression, applying containsKey semantics.
When using relationship operators <, <=, >, >= the operator applies to each key in the map, and non-numeric map keys are ignored.
Constants, arrays, Collection and Map expressions or event properties can be used combined.
The next statement demonstrates the use of the all operator:
select * from ProductOrder where category = all (categoryArray)
The above statement selects ProductOrder event that have a category field and a category array, and returns only those events in which the category value matches all values in the array.
The new has two uses:
Populate a new data structure by evaluating column names and assignment expressions.
Instantiate an object of a given class by its constructor.
The new data structure operator populates a new data structure by evaluating column names and assignment expressions. This is useful when an expression should return multiple results, for performing a transformation or inside enumeration method lambda expressions.
The synopsis is as follows:
new { column_name = [assignment_expression] [,column_name...] }The result of the new-operator is a map data structure that contains column_name keys and values. If an assignment expression is provided for a column, the operator evaluates the expression and assigns the result to the column name. If no assignment expression is provided, the column name is assumed to be an event property name and the value is the event property value.
The next statement demonstrates the use of the new operator:
select new {category, price = 2*price} as priceInfo from ProductOrder
The above statement returns a single property priceInfo for each arriving ProductOrder event. The property value is itself a map that contains two entries: For the key name category the value of the category property and for the key name price the value of the price property multiplied by two.
The next EPL is an example of the new operator within an expression definition and a case-statement (one statement not multiple):
expression calcPrice {
productOrder => case
when category = 'fish' then new { sterialize = 'XRAY', priceFactor = 1.01 }
when category = 'meat' then new { sterialize = 'UVL', priceFactor = 1 }
end
}
select calcPrice(po) as priceDetail from ProductOrder po
In above example the expression calcPrice returns both a sterialize string value and a priceFactor double value. The expression is evaluated as part of the select-clause and the map-type result placed in the priceDetail property of output events.
When used within the case operator, the operator validates that the data structure is compatible between each case-when result in terms of column names and types. The default value for else in case is null.
The new instantiation operator can instantiate an object of the given class.
The synopsis is as follows:
new class-name([parameter [, parameter [,...]]])
The class-name is the name of the class to instantiate an object for. The classname can either be fully-qualified or you can add the package or classname to the imports.
After the classname follow parenthesis and any number of parameter expressions. The compiler expects that the class declares a public constructor matching the number and return types of parameter expressions.
Assuming that OrderHolder is an imported class, the next statement demonstrates the use of the new operator:
select new OrderHolder(po) as orderHolder from ProductOrder as po
The new instantiation operator can instantiate an array of the given type. The syntax follows common programming language syntax.
The synopsis for one-dimensional arrays is:
new class-name[dimension-one]
The synopsis for two-dimensional arrays is:
new class-name[dimension-one][dimension-two]
The class-name is the name of the class that is the component type of the array.
For a one-dimensional array provide single square brackets, i.e. [dimension-one], wherein the dimension-one expression returns an integer value providing the size of the array.
For a two-dimensional array provide two square brackets, i.e. [dimension-one][dimension-two], wherein the dimension-one expression returns an integer value providing the size of the first dimension and the dimension-two expression returns an integer value providing the size of the second dimension of the array.
The next EPL allocates a one-dimensional array of size 5 holding double-type values, and a two-dimensional array of size 2 by 4 holding string-type values:
select new double[5] as doubleArrayOneDimensional, new string[2][4] as stringArrayTwoDimensional from ProductOrder
The operator allocates the respective array without initializing and without setting array element values. Thereby array element values are the JVM default values for the respective type.
In the case that any dimension expression returns a null value the runtime throws an EPException.
Only one- or two-dimensional arrays are supported by the new-operator and otherwise arrays can also be allocated using a single-row function.
The new instantiation operator can instantiate an array of the given type and initialize its array element values. The syntax follows common programming language syntax.
The synopsis for one-dimensional arrays is:
new class-name[] { [expression [,expression...]] }
The synopsis for two-dimensional arrays is:
new class-name[][] { {[expression [,expression...]]}, [{...}] }
The class-name is the name of the class that is the component type of the array.
The array initialization consist of zero or more expressions within curly ({ and }) braces. For two-dimensional arrays the curly braces must be nested.
The array dimensions are implied by the number of initialization expressions.
This sample EPL allocates a one-dimensional array of size 5 holding double-type values and initializes the array to values between 1 and 5, and also allocates and initializes a two-dimensional array of size 2 by 4 holding string-type values:
select new double[] {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} as doubleArrayOneDimensional,
new string[][] {{'0-0', '0-1', '0-2', '0-3'}, {'1-0', '1-1', '1-2', '1-3'}} as stringArrayTwoDimensional from ProductOrder
In the case that the array component type is a primitive type (i.e. int, long, double etc.) and when any expression returns a null value the runtime throws an EPException.
Only one- or two-dimensional arrays are supported by the new-operator and otherwise arrays can also be allocated and initialized using a single-row function.
- 10.1. Single-Row Function Reference
- 10.1.1. The Case Control Flow Function
- 10.1.2. The Cast Function
- 10.1.3. The Coalesce Function
- 10.1.4. The Current_Evaluation_Context Function
- 10.1.5. The Current_Timestamp Function
- 10.1.6. The Event_Identity_Equals Function
- 10.1.7. The Exists Function
- 10.1.8. The Grouping Function
- 10.1.9. The Grouping_Id Function
- 10.1.10. The Instance-Of Function
- 10.1.11. The Istream Function
- 10.1.12. The Min and Max Functions
- 10.1.13. The Previous Function
- 10.1.14. The Previous-Tail Function
- 10.1.15. The Previous-Window Function
- 10.1.16. The Previous-Count Function
- 10.1.17. The Prior Function
- 10.1.18. The Type-Of Function
- 10.2. Aggregation Functions
- 10.3. User-Defined Functions
- 10.4. Select-Clause Transpose Function
Single-row functions return a single value for every single result row generated by your statement. These functions can appear anywhere where expressions are allowed.
EPL allows static Java library methods as single-row functions, and also features built-in single-row functions. In addition, EPL allows instance method invocations on named streams.
You may also register your own single-row function name with the compiler so that your statements become less cluttered. This is described in detail in Section 22.2, “Single-Row Function”. Single-row functions that return an object can be chained.
The compiler auto-imports the following Java library packages:
java.lang.*
java.math.*
java.text.*
java.util.*
Thus Java static library methods can be used in all expressions as shown in below example:
select symbol, Math.round(volume/1000) from StockTickEvent#time(30 sec)
In general, arbitrary Java class names have to be fully qualified (e.g. java.lang.Math) but EPL provides a mechanism for user-controlled imports of classes and packages as outlined in Section 17.4.2, “Class and Package Imports”.
The below table outlines the built-in single-row functions available.
Table 10.1. Syntax and Results of Single-Row Functions
| Single-row Function | Result |
|---|---|
case value when compare_value then result [when compare_value then result ...] [else result] end |
Returns |
case when condition then result [when condition then result ...] [else result] end |
Returns the |
cast(expression, type_name) |
Casts the result of an expression to the given type. |
coalesce(expression, expression [, expression ...]) |
Returns the first non- |
current_evaluation_context() |
Returns an object containing the runtime URI, statement name and context partition id (when applicable). |
current_timestamp[()] |
Returns the current runtime time as a |
exists(dynamic_property_name) |
Returns true if the dynamic property exists for the event, or false if the property does not exist. |
instanceof(expression, type_name [, type_name ...]) |
Returns true if the expression returns an object whose type is one of the types listed. |
istream() |
Returns true if the event is part of the insert stream and false if the event is part of the remove stream. |
max(expression, expression [, expression ...]) |
Returns the highest numeric value among the 2 or more comma-separated expressions. |
min(expression, expression [, expression ...]) |
Returns the lowest numeric value among the 2 or more comma-separated expressions. |
prev(expression, event_property) |
Returns a property value or all properties of a previous event, relative to the event order within a data window, or according to an optional index parameter (N) the positional Nth-from-last value. |
prevtail(expression, event_property) |
Returns a property value or all properties of the first event in a data window relative to the event order within a data window, or according to an optional index parameter (N) the positional Nth-from-first value. |
prevwindow(event_property) |
Returns a single property value of all events or all properties of all events in a data window in the order that reflects the sort order of the data window. |
prevcount(event_property) |
Returns the count of events (number of data points) in a data window. |
prior(expression, event_property) |
Returns a property value of a prior event, relative to the natural order of arrival of events |
typeof(expression) |
If expression is a stream name, returns the event type name of the evaluated event, often used with variant streams. If expression is a property name or expression, returns the name of the expression result type. |
The case control flow function has two versions. The first version takes a value and a list of compare values to compare against, and returns the result where the first value equals the compare value. The second version takes a list of conditions and returns the result for the first condition that is true.
The return type of a case expression is the compatible aggregated type of all return values.
The case expression is sometimes used with the new operator to return multiple results, see Section 9.14, “The 'New' Keyword”.
The example below shows the first version of a case statement. It has a String return type and returns the value 'one'.
select case myexpression when 1 then 'one' when 2 then 'two' else 'more' end from ...
The second version of the case function takes a list of conditions. The next example has a Boolean return type and returns the boolean value true.
select case when 1>0 then true else false end from ...
The cast function casts the return type of an expression to a designated type. The function accepts two parameters:
The first parameter is the property name or expression that returns the value to be casted. The second parameter is the type to cast to.
You can use the as keyword instead of comma (,) to separate parameters.
Valid parameters for the second (type) parameter are:
Any of the Java built-in types:
int, long, byte, short, char, double, float, string, BigInteger, BigDecimal, wherestringis a short notation forjava.lang.StringandBigIntegeras well asBigDecimalare the classes injava.math. The type name is not case-sensitive. Use[]for array types. For example:cast(price, double)
The fully-qualified class name of the class to cast to, for example:
cast(product as org.myproducer.Product)
For parsing date-time values, any of the date-time types:
date, calendar, long, localdatetime, zoneddatetime, localdate, localtime. For these types thedateformatparameter is required as discussed below.
The cast function is often used to provide a type for dynamic (unchecked) properties. Dynamic properties are properties whose type is not known at compile type.
These properties are always of type java.lang.Object.
The cast function as shown in the next statement casts the dynamic "price" property of an "item" in the OrderEvent to a double value.
select cast(item.price?, double) from OrderEvent
The cast function returns a null value if the expression result cannot be casted to the desired type, or if the expression result itself is null.
The cast function adheres to the following type conversion rules:
For all numeric types, the
castfunction utilitzesjava.lang.Numberto convert numeric types, if required.For casts to
stringorjava.lang.String, the function callstoStringon the expression result.For casts to other objects including application objects, the
castfunction considers a Java class's superclasses as well as all directly or indirectly-implemented interfaces by superclasses.
The cast function supports specifying a parameterized type, for example:
select cast(item.listOfAlternativeNames, java.util.List<String>) from OrderEvent
The cast function can parse string-type date-time values to long-type milliseconds, Date, Calendar, LocalDateTime, ZonedDateTime, LocalDate and LocalTime objects.
You must provide the dateformat named parameter as the last parameter to the cast function.
The dateformat parameter expression must return a String-typed value, a SimpleDateFormat-type value or a DateTimeFormatter-type value.
Return a SimpleDateFormat for long/Date/Calendar.
Return a DateTimeFormatter for LocalDateTime/ZonedDateTime/LocalDate/LocalTime.
The next EPL outputs the date May 2, 2010 as a Date-type value:
select cast('20100502', date, dateformat: 'yyyyMMdd') from OrderEvent
You may use date-time methods when cast is returning a date-time value. Expressions can be any expression and do not need to be string constants.
You may parse dates that are ISO 8601-formatted dates by specifying iso as the date format. The ISO 8601 date format is described in Section 7.6.5.1.1, “Specifying Dates”.
For example, assuming the orderDate property is a ISO 8601 formatted date, the runtime can convert it to a long millisecond value like this:
select cast(orderDate, long, dateformat: 'iso') from OrderEvent
The next table shows the recognized date types available:
Table 10.2. Date Types for Casting/Parsing
| Value provided to Cast as the second parameter | Result Type |
|---|---|
date, java.util.Date | java.util.Date |
calendar, java.util.Calendar | java.util.Calendar |
long, java.lang.Long | long |
localdatetime, java.time.LocalDateTime | java.time.LocalDateTime |
localdate, java.time.LocalDate | java.time.LocalDate |
localtime, java.time.LocalTime | java.time.LocalTime |
zoneddatetime, java.time.ZonedDateTime | java.time.ZonedDateTime |
Additional examples are:
select cast(orderDate, localdatetime, dateformat:java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME) from OrderEvent
select cast(orderDate, calendar, dateformat:SimpleDateFormat.getInstance()) from OrderEvent
You may add array brackets ([]) to the type to indicate that the cast-to type is an array. You may add array brackets with the primitive keyword ([primitive]) for casting to an array of primitive values.
Some examples are:
select cast(string_array, string[]), cast(int_primitive_array, int[primitive]), cast(int_boxed_array, int[]), cast(two_dimensional, string[][]), cast(object_array, java.lang.Object[]) from MyEvent
The result of the coalesce function is the first expression in a list of expressions that returns a non-null value. The return type is the compatible aggregated type of all return values.
This example returns a String-typed result of value 'foo':
select coalesce(null, 'foo') from ...
The current_evaluation_context function takes no parameters and returns expression evaluation contextual information as an object of type
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.expr.EPLExpressionEvaluationContext. The object provides the runtime URI, the statement name and the context partition id of
the currently-evaluated expression.
For example:
select current_evaluation_context().getRuntimeURI() as runtimeURI from MyEvent
The context partition id will be -1 when the statement is not associated to a context.
The current_timestamp function is a reserved keyword and requires no parameters. The result of the current_timestamp function is the long-type value of the current runtime time.
The function returns the current runtime timestamp at the time of expression evaluation. When using external-timer events, the function provides the last value of the externally-supplied time at the time of expression evaluation.
This example selects the current runtime time:
select current_timestamp from MyEvent // equivalent to select current_timestamp() from MyEvent
The event_identity_equals function returns a boolean value indicating whether two events are the same event. The function accepts two parameters and both parameters must be a stream name.
It validates that the event type of each stream is the same event type.
In a subquery, the function can be used to exclude the currently-arriving event from results, as shown below.
select * from OrderEvent as arrivingEvent
where exists (select * from OrderEvent#time(5) as last5
where not event_identity_equals(arrivingEvent, last5) and arrivingEvent.orderId = last5.orderId)You may also use this function with enumeration methods that process events. The next sample totals up window amounts excluding the current event.
select orderId, window(*) .aggregate(0d, (result, e) => result + (case when event_identity_equals(oe, e) then 0d else e.amount end)) as c0 from OrderEvent#time(10) as oe
The function returns null when either of the streams have no event.
The exists function returns a boolean value indicating whether the dynamic property, provided as a parameter to the function, exists on the event. The exists function accepts a single dynamic property name as its only parameter.
The exists function is for use with dynamic (unchecked) properties. Dynamic properties are properties whose type is not known at compile type. Dynamic properties return a null value
if the dynamic property does not exists on an event, or if the dynamic property exists but the value of the dynamic property is null.
The exists function as shown next returns true if the "item" property contains an object that has a "serviceName" property. It returns false if the "item" property is null, or if the "item" property does not
contain an object that has a property named "serviceName" :
select exists(item.serviceName?) from OrderEvent
The grouping function is a SQL-standard function useful in statements that have a group by-clause and that utilize one of the rollup, cube or grouping sets keywords. The function can be used only in the select-clause, having-clause and order by-clauses.
The function takes a single expression as a parameter and returns an integer value of zero or one indicating whether a specified expression in a group-by-clause is aggregated or not.
The function returns 1 for aggregated or 0 for not aggregated.
The grouping function can help you distinguish null values returned because of the output row's aggregation level from null values returned by event properties or other expressions.
The parameter expression must match exactly one of the expressions in the group-by-clause.
Please see an example in the next section.
The grouping_id function is a SQL-standard function useful in statements that have a group by-clause and that utilize one of the rollup, cube or grouping sets keywords. The function can be used only in the select-clause, having-clause and order by-clauses.
The function takes one or more expressions as a parameter and returns an integer value indicating grouping level. The runtime computes the grouping level by taking the results of multiple grouping functions and concatenating them into a bit vector (a string of ones and zeros).
Assume a car event that has a property for name, place and number of cars:
create schema CarEvent(name string, place string, numcars int)
The next EPL computes the total number of cars for each of the following groupings: per name and place, per name, per place and overall.
select name, place, sum(numcars), grouping(name), grouping(place), grouping_id(name, place) from CarEvent group by grouping sets((name, place),name, place,())
Assume your application processes a car event with properties like so: CarEvent={name='skoda', place='france', numcars=100}.
The runtime outputs 4 rows as shown in the next table:
Table 10.3. Example Output for Grouping and Grouping_id Functions (CarEvent 1)
| name | place | sum(numcars) | grouping(name) | grouping(place) | grouping_id(name, place) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| skoda | france | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| skoda | null | 100 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| null | france | 100 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| null | null | 100 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
Assume your application processes a second car event: CarEvent={name='skoda', place='germany', numcars=75}.
The runtime outputs 4 rows as shown in the next table:
Table 10.4. Example Output for Grouping and Grouping_id Functions (CarEvent 2)
| name | place | sum(numcars) | grouping(name) | grouping(place) | grouping_id(name, place) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| skoda | germany | 75 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| skoda | null | 175 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| null | germany | 75 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| null | null | 175 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
The parameter expressions must match exactly to expressions in the group-by-clause.
The instanceof function returns a boolean value indicating whether the type of value returned by the expression is one of the given types. The first parameter to the instanceof function is an expression to evaluate. The second and subsequent parameters are Java type names.
The function determines the return type of the expression at runtime by evaluating the expression, and compares the type of object returned by the expression to the defined types.
If the type of object returned by the expression matches any of the given types, the function returns true. If the expression returned null or a type that does not
match any of the given types, the function returns false.
The instanceof function is often used in conjunction with dynamic (unchecked) properties. Dynamic properties are properties whose type is not known at compile type.
This example uses the instanceof function to select different properties based on the type:
select case when instanceof(item, com.mycompany.Service) then serviceName? when instanceof(item, com.mycompany.Product) then productName? end from OrderEvent
The instanceof function returns false if the expression tested by instanceof returned null.
Valid parameters for the type parameter list are:
Any of the Java built-in types:
int, long, byte, short, char, double, float, string, wherestringis a short notation forjava.lang.String. The type name is not case-sensitive. For example, the next function tests if the dynamic "price" property is either of type float or type double:instanceof(price?, double, float)
The fully-qualified class name of the class to cast to, for example:
instanceof(product, org.myproducer.Product)
The function considers an event class's superclasses as well as all the directly or indirectly-implemented interfaces by superclasses.
The istream function returns a boolean value indicating whether within the context of expression evaluation the current event or set of events (joins) are part of the insert stream (true) or part of the remove stream (false). The function takes no parameters.
Use the istream function with data windows and select irstream and insert irstream into.
In the following example the istream function always returns boolean true since no data window is declared:
select irstream *, istream() from OrderEvent
The next example declares a data window. For newly arriving events the function returns boolean true, for events that expire after 10 seconds the function returns boolean false:
select irstream *, istream() from OrderEvent#time(10 sec)
The istream function returns true for all cases where insert or remove stream does not apply, such as when used in parameter expressions to data windows
or in stream filter expressions.
The min and max function take two or more parameters that itself can be expressions. The min function returns the lowest numeric value among the 2 or more comma-separated expressions, while the max function returns the highest numeric value.
The return type is the compatible aggregated type of all return values.
The next example shows the max function that has a Double return type and returns the value 1.1.
select max(1, 1.1, 2 * 0.5) from ...
The min function returns the lowest value. The statement below uses the function to determine the smaller of two timestamp values.
select symbol, min(ticks.timestamp, news.timestamp) as minT from StockTickEvent#time(30 sec) as ticks, NewsEvent#time(30 sec) as news where ticks.symbol = news.symbol
The prev function returns the property value or all event properties of a previous event. For data windows that introduce a sort order other than the order of arrival, such as the sorted data window and the time order data window, the function returns the event at the specified position.
The prev function is not an aggregation function and therefore does not return results per group when used with group by. Please consider the last, lastever or first aggregation functions instead as described in Section 10.2.2, “Event Aggregation Functions”. You must use an aggregation function instead of prev when querying a named window or table.
The first parameter to the prev function is an index parameter and denotes the i-th previous event, in the order established by the data window. If no index is provided, the default index is 1 and the function returns the previous event.
The second parameter is a property name or stream name. If specifying a property name, the function returns the value for the previous event property value. If specifying a stream name, the function returns the previous event underlying object.
This example selects the value of the price property of the 2nd-previous event from the current Trade event:
select prev(2, price) from Trade#length(10)
By using the stream alias in the previous function, the next example selects the trade event itself that is immediately previous to the current Trade event
select prev(1, trade) from Trade#length(10) as trade
Since the prev function takes the order established by the data window into account, the function works well with sorted windows.
In the following example the statement selects the symbol of the 3 Trade events that had the largest, second-largest and third-largest volume.
select prev(0, symbol), prev(1, symbol), prev(2, symbol) from Trade#sort(3, volume desc)
The i-th previous event parameter can also be an expression returning an Integer-type value. The next statement joins the Trade data window with an RankSelectionEvent event that provides a rank property used to look up a certain position in the sorted Trade data window:
select prev(rank, symbol) from Trade#sort(10, volume desc), RankSelectionEvent unidirectional
Use the prev function in combination with a grouped data window to access a previous event per grouping criteria.
The example below returns the price of the previous Trade event for the same symbol, or null if for that symbol there is no previous Trade event:
select prev(1, price) from Trade#groupwin(symbol)#length(2)
The prev function returns a null value if the data window does not currently hold the i-th previous event. The example below illustrates this using a time batch window. Here the prev
function returns a null value for any events in which the previous event is not in the same batch of events. Note that the prior function as discussed below can be used if a null value is not the desired result.
select prev(1, symbol) from Trade#time_batch(1 min)
An alternative form of the prev function allows the index to not appear or appear after the property name if the index value is a constant and not an expression:
select prev(1, symbol) from Trade // ... equivalent to ... select prev(symbol) from Trade // ... and ... select prev(symbol, 1) from Trade
The combination of the prev function and #groupwin returns the property value for a previous event in the given data window group.
The following example returns for each event the current smallest price per symbol:
select symbol, prev(0, price) as topPricePerSymbol from Trade#groupwin(symbol)#sort(1, price asc)
The following restrictions apply to the prev functions and its results:
The function always returns a
nullvalue for remove stream (old data) events.The function requires a data window, or
#groupwinand a data window. See Section 14.3, “Data Windows” for data windows.
The prev function is similar to the prior function. The key differences between the two functions are as follows:
The
prevfunction returns previous events in the order provided by the data window, while thepriorfunction returns prior events in the order of arrival as posted by a stream's declared windows.The
prevfunction requires a data window while thepriorfunction does not have any such requirement.The
prevfunction returns the previous event grouped by a criteria by combining the#groupwinand a data window. Thepriorfunction returns prior events posted regardless of data window grouping.The
prevfunction returns anullvalue for remove stream events, i.e. for events leaving a data window. Thepriorfunction does not have this restriction.
The prevtail function returns the property value or all event properties of the positional-first event in a data window. For data windows that introduce a sort order other than the order of arrival, such as the sorted data window and the time order data window, the function returns the first event at the specified position.
The prevtail function is not an aggregation function and therefore does not return results per group when used with group by. Please consider the first, firstever or window aggregation functions instead as described in Section 10.2.2, “Event Aggregation Functions”. You must use an aggregation function instead of prevtail when querying a named window or table.
The first parameter is an index parameter and denotes the i-th from-first event in the order established by the data window. If no index is provided the default is zero and the function returns the first event in the data window. The second parameter is a property name or stream name. If specifying a property name, the function returns the value for the previous event property value. If specifying a stream name, the function returns the previous event underlying object.
This example selects the value of the price property of the first (oldest) event held in the length window:
select prevtail(price) from Trade#length(10)
By using the stream alias in the prevtail function, the next example selects the trade event itself that is the second event held in the length window:
select prevtail(1, trade) from Trade#length(10) as trade
Since the prevtail function takes the order established by the data window into account, the function works well with sorted windows.
In the following example the statement selects the symbol of the 3 Trade events that had the smallest, second-smallest and third-smallest volume.
select prevtail(0, symbol), prevtail(1, symbol), prevtail(2, symbol) from Trade#sort(3, volume asc)
The i-th previous event parameter can also be an expression returning an Integer-type value. The next statement joins the Trade data window with an RankSelectionEvent event that provides a rank property used to look up a certain position in the sorted Trade data window:
select prevtail(rank, symbol) from Trade#sort(10, volume asc), RankSelectionEvent unidirectional
The prev function returns a null value if the data window does not currently holds positional-first or the Nth-from-first event. For batch data windows the value returned is relative to the current batch.
The following example returns the first and second symbol value in the batch:
select prevtail(0, symbol), prevtail(1, symbol) from Trade#time_batch(1 min)
An alternative form of the prevtail function allows the index to not appear or appear after the property name if the index value is a constant and not an expression:
select prevtail(1, symbol) from Trade // ... equivalent to ... select prevtail(symbol) from Trade // ... and ... select prevtail(symbol, 1) from Trade
The combination of the prevtail function and #groupwin returns the property value for a positional first event in the given data window group.
Let's look at an example. This statement outputs the oldest price per symbol retaining the last 10 prices per symbol:
select symbol, prevtail(0, price) as oldestPrice from Trade#groupwin(symbol)#length(10)
The following restrictions apply to the prev functions and its results:
The function always returns a
nullvalue for remove stream (old data) events.The function requires a data window, or a
#groupwinand a data window. See Section 14.3, “Data Windows” for built-in data windows.
The prevwindow function returns property values or all event properties for all events in a data window. For data windows that introduce a sort order other than the order of arrival, such as the sorted data window and the time order data window, the function returns the event data sorted in that order, otherwise it returns the events sorted by order of arrival with the newest arriving event first.
The prevwindow function is not an aggregation function and therefore does not return results per group when used with group by. Please consider the window aggregation function instead as described in Section 10.2.2, “Event Aggregation Functions”. You must use an aggregation function instead of prevwindow when querying a named window or table.
The single parameter is a property name or stream name. If specifying a property name, the function returns the value of the event property for all events held by the data window. If specifying a stream name, the function returns the event underlying object for all events held by the data window.
This example selects the value of the price property of all events held in the length window:
select prevwindow(price) from Trade#length(10)
By using the stream alias in the prevwindow function, the next example selects all trade events held in the length window:
select prevwindow(trade) from Trade#length(10) as trade
When used with a data window that introduces a certain sort order, the prevwindow function returns events sorted according to that sort order.
The next statement outputs for every arriving event the current 10 underying trade event objects that have the largest volume:
select prevwindow(trade) from Trade#sort(10, volume desc) as trade
The prevwindow function returns a null value if the data window does not currently hold any events.
The combination of the prevwindow function and #groupwin returns the property value(s) for all events in the given data window group.
This example statement outputs all prices per symbol retaining the last 10 prices per symbol:
select symbol, prevwindow(price) from Trade#groupwin(symbol)#length(10)
The following restrictions apply to the prev functions and its results:
The function always returns a
nullvalue for remove stream (old data) events.The function requires a data window, or
#groupwinand a data window. See Section 14.3, “Data Windows” for built-in data windows.
The prevcount function returns the number of events held in a data window.
The prevcount function is not an aggregation function and therefore does not return results per group when used with group by. Please consider the count(*) or countever aggregation functions instead as described in Section 10.2, “Aggregation Functions”. You must use an aggregation function instead of prevcount when querying a named window or table.
The single parameter is a property name or stream name of the data window to return the count for.
This example selects the number of data points for the price property held in the length window:
select prevcount(price) from Trade#length(10)
By using the stream alias in the prevcount function the next example selects the count of trade events held in the length window:
select prevcount(trade) from Trade#length(10) as trade
The combination of the prevcount function and #groupwin returns the count of events in the given data window group.
This example statement outputs the number of events retaining the last 10 events per symbol:
select symbol, prevcount(price) from Trade#groupwin(symbol)#length(10)
The following restrictions apply to the prev functions and its results:
The function always returns a
nullvalue for remove stream (old data) events.The function requires a data window, or a
#groupwinand a data window. See Section 14.3, “Data Windows” for built-in data windows.
The prior function returns the property value of a prior event.
The first parameter is an expression returning a constant integer-typed value that denotes the i-th prior event in the natural order of arrival.
The second parameter is a property name for which the function returns the value for the prior event.
The second parameter is a property name or stream name. If specifying a property name, the function returns the property value for the prior event. If specifying a stream name, the function returns the prior event underlying object.
This example selects the value of the price property of the 2nd-prior event to the current Trade event.
select prior(2, price) from Trade
By using the stream alias in the prior function, the next example selects the trade event itself that is immediately prior to the current Trade event
select prior(1, trade) from Trade as trade
The prior function can be used on any event stream and does not require declaring a data window. The function operates on the order of arrival of events by the event stream that provides the events.
The next statement uses a time batch window to compute an average volume for 1 minute of Trade events, posting results every minute. The select-clause
employs the prior function to select the current average and the average before the current average:
select average, prior(1, average)
from TradeAverages#time_batch(1 min)#uni(volume)
The typeof function, when parameterized by a stream name, returns the event type name of the evaluated event which can be useful with variant streams. When parameterized by an expression or property name, the function returns the type name of the expression result or null if the expression result is null.
In summary, the function determines the return type of the expression at runtime by evaluating the expression and returns the type name of the expression result.
The typeof function is often used in conjunction with variant streams. A variant stream is a predefined stream into which events of multiple disparate event types can be inserted. The typeof function, when passed a stream name alias, returns the name of the event type of each event in the stream.
The following example elaborates on the use of variant streams with typeof. The first statement declares a variant stream SequencePatternStream:
create variant schema SequencePatternStream as *
The next statement inserts all order events and is followed by a statement to insert all product events:
insert into SequencePatternStream select * from OrderEvent;
insert into SequencePatternStream select * from PriceEvent;
This example statement returns the event type name for each event in the variant stream:
select typeof(sps) from SequencePatternStream as sps
The next example statement detects a pattern by utilizing the typeof function to find pairs of order event immediately followed by product event:
select * from SequencePatternStream match_recognize(
measures A as a, B as b
pattern (A B)
define A as typeof(A) = "OrderEvent",
B as typeof(B) = "ProductEvent"
)
When passing a property name to the typeof function, the function evaluates whether the property type is event type (a fragment event type). If the property type is event type, the function returns the type name of the event in the property value or null if not provided.
If the property type is not event type, the function returns the simple class name of the property value.
When passing an expression to the typeof function, the function evaluates the expression and returns the simple class name of the expression result value or null if the expression result value is null.
This example statement returns the simple class name of the value of the dynamic property prop of events in stream MyStream, or a null value if the property is not found for an event or the property value itself is null:
select typeof(prop?) from MyStream
When using subclasses or interface implementations as event classes or when using Map-event type inheritance, the function returns the event type name provided when the class or Map-type event was registered, or if the event type was not registered, the function returns the fully-qualified class name.
Aggregation functions are stateful and consider sets of events or value points. The group by clause is often used in conjunction with aggregation functions to group the result-set by one or more columns.
Aggregation functions can be a column type for table declarations. This allows easy sharing of aggregated state, co-location of aggregations and other data as well as co-aggregation by multiple statements into the same aggregation state. Please see Section 6.1.2, “Table Overview” for details.
The EPL language extends the standard SQL aggregation functions by allowing filters and by further useful aggregation functions that can track a data window or compute event rates, for example. Your application may also add its own aggregation function as Section 22.5, “Aggregation Function” describes.
The EPL language allows each aggregation function to specify its own grouping criteria. Please find further information in Section 5.6.4, “Specifying Grouping for Each Aggregation Function”.
The EPL language allows each aggregation function to specify its own filter criteria. Please find further information in Section 5.6.5, “Specifying a Filter Expression for Each Aggregation Function”.
Aggregation values are always computed incrementally: Insert and remove streams result in aggregation value changes. The exceptions are fire-and-forget queries and joins when using the unidirectional keyword. Aggregation functions are optimized to retain the minimal
information necessary to compute the aggregated result, and to share aggregation state between eligible other aggregation functions in the same statement so that same-kind aggregation state is
never held multiple times unless required.
Most aggregation functions can also be used with unbound streams when no data window is specified. A few aggregation functions require a data window or named window as documented below.
The SQL-standard aggregation functions are shown in below table.
Table 10.5. Syntax and Results of SQL-Standard Aggregation Functions
| Aggregate Function | Result |
|---|---|
avedev([all|distinct] expression [, filter_expr]) |
Mean deviation of the (distinct) values in the expression, returning a value of The optional filter expression limits the values considered for computing the mean deviation. |
avg([all|distinct] expression [, filter_expr]) |
Average of the (distinct) values in the expression, returning a value of The optional filter expression limits the values considered for computing the average. |
count([all|distinct] expression [, filter_expr]) |
Number of the (distinct) non-null values in the expression, returning a value of The optional filter expression limits the values considered for the count. Further detail on key expressions that return arrays can be found at Section 5.2.13, “Composite Keys and Array Values as Keys”. |
count(* [, filter_expr]) |
Number of events, returning a value of The optional filter expression limits the values considered for the count. |
|
max([all|distinct] expression)
fmax([all|distinct] expression, filter_expr)
|
Highest (distinct) value in the expression, returning a value of the same type as the expression itself returns.
Use
Consider using |
|
maxever([all|distinct] expression)
fmaxever([all|distinct] expression, filter_expr)
|
Highest (distinct) value - ever - in the expression, returning a value of the same type as the expression itself returns.
Use
Consider using |
median([all|distinct] expression [, filter_expr]) |
Median (distinct) value in the expression, returning a value of The optional filter expression limits the values considered for computing the median. |
|
min([all|distinct] expression)
fmin([all|distinct] expression, filter_expr)
|
Lowest (distinct) value in the expression, returning a value of the same type as the expression itself returns.
Use
Consider using |
|
minever([all|distinct] expression)
fminever([all|distinct] expression, filter_expr)
|
Lowest (distinct) value - ever - in the expression, returning a value of the same type as the expression itself returns.
Use
Consider using |
stddev([all|distinct] expression [, filter_expr]) |
Standard deviation of the (distinct) values in the expression, returning a value of The optional filter expression limits the values considered for computing the standard deviation. |
sum([all|distinct] expression [, filter_expr]) |
Totals the (distinct) values in the expression, returning a value of The optional filter expression limits the values considered for computing the total. |
If your application provides double-type values to an aggregation function, avoid using Not-a-Number (NaN) and infinity. Also when using double-type values, round-off errors (or rounding errors) may occur due to double-type precision. Consider rounding your result value to the desired precision.
Each of the aggregation functions above takes an optional filter expression as a parameter. The filter expression must return a boolean-type value and applies to the events considered for the aggregation. If a filter expression is provided, then only if the filter expression returns a value of true does the runtime update the aggregation for that event or combination of events.
Consider the following example, which computes the quantity fraction of buy orders among all orders:
select sum(quantity, side='buy') / sum(quantity) as buy_fraction from Orders
Use the fmin and fmax aggregation functions instead of the min and max aggregation functions when providing a filter expression (the min and max functions are also single-row functions).
The next example computes the minimum quantity for buy orders and a separate minimum quantity for sell orders:
select fmin(quantity, side='buy'), fmin(quantity, side = 'sell') from Orders
This sample statement demonstrates specifying grouping criteria for an aggregation function using the group_by named parameter.
It computes, for the last one minute of orders, the ratio of orders per account compared to all orders:
select count(*)/count(*, group_by:()) as ratio from Orders#time(1 min) group by account
The event aggregation functions return one or more events or event properties. When used with group by the event aggregation functions
return one or more events or event properties per group.
The sorted and the window event aggregation functions require that a data window or named window is declared for the applicable stream.
They cannot be used on unbound streams.
The below table summarizes the event aggregation functions available:
Table 10.6. Event Aggregation Functions
| Function | Result |
|---|---|
| first(...) |
Returns the first event or an event property value of the first event. |
| last(...) |
Returns the last event or an event property value of the last event. |
| maxby(criteria) |
Returns the event with the highest sorted value according to criteria expressions. |
| maxbyever(criteria) |
Returns the event with the highest sorted value, ever, according to criteria expressions. |
| minby(criteria) |
Returns the event with the lowest sorted value according to criteria expressions. |
| minbyever(criteria) |
Returns the event with the lowest sorted value, ever, according to criteria expressions. |
| sorted(criteria) |
Returns events sorted according to criteria expressions. Section 10.2.2.7, “Sorted Aggregation Function”.
Also see Section 13.3, “Aggregation Methods for Sorted Aggregations” for methods such as |
| window(...) |
Returns all events or all event's property values. Section 10.2.2.8, “Window Aggregation Function”.
Also see Section 13.4, “Aggregation Methods for Window Aggregations” for methods such as |
In connection with named windows and tables, event aggregation functions can also be used in on-select,
selects with named window or table in the from clause, subqueries against named windows or tables and fire-and-forget queries.
The event aggregation functions are often useful in connection with enumeration methods and they can provide input events for enumeration. Please see Chapter 11, EPL Reference: Enumeration Methods for more information.
When comparing the last aggregation function to the prev function, the differences are as follows. The prev function is not an aggregation function and thereby not sensitive to the presence of group by. The prev function accesses data window contents directly and respects the sort order of the data window. The last aggregation function returns results based on arrival order and tracks data window contents in a separate shared data structure.
When comparing the first aggregation function to the prevtail function, the differences are as follows. The prevtail function is not an aggregation function and thereby not sensitive to the presence of group by. The prevtail function accesses data window contents directly and respects the sort order of the data window. The first aggregation function returns results based on arrival order and tracks data window contents in a separate shared data structure.
When comparing the window aggregation function to the prevwindow function, the differences are as follows. The prevwindow function is not an aggregation function and thereby not sensitive to the presence of group by. The prevwindow function accesses data window contents directly and respects the sort order of the data window. The window aggregation function returns results based on arrival order and tracks data window contents in a separate shared data structure.
When comparing the count aggregation function to the prevcount function, the differences are as follows. The prevcount function is not an aggregation function and thereby not sensitive to the presence of group by.
When comparing the last aggregation function to the nth aggregation function, the differences are as follows. The nth aggregation function does not consider out-of-order deletes (for example with on-delete and sorted windows) and does not revert to the prior expression value when the last event or nth-event was deleted from a data window. The last aggregation function tracks the data window and reflects out-of-order deletes.
From an implementation perspective, the first, last and window aggregation functions share a common data structure for each stream.
The sorted, minby and maxby aggregation functions share a common data structure for each stream.
The synopsis for the first aggregation function is:
first(*|stream.*|value_expression [, index_expression] [, filter:filter_expression])
The first aggregation function returns properties of the very first event. When used with group by, it returns properties of the first event for each group. When specifying an index expression, the function returns properties of the Nth-subsequent event to the first event, all according to order of arrival.
The first parameter to the function is required and defines the event properties or expression result to return. The second parameter is an optional index_expression that must return an integer value used as an index to evaluate the Nth-subsequent event to the first event.
You may specify the wildcard (*) character in which case the function returns the underlying event of the single selected stream. When selecting a single stream you may specify no parameter instead of wildcard. For joins and subqueries you must use the stream wildcard syntax below.
You may specify the stream name and wildcard (*) character in the stream.* syntax. This returns the underlying event for the specified stream.
You may specify a value_expression to evaluate for the first event. The value expression may not select properties from multiple streams.
The index_expression is optional. If no index expression is provided, the function returns the first event. If present, the function evaluates the index expression to determine the value for N, and evaluates the Nth-subsequent event to the first event. A value of zero returns the first event and a value of 1 returns the event subsequent to the first event. You may not specify event properties in the index expression.
The function returns null if there are no events or when the index is larger than the number of events held. When used with group by, it returns null if there are no events for that group or when the index is larger than the number of events held for that group.
To explain, consider the statement below which selects the underlying event of the first sensor event held by the length window of 2 events.
select first(*) from SensorEvent#length(2)
Assume event E1, event E2 and event E3 are of type SensorEvent. When event E1 arrives the statement outputs the underlying event E1. When event E2 arrives the statement again outputs the underlying event E1. When event E3 arrives the statement outputs the underlying event E2, since event E1 has left the data window.
The stream wildcard syntax is useful for joins and subqueries. This example demonstrates a subquery that returns the first SensorEvent when a DoorEvent arrives:
select (select first(se.*) from SensorEvent#length(2) as se) from DoorEvent
The following example shows the use of an index expression. The output value for f1 is the temperature property value of the first event, the value for f2 is the temperature property value of the second event:
select first(temperature, 0) as f1, first(temperature, 1) as f2 from SensorEvent#time(10 sec)
You may use dot-syntax to invoke a method on the first event. You may also append a property name using dot-syntax.
The synopsis for the last aggregation function is:
last(*|stream.*|value_expression [, index_expression][, filter:filter_expression])
The last aggregation function returns properties of the very last event. When used with group by, it returns properties of the last event for each group. When specifying an index expression, the function returns properties of the Nth-prior event to the last event, all according to order of arrival.
Similar to the first aggregation function described above, you may specify the wildcard (*) character, no parameter or stream name and wildcard (*) character or a value_expression to evaluate for the last event.
The index_expression is optional. If no index expression is provided, the function returns the last event. If present, the function evaluates the index expression to determine the value for N, and evaluates the Nth-prior event to the last event. A value of zero returns the last event and a value of 1 returns the event prior to the last event. You may not specify event properties in the index expression.
The function returns null if there are no events or when the index is larger than the number of events held. When used with group by, it returns null if there are no events for that group or when the index is larger than the number of events held for that group.
The next statement selects the underlying event of the first and last sensor event held by the time window of 10 seconds:
select first(*), last(*) from SensorEvent#time(10 sec)
The statement shown next selects the last temperature (f1) and the prior-to-last temperature (f1) of sensor events in the last 10 seconds:
select last(temperature, 0) as f1, select last(temperature, 1) as f2 from SensorEvent#time(10 sec)
The synopsis for the maxby aggregation function is:
maxby(sort_criteria_expression [asc/desc][, sort_criteria_expression [asc/desc]...][, filter:filter_expression])
The maxby aggregation function returns the greatest of all events, compared by using criteria expressions.
When used with group by, it returns the greatest of all events per group.
This example statement returns the sensor id and the temperature of the sensor event that had the highest temperature among all sensor events:
select maxby(temperature).sensorId, maxby(temperature).temperature from SensorEvent
The next EPL returns the sensor event that had the highest temperature and the sensor event that had the lowest temperature, per zone, among the last 10 seconds of sensor events:
select maxby(temperature), minby(temperature) from SensorEvent#time(10 sec) group by zone
Your EPL may specify multiple criteria expressions. If the sort criteria expression is descending please append the desc keyword.
The following EPL returns the sensor event with the highest temperature and if there are multiple sensor events with the highest temperature the statement returns the sensor event that has the newest timestamp value:
select maxby(temperature asc, timestamp desc) from SensorEvent
Event properties that are listed in criteria expressions must refer to the same event stream and cannot originate from different event streams.
If your statement does not define a data window and does not refer to a named window, the semantics of maxby are the same as maxbyever.
The synopsis for the maxbyever aggregation function is:
maxbyever(sort_criteria_expression [asc/desc][, sort_criteria_expression [asc/desc]...][, filter:filter_expression])
The maxbyever aggregation function returns the greatest of all events that ever occurred, compared by using criteria expressions.
When used with group by, it returns the greatest of all events that ever occurred per group.
Compared to the maxby aggregation function the maxbyever does not consider the data window or named window contents
and instead considers all arriving events.
The next EPL computes the difference, per zone, between the maximum temperature considering all events and the maximum temperature considering only the events in the last 10 seconds:
select maxby(temperature).temperature - maxbyever(temperature).temperature from SensorEvent#time(10) group by zone
The synopsis for the minby aggregation function is:
minby(sort_criteria_expression [asc/desc][, sort_criteria_expression [asc/desc]...][, filter:filter_expression])
Similar to the maxby aggregation function, the minby aggregation function returns the lowest of all events, compared by using criteria expressions.
When used with group by, it returns the lowest of all events per group.
Please review the section on maxby for more information.
Similar to the maxbyever aggregation function, the minbyever aggregation function returns the lowest of all events that ever occurred, compared by using criteria expressions.
When used with group by, it returns the lowest of all events per group that ever occured.
Please review the section on maxbyever for more information.
The synopsis for the sorted aggregation function is:
sorted(sort_criteria_expression [asc/desc][, sort_criteria_expression [asc/desc]...][, filter:filter_expression])
The sorted aggregation function maintains a list of events sorted according to criteria expressions.
When used with group by, it maintains a list of events sorted according to criteria expressions per group.
The sorted aggregation offers a number of additional lookup methods such as lowerKey or higherKey, see Section 13.3, “Aggregation Methods for Sorted Aggregations”.
The sample EPL listed next returns events sorted according to temperature ascending for the same zone:
select sorted(temperature) from SensorEvent group by zone
Your EPL may specify multiple criteria expressions. If the sort criteria expression is descending please append the desc keyword.
Enumeration methods can be useful in connection with sorted as the function provides the sorted events as input.
This statement finds the sensor event that when sorted according to temperature is the first sensor event for a Friday timestamp among sensor events for the same zone:
select sorted(temperature).firstOf(v => timestamp.getDayOfWeek()=6) from SensorEvent
Event properties that are listed in criteria expressions must refer to the same event stream and cannot originate from different event streams.
If used in a regular select statement, the use of sorted requires that your EPL defines a data window for the stream or utilizes a named window.
The synopsis for the window aggregation function is:
window(*|stream.*|value_expression [, filter:filter_expression])
The window aggregation function returns all rows. When used with group by, it returns the rows for each group.
The window aggregation offers a number of additional lookup methods such as last or listReference, see Section 13.4, “Aggregation Methods for Window Aggregations”.
Similar to the first aggregation function described above, you may specify the wildcard (*) character or stream name and wildcard (*) character or a value_expression to evaluate for all events.
The function returns null if there are no rows. When used with group by, it returns null if there are no rows for that group.
The next statement selects the underlying event of all events held by the time window of 10 seconds:
select window(*) from SensorEvent#time(10 sec)
If used in a regular select statement, the window aggregation function requires that your stream is bound by a data window or a named window. You may not use the window aggregation function on unbound streams with the exception of fire-and-forget queries or subqueries.
This example statement assumes that the OrderWindow named window exists. For each event entering or leaving the OrderWindow named window
it outputs the total amount removing negative amounts:
select window(*).where(v => v.amount > 0).aggregate(0d, (r, v) => r + v.amount) from OrderWindow
Approximation aggregation functions are aggregations that perform approximate analysis. Compared to the previously-introduced aggregation functions, the functions discussed here have a degree of accuracy and probabilistic behavior.
Count-min sketch (or CM sketch) is a probabilistic sub-linear space streaming algorithm (source: Wikipedia). Count-min sketch computes an approximate frequency, without retaining distinct values in memory, making the algorithm suitable for summarizing very large spaces of distinct values. The estimated count can be used for estimated top-K and estimated heavy-hitters, for example.
The original and detail of the algorithm is described in the paper by Graham Cormode and S. Muthukrishnan. An improved data stream summary: The Count-min sketch and its applications (2004. 10.1016/j.jalgor.2003.12.001).
Count-min sketch can only be used with tables and is not available as an aggregation function other than in a table declaration.
Count-min sketch does not consider events leaving a data window and does not process a remove stream.
The table column type for Count-min sketch is countMinSketch.
For example, the next EPL declares a table that holds a Count-min sketch (does not provision a top-K):
create table WordCountTable(wordcms countMinSketch())
You can parameterize the algorithm by providing a JSON-format structure to the declaration. The available parameters are all optional:
Table 10.7. Count-min Sketch Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
epsOfTotalCount |
Specifies the accuracy (number of values counted * accuracy >= number of errors) of type double. This value defaults to 0.0001. |
confidence |
Provides the certainty with which you reach the accuracy of type double. The default is 0.99. |
seed |
A seed value for computing hash codes of type integer. This default is 123456. |
topk |
The number of top-K values as an integer. If null, the algorithm maintains no top-K list. This value defaults to null (no top-K available). |
agent |
The agent is an extension API class that can interact with Count-min sketch state and also receives the value objects. The agent defines the type of the values that can be counted. The default agent only allows string-type values and utilizes UTF-16 charset encoding.
The default agent is |
The next example EPL declares all available parameters:
create table WordCountTable (wordcms countMinSketch({
epsOfTotalCount: 0.000002,
confidence: 0.999,
seed: 38576,
topk: 20,
agent: 'com.mycompany.CountMinSketchCustomAgent'
}))
The default for the topk parameter is null. Thereby the runtime by default does not compute top-K.
By specifying a positive integer value for topk the algorithm maintains a list of values representing the top estimated counts.
By default, the Count-min sketch group of aggregation functions operates on string-type values only.
The aggregation function allows registering an agent that can handle any other type of value objects and that allows overriding behavior.
The agent class must implement the interface com.espertech.esper.common.client.util.CountMinSketchAgent.
Please see the JavaDoc for implementing an agent. The agent API is an extension API and is subject to change between versions.
The countMinSketchAdd function counts value(s). It expects a single parameter expression returning the value(s) to be counted.
The function can only be used with statements that utilize into table and can accept a filter: filter expression as a parameter.
This example EPL counts words:
into table WordCountTable select countMinSketchAdd(word) as wordcms from WordEvent
The countMinSketchFrequency function returns an estimated count for a given value.
It expects a single parameter expression returning the value(s) for which to estimate and return the long-type count.
The function can only be used as a table-access function against a table column that declares the aggregation countMinSketch.
The next example EPL returns, when a EstimateWordCountEvent event arrives, the estimated frequency of a given word:
select WordCountTable.wordcms.countMinSketchFrequency(word) from EstimateWordCountEvent
The countMinSketchTopK function returns top-K. The function expects no parameters.
The function can only be used as a table-access function against a table column that declares the aggregation countMinSketch
and only if the Count-min sketch was parameterized with a non-null topk parameter (the default is null, see declaration above).
The function returns an array of com.espertech.esper.common.client.util.CountMinSketchTopK.
The following EPL outputs top-K every 10 seconds:
select WordCountTable.wordcms.countMinSketchTopk() from pattern[every timer:interval(10 sec)]
We provide a sample agent code that handles String-type values below. The complete code is available for class CountMinSketchAgentStringUTF16 as part of sources.
public class CountMinSketchAgentStringUTF16 implements CountMinSketchAgent {
public Class[] getAcceptableValueTypes() {
return new Class[] {String.class};
}
public void add(CountMinSketchAgentContextAdd ctx) {
String text = (String) ctx.getValue();
if (text == null) {
return;
}
byte[] bytes = toBytesUTF16(text);
ctx.getState().add(bytes, 1); // increase count by 1
}
public Long estimate(CountMinSketchAgentContextEstimate ctx) {
String text = (String) ctx.getValue();
if (text == null) {
return null;
}
byte[] bytes = toBytesUTF16(text);
return ctx.getState().frequency(bytes);
}
}EPL provides the following additional aggregation functions beyond those in the SQL standard:
Table 10.8. Syntax and Results of EPL Aggregation Functions
| Aggregate Function | Result |
|---|---|
|
countever(* [, filter_expr]) countever(expression [, filter_expr]) |
The
When used with a data window, the result of the function does not change as data points leave a data window. Use the
The optional filter expression limits the values considered for counting rows. The The next example statement outputs the count-ever for sell orders: select countever(*, side='sell') from Order |
| firstever(expression [, filter_expr]) |
The
When used with a data window, the result of the function does not change as data points leave a data window. Use the The optional filter expression limits the values considered for retaining the first-ever value. The next example statement outputs the first price ever for sell orders: select firstever(price, side='sell') from Order |
| lastever(expression [, filter_expr]) |
Returns the last value or last value per group, when used with This sample statement outputs the total price, the first price and the last price per symbol for the last 30 seconds of events and every 5 seconds: select symbol, sum(price), lastever(price), firstever(price) from StockTickEvent#time(30 sec) group by symbol output every 5 sec
When used with a data window, the result of the function does not change as data points leave a data window (for example when all data points leave the data window). Use the The optional filter expression limits the values considered for retaining the last-ever value. The next example statement outputs the last price (ever) for sell orders: select lastever(price, side='sell') from Order |
| leaving([filter:filter_expression]) |
Returns true when any remove stream data has passed, for use in the
The
This sample statement uses select symbol, sum(price) from StockTickEvent#time(30 sec) having leaving() |
| nth(expression, N_index [, filter:filter_expression]) |
Returns the Nth oldest element; If N=0 returns the most recent value. If N=1 returns the value before the most recent value. If N is larger than the events held in the data window for this group, returns null. A maximum N historical values are stored, so it can be safely used to compare recent values in data windows with a large number of events without incurring excessive overhead.
As compared to the This statement outputs every 2 seconds the groups that have new data and their last price and the previous-to-last price: select symbol, nth(price, 1), last(price) from StockTickEvent group by symbol output last every 2 sec |
|
rate(number_of_seconds [, filter:filter_expression]) |
Returns an event arrival rate per second over the provided number of seconds, computed based on runtime time.
Returns null until events fill the number of seconds. Useful with A sample statement to output, every 2 seconds, the arrival rate per second considering the last 10 seconds of events is shown here: select rate(10) from StockTickEvent output snapshot every 2 sec The aggregation function retains a runtime timestamp value for each arriving event. |
|
rate(timestamp_property[, accumulator] [, filter:filter_expression]) |
Returns an event arrival rate over the data window including the last remove stream event. The timestamp_property is the name of a long-type property of the event that provides a timestamp value. The first parameter is a property name or expression providing millisecond timestamp values. The optional second parameter is a property or expression for computing an accumulation rate: If a value is provided as a second parameter then the accumulation rate for that quantity is returned (e.g. turnover in dollars per second). This footprint is designed for use with a data window and requires a data window declared onto the stream. Returns null until events start leaving the window.
This sample statement outputs event rate for each group (symbol) with fixed sample size of four events
(and considering the last event that left). The select colour, rate(timestamp) as rate from StockTickEvent#groupwin(symbol)#length(4) group by symbol |
Built-in aggregation functions can be disabled via configuration (see Section 17.5.6.3, “Extended Built-in Aggregation Functions”). A custom aggregation function of the same name as a built-on function may be registered to override the built-in function.
A user-defined function (UDF) is a single-row function that can be invoked anywhere as an expression itself or within an expresson. The function must simply be a public static method of a public class that the classloader can resolve at statement deployment time. The compiler resolves the function reference at compile-time and verifies parameter types.
For information on calling external services via instance method invocation, please see Section 5.17.5, “Class and Event-Type Variables”. For invoking methods on events, please see Section 5.4.5, “Using the Stream Name”
You may register your own function name for the user-defined function. Please see the instructions in Section 22.2, “Single-Row Function” for registering a function name for a user-defined single-row function.
A single-row function that has been registered with a function name can simply be referenced as function_name(parameters) thus statements can be less cluttered as no class name is required.
The compiler also optimizes evaluation of such registered single-row functions when used in filter predicate expressions as described in Section 22.2.4, “Single-Row Functions in Filter Predicate Expressions”.
An example statement that utilizes the discount function is shown next (assuming that function has been registered).
select discount(quantity, price) from OrderEvent
When selecting from a single stream, use the wildcard (*) character to pass the underlying event:
select discount(*) from OrderEvent
Alternatively use the stream alias or EPL pattern tag to pass an event:
select discount(oe) from OrderEvent as oe
User-defined functions can be also be invoked on instances of an event: Please see Section 5.4.5, “Using the Stream Name” to invoke event instance methods on a named stream.
Note that user-defined functions (not single-row functions) are candidate for caching their return result if the parameters passed are constants and they are not used chained. Please see below for details and configuration.
The example below assumes a class MyClass that exposes a public static method myFunction accepting 2 parameters, and
returing a numeric type such as double.
select 3 * com.mycompany.MyClass.myFunction(price, volume) as myValue from StockTick#time(30 sec)
User-defined functions also take array parameters as this example shows. The section on Section 9.5, “Array Definition Operator” outlines in more detail the types of arrays produced.
select * from RFIDEvent where com.mycompany.rfid.MyChecker.isInZone(zone, {10, 20, 30})Java class names have to be fully qualified (e.g. java.lang.Math) but EPL provides a mechanism for user-controlled imports of classes and packages as outlined in Section 17.4.2, “Class and Package Imports”.
User-defined functions can return any value including null, Java objects or arrays. Therefore user-defined functions can serve to transform, convert or map events, or to extract information and assemble further events.
The following statement is a simple pattern that looks for events of type E1 that are followed by events of type E2. It assigns the tags "e1" and "e2" that the function can use to assemble a final event for output:
select MyLib.mapEvents(e1, e2) from pattern [every e1=E1 -> e2=E2]
User-defined functions may also be chained: If a user-defined function returns an object then the object can itself be the target of the next function call and so on.
Assume that there is a calculator function in the MyLib class that returns a class which provides the search method taking two parameters. The EPL
that takes the result of the calculator function and that calls the search method on the result and returns its return value is shown below:
select MyLib.calculator().search(zonevariable, zone) from RFIDEvent]
A user-defined function should be implemented thread-safe.
A function that converts from one event type to another event type is shown in the next example. The first statement declares a stream that consists of MyEvent events. The second statement employs a conversion function to convert MyOtherEvent events to events of type MyEvent:
insert into MyStream select * from MyEvent insert into MyStream select MyLib.convert(other) from MyOtherEvent as other
In the example above, assuming the event classes MyEvent and MyOtherEvent are Java classes, the static method should have the following footprint:
public static MyEvent convert(MyOtherEvent otherEvent)
For user-defined functions that take no parameters or only constants as parameters the runtime automatically caches the return result of the function, and invokes the function only once. This is beneficial to performance if your function indeed returns the same result for the same input parameters.
You may disable caching of return values of user-defined functions via configuration as described in Section 17.5.6.2, “User-Defined Function or Static Method Cache”.
EPL follows Java standards in terms of widening, performing widening automatically in cases where widening type conversion is allowed without loss of precision, for both boxed and primitive types.
When user-defined functions are overloaded, the function with the best match is selected based on how well the arguments to a function can match up with the parameters, giving preference to the function that requires the least number of widening conversions.
User-defined functions that can receive an arbitrary number of parameter values can use varargs, i.e. can define a function such as function(T arg1, T... args) {...}.
Boxing and unboxing of arrays is not supported in UDF as it is not supported in Java. For example, an array of Integer and an array of int are not compatible types.
When passing the event or underlying event to your method, either declare the parameter to take EventBean (i.e. myfunc(EventBean event))
or as the underlying event type (i.e. myfunc(OrderEvent event)).
When using {} array syntax in EPL, the resulting type is always a boxed type: "{1, 2}" is an array of Integer (and not int since it may contain null values), "{1.0, 2d}" is an array of Double and "{'A', "B"}" is an array of String, while "{1, "B", 2.0}" is an array of Object (Object[]).
The runtime can pass an object containing contextual information such as statement name, function name, runtime URI and context partition id to your
method. The container for this information is EPLMethodInvocationContext in package com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.expr.
Please declare your method to take EPLMethodInvocationContext as the last parameter. The runtime then passes the information along.
A sample method footprint and EPL are shown below:
public static double computeSomething(double number, EPLMethodInvocationContext context) {...}select MyLib.computeSomething(10) from MyEvent
The transpose function is only valid in the select-clause and indicates that the result of the parameter expression should become the underlying event object of the output event.
The transpose function takes a single expression as a parameter. The result object of the parameter expression is subject to transposing as described below.
The function can be useful with insert into to allow an object returned by an expression to become the event itself in the output stream.
Any expression returning a Java object can be used with the transpose function. Typical examples for expressions are a static method invocation, the result of an enumeration method, a plug-in single row function or a subquery.
The examples herein assume that a single-row function by name makeEvent returns an OrderEvent instance (a POJO object, not shown).
The following EPL takes the result object of the invocation of the makeEvent method (assumed to be an OrderEvent instance) and returns the OrderEvent instance as the underlying event of the output event:
select transpose(makeEvent(oi)) from OrderIndication oi
Your select-clause can select additional properties or expressions. In this case the output event underlying object is a pair of the expression result object and the additional properties.
The next EPL also selects the origin property of the order indication event. The output event is a pair of the OrderEvent instance and a map containing the property name and value of origin:
select origin, transpose(makeEvent(oi)) from OrderIndication oi
If the transpose function is not a top-level function, i.e. if it occurs within another expression or within any other clause then the select-clause, the function simply returns the expression result of the parameter expression.
You may insert transposed output events into another stream.
If the stream name in the insert-into clause is already associated to an event type, the compiler checks whether the event type associated to the stream name provided in the insert-into clause matches the event type associated to the object returned by the expression. If the stream name in the insert-into clause is not already associated to an existing event type the compiler associates a new event type using the stream name provided in the insert-into clause.
The type returned by the expression must match the event representation that is defined for the stream, i.e. must be a subtype or implementation of the respective class (POJO, object-array or Map).
For example, the next statement associates the stream name OrderEvent with a class:
create schema OrderEvent as com.mycompany.OrderEvent
A statement can insert into the OrderEvent stream the OrderEvent instance returned by the makeEvent method, as follows:
insert into OrderEvent select transpose(makeEvent(oi)) from OrderIndication oi
It is not valid to select additional properties or expressions in this case, as they would not be part of the output event. The following is not valid:
// not valid insert into OrderEvent select origin, transpose(makeEvent(oi)) from OrderIndication oi
- 11.1. Overview
- 11.2. Example Events
- 11.3. How to Use
- 11.4. Inputs
- 11.4.1. Subquery Results
- 11.4.2. Named Window
- 11.4.3. Table
- 11.4.4. Event Property and Insert-Into With @eventbean
- 11.4.5. Event Aggregation Function
- 11.4.6. Prev, Prevwindow and Prevtail Single-Row Functions as Input
- 11.4.7. Single-Row Function, User-Defined Function and Enum Types
- 11.4.8. Declared Expression
- 11.4.9. Variables
- 11.4.10. Substitution Parameters
- 11.4.11. Match-Recognize Group Variable
- 11.4.12. Pattern Repeat and Repeat-Until Operators
- 11.5. Example
- 11.6. Reference
- 11.6.1. Aggregate
- 11.6.2. AllOf
- 11.6.3. AnyOf
- 11.6.4. ArrayOf
- 11.6.5. Average
- 11.6.6. CountOf
- 11.6.7. DistinctOf
- 11.6.8. Except
- 11.6.9. FirstOf
- 11.6.10. GroupBy
- 11.6.11. Intersect
- 11.6.12. LastOf
- 11.6.13. LeastFrequent
- 11.6.14. Max
- 11.6.15. MaxBy
- 11.6.16. Min
- 11.6.17. MinBy
- 11.6.18. MostFrequent
- 11.6.19. OrderBy and OrderByDesc
- 11.6.20. Reverse
- 11.6.21. SelectFrom
- 11.6.22. SequenceEqual
- 11.6.23. SumOf
- 11.6.24. Take
- 11.6.25. TakeLast
- 11.6.26. TakeWhile
- 11.6.27. TakeWhileLast
- 11.6.28. ToMap
- 11.6.29. Union
- 11.6.30. Where
EPL provides enumeration methods that work with lambda expressions to perform common tasks on subquery results, named windows, tables, event properties or inputs that are or can be projected to a collection of events, scalar values or objects.
Enumeration methods are stateless and the use of enumeration methods alone does not cause the runtime to retain any events or other state (with the possible exception of short-lived caching of evaluation results).
A lambda expression is an anonymous expression. Lambda expressions are useful for encapsulating user-defined expressions that are applied to each element in a collection. This section discusses built-in enumeration methods and their lambda expression parameters.
Lambda expressions use the lambda operator =>, which is read as "goes to" (-> may be used and is equivalent). The left side of the lambda operator specifies the lambda expression input parameter(s) (if any) and the right side holds the expression. The lambda expression x => x * x is read "x goes to x times x.".
Lambda expressions are also used for expression declaration as discussed in Section 5.2.9, “Expression Declaration”.
When writing lambdas, you do not have to specify a type for the input parameter(s) or output result(s) because the compiler can infer all types based on the input and the expression body. So if you are querying an RFIDEvent, for example, then the input variable is inferred to be an RFIDEvent event, which means you have access to its properties and methods.
The term element in respect to enumeration methods means a single event, scalar value or object in a collection that is the input to an enumeration method. The term collection means a sequence or group of elements.
The below table summarizes the built-in enumeration methods available:
Table 11.1. Enumeration Methods
| Method | Result |
|---|---|
|
aggregate(seed, (result, value) lambda) aggregate(seed, (result, value, index) lambda) aggregate(seed, (result, value, index, size) lambda) |
Aggregate elements by using seed as an initial accumulator value and applying an accumulator expression consisting of the result and the value. |
|
allof(predicate lambda) allof( (predicate, index) lambda) allof( (predicate, index, size) lambda) |
Return true when all elements satisfy a condition. |
|
anyof(predicate lambda) anyof( (predicate, index) lambda) anyof( (predicate, index, size) lambda) |
Return true when any element satisfies a condition. |
| arrayOf() |
Returns an array of the scalar elements. |
|
arrayOf(value-selector lambda) arrayOf( (value-selector, index) lambda) arrayOf( (value-selector, index, size) lambda) |
Returns the array containing each value returned by the value-selector expression when applied to each element. |
| average() |
Computes the average of values obtained from numeric elements. |
|
average(projection lambda) average( (projection, index) lambda) average( (projection, index, size) lambda) |
Computes the average of values obtained from elements by invoking a projection expression on each element. |
| countof() |
Returns the number of elements. |
|
countof(predicate lambda) countof( (predicate, index) lambda) countof( (predicate, index, size) lambda) |
Returns the number of elements that satisfy a condition. |
| distinctOf() |
Returns distinct elements according to default hash and equals semantics. |
|
distinctOf(key-selector lambda) distinctOf( (key-selector, index) lambda) distinctOf( (key-selector, index, size) lambda) |
Returns distinct elements according using the key function provided. |
| except(source) |
Produces the set difference of the two collections. |
| firstof() |
Returns the first element. |
|
firstof(predicate lambda) firstof( (predicate, index) lambda) firstof( (predicate, index, size) lambda) |
Returns the first element that satisfies a condition. |
|
groupby(key-selector lambda) groupby( (key-selector, index) lambda) groupby( (key-selector, index, size) lambda) |
Groups the elements according to a specified key-selector expression. |
|
groupby(key-selector lambda, value-selector lambda) groupby( (key-selector, index) lambda, (value-selector, index) lambda) groupby( (key-selector, index, size) lambda, (value-selector, index, size) lambda) |
Groups the elements according to a key-selector expression mapping each element to a value according to a value-selector. |
| intersect(source) |
Produces the set intersection of the two collections. |
| lastof() |
Returns the last element. |
|
lastof(predicate lambda) lastof( (predicate, index) lambda) lastof( (predicate, index, size) lambda) |
Returns the last element that satisfies a condition. |
| leastFrequent() |
Returns the least frequent value among a collection of values. |
|
leastFrequent(transform lambda) leastFrequent( (transform, index) lambda) leastFrequent( (transform, index, size) lambda) |
Returns the least frequent value returned by the transform expression when applied to each element. |
| max() |
Returns the maximum value among a collection of elements. |
|
max(value-selector lambda) max( (value-selector, index) lambda) max( (value-selector, index, size) lambda) |
Returns the maximum value returned by the value-selector expression when applied to each element. |
|
maxby(value-selector lambda) maxby( (value-selector, index) lambda) maxby( (value-selector, index, size) lambda) |
Returns the element that provides the maximum value returned by the value-selector expression when applied to each element. |
| min() |
Returns the minimum value among a collection of elements. |
|
min(value-selector lambda) min( (value-selector, index) lambda) min( (value-selector, index, size) lambda) |
Returns the minimum value returned by the value-selector expression when applied to each element. |
|
minby(value-selector lambda) minby( (value-selector, index) lambda) minby( (value-selector, index, size) lambda) |
Returns the element that provides the minimum value returned by the value-selector expression when applied to each element.. |
| mostFrequent() |
Returns the most frequent value among a collection of values. |
|
mostFrequent(transform lambda) mostFrequent( (transform, index) lambda) mostFrequent( (transform, index, size) lambda) |
Returns the most frequent value returned by the transform expression when applied to each element. |
| orderBy() |
Sorts the elements in ascending order. |
|
orderBy(key-selector lambda) orderBy( (key-selector, index) lambda) orderBy( (key-selector, index, size) lambda) |
Sorts the elements in ascending order according to a key. |
| orderByDesc() |
Sorts the elements in descending order. |
|
orderByDesc(key-selector lambda) orderByDesc( (key-selector, index) lambda) orderByDesc( (key-selector, index, size) lambda) |
Sorts the elements in descending order according to a key. |
| reverse |
Reverses the order of elements. |
|
selectFrom(transform lambda) selectFrom( (transform, index) lambda) selectFrom( (transform, index, size) lambda) |
Transforms each element resulting in a collection of transformed elements. |
| sequenceEqual(second) |
Determines whether two collections are equal by comparing each element ( |
| sumOf() |
Computes the sum from a collection of numeric elements. |
|
sumOf(projection lambda) sumOf( (projection, index) lambda) sumOf( (projection, index, size) lambda) |
Computes the sum by invoking a projection expression on each element. |
| take(numElements) |
Returns a specified number of contiguous elements from the start. |
| takeLast(numElements) |
Returns a specified number of contiguous elements from the end. |
|
takeWhile(predicate lambda) takeWhile( (predicate, index) lambda) takeWhile( (predicate, index, size) lambda) |
Returns elements from the start as long as a specified condition is true. |
|
takeWhileLast(predicate) takeWhileLast( (predicate, index) lambda) takeWhileLast( (predicate, index, size) lambda) |
Returns elements from the end as long as a specified condition is true. |
|
toMap(key-selector lambda, value-selector lambda) toMap( (key-selector, index) lambda, (value-selector, index) lambda) toMap( (key-selector, index, size) lambda, (value-selector, index, size) lambda) |
Returns a Map according to specified key selector and value-selector expressions. |
| union(source) |
Forms a union of the input elements with source elements. |
|
where(predicate lambda) where( (predicate, index) lambda) where( (predicate, index, size) lambda) |
Filters elements based on a predicate. |
The examples in this section come out of the domain of location report (aka. RFID, asset tracking etc.) processing:
The
Itemevent is a report of the location of a certain item. An item can be either a piece of luggage or a passenger.The
LocationReportevent contains a list ofItemitems for which it reports location.The
Zoneevent describes areas that items may move through.
The examples use example single-row functions for computing the distance (distance) and for determining if a location falls within a rectangle (inrect) that are not provided by the EPL language. These example UDF functions are not enumeration methods
and are used in statements to provide a sensible example.
The Item event contains an assetId id, a (x,y) location, a luggage flag to indicate whether the item represents a luggage (true) or passenger (false), and the assetIdPassenger that holds the asset id of the associated passenger when the item is a piece of luggage.
The Item event is defined as follows (access methods not shown for brevity):
public class Item {
String assetId; // passenger or luggage asset id
Location location; // (x,y) location
boolean luggage; // true if this item is a luggage piece
String assetIdPassenger; // if the item is luggage, contains passenger associated
...
The LocationReport event contains a list of Item items for which it reports events.
The LocationReport event is defined as follows:
public class LocationReport {
List<Item> items;
...
The Zone event contains a zone name and (x1, y1, x2, y2) rectangle.
The Zone event is defined as follows:
public class Zone {
String name;
Rectangle rectangle;
...
The Location object is a nested object to Item and provides the current (x,y) location:
public class Location {
int x;
int y;
...
The Rectangle object is a nested object to Zone and provides a zone rectangle(x1,y1,x2,y2):
public class Rectangle {
int x1;
int y1;
int x2;
int y2;
...The syntax for enumeration methods is the same syntax as for any chained invocation:
input_coll.enum_method_name( [method_parameter [, method_parameter [,...]]]) .[ [enum_method_name(...) [...]] | property_name]
Following the input_coll input collection (options outlined below), is the . (dot) operator and the enum_method_name enumeration method name. It follows in parenthesis a comma-separated list of method parameter expressions. Additional enumeration methods can be chained thereafter. An event property name can follow for those enumeration methods returning an event-typed (non-scalar) element.
If the method parameter is a lambda expression with a single lambda-parameter, specify the lambda-parameter name followed by the => lambda operator and followed by the expression. The synopsis for use with a single lambda-parameter is:
method_parameter: lambda_param => lambda_expression
If the method parameter is a lambda expression with two or more lambda-parameters, specify the lambda parameter names in parenthesis followed by the => lambda operator followed by the expression. The synopsis for use with multiple lambda-parameters is:
method_parameter: (lambda_param [,lambda_param [,...]]) => lambda_expression
Generally for lambda expressions, the runtime applies the lambda expression to each element in the input collection. The expression yields a result that, depending on the particular enumeration method, is used for aggregation, as a filter or for output, for example.
Let's look at a statement that employs the where enumeration method and a lambda expression. This example returns items that have a (x, y) location of (0, 0):
select items.where(i => i.location.x = 0 and i.location.y = 0) as zeroloc from LocationReport
As enumeration methods can be chained, this selection is equivalent:
select items.where(i => i.location.x = 0).where(i => i.location.y = 0) as zeroloc from LocationReport
According to above statement the runtime outputs in field zeroloc a collection of Item objects matching the condition.
The where enumeration method has a second version that has two lambda-parameters. The second parameter is the name of the index property which represents the current index of the element within the collection.
This sample statement returns a collection that consists of the first 3 items. This sample statement does not use the item lambda parameter:
select items.where( (item, indexElement) => indexElement < 3) as firstThreeItems from LocationReport
All enumeration methods that have a lambda expression as a parameter allow the lambda expression to declare index and size formal parameters. Index is always the second formal parameter. Size is always the third formal parameter and must appear with the index formal parameter.
The synopsis for passing the index of each collection element to the lambda expression is:
method_parameter: (lambda_param,index_lambda_param) => lambda_expression
The index value starts at zero for the first item.
For example, the next lambda expression concatenates to each element an underscore and the index of each element:
{'A', 'B', 'C'}.selectFrom( (v, i) => v || '_' || Integer.toString(i)) // Returns {'A_0', 'B_1', 'C_2'}The synopsis for passing the index of each collection element as well as the size of the collection to the lambda expression is:
method_parameter: (lambda_param, index_lambda_param, size_lambda_param) => lambda_expression
The following lambda expression concatenates to each element the index and size separated by underscore:
{'A', 'B', 'C'}.selectFrom( (v, i, s) => v || '_' || Integer.toString(i) || '_' || Integer.toString(s)) // Returns {'A_0_3', 'B_1_3', 'C_2_3'}It is not necessary to use classes for event representation. The example above applies the same to Object-array, Map or XML underlying events.
For most enumeration methods the input can be any collection of events, scalar values or objects. For some enumeration methods limitations apply that are documented below. For example, the sumOf enumeration method requires a collection of numeric scalar values if used without parameters.
If the input to sumOf is a collection of events or scalar values the enumeration method requires a lambda expression as parameter that yields the numeric value to use to compute the sum.
Many examples of this section operate on the collection returned by the event property items in the LocationReport event class.
There are many other inputs yielding collections as listed below. Most examples herein use an event property as a input simply because the example can thus be brief and does not need to refer to a subquery, named window, table or other concept.
For enumeration methods that return a collection, for example where and orderBy, the runtime outputs an implementation of the Collection interface that contains the selected value(s). The collection returned must be considered read-only. As Java does not allow resettable iterators, the Collection interface allows more flexibility to query size and navigate among collection elements. We recommend against down-casting a collection returned by the runtime to a more specific subclass of the Collection interface.
For enumeration methods that return an element, for example firstOf, lastOf, minBy and maxBy the runtime outputs the scalar value or the underlying event if operating on events. You may add an event property name after the enumeration method to return a property value.
Enumeration methods generally retain the order of elements provided by the collection.
The following restrictions apply to enumeration methods:
Enumeration methods returning a collection return a read-only implementation of the
Collectioninterface. You may not use any of the write-methods such asaddorremoveon a result collection.
The input of data for built-in enumeration methods is a collection of scalar values, events or other objects. Input can originate from any of the following:
A subquery.
A named window.
A table.
A property of an event that is itself a collection of events or classes, for example indexed properties, or selected properties when using insert-into and
@eventbean.Any of the event aggregation functions (
window,first,last,sorted,maxby,minby,maxbyever,minbyever).The special
prevwindow,prevandprevtailsingle-row functions.A plug-in single-row function, a user-defined function, a script or an enum type.
A declared expression.
Another enumeration method that returns a collection.
An array returned by the
{}array operator.A collection or array returned by a method call on an event or a method call on a variable.
A variable. Usually variables declared as an array.
A substitution parameter value provided by a prepared statement.
In a match-recognize pattern, a group variable.
In an EPL pattern, events collected in a repeat (
[...]) and a repeat-until (... until ...).
Subqueries can return the rows of another stream's data window or rows from a named window or table. By providing a where-clause the rows returned by a subquery can be correlated to data provided by stream(s) in the from-clause. See Section 5.11, “Subqueries”.
A subquery that selects (*) wildcard provides a collection of events as input. A subquery that selects a single value expression provides a collection of scalar values as input. Subqueries that select multiple value expressions are not allowed as input to enumeration methods.
The following example uses a subquery to retrieve all zones for each location report item where the location falls within the rectangle of the zone. Please see a description of example events and functions above.
select assetId, (select * from Zone#unique(name)).where(z => inrect(z.rectangle, location)) as zones from Item
You may place the subquery in an expression declaration to reuse the subquery in multiple places of the same statement.
This sample EPL declares the same statement as above in an expression declaration:
expression myquery {itm =>
(select * from Zone#unique(name)).where(z => inrect(z.rectangle, itm.location))
}
select assetId, myquery(item) as subq,
myquery(item).where(z => z.zone = 'Z01') as assetItem
from Item as item
The above statement also demonstrates how an enumeration method, in the example the where-method, can be run across the results returned by a subquery in an expression declaration.
Place a single column in the subquery select-clause to provide a collection of scalar values as input.
The next example selects all names of zones and orders the names returning an order collection of string names every 30 seconds:
select (select name from Zone#unique(name)).orderBy() as orderedZones from pattern[every timer:interval(30)]
The next example utilizes a subquery that counts zone events per name and finds those that have a count greater than 1:
select (select name, count(*) as cnt from Zone#keepall group by name) .where(v => cnt > 1) from LocationReport]
When the subquery selects a single column that is itself an event, the result of the subquery is a collection of events of that type and can provide input to enumeration methods.
For example:
create schema SettlementEvent (symbol string);
create schema PriceEvent (symbol string, price double);
create schema OrderEvent (orderId string, pricedata PriceEvent);
select (select pricedata from OrderEvent#unique(orderId)) .anyOf(v => v.symbol = 'GE') as has_ge from SettlementEvent(symbol = 'GE')
Note that the runtime can cache intermediate results thereby is not forced to re-evaluate the subquery for each occurrence in the select-clause.
Named windows are globally-visible data windows. See Section 6.2, “Named Window Usage”.
You may specify the named window name as input for an enumeration method and can optionally provide a correlation where-clause. The syntax is equivalent to a sub-query against a named window but much shorter.
Synopsis:
named-window-name[(correlation-expression)].enum-method-name(...)
When selecting all events in a named window you do not need the correlation-expression. To select a subset of data in the named window, specify a correlation-expression. From the perspective of best runtime performance, a correlation expression is preferred to reduce the number of rows returned.
The following example first declares a named window to hold the last zone event per zone name:
create window ZoneWindow#unique(name) as Zone
Then you create a statement to insert zone events that arrive to the named window:
insert into ZoneWindow select * from Zone
Finally this statement queries the named window to retrieve all zones for each location report item where the location falls within the rectangle of the zone:
select ZoneWindow.where(z => inrect(z.rectangle, location)) as zones from Item
If you have a filter or correlation expression, append the expression to the named window name and place in parenthesis.
This slightly modified statement is the example above except that it adds a filter expression such that only zones with name Z1, Z2 or Z3 are considered:
select ZoneWindow(name in ('Z1', 'Z2', 'Z3')).where(z => inrect(z.rectangle, location)) as zones
from ItemYou may prefix property names provided by the named window with the name to disambiguate property names.
This sample statement prefixed the name property and returns the count of matching zones:
select ZoneWindow(ZoneWindow.name in ('Z1', 'Z2', 'Z3')).countof()) as zoneCount
from ItemThe runtime internally interprets the shortcut syntax and creates a subquery from it. Thus all indexing and query planning for subqueries against named windows apply here as well.
Tables are globally-visible data structures. See Section 6.3, “Table Usage”.
Tables can hold aggregation state such as the window and sorted aggregation state.
The example EPL below declares a table to hold StockTick events in a column named theTicks:
create table MyTable(theTicks window(*) @type(StockTick))
The table column can be input to an enumeration method, for example:
select MyTable.theTicks.anyOf(v=> price > 100) from MyEvent
Event properties that are a collection, array or iterable of scalar values or objects can be an input to enumeration methods.
Event properties that hold a collection or array of events can be an input to enumeration methods. Use @eventbean in the select-clause with insert into to select events.
The LocationReport event from the example contains a list of Item events. Any indexed property (list, array, collection, iterable) is eligible for use as input to an enumeration method. If the indexed property contains non-scalar objects the objects are treated as events and can be used as input to enumeration methods as a collection of events.
The next sample statement returns items that are less than 20 units away from the center, taking the items event property provided by each LocationReport event as input:
select items.where(p => distance(0, 0, p.location.x, p.location.y) < 20) as centeritems from LocationReport
The next three statements declare an OrderEvent type that contains OrderDetail events and a statement that enumerates order detail:
create schema OrderDetail(itemId string)
create schema OrderEvent(details OrderDetail[])
select details.where(i => i.itemId = '001') from OrderEvent
The first statement in this two-statement explanation selects the events that have a price of greater than 100 from a 10-second time window if the count of events is at least 10. It inserts the
events into stream TicksLarge. The use of @eventbean means that the event property ticksLargePrice holds events (and not underlying objects).
The second statement further filters the events and returns a collection of events that have price of less than 100.
insert into TicksLarge select window(*).where(e => e.price > 100) @eventbean as ticksLargePrice from StockTick#time(10) having count(*) > 10
select ticksLargePrice.where(e => e.price < 200) as ticksLargeLess200 from TicksLarge
Event aggregation functions return an event or multiple events. They are aggregation functions and as such sensitive to the presence of group by. See Section 10.2.2, “Event Aggregation Functions”.
You can use window, first or last event aggregation functions as input to an enumeration method. Specify the * wildcard as the parameter to the event aggregation function to provide a collection of events as input. Or specify a property name as the parameter to event aggregation function to provide a collection of scalar values as input.
You can use the sorted, maxby, minby, maxbyever or minbyever event aggregation functions as input to an enumeration method. Specify one or more criteria expressions that provide the sort order as parameters to the event aggregation function.
Aggregation methods are used in conjunction with aggregations and can also provide input to an enumeration method. Please go to Section 13.2.5, “Using Dot to Enumerate Events”.
In this example statement the window(*) aggregation function returns the last 10 seconds of item location reports for the same asset id as the incoming event. Among that last 10 seconds of events for the same asset id, the
enumeration method returns those item location reports where the distance to center is less than 20, for each arriving Item event.
Sample statement:
select window(*).where(p => distance(0, 0, p.location.x, p.location.y) < 20) as centeritems from Item(type='P')#time(10) group by assetId
The next sample statement instead selects the asset id property of all events and returns an ordered collection:
select window(assetId).orderBy() as orderedAssetIds from Item#time(10) group by assetId
The following example outputs the 5 highest prices per symbol among the last 10 seconds of stock ticks:
select sorted(price desc).take(5) as highest5PricesPerSymbol from StockTick#time(10) group by symbol
The prev, prevwindow and prevtail single-row functions allow access into a stream's data window however are not aggregation functions and and as such not sensitive to the presence of group by. See Section 10.1.15, “The Previous-Window Function”.
When using any of the prev single-row functions as input to a built-in enumeration method you can specify the stream name as a parameter to the function or an event property. The input to the enumeration method is a collection of events if you specify the stream name, or a collection of scalar value if you specify an event property.
In this example statement the prevwindow(stream) single-row function returns the last 10 seconds of item location reports, among which the
enumeration method filters those item location reports where the distance to center is less than 20, for each Item event that arrived in the last 10 seconds considering passenger-type Item events only (see filter type = 'P').
Sample statement:
select prevwindow(items)
.where(p => distance(0, 0, p.location.x, p.location.y) < 20) as centeritems
from Item(type='P')#time(10) as items
This sample statement demonstrates the use of the prevwindow function to return a collection of scalar values (collection of asset id) as input to orderby:
select prevwindow(assetId).orderBy() as orderedAssetIds from Item#time(10) as items
Your single-row or user-defined function can return either an array or any collection that implements either the Collection or Iterable interface. For arrays, the array component type and for collections, the collection or iterable generic type should be the class providing event properties.
As an example, assume a ZoneFactory class exists and a static method getZones() returns a list of zones to filter items, for example:
public class ZoneFactory {
public static Iterable<Zone> getZones() {
List<Zone> zones = new ArrayList<Zone>();
zones.add(new Zone("Z1", new Rectangle(0, 0, 20, 20)));
return zones;
}
}Import the class through runtime or static configuration, or add the method above as a plug-in single-row function.
The following statement returns for each Item event all zones that the item belongs to:
select ZoneFactory.getZones().where(z => inrect(z.rectangle, item.location)) as zones from Item as item
If the class and method were registered as a plug-in single-row function, you can leave the class name off, for example:
select getZones().where(z => inrect(z.rectangle, item.location)) as zones from Item as item
Your single-row or user-defined function can also return an array, collection or iterable or scalar values.
For example, the static method getZoneNames() returns a list of zone names:
public static String[] getZoneNames() {
return new String[] { "Z1", "Z2"};
}The following statement returns zone names every 30 seconds and excludes zone Z1:
select getZoneNames().where(z => z != "Z1") from pattern[every timer:interval(30)]
An enum type can also be a useful source for enumerable values.
The following sample Java declares an enum type EnumOfZones:
public enum EnumOfZones {
ZONES_OUTSIDE(new String[] {"z1", "z2"}),
ZONES_INSIDE(new String[] {"z3", "z4"})
private final String[] zones;
private EnumOfZones(String[] zones) {
this.zones = zones;
}
public String[] getZones() {
return zones;
}
}A sample statement that utilizes the enum type is shown next:
select EnumOfZones.ZONES_OUTSIDE.getZones().anyOf(v => v = zone) from Item
A declared expression may return input data for an enumeration method.
The below statement declares an expression that returns all passenger location reports among the items in the location report event in a column named passengerCollection. The statement uses the result returned by the declared expression
a second time to filter through the list returning the passenger location report where the asset id is a given value in a column named passengerP01.
Sample statement:
expression passengers {
lr => lr.items.where(l => l.type='P')
}
select passengers(lr) as passengerCollection,
passengers(lr).where(x => assetId = 'P01') as passengerP01
from LocationReport lrThe runtime applies caching techniques to avoid re-evaluating the declared expression multiple times.
A variable may provide input data for an enumeration method.
This constant of array type carries a list of invalid zones:
create constant variable string[] invalid_zones = { 'Z1', 'Z2' };Sample statement:
select invalid_zones.anyOf(v => v = name) as flagged from Zone
A substitution parameter may provide input data for an enumeration method. The value of the parameter must be array-typed.
Sample statement:
select ?.anyOf(v => v = name) as flagged from Zone
In a match-recognize pattern, the term group variables refers to identifiers that can collect multiple events.
This example assumes an order event type and each order has an item id. This sample match-recognize pattern finds a sequence of order events that concludes with an item id matching any of the collected item ids since the last pattern match:
select * from Order match_recognize ( measures A as a_array, B as b pattern (A* B) define B as A.anyOf(v=> v.itemId = B.itemId) )
Both the define and the measures clause can contain expressions utilizing enumeration methods.
In an EPL pattern, the repeat and repeat-until pattern operators may collect multiple events.
The following pattern fires when two order events arrive followed by an order amendment event that has an amount larger than the largest amount of any of the preceding order events:
select * from pattern [ ([2] a=Order) -> b=OrderAmendment(amount > a.max(i => i.amount)) ]
Following the RFID asset tracking example as introduced earlier, this section introduces two use cases solved by enumeration methods.
The first use case requires us to find any luggage that is more than 20 units away from the passenger that the luggage belongs to.
The declared expression lostLuggage solves this question.
The second question to answer is: For each of such lost luggage what single other passenger is nearest to that luggage.
The declared expression nearestOwner which uses lostLuggage answers this question.
Below is the complete statement (one statement not multiple):
// expression to return a collection of lost luggage
expression lostLuggage {
lr => lr.items.where(l => l.type='L' and
lr.items.some(p => p.type='P' and p.assetId=l.assetIdPassenger
and LRUtil.distance(l.location.x, l.location.y, p.location.x, p.location.y) > 20))
}
// expression to return all passengers
expression passengers {
lr => lr.items.where(l => l.type='P')
}
// expression to find the nearest owner
expression nearestOwner {
lr => lostLuggage(lr).toMap(key => key.assetId,
value => passengers(lr).minBy(
p => LRUtil.distance(value.location.x, value.location.y, p.location.x, p.location.y))
)
}
select lostLuggage(lr) as val1, nearestOwner(lr) as val2 from LocationReport lr
The aggregate enumeration method takes an expression providing the initialization value (seed) and an accumulator lambda expression. The return value is the final accumulator value.
Via the aggregate method you may perform a calculation over elements. The method initializes the aggregated value by evaluating the expression provided in the first parameter. The method then calls the lambda expression of the second parameter once for each element in the input. The lambda expression receives the last aggregated value and the element from the input. The result of the expression replaces the previous aggregated value and returns the final result after completing all elements.
The collection element index and collection size are additional optional formal parameters.
Some expression examples with scalar values as input and with the optional collection element index and collection size formal parameters are:
{1, 2, 3}.aggregate(0, (result, value) => result + value) // Returns 6
{1, 2, 3}.aggregate(0, (result, value, index) => result + value + index*10) // Returns 36 = 1 + 12 + 23
{1, 2, 3}.aggregate(0, (result, value, index, size) => result + value + index*10 + size*100) // Returns 936 = 301 + 312 + 323The example below aggregates price of each OrderEvent in the last 10 seconds computing a total price:
// Initialization value is zero. // Aggregate by adding up the price. select window(*).aggregate(0, (result, order) => result + order.price) as totalPrice from OrderEvent#time(10)
In the statement above, the initialization value is zero, result is used for the last aggregated value and order denotes the element that the expression adds the value of the price property.
This example aggregation builds a comma-separated list of all asset ids of all items:
select items.aggregate('',
(result, item) => result || (case when result='' then '' else ',' end) || item.assetId) as assets
from LocationReport
In above statement, the empty string represents the initialization value. The name result is used for the last aggregated value and the name item is used to denote the element.
The type value returned by the initialization expression must match to the type of value returned by the accumulator lambda expression.
If the input is null the method returns null. If the input is empty the method returns the initialization value.
The allof enumeration method determines whether all elements satisfy the predicate condition.
The method takes a single parameter: The predicate lambda expression that must yield a Boolean result. The enumeration method applies the lambda expression to each element and if the expression returns true for all elements, the method returns true.
An expression example with scalar values:
{1, 2, 3}.allOf(v => v > 0) // Returns true as all values are > 0
{1, 2, 3}.allOf(v => v > 1) // Returns false
{1, 2, 3}.allOf( (v, index) => case when index < 2 then true else v > 1 end) // Returns true
{1, 2, 3}.allOf( (v, index, size) => v > 1 or size >= 3) // Returns trueThe statement below returns true when all items are within 1000 unit distance of center:
select items.allof(i => distance(i.location.x, i.location.y, 0, 0) < 1000) as centered from LocationReport
If the input is null the method returns null. If the input is empty the method returns true.
The anyof enumeration method determines whether any element satisfies the predicate condition.
The only parameter is the predicate lambda expression that must yield a Boolean result. The enumeration method applies the lambda expression to each element and if the expression returns true for all elements, the method returns true.
An expression example with scalar values:
{1, 2, 3}.anyOf(v => v > 0) // Returns true
{1, 2, 3}.anyOf(v => v > 1) // Returns true
{1, 2, 3}.anyOf(v => v > 3) // Returns false
{1, 2, 3}.anyOf( (v, index) => case when index < 2 then false else v = 3 end) // Returns true
{1, 2, 3}.anyOf( (v, index, size) => v > 100 or size >= 3) // Returns trueThe statement below return true when any of the items are within 10 unit distance of center:
select items.anyof(i => distance(i.location.x, i.location.y, 0, 0) < 10) as centered from LocationReport
If the input is null the method returns null. If the input is empty the method returns false.
The arrayOf enumeration method returns values as an array.
If no value-selector lambda expression is provided, the method accepts only scalar input and returns the array of scalar values.
If a value-selector lambda expression is provided, the enumeration method invokes a value-selector lambda expression on each element and returns the result values as an array. The type of array returned follows the return type of the lambda expression that was provided as the sole parameter.
The next expressions are examples with scalar input:
{1, 2, 3}.arrayOf() // Returns [1, 2, 3] as an array of Integer
{1, 2, 3}.arrayOf(v => v+1) // Returns [2, 3, 4] as an array of Integer
{1, 2, 3}.arrayOf((v, index) => v+index) // Returns [1, 3, 5] as an array of Integer
{1, 2, 3}.arrayOf((v, index, size) => v+index+size) // Returns [4, 6, 8] as an array of IntegerThe next statement returns the array of distances of any item from center:
select items.arrayOf(i => distance(i.location.x, i.location.y, 0, 0)) as distancesArray from LocationReport
If the input is null the method returns null. If the input is empty the method returns an empty array.
The average enumeration method computes the average of scalar values. If passing a projection lambda expression the method computes the average obtained by invoking the projection lambda expression on each element.
The method takes a projection lambda expression yielding a numeric value as a parameter. It applies the lambda expression to each element and computes the average of the result, returning a Double value. A BigDecimal is returned for expressions returning BigInteger or BigDecimal.
The following are expression examples with scalar values:
{1, 2, 3}.average() // Returns 2
{1, 2, 3}.average(v => v+1) // Returns 3
{1, 2, 3}.average((v, index) => v+10*index) // Returns 12 = (1+12+23)/3
{1, 2, 3}.average((v, index, size) => v+10*index + 100*size) // Returns 312 = (301+312+323)/3The statement as shown next computes the average distance from center among all items in the location report event:
select items.average(i => distance(i.location.x, i.location.y, 0, 0)) as avgdistance from LocationReport
If the input is null the method returns null. If the input is empty the method returns double zero or BigDecimal zero. For BigDecimal precision and rounding, please see Section 17.5.6.5, “Math Context”.
The countof enumeration method returns the number of elements, or the number of elements that satisfy a condition.
The enumeration method has two versions: The first version takes no parameters and computes the number of elements. The second version takes a predicate lambda expression that must yield Boolean true or false, and computes the number of elements that satisfy the condition.
An expression example with scalar values:
{1, 2, 3}.countOf() // Returns 3
{1, 2, 3}.countOf(v => v < 2) // Returns 1
{1, 2, 3}.countOf( (v, index) => v > index) // Returns 3
{1, 2, 3}.countOf( (v, index, size) => v >= size) // Returns 1The next sample statement counts the number of items:
select items.countOf() as cnt from LocationReport
This example statement counts the number of items that have a distance to center that is less than 20 units:
select items.countOf(i => distance(i.location.x, i.location.y, 0, 0) < 20) as cntcenter from LocationReport
If the input is null the method returns null. If the input is empty the method returns integer zero.
The distinctOf enumeration method returns distinct elements.
The enumeration method can take a single key-selector lambda expression as parameter and returns distinct elements according to the key yielded by the expression. For same-value keys, distinct returns the first element for that key. Further detail on key expressions can be found at Section 5.2.13, “Composite Keys and Array Values as Keys”.
An expression example with scalar values:
{2, 3, 2, 1}.distinctOf() // Returns {2, 3, 1}
{2, 3, 2, 1}.distinctOf(v => case when v > 1 then 0 else -1 end) // Returns {2, 1}
{2, 3, 2, 1}.distinctOf((v, index) => case when index = 0 then 1 else 2 end) // Returns {2, 3}
{2, 3, 2, 1}.distinctOf((v, index, size) => case when index+1=size then 1 else 2 end) // Returns {2, 1}This example returns items distinct by item id returning the first item for each distinct item id:
select items.distinctOf(i => itemId) as itemsNearFirst from LocationReport
The key-selector lambda expression, when provided, must return a comparable type: Any primitive or boxed or Comparable type is permitted.
If the input is null the method returns null. If the input is empty the method returns an empty collection.
The except enumeration method forms a set difference of the input elements with the elements that the parameter expression yields.
The enumeration method takes a single parameter that must itself return a collection of events, objects or scalar values. The method returns the elements of the first collection that do not appear in the second collection.
An expression example with scalar values:
{1, 2, 3}.except({1}) // Returns {2, 3}The following statement compares the items of the last location report against all items in the previous 10 location reports, and reports for each combination only those items in the current item report that are not also in the location report compared to:
select za.items.except(zb.items) as itemsCompared from LocationReport as za unidirectional, LocationReport#length(10) as zb
If the input is null the method returns null. For scalar values and objects equals-semantics apply.
The firstOf enumeration method returns the first element or the first element that satisfies a condition.
The method has two versions: The first version takes no parameters and returns the first element. The second version takes a predicate lambda expression yielding true or false. It applies the lambda expression to each element and returns the first element for which the expression returns true. The return type is the element itself and not a collection. You may append a property name to return the property value for the first element.
The example expressions with scalar values are:
{1, 2, 3}.firstOf() // Returns 1
{1, 2, 3}.firstOf(v => v / 2 > 1) // Returns 3
{1, 2, 3}.firstOf((v, index) => index = 1) // Returns 2
{1, 2, 3}.firstOf((v, index, size) => v = size-1) // Returns 2In the following EPL sample the statement returns the first item that has a distance to center that is less than 20 units:
select items.firstof(i => distance(i.location.x, i.location.y, 0, 0) < 20) as firstcenter from LocationReport
The next sample EPL returns the first item's asset id:
select items.firstof().assetId as firstAssetId from LocationReport
If the input is null, empty or if none of the elements match the condition the method returns null.
The groupby enumeration method groups the elements according to a specified key-selector lambda expression. There are two version of the groupby method.
The first version of the method takes a key-selector lambda expression and returns a Map of key with each value a list of objects, one for each distinct key that was encountered. The result is a Map<Object, Collection<Object>> wherein object is the event underlying object.
The second version of the method takes a key-selector lambda expression and value-selector lambda expression and returns a Map of key with each value a list of values, one for each distinct key that was encountered. The result is a Map<Object, Collection<Object>> wherein object is the result of applying the value-selector expression.
The example expressions with scalar values are:
{1, 2, 3}.groupby(k => 'K' || Integer.toString(k)) // Returns map {K1=[1], K2=[2], K3=[3]}
{1, 2, 3}.groupby(k => 'K' || Integer.toString(k), v => 'V' || Integer.toString(v)) // Returns map {K1=[V1], K2=[V2], K3=[V3]}
{1, 2, 3}.groupby(
(k, i) => 'K' || Integer.toString(k) || "_" || Integer.toString(i),
(v, i) => 'V' || Integer.toString(v) || "_" || Integer.toString(i)
) // Returns map {K1_0=[V1_0], K2_1=[V2_1], K3_2=[V3_2]}
{1, 2, 3}.groupby(
(k, i, s) => 'K' || Integer.toString(k) || "_" || Integer.toString(s),
(v, i, s) => 'V' || Integer.toString(v) || "_" || Integer.toString(s)
) // Returns map {K1_3=[V1_3], K2_3=[V2_3], K3_3=[V3_3]}
The next statement filters out all luggage items using a where method and then groups by the luggage's passenger asset id. It returns a map of
passenger asset id and the collection of luggage items for each passenger:
select items.where(type='L').groupby(i => assetIdPassenger) as luggagePerPerson from LocationReport
The statement shown below generates a map of item asset id and distance to center:
select items.groupby(
k => assetId, v => distance(v.location.x, v.location.y, 0, 0)) as distancePerItem
from LocationReportIf the input is null the method returns null. Null values as key and value are allowed.
The intersect enumeration method forms a set intersection of the input elements with the elements that the parameter expression yields.
The enumeration method takes a single parameter that must itself return a collection of events, objects or scalar values. The method returns the elements of the first collection that also appear in the second collection.
An expression example with scalar values:
{1, 2, 3}.intersect({2, 3}) // Returns {2, 3}The following statement compares the items of the last location report against all items in the previous 10 location reports, and reports for each combination all items in the current item report that also occur in the other location report:
select za.items.intersect(zb.items) as itemsCompared from LocationReport as za unidirectional, LocationReport#length(10) as zb
If the input is null the method returns null. For scalar values and objects equals-semantics apply.
The lastOf enumeration method returns the last element or the last element that satisfies a condition.
The method has two versions: The first version takes no parameters and returns the last element. The second version takes a predicate lambda expression yielding true or false. It applies the lambda expression to each element and returns the last element for which the expression returns true. The return type is the element itself and not a collection. You may append a property name to return the property value for the last element.
An expression example with scalar values:
{1, 2, 3}.lastOf() // Returns 3
{1, 2, 3}.lastOf(v => v < 3) // Returns 2
{1, 2, 3}.lastOf((v, index) => index < 2 ) // Result 2
{1, 2, 3}.lastOf((v, index, size) => index < size - 2 ) // Result 1In the following EPL sample the statement returns the last item that has a distance to center that is less than 20 units:
select items.lastof(i => distance(i.location.x, i.location.y, 0, 0) < 20) as lastcenter from LocationReport
The next sample EPL returns the last item's asset id:
select items.lastof().assetId as lastAssetId from LocationReport
If the input is null, empty or if none of the elements match the condition the method returns null.
The leastFrequent enumeration method returns the least frequent value among a collection of values, or the least frequent value after applying a transform expression to each element.
The method has two versions: The first version takes no parameters and returns the least frequent value. The second version takes a transform lambda expression yielding the value to count occurrences for. The method applies the lambda expression to each element and returns the expression result value with the least number of occurrences. The return type is the type of value in the collection or the type of value returned by the transform lambda expression if one was provided.
An expression example with scalar values:
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1}.leastFrequent() // Returns 3
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1}.leastFrequent(v => case when v = 3 then 4 else v end) // Returns 4
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1}.leastFrequent((v, index) => case when index = 2 then 4 else v end) // Returns 4
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1}.leastFrequent((v, index, size) => case when index = size - 2 then 4 else v end) // Returns 2The example EPL below returns the least frequent item type, counting the distinct item types among all items for the current LocationReport event:
select items.leastFrequent(i => type) as leastFreqType from LocationReport
If the input is null or empty the method returns null. The transform expression may also yield null. A null value can be returned as the most frequent value if the most frequent value is null. If multiple values have the same number of occurrences the method returns the first value with the least number of occurrences considering the ordering of the collection.
The max enumeration method returns the maximum value among a collection of values.
If no value-selector lambda expression is provided, the method finds the maximum.
If a value-selector lambda expression is provided, the enumeration method invokes a value-selector lambda expression on each element and returns the maximum value. The type of value returned follows the return type of the lambda expression that was provided as parameter.
An expression example with scalar values:
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1}.max() // Returns 3
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1}.max(v => case when v >= 3 then 0 else v end) // Returns 2
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1}.max((v, index) => case when index = 2 then 0 else v end) // Returns 2
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1}.max((v, index, size) => case when index > size - 4 then 0 else v end) // Returns 2The next statement returns the maximum distance of any item from center:
select items.max(i => distance(i.location.x, i.location.y, 0, 0)) as maxcenter from LocationReport
The value-selector lambda expression must return a comparable type: Any primitive or boxed type or Comparable type is permitted.
If the input is null, empty or if none of the elements when transformed return a non-null value the method returns null.
The maxBy enumeration method returns the element that provides the maximum value returned by the value-selector lambda expression when applied to each element.
The enumeration method returns the element itself. You may append an event property name to return a property value of the element.
An expression example with scalar values:
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1}.maxby(v => v) // Result 3
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1}.maxby((v, index) => case when index < 3 then -1 else 0 end) // Result 2
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1}.maxby((v, index, size) => case when index < size - 2 then -1 else 0 end) // Result 2The next statement returns the first item with the maximum distance to center:
select items.maxBy(i => distance(i.location.x, i.location.y, 0, 0)) as maxItemCenter from LocationReport
The next sample returns the type of the item with the largest asset id (string comparison) among all items:
select items.maxBy(i => assetId).type as minAssetId from LocationReport
The transform expression must return a comparable type: Any primitive or boxed type or Comparable type is permitted.
If the input is null, empty or if none of the elements when transformed return a non-null value the method returns null.
The min enumeration method returns the minimum value among a collection of values.
If no value-selector lambda expression is provided, the method finds the minimum.
If a value-selector lambda expression is provided, the enumeration method invokes a value-selector lambda expression on each element and returns the minimum value. The type of value returned follows the return type of the lambda expression that was provided as parameter.
Some expression examples with scalar values are:
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1}.min() // Returns 1
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1}.min(v => v + 1) // Returns 2
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1}.min((v, index) => v - index) // Returns -3
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1}.min((v, index, size) => v - size) // Returns -4The next statement returns the minimum distance of any item to center:
select items.min(i => distance(i.location.x, i.location.y, 0, 0)) as mincenter from LocationReport
The transform expression must return a comparable type: Any primitive or boxed type or Comparable type is permitted.
If the input is null, empty or if none of the elements when transformed return a non-null value the method returns null.
The minBy enumeration method returns the element that provides the minimum value returned by the value-selector lambda expression when applied to each element.
The enumeration method returns the element itself. You may append an event property name to return a property value of the element.
Some expression examples with scalar values are:
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1}.minby(v => v) // Result 1
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1}.minby((v, index) => case when index < 3 then -1 else 0 end) // Result 1
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1}.minby((v, index, size) => case when index < size - 2 then -1 else 0 end) // Result 1The next statement returns the first item with the minimum distance to center:
select items.minBy(i => distance(i.location.x, i.location.y, 0, 0)) as minItemCenter from LocationReport
The next sample returns the type of the item with the smallest asset id (string comparison) among all items:
select items.minBy(i => assetId).type as minAssetId from LocationReport
The transform expression must return a comparable type: Any primitive or boxed or Comparable type is permitted.
If the input is null, empty or if none of the elements when transformed return a non-null value the method returns null.
The mostFrequent enumeration method returns the most frequent value among a collection of values, or the most frequent value after applying a transform expression to each element.
The method has two versions: The first version takes no parameters and returns the most frequent value. The second version takes a transform lambda expression yielding the value to count occurrences for. The method applies the lambda expression to each element and returns the expression result value with the most number of occurrences. The return type is the type of value in the collection or the type of value returned by the transform lambda expression if one was provided.
An expression example with scalar values:
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1, 2}.mostFrequent() // Returns 2
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1, 2}.mostFrequent(v => case when v = 2 then 10 else v end) // Returns 10
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1, 2}.mostFrequent((v, index) => case when index > 2 then 4 else v end) // Returns 4
{1, 2, 3, 2, 1, 2}.mostFrequent((v, index, size) => case when size > 3 then 0 else v end) // Returns 0The example EPL below returns the least frequent item type, counting the distinct item types among all items for the current LocationReport event:
select items.leastFrequent(i => type) as leastFreqType from LocationReport
If the input is null or empty the method returns null. The transform expression may also yield null. A null value can be returned as the most frequent value if the most frequent value is null. If multiple values have the same number of occurrences the method returns the first value with the most number of occurrences considering the ordering of the collection.
The orderBy enumeration method sorts elements in ascending order according to a key. The orderByDesc enumeration method sorts elements in descending order according to a key.
The enumeration method takes a single key-selector lambda expression as parameter and orders elements according to the key yielded by the expression. For same-value keys, it maintains the existing order.
An expression example with scalar values:
{2, 3, 2, 1}.orderBy() // Returns {1, 2, 2, 3}
{2, 3, 2, 1}.orderBy(v => -v) // Returns {3, 2, 2, 1}
{2, 3, 2, 1}.orderBy((v, index) => index) // Returns {2, 3, 2, 1}
{2, 3, 2, 1}.orderBy((v, index, size) => case when index < size - 2 then v else -v end) // Returns {2, 1, 2, 3}This example orders all items from a location report according to their distance from center:
select items.orderBy(i => distance(i.location.x, i.location.y, 0, 0)) as itemsNearFirst, items.orderByDesc(i => distance(i.location.x, i.location.y, 0, 0)) as itemsFarFirst from LocationReport
The key-selector lambda expression must return a comparable type: Any primitive or boxed or Comparable type is permitted.
If the input is null the method returns null. If the input is empty the method returns an empty collection.
The reverse enumeration method simply reverses the order of elements returning a collection.
An expression example with scalar values:
{2, 3, 2, 1}.reverse() // Returns {1, 2, 3, 2}The following EPL reverses the items:
select items.reverse() as reversedItems from LocationReport
If the input is null the method returns null. If the input is empty the method returns an empty collection.
The selectFrom enumeration method transforms each element resulting in a collection of transformed elements.
The enumeration method has two versions. The first version takes only a transformation lambda expression and applies that to each element and returns the result of each transformation as a collection. The second version takes a transformation lambda expression and index for use within the transformation expression.
Use the new operator to yield multiple values for each element, see Section 9.14, “The 'New' Keyword”.
The following are expression examples with scalar values:
{'A','B','C'}.selectFrom(v => '<' || v || '>') // Returns [<A>, <B>, <C>]
{'A','B','C'}.selectFrom((v, index) => v || '_' || Integer.toString(index)) // Returns [A_0, B_1, C_2]
{'A','B','C'}.selectFrom((v, index, size) => v || '_' || Integer.toString(size)) // Returns [A_3, B_3, C_3]The next statement returns a collection of asset ids:
select items.selectFrom(i => assetId) as itemAssetIds from LocationReport
This sample statement evaluates each item and returns the asset id as well as the distance from center for each item:
select items.selectFrom(i =>
new {
assetId,
distanceCenter = distance(i.location.x, i.location.y, 0, 0)
} ) as itemInfo from LocationReport
The second version of the selectFrom enumeration method also represents the index of the input element starting at zero for the first element.
The example appends the passenger-type and the index returning a string-type value for each item:
select items.selectFrom((p, ind) => p.type || Integer.toString(ind)) from LocationReport
If the input is null the method returns null. If the input is empty the method returns an empty collection.
The sequenceEqual enumeration method determines whether two collections are equal by comparing each element.
The method enumerates the two source collections in parallel and compares corresponding elements by using the equals method to compare. The method takes a single parameter expression that must return a collection containing elements of the same type as the input. The method returns true if the two source sequences are of equal length and their corresponding elements are equal.
An expression example with scalar values:
{1, 2, 3}.sequenceEqual({1}) // Returns false
{1, 2, 3}.sequenceEqual({1, 2, 3}) // Returns true
The following example compares the asset id of all items to the asset ids returned by a method ItemUtil.redListed() which is assumed to return a list of asset id of string type:
select items.selectFrom(i => assetId).sequenceEquals(ItemUtil.redListed()) from LocationReport
If the input is null the method returns null.
The sumOf enumeration method computes the sum. If a projection lambda expression is provided, the method invokes the projection lambda expression on each element and computes the sum on each returned value.
The projection lambda expression should yield a numeric value, BigDecimal or BigInteger value. Depending on the type returned by the projection lambda expression the method returns either Integer, Long, Double, BigDecimal or BigInteger.
An expression example with scalar values:
{1, 2, 3}.sumOf() // Returns 6
{1, 2, 3}.sumOf(v => v+1) // Returns 9 = 2+3+4
{1, 2, 3}.sumOf((v, index) => v+index) // Returns 9 = 1+3+5
{1, 2, 3}.sumOf((v, index, size) => v+index+size) // Returns 18 = 4+6+8The following example computes the sum of the distance of each item to center:
select items.sum(i => distance(i.location.x, i.location.y, 0, 0) as totalAllDistances from LocationReport
If the input is null or empty the method returns null.
The take enumeration method returns a specified number of contiguous elements from the start.
The enumeration method takes a single size (non-lambda) expression that returns an Integer value.
An expression example with scalar values:
{1, 2, 3}.take(2) // Returns {1, 2}The following example returns the first 5 items:
select items.take(5) as first5Items from LocationReport
If the input is null the method returns null. If the input is empty the method returns an empty collection.
The takeLast enumeration method returns a specified number of contiguous elements from the end.
The enumeration method takes a single size (non-lambda) expression that returns an Integer value.
An expression example with scalar values:
{1, 2, 3}.takeLast(2) // Returns {2, 3}The following example returns the last 5 items:
select items.takeLast(5) as last5Items from LocationReport
If the input is null the method returns null. If the input is empty the method returns an empty collection.
The takeWhile enumeration method returns elements from the start as long as a specified condition is true.
The enumeration method has two versions. The first version takes a predicate lambda expression and the second version takes a predicate lambda expression and index for use within the predicate expression. Both versions return elements from the start as long as the specified condition is true.
An expression example with scalar values:
{1, 2, 3}.takeWhile(v => v < 3) // Returns {1, 2}
{1, 2, 3}.takeWhile((v,ind) => ind > 2) // Returns {1, 2}
{1, 2, -1, 4, 5, 6}.takeWhile((v,ind,sz) => ind < sz - 5 and v > 0) // Returns {1}This example selects all items from a location report in the order provided until the first item that has a distance to center greater than 20 units:
select items.takeWhile(i => distance(i.location.x, i.location.y, 0, 0) < 20) from LocationReport
The second version of the where represents the index of the input element starting at zero for the first element.
The next example is similar to the statement above but also limits the result to the first 10 items:
select items.takeWhile((i, ind) => distance(i.location.x, i.location.y, 0, 0) < 20) and ind < 10) from LocationReport
If the input is null the method returns null. If the input is empty the method returns an empty collection.
The takeWhileLast enumeration method returns elements from the end as long as a specified condition is true.
The enumeration method has two versions. The first version takes a predicate lambda expression and the second version takes a predicate lambda expression and index for use within the predicate expression. Both versions return elements from the end as long as the specified condition is true.
The expression examples with scalar values are:
{1, 2, 3}.takeWhileLast(v => v < 3) // Returns {} (empty collection)
{1, 2, 3}.takeWhileLast(v => v > 1) // Returns {2, 3}
{1, 2, 3}.takeWhileLast((v,ind) => ind > 2) // Returns {2, 3}
{1, 2, -1, 4, 5, 6}.takeWhileLast((v,ind) => ind < 5 and v > 0) // Returns {4, 5, 6} (Take while index<5 amd value>0)
{1, 2, -1, 4, 5, 6}.takeWhileLast((v,ind,sz) => ind < sz-4 and v > 0) // Returns {5, 6}This example selects all items from a location report, starting from the last element and proceeding backwards, until the first item that has a distance to center greater than 20 units:
select items.takeWhile(i => distance(i.location.x, i.location.y, 0, 0) < 20) from LocationReport
The second version provides the index of the input element starting at zero for the last element (reverse index).
The next example is similar to the statement above but also limits the result to the last 10 items:
select items.takeWhile((i, ind) => distance(i.location.x, i.location.y, 0, 0) < 20) and ind < 10) from LocationReport
If the input is null the method returns null. If the input is empty the method returns an empty collection.
The toMap enumeration method returns a Map according to specified key-selector lambda expression and value-selector lambda expression.
The enumeration method takes a key-selector expression and a value-selector expression. For each element the method applies the key-selector expression to determine the map key and the value-selector expression to determine the map value. If the key already exists in the map the value is overwritten.
The expression examples with scalar values are:
{1, 2, 3}.toMap(k => 'K' || Integer.toString(k), v => 'V' || Integer.toString(v)) // Returns map {K1=V], K2=V2, K3=V3}
{1, 2, 3}.toMap(
(k, i) => 'K' || Integer.toString(k) || "_" || Integer.toString(i),
(v, i) => 'V' || Integer.toString(v) || "_" || Integer.toString(i)
) // Returns map {K1_0=V1_0, K2_1=V2_1, K3_2=V3_2}
{1, 2, 3}.toMap(
(k, i, s) => 'K' || Integer.toString(k) || "_" || Integer.toString(s),
(v, i, s) => 'V' || Integer.toString(v) || "_" || Integer.toString(s)
) // Returns map {K1_3=V1_3, K2_3=V2_3, K3_3=V3_3}The next example EPL outputs a map of item asset id and distance to center for each item:
select items.toMap(k => k.assetId, v => distance(v.location.x, v.location.y, 0, 0)) as assetDistance from LocationReport
If the input is null the method returns null. If the input is empty the method returns an empty map.
The union enumeration method forms a union of the input elements with the elements that the parameter expression yields.
The enumeration method takes a single parameter that must itself return a collection of events (input), objects or scalar values. It appends the collection to the input elements and returns the appended collection of elements.
An expression example with scalar values:
{1, 2, 3}.union({4, 5}) // Returns {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}This example selects a union of all items that have an asset id of L001 or that are of type passenger:
select items.where(i => i.assetId = 'L001')
.union(items.where(i => i.type = 'P')) as itemsUnion
from LocationReportIf the input is null the method returns null.
The where enumeration method filters elements based on a predicate.
The enumeration method has two versions. The first version takes a predicate lambda expression and the second version takes a predicate lambda expression and index for use within the predicate expression. Both versions return all elements for which the predicate expression is true.
An expression example with scalar values:
{1, 2, 3}.where(v => v != 2) // Returns {1, 3}
{1, 2, 3}.where((v, index) => v != 2 and index < 2) // Returns {1}
{1, 2, 3}.where((v, index, size) => v != 2 and index < size - 2) // Returns {1}This example selects all items from a location report that are passenger-type:
select items.where(p => p.type = 'P') from LocationReport
The second version of the where represents the index of the input element starting at zero for the first element.
The example below selects all items from a location report that are passenger-type but ignores the first 3 elements:
select items.where((p, ind) => p.type = 'P' and ind > 2) from LocationReport
If the input is null the method returns null. If the input is empty the method returns an empty collection.
- 12.1. Overview
- 12.2. How to Use
- 12.3. Calendar and Formatting Reference
- 12.4. Interval Algebra Reference
- 12.4.1. Examples
- 12.4.2. Interval Algebra Parameters
- 12.4.3. Performance
- 12.4.4. Limitations
- 12.4.5. After
- 12.4.6. Before
- 12.4.7. Coincides
- 12.4.8. During
- 12.4.9. Finishes
- 12.4.10. Finished By
- 12.4.11. Includes
- 12.4.12. Meets
- 12.4.13. Met By
- 12.4.14. Overlaps
- 12.4.15. Overlapped By
- 12.4.16. Starts
- 12.4.17. Started By
EPL date-time methods work on date-time values to perform common tasks such as comparing times and time periods, adding or subtracting time periods, setting or rounding calendar fields and querying fields.
Date-time methods operate on:
Any expression or event property that returns one of the below values:
A long-type millisecond or microsecond value.
A
java.util.Calendarobject including subclasses.A
java.util.Dateobject including subclasses.A
java.time.LocalDateTimeobject including subclasses.A
java.time.ZonedDateTimeobject including subclasses.
Any event for which the event type declares a start timestamp property name and optionally also an end timestamp property name. Date-time methods operate on events by means of the stream-alias.method-name syntax.
Your application may add additional date-time methods by following the recipe described at Section 22.8, “Date-Time Method”.
The below table summarizes the built-in date-time methods available:
Table 12.1. Date-Time Methods
| Method | Result |
|---|---|
| after(event or timestamp) |
Returns true if an event happens after another event, or a timestamp is after another timestamp. |
| before(event or timestamp) |
Returns true if an event happens before another event, or a timestamp is before another timestamp. |
| between(timestamp, timestamp, boolean, boolean) |
Returns true if a timestamp is between two timestamps. |
| coincides(event or timestamp) |
Returns true if an event and another event happen at the same time, or two timestamps are the same value. |
| during(event or timestamp) |
Returns true if an event happens during the occurrence of another event, or when a timestamps falls within the occurrence of an event. |
| finishes(event or timestamp) |
Returns true if an event starts after another event starts and the event ends at the same time as the other event. |
| finishedBy(event or timestamp) |
Returns true if an event starts before another event starts and ends at the same time as the other event. |
|
format() format(format) |
Formats the date-time returning a string. |
| get(field) |
Returns the value of the given date-time value field. |
getMillisOfSecond() getSecondOfMinute() getMinuteOfHour() getHourOfDay() getDayOfWeek() getDayOfMonth() getDayOfYear() getWeekyear() getMonthOfYear() getYear() getEra() |
Returns the value of the given date-time value field. |
| includes(event or timestamp) |
Returns true if the parameter event happens during the occurrence of the event, or when a timestamps falls within the occurrence of an event. |
| meets(event or timestamp) |
Returns true if the event's end time is the same as another event's start time. |
| metBy(event or timestamp) |
Returns true if the event's start time is the same as another event's end time. |
| minus(duration-millis) |
Returns a date-time with the specified duration in long-type milliseconds taken away. |
| minus(time-period) |
Returns a date-time with the specified duration in time-period syntax taken away. |
| overlaps(event or timestamp) |
Returns true if the event starts before another event starts and finishes after the other event starts, but before the other event finishes (events have an overlapping period of time). |
| overlappedBy(event or timestamp) |
Returns true if the parameter event starts before the input event starts and the parameter event finishes after the input event starts, but before the input event finishes (events have an overlapping period of time). |
| plus(duration-millis) |
Returns a date-time with the specified duration in long-type milliseconds added. |
| plus(time-period) |
Returns a date-time with the specified duration in time-period syntax added. |
| roundCeiling(field) |
Returns a date-time rounded to the highest whole unit of the date-time field. |
| roundFloor(field) |
Returns a date-time rounded to the lowest whole unit of the date-time field. |
| roundHalf(field) |
Returns a date-time rounded to the nearest whole unit of the date-time field. |
| set(field, value) |
Returns a date-time with the specified field set to the value returned by a value expression. |
| starts(event or timestamp) |
Returns true if an event and another event start at the same time and the event's end happens before the other event's end. |
| startedBy(event or timestamp) |
Returns true if an event and another event start at the same time and the other event's end happens before the input event's end. |
| withDate(year,month,day) |
Returns a date-time with the specified date, retaining the time fields. |
| withMax(field) |
Returns a date-time with the field set to the maximum value for the field. |
| withMin(field) |
Returns a date-time with the field set to the minimum value for the field. |
| withTime(hour,minute,sec,msec) |
Returns a date-time with the specified time, retaining the date fields. |
| toCalendar() |
Returns the |
| toDate() |
Returns the |
| toMillisec() |
Returns the long-type milliseconds value for this date-time value. |
The syntax for date-time methods is the same syntax as for any chained invocation:
input_val.datetime_method_name( [method_parameter [, method_parameter [,...]]]) .[ datetime_method_name(...) [...]]
Following the input_val input value is the . (dot) operator and the datetime_method_name date-time method name. It follows in parenthesis a comma-separated list of method parameter expressions. Additional date-time methods can be chained thereafter.
The input value can be any expression or event property that returns a value of type long or java.util.Calendar or java.util.Date or java.time.LocalDateTime or java.time.ZonedDateTime. If the input value is null, the expression result is also null.
The input value can also be an event. In this case the event type of the event must have the start timestamp property name defined and optionally also the end timestamp property name.
The following example statement employs the withTime date-time method. This example returns the current runtime time with the time-part set to 1 am:
select current_timestamp.withTime(1, 0, 0, 0) as time1am from MyEvent
As date-time methods can be chained, this EPL is equivalent:
select current_timestamp.set('hour', 1).set('min', 0).set('sec', 0).set('msec', 0) as time1am
from MyEvent
The statement above outputs in field time1am a long-type value (milliseconds or microseconds) reflecting 1am on the same date as runtime time. Since the input value is provided by the built-in current_timestamp function which returns current runtime time as a long-type value the output is also a long-type value.
You may apply a date-time method to an event property.
Assume that the RFIDEvent event type has a Date-type property by name timeTaken. The following statement rounds each time-taken value down to the nearest minute and outputs a Date-type value in column timeTakenRounded:
select timeTaken.roundFloor('min') as timeTakenRounded from RFIDEventYou may apply a date-time method to events. This example assumes that the RFIDEvent and WifiEvent event types both have a timestamp property defined. The EPL compares the timestamps of the RFIDEvent and the WifiEvent:
select rfid.after(wifi) as isAfter from RFIDEvent#lastevent rfid, WifiEvent#lastevent wifi
For comparing date-time values and considering event duration (event start and end timestamps) we recommend any of the interval algebra methods. You may also compare long-type values using the between or in ranges and inverted ranges or relational operators (> , <, >=, <=).
From a performance perspective, the date-time method evaluation ensures that for each unique chain of date-time methods only a single calendar objects is copied or created when necessary.
The between date-time method compares the input date-time value to the two date-time values passed in and returns true if the input value falls between the two parameter values.
The synopsis is:
input_val.between(range_start, range_end [, include_start, include_end])
The method takes either 2 or 4 parameters. The first two parameters range_start and range_end are expressions or properties that yield either a long-typed, Date-typed or Calendar-typed range start and end value.
The next two parameters include_start and include_end are optional. If not specified, the range start value and range end value are included in the range i.e. specify a closed range where both endpoints are included. If specified, the expressions must return a boolean-value indicating whether to include the range start value and range end value in the range.
The example below outputs true when the time-taken property value of the RFID event falls between the time-start property value and the time-end property value (closed range includes endpoints):
select timeTaken.between(timeStart, timeEnd) from RFIDEvent
The example below performs the same test as above but does not include endpoints (open range includes neither endpoint):
select timeTaken.between(timeStart, timeEnd, false, false) from RFIDEvent
If the range end value is less then the range start value, the algorithm reverses the range start and end value.
If the input date-time value or any of the parameter values evaluate to null the method returns a null result value.
The format date-time method formats the date-time returning a string.
The method takes either no parameter or a single format parameter.
When passing no parameter, the method returns the date-time value formatted using the default formatter as follows:
Table 12.2. RoundHalf Examples
| Input | String Formatter |
|---|---|
long, Date, Calendar | new SimpleDateFormat() |
java.time.LocalTimeDate | DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME |
java.time.ZonedTimeDate | DateTimeFormatter.ISO_ZONED_DATE_TIME |
The example below outputs the time-taken property value of the RFID event:
select timeTaken.format() as timeTakenStr from RFIDEvent
For input values that are long-typed, Date-typed or Calendar-typed you must provide an expression that returns either:
A
String-type format that adheres toSimpleDateFormatrules.A
DateFormatinstance.
For input values that are LocalDateTime-typed or ZonedDateTime-typed you must provide an expression that returns either:
A
String-type format that adheres toDateTimeFormatterrules.A
DateTimeFormatterinstance.
The runtime evaluates the format expression at statement compilation time therefore the format expression must return a value that is not computed from time or events.
For example:
select timeTaken.format('yyyy.MM.dd G 'at' HH:mm:ss') from RFIDEventselect timeTaken.format(SimpleDateFormat.getDateInstance()) from RFIDEvent
select localDateTime.format(java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter.BASIC_ISO_DATE) from RFIDEvent
The get date-time method returns the value of the given date-time value field.
The method takes a single string-constant field name as parameter. Please see Section 5.2.1, “Specifying Time Periods” for a list of recognized keywords (not case-sensitive).
The method returns the numeric value of the field within the date-time value. The value returned adheres to Calendar-class semantics: For example, the value for month starts at zero and has a maximum of 11 (Note: for LocalDateTime and ZonedDateTime the range for month is 1 to 12).
The example below outputs the month value of the time-taken property value of the RFID event:
select timeTaken.get('month') as timeTakenMonth from RFIDEvent
The following list of getter-methods are available: getMillisOfSecond(), getSecondOfMinute(), getMinuteOfHour(), getHourOfDay(), getDayOfWeek(), getDayOfMonth(), getDayOfYear(), getWeekYear(), getMonthOfYear(), getYear() and getEra().
All get-methods take no parameter and return the numeric value of the field within the date-time value. The value returned adheres to Calendar-class semantics: For example, the value for month starts at zero and has a maximum of 11 (Note: for LocalDateTime and ZonedDateTime the range for month is 1 to 12).
The example below outputs the month value of the time-taken property value of the RFID event:
select timeTaken.getMonthOfYear() as timeTakenMonth from RFIDEvent
The minus date-time method returns a date-time with the specified duration taken away.
The method has two versions: The first version takes the duration as a long-type millisecond value. The second version takes the duration as a time-period expression, see Section 5.2.1, “Specifying Time Periods”.
The example below demonstrates the time-period parameter to subtract two minutes from the time-taken property value of the RFID event:
select timeTaken.minus(2 minutes) as timeTakenMinus2Min from RFIDEvent
The next example is equivalent but passes a millisecond-value instead:
select timeTaken.minus(2*60*1000) as timeTakenMinus2Min from RFIDEvent
The plus date-time method returns a date-time with the specified duration added.
The method has two versions: The first version takes the duration as a long-type millisecond value. The second version takes the duration as a time-period expression, see Section 5.2.1, “Specifying Time Periods”.
The next example adds two minutes to the time-taken property value of the RFID event:
select timeTaken.plus(2 minutes) as timeTakenPlus2Min from RFIDEvent
The next example is equivalent but passes a millisecond-value instead:
select timeTaken.plus(2*60*1000) as timeTakenPlus2Min from RFIDEvent
The roundCeiling date-time method rounds to the highest whole unit of the date-time field.
The method takes a single string-constant field name as parameter. Please see Section 5.2.1, “Specifying Time Periods” for a list of recognized keywords (not case-sensitive).
The next example rounds-to-ceiling the minutes of the time-taken property value of the RFID event:
select timeTaken.roundCeiling('min') as timeTakenRounded from RFIDEvent
If the input time is 2002-05-30 09:01:23.050, for example, the output is 2002-05-30 09:02:00.000 (example timestamps are in format yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS).
The roundFloor date-time method rounds to the lowest whole unit of the date-time field.
The method takes a single string-constant field name as parameter. Please see Section 5.2.1, “Specifying Time Periods” for a list of recognized keywords (not case-sensitive).
The next example rounds-to-floor the minutes of the time-taken property value of the RFID event:
select timeTaken.roundFloor('min') as timeTakenRounded from RFIDEvent
If the input time is 2002-05-30 09:01:23.050, for example, the output is 2002-05-30 09:01:00.000 (example timestamps are in format yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS).
The roundFloor date-time method rounds to the nearest whole unit of the date-time field.
The method takes a single string-constant field name as parameter. Please see Section 5.2.1, “Specifying Time Periods” for a list of recognized keywords (not case-sensitive).
The next example rounds the minutes of the time-taken property value of the RFID event:
select timeTaken.roundHalf('min') as timeTakenRounded from RFIDEvent
The following table provides a few examples of the rounding (example timestamps are in format yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS):
Table 12.3. RoundHalf Examples
| Input | Output |
|---|---|
| 2002-05-30 09:01:23.050 | 2002-05-30 09:01:00.000 |
| 2002-05-30 09:01:29.999 | 2002-05-30 09:01:00.000 |
| 2002-05-30 09:01:30.000 | 2002-05-30 09:02:00.000 |
This method is not support for LocalDateTime and ZonedDateTime input values.
The set date-time method returns a date-time with the specified field set to the value returned by an expression.
The method takes a string-constant field name and an expression returning an integer-value as parameters. Please see Section 5.2.1, “Specifying Time Periods” for a list of recognized keywords (not case-sensitive).
The method returns the new date-time value with the field set to the provided value. Note that value adheres to Calendar-class semantics: For example, the value for month starts at zero and has a maximum of 11 (Note: for LocalDateTime and ZonedDateTime the range for month is 1 to 12).
The example below outputs the time-taken with the value for month set to April:
select timeTaken.set('month', 3) as timeTakenMonth from RFIDEvent
The withDate date-time method returns a date-time with the specified date, retaining the time fields.
The method takes three expressions as parameters: An expression for year, month and day.
The method returns the new date-time value with the date fields set to the provided values. For expressions returning null the method ignores the field for which null is returned. Note the Calendar-class semantics: For example, the value for month starts at zero and has a maximum of 11.
The example below outputs the time-taken with the date set to May 30, 2002:
select timeTaken.withDate(2002, 4, 30) as timeTakenDated from RFIDEvent
The withMax date-time method returns a date-time with the field set to the maximum value for the field.
The method takes a string-constant field name as parameter. Please see Section 5.2.1, “Specifying Time Periods” for a list of recognized keywords (not case-sensitive).
The method returns the new date-time value with the specific date field set to the maximum value.
The example below outputs the time-taken property value with the second-part as 59 seconds:
select timeTaken.withMax('sec') as timeTakenMaxSec from RFIDEvent
The withMin date-time method returns a date-time with the field set to the minimum value for the field.
The method takes a string-constant field name as parameter. Please see Section 5.2.1, “Specifying Time Periods” for a list of recognized keywords (not case-sensitive).
The method returns the new date-time value with the specific date field set to the minimum value.
The example below outputs the time-taken property value with the second-part as 0 seconds:
select timeTaken.withMin('sec') as timeTakenMaxSec from RFIDEvent
The withTime date-time method returns a date-time with the specified time, retaining the date fields.
The method takes four expressions as parameters: An expression for hour, minute, second and millisecond.
The method returns the new date-time value with the time fields set to the provided values. For expressions returning null the method ignores the field for which null is returned.
The example below outputs the time-taken with the time set to 9am:
select timeTaken.withTime(9, 0, 0, 0) as timeTakenDated from RFIDEvent
The toCalendar date-time method returns the Calendar object for this date-time value.
The method takes no parameters.
The example below outputs the time-taken as a Calendar object:
select timeTaken.toCalendar() as timeTakenCal from RFIDEvent
The toDate date-time method returns the Date object for this date-time value.
The method takes no parameters.
The example below outputs the time-taken as a Date object:
select timeTaken.toDate() as timeTakenDate from RFIDEvent
Interval algebra methods compare start and end timestamps of events or timestamps in general.
When the expression input is only a timestamp value, such as a long-type value or a Date or Calendar object, the start and end timestamp represented by that value are the same timestamp value.
When expression input is an event stream alias, the compiler determine the event type for the stream. If the event type declares a start timestamp property name, the compiler uses that start timestamp property to determine the start timestamp for the event. If the event type also declares an end timestamp property name, the compiler uses that end timestamp property to determine the end timestamp for the event (i.e. an event with duration). If an end timestamp property name is not declared, the start and end timestamp for each event is the same value and the event is considered to have zero duration (i.e. a point-in-time event).
Interval algebra methods all return Boolean-type value. When the input value start timestamp is null, or the end timestamp (if declared for the event type) is null or any of the start timestamp and end timestamp (if declared for the event type) values of the first parameter is null, the result value is null.
The examples in this section simply use A and B as event type names. The alias a is used to represent A-type events and respectively the alias b represents B-type events.
The create-schema for types A and B is shown next. The two types are declared the same. The example declares the property providing start timestamp values as startts and the property providing end timestamp values as endts:
create schema A as (startts long, endts long) starttimestamp 'startts' endtimestamp 'endts'
create schema B as (startts long, endts long) starttimestamp 'startts' endtimestamp 'endts'
The sample EPL below joins the last A and the last B event. It detects A-B event combinations for which, when comparing timestamps, the last A event that occurs before the last B event. The example employs the before method:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.before(b)
For simplicity, the examples in this section refer to A and the alias a as the input event. The examples refer to B and the alias b as the parameter event.
The first parameter of each interval algebra methods is the event or timestamp to compare to.
All remaining parameters to interval algebra methods are intervals and can be any of the following:
A constant, an event property or more generally any expression returning a numeric value that is the number of seconds. For example, in the expression
a.before(b, 2)the parameter 2 is interpreted to mean 2 seconds. The expressiona.before(b, myIntervalProperty)is interpreted to meanmyIntervalPropertyseconds.A time period expression as described in Section 12.4.11, “Includes”. For example:
a.before(b, 1 hour 2 minutes).
When an interval parameter is provided and is null, the method result value is null.
The compiler analyzes interval algebra methods as well as the between date-time method in the where-clause and builds a query plan for execution of joins and subqueries. The query plan can include hash and btree index lookups using the start and end timestamps as computed by expressions or provided by events as applicable. Consider turning on query plan logging to obtain information on the query plan used.
The query planning is generally most effective when no additional thresholds or ranges are provided to interval algebra methods, as the query planner may not consider an interval algebra method that it cannot plan.
The query planner may also not optimally plan the query execution if events or expressions return different types of date representation. Query planning works best if all date representations use the same long, Date or Calendar types.
Date-time method that change date or time fields, such as withTime, withDate, set or round methods set the end timestamp to the start timestamp.
For example, in the following expression the parameter to the after method has a zero duration, and not the end timestamp that the event B endts property provides.
a.after(b.withTime(9, 0, 0, 0))
The after date-time method returns true if an event happens after another event, or a timestamp is after another timestamp.
The method compares the input value's start timestamp (a.startTimestamp) to the first parameter's end timestamp (b.endTimestamp) to determine whether A happens after B.
If used with one parameter, for example in a.after(b), the method returns true if A starts after B ends.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.after(b) // Above matches when: // a.startTimestamp - b.endTimestamp > 0
If providing two parameters, for example in a.after(b, 5 sec), the method returns true if A starts at least 5 seconds after B ends.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.after(b, 5 sec) // Above matches when: // a.startTimestamp - b.endTimestamp >= 5 seconds
If providing three parameters, for example in a.after(b, 5 sec, 10 sec), the method returns true if A starts at least 5 seconds but no more then 10 seconds after B ends.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.after(b, 5 sec, 10 sec) // Above matches when: // 5 seconds <= a.startTimestamp - b.endTimestamp <= 10 seconds
Negative values for the range are allowed. For example in a.after(b, -5 sec, -10 sec), the method returns true if A starts at least 5 seconds but no more then 10 seconds before B ends.
If the range low endpoint is greater than the range high endpoint, the compiler automatically reverses them. Thus a.after(b, 10 sec, 5 sec) is the same semantics as a.after(b, 5 sec, 10 sec).
The before date-time method returns true if an event happens before another event, or a timestamp is before another timestamp.
The method compares the input value's end timestamp (a.endTimestamp) and the first parameter's start timestamp (b.startTimestamp) to determine whether A happens before B.
If used with one parameter, for example in a.before(b), the method returns true if A ends before B starts.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.before(b) // Above matches when: // b.startTimestamp - a.endTimestamp > 0
If providing two parameters, for example in a.before(b, 5 sec), the method returns true if A ends at least 5 seconds before B starts.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.before(b, 5 sec) // Above matches when: // b.startTimestamp - a.endTimestamp >= 5 seconds
If providing three parameters, for example in a.before(b, 5 sec, 10 sec), the method returns true if A ends at least 5 seconds but no more then 10 seconds before B starts.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.before(b, 5 sec, 10 sec) // Above matches when: // 5 seconds <= b.startTimestamp - a.endTimestamp <= 10 seconds
Negative values for the range are allowed. For example in a.before(b, -5 sec, -10 sec), the method returns true if A starts at least 5 seconds but no more then 10 seconds after B starts.
If the range low endpoint is greater than the range high endpoint, the compiler automatically reverses them. Thus a.before(b, 10 sec, 5 sec) is the same semantics as a.before(b, 5 sec, 10 sec).
The coincides date-time method returns true if an event and another event happen at the same time, or two timestamps are the same value.
The method compares the input value's start and end timestamp with the first parameter's start and end timestamp and determines if they equal.
If used with one parameter, for example in a.coincides(b), the method returns true if the start timestamp of A and B are the same and the end timestamps of A and B are also the same.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.coincides(b) // Above matches when: // a.startTimestamp = b.startTimestamp and a.endTimestamp = b.endTimestamp
If providing two parameters, for example in a.coincides(b, 5 sec), the method returns true if the difference between the start timestamps of A and B is equal to or less then 5 seconds and the difference between the end timestamps of A and B is also equal to or less then 5 seconds.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.coincides(b, 5 sec) // Above matches when: // abs(a.startTimestamp - b.startTimestamp) <= 5 sec and // abs(a.endTimestamp - b.endTimestamp) <= 5 sec
If providing three parameters, for example in a.coincides(b, 5 sec, 10 sec), the method returns true if the difference between the start timestamps of A and B is equal to or less then 5 seconds and the difference between the end timestamps of A and B is equal to or less then 10 seconds.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.coincides(b, 5 sec, 10 sec) // Above matches when: // abs(a.startTimestamp - b.startTimestamp) <= 5 seconds and // abs(a.endTimestamp - b.endTimestamp) <= 10 seconds
A negative value for interval parameters is not allowed. If your interval parameter is itself an expression that returns a negative value the runtime logs a warning message and returns null.
The during date-time method returns true if an event happens during the occurrence of another event, or when a timestamps falls within the occurrence of an event..
The method determines whether the input value's start and end timestamp are during the first parameter's start and end timestamp. The symmetrical opposite is Section 12.4.11, “Includes”.
If used with one parameter, for example in a.during(b), the method returns true if the start timestamp of A is after the start timestamp of B and the end timestamp of A is before the end timestamp of B.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.during(b) // Above matches when: // b.startTimestamp < a.startTimestamp <= a.endTimestamp < b.endTimestamp
If providing two parameters, for example in a.during(b, 5 sec), the method returns true if the difference between the start timestamps of A and B is equal to or less then 5 seconds and the difference between the end timestamps of A and B is also equal to or less then 5 seconds.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.during(b, 5 sec) // Above matches when: // 0 < a.startTimestamp - b.startTimestamp <= 5 sec and // 0 < a.endTimestamp - b.endTimestamp <= 5 sec
If providing three parameters, for example in a.during(b, 5 sec, 10 sec), the method returns true if the difference between the start timestamps of A and B and the difference between the end timestamps of A and B is between 5 and 10 seconds.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.during(b, 5 sec, 10 sec) // Above matches when: // 5 seconds <= a.startTimestamp - b.startTimestamp <= 10 seconds and // 5 seconds <= a.endTimestamp - b.endTimestamp <= 10 seconds
If providing five parameters, for example in a.during(b, 5 sec, 10 sec, 20 sec, 30 sec), the method returns true if the difference between the start timestamps of A and B is between 5 seconds and 10 seconds and the difference between the end timestamps of A and B is between 20 seconds and 30 seconds.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.during(b, 5 sec, 10 sec, 20 sec, 30 sec) // Above matches when: // 5 seconds <= a.startTimestamp - b.startTimestamp <= 10 seconds and // 20 seconds < a.endTimestamp - b.endTimestamp <= 30 seconds
The finishes date-time method returns true if an event starts after another event starts and the event ends at the same time as the other event.
The method determines whether the input value's start timestamp is after the first parameter's start timestamp and the end timestamp of the input value and the first parameter are the same. The symmetrical opposite is Section 12.4.10, “Finished By”.
If used with one parameter, for example in a.finishes(b), the method returns true if the start timestamp of A is after the start timestamp of B and the end timestamp of A and B are the same.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.finishes(b) // Above matches when: // b.startTimestamp < a.startTimestamp and a.endTimestamp = b.endTimestamp
If providing two parameters, for example in a.finishes(b, 5 sec), the method returns true if the start timestamp of A is after the start timestamp of B and the difference between the end timestamps of A and B is equal to or less then 5 seconds.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.finishes(b, 5 sec) // Above matches when: // b.startTimestamp < a.startTimestamp and // abs(a.endTimestamp - b.endTimestamp ) <= 5 seconds
A negative value for interval parameters is not allowed. If your interval parameter is itself an expression that returns a negative value the runtime logs a warning message and returns null.
The finishedBy date-time method returns true if an event starts before another event starts and the event ends at the same time as the other event.
The method determines whether the input value's start timestamp happens before the first parameter's start timestamp and the end timestamp of the input value and the first parameter are the same. The symmetrical opposite is Section 12.4.9, “Finishes”.
If used with one parameter, for example in a.finishedBy(b), the method returns true if the start timestamp of A is before the start timestamp of B and the end timestamp of A and B are the same.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.finishedBy(b) // Above matches when: // a.startTimestamp < b.startTimestamp and a.endTimestamp = b.endTimestamp
If providing two parameters, for example in a.finishedBy(b, 5 sec), the method returns true if the start timestamp of A is before the start timestamp of B and the difference between the end timestamps of A and B is equal to or less then 5 seconds.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.finishedBy(b, 5 sec) // Above matches when: // a.startTimestamp < b.startTimestamp and // abs(a.endTimestamp - b.endTimestamp ) <= 5 seconds
The includes date-time method returns true if the parameter event happens during the occurrence of the input event, or when a timestamps falls within the occurrence of an event.
The method determines whether the first parameter's start and end timestamp are during the input value's start and end timestamp. The symmetrical opposite is Section 12.4.8, “During”.
If used with one parameter, for example in a.includes(b), the method returns true if the start timestamp of B is after the start timestamp of A and the end timestamp of B is before the end timestamp of A.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.includes(b) // Above matches when: // a.startTimestamp < b.startTimestamp <= b.endTimestamp < a.endTimestamp
If providing two parameters, for example in a.includes(b, 5 sec), the method returns true if the difference between the start timestamps of A and B is equal to or less then 5 seconds and the difference between the end timestamps of A and B is also equal to or less then 5 seconds.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.includes(b, 5 sec) // Above matches when: // 0 < b.startTimestamp - a.startTimestamp <= 5 sec and // 0 < a.endTimestamp - b.endTimestamp <= 5 sec
If providing three parameters, for example in a.includes(b, 5 sec, 10 sec), the method returns true if the difference between the start timestamps of A and B and the difference between the end timestamps of A and B is between 5 and 10 seconds.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.includes(b, 5 sec, 10 sec) // Above matches when: // 5 seconds <= a.startTimestamp - b.startTimestamp <= 10 seconds and // 5 seconds <= a.endTimestamp - b.endTimestamp <= 10 seconds
If providing five parameters, for example in a.includes(b, 5 sec, 10 sec, 20 sec, 30 sec), the method returns true if the difference between the start timestamps of A and B is between 5 seconds and 10 seconds and the difference between the end timestamps of A and B is between 20 seconds and 30 seconds.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.includes(b, 5 sec, 10 sec, 20 sec, 30 sec) // Above matches when: // 5 seconds <= a.startTimestamp - b.startTimestamp <= 10 seconds and // 20 seconds <= a.endTimestamp - b.endTimestamp <= 30 seconds
The meets date-time method returns true if the event's end time is the same as another event's start time.
The method compares the input value's end timestamp and the first parameter's start timestamp and determines whether they equal.
If used with one parameter, for example in a.meets(b), the method returns true if the end timestamp of A is the same as the start timestamp of B.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.meets(b) // Above matches when: // a.endTimestamp = b.startTimestamp
If providing two parameters, for example in a.meets(b, 5 sec), the method returns true if the difference between the end timestamp of A and the start timestamp of B is equal to or less then 5 seconds.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.meets(b, 5 sec) // Above matches when: // abs(b.startTimestamp - a.endTimestamp) <= 5 seconds
A negative value for the interval parameter is not allowed. If your interval parameter is itself an expression that returns a negative value the runtime logs a warning message and returns null.
The metBy date-time method returns true if the event's start time is the same as another event's end time.
The method compares the input value's start timestamp and the first parameter's end timestamp and determines whether they equal.
If used with one parameter, for example in a.metBy(b), the method returns true if the start timestamp of A is the same as the end timestamp of B.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.metBy(b) // Above matches when: // a.startTimestamp = b.endTimestamp
If providing two parameters, for example in a.metBy(b, 5 sec), the method returns true if the difference between the end timestamps of B and the start timestamp of A is equal to or less then 5 seconds.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.metBy(b, 5 sec) // Above matches when: // abs(a.startTimestamp - b.endTimestamp) <= 5 seconds
A negative value for the interval parameter is not allowed. If your interval parameter is itself an expression that returns a negative value the runtime logs a warning message and returns null.
The overlaps date-time method returns true if the event starts before another event starts and finishes after the other event starts, but before the other event finishes (events have an overlapping period of time).
The method determines whether the input value's start and end timestamp indicate an overlap with the first parameter's start and end timestamp, such that A starts before B starts and A ends after B started but before B ends.
If used with one parameter, for example in a.overlaps(b), the method returns true if the start timestamp of A is before the start timestamp of B and the end timestamp of A and is before the end timestamp of B.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.overlaps(b) // Above matches when: // a.startTimestamp < b.startTimestamp < a.endTimestamp < b.endTimestamp
If providing two parameters, for example in a.overlaps(b, 5 sec), the method returns true if, in addition, the difference between the end timestamp of A and the start timestamp of B is equal to or less then 5 seconds.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.overlaps(b, 5 sec) // Above matches when: // a.startTimestamp < b.startTimestamp < a.endTimestamp < b.endTimestamp and // 0 <= a.endTimestamp - b.startTimestamp <= 5 seconds
If providing three parameters, for example in a.overlaps(b, 5 sec, 10 sec), the method returns true if, in addition, the difference between the end timestamp of A and the start timestamp of B is between 5 and 10 seconds.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.overlaps(b, 5 sec, 10 sec) // Above matches when: // a.startTimestamp < b.startTimestamp < a.endTimestamp < b.endTimestamp and // 5 seconds <= a.endTimestamp - b.startTimestamp <= 10 seconds
The overlappedBy date-time method returns true if the parameter event starts before the input event starts and the parameter event finishes after the input event starts, but before the input event finishes (events have an overlapping period of time).
The method determines whether the input value's start and end timestamp indicate an overlap with the first parameter's start and end timestamp, such that B starts before A starts and B ends after A started but before A ends.
If used with one parameter, for example in a.overlappedBy(b), the method returns true if the start timestamp of B is before the start timestamp of A and the end timestamp of B and is before the end timestamp of A.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.overlappedBy(b) // Above matches when: // b.startTimestamp < a.startTimestamp < b.endTimestamp < a.endTimestamp
If providing two parameters, for example in a.overlappedBy(b, 5 sec), the method returns true if, in addition, the difference between the end timestamp of B and the start timestamp of A is equal to or less then 5 seconds.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.overlappedBy(b, 5 sec) // Above matches when: // b.startTimestamp < a.startTimestamp < b.endTimestamp < a.endTimestamp and // 0 <= b.endTimestamp - a.startTimestamp <= 5 seconds
If providing three parameters, for example in a.overlappedBy(b, 5 sec, 10 sec), the method returns true if, in addition, the difference between the end timestamp of B and the start timestamp of A is between 5 and 10 seconds.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.overlappedBy(b, 5 sec, 10 sec) // Above matches when: // b.startTimestamp < a.startTimestamp < b.endTimestamp < a.endTimestamp and // 5 seconds <= b.endTimestamp - a.startTimestamp <= 10 seconds
The starts date-time method returns true if an event and another event start at the same time and the event's end happens before the other event's end.
The method determines whether the start timestamps of the input value and the first parameter are the same and the end timestamp of the input value is before the end timestamp of the first parameter.
If used with one parameter, for example in a.starts(b), the method returns true if the start timestamp of A and B are the same and the end timestamp of A is before the end timestamp of B.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.starts(b) // Above matches when: // a.startTimestamp = b.startTimestamp and a.endTimestamp < b.endTimestamp
If providing two parameters, for example in a.starts(b, 5 sec), the method returns true if the difference between the start timestamps of A and B is between is equal to or less then 5 seconds.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.starts(b, 5 sec) // Above matches when: // abs(a.startTimestamp - b.startTimestamp) <= 5 seconds and // a.endTimestamp < b.endTimestamp
A negative value for the interval parameter is not allowed. If your interval parameter is itself an expression that returns a negative value the runtime logs a warning message and returns null.
The startedBy date-time method returns true if an event and another event start at the same time and the other event's end happens before the input event's end.
The method determines whether the start timestamp of the input value and the first parameter are the same and the end timestamp of the first parameter is before the end timestamp of the input value.
If used with one parameter, for example in a.startedBy(b), the method returns true if the start timestamp of A and B are the same and the end timestamp of B is before the end timestamp of A.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.startedBy(b) // Above matches when: // a.startTimestamp = b.startTimestamp and b.endTimestamp < a.endTimestamp
If providing two parameters, for example in a.startedBy(b, 5 sec), the method returns true if the difference between the start timestamps of A and B is between is equal to or less then 5 seconds.
Sample EPL:
select * from A#lastevent as a, B#lastevent as b where a.startedBy(b, 5 sec) // Above matches when: // abs(a.startTimestamp - b.startTimestamp) <= 5 seconds and // b.endTimestamp < a.endTimestamp
A negative value for the interval parameter is not allowed. If your interval parameter is itself an expression that returns a negative value the runtime logs a warning message and returns null.
- 13.1. Overview
- 13.2. How to Use
- 13.3. Aggregation Methods for Sorted Aggregations
- 13.3.1. Overview
- 13.3.2. Specifying Composite Keys
- 13.3.3. CeilingEvent, FloorEvent, HigherEvent, LowerEvent, GetEvent
- 13.3.4. CeilingEvents, FloorEvents, HigherEvents, LowerEvents, GetEvents
- 13.3.5. CeilingKey, FloorKey, HigherKey, LowerKey
- 13.3.6. FirstEvent, LastEvent, MinBy, MaxBy
- 13.3.7. FirstEvents, LastEvents
- 13.3.8. FirstKey, LastKey
- 13.3.9. ContainsKey
- 13.3.10. CountEvents
- 13.3.11. CountKeys
- 13.3.12. EventsBetween
- 13.3.13. Submap
- 13.3.14. NavigableMapReference
- 13.4. Aggregation Methods for Window Aggregations
- 13.5. Aggregation Methods for CountMinSketch Aggregations
- 13.6. Aggregation Methods for Custom Plug-In Multi-Function Aggregations
Aggregation methods are methods that work with aggregations to perform lookups into aggregation state.
Aggregation methods are stateless and the use of aggregation methods alone does not cause the runtime to retain any events or other state.
There are four types of aggregations that offer aggregation methods:
-
The
windowaggregation, see Section 10.2.2.8, “Window Aggregation Function”. -
The
sortedaggregation, see Section 10.2.2.7, “Sorted Aggregation Function”. -
The
countminsketchaggregation, see Section 10.2.3, “Approximation Aggregation Functions”. - Plug-in multi-function aggregations, see Section 22.5.2, “Aggregation Multi-Function Development”.
Aggregation methods are handy when an aggregation organizes events or other data for further lookup. For example, the sorted aggregation organizes events according to sort criteria
and offers operations for floor, ceiling, higher and lower keys, and many other operations.
Each aggregation makes different aggregation methods available. For example, sorted provides the higherKey aggregation method. The higherKey method is only available for
use with the sorted aggregation and not with the window aggregation.
You may use aggregation methods together with aggregation functions without tables, and you may use aggregation methods with table columns that hold aggregations. Further examples are provided below.
You may also use aggregation methods with enumeration methods, date-time methods and the dot-syntax to access event properties.
The syntax for aggregation methods is the same syntax as for any chained invocation:
input_aggregation.aggregation_method_name( [method_parameter [, method_parameter [,...]]]) .[ [other_method(...) [...]] | property_name]
Following the input_aggregation input aggregation (options outlined below), is the . (dot) operator and the aggregation_method_name aggregation method name.
It follows, in parenthesis, a comma-separated list of method parameter expressions. Additional enumeration or date-time methods can be chained thereafter.
An event property name can follow for those aggregation or enumeration methods returning an event-typed (non-scalar) element.
The examples in this section focus on the sorted aggregation.
You may use aggregation methods with the respective aggregation function.
The following statement outputs the greatest price strictly less than the current order event price, or null if there is no such value, considering the last 10 minutes of order events.
select sorted(price).lowerKey(price) as lowerPrice from OrderEvent#time(10 minutes)
You may use aggregation methods with table columns.
The sample statement below creates a simple un-keyed table that keeps order events sorted by price:
create table OrderPrices(prices sorted(price) @type('OrderEvent'))
The next statement aggregates order events into the table column prices considering the last 10 minutes of order events (the example specifies priority 1 so the runtime always updates the table before other selects):
@Priority(1) into table OrderPrices select sorted(*) as prices from OrderEvent#time(10 minutes)
Now the prices column of table OrderPrices is ready. The runtime keeps it continually updated from the last 10 minutes of order events.
You may access the table column by providing a table name, column name and the aggregation method. For more information please see Section 6.3.3, “Table Column Keyed-Access Expressions”.
The following statement access the table column to output the first (least) and last (greatest) current price for each order event:
select OrderPrices.prices.firstKey() as leastPrice,
OrderPrices.prices.lastKey() as greatestPrice
from OrderEventYou may access the table column by putting the table into the from-clause such as in a subquery or join.
The following statement uses a subquery and outputs the least price as well as the order event itself:
select (select prices.firstKey() from OrderPrices) as leastPrice, * from OrderEvent
Use the dot (.) and the event property name to select an event property of the event, for aggregation methods that return a single event.
The example statement below selects the order id of the least price order:
select OrderPrices.prices.firstEvent().orderId as leastPriceOrderId from OrderEvent
Use the dot (.) and an enumeration method to enumerate events returned by aggregation methods that return one or more events.
The example statement below selects the first 3 events among the order events with prices between one and ten:
select OrderPrices.prices.eventsbetween(0, true, 10, true).take(3) as first3Events from OrderEvent
This table lists methods for key-up and key-down:
Table 13.1. Sorted Aggregation Methods For Key Up/Down
| Method | Result |
|---|---|
| ceilingEvent(key) |
Returns the first event associated with the least key greater than or equal to the given key, or null if there is no such key. Section 13.3.3, “CeilingEvent, FloorEvent, HigherEvent, LowerEvent, GetEvent”. |
| ceilingEvents(key) |
Returns all events associated with the least key greater than or equal to the given key, or null if there is no such key. Section 13.3.4, “CeilingEvents, FloorEvents, HigherEvents, LowerEvents, GetEvents”. |
| ceilingKey(key) |
Returns the least key greater than or equal to the given key, or null if there is no such key. Section 13.3.5, “CeilingKey, FloorKey, HigherKey, LowerKey”. |
| floorEvent(key) |
Returns the first event associated with the greatest key less than or equal to the given key, or null if there is no such key. Section 13.3.3, “CeilingEvent, FloorEvent, HigherEvent, LowerEvent, GetEvent”. |
| floorEvents(key) |
Returns all events associated with the greatest key less than or equal to the given key, or null if there is no such key. Section 13.3.4, “CeilingEvents, FloorEvents, HigherEvents, LowerEvents, GetEvents”. |
| floorKey(key) |
Returns the greatest key less than or equal to the given key, or null if there is no such key. Section 13.3.5, “CeilingKey, FloorKey, HigherKey, LowerKey”. |
| higherEvent(key) |
Returns the first event associated with the least key strictly greater than the given key, or null if there is no such key. Section 13.3.3, “CeilingEvent, FloorEvent, HigherEvent, LowerEvent, GetEvent”. |
| higherEvents(key) |
Returns all events associated with the least key strictly greater than the given key, or null if there is no such key. Section 13.3.4, “CeilingEvents, FloorEvents, HigherEvents, LowerEvents, GetEvents”. |
| higherKey(key) |
Returns the least key strictly greater than the given key, or null if there is no such key. Section 13.3.5, “CeilingKey, FloorKey, HigherKey, LowerKey”. |
| lowerEvent(key) |
Returns the first event associated with the greatest key strictly less than the given key, or null if there is no such key. Section 13.3.3, “CeilingEvent, FloorEvent, HigherEvent, LowerEvent, GetEvent”. |
| lowerEvents(key) |
Returns all events associated with the greatest key strictly less than the given key, or null if there is no such key. Section 13.3.4, “CeilingEvents, FloorEvents, HigherEvents, LowerEvents, GetEvents”. |
| lowerKey(key) |
Returns the greatest key strictly less than the given key, or null if there is no such key. Section 13.3.5, “CeilingKey, FloorKey, HigherKey, LowerKey”. |
This table lists methods for least and greatest:
Table 13.2. Sorted Aggregation Methods For Key First/Last
| Method | Result |
|---|---|
| firstEvent() or minBy() |
Returns the first event associated with the least key, or null if empty. |
| firstEvents() |
Returns all events associated with the least key, or null if empty. |
| firstKey() |
Returns the first (least) key. |
| lastEvent() or maxBy() |
Returns the first event associated with the greatest key, or null if empty. |
| lastEvents() |
Returns all events associated with the greatest key, or null if empty. |
| lastKey() |
Returns the last (greatest) key. |
This table lists methods for getting for specific keys, checking contains and getting counts:
Table 13.3. Sorted Aggregation Methods For Get, Contains, Count
| Method | Result |
|---|---|
| containsKey(key) |
Returns true if the aggregation contains the specified key. |
| countEvents() |
Returns the number of events in the aggregation. |
| countKeys() |
Returns the number of keys in the aggregation. |
| getEvent(key) |
Returns the first event for the specified key, or null if there is no such key. Section 13.3.3, “CeilingEvent, FloorEvent, HigherEvent, LowerEvent, GetEvent”. |
| getEvents(key) |
Returns all events for the specified key, or null if there is no such key. Section 13.3.4, “CeilingEvents, FloorEvents, HigherEvents, LowerEvents, GetEvents”. |
This table lists methods for sub-map, between-values and reference:
Table 13.4. Sorted Aggregation Methods For Submap, Between and Reference
| Method | Result |
|---|---|
| eventsBetween(fromKey, fromInclusive, toKey, toInclusive) |
Returns all events of a portion of this aggregation whose keys range from |
| submap(fromKey, fromInclusive, toKey, toInclusive) |
Returns a submap of type |
| navigableMapReference() |
NOTE: This method returns an object that the runtime may concurrently modify and that is only valid for the period of evaluation of the current event or time.
Returns a |
Use com.espertech.esper.common.client.util.HashableMultiKey when the sorted aggregation has multiple keys.
E.g. for sorted(string, double) use new HashableMultiKey(orderId, price).
The methods accept a single key parameter and return the event or null if an event was not found. If the result is multiple events, the method returns the oldest ceiling/floor/lower/higher/keyed event.
Table 13.5. Sorted Aggregation Methods - Keyed Returning Single Event
| Method | Result |
|---|---|
| ceilingEvent(key) |
Returns the first event associated with the least key greater than or equal to the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| floorEvent(key) |
Returns the first event associated with the greatest key less than or equal to the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| higherEvent(key) |
Returns the first event associated with the least key strictly greater than the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| lowerEvent(key) |
Returns the first event associated with the greatest key strictly less than the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| getEvent(key) |
Returns the first event for the specified key, or null if there is no such key. |
Assuming the OrderPrices table exists as defined above, this example statement, when an order event arrives, returns the order event associated with the greatest price strictly less than the given price, or null if there is no such price:
select OrderPrices.prices.lowerEvent(price) as lowerPriceEvent from OrderEvent
The methods accepts a single key parameter and return all events or null if no events are found.
Table 13.6. Sorted Aggregation Methods - Keyed Returning Multiple Events
| Method | Result |
|---|---|
| ceilingEvents(key) |
Returns all events associated with the least key greater than or equal to the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| floorEvents(key) |
Returns all events associated with the greatest key less than or equal to the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| higherEvents(key) |
Returns all events associated with the least key strictly greater than the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| lowerEvents(key) |
Returns all events associated with the greatest key strictly less than the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| getEvents(key) |
Returns all events for the specified key, or null if there is no such key. |
Assuming the OrderPrices table exists as defined above, this example statement, when an order event arrives, returns all order events associated with the greatest price strictly less than the given price, or null if there is no such price:
select OrderPrices.prices.lowerEvents(price) as lowerPriceEvents from OrderEvent
The methods accepts a single key parameter and return the key or null if no key is found.
Table 13.7. Sorted Aggregation Methods - Keyed Returning Key
| Method | Result |
|---|---|
| ceilingKey(key) |
Returns the least key greater than or equal to the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| floorKey(key) |
Returns the greatest key less than or equal to the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| higherKey(key) |
Returns the least key strictly greater than the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| lowerKey(key) |
Returns the greatest key strictly less than the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
Assuming the OrderPrices table exists as defined above, this example statement, when an order event arrives, returns the greatest price strictly less than the given price, or null if there is no such price:
select OrderPrices.prices.lowerKey(price) as lowerPrice from OrderEvent
The methods have no parameter and return the first (least) or last (greatest) event or null if an event was not found. If the result is multiple events, the method returns the oldest first/last (least/greatest) event.
Table 13.8. Sorted Aggregation Methods - Unparameterized Returning Single Event
| Method | Result |
|---|---|
| firstEvent() or minBy() |
Returns the first event associated with the least key, or null if empty. |
| lastEvent() or maxBy() |
Returns the first event associated with the greatest key, or null if empty. |
Assuming the OrderPrices table exists as defined above, this example statement, when an order event arrives, returns the order event associated with the least price , or null if there is no such price:
select OrderPrices.prices.firstEvent() as leastPriceEvent from OrderEvent
The methods have no parameter and return the first (least) or last (greatest) events or null if no events are found.
Table 13.9. Sorted Aggregation Methods - Unparameterized Returning Multiple Events
| Method | Result |
|---|---|
| firstEvents() |
Returns all events associated with the least key, or null if empty. |
| lastEvents() |
Returns all events associated with the greatest key, or null if empty. |
Assuming the OrderPrices table exists as defined above, this example statement, when an order event arrives, returns all order events associated with the least price or null if there is no such price:
select OrderPrices.prices.firstEvents(price) as lowerPriceEvents from OrderEvent
The methods have no parameter and return the the first (least) or last (greatest) key or null if no key is found.
Table 13.10. Sorted Aggregation Methods - Unparameterized Returning Key
| Method | Result |
|---|---|
| firstKey() |
Returns the first (least) key. |
| lastKey() |
Returns the last (greatest) key. |
Assuming the OrderPrices table exists as defined above, this example statement, when an order event arrives, returns the least price or null if there is no such price:
select OrderPrices.prices.firstKey() as leastPrice from OrderEvent
This method accepts a single key parameter and returns a boolean-type value indicating whether the key is found, or null if using tables and the table row is not found.
Assuming the OrderPrices table exists as defined above, this example statement, when an order event arrives, returns true if a price of zero exists:
select OrderPrices.prices.containsKey(0) as priceZeroFound from OrderEvent
This method has no parameters and returns an int-type count of the number of events, or null if using tables and the table row is not found.
Assuming the OrderPrices table exists as defined above, this example statement, when an order event arrives, returns the number of events:
select OrderPrices.prices.countEvents() as numEvents from OrderEvent
This method has no parameters and returns an int-type count of the number of keys, or null if using tables and the table row is not found.
Assuming the OrderPrices table exists as defined above, this example statement, when an order event arrives, returns the number of prices:
select OrderPrices.prices.countKeys() as numPrices from OrderEvent
This method accepts four parameters, namely the from-key, the boolean-typed from-inclusive indicator, the to-key and the boolean-typed to-inclusive indicator.
The method returns all events whose keys range from from-key to to-key.
If from-key and to-key are equal, the returned value is empty unless from-inclusive and to-inclusive are both true.
The from-key must be less or equal to to-key.
Assuming the OrderPrices table exists as defined above, this example statement, when an order event arrives, returns all events with prices between one (inclusive) and ten (inclusive):
select OrderPrices.prices.eventsBetween(1, true, 10, true) as eventsPricedOneToTen from OrderEvent
This method accepts four parameters, namely the from-key, the boolean-typed from-inclusive indicator, the to-key and the boolean-typed to-inclusive indicator.
The method returns an object of type NavigableMap<Object, Object[]> that is a shallow copy of all keys of a portion of this aggregation whose keys range from fromKey to toKey.
If from-key and to-key are equal, the returned value is empty unless from-inclusive and to-inclusive are both true.
The from-key must be less or equal to to-key.
Assuming the OrderPrices table exists as defined above, this example statement, when an order event arrives, returns all keys and events as a navigable map with prices between one (inclusive) and ten (inclusive):
select OrderPrices.prices.submap(1, true, 10, true) as keysAndEventsPricedOneToTen from OrderEvent
The map keys are the key objects. Each map value is an array containing the event underlying object of the events for the key.
Modifications on the map returned by the method are not reflected back into the aggregation state. The map returned by the method is in effect a shallow copy.
This method has no parameters and returns an object of type NavigableMap<Object, Collection<EventBean>> that is an unmodifiable view of keys and unmodifiable collections of EventBean instances.
Warning
This method returns an object that the runtime may concurrently modify and that is only valid for the period of evaluation of the current event or time.
Assuming the OrderPrices table exists as defined above, this example statement, when an order event arrives, returns all keys and events as a navigable map:
select OrderPrices.prices.navigableMapReference() as prices from OrderEvent
The map keys are the key objects. Each map value is an a collection of EventBean events for the key.
Modifications on the map returned by the method are not allowed. The map returned by the method is in effect a wrapper of the actual aggregation state.
The below table summarizes the built-in aggregation methods for use with the window aggregation:
Table 13.11. Window Aggregation Methods
| Method | Result |
|---|---|
| listReference() |
NOTE: This method returns an object that the runtime may concurrently modify and that is only valid for the period of evaluation of the current event or time.
Returns a |
| countEvents() |
Returns the number of events. |
| first() |
Returns the oldest event or null if the aggregation is empty. |
| last() |
Returns the newest event or null if the aggregation is empty. |
The sample statement below creates a simple un-keyed table that keeps order events:
create table OrdersTable(orders window(*) @type('OrderEvent'))
The next statement aggregates order events into the table column orders considering the last 10 minutes of order events (the example specifies priority 1 so the runtime always updates the table before other selects):
@Priority(1) into table OrdersTable select window(*) as orders from OrderEvent#time(10 minutes)
This method has no parameters and returns an int-type count of the number of events, or null if using tables and the table row is not found.
Assuming the OrdersTable table exists as defined above, this example statement, when an order event arrives, returns the number of events:
select OrdersTable.orders.countEvents() as numEvents from OrderEvent
This method has no parameters and returns an object of type List<EventBean> that is an unmodifiable list of EventBean instances.
Warning
This method returns an object that the runtime may concurrently modify and that is only valid for the period of evaluation of the current event or time.
Assuming the OrdersTable table exists as defined above, this example statement, when an order event arrives, returns all events as a list:
select OrderPrices.orders.listReference() as prices from OrderEvent
Modifications on the list returned by the method are not allowed. The list returned by the method is in effect a wrapper of the actual aggregation state.
The method has no parameter and return the first (oldest) or last (newest) event or null if an event was not found.
Assuming the OrdersTable table exists as defined above, this example statement, when an order event arrives, returns the oldest order event, or null if there is no such event:
select OrdersTable.orders.first() as oldestOrder from OrderEvent
You may optionally specify an event property name as a parameter, in which case the method returns the event property value of the oldest/newest event or null if there is no such event.
The aggregation methods for count-min sketch are countMinSketchFrequency and countMinSketchTopk and are already described in Section 10.2.3, “Approximation Aggregation Functions”.
The extension code defines the aggregation methods and their parameters. For more information please see Section 22.5.2, “Aggregation Multi-Function Development”.
- 14.1. A Note on Data Window Name and Parameters
- 14.2. A Note on Batch Windows
- 14.3. Data Windows
- 14.3.1. Length Window (length or win:length)
- 14.3.2. Length Batch Window (length_batch or win:length_batch)
- 14.3.3. Time Window (time or win:time)
- 14.3.4. Externally-timed Window (ext_timed or win:ext_timed)
- 14.3.5. Time batch Window (time_batch or win:time_batch)
- 14.3.6. Externally-timed Batch Window (ext_timed_batch or win:ext_timed_batch)
- 14.3.7. Time-Length Combination Batch Window (time_length_batch or win:time_length_batch)
- 14.3.8. Time-Accumulating Window (time_accum or win:time_accum)
- 14.3.9. Keep-All Window (keepall or win:keepall)
- 14.3.10. First Length Window(firstlength or win:firstlength)
- 14.3.11. First Time Window (firsttime or win:firsttime)
- 14.3.12. Expiry Expression Window (expr or win:expr)
- 14.3.13. Expiry Expression Batch Window (expr_batch or win:expr_batch)
- 14.3.14. Unique Window (unique or std:unique)
- 14.3.15. Grouped Data Window (groupwin or std:groupwin)
- 14.3.16. Last Event Window (std:lastevent)
- 14.3.17. First Event Window (firstevent or std:firstevent)
- 14.3.18. First Unique Window (firstunique or std:firstunique)
- 14.3.19. Sorted Window (sort or ext:sort)
- 14.3.20. Ranked Window (rank or ext:rank)
- 14.3.21. Time-Order Window (time_order or ext:time_order)
- 14.3.22. Time-To-Live Window (timetolive or ext:timetolive)
- 14.4. Special Derived-Value Windows
- 14.4.1. Size Derived-Value Window (size) or std:size)
- 14.4.2. Univariate Statistics Derived-Value Window (uni or stat:uni)
- 14.4.3. Regression Derived-Value Window (linest or stat:linest)
- 14.4.4. Correlation Derived-Value Window (correl or stat:correl)
- 14.4.5. Weighted Average Derived-Value Window (weighted_avg or stat:weighted_avg)
This chapter outlines the data windows.
The section on Chapter 2, Basic Concepts provides additional information on the relationship of filtering, windows and aggregation. Please also see Section 5.4.3, “Specifying Data Windows” for the use of windows in the from clause with streams, patterns and named windows.
Data windows retain incoming events until an expiry policy indicates to release events. Thus data windows are a means of indicating what subset of events to analyze.
Two or more data windows can be combined. This allows a sets of events retained by one data window to be placed into a union or an intersection with the set of events retained by one or more other data windows. Please see Section 5.4.4, “Multiple Data Windows” for more detail.
The keep-all data window counts as a data window but has no expiry policy: it retains all events received. The grouped-window declaration allocates a new data window per grouping criteria and thereby counts as a data window, but cannot appear alone.
The next table summarizes data windows:
Table 14.1. Built-in Data Windows
| Data Window | Syntax | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Length Window | length(size) | Sliding length window extending the specified number of elements into the past. |
| Length Batch Window | length_batch(size) | Tumbling window that batches events and releases them when a given minimum number of events has been collected. |
| Time Window | time(time period) | Sliding time window extending the specified time interval into the past. |
| Externally-timed Window | ext_timed(timestamp expression, time period) | Sliding time window, based on the long-type time value supplied by an expression. |
| Time Batch Window | time_batch(time period[,optional reference point] [, flow control]) | Tumbling window that batches events and releases them every specified time interval, with flow control options. |
| Externally-timed Batch Window | ext_timed_batch(timestamp expression, time period[,optional reference point]) | Tumbling window that batches events and releases them every specified time interval based on the long-type value supplied by an expression. |
| Time-Length Combination Batch Window | time_length_batch(time period, size [, flow control]) | Tumbling multi-policy time and length batch window with flow control options. |
| Time-Accumulating Window | time_accum(time period) | Sliding time window accumulates events until no more events arrive within a given time interval. |
| Keep-All Window | keepall | The keep-all data window simply retains all events. |
| Sorted Window | sort(size, sort criteria) | Sorts by values returned by sort criteria expressions and keeps only the top events up to the given size. |
| Ranked Window | rank(unique criteria(s), size, sort criteria(s)) | Retains only the most recent among events having the same value for the criteria expression(s) sorted by sort criteria expressions and keeps only the top events up to the given size. |
| Time-Order Window | time_order(timestamp expression, time period) | Orders events that arrive out-of-order, using an expression providing timestamps to be ordered. |
| Time-To-Live Window | timetolive(timestamp expression) | Retains events until the time returned by the timestamp expression. |
| Unique Window | unique(unique criteria(s)) | Retains only the most recent among events having the same value for the criteria expression(s). Acts as a length window of size 1 for each distinct expression value. |
| Grouped Data Window | groupwin(grouping criteria(s)) | Groups events into sub-data-windows by the value of the specified expression(s), generally used to provide a separate data window per group. |
| Last Event Window | lastevent | Retains the last event, acts as a length window of size 1. |
| First Event Window | firstevent | Retains the very first arriving event, disregarding all subsequent events. |
| First Unique Window | firstunique(unique criteria(s)) | Retains only the very first among events having the same value for the criteria expression(s), disregarding all subsequent events for same value(s). |
| First Length Window | firstlength(size) | Retains the first size events, disregarding all subsequent events. |
| First Time Window | firsttime(time period) | Retains the events arriving until the time interval has passed, disregarding all subsequent events. |
| Expiry Expression Window | expr(expiry expression) | Expire events based on the result of an expiry expression passed as a parameter. |
| Expiry Expression Batch Window | expr_batch(expiry expression) | Tumbling window that batches events and releases them based on the result of an expiry expression passed as a parameter. |
There is a special kind of data window that is used less frequently, and is called a derived-value window. They are windows that derive a new value from event streams and post the result as events of a new type. The table below summarizes these special derived-value windows.
Table 14.2. Built-in Derived-Value Data Windows
| Data Window | Syntax | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Size | size([expression, ...]) | Derives a count of the number of events in a data window, or in an insert stream if used without a data window, and optionally provides additional event properties as listed in parameters. |
| Univariate statistics | uni(value expression [,expression, ...]) | Calculates univariate statistics on the values returned by the expression. |
| Regression | linest(value expression, value expression [,expression, ...]) | Calculates regression on the values returned by two expressions. |
| Correlation | correl(value expression, value expression [,expression, ...]) | Calculates the correlation value on the values returned by two expressions. |
| Weighted average | weighted_avg(value expression, value expression [,expression, ...]) | Calculates weighted average given a weight expression and an expression to compute the average for. |
The syntax for data windows starts with data window name and is followed by optional parameter expressions in parenthesis:
name(window_parameters)
This example specifies a time window of 5 seconds:
select * from StockTickEvent#time(5 sec)
EPL organizes built-in data windows in namespaces and names. Windows that provide sliding or tumbling data windows are in the win namespace. Other most commonly used windows are in the std namespace. The ext namespace are window that order events. The stat namespace is used for windows that derive statistical data.
Alternatively you may specify the namespace name and : colon character.
namespace:name(window_parameters)
The below examples all specify a time window of 5 seconds:
select * from StockTickEvent#time(5 sec)
select * from StockTickEvent#win:time(5 sec)
select * from StockTickEvent.win:time(5 sec)
All expressions are allowed as parameters to data windows, including expressions that contain variables or substitution parameters for prepared statements. Subqueries, the special prior and prev functions and aggregations (with the exception of the expression window and expression batch window) are not allowed as data window parameters.
For example, assuming a variable by name VAR_WINDOW_SIZE is defined:
select * from StockTickEvent#time(VAR_WINDOW_SIZE)
The system evaluates expression parameters for data windows at the time of context partition instantiation with the exception of the expression window (expr) and expression batch window (expr_batch).
Also consider multiple data windows in intersection or union (keywords retain-intersection and retain-union). Consider writing a custom plug-in data window if your application requires behavior that is not yet provided by any of the built-in windows.
If a window takes no parameters you may leave parenthesis off or the use empty parenthesis ().
The below examples all specify a keep-all window:
select * from StockTickEvent#keepall
select * from StockTickEvent#keepall()
select * from StockTickEvent.win:keepall()
select * from StockTickEvent.win:keepall
Expression parameters can reference context-provided properties. For example:
create schema ParameterEvent(windowSize int)
create context MyContext initiated by ParameterEvent as params terminated after 1 year
context MyContext select * from StockTickEvent#length(context.params.windowSize)
Batch windows buffer events until a certain threshold is reached and then release the batched events for processing. The released events become the insert stream events and the previous batch of events constitutes the remove stream events. Batch windows thus retain the current and the last batch of events in memory.
It is often desirable to aggregate without retaining events in memory, or with just keeping the current events in memory (and not also the last batch of events). You can declare a context and define what starts and ends a "batch" instead. Contexts provide a large degree of freedom in allowing batches to overlap, in allowing batches to span multiple statements and in allowing batches to have complex start and end conditions. They are further described in Chapter 4, Context and Context Partitions.
This example declares a non-overlapping context that spans a time interval of 3 seconds (i.e. a batch of 3 seconds):
create context IntervalSpanning3Seconds start @now end after 3 sec
The next example EPL aggregates events without retaining events in memory and outputs at the end of each interval:
context IntervalSpanning3Seconds select count(*) from Events output snapshot when terminated
Here is an example that outputs all events when at least 10 events, in the 3-second interval, have collected:
context IntervalSpanning3Seconds select window(*) from Events#keepall having count(*) >= 10
For the examples above, at the end of each 3-second interval, the runtime discards all data windows and aggregation state. If your application would like 3-second intervals keyed by some fields please consider a nested context declaration with a keyed segmented context, for example:
create context PerSymbolInterval3Sec context ById partition by symbol from StockTick, context Interval3Sec start @now end after 3 sec
Batch windows keep not only the current batch in memory but also the previous batch of events. For example, let's say at time 0 an event arrives and enters the batch window. At time 3 seconds (3-second batch window) the event becomes an insert-stream event and the runtime now updates aggregations for that batch (i.e. count goes up to 1). At time 6 seconds the event becomes a remove-stream event and the runtime now updates aggregations for that batch (i.e. count goes down to 0). Since the runtime continually updates aggregations from insert and remove stream events, and does not re-compute aggregations, batch windows follow the same paradigm.
This window is a moving (sliding) length window extending the specified number of elements into the past. The window takes a single expression as a parameter providing a numeric size value that defines the window size:
length(size_expression)The below example sums the price for the last 5 stock ticks for symbol GE.
select sum(price) from StockTickEvent(symbol='GE')#length(5)
The next example keeps a length window of 10 events of stock trade events, with a separate window for each symbol. The sum of price is calculated only for the last 10 events for each symbol and aggregates per symbol:
select sum(price) from StockTickEvent#groupwin(symbol)#length(10) group by symbol
A length window of 1 is equivalent to the last event window lastevent. The lastevent data window is the preferred notation:
select * from StockTickEvent#lastevent // Prefer this // ... equivalent to ... select * from StockTickEvent#length(1)
This window buffers events (tumbling window) and releases them when a given minimum number of events has been collected. Provide an expression defining the number of events to batch as a parameter:
length_batch(size_expression)The next statement buffers events until a minimum of 10 events have collected. Listeners to updates posted by this window receive updated information only when 10 or more events have collected.
select * from StockTickEvent#length_batch(10)
This window is a moving (sliding) time window extending the specified time interval into the past based on the system time. Provide a time period (see Section 5.2.1, “Specifying Time Periods”) or an expression defining the number of seconds as a parameter:
time(time period)time(seconds_interval_expression)For the GE stock tick events in the last 1 second, calculate a sum of price.
select sum(price) from StockTickEvent(symbol='GE')#time(1 sec)
The following time windows are equivalent specifications:
time(2 minutes 5 seconds) time(125 sec) time(125) time(MYINTERVAL) // MYINTERVAL defined as a variable
Similar to the time window, this window is a moving (sliding) time window extending the specified time interval into the past, but based on the long-type time value supplied by a timestamp expression. The window takes two parameters: the expression to return long-typed timestamp values, and a time period or expression that provides a number of seconds:
ext_timed(timestamp_expression, time_period)
ext_timed(timestamp_expression, seconds_interval_expression)
The key difference comparing the externally-timed window to the regular time window is that the window slides not based on the runtime time, but strictly based on the result of the timestamp expression when evaluated against the events entering the window.
The algorithm underlying the window compares the timestamp value returned by the expression when the oldest event arrived with the timestamp value returned by the expression for the newest arriving event on event arrival. If the time interval between the timestamp values is larger then the timer period parameter, then the algorithm removes all oldest events tail-first until the difference between the oldest and newest event is within the time interval. The window therefore slides only when events arrive and only considers each event's timestamp property (or other expression value returned) and not runtime time.
This window holds stock tick events of the last 10 seconds based on the timestamp property in StockTickEvent.
select * from StockTickEvent#ext_timed(timestamp, 10 seconds)
The externally-timed data window expects strict ordering of the timestamp values returned by the timestamp expression. The window is not useful for ordering events in time order, please use the time-order window instead.
On a related subject, runtime time itself can be entirely under control of the application as described in Section 16.9, “Controlling Time-Keeping”, allowing control over all time-based aspects of processing in one place.
This window buffers events (tumbling window) and releases them every specified time interval in one update. The window takes a time period or an expression providing a number of seconds as a parameter, plus optional parameters described next.
time_batch(time_period [,optional_reference_point] [,flow_control])
time_batch(seconds_interval_expression [,optional_reference_point] [,flow_control])
The time batch window takes a second, optional parameter that serves as a reference point to batch flush times. If not specified, the arrival of the first event into the batch window sets the reference point. Therefore if the reference point is not specified and the first event arrives at time t1, then the batch flushes at time t1 plus time_period and every time_period thereafter.
Note
Please see Section 14.2, “A Note on Batch Windows” for information on what a batch window is and how to best to compute over intervals.
Note that using this window means that the runtime keeps events in memory until the time is up: Consider your event arrival rate and determine if this is the behavior you want. Use context declaration or output rate limiting such as output snapshot as an alternative.
The below example batches events into a 5 second window releasing new batches every 5 seconds. Listeners to updates posted by this window receive updated information only every 5 seconds.
select * from StockTickEvent#time_batch(5 sec)
By default, if there are no events arriving in the current interval (insert stream), and no events remain from the prior batch (remove stream), then the window does not post results to listeners. The window allows overriding this default behavior via flow control keywords.
The synopsis with flow control parameters is:
time_batch(time_period or seconds_interval_expr [,optional_reference_point] [, "flow-control-keyword [, keyword...]"] )
The FORCE_UPDATE flow control keyword instructs the window to post an empty result set to listeners if there is no
data to post for an interval. When using this keyword the irstream keyword should be used in the select clause to ensure the remove stream is also output.
Note that FORCE_UPDATE is for use with listeners to the same statement and not for use with named windows. Consider output rate limiting instead.
The START_EAGER flow control keyword instructs the window to post empty result sets even before the first event arrives, starting a time interval at statement deployment time. As when using FORCE_UPDATE, the window also posts an empty result set to listeners if there is no data to post for an interval, however it starts doing so at time of statement deployment rather then at the time of arrival of the first event.
Taking the two flow control keywords in one sample statement, this example presents a window that waits for 10 seconds. It posts empty result sets after one interval after the statement gets deployed and keeps posting an empty result set as no events arrive during intervals:
select * from MyEvent#time_batch(10 sec, "FORCE_UPDATE, START_EAGER")
The optional reference point is provided as a long-value of milliseconds (or microseconds for microsecond runtime time unit) relative to January 1, 1970 and time 00:00:00.
The following example statement sets the reference point to 5 seconds and the batch size to 1 hour, so that each batch output is 5 seconds after each hour:
select * from OrderSummaryEvent#time_batch(1 hour, 5000L)
Similar to the time batch window, this window buffers events (tumbling) and releases them every specified time interval in one update, but based on the long-type time value supplied by a timestamp expression. The window has two required parameters taking an expression that returns long-typed timestamp values and a time period or constant-value expression that provides a number of seconds:
ext_timed_batch(timestamp_expression, time_period [,optional_reference_point])
ext_timed_batch(timestamp_expression, seconds_interval_expression [,optional_reference_point])
The externally-timed batch window takes a third, optional parameter that serves as a reference point to batch flush times. If not specified, the arrival of the first event into the batch window sets the reference point. Therefore if the reference point is not specified and the first event arrives at time t1, then the batch flushes at time t1 plus time_period and every time_period thereafter.
The key difference comparing the externally-timed batch window to the regular time batch window is that the window tumbles not based on the runtime time, but strictly based on the result of the timestamp expression when evaluated against the events entering the window.
The algorithm underlying the window compares the timestamp value returned by the expression when the oldest event arrived with the timestamp value returned by the expression for the newest arriving event on event arrival. If the time interval between the timestamp values is larger then the timer period parameter, then the algorithm posts the current batch of events. The window therefore posts batches only when events arrive and only considers each event's timestamp property (or other expression value returned) and not runtime time.
Note that using this window means that the runtime keeps events in memory until the time is up: Consider your event arrival rate and determine if this is the behavior you want. Use context declaration or output rate limiting such as output snapshot as an alternative.
The below example batches events into a 5 second window releasing new batches every 5 seconds. Listeners to updates posted by this window receive updated information only when event arrive with timestamps that indicate the start of a new batch:
select * from StockTickEvent#ext_timed_batch(timestamp, 5 sec)
The optional reference point is provided as a long-value of milliseconds (or microseconds) relative to January 1, 1970 and time 00:00:00.
The following example statement sets the reference point to 5 seconds and the batch size to 1 hour, so that each batch output is 5 seconds after each hour:
select * from OrderSummaryEvent#ext_timed_batch(timestamp, 1 hour, 5000L)
The externally-timed data window expects strict ordering of the timestamp values returned by the timestamp expression. The window is not useful for ordering events in time order, please use the time-order window instead.
On a related subject, runtime time itself can be entirely under control of the application as described in Section 16.9, “Controlling Time-Keeping”, allowing control over all time-based aspects of processing in one place.
This data window is a combination of time and length batch (tumbling) windows. Similar to the time and length batch windows, this batches events and releases the batched events when either one of the following conditions occurs, whichever occurs first: the data window has collected a given number of events, or a given time interval has passed.
The parameters take 2 forms. The first form accepts a time period or an expression providing a number of seconds, and an expression for the number of events:
time_length_batch(time_period, number_of_events_expression)
time_length_batch(seconds_interval_expression, number_of_events_expression)
The next example shows a time-length combination batch window that batches up to 100 events or all events arriving within a 1-second time interval, whichever condition occurs first:
select * from MyEvent#time_length_batch(1 sec, 100)
In this example, if 100 events arrive into the window before a 1-second time interval passes, the window posts the batch of 100 events. If less then 100 events arrive within a 1-second interval, the window posts all events that arrived within the 1-second interval at the end of the interval.
By default, if there are no events arriving in the current interval (insert stream), and no events remain from the prior batch (remove stream), then the window does not post results to listeners. This window allows overriding this default behavior via flow control keywords.
The synopsis of the window with flow control parameters is:
time_length_batch(time_period or seconds_interval_expression, number_of_events_expression, "flow control keyword [, keyword...]")
The FORCE_UPDATE flow control keyword instructs the window to post an empty result set to listeners if there is no data to post for an interval. The window begins posting no later then after one time interval passed after the first event arrives. When using this keyword the irstream keyword should be used in the select clause to ensure the remove stream is also output.
The START_EAGER flow control keyword instructs the window to post empty result sets even before the first event arrives, starting a time interval at statement deployment time. As when using FORCE_UPDATE, the window also posts an empty result set to listeners if there is no data to post for an interval, however it starts doing so at time of statement deployment rather then at the time of arrival of the first event.
Taking the two flow control keywords in one sample statement, this example presents a window that waits for 10 seconds or reacts when the 5th event arrives, whichever comes first. It posts empty result sets after one interval after the statement gets deployed and keeps posting an empty result set as no events arrive during intervals:
select * from MyEvent#time_length_batch(10 sec, 5, "FORCE_UPDATE, START_EAGER")
This data window is a specialized moving (sliding) time window that differs from the regular time window in that it accumulates events until no more events arrive within a given time interval, and only then releases the accumulated events as a remove stream.
The window accepts a single parameter: the time period or seconds-expression specifying the length of the time interval during which no events must arrive until the window releases accumulated events. The synopsis is as follows:
time_accum(time_period)time_accum(seconds_interval_expression)The next example shows a time-accumulating window that accumulates events, and then releases events if within the time interval no more events arrive:
select * from MyEvent#time_accum(10 sec)
This example accumulates events, until when for a period of 10 seconds no more MyEvent events arrive, at which time it posts all accumulated MyEvent events.
Your application may only be interested in the batches of events as events leave the data window. This can be done simply by selecting the remove stream of this data window, populated by the runtime as accumulated events leave the data window all-at-once when no events arrive during the time interval following the time the last event arrived:
select rstream * from MyEvent#time_accum(10 sec)
If there are no events arriving, then the window does not post results to listeners.
This keep-all data window simply retains all events. The window does not remove events from the data window, unless used with a named window and the on delete clause.
The window accepts no parameters. The synopsis is as follows:
keepall
The next example shows a keep-all window that accumulates all events received into the window:
select * from MyEvent#keepall
Note that since the window does not release events, care must be taken to prevent retained events from using all available resources.
The firstlength window retains the very first size_expression events.
The synopsis is:
firstlength(size_expression)
If used within a named window and an on-delete clause deletes events, the window accepts further arriving events until the number of retained events reaches the size of size_expression.
The below example creates a window that retains only the first 10 events:
select * from MyEvent#firstlength(10)
The firsttime window retains all events arriving within a given time interval after statement start.
The synopsis is:
firsttime(time_period)firsttime(seconds_interval_expression)The below example creates a window that retains only those events arriving within 1 minute and 10 seconds of statement start:
select * from MyEvent#firsttime(1 minute 10 seconds)
The expr data window applies an expiry expression and removes events from the data window when the expression returns false.
Use this window to implement rolling and dynamically shrinking or expanding time, length or other windows. Rolling can, for example, be controlled based on event properties of arriving events, based on aggregation values or based on the return result of user-defined functions. Use this window to accumulate events until a value changes or other condition occurs based on arriving events or change of a variable value.
The synopsis is:
expr(expiry_expression)The expiry expression can be any expression including expressions on event properties, variables, aggregation functions or user-defined functions. The window applies this expression to the oldest event(s) currently in the window, as described next.
When a new event arrives or when a variable value referenced by the expiry expression changes then the window applies the expiry expression starting from the oldest event in the data window. If the expiry expression returns false for the oldest event, the window removes the event from the data window. The window then applies the expression to the next oldest event. If the expiry expression returns true for the oldest event, no further evaluation takes place and the window indicates any new and expired events through insert and remove stream.
By using variables in the expiry expression it is possible to change the behavior of the window dynamically at runtime. When one or more variables used in the expression are updated the window evaluates the expiry expression starting from the oldest event.
Aggregation functions, if present in the expiry expression, are continuously updated as events enter and leave the data window. Use the grouped data window with this window to compute aggregations per group.
The runtime makes the following built-in properties available to the expiry expression:
Table 14.3. Built-in Properties of the Expiry Expression Data Window
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
current_count | int | The number of events in the data window including the currently-arriving event. |
expired_count | int | The number of events expired during this evaluation. |
newest_event | (same event type as arriving events) | The last-arriving event itself. |
newest_timestamp | long | The runtime timestamp associated with the last-arriving event. |
oldest_event | (same event type as arriving events) | The currently-evaluated event itself. |
oldest_timestamp | long | The runtime timestamp associated with the currently-evaluated event. |
view_reference | Object | The object handle to this data window. |
This EPL declares an expiry expression that retains the last 2 events:
select * from MyEvent#expr(current_count <= 2)
The following example implements a dynamically-sized length window by means of a SIZE variable. As the SIZE variable value changes the window retains the number of events according to the current value of SIZE:
create variable int SIZE = 1000
select * from MyEvent#expr(current_count <= SIZE)
The next EPL retains the last 2 seconds of events:
select * from MyEvent#expr(oldest_timestamp > newest_timestamp - 2000)
The following example implements a dynamically-sized time window. As the SIZE long-type variable value changes the window retains a time interval accordingly:
create variable long SIZE = 1000
select * from MyEvent#expr(newest_timestamp - oldest_timestamp < SIZE)
The following example declares a KEEP variable and flushes all events from the data window when the variable turns false:
create variable boolean KEEP = true
select * from MyEvent#expr(KEEP)
The next example specifies a rolling window that removes the oldest events from the window until the total price of all events in the window is less then 1000:
select * from MyEvent#expr(sum(price) < 1000)
This example retains all events that have the same value of the flag event property. When the flag value changes,
the data window expires all events with the old flag value and retains only the most recent event of the new flag value:
select * from MyEvent#expr(newest_event.flag = oldest_event.flag)
You may not use subqueries or the prev and prior functions as part of the expiry expression. Consider using a named window and on-delete or on-merge instead.
When using variables in the expiry expression, the thread that updates the variable does not evaluate the window. The thread that updates the variable instead schedules a reevaluation and window evaluates by timer execution.
The expr_batch buffers events (tumbling window) and releases them when a given expiry expression returns true.
Use this window to implement dynamic or custom batching behavior, such as for dynamically shrinking or growing time, length or other batches, for batching based on event properties of arriving events, aggregation values or for batching based on a user-defined function.
The synopsis is:
expr_batch(expiry_expression, [include_triggering_event])
The expiry expression can be any expression including expressions on event properties, variables, aggregation functions or user-defined functions. The window applies this expression to arriving event(s), as described next.
The optional second parameter include_triggering_event defines whether to include the event that triggers the batch in the current batch (true, the default) or in the next batch (false).
When a new event arrives or when a variable value referenced by the expiry expression changes or when events get removed from the data window then the window applies the expiry expression. If the expiry expression returns true the data window posts the collected events as the insert stream and the last batch of events as remove stream.
By using variables in the expiry expression it is possible to change the behavior of the window dynamically at runtime. When one or more variables used in the expression are updated the window evaluates the expiry expression as well.
Aggregation functions, if present in the expiry expression, are continuously updated as events enter the data window and reset when the runtime posts a batch of events. Use the grouped data window with this window to compute aggregations per group.
The compiler makes the following built-in properties available to the expiry expression:
Table 14.4. Built-in Properties of the Expiry Expression Data Window
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
current_count | int | The number of events in the data window including the currently-arriving event. |
newest_event | (same event type as arriving events) | The last-arriving event itself. |
newest_timestamp | long | The runtime timestamp associated with the last-arriving event. |
oldest_event | (same event type as arriving events) | The currently-evaluated event itself. |
oldest_timestamp | long | The runtime timestamp associated with the currently-evaluated event. |
view_reference | Object | The object handle to this window. |
This EPL declares an expiry expression that posts event batches consisting of 2 events:
select * from MyEvent#expr_batch(current_count >= 2)
The following example implements a dynamically-sized length batch window by means of a SIZE variable. As the SIZE variable value changes the window accumulates and posts the number of events according to the current value of SIZE:
create variable int SIZE = 1000
select * from MyEvent#expr_batch(current_count >= SIZE)
The following example accumulates events until an event arrives that has a value of postme for property myvalue:
select * from MyEvent#expr_batch(myvalue = 'postme')
The following example declares a POST variable and posts a batch of events when the variable turns true:
create variable boolean POST = false
select * from MyEvent#expr_batch(POST)
The next example specifies a tumbling window that posts a batch of events when the total price of all events in the window is greater then 1000:
select * from MyEvent#expr_batch(sum(price) > 1000)
Specify the second parameter as false when you want the triggering event not included in the current batch.
This example batches all events that have the same value of the flag event property. When the flag value changes,
the data window releases the batch of events collected for the old flag value. The data window collects the most recent event and the future arriving events of the same new flag value:
select * from MyEvent#expr_batch(newest_event.flag != oldest_event.flag, false)
You may not use subqueries or the prev and prior functions as part of the expiry expression. Consider using a named window and on-delete or on-merge instead.
When using variables in the expiry expression, the thread that updates the variable does not evaluate the window. The thread that updates the variable instead schedules a reevaluation and window evaluates by timer execution.
The unique window is a window that includes only the most recent among events having the same value(s) for the result of the specified expression or list of expressions.
The synopsis is:
unique(unique_expression [, unique_expression ...])
The window acts as a length window of size 1 for each distinct value returned by an expression, or combination of values returned by multiple expressions. It thus posts as old events the prior event of the same value(s), if any.
An expression may return a null value. The compiler treats a null value as any other value. An expression can also return a custom application object, whereby the application class should implement the hashCode and equals methods. Further detail on key expressions can be found at Section 5.2.13, “Composite Keys and Array Values as Keys”.
The below example creates a window that retains only the last event per symbol.
select * from StockTickEvent#unique(symbol)
The next example creates a window that retains the last event per symbol and feed.
select * from StockTickEvent#unique(symbol, feed)
When using unique the compiler plans statements applying an implicit unique index, where applicable.
Specify @Hint('disable_unique_implicit_idx') to force the compiler to plan statement using a non-unique index.
Specifying #groupwin groups events into sub-data-window by the value returned by the specified expression or the combination of values returned by a list of expressions. The #groupwin takes a single expression to supply the group criteria values, or a list of expressions as parameters, as the synopsis shows:
groupwin(grouping_expression [, grouping_expression ...])
The grouping_expression expression(s) return one or more group keys, by which it creates a separate data window for each distinct group key. Note that the expression should not return an unlimited number of values: the grouping expression should not return a time value or otherwise unlimited key. Further detail on key expressions can be found at Section 5.2.13, “Composite Keys and Array Values as Keys”.
An expression may return a null value. The runtime treats a null value as any other value. An expression can also return a custom application object, whereby the application class should implement the hashCode and equals methods.
You can specify a single groupwin per stream. Multiple groupwin declarations for the same stream are not allowed.
Use group by instead of the grouped data window to control how aggregations are grouped.
A grouped data window with a length window of 1 is equivalent to the unique data window unique. The unique data window is the preferred notation:
select * from StockTickEvent#unique(symbol) // Prefer this // ... equivalent to ... select * from StockTickEvent#groupwin(symbol)#length(1)
This example computes the total price for the last 5 events considering the last 5 events per each symbol, aggregating the price across all symbols (since no group by clause is specified the aggregation is across all symbols):
select symbol, sum(price) from StockTickEvent#groupwin(symbol)#length(5)
The @Hint("reclaim_group_aged=age_in_seconds") hint instructs the runtime to discard grouped data window state that has not been updated for age_in_seconds seconds.
The optional @Hint("reclaim_group_freq=sweep_frequency_in_seconds") can be specified in addition to control the frequency at which the runtime sweeps data window state.
If the hint is not specified, the frequency defaults to the same value as age_in_seconds. Use the hints when your group criteria returns a changing or unlimited number of values. By default and without hints the data window does not reclaim or remove data windows for group criteria values.
The updated sample statement with both hints:
// Remove data window for symbols not updated for 10 seconds or more and sweep every 30 seconds
@Hint('reclaim_group_aged=10,reclaim_group_freq=30')
select symbol, sum(price) from StockTickEvent#groupwin(symbol)#length(5)Reclaim executes when an event arrives and not in the timer thread. In the example above reclaim can occur up to 40 seconds of runtime time after the newest event arrives. Reclaim may affect iteration order for the statement and iteration order becomes indeterministic with reclaim.
To compute the total price for the last 5 events considering the last 5 events per each symbol and outputting a price per symbol, add the group by clause:
select symbol, sum(price) from StockTickEvent#groupwin(symbol)#length(5) group by symbol
The groupwin grouped-window can also take multiple expressions that provide values to group by. This example computes the total price for each symbol and feed for the last 10 events per symbol and feed combination:
select sum(price) from StockTickEvent#groupwin(symbol, feed)#length(10)
The order in which the groupwin grouped-window appears controls the data the runtime derives from events for each group. The next 2 statements demonstrate this using a length window.
Without the groupwin declaration the same statement returns the total price per symbol for only the last 10 events across all symbols. Here the runtime allocates only one length window for all events:
select sum(price) from StockTickEvent#length(10)
We have learned that by placing the groupwin grouped-window before other data windows, these other data windows become part of the grouped set of windows. The runtime dynamically allocates a new window instance for each, every time it encounters a new group key such as a new value for symbol. Therefore, in groupwin(symbol)#length(10) the runtime allocates a new length window for each distinct symbol. However in length(10) alone the runtime maintains a single length window.
The groupwin can be used with multiple data windows to achieve a grouped intersection or union policy.
The next statement retains the last 4 events per symbol and only those events that are also not older then 10 seconds:
select * from StockTickEvent#groupwin(symbol)#length(4)#time(10)
Last, considers a grouped data window for two group criteria. Here, the statement results are total price per symbol and feed for the last 100 events per symbol and feed.
select sum(price) from StockTickEvent#groupwin(symbol, feed)#length(100)
Note
A note on grouped time windows: When using grouped-window with time windows, note that whether the runtime retains 5 minutes of events or retains 5 minutes of events per group, the result is the same from the perspective of retaining events as both policies retain, considering all groups, the same set of events. Therefore please specify the time window alone (ungrouped).
For example:
// Use this: select sum(price) from StockTickEvent#time(1 minute) // is equivalent to (don't use this): // select sum(price) from StockTickEvent#groupwin(symbol)#time(1 minute) // Use the group-by clause for grouping aggregation by symbol.
For advanced users: There is an optional declaration that can control how the groupwin grouped-window gets evaluated and that is #merge.
The merge can only occur after a groupwin grouped-window. It controls the end of the grouped declaration.
Compare the following statements:
select * from Market#groupwin(ticker)#length(1000000)
#weighted_avg(price, volume)#merge(ticker)
// ... and ...
select * from Market#groupwin(ticker)#length(1000000)#merge(ticker)
#weighted_avg(price, volume)
If your statement does not specify the optional #merge, the semantics are the same as the first statement.
The first statement, in which the #mergeis added to the end (same as no merge), computes weighted average per ticker, considering, per-ticker, the last 1M Market events for each ticker.
The second statement, in which the merge is added to the middle, computes weighted average considering, per-ticker, the last 1M Market events, computing the weighted average for all such events using a single data window rather then multiple data window instances with one window per ticker.
This window exposes the last element:
lastevent
The window acts as a length window of size 1. It thus posts as old events the prior event in the stream, if any.
This example statement retains the last stock tick event for the symbol GE.
select * from StockTickEvent(symbol='GE')#lastevent
If you want to output the last event within a sliding window, please see Section 10.1.13, “The Previous Function”. That function accepts a relative (count) or absolute index and returns event properties or an event in the context of the specified data window.
This window retains only the first arriving event:
firstevent
All events arriving after the first event are discarded.
If used within a named window and an on-delete clause deletes the first event, the window resets and will retain the next arriving event.
An example of a statement that retains the first ReferenceData event arriving is:
select * from ReferenceData#firstevent
If you want to output the first event within a sliding window, please see Section 10.1.13, “The Previous Function”. That function accepts a relative (count) or absolute index and returns event properties or an event in the context of the specified data window.
The firstunique window retains only the very first among events having the same value for the specified expression or list of expressions.
The synopsis is:
firstunique(unique_expression [, unique_expression ...])
Further detail on key expressions can be found at Section 5.2.13, “Composite Keys and Array Values as Keys”.
If used within a named window and an on-delete clause deletes events, the window resets and will retain the next arriving event for the expression result value(s) of the deleted events.
The below example creates a window that retains only the first event per category:
select * from ReferenceData#firstunique(category)
When using firstunique the compiler plans statements applying an implicit unique index, where applicable.
Specify @Hint('disable_unique_implicit_idx') to force the compiler to plan statements using a non-unique index.
This window sorts by values returned by the specified expression or list of expressions and keeps only the top (or bottom) events up to the given size.
This window retains all events in the stream that fall into the sort range. Use the ranked window as described next to retain events per unique key(s) and sorted.
The syntax is as follows:
sort(size_expression, sort_criteria_expression [asc/desc][, sort_criteria_expression [asc/desc]...])
An expression may be followed by the optional asc or desc keywords to indicate that the values returned by that expression are sorted in ascending or descending sort order.
The window below retains only those events that have the highest 10 prices considering all events (and not only the last event per symbol, see rank below) and reports a total price:
select sum(price) from StockTickEvent#sort(10, price desc)
The following example sorts events first by price in descending order, and then by symbol name in ascending (alphabetical) order, keeping only the 10 events with the highest price (with ties resolved by alphabetical order of symbol).
select * from StockTickEvent#sort(10, price desc, symbol asc)
The sorted window is often used with the prev, prevwindow or prevtail single-row functions to output properties of events at a certain position or to output the complete data window according to sort order.
Use the grouped window to retain a separate sort window for each group. For example, the windows groupwin(market)#sort(10, price desc) instruct the runtime to retain, per market, the highest 10 prices.
This window retains only the most recent among events having the same value for the criteria expression(s), sorted by sort criteria expressions and keeps only the top events up to the given size.
This window is similar to the sorted window in that it keeps only the top (or bottom) events up to the given size, however the window also retains only the most recent among events having the same value(s) for the specified uniqueness expression(s).
The syntax is as follows:
rank(unique_expression [, unique_expression ...], size_expression, sort_criteria_expression [asc/desc][, sort_criteria_expression [asc/desc]...])
Specify the expressions returning unique key values first. Further detail on key expressions can be found at Section 5.2.13, “Composite Keys and Array Values as Keys”.
Then specify a constant value that is the size of the ranked window. Then specify the expressions returning sort criteria values. The sort criteria expressions may be followed by the optional asc or desc keywords to indicate that the values returned by that expression are sorted in ascending or descending sort order.
The window below retains only those events that have the highest 10 prices considering only the last event per symbol and reports a total price:
select sum(price) from StockTickEvent#rank(symbol, 10, price desc)
The following example retains, for the last event per market and symbol, those events that sort by price and quantity ascending into the first 10 ranks:
select * from StockTickEvent#rank(market, symbol, 10, price, quantity)
The ranked window is often used with the prev, prevwindow or prevtail single-row functions to output properties of events at a certain position or to output the complete data window according to sort order.
This example outputs every 5 seconds the top 10 events according to price descending and considering only the last event per symbol:
select prevwindow(*) from StockTickEvent#rank(symbol, 10, price desc) output snapshot every 5 seconds limit 1 // need only 1 row
Use the grouped window to retain a separate rank for each group. For example, the windows groupwin(market)#rank(symbol, 10, price desc) instruct the runtime to retain, per market, the highest 10 prices considering the last event per symbol.
This window orders events that arrive out-of-order, using timestamp-values provided by an expression, and by comparing that timestamp value to runtime time.
The syntax for this window is as follows.
time_order(timestamp_expression, time_period)
time_order(timestamp_expression, seconds_interval_expression)
The first parameter to the window is the expression that supplies timestamp values. The timestamp is expected to be a long-typed value that denotes an event's time of consideration by the window (or other expression). This is typically the time of arrival. The second parameter is a number-of-seconds expression or the time period specifying the time interval that an arriving event should maximally be held, in order to consider older events arriving at a later time.
Since the window compares timestamp values to runtime time, the window requires that the timestamp values and runtime time are both following the same clock. Therefore, to the extend that the clocks that originated both timestamps differ, the window may produce inaccurate results.
As an example, the next statement uses the arrival_time property of MyTimestampedEvent events to order and release events by arrival time:
insert rstream into ArrivalTimeOrderedStream select rstream * from MyTimestampedEvent#time_order(arrival_time, 10 sec)
In the example above, the arrival_time property holds a long-typed timestamp value. On arrival of an event, the runtime compares the timestamp value of each event to the tail-time of the window. The tail-time of the window is, in this example, 10 seconds before runtime time (continuously sliding). If the timestamp value indicates that the event is older then the tail-time of the time window, the event is released immediately in the remove stream. If the timestamp value indicates that the event is newer then the tail-time of the window, the window retains the event until runtime time moves such that the event timestamp is older then tail-time.
The examples thus holds each arriving event in memory anywhere from zero seconds to 10 seconds, to allow for older events (considering arrival time timestamp) to arrive. In other words, the window holds an event with an arrival time equal to runtime time for 10 seconds. The window holds an event with an arrival time that is 2 seconds older then runtime time for 8 seconds. The window holds an event with an arrival time that is 10 or more seconds older then runtime time for zero seconds, and releases such (old) events immediately into the remove stream.
The insert stream of this sliding window consists of all arriving events. The remove stream of the window is ordered by timestamp value: The event that has the oldest timestamp value is released first, followed by the next newer events. The window preserves the order of events that arrived into the window for same timestamp values. Note the statement above uses the rstream keyword in both the insert into clause and the select clause to select ordered events only. It uses the insert into clause to makes such ordered stream available for subsequent statements to use.
It is up to your application to populate the timestamp property into your events or use a sensible expression that returns timestamp values for consideration by the window. The window also works well if you use externally-provided time via timer events.
This window retains events until runtime time reaches the value returned by the given timestamp expression.
The syntax for this window is as follows:
timetolive(timestamp_expression)The only parameter to the window is the expression that supplies timestamp values. The timestamp is expected to be a long-typed value that denotes an event's time-to-live.
Since the window compares timestamp values to runtime time, the window requires that the timestamp values and runtime time are both following the same clock.
On arrival of an event, the runtime evaluates the timestamp expression and obtains a long-type timestamp. The runtime compares that timestamp value to runtime time:
If the timestamp is older than runtime time or the same as runtime time, the runtime releases the event immediately into the remove stream and does not retain the event at all.
If the timestamp value is newer than the runtime time, the data window retains the event until runtime time moves forward such that the timestamp is the same or older than runtime time.
As an example, the next statement uses the arrival_time property of MyTimestampedEvent events to release events by arrival time:
insert rstream into ArrivalTimeOrderedStream select rstream * from MyTimestampedEvent#timetolive(arrival_time)
For example, assume runtime time is 8:00:00 (8 am).
If the
arrival_timetimestamp is8:00:00or older (such as7:59:00), the data window does not retain the event at all, i.e. the runtime releases the event into the remove stream upon arrival.If the
arrival_timetimestamp is after8:00:00the data window retains the event. Let's say thearrival_timetimestamp is8:02:00the runtime retains the event until runtime time is8:02:00or newer.
The runtime evaluates the expression only once at the arrival of each event to determine that event's time-to-live. The time-to-live data structure organizes events by the value returned by the expression on event arrival into the data window.
The insert stream of this sliding window consists of all arriving events. The remove stream of the window is ordered by timestamp value: The event that has the oldest timestamp value is released first, followed by the next newer events. Note the statement above uses the rstream keyword in both the insert into clause and the select clause to select ordered events only. It uses the insert into clause to makes such ordered stream available for subsequent statements to use.
It is up to your application to populate the timestamp property into your events or use a sensible expression that returns timestamp values for consideration by the window. The window also works well if you use externally-provided time via timer events and if you have runtime time track watermarks.
The time-to-live data window is fully equivalent to the time-order data window with a zero value for the time period.
The derived-value windows can be used combined with data windows or alone. Very similar to aggregation functions, these windows aggregate or derive information from an event stream. As compared to aggregation functions,
statistics windows can post multiple derived fields all-in-one including properties from the last event that was received. The derived fields and event properties are available for querying in the where-clause and are often compared to prior values using the prior function. Derived-value window do not retain events.
This window posts the number of events received from a stream or window plus any additional event properties or expression values listed as parameters. The synopsis is:
size([expression, ...] [ * ])
The window posts a single long-typed property named size. The window posts the prior size as old data, and the current size as new data to update listeners of the window. Via the iterator method of the statement the size value can also be polled (read). The window only posts output events when the size count changes and does not stay the same.
As optional parameters the window takes a list of expressions that the window evaluates against the last arriving event and provides along the size field. You may also provide the * wildcard selector to have the window output all event properties.
An alternative to receiving a data window event count is the prevcount function. Compared to the size window the prevcount function requires a data window while the size window does not. The related count(...) aggregation function provides a count per group when used with group by.
When combined with a data window, the size window reports the current number of events in the data window in the insert stream and the prior number of events in the data window as the remove stream. This example reports the number of tick events within the last 1 minute:
select size from StockTickEvent#time(1 min)#size
To select additional event properties you may add each event property to output as a parameter to the window.
The next example selects the symbol and feed event properties in addition to the size property:
select size, symbol, feed from StockTickEvent#time(1 min)#size(symbol, feed)
This example selects all event properties in addition to the size property:
select * from StockTickEvent#time(1 min)#size(*)
The size window is also useful in conjunction with a groupwin grouped-window to count the number of events per group. The EPL below returns the number of events per symbol.
select size from StockTickEvent#groupwin(symbol)#size
When used without a data window, the window simply counts the number of events:
select size from StockTickEvent#size
All windows can be used with pattern statements as well. The next EPL snippet shows a pattern that looks for tick events followed by trade events for the same symbol. The size window counts the number of occurrences of the pattern.
select size from pattern[every s=StockTickEvent -> TradeEvent(symbol=s.symbol)]#size
This window calculates univariate statistics on a numeric expression. The window takes a single value expression as a parameter plus any number of optional additional expressions to return properties of the last event. The value expression must return a numeric value:
uni(value_expression [,expression, ...] [ * ])
After the value expression you may optionally list additional expressions or event properties to evaluate for the stream and return their value based on the last arriving event. You may also provide the * wildcard selector to have the window output all event properties.
Table 14.5. Univariate Statistics Derived Properties
| Property Name | Description |
|---|---|
datapoints | Number of values, equivalent to count(*) for the stream |
total | Sum of values |
average | Average of values |
variance | Variance |
stddev | Sample standard deviation (square root of variance) |
stddevpa | Population standard deviation |
The below example selects the standard deviation on price for stock tick events for the last 10 events.
select stddev from StockTickEvent#length(10)#uni(price)
To add properties from the event stream you may simply add all additional properties as parameters to the window.
This example selects all of the derived values, based on the price property, plus the values of the symbol and feed event properties:
select * from StockTickEvent#length(10)#uni(price, symbol, feed)
The following example selects all of the derived values plus all event properties:
select * from StockTickEvent#length(10)#uni(price, symbol, *)
This window calculates regression and related intermediate results on the values returned by two expressions. The window takes two value expressions as parameters plus any number of optional additional expressions to return properties of the last event. The value expressions must return a numeric value:
linest(value_expression, value_expression [,expression, ...] [ * ])
After the two value expressions you may optionally list additional expressions or event properties to evaluate for the stream and return their value based on the last arriving event. You may also provide the * wildcard selector to have the window output all event properties.
Table 14.6. Regression Derived Properties
| Property Name | Description |
|---|---|
slope | Slope. |
YIntercept | Y intercept. |
XAverage | X average. |
XStandardDeviationPop | X standard deviation population. |
XStandardDeviationSample | X standard deviation sample. |
XSum | X sum. |
XVariance | X variance. |
YAverage | X average. |
YStandardDeviationPop | Y standard deviation population. |
YStandardDeviationSample | Y standard deviation sample. |
YSum | Y sum. |
YVariance | Y variance. |
dataPoints | Number of data points. |
n | Number of data points. |
sumX | Sum of X (same as X Sum). |
sumXSq | Sum of X squared. |
sumXY | Sum of X times Y. |
sumY | Sum of Y (same as Y Sum). |
sumYSq | Sum of Y squared. |
The next example calculates regression and returns the slope and y-intercept on price and offer for all events in the last 10 seconds.
select slope, YIntercept from StockTickEvent#time(10 seconds)#linest(price, offer)
To add properties from the event stream you may simply add all additional properties as parameters to the window.
This example selects all of the derived values, based on the price and offer properties, plus the values of the symbol and feed event properties:
select * from StockTickEvent#time(10 seconds)#linest(price, offer, symbol, feed)
The following example selects all of the derived values plus all event properties:
select * from StockTickEvent#time(10 seconds)#linest(price, offer, *)
This window calculates the correlation value on the value returned by two expressions. The window takes two value expressions as parameters plus any number of optional additional expressions to return properties of the last event. The value expressions must be return a numeric value:
correl(value_expression, value_expression [,expression, ...] [ * ])
After the two value expressions you may optionally list additional expressions or event properties to evaluate for the stream and return their value based on the last arriving event. You may also provide the * wildcard selector to have the window output all event properties.
Table 14.7. Correlation Derived Properties
| Property Name | Description |
|---|---|
correlation | Correlation between two event properties |
The next example calculates correlation on price and offer over all stock tick events for GE:
select correlation from StockTickEvent(symbol='GE')#correl(price, offer)
To add properties from the event stream you may simply add all additional properties as parameters to the window.
This example selects all of the derived values, based on the price and offer property, plus the values of the feed event property:
select * from StockTickEvent(symbol='GE')#correl(price, offer, feed)
The next example selects all of the derived values plus all event properties:
select * from StockTickEvent(symbol='GE')#correl(price, offer, *)
This window returns the weighted average given an expression returning values to compute the average for and an expression returning weight. The window takes two value expressions as parameters plus any number of optional additional expressions to return properties of the last event. The value expressions must return numeric values:
weighted_avg(value_expression_field, value_expression_weight [,expression, ...] [ * ])
After the value expression you may optionally list additional expressions or event properties to evaluate for the stream and return their value based on the last arriving event. You may also provide the * wildcard selector to have the window output all event properties.
A statement that derives the volume-weighted average price for the last 3 seconds for a given symbol is shown below:
select average from StockTickEvent(symbol='GE')#time(3 seconds)#weighted_avg(price, volume)
To add properties from the event stream you may simply add all additional properties as parameters to the window.
This example selects all of the derived values, based on the price and volume properties, plus the values of the symbol and feed event properties:
select * from StockTickEvent#time(3 seconds)#weighted_avg(price, volume, symbol, feed)
The next example selects all of the derived values plus the values of all event properties:
select * from StockTickEvent#time(3 seconds)#weighted_avg(price, volume, *)
Aggregation functions could instead be used to compute the weighted average as well. The next example also posts weighted average per symbol considering the last 3 seconds of stock tick data:
select symbol, sum(price*volume)/sum(volume) from StockTickEvent#time(3 seconds) group by symbol
The following example computes weighted average keeping a separate data window per symbol considering the last 5 events of each symbol:
select symbol, average from StockTickEvent#groupwin(symbol)#length(5)#weighted_avg(price, volume)
- 15.1. Introduction
- 15.2. Concepts
- 15.3. Compiling a Module
- 15.4. Reading and Writing a Compiled Module
- 15.5. Reading Module Content
- 15.6. Compiler Arguments
- 15.7. Statement Object Model
- 15.8. Substitution Parameters
- 15.9. OSGi, Class Loader, Class-For-Name
- 15.10. Authoring Tools
- 15.11. Testing Tools
- 15.12. Debugging
- 15.13. Ordering Multiple Modules
- 15.14. Logging
- 15.15. Debugging Generated Code
- 15.16. Compiler Version and Runtime Version
- 15.17. Compiler Byte Code Optimizations
- 15.18. Compiler Filter Expression Analysis
- 15.19. Limitations
The compiler provides the following functions:
Compiles a module to JVM byte code.
Compiles a fire-and-forget query to JVM byte code.
Parses a module producing a module object model.
Parses a statement producing a statement object model.
Validates the syntax of a module.
Reads a module from external sources.
The most important function of the compiler is to produce byte code for your module. Deploy the byte code into a runtime for execution.
The compiler interface is EPCompiler in package com.espertech.esper.compiler.client.
Your application obtains a compiler instance by calling the getCompiler method of EPCompilerProvider.
For example:
EPCompiler epCompiler = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler();
Use the compiler as follows:
The compiler is a stateless service. It does not have any state that it keeps between calls.
You may obtain and use any number of compiler instances in parallel.
You may share a compiler instance between threads.
All compiler methods are thread-safe.
The compiler internally uses multiple threads for compiling each statement in parallel, for modules that have multiple statements.
Tip
When using the compiler in separate threads, make sure the input to the compiler does not get modified while the compiler is using it. For example, the application should not modify compiler configuration or compiler path at the same time as invoking a compiler method.
A module contains zero, one or multiple statements. A module is a source code unit as the compiler turns a module into byte code. A module does not need to be a text - a module can also be an object model.
In module text, statements appear separated by the semicolon (;) character. If there is a single statement in the module the semicolon can be left off.
The synopsis of a module file is:
[module module_name;] [uses module_name; | import import_name;] [uses module_name; | import import_name;] [...] [epl_statement;] [epl_statement;] [...]
Use the module keyword followed a module_name identifier or a package (identifiers separated by dots) to declare the name of the module. The module name declaration must be at the beginning of the file, comments and whitespace excluded. The module name
serves to check uses-dependences of other modules.
If a module file requires certain constructs that may be shared by other modules, such as named windows, tables, variables, event types, variant streams or inserted-into streams required by statements,
a module file may specify dependent modules with the uses keyword. It can be used to avoid name conflicts and automatic deployment can use this information to determine deployment order.
If the statements in the module require Java classes such as for underlying events or user-defined functions, use the import keyword followed by the fully-qualified class name or package name in the format package.*.
The uses and import keywords are optional and must occur after the module declaration.
Following the optional deployment instructions are any number of epl_statement statements that are separated by semicolon (;).
The following is a sample module file explained in detail thereafter:
// Declare the name for the module (optional).
module org.myorganization.switchmonitor;
// Declare other module(s) that this module depends on (optional).
// This can be used to resolve name conflicts.
uses org.myorganization.common;
// Import any Java/.NET classes of the given package name (optional).
// Imports only handle classpath and do not import other modules.
import org.myorganization.events.*;
// Declare an event type based on a Java class in the package that was imported as above
create schema MySwitchEvent as MySwitchEventPOJO;
// Sample statement
@Name('Off-On-Detector')
insert into MyOffOnStream
select * from pattern[every-distinct(id) a=MySwitchEvent(status='off')
-> b=MySwitchEvent(id=a.id, status='on')];
// Sample statement
@Name('Count-Switched-On')
@Description('Count per switch id of the number of Off-to-On switches in the last 1 hour')
select id, count(*) from MyOffOnStream#time(1 hour) group by id;
The example above declares a module name of org.myorganization.switchmonitor.
The example demonstrates the import keyword to make a package name known to the compiler for resolving classpath items, as the example assumes that MySwitchEventPOJO is a POJO event class.
In addition the example module contains two statements separated by semicolon characters.
The following types of EPL-objects are managed by the compiler and runtime:
Event types define stream type information and are added using
create schemaor by configuration.Variables are free-form value holders and are added using
create variableor by configuration.Named windows are sharable named data windows and are added using
create window.Tables are sharable organized rows with columns that are simple, aggregation and complex types, and are added using
create table.Contexts define analysis lifecycle and are added using
create context.Expressions and Scripts are reusable expressions and are added using
create expression.Inlined-Classes are classes in Java (or C# for NEsper) that are part of the EPL code and are added using
create inlined_class.Indexes organize named window events and table rows for fast lookup and are added using
create index.
Your application can pre-configure event types and variables in a Configuration object.
A module can create any number of EPL-objects.
A module can depend on EPL-objects that are pre-configured or other modules created.
A module usually depends on event types and may also depend on other EPL-objects such as named windows or tables, for example. The compiler resolves all dependencies at compile-time. It produces byte code based on the information associated with the EPL-object. Upon deploying a compiled module's byte code into the runtime the runtime validates that dependencies exist.
For example, consider the following module:
select accountId, amount from Withdrawal
The module above depends on the event type Withdrawal. The compiler resolves the event type name to an EventType instance.
It produces code according to the event type. At time of deployment of the compiled module the runtime verifies that the Withdrawal event type exists.
Specifically, the compiler generates code like this:
If the
Withdrawalevent type is a Map-based event type, the compiler produces code such asevent.get("accountId").If the
Withdrawalevent type is an Object-Array-based event type, the compiler produces code such asevent[index].If the
Withdrawalevent type is a Bean-based event type, the compiler produces code such asevent.getAccountId().
Note
The compiler only tracks dependencies on EPL-objects.
The compiler does not track classpath dependencies. The runtime does not validate classpath dependencies.
The runtime validates that EPL-object dependencies exist before deploying a compiled module.
The runtime does not validate that the information about the EPL-object is the same as at compile-time.
In other words, the runtime does not validate that event property names, event property types, table column names and types, variable types, index property names and other compile-time information matches the information that was provided at compile time.
The compiler resolves an EPL-object by its name by looking at:
The EPL-objects created by the same module (also known as
local)The EPL-objects created by the other modules (also known as
path).The pre-configured event types and variables.
The term path encompasses the EPL-objects other modules define. The term local encompasses the EPL-objects the same module defines.
Coming back to the previous example:
select accountId, amount from Withdrawal
The compiler finds an event type by name Withdrawal by:
Checking whether
Withdrawalis an event type that the same module defined bycreate schema(local).Checking whether
Withdrawalis an event type that another modules defined bycreate schema(path).Checking whether
Withdrawalis a pre-configured event type.
In case the name cannot be resolved the compilation fails.
In case the name is found multiple times, the compiler checks as follows:
If the name is a pre-configured EPL-object and the name is also found in path the validation fails.
If the name is found in local, and the name is found in path or preconfigured, the validation fails.
If the name is found in path for multiple modules, and if there is no module-uses provided, the validation fails.
If the name is found in path for multiple modules and there are module-uses module names provided the EPL object module name must match one of the module names in module-uses.
Access level modifiers determine whether other modules can use a particular EPL-object.
An EPL-object may be declared with the modifier public, in which case that EPL-object is visible to all other modules.
An EPL-object may be declared with the modifier protected, in which case that EPL-object is visible to other modules that have the same module name.
An EPL-object may be declared with the modifier private (the default), in which case that EPL-object is not visible to other modules.
Your application may set access modifiers by:
Using an annotation i.e.
@public,@protected,@private.Setting default access modifiers in the
ConfigurationCompilerByteCodethat is part of theConfigurationobject.Computing access modifiers by providing a callback in
CompilerOptionscompiler options. Any computed value overrides the annotation or configuration default.
The following module declares a public named window to hold the last 10 seconds of withdrawal events:
@public create window WithdrawalWindow#time(10) as Withdrawal
For event types there is a bus modifier that determines whether or not the event type is available for use with the sendEventType methods of the EPEventService runtime event service.
An event type may be declared with the bus modifier, in which case calls to sendEventType process the event.
An event type may be declared with the non-bus modifier (the default), in which case calls to sendEventType cause an exception to be thrown.
To understand this better, here is what sendEventType of EPEventService does:
When your application calls any of the sendEventBean, sendEventMap, sendEventObjectArray, sendEventJson,
sendEventXMLDOM or sendEventAvro methods of EPEventService, the runtime finds the event type using the event type name that is passed.
It associates the event type to the event object for processing the given event. If the event type name is not recognized or the event type does not have the bus modifier it throws an exception.
The bus modifier is not required for pre-configured event types. The bus modifier requires public access.
Your application may set the bus modifier by:
Using the
@buseventtypeannotation.Setting the default bus modifier in the
ConfigurationCompilerByteCodethat is part of theConfigurationobject.Computing a bus modifier by providing a callback in
CompilerOptionscompiler options. Any computed value overrides the annotation or configuration default.
The following module declares a public event type that allows an application to send in events of that name:
@public @buseventtype create schema AccountQueryEvent (accountId string)
The information herein pertains to the routeEventType and EventSender as well.
The compile method takes two parameters. The first parameter is the module text or an module object model. The second parameter are compiler arguments.
The output of the compiler is an EPCompiled instance. You can deploy EPCompiled instances directly into a runtime as described in Section 16.4, “Deploying and Undeploying Using EPDeploymentService”.
The EPCompiledIOUtil class is a utility for writing and reading EPCompiled instances to and from jar-files:
Write an
EPCompiledinstance to a jar file.Read a jar file previously written by
EPCompiledIOUtiland return anEPCompiledinstance.
Read and parse module files using the readModule and parseModule methods, which return a Module instance to represent the module information.
This code snippet demonstrates reading and parsing a module given a file name:
Module module = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler().read(new File("switchmonitor.epl"));The compiler arguments are:
The
Configurationobject can provide pre-configured event types and variables as well as other compiler settings.The
CompilerPathpasses information that the compiler uses to determine the EPL-objects that the module may depend on.The
CompilerOptionsare compiler instructions.
Pass a Configuration instance to the compiler to configure the compiler. By default the compiler uses an empty configuration object.
The compiler only uses the common section and the compiler section of the configuration. The compiler ignores the runtime section of the configuration.
It is not necessary to pass a configuration object or to pre-configure event types. You may create event types by means of create schema.
A pre-configured event types is a convenience since the event type is already defined and ready to use.
The common section of the configuration holds the pre-configured event types. The following sample adds a pre-configured WithdrawalEvent map-based event type:
Map<String, Object> columns = new LinkedHashMap<>();
columns.put("accountId", String.class);
columns.put("amount", double.class);
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("WithdrawalEvent", columns);
CompilerArguments args = new CompilerArguments(configuration);
To obtain a configuration object from a runtime call getConfigurationDeepCopy on EPRuntime:
Configuration configuration = epRuntime.getConfigurationDeepCopy(); CompilerArguments args = new CompilerArguments(configuration);
More information on the common and compiler configuration can be found at Chapter 17, Configuration.
By default the compiler does not generate code for subscribers and the setSubscriber method on EPStatement throws an exception.
You may set the allowSubscriber option:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); configuration.getCompiler().getByteCode().setAllowSubscriber(true); CompilerArguments args = new CompilerArguments(configuration);
The compiler path provides EPL-objects that other modules may declare and that the current module may use.
For example, assume a module M1 that declares a named window WithdrawalWindow:
@public create window WithdrawalWindow#time(10) as Withdrawal
A second module M2 may query the named window like so:
select (select count(*) from WithdrawalWindow) as cnt from Withdrawal
Module M2 depends on the EPL-object WithdrawalWindow (a named window) that module M1 declares.
You can build a path from:
- An existing runtime. This adds all EPL-objects that are currently deployed into the runtime to the path.
- Compiled modules.
Assume that your application compiled module M1 like so:
Map<String, Object> columns = new LinkedHashMap<>();
columns.put("accountId", String.class);
columns.put("amount", double.class);
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("WithdrawalEvent", columns);
CompilerArguments arguments = new CompilerArguments(configuration);
EPCompiled compiledModuleM1 = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler().compile("@public create window WithdrawalWindow#time(10) as Withdrawal", arguments);
The compiledModuleM1 instance holds the byte code of module M1.
After deploying compiled modules to a runtime, the compiler can build the path from the runtime.
The getRuntimePath method of EPRuntime returns the path object for use by the compiler. The path object is an instance of EPCompilerPathable.
The add method of CompilerPath accepts a EPCompilerPathable instance provided by a runtime.
For example, as follows:
Map<String, Object> columns = new LinkedHashMap<>();
columns.put("accountId", String.class);
columns.put("amount", double.class);
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("WithdrawalEvent", columns);
// Get a runtime
EPRuntime runtime = EPRuntimeProvider.getDefaultRuntime(configuration);
runtime.getDeploymentService().deploy(compiledModuleM1);
// Compile another module
CompilerArguments arguments = new CompilerArguments(configuration);
arguments.getPath().add(runtime.getRuntimePath());
EPCompiled compiledModuleM2 = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler().compile("select (select count(*) from WithdrawalWindow) as cnt from Withdrawal", arguments);
Use the addPath method of CompilerPath to add a compiled module to path.
For example, as follows:
CompilerArguments arguments = new CompilerArguments(configuration);
arguments.getPath().add(compiledModuleM1);
EPCompiled compiledModuleM2 = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler().compile("select (select count(*) from WithdrawalWindow) as cnt from Withdrawal", arguments);Tip
Use a path cache when there are many compiled modules in the path, see Section 15.6.4, “Compiler Path Cache”.
Compiler options provide compiler callbacks and other compile-time parameters:
Provide or override access modifiers and bus event type modifier.
Provide or override the statement name.
Provide a statement user object and that can be obtained from an
EPStatementwithgetUserObjectCompileTime.Provide or override the module name.
Provide or override module-uses information.
Receive Janino class-level compiler output for inlined-classes for example for use with black-listing or white-listing classes based on class constant pool information.
Please consult the JavaDoc for more information.
The path cache is not used by default and can optionally be set. It is only for use when your application adds compiled modules (EPCompiled instances) to the path as described in Section 15.6.2.2, “Adding a Compiled Module to Path”.
The compiler is a stateless service and does not retain any information between calls. It therefore does not know, for each of the EPCompiled instances in the path, the visible EPL objects that the EPCompiled in the path provides.
The path cache retains this information so that subsequent calls to the compiler do not need to inspect each EPCompiled in the path.
Use CompilerPathCache.getInstance() and the setPathCache method of CompilerOptions to use a path cache. A path cache is thread-safe.
Obtain the path cache as follows:
// Obtain path cache for reuse when compiling modules CompilerPathCache pathCache = CompilerPathCache.getInstance();
Set the path cache like so:
arguments.getOptions().setPathCache(pathCache);
The compiler automatically adds the current EPCompiled output and all EPCompiled instances in path to the cache.
The statement object model is a set of classes that provide an object-oriented representation of statement. The object model classes are found in package com.espertech.esper.common.client.soda. An instance of EPStatementObjectModel represents a statement's object model.
The statement object model classes are a full and complete specification of a statement. All EPL constructs including expressions and sub-queries are available in the statement object model.
The statement object model provides the means to building, changing or interrogating statements beyond the string representation. The object graph of the statement object model is fully navigable for easy querying by code, and is also serializable allowing applications to persist or transport statements in object form, when required.
The statement object model supports full round-trip from object model to statement string and back to object model: A statement object model can be rendered into a string representation via the toEPL method on EPStatementObjectModel. Further, the compiler API allows compiling a statement string into an object model representation via the eplToModel method on EPCompiler.
The statement object model is fully mutable. Mutating any list such as returned by getChildren(), for example, is acceptable and supported.
The following limitations apply:
Statement object model classes are not safe for sharing between threads other than for read access.
Between versions the serialized form of the object model is subject to change. There are no guarantees that the serialized object model of one version will be fully compatible with the serialized object model generated by another version. Please consider this issue when storing object models in persistent store.
A EPStatementObjectModel consists of an object graph representing all possible clauses that can be part of a statement.
Among all clauses, the SelectClause and FromClause objects are required clauses that must be present, in order to define what to select and where to select from.
Table 15.1. Required Statement Object Model Instances
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| EPStatementObjectModel | All statement clauses for a statement, such as the select-clause and the from-clause, are specified within the object graph of an instance of this class |
| SelectClause | A list of the selection properties or expressions, or a wildcard |
| FromClause | A list of one or more streams; A stream can be a filter-based, a pattern-based, SQL-based and other; Add data windows here. |
Part of the statement object model package are convenient builder classes that make it easy to build a new object model or change an existing object model. The SelectClause and FromClause are such builder classes and provide convenient create methods.
Within the from-clause you have a choice of different streams to select on. The FilterStream class represents a stream that is filled by events of a certain type and that pass an optional filter expression.
We can use the classes introduced above to create a simple statement object model:
EPStatementObjectModel model = new EPStatementObjectModel();
model.setSelectClause(SelectClause.createWildcard());
model.setFromClause(FromClause.create(FilterStream.create("ReadyEvent")));The model as above is equivalent to:
select * from ReadyEvent
Notes on usage:
Variable names can simply be treated as property names.
When selecting from named windows or tables, the name of the named window or table is the event type name for use in
FilterStreaminstances or patterns.To compile an arbitrary sub-expression text into an
Expressionobject representation, simply add the expression text to awhereclause, compile the EPL string into an object model via theeplToModelmethod onEPCompiler, and obtain the compiledwherefrom theEPStatementObjectModelvia thegetWhereClausemethod.
The EPStatementObjectModel includes an optional where-clause. The where-clause is a filter expression that the runtime applies to events in one or more streams. The key interface for all expressions is the Expression interface.
The Expressions class provides a convenient way of obtaining Expression instances for all possible expressions. Please consult the JavaDoc for detailed method information.
The next example discusses sample where-clause expressions.
Use the Expressions class as a service for creating expression instances, and add additional expressions via the add method that most expressions provide.
The next example adds a simple where-clause to the EPL as shown earlier:
select * from ReadyEvent where line=8
And the code to add a where-clause to the object model is below.
model.setWhereClause(Expressions.eq("line", 8));The following example considers a more complex where-clause. Assume you need to build an expression using logical-and and logical-or:
select * from ReadyEvent where (line=8) or (line=10 and age<5)
The code for building such a where-clause by means of the object model classes is:
model.setWhereClause(Expressions.or()
.add(Expressions.eq("line", 8))
.add(Expressions.and()
.add(Expressions.eq("line", 10))
.add(Expressions.lt("age", 5))
));
The Patterns class is a factory for building pattern expressions. It provides convenient methods to create all pattern expressions of the pattern language.
Patterns in EPL are seen as a stream of events that consist of patterns matches. The PatternStream class represents a stream of pattern matches and contains a pattern expression within.
For instance, consider the following pattern statement.
select * from pattern [every a=MyAEvent and not b=MyBEvent]
The next code snippet outlines how to use the statement object model and specifically the Patterns class to create a statement object model that is equivalent to the pattern statement above.
EPStatementObjectModel model = new EPStatementObjectModel();
model.setSelectClause(SelectClause.createWildcard());
PatternExpr pattern = Patterns.and()
.add(Patterns.everyFilter("MyAEvent", "a"))
.add(Patterns.notFilter("MyBEvent", "b"));
model.setFromClause(FromClause.create(PatternStream.create(pattern)));This section builds a complete example statement and includes all optional clauses in one statement, to demonstrate the object model API.
A sample statement:
insert into ReadyStreamAvg(line, avgAge) select line, avg(age) as avgAge from ReadyEvent(line in (1, 8, 10))#time(10) as RE where RE.waverId != null group by line having avg(age) < 0 output every 10.0 seconds order by line
Finally, this code snippet builds the above statement from scratch:
EPStatementObjectModel model = new EPStatementObjectModel();
model.setInsertInto(InsertIntoClause.create("ReadyStreamAvg", "line", "avgAge"));
model.setSelectClause(SelectClause.create()
.add("line")
.add(Expressions.avg("age"), "avgAge"));
Filter filter = Filter.create("ReadyEvent", Expressions.in("line", 1, 8, 10));
model.setFromClause(FromClause.create(
FilterStream.create(filter, "RE").addView("win", "time", 10)));
model.setWhereClause(Expressions.isNotNull("RE.waverId"));
model.setGroupByClause(GroupByClause.create("line"));
model.setHavingClause(Expressions.lt(Expressions.avg("age"), Expressions.constant(0)));
model.setOutputLimitClause(OutputLimitClause.create(OutputLimitSelector.DEFAULT, Expressions.timePeriod(null, null, null, 10.0, null)));
model.setOrderByClause(OrderByClause.create("line"));This sample statement creates a variable:
create variable integer var_output_rate = 10
The code to build the above statement using the object model:
EPStatementObjectModel model = new EPStatementObjectModel();
model.setCreateVariable(CreateVariableClause.create("integer", "var_output_rate", 10));A second statement sets the variable to a new value:
on NewValueEvent set var_output_rate = new_rate
The code to build the above statement using the object model:
EPStatementObjectModel model = new EPStatementObjectModel();
model.setOnExpr(OnClause.createOnSet("var_output_rate", Expressions.property("new_rate")));
model.setFromClause(FromClause.create(FilterStream.create("NewValueEvent")));This sample statement creates a named window:
create window OrdersTimeWindow#time(30 sec) as select symbol as sym, volume as vol, price from OrderEvent
The is the code that builds the create-window statement as above:
EPStatementObjectModel model = new EPStatementObjectModel();
model.setCreateWindow(CreateWindowClause.create("OrdersTimeWindow").addView("win", "time", 30));
model.setSelectClause(SelectClause.create()
.addWithName("symbol", "sym")
.addWithName("volume", "vol")
.add("price"));
model.setFromClause(FromClause.create(FilterStream.create("OrderEvent)));A second statement deletes from the named window:
on NewOrderEvent as myNewOrders delete from OrdersNamedWindow as myNamedWindow where myNamedWindow.symbol = myNewOrders.symbol
The object model is built by:
EPStatementObjectModel model = new EPStatementObjectModel();
model.setOnExpr(OnClause.createOnDelete("OrdersNamedWindow", "myNamedWindow"));
model.setFromClause(FromClause.create(FilterStream.create("NewOrderEvent", "myNewOrders")));
model.setWhereClause(Expressions.eqProperty("myNamedWindow.symbol", "myNewOrders.symbol"));A third statement selects from the named window using the non-continuous on-demand selection via on-select:
on QueryEvent(volume>0) as query select count(*) from OrdersNamedWindow as win where win.symbol = query.symbol
The on-select statement is built from scratch via the object model as follows:
EPStatementObjectModel model = new EPStatementObjectModel();
model.setOnExpr(OnClause.createOnSelect("OrdersNamedWindow", "win"));
model.setWhereClause(Expressions.eqProperty("win.symbol", "query.symbol"));
model.setFromClause(FromClause.create(FilterStream.create("QueryEvent", "query",
Expressions.gt("volume", 0))));
model.setSelectClause(SelectClause.create().add(Expressions.countStar()));Substitution parameters have the following syntax:
? [:[name] [:type]]
The name is optional. The absence of a name means the substitution parameter is only addressable by index.
The type is optional. The absence of the type means the type of the substitution parameter is java.lang.Object. Use cast or provide a type name when your expression requires a strongly-typed value.
The type can also be a parameterized type such as java.util.List<String>.
Here are a few examples of valid substitution parameters:
Table 15.2. Valid Substitution Parameters
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
? | Unnamed and typed Object. |
?::int | Unnamed and typed int. |
?:param:string | Named and typed string. |
All substitution parameters must either be unnamed or named. It is not possible to mix the two styles.
If not assigning a name to substitution parameters, the compiler assigns the first substitution parameter an index of 1 and subsequent parameters increment the index by one.
If assigning a name to each substitution parameter, the name can include slash (/) characters and can occur multiple times.
Substitution parameters can be inserted into any EPL construct that takes an expression. They are therefore valid in any clauses such as the select-clause, from-clause filters, where-clause, group-by-clause, having-clause or order-by-clause, including data window parameters and pattern observers and guards, for example. Substitution parameters cannot be used where a numeric constant is required rather than an expression.
You may use square brackets ([]) to denote array-types and [primitive] for array of primitive. For
example int[primitive] for array of int-primitive and int[] for array of Integer.
All substitution parameters must be replaced by actual values at time of deployment.
The configuration object (Configuration), in respect to classes, holds the fully-qualified class name and does not generally hold Class references.
This is by design since the configuration object can be populated from XML.
The compiler may need to look up a class by name and may need to obtain a class loader. Your application has full control over class-for-name and classloader use. OSGi environments can provide a specific class-for-name and class loader. Please refer to Section 17.7, “Passing Services or Transient Objects”.
Enterprise Edition includes authoring tools for statements and modules by providing form-based dialogs, templates, an expression builder, simulation tool and other tools. Enterprise Edition also supports hot deployment and packaging options for EPL and related code.
Statements can be organized into modules as described above. Any text editor can edit statements and module text. A text editor or IDE that highlights SQL syntax or keywords works.
For authoring configuration files please consult the XSD schema files as provided with the distribution.
For information on authoring event classes or event definitions in general please see Chapter 3, Event Representations or Section 5.15, “Declaring an Event Type: Create Schema”.
We recommend testing modules using a test framework such as JUnit or TestNG. Please consult the regression test suite for extensive examples, which can be downloaded from the distribution site.
Esper's API provides test framework classes to simplify automated testing of statements. Please see Section 16.18, “Test and Assertion Support” for more information.
We recommend performing latency and throughput tests early in the development lifecycle. Please consider the performance tips in Chapter 24, Performance for optimal performance.
Consider runtime and statement metrics reporting for identifying slow-performing statements, for example. See Section 16.12, “Runtime and Statement Metrics Reporting”.
Enterprise Edition includes a debugger for module execution.
One important tool for debugging without Enterprise Edition is the parameterized @Audit annotation. This annotation allows to output, on statement-level, detailed information about many aspects of statement processing.
Another tool for logging runtime-level detail is Section 17.6.2.1, “Execution Path Debug Logging”.
Please see Section 17.9, “Logging Configuration” for information on configuring logging in general.
Use the @Audit annotation to have the runtime output detailed information about statement processing. The runtime reports, at INFO level, the information under log name com.espertech.esper.audit. You may define an output format for audit information via configuration.
You may provide a comma-separated list of category names to @Audit to output information related to specific categories only. The table below lists all available categories. If no parameter is provided, the runtime outputs information for all categories. Category names are not case-sensitive.
For the next statement the runtime produces detailed processing information (all categories) for the statement:
@Name('All Order Events') @Audit select * from OrderEventFor the next statement the runtime provides information about new events and also about event property values (2 categories are listed):
@Name('All Order Events') @Audit('stream,property') select price from OrderEventHere is a more complete example that uses the API to create the schema, create above statement and send an event:
try {
String module =
"@public @buseventtype create schema OrderEvent(price double);\n" +
"@name('All-Order-Events') @Audit('stream,property') select price from OrderEvent;\n";
EPCompiled compiled = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler().compile(module, null);
EPRuntime runtime = EPRuntimeProvider.getDefaultRuntime();
EPDeployment deployment = runtime.getDeploymentService().deploy(compiled);
deployment.getStatements()[0].addListener(new SupportUpdateListener());
runtime.getEventService().sendEventMap(Collections.singletonMap("price", 100d), "OrderEvent");
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error(t.getMessage(), t);
}The output is similar to the following:
INFO [audit] Statement All-Order-Events stream OrderEvent inserted {price=100.0}
INFO [audit] Statement All-Order-Events property price value 100.0Table 15.3. @Audit Categories
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| ContextPartition | Each context partition allocation and de-allocation (only for statements that declare a context). |
| Dataflow-Source | Each data flow source operator providing an event. |
| Dataflow-Op | Each data flow operator processing an event. |
| Dataflow-Transition | Each data flow instance state transition. |
| Exprdef | Each expression declaration name and return value. |
| Expression | Each top-level expression and its return value. |
| Expression-nested | Each expression including child or nested expressions and their return value. |
| Insert | Each event inserted via insert-into. |
| Pattern | Each pattern sub-expression and its change in truth-value. |
| Pattern-instances | Each pattern sub-expression and its count of active instances. |
| Property | Each property name and the event's property value. |
| Schedule | Each schedule modification and trigger received by a statement. |
| Stream | Each new event received by a statement. |
| View | Each data window name and its insert and remove stream. |
Note that the runtime only evaluates select-clause expressions if either a listener or subscriber is attached to the statement or if used with insert-into.
Since modules may have inter-dependencies as discussed under the uses declaration, there is a ModuleOrderUtil class that provides the getModuleOrder method to order a collection of modules before deployment.
Assuming your application reads multiple modules into a mymodules module list, this code snippet orders the modules for deployment and validates dependency declarations for each module:
List<Module> mymodules = ... read modules...; ModuleOrder order = ModuleOrderUtil.getModuleOrder(mymodules, new ModuleOrderOptions());
You can log generated classes at INFO log level by setting the configuration flag for code logging as described in Section 17.5.3.1, “Byte Code Generation Logging”.
The information herein is for developers and is specific to the Janino compiler at the version provided with the distribution.
Set the system property org.codehaus.janino.source_debugging.enable to true to have Janino compile code with debug symbols.
Set the system property org.codehaus.janino.source_debugging.dir to a file system directory to have Janino generate classes into a given directory.
The IDE can debug into generated classes and show the source code provided that the IDE can access the source code. For example:
-Dorg.codehaus.janino.source_debugging.dir=/path/to/directory -Dorg.codehaus.janino.source_debugging.enable=true
To include additional EPL-related comments in the generated code you can change the configuration as outlined in Section 17.5.1, “Compiler Settings Related to Byte Code Generation”.
The version format is major.minor.patch-level.
When deploying a compiled module to a runtime, or when executing a compiled fire-and-forget query, the runtime compares the compiler version that produced the compiled module or compiled query with the runtime version. If the major or minor version does not match, the runtime indicates a version mismatch by throwing an exception.
For example, an application may compile an EPL module using the version 8.0.0 compiler, i.e. the compiler major version is eight and the compiler minor version is zero and the compiler patch level is zero.
Assume the application attempts to deploy the compiled module to a runtime of version 8.1.0, i.e. the runtime major version is eight and the runtime minor version is one and the runtime patch level is zero.
The runtime throws an EPDeployDeploymentVersionException exception to indicate that the minor version mismatches.
The compiler generates byte code that avoids down-casts and branching. It also removes many virtual calls as it transforms expression trees into byte code.
For aggregations the compiler produces a custom aggregation row class that has fields which represent the aggregation state. Therefore each aggregation row does not need additional objects to represent aggregations such as averages or sums and instead the aggregations are fields of the same class, reducing the number objects that the runtime manages per group-by key.
For any composite keys out of two or more expressions the compiler produces a class that represents the composite key and that implements equals and hashCode. This is applicable to the group-by clause including rollup, data windows with keys (such as #unique, #firstunique, #groupwin, #rank), partition-by for keyed segmented contexts, contexts with distinct, the select-clause distinct keyword, the query planner when planning implicit and explicit indexes, create index, every-distinct, the partition-by clause for match-recognize, table column keyed-access expressions, the for-clause for grouped delivery and the distinctOf enumeration method.
The compiler analyzes filter expressions so that the runtime can build filter indexes. For more information on filter indexes please see Section 2.18.2, “Filter Indexes”.
By default the compiler uses advanced techniques for planning filter indexes. Your application may disable some or all of the advanced techniques as described in Section 17.5.8.2, “Filter Index Planning”.
To output the filter plans please set a compiler flag as described in Section 17.5.3.2, “Filter Plan Logging”.
Tip
Filter indexed planning, like all index planning, reflects a trade-off of amount of space needed for the index, the processing time required to build and maintain an index versus the performance gain of matching incoming events to statements and their partitions when there are many (same or different) filters.
The compiler does automatically plan all possible filter indexes. For performance tuning the
ConfigurationCompilerExecution.FilterIndexPlanning.BASICsetting andConfigurationCompilerExecution.FilterIndexPlanning.NONEsetting and the hints are also available.
This section applies in the default configuration (FilterIndexPlanning.ADVANCED) and the non-default FilterIndexPlanning.BASIC configuation.
The compiler analyzes filter expressions by first determining the constituents. Constituents are the individual expressions, connected by the and and or logical operator, that each return a boolean-type value and that make up the overall expression.
For instance, this EPL statement:
select * from Withdrawal(accountId = '123' and accountType = 'Checking')
The constituent expressions are accountId = '123' and accountType = 'Checking' (two constituent expressions).
The compiler analyzes each constituent expression separately. From a single constituent expression it attempts to form a lookupable-expression, filter-index-operator and value-expression triplet. For those constituent expressions that the compiler cannot form a triplet the compiler aggregates such expression into a common boolean expression. The remainder of the discussion focuses on a constituent expression and forming a triplet from it.
The lookupable-expression is the expression providing the filter index lookup value, for example the accountId expression in accountId = '123'.
The value-expression is the expression providing the indexed value, for instance the '123' expression in accountId = '123'.
The filter-index-operator means the type of index such as equals(=), relational (<,>,<=, >=) etc..
Therefore, in Withdrawal(accountId = '123'), the filter-index-operator is equals and the lookupable-expression is accountId and the value-expression is '123'.
The expressions that are left and right of a filter-index-operator are commutative, meaning they give the same result whatever the expression occurs on either side of the operator.
It is equivalent to say accountId = '123' and '123' = accountId.
The order in which constituent expressions appear does matter. Place the most frequent constituent expressions first. Each filter-index-operator has a precedence level and the compiler orders by precedence level keeping the order as provided within the same precedence level. The precedence levels are, sorted by higher precedence level first, as follows: equal, is, in-list-of-values, advanced-index, range-open, range-half-open, range-half-closed, range-closed, less, less-or-equal, greater-or-equal, greater, not-range-closed, not-range-half-closed, not-range-half-open, not-range-open, not-in-list-of-values, not-equal, is-not.
The lookupable-expression in a triplet must be any of the following:
Event property of the arriving event
Plug-in single-row node with filter-optimizable setting enabled
Declared expression
The
typeOffunctionOther expressions; See hint Section 15.18.3, “Lookupable Composite Expression Analysis” for more information.
The following operators are the triplet filter-index-operator operators. A constituent expression that has one of these operators qualifies for a triplet:
equals
=not equals
!=comparison operators
< , > , >=, <=ranges
use the
betweenkeyword for a closed range where both endpoints are includeduse the
inkeyword and round()or square brackets[]to control how endpoints are includedfor inverted ranges use the
notkeyword and thebetweenorinkeywords
list-of-values checks using the
inkeyword or thenot inkeywords followed by a comma-separated list of valuesOther operators; See hint Section 15.18.4, “Boolean Reusable Expression Analysis” for more information.
The value-expression in a triplet can only be any of the expressions below:
Constant
Substitution parameter
Event property of a prior-matching event (not the currently arriving event)
Context property
The
typeOffunctionPlug-in single-row node with filter-optimizable setting enabled
Declared expression
Other expressions; See hint Section 15.18.2, “Value Composite Expression Analysis” for more information.
The or logical operator plays a special role in compiler analysis. The compiler rewrites the expression accountId = '123' or accountId = '456' to accountId in ('123', '456'). It also plans multiple filter index path
which is further described at Section 17.5.8.1, “Filter Service Max Filter Width”.
The order of the triplets, which follows the ordering of the constituents and the ordering according to filter-index-operator precedence level (see above), defines the default nesting of filter indexes. The runtime, upon adding to the filter, may however encounter existing filter indexes and always prefers to add to existing filter indexes and following an existing path where possible, or creating new branches and leafs from the existing path.
The compiler unwinds logical and and or and may also rewind such expressions for planning as below.
Therefore the expression a and (b and c) is the same as a and b and c and the expression a or (b or c) is the same as a or b or c.
This section applies to the default configuration (FilterIndexPlanning.ADVANCED) and also
when the configuration is FilterIndexPlanning.BASIC and the EPL contains the @Hint('filterindex(valuecomposite)') hint.
The compiler considers an expression that is meeting certain criteria to be a value-expression provided that there is one of the filter-index-operators as described above.
The compiler considers value expressions that are any expression and that do not have any of the following:
Subquery
Non-constant variable
Event property of the currently-arriving event
Expression returning the currently-arriving event i.e. wildcard or stream alias
Table access
Plug-in single-row node with filter-optimizable setting disabled
Lamda expression
Declared expression
current_timestampFunction
For example, consider the following EPL statements:
create constant variable string PREFIX = "CHK"; select * from Withdrawal(accountId = PREFIX || '123')
The expression PREFIX || '123' is a filter index value-expression and its return value is subject to entry into a filter index as a key.
The following example demonstrates the concept further:
create context TransactionContext initiated by Transaction as txn terminated after 10 minutes;
@Hint('filterindex(valuecomposite)')
context TransactionContext select * from Withdrawal(accountId = context.txn.transactionTarget || '-A')Assume the following events arrive:
Transaction(transactionId=1, transactionTarget='123').Transaction(transactionId=2, transactionTarget='456').Transaction(transactionId=3, transactionTarget='123').
The below table is a sample filter index:
Table 15.4. Sample Filter Index
Value of context.txn.transactionTarget || '-A' | Statements and their partitions |
|---|---|
'123-A' | Statement Stmt-1 Partition context.txn.transactionId=1, Statement Stmt-1 Partition context.txn.transactionId=3 |
'456-A' | Statement Stmt-1 Partition context.txn.transactionId=2 |
When a Withdrawal event arrives, the runtime evaluates accountId just once and performs one keyed lookup into the filter index to determine which statements and
their partitions should process the event.
The following example pattern results in equivalent filter index planning:
select * from pattern[txn=Transaction -> Withdrawal(accountId = txn.transactionTarget || '-A')]
This section applies to the default configuration (FilterIndexPlanning.ADVANCED) and also
when the configuration is FilterIndexPlanning.BASIC and the EPL contains the @Hint('filterindex(lkupcomposite)') hint.
The compiler considers an expression that is meeting certain criteria to be a lookupable-expression provided that there is one of the filter-index-operators as described above.
The lookupable-expression, in any subexpression, must reference at least one event property or the event itself and cannot have any of the following:
Subquery
Non-constant variable
Context property
Table access
Plug-in single-row node with filter-optimizable setting disabled
Lambda expression
Script expression
In a pattern, event property of a tagged event, or the tagged event itself (other than self)
Method invocation of non-public inlined class
This hint is usually used when:
Using a context and there are many context partitions
Using patterns and there are many active pattern subexpressions
There are many statements that have the same filter expression(s)
Consider the following EPL statement:
select * from Withdrawal(accountId || accountType = '123Checking')
The expression accountId || accountType can serve as a lookupable-expression. The compiler plans a filter index that indexes values such as '123Checking'
and that uses the return value of accountId || accountType to perform a keyed lookup into the indexed values.
Extending the example above, please look at the following EPL:
create context TransactionContext initiated by Transaction as txn terminated after 10 minutes;
@Hint('filterindex(lkupcomposite)')
context TransactionContext select * from Withdrawal(accountId || accountType = context.txn.transactionTarget)Assume the following events arrive:
Transaction(transactionId=1, transactionTarget='123A').Transaction(transactionId=2, transactionTarget='456B').Transaction(transactionId=3, transactionTarget='123A').
The below table is a sample filter index:
Table 15.5. Sample Filter Index
Value of context.txn.transactionTarget | Statements and their partitions |
|---|---|
'123A' | Statement Stmt-1 Partition context.txn.transactionId=1, Statement Stmt-1 Partition context.txn.transactionId=3 |
'456B' | Statement Stmt-1 Partition context.txn.transactionId=2 |
When a Withdrawal event arrives, the runtime evaluates accountId || accountType just once and performs one keyed lookup into the filter index to determine which statements and
their partitions should process the event.
This section applies to the default configuration (FilterIndexPlanning.ADVANCED) and also
when the configuration is FilterIndexPlanning.BASIC and the EPL contains the @Hint('filterindex(boolcomposite)') hint.
The compiler considers any expression that is meeting certain criteria to be a reusable boolean expression (does not require any of the filter-index-operators).
The expression must not have any of the following:
Subquery
Non-constant variable
Table access
Plug-in single-row node with filter-optimizable setting disabled
Lambda expression
Method invocation of non-public inlined class
Declared expression
Chained expression
The expression must, in any subexpression, reference at least one event property or the event itself. All other expressions must be value-expressions that meet the same requirements as outlined for valuecomposite.
The expression may not, in all subexpressions, have multiple value expressions that reference context properties or, in a pattern, event properties of prior events or prior events themselves.
Review the following EPL statement:
select * from Withdrawal(accountId regexp '.*123.*')
The compiler plans a filter index that holds the expression itself and all actual values (determined at runtime, such as '.*123.*') and their related statements and partitions.
Consider the following wherein Transaction events have a regexpFilter field that provides the regexp-right-hand-side value:
create context TransactionContext initiated by Transaction as txn terminated after 10 minutes;
@name('Stmt-1') context TransactionContext select * from Withdrawal(accountId regexp context.txn.regexpFilter)Assume the following events arrive:
Transaction(transactionId=1, regexpFilter='.*123.*).Transaction(transactionId=2, regexpFilter='.*456.*).Transaction(transactionId=3, regexpFilter='.*123.*).
The below table is a sample filter index:
Table 15.6. Sample Filter Index
Value of context.txn.regexpFilter | Statements and their partitions |
|---|---|
'.*123.*' | Statement Stmt-1 Partition context.txn.transactionId=1, Statement Stmt-1 Partition context.txn.transactionId=3 |
'.*456.*' | Statement Stmt-1 Partition context.txn.transactionId=2 |
When a Withdrawal event arrives, the runtime evaluates accountId regexp '.*123.*' and accountId regexp '.*456.*' both once.
This section applies to the default configuration (FilterIndexPlanning.ADVANCED) and also
when the configuration is FilterIndexPlanning.BASIC and the EPL contains the @Hint('filterindex(condition)') hint.
The compiler identifies:
Any filter-negating-expression expressions.
Any filter-confirming-expression expressions.
Any path-negating-expression expressions.
Any triplet-confirming-expression expressions.
A filter-negating-expression is a value-composite-expression that, when false, negates the filter. An example follows.
create context TransactionContext initiated by Transaction as txn terminated after 10 minutes; context TransactionContext select * from Withdrawal(accountId='123' and context.txn.counterparty='A')
The filter-negating-expression is context.txn.counterparty='A'. When false the runtime does not look for Withdrawal events.
A filter-confirm-expression is a value-composite-expression that, when true, means there are no other filter criteria. Here is an example:
create context TransactionContext initiated by Transaction as txn terminated after 10 minutes; context TransactionContext select * from Withdrawal(accountId='123' or context.txn.counterparty='A')
The filter-confirming-expression is context.txn.counterparty='A'. When true the runtime does not look at the accountId value of Withdrawal events.
A path-negating-expression is a value-composite-expression that, when false, negates an alternative, for instance:
create context TransactionContext initiated by Transaction as txn terminated after 10 minutes; context TransactionContext select * from Withdrawal(accountId='123' or (accountType='Checking' and context.txn.counterparty='A'))
The path-negating-expression is context.txn.counterparty='A'. When false the runtime does not look at the accountType value of Withdrawal events.
A triplet-confirming-expression is a value-composite-expression that, when true, skips a triplet. The example is:
create context TransactionContext initiated by Transaction as txn terminated after 10 minutes; context TransactionContext select * from Withdrawal( (accountId='123' or context.txn.counterparty='A') and (accountType='Checking' or context.txn.counterparty='B'))
There are two triplet-confirming-expressions. When context.txn.counterparty='A' is true the runtime does not look at the accountId value of Withdrawal events.
When context.txn.counterparty='B' is true the runtime does not look at the accountType value of Withdrawal events.
The JVM platform limits the constant pool of classes and method size of methods. The EPL compiler minimizes the chance of stepping over JVM limits, see Section 17.5.1.1, “Byte Code General Settings”. This section provides information on known limitations of the EPL compiler.
The EPL compiler does not enforce hard limits and this documentation does not list exact limits. Below applies within a single given statement only. Below does not apply across statements and does not apply across modules or the runtime overall.
Per statement, there are however limits to compiler processing. Here is a non-comprehensive list of limits per statement:
Number of expressions in a
group byclause.Number of aggregations.
Number of expressions in a
select-clause.Number of property names in an
insert intoclause.Number of uniqueness expressions provided to a
#unique,#firstuniqueor#groupwindata window.Number of expressions provided to
for grouped_deliveryclause.Number of key expressions in a keyed context, number of hash functions in a hashed context, number of categories in a category context, number of contexts in a nested context.
Number of EPL objects consumed or provided by module.
Number of inlined-classes, declared expressions, scripts.
In patterns, the number of subexpressions to an
and,or,-> (followed-by)and the overall number of subexpressions and the number of filter tags.For filter index planning, the number of expressions considered or used by the compiler's filter index planner.
For query planning for joins and subqueries, the number of expressions and streams considered or used by the compiler's query planner.
Number of streams in the
from-clause.Number of inlined-classes, declared expressions, scripts.
For subqueries, the number of subqueries and the number of expressions in the
select-clause of the subquery.For data windows, the number of data windows that are placed in an intersection or union; and the number of additional parameters to statistics views.
Number of annotations for a given statement.
Number and serialized size of any application-provided user object that is associated to statements or deployments.
Number of expressions that are sort criteria in an
order by-clause, or a#sortor#rankdata window or the#sortedaggregation.Number of rollup levels for rollup aggregation and the number of group expressions and group levels when provided as an aggregation
group_by:parameter.Number of parameters passed to static methods, instance methods, constructors, user-defined functions, inlined-classes, declared expressions, scripts, subscriber update methods or as parameters within the
from-clause with joins for for accessing relational data via SQL and for accessing non-relational data.Number of sub-expressions that are chained into one expression.
Number of event properties that appear chained into one nested event property.
For tables, the number of columns and number of aggregations and the number of table primary keys.
For named windows, the number of properties.
For case control flow (
case),coalesce,new,and,or,{}(array expression),in-keyword,||(concat), arithmetic,allandanythe number of sub-expressions.Number of
when matched-clauses and the number of actions in anon-merge-clause.Number of crontabs wherever multiple crontabs are allowed.
For match-recognize, the number of aggregations and the number of variables and the number of pattern elements.
Number of
setassignments.Number of variables used by a given statement.
Number of properties and number of supertypes in
create schema.Number of columns in
create index.Number of JDBC fields returned by accessing relational data via SQL.
For dataflows, the number of types, operators and channels.
Generally the upper limit for above list is around 1000 for a single statement (this is an estimate). For example, the number of expressions in a group by clause is limited to somewhere around 1000 expressions or higher for a statement.
A statement that has, for example, 100000 expressions in a group by clause may experience a compiler exception.
As part of automated regression testing are tests such as below:
1000 aggregations including for tables.
1000 expressions in the
select-clause (non-subquery) when the output event is map or objectarray.create schemawith 1000 properties for map and objectarray event types.1000 substitution parameters.
- 16.1. Introduction
- 16.2. Obtaining a Runtime From EPRuntimeProvider
- 16.3. The EPRuntime Runtime Interface
- 16.4. Deploying and Undeploying Using EPDeploymentService
- 16.5. Obtaining Results Using EPStatement
- 16.6. Processing Events and Time Using EPEventService
- 16.7. Execute Fire-and-Forget Queries Using EPFireAndForgetService
- 16.8. Runtime Threading and Concurrency
- 16.9. Controlling Time-Keeping
- 16.10. Exception Handling
- 16.11. Condition Handling
- 16.12. Runtime and Statement Metrics Reporting
- 16.13. Monitoring and JMX
- 16.14. Event Rendering to XML and JSON
- 16.15. Plug-In Loader
- 16.16. Context Partition Selection
- 16.17. Context Partition Administration
- 16.18. Test and Assertion Support
- 16.19. OSGi, Class Loader, Class-For-Name
- 16.20. When Deploying with J2EE
- 16.21. Stages
The runtime takes on these functions:
Provide an environment to execute compiled modules.
Provide an environment to run compiled fire-and-forget queries.
Process incoming events and time against deployed modules.
Your application obtains a runtime from EPRuntimeProvider. You may pass an arbitrary string-type runtime URI that uniquely identifies the runtime instance.
A runtime is an instance of EPRuntime. Use the runtime as follows:
The runtime is a stateful service.
You may obtain and use any number of runtime instances in parallel, each runtime instance uniquely identified by the runtime URI.
You may share a runtime instance between threads.
All runtime methods are thread-safe.
Each runtime is completely independent of other runtimes.
The EPRuntimeProvider class provides static methods that return EPRuntime runtimes.
Each runtime has a unique runtime URI which can be any string value.
If your application does not pass a runtime URI then the default URI is default (as defined by EPRuntimeProvider.DEFAULT_RUNTIME_URI).
For the getRuntime methods, your application can pass a runtime URI to obtain different runtimes. The EPRuntimeProvider
determines whether the provided runtime URI matches any existing runtime URIs and returns the existing runtime, or allocates a new runtime if none was found.
The getExistingRuntime method takes a runtime URI and returns the existing runtime for that URI or null if there is none.
The code snip below gets the default runtime. Subsequent calls to get the default runtime return the same runtime.
EPRuntime runtime = EPRuntimeProvider.getDefaultRuntime();
The next code gets a runtime for the runtime URI RFIDProcessor1. Subsequent calls to get a runtime with the same runtime URI return the same runtime instance.
EPRuntime runtime = EPRuntimeProvider.getRuntime("RFIDProcessor1");
Since the getRuntime methods return the same runtime for each URI there is no need to statically cache a runtime in your application.
You may also pass an optional Configuration.
The next code snippet outlines a typical sequence of use:
// Configure the runtime, this is optional
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.configure("configuration.xml"); // load a configuration from file
// Optionally set additional configuration values like so:
// config.getCommon().add....(...);
// Obtain a runtime
EPRuntime runtime = EPRuntimeProvider.getDefaultRuntime(config);
// Optionally, use initialize if the same runtime has been used before to start clean
runtime.initialize();
// Destroy the runtime when no longer needed, frees up resources, releases the runtime URI
runtime.destroy();
The EPRuntime interface represents a runtime. Only the static methods of the EPRuntimeProvider class allocate new runtimes.
A runtime is uniquely identified by runtime URI. The runtime URI is an arbitrary string. The default runtime has a runtime URI of default.
A runtime provides these services:
Table 16.1. Choices For Receiving Statement Results
| Service | Runtime Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
EPDeploymentService | getDeploymentService | For deploying and undeploying compiled modules. |
EPEventService | getEventService | For processing events and advancing time. |
EPContextPartitionService | getContextPartitionService | For information about context partitions. |
EPVariableService | getVariableService | For access to variables. |
EPEventTypeService | getEventTypeService | For obtaining event types. |
EPFireAndForgetService | getFireAndForgetService | For executing fire-and-forget queries. |
EPDataFlowService | getDataFlowService | For managing data flows. |
EPMetricsService | getMetricsService | For control over metrics, and for reading current metrics. |
EPRenderEventService | getRenderEventService | For rendering events. |
You can reset a runtime by calling the initialize method. This operation resets the runtime to the configuration last provided to EPRuntimeProvider. If no configuration is provided, an empty (default) configuration applies.
Your application must obtain new services from the initialized runtime as initialize marks existing services as invalid.
A runtime can be destroyed via the destroy method. This frees all resources held by the runtime. After a call to destroy the runtime can no longer be used.
You may register callbacks to receive notifications about runtime state. The runtime invokes any EPRuntimeStateListener callbacks when a runtime instance is about to be destroyed and after a runtime has been initialized.
Use the addRuntimeStateListener methods to register interest.
When destroying a runtime your application must make sure that threads that are sending events into the runtime have completed their work. More generally, the runtime should not be currently in use during or after the destroy operation.
All runtime instances are completely independent. Your application may not send EventBean instances obtained from one runtime into a second runtime since the event type space between two runtimes is not shared.
Your application must first compile a module or obtain a compiled module before it can deploy. The object representation of a compiled module is EPCompiled.
Call the deploy method and pass the compiled module. The runtime loads the byte code and adds the information contained in the byte code, causing all the compiled module's statements to begin receiving events and time.
Deploying is an atomic operation. At deployment completion all statements of the deployment begin to see events arriving and time passing consistently. In case the deployment fails the runtime rolls back all deployment changes.
The runtime resolves dependencies of the compiled module upon its deployment. The runtime does not validate that the information about EPL-object dependencies that existed at compile-time matches the runtime EPL-objects.
For example, assume there is a compiled module by name compiledModuleM1. Deploy as follows:
EPDeployment deployment = runtime.getDeploymentService().deploy(compiledModuleM1);
The runtime returns a EPDeployment instance that contains the deployment id, the EPStatement statement instances, module name and module properties.
The deployment id is an arbitrary string-type identifier that uniquely identifies the deployment in the runtime.
The undeploy method takes the deployment id and undeploys the deployment. The undeployAll method undeploys all deployments.
A compiled module may be deployed any number of times. Substitution parameters can be handy for parameterizing deployed modules.
Your application may deploy and undeploy using any thread and also within listener or subscriber code. If using Bean-style class-based events your application may not invoke deploy or undeploy methods as part of getter or setter code. Extension API code and plug-in single-row methods also may not invoke deploy or undeploy methods.
You may pass a DeploymentOptions instance. Deployment options provide deployment callbacks and other deploy-time parameters:
Provide a deployment id. If none is provided the runtime generates a unique deployment id.
Provide substitution parameter values for parameterized modules.
Provide or override statement names.
Provide a runtime statement user object that gets associated to the statement and that can be obtained from an
EPStatementwithgetUserObjectRuntime.
Please consult the JavaDoc for more information.
The compiled module may have substitution parameters as explained in the compiler documentation.
All substitution parameters must be replaced by actual values before a compiled module with substitution parameters can be deployed. A compiled module may be deployed multiple times. Substitution parameters can be set to new values for every deployment.
To set substitution parameter values pass a Deployment Options object to the deploy method that provides a StatementSubstitutionParameterOption.
If not assigning a name to substitution parameters, replace the substitution parameter with an actual value using the setObject(int index, Object value) method for each index, starting from 1.
If assigning a name to each substitution parameter, replace the substitution parameter with an actual value using the setObject(String name, Object value) method for each name.
While the setObject method allows substitution parameters to assume any actual value including application Java objects or enumeration values, the application must provide the correct type of substitution parameter that matches the requirements of the expression the parameter resides in.
The below sample code compiles and deploys a parameterized module:
String stmt = "select * from PersonEvent(firstName=?::string)"; Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); configuration.getCommon().addEventType(PersonEvent.class); CompilerArguments compilerArguments = new CompilerArguments(configuration); EPCompiled compiled = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler().compile(stmt, compilerArguments); DeploymentOptions deploymentOptions = new DeploymentOptions(); deploymentOptions.setStatementSubstitutionParameter(prepared -> prepared.setObject(1, "Joe")); EPDeployment deployment = runtime.getDeploymentService().deploy(compiled, deploymentOptions); EPStatement statement = deployment.getStatements()[0];
Your application may deploy multiple compiled modules by calling the rollout method of EPDeploymentService. Roll-out deploys each compiled module, either deploying all compiled modules or deploying none of the compiled modules.
Internally to the runtime, a roll-out generally follows these steps:
For each compiled module, determine the deployment id or use the deployment id when provided in the deployment options; Check that all deployment ids do not already exist
For each compiled module, load the compilation unit via classloader and validate basic class-related information such as manifest information and version
For each compiled module, check deployment preconditions and resolve deployment dependencies on EPL objects
For each compiled module, initialize statement-internal objects
For each compiled module, perform internal deployment of each statement of each module
In case any of the above steps fail the runtime completely rolls back all changes.
Note
Roll-out does not re-order compiled modules and expects EPCompiled instances to be ordered according to module dependencies (if any).
For multiple rollouts or for atomically adding listeners and subscribers use Section 16.4.3, “Atomic Deployment Management”.
Your application can concurrently send events into the runtime while deploying and undeploying statements and adding or removing listeners. It is safe to undeploy and deploy compiled modules while sending in events from other threads concurrently.
However in some cases your application may need more control over deployment, for example when deploying multiple modules or when attaching custom listener code.
Your application can use the API described below to obtain a lock and perform deployment actions as an atomic unit. For example, if your application would like to undeploy and re-deploy as a single atomic unit, while at the same time sending events into the runtime from different threads, it can obtain a lock to ensure that no events are concurrently processed while the operations take place.
Note
Deploying or undeploying a single compiled module is already an atomic operation by default and does not require taking an explicit lock. If your application would like to deploy multiple compiled modules or add custom listeners or subscribers during deployment it may obtain a lock as discussed below.
The below code sample obtains the runtime exclusive write lock to perform multiple management operations as a unit, excluding concurrent processing of events.
runtime.getRuntimeInstanceWideLock().writeLock().lock();
// Start atomic management unit.
// Any events concurrently being processed by other threads must complete before the code completes obtaining the lock.
// Any events sent in by other threads will await the release of the lock.
try {
// Perform operations such as :
// - deploy and/or undeploy multiple compiled modules (deployment admin API)
// - set statement listeners and subscribers while deploying
// There is no need to obtain this lock when deploying or undeploying a single module.
// The lock is reentrant and can be safely taken multiple times by the same thread.
// Make sure you use "try" and "finally" just like we have it here.
}
finally {
// Complete atomic management unit.
// Any events sent in by other threads will now continue processing against the changed set of statements.
runtime.getRuntimeInstanceWideLock().writeLock().unlock();
}Note
There should always be a finally block in your code to ensure the lock is released in all cases.
A compiled module contains zero, one or multiple statements. You can attach callbacks (listeners, subscribers) to statements to receive results (aka push, observer pattern). You can iterate statement current results (aka. poll).
Each statement is uniquely identified in the runtime by the combination of deployment id and statement name. The compiler or runtime always assign a statement name if none was provided.
The EPStatement instance represents the statement. Your application receives statements when deploying a module by calling getStatements on EPDeployment.
Your application may also look up a statement by it's deployment id and statement name using the getStatement method on EPDeploymentService.
For NEsper .NET also see Section J.15, “.NET API - Receiving Statement Results”.
Esper provides three choices for your application to receive statement results. Your application can use all three mechanisms alone or in any combination for each statement. The choices are:
Table 16.2. Choices For Receiving Statement Results
| Name | Methods on EPStatement | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Listener Callbacks | addListener and removeListener |
Your application provides implementations of the The runtime continuously indicates results to all listeners. |
| Subscriber Object | setSubscriber |
Requires setting the Your application provides a POJO (plain Java object) that exposes methods to receive statement results.
The name of the method that a subscriber object provides to receive results is The runtime continuously indicates results to the single subscriber.
This is the fastest method to receive statement results, as the runtime delivers strongly-typed results directly to your application objects without the need for
building an There can be at most one subscriber object registered per statement. If you require more than one listener, use the listener instead (or in addition). The subscriber object is bound to the statement with a strongly typed support which ensure direct delivery of new events without type conversion. This optimization is made possible because there can only be zero or one subscriber object per statement. |
| Pull API | safeIterator and iterator |
Your application asks the statement for results and receives a set of events via This is useful if your application does not need continuous indication of new results in real-time. |
Tip
The runtime calls application-provided update listeners and subscribers for output. These commonly encapsulate the actions to take when there is output. This design decouples statements from actions and places actions outside of EPL. It allows actions to change independently from statements: A statement does not need to be updated when its associated action(s) change.
While action-taking, in respect to the code or script taking action, is not a part of the EPL language, here are a few noteworthy points.
Through the use of EPL annotations you can attach information to EPL that can be used by applications to flexibly determine actions.
The insert into-clause can be used to send results into a further stream and input and output adapters or data flows can exist to process output events from that stream.
Also the data flow EPStatementSource operator can be used to hook up actions declaratively.
The DeploymentStateListener can inform your application of newly-deployed statements and currently-undeployed statements.
Your application may attach one or more listeners, zero or one single subscriber and in addition use the pull API on the same statement. There are no limitations to the use of iterator, subscriber or listener alone or in combination to receive statement results.
The best delivery performance can generally be achieved by attaching a subscriber and by not attaching listeners. The runtime is aware of the listeners and subscriber attached to a statement. The runtime uses this information internally to reduce statement overhead. For example, if your statement does not have listeners or a subscriber attached, the runtime does not need to continuously generate results for delivery.
If your application attaches both a subscriber and one or more listeners then the subscriber receives the result first before any of the listeners.
If your application attaches more than one listener then the UpdateListener listeners receive results in the order they were added to the statement.
To change the order of delivery among listeners your application can add and remove listeners at runtime.
If you have configured outbound threading, it means a thread from the outbound thread pool delivers results to the subscriber and listeners instead of the processing or event-sending thread.
If outbound threading is turned on, we recommend turning off the runtime setting preserving the order of events delivered to listeners as described in Section 17.6.1.1, “Preserving the Order of Events Delivered to Listeners”. If outbound threading is turned on statement execution is not blocked for the configured time in the case a subscriber or listener takes too much time.
Note
The compiler option allowSubscriber must be set at compile-time.
A subscriber object is a direct binding of statement results to an object. The object, receives statement results via method invocation. The subscriber class does not need to implement an interface or extend a superclass. Only one subscriber object may be set for a statement.
Subscriber objects have several advantages over listeners. First, they offer a substantial performance benefit: Statement results are delivered directly to your method(s) through Java virtual machine method calls, and there is no intermediate representation (EventBean). Second, as subscribers receive strongly-typed parameters, the subscriber code tends to be simpler.
This chapter describes the requirements towards the methods provided by your subscriber class.
The runtime can deliver results to your subscriber in two ways:
Each evert in the insert stream results in a method invocation, and each event in the remove stream results in further method invocations. This is termed row-by-row delivery.
A single method invocation that delivers all rows of the insert and remove stream. This is termed multi-row delivery.
In the case that your subscriber object wishes to receive the EPStatement instance along with output data,
please add EPStatement as the very first parameter of any of the delivery method footprints that are discussed next.
For example, your statement may be:
select count(*) from OrderEvent
Your subscriber class exposes the method:
public void update(EPStatement statement, long currentCount) {...}
Your subscriber class must provide a method by name update to receive insert stream events row-by-row. The number and types of parameters declared by the update method must match the number and types of columns as specified in the select clause, in the same order as in the select clause.
For example, if your statement is:
select orderId, price, count(*) from OrderEvent
Then your subscriber update method looks as follows:
public class MySubscriber {
...
public void update(String orderId, double price, long count) {...}
...
}
Each method parameter declared by the update method must be assignable from the respective column type as listed in the select-clause, in the order selected. The assignability rules are:
Widening of types follows Java standards. For example, if your
selectclause selects an integer value, the method parameter for the same column can be typed int, long, float or double (or any equivalent boxed type).Auto-boxing and unboxing follows Java standards. For example, if your
selectclause selects anjava.lang.Integervalue, the method parameter for the same column can be typedint. Note that if yourselectclause column may generatenullvalues, an exception may occur at runtime unboxing thenullvalue.Interfaces and super-classes are honored in the test for assignability. Therefore
java.lang.Objectcan be used to accept anyselectclause column type
In the case that your subscriber class offers multiple update method footprints, the runtime selects the closest-matching footprint by comparing the output types and method parameter types. The runtime prefers the update method that is an exact match of types, followed by an update method that requires boxing or unboxing, followed by an update method that requires widening and finally any other allowable update method.
Within the above criteria, in the case that your subscriber class offers multiple update method footprints with same method parameter types, the runtime prefers the update method that has EPStatement as the first parameter.
If your select clause contains one or more wildcards (*), then the equivalent parameter type is the underlying event type of the stream selected from.
For example, your statement may be:
select *, count(*) from OrderEvent
Then your subscriber update method looks as follows:
public void update(OrderEvent orderEvent, long count) {...}
In a join, the wildcard expands to the underlying event type of each stream in the join in the order the streams occur in the from clause. An example statement for a join is:
select *, count(*) from OrderEvent order, OrderHistory hist
Then your subscriber update method should be:
public void update(OrderEvent orderEvent, OrderHistory orderHistory, long count) {...}The stream wildcard syntax and the stream name itself can also be used:
select hist.*, order from OrderEvent order, OrderHistory hist
The matching update method is:
public void update(OrderHistory orderHistory, OrderEvent orderEvent) {...}
Alternatively, your update method may simply choose to accept java.util.Map as a representation for each row. Each column in the select clause is
then made an entry in the resulting Map. The Map keys are the column name if supplied, or the expression string itself for columns without a name.
The update method for Map delivery is:
public void update(Map row) {...}
The runtime also supports delivery of select clause columns as an object array. Each item in the object array represents a column in the select clause. The update method then looks as follows:
public void update(Object[] row) {...}
Your subscriber receives remove stream events if it provides a method named updateRStream. The method must accept the same number and types of parameters as the update method (including EPStatement if present).
An example statement:
select orderId, count(*) from OrderEvent#time(20 sec) group by orderId
Then your subscriber update and updateRStream methods should be:
public void update(String, long count) {...}
public void updateRStream(String orderId, long count) {...}
If your subscriber requires a notification for begin and end of event delivery, it can expose methods by name updateStart and updateEnd.
The updateStart method must take two integer parameters that indicate the number of events of the insert stream and remove stream to be delivered. The runtime invokes the updateStart method immediately prior to delivering events to the update and updateRStream methods.
The updateEnd method must take no parameters. The runtime invokes the updateEnd method immediately after delivering events to the update and updateRStream methods.
An example set of delivery methods:
// Called by the runtime before delivering events to update methods
public void updateStart(int insertStreamLength, int removeStreamLength)
// To deliver insert stream events
public void update(String orderId, long count) {...}
// To deliver remove stream events
public void updateRStream(String orderId, long count) {...}
// Called by the runtime after delivering events
public void updateEnd() {...}In place of row-by-row delivery, your subscriber can receive all events in the insert and remove stream via a single method invocation. This is applicable when an EPL delivers multiple output rows for a given input event or time advancing, for example when multiple pattern matches occur for the same incoming event, for a join producing multiple output rows or with output rate limiting, for example.
The event delivery follow the scheme as described earlier in Section 16.5.2.2.2, “Row Delivery as Map and Object Array ”. The subscriber class must provide one of the following methods:
Table 16.3. Update Method for Multi-Row Delivery of Underlying Events
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
update(Object[][] insertStream, Object[][] removeStream) |
The first dimension of each Object array is the event row, and the second dimension is the column matching the column order of the statement |
update(Map[] insertStream, Map[] removeStream) |
Each map represents one event, and Map entries represent columns of the statement |
If your select clause contains a single wildcard (*) or wildcard stream selector, the subscriber object may also directly receive arrays of the underlying events. In this case, the subscriber class should provide a method update(Underlying[] insertStream, Underlying[] removeStream) , such that Underlying represents the class of the underlying event.
For example, your statement may be:
select * from OrderEvent#time(30 sec)
Your subscriber class exposes the method:
public void update(OrderEvent[] insertStream, OrderEvent[] removeStream) {...}In the case that your subscriber object wishes to receive no data from a statement please follow the instructions here.
You statement must select a single null value.
For example, your statement may be:
select null from OrderEvent(price > 100)
Your subscriber class exposes the method:
public void update() {...}For NEsper .NET also see Section J.16, “.NET API - Adding Listeners”.
Your application can subscribe to updates posted by a statement via the addListener and removeListener methods on EPStatement . Your application must to provide an implementation of the UpdateListener interface to the statement:
UpdateListener myListener = new MyUpdateListener(); countStmt.addListener(myListener);
Statements publish old data and new data to registered UpdateListener listeners.
New data published by statements is the events representing the new values of derived data held by the statement.
Old data published by statements consists of the events representing the prior values of derived data held by the statement.
Important
UpdateListener listeners receive multiple result rows in one invocation by the runtime: the new data and old data parameters to your listener are array parameters. For example, if your application uses one of the batch data windows, or your application creates a pattern that matches multiple times when a single event arrives, then the runtime indicates such multiple result rows in one invocation and your new data array carries two or more rows.
To indicate results the runtime invokes the following method on UpdateListener listeners: update(EventBean[] newEvents, EventBean[] oldEvents, EPStatement statement, EPRuntime runtime)
The addListenerWithReplay method provided by EPStatement makes it possible to send a snapshot of current statement results to a listener when the listener is added.
When using the addListenerWithReplay method to register a listener, the listener receives current statement results as the first call to the update method of the listener, passing in the newEvents parameter the current statement results as an array of zero or more events. Subsequent calls to the update method of the listener are statement results.
Current statement results are the events returned by the iterator or safeIterator methods.
Delivery is atomic: Events occurring during delivery of current results to the listener are guaranteed to be delivered in a separate call and not lost. The listener implementation should thus minimize long-running or blocking operations to reduce lock times held on statement-level resources.
Subscribing to events posted by a statement is following a push model. The runtime pushes data to listeners when events are received that cause data to change or patterns to match. Alternatively, you need to know that statements serve up data that your application can obtain via the safeIterator and iterator methods on EPStatement. This is called the pull API and can come in handy if your application is not interested in all new updates, and only needs to perform a frequent or infrequent poll for the latest data.
The safeIterator method on EPStatement returns a concurrency-safe iterator returning current statement results, even while concurrent threads may send events into the runtime for processing. The runtime employs a read-write lock per context partition and obtains a read lock for iteration. Thus safe iterator guarantees correct results even as events are being processed by other threads and other context partitions. The cost is that the iterator obtains and holds zero, one or multiple context partition locks for that statement that must be released via the close method on the SafeIterator instance.
The iterator method on EPStatement returns a concurrency-unsafe iterator. This iterator is only useful for applications that are single-threaded, or applications that themselves perform coordination between the iterating thread and the threads that send events into the runtime for processing. The advantage to this iterator is that it does not hold a lock.
When statements are used with contexts and context partitions, the APIs to identify, filter and select context partitions for statement iteration are described in Section 16.16, “Context Partition Selection”.
The next code snippet shows a short example of use of safe iterators:
EPStatement statement = epAdmin.createEPL("select avg(price) as avgPrice from MyTick");
// .. send events into the runtime
// then use the pull API...
SafeIterator<EventBean> safeIter = statement.safeIterator();
try {
for (;safeIter.hasNext();) {
// .. process event ..
EventBean event = safeIter.next();
System.out.println("avg:" + event.get("avgPrice");
}
}
finally {
safeIter.close(); // Note: safe iterators must be closed
}This is a short example of use of the regular iterator that is not safe for concurrent event processing:
double averagePrice = (Double) eplStatement.iterator().next().get("average");
The safeIterator and iterator methods can be used to pull results out of all statements, including statements that join streams, contain aggregation functions, pattern statements, and statements that contain a where clause, group by clause, having clause or order by clause.
For statements without an order by clause, the iterator method returns events in the order maintained by the data window. For statements that contain an order by clause, the iterator method returns events in the order indicated by the order by clause.
Consider using the on-select clause and a named window if your application requires iterating over a partial result set or requires indexed access for fast iteration; Note that on-select requires that you sent a trigger event, which may contain the key values for indexed access.
Esper places the following restrictions on the pull API and usage of the safeIterator and iterator methods:
In multithreaded applications, use the
safeIteratormethod. Note: make sure your application closes the iterator via theclosemethod when done, otherwise the iterated statement context partitions stay locked and event processing for statement context partitions does not resume.In multithreaded applications, the
iteratormethod does not hold any locks. The iterator returned by this method does not make any guarantees towards correctness of results and fail-behavior, if your application processes events into the runtime by multiple threads. Use thesafeIteratormethod for concurrency-safe iteration instead.Since the
safeIteratoranditeratormethods return events to the application immediately, the iterator does not honor an output rate limiting clause, if present. That is, the iterator returns results as if there is no output-rate clause for the statement in statements without grouping or aggregation. For statements with grouping or aggregation, the iterator in combination with an output clause returns last output group and aggregation results. Use a separate statement and theinsert intoclause to control the output rate for iteration, if so required.When iterating a statement that operates on an unbound stream (no data window declared), please note the following:
When iterating a statement that groups and aggregates values from an unbound stream and that specifies
output snapshot, the runtime retains groups and aggregations for output as iteration results or upon the output snapshot condition .When iterating a statement that groups and aggregates values from an unbound stream and that does not specify
output snapshot, the runtime only retains the last aggregation values and the iterated result contains only the last updated group.When iterating a statement that operates on an unbound stream the iterator returns no rows. This behavior can be changed by specifying either the
@IterableUnboundannotation or by changing the global view resources configuration.
An EventBean object represents a row (event) in your statement's result set. Each EventBean object has an associated EventType object providing event metadata.
An UpdateListener implementation receives one or more EventBean events with each invocation. Via the iterator method on EPStatement your application can poll or read data out of statements. Statement iterators also return EventBean instances.
Each statement provides the event type of the events it produces, available via the getEventType method on EPStatement.
An EventType object encapsulates all the metadata about a certain type of events. As Esper supports an inheritance hierarchy for event types, it also provides information about super-types to an event type.
An EventType object provides the following information:
For each event property, it lists the property name and type as well as flags for indexed or mapped properties and whether a property is a fragment.
The direct and indirect super-types to the event type.
Value getters for property expressions.
Underlying class of the event representation.
For each property of an event type, there is an EventPropertyDescriptor object that describes the property.
The EventPropertyDescriptor contains flags that indicate whether a property is an indexed (array) or a mapped property and whether access to property values require an integer index value (indexed properties only) or string key value (mapped properties only). The descriptor also contains a fragment flag that indicates whether a property value is available as a fragment.
The term fragment means an event property value that is itself an event, or a property value that can be represented as an event. The getFragmentType on EventType may be used to determine a fragment's event type in advance.
A fragment event type and thereby fragment events allow navigation over a statement's results even if the statement result contains nested events or a graph of events. There is no need to use the Java reflection API to navigate events, since fragments allow the querying of nested event properties or array values, including nested Java classes.
When using the Map or Object-array event representation, any named Map type or Object-array type nested within a Map or Object-array as a simple or array property is also available as a fragment. When using Java objects either directly or within Map or Object-array events, any object that is neither a primitive or boxed built-in type, and that is not an enumeration and does not implement the Map interface is also available as a fragment.
The nested, indexed and mapped property syntax can be combined to a property expression that may query an event property graph. Most of the methods on the EventType interface allow a property expression to be passed.
Your application may use an EventType object to obtain special getter-objects. A getter-object is a fast accessor to a property value of an event of a given type. All getter objects implement the EventPropertyGetter interface. Getter-objects work only for events of the same type or sub-types as the EventType that provides the EventPropertyGetter. The performance section provides additional information and samples on using getter-objects.
An event object is an EventBean that provides:
The property value for a property given a property name or property expression that may include nested, indexed or mapped properties in any combination.
The event type of the event.
Access to the underlying event object.
The
EventBeanfragment or array ofEventBeanfragments given a property name or property expression.
The getFragment method on EventBean and EventPropertyGetter return the fragment EventBean or array of EventBean, if the property is itself an event
or can be represented as an event. Your application may use EventPropertyDescriptor to determine which properties are also available as fragments.
The underlying event object of an EventBean can be obtained via the getUnderlying method. Please see Chapter 3, Event Representations for more information on different event representations.
From a threading perspective, it is safe to retain and query EventBean and EventType objects in multiple threads.
Consider a statement that returns the symbol, count of events per symbol and average price per symbol for tick events. Our sample statement uses the event type: StockTickEvent. Assume that this event type was declared previously and exposes a symbol property of type String and a price property of type (Java primitive) double.
select symbol, avg(price) as avgprice, count(*) as mycount from StockTickEvent group by symbol
The next table summarizes the property names and types as posted by the statement above:
Table 16.4. Properties Offered by Sample Statement Aggregating Price
| Name | Type | Description | Java code snippet |
|---|---|---|---|
symbol | java.lang.String | Value of symbol event property | eventBean.get("symbol") |
avgprice | java.lang.Double | Average price per symbol | eventBean.get("avgprice") |
mycount | java.lang.Long | Number of events per symbol | eventBean.get("mycount") |
A code snippet out of a possible UpdateListener implementation to this statement may look as below:
String symbol = (String) newEvents[0].get("symbol");
Double price= (Double) newEvents[0].get("avgprice");
Long count= (Long) newEvents[0].get("mycount");
The runtime supplies the boxed java.lang.Double and java.lang.Long types as property values rather than primitive Java types. This is because aggregated values can return a null value to indicate that no data is available for aggregation. Also, in a select statement that computes expressions, the underlying event objects to EventBean instances are either of type Object[] (object-array) or of type java.util.Map.
Use statement.getEventType().getUnderlyingType() to inspect the underlying type for all events delivered to listeners. Whether the runtime delivers Map or Object-array events to listeners can be specified as follows. If the statement provides the @EventRepresentation(objectarray) annotation the runtime delivers the output events as object array. If the statement provides the @EventRepresentation(map) annotation the runtime delivers output events as a Map. If neither annotation is provided, the runtime delivers the configured default event representation as discussed in Section 17.4.9.1, “Default Event Representation”.
Consider the next statement that specifies a wildcard selecting the same type of event:
select * from StockTickEvent where price > 100
The property names and types provided by an EventBean query result row, as posted by the statement above are as follows:
Table 16.5. Properties Offered by Sample Wildcard-Select Statement
| Name | Type | Description | Java code snippet |
|---|---|---|---|
symbol | java.lang.String | Value of symbol event property | eventBean.get("symbol") |
price | double | Value of price event property | eventBean.get("price") |
As an alternative to querying individual event properties via the get methods, the getUnderlying method on EventBean returns the underlying object representing the statement result.
In the sample statement that features a wildcard-select, the underlying event object is of type org.sample.StockTickEvent:
StockTickEvent tick = (StockTickEvent) newEvents[0].getUnderlying();
Composite events are events that aggregate one or more other events. Composite events are typically created by the runtime for statements that join two event streams, and for event patterns in which the causal events are retained and reported in a composite event. The example below shows such an event pattern.
// Look for a pattern where BEvent follows AEvent select * from pattern [a=AEvent -> b=BEvent]
// Example listener code
public class MyUpdateListener implements UpdateListener {
public void update(EventBean[] newData, EventBean[] oldData, EPStatement statement, EPRuntime runtime) {
System.out.println("a event=" + newData[0].get("a"));
System.out.println("b event=" + newData[0].get("b"));
}
}
Note that the update method can receive multiple events at once as it accepts an array of EventBean instances. For example, a time batch window may post multiple events to listeners representing a batch of events received during a given time period.
Pattern statements can also produce multiple events delivered to update listeners in one invocation. The pattern statement below, for instance, delivers an event for each A event that was not followed by a B event with the same id property within 60 seconds of the A event. The runtime may deliver all matching A events as an array of events in a single invocation of the update method of each listener to the statement:
select * from pattern[every a=A -> (timer:interval(60 sec) and not B(id=a.id))]
A code snippet out of a possible UpdateListener implementation to this statement that retrives the events as fragments may look as below:
EventBean a = (EventBean) newEvents[0].getFragment("a");
// ... or using a nested property expression to get a value out of A event...
double value = (Double) newEvent[0].get("a.value");Some pattern objects return an array of events. An example is the unbound repeat operator. Here is a sample pattern that collects all A events until a B event arrives:
select * from pattern [a=A until b=B]
A possible code to retrieve different fragments or property values:
EventBean[] a = (EventBean[]) newEvents[0].getFragment("a");
// ... or using a nested property expression to get a value out of A event...
double value = (Double) newEvent[0].get("a[0].value");
The Esper compiler and runtime use the EPType interface for tracking all Java (or C# for .NET) type information. The EPType interface can be found in package com.espertech.esper.common.client.type.
EPL uses three-valued logic and thus null is a viable type. More information can be found at Section 2.19, “Basic Null”. The null-type is represented by EPTypeNull.
EPL supports un-parameterized types and a type that is not parameterized is represented by EPTypeClass.
EPL also supports parameterized types and a type that is parameterized is represented by EPTypeClassParameterized. Since an instance of java.lang.Class does not provide information about actual type parameters (aka. type erasure)
and since there is no null-type class the compiler and runtime use EPType instead of java.lang.Class.
To obtain the event property type use the getPropertyEPType method of EventType or EventPropertyDescriptor. Please consult the JavaDoc for additional information.
As discussed in Section 5.2.7, “Annotation” an EPL annotation is an addition made to statement information. The API and examples to interrogate annotations are described here.
You may use the getAnnotations method of EPStatement to obtain annotations specified for a statement. Or when compiling an EPL expression to a EPStatementObjectModel statement object model you may also query, change or add annotations.
The following example code demonstrates iterating over an EPStatement statement's annotations and retrieving values:
String exampleEPL = "@Tag(name='direct-output', value='sink 1') select * from RootEvent";
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("RootEvent", Collections.emptyMap()); // add an event type without properties
CompilerArguments compilerArguments = new CompilerArguments(configuration);
EPCompiled compiled = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler().compile(stmt, compilerArguments);
EPDeployment deployment = runtime.getDeploymentService().deploy(compiled);
EPStatement stmt = deployment.getStatements()[0];
for (Annotation annotation : stmt.getAnnotations()) {
if (annotation instanceof Tag) {
Tag tag = (Tag) annotation;
System.out.println("Tag name " + tag.name() + " value " + tag.value());
}
}
The output of the sample code shown above is Tag name direct-output value sink 1.
The EPEventService interface is used to send events and advance time. Obtain the event service from a runtime by calling getEventService on EPRuntime.
This section focuses on processing events. For more information on controlling time using the event service please skip forward to Section 16.9, “Controlling Time-Keeping”.
Your application invokes any of the sendEventType methods listed below and must provide an event type name along with the actual event object:
Table 16.6. Send-Event Methods
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
sendEventBean(Object event, String eventTypeName) | Call when the event is a Bean-style event. The event type name should be associated to a class event representation. |
sendEventMap(Map<String, Object> event, String eventTypeName) | Call when the event is a map. The event type name should be associated to a map event representation. |
sendEventObjectArray(Object[] event, String eventTypeName); | Call when the event is an object-array. The event type name should be associated to an object-array event representation. |
sendEventXMLDOM(Node node, String eventTypeName); | Call when the event is a DOM-Node. The event type name should be associated to an XML event representation. |
void sendEventJson(String json, String jsonEventTypeName); | Call when the event is an JSON-formatted string-type document. The event type name should be associated to a JSON event representation. |
void sendEventAvro(Object avroGenericDataDotRecord, String avroEventTypeName); | Call when the event is an Avro object. The event type name should be associated to an Avro event representation. |
The Chapter 3, Event Representations section explains the types of event representations.
The below sample code assumes that the event type name MarketDataBean refers to a class event representation that matches the class MarketDataBean:
EPRuntime runtime = EPRuntimeProvider.getDefaultRuntime();
EPEventService eventService = runtime.getEventService();
// Send an example event containing stock market data
eventService.sendEventBean(new MarketDataBean("IBM", 75.0), "MarketDataBean");Tip
Events, in theoretical terms, are observations of a state change that occurred in the past. Since you cannot change an event that happened in the past, events are best modelled as immutable objects.
If you find that your application requires processing events and control over time only for specific deployments and not for other deployments, please read up on Section 16.21, “Stages”.
Caution
The runtime relies on events that are sent into the runtime to not change their state. Typically, applications create a new event object for every new event, to represent that new event. Application should not modify an existing event that was sent into the runtime.
Important
Another important method in the runtime interface are the routeEventType methods. These methods are designed for use by UpdateListener and
subscriber implementations as well as runtime extensions that need to send events into a runtime to avoid the possibility of a stack overflow due to nested calls
to sendEvent and to ensure correct processing of the current and routed event.
Note that if outbound-threading is enabled, listeners and subscribers should use sendEvent and not routeEvent.
The EventSender interface processes event objects that are of a known type. This facility can reduce the overhead of event object reflection and type lookup as an event sender
is always associated to a single concrete event type.
Use the method getEventSender(String eventTypeName) to obtain an event sender for processing events of the named type:
EventSender sender = runtime.getEVentService().getEventSender("MyEvent");
sender.sendEvent(myEvent);For events backed by a Java class (JavaBean events), the event sender ensures that the event object equals the underlying class, or implements or extends the underlying class for the given event type name.
For events backed by a java.util.Map (Map events), the event sender does not perform any checking other than checking that the event object implements Map.
For events backed by a Object[] (Object-array events), the event sender does not perform any checking other than checking that the event object implements Object[]. The array elements must be in the exact same order of properties as declared and array length must always be at least the number of properties declared.
For JSON events, the event sender checks that the event object is a string-type value or is an JsonEventUnderlying object returned by the parse method of EventSenderJson. The JSON document should match the fields defined in create schema.
For Avro events backed by a Apache Avro GenericData.Record, the event sender does not perform any checking other than checking that the event object is a GenericData.Record. The schema associated to the record should match the event type's Avro schema.
For events backed by a org.w3c.Node (XML DOM events), the event sender checks that the root element name equals the root element name for the event type.
Your application can register an implementation of the UnmatchedListener interface with the event service by calling the setUnmatchedListener method to receive events that were not matched by any statement.
Events that can be unmatched are all events that your application sends into the runtime via one of the sendEvent or routeEvent methods, or that have been generated via an insert into clause.
For an event to become unmatched by any statement, the event must not match any statement's event stream filter criteria. Note that the EPL where clause or having clause are not considered part of the filter criteria for a stream, as explained by example below.
In the following statement a MyEvent event with a 'quantity' property value of 5 or less does not match this statement's event stream filter criteria. The runtime delivers such an event to the registered UnmatchedListener instance provided no other statement matches on the event:
select * from MyEvent(quantity > 5)
For patterns, if no pattern sub-expression is active for an event type, an event of that type also counts as unmatched in regards to the pattern statement.
The EPFireAndForgetService interface offers methods to execute fire-and-forget queries. Obtain the fire-and-forget service from a runtime by calling getFireAndForgetService on EPRuntime.
As your application may not require streaming results and may not know each statement in advance, the fire-and-forget query facility provides for ad-hoc on-demand execution of an EPL query.
Fire-and-forget queries are not continuous in nature: The fire-and-forget query runtime executes the query once and returns all result rows to the application. Fire-and-forget query execution is very lightweight as the runtime performs no statement deployment and the query leaves no traces within the runtime.
Esper provides the facility to explicitly index named windows and tables to speed up fire-and-forget queries and statements. Please consult Section 6.9, “Explicitly Indexing Named Windows and Tables” for more information.
When named windows and tables are used with contexts and context partitions, the APIs to identify, filter and select context partitions for fire-and-forget queries can be found in Section 16.16, “Context Partition Selection”.
There are three ways to run fire-and-forget queries:
Use the
executeQuerymethod to executes a given fire-and-forget query exactly once, see Section 16.7.1, “Fire-and-forget Query Single Execution”.Use the
prepareQuerymethod to prepare a given fire-and-forget query such that the same query can be executed multiple times, see Section 16.7.2, “Fire-and-forget Query Prepared Unparameterized Execution”.Use the
prepareQueryWithParametersmethod to prepare a given fire-and-forget query that may have substitution parameters such that the same query can be parameterized and executed multiple times without repeated parsing, see Section 16.7.3, “Fire-and-forget Query Prepared Parameterized Execution”
If your application must execute the same fire-and-forget query multiple times with different parameters use prepareQueryWithParameters.
If your application must execute the same fire-and-forget query multiple times without parameters use either prepareQuery or prepareQueryWithParameters and specify no substitution parameters.
By using any of the prepare... methods the runtime can load the byte code for the query once and reuse the byte code and thereby speed up repeated execution.
The following limitations apply:
A fire-and-forget only evaluates against the named windows and tables that your application creates. Fire-and-forget queries may not specify any other streams or application event types.
The following clauses are not allowed in fire-and-forget EPL queries:
insert intoandoutput.Data windows and patterns are not allowed to appear in fire-and-forget queries.
Fire-and-forget EPL may not perform subqueries.
The
previousandpriorfunctions may not be used.
Use the executeQuery method for executing a fire-and-forget query once. For repeated execution, please consider any of the prepare... methods instead.
The next program listing runs a fire-and-forget query against a named window MyNamedWindow and prints a column of each row result of the query (this sample uses the compiler runtime-path):
String query = "select * from MyNamedWindow";
CompilerArguments compilerArguments = new CompilerArguments();
compilerArguments.getPath().add(runtime.getRuntimePath());
EPCompiled compiled = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler().compileQuery(query, compilerArguments);
EPFireAndForgetQueryResult result = runtime.getFireAndForgetService().executeQuery(compiled);
for (EventBean row : result.getArray()) {
System.out.println("name=" + row.get("name"));
}
For executing a fire-and-forget against a table please put the table name into the from-clause instead.
Prepared fire-and-forget queries are designed for repeated execution and may perform better then the dynamic single-execution method if running the same query multiple times. For use with parameter placeholders please see Section 16.7.3, “Fire-and-forget Query Prepared Parameterized Execution”.
The next code snippet demonstrates prepared fire-and-forget queries without parameter placeholder:
String query = "select * from MyNamedWindow where orderId = '123'"; CompilerArguments compilerArguments = new CompilerArguments(); compilerArguments.getPath().add(runtime.getRuntimePath()); EPCompiled compiled = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler().compileQuery(query, compilerArguments); EPFireAndForgetPreparedQuery prepared = runtime.getFireAndForgetService().prepareQuery(compiled); EPFireAndForgetQueryResult result = prepared.execute(); // ...later on execute once more ... prepared.execute(); // execute a second time
Please see the compiler documentation for specifying substitution parameters.
All substitution parameters must be replaced by actual values before a fire-and-forget query with substitution parameters can be executed. Substitution parameters can be replaced with an actual value using the setObject method for each index or name. Substitution parameters can be set to new values and the query executed more than once.
While the setObject method allows substitution parameters to assume any actual value including application Java objects or enumeration values, the application must provide the correct type of substitution parameter that matches the type that
was specified, if any, and the requirements of the expression the parameter resides in.
The next program listing runs a prepared and parameterized fire-and-forget query against a named window MyNamedWindow (this example does not assign names to substitution parameters):
String query = "select * from MyNamedWindow where orderId = ?::string"; CompilerArguments compilerArguments = new CompilerArguments(); compilerArguments.getPath().add(runtime.getRuntimePath()); EPCompiled compiled = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler().compileQuery(query, compilerArguments); EPFireAndForgetPreparedQueryParameterized prepared = runtime.getFireAndForgetService().prepareQueryWithParameters(query); // Set the required parameter values before each execution prepared.setObject(1, "123"); EPFireAndForgetQueryResult result = runtime.getFireAndForgetService().executeQuery(prepared); // ...execute a second time with new parameter values... prepared.setObject(1, "456"); result = runtime.getFireAndForgetService().executeQuery(prepared);
This second example uses the in operator and has multiple parameters:
String query = "select * from MyNamedWindow where orderId in (?::string[]) and price > ?::double";
CompilerArguments compilerArguments = new CompilerArguments();
compilerArguments.getPath().add(runtime.getRuntimePath());
EPCompiled compiled = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler().compileQuery(query, compilerArguments);
EPFireAndForgetPreparedQueryParameterized prepared = runtime.getFireAndForgetService().prepareQueryWithParameters(compiled);
prepared.setObject(1, new String[] {"123", "456"});
prepared.setObject(2, 1000.0);
The from-clause in EPL is optional and is only required for subqueries. You may execute fire-and-forget queries without a from-clause. For example:
select 1 as value
You may use fire-and-forget queries to obtain information about the current context partitions. More information can be found at Section 4.5, “Output When a Context Partition Starts (Non-Overlapping Context) or Initiates (Overlapping Context)”. For example:
context CtxPerOrder select context.orderEvent as orderEvent
The from-clause can have an SQL query:
... from sql:database_name["parameterized_sql_query"]
The Esper runtime executes such fire-and-forget queries with SQL using the JDBC API. Please also refer to Section 5.13, “Accessing Relational Data via SQL” for more information.
The sample EPL below returns the results of an SQL query against the database named MyCustomerDB and table Customer:
select * from sql:MyCustomerDB ['select cust_name from Customer where cust_id = 10']
Tip
Use prepared execution (unparameterized or parameterized) when executing the same SQL query multiple times with same or different parameters. This allows the Esper runtime to reuse the JDBC
java.sql.Connectionand JDBCPreparedStatement. EPL Expressions including expressions with (public) variables and substitution parameters can be placed within${...}within the SQL text.To execute a query once an application can use single execution (see above). In single execution the runtime obtains a new JDBC
java.sql.Connection, creates a JDBCPreparedStatementand discards the JDBC connection and JDBC statement after execution. This is not recommended for best performance.
This code snippet illustrates executing the SQL query by fire-and-forget API prepared unparameterized execution:
String query = "select * from sql:MyCustomerDB ['select cust_name from Customer where cust_id = 10"; EPCompiled compiled = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler().compileQuery(query, new CompilerArguments()); EPFireAndForgetPreparedQuery prepared = runtime.getFireAndForgetService().prepareQuery(compiled); EPFireAndForgetQueryResult result = prepared.execute(); // ...close() ... prepared.close(); // close when done executing
Warning
Call the close method of EPFireAndForgetPreparedQuery and EPFireAndForgetPreparedQueryParameterized
to release JDBC resources held by the runtime.
The following limitations apply:
Joins are not allowed when using
sql:SQL queries in thefrom-clause however the SQL itself can be any SQL including a join.A
contextcannot be specified.
For NEsper .NET also see ???.
The runtime is designed from the ground up to operate as a component to multi-threaded, highly-concurrent applications that require efficient use of Java VM resources. In addition, multi-threaded execution requires guarantees in predictability of results and deterministic processing. This section discusses these concerns in detail.
In Esper, a runtime instance is a unit of separation. Applications can obtain and discard (initialize) one or more runtime instances within the same Java VM and can provide the same or different configurations to each instance. A runtime instance shares resources between statements by means of named windows, tables and variables.
Applications can use Esper APIs to concurrently, by multiple threads of execution, perform such functions as deploying modules, or sending events into the runtime for processing. Applications can use application-managed threads or thread pools or any set of same or different threads of execution with any of the public runtime APIs. There are no restrictions towards threading other than those noted in specific sections of this document.
The runtime does not prescribe a specific threading model. Applications using Esper retain full control over threading, allowing a runtime to be easily embedded and used as a component or library in your favorite Java container or process.
In the default configuration it is up to the application code to use multiple threads for processing events by the runtime, if so desired. All event processing takes places within your application thread call stack. The exception is timer-based processing if your runtime relies on the internal timer (default). If your application relies on external timer events instead of the internal timer then there need not be any runtime-managed internal threads.
The fact that event processing can take place within your application thread's call stack makes developing applications with the Esper runtime easier: Any common Java integrated development environment (IDE) can host a compiler and runtime instance. This allows developers to easily set up test cases, debug through listener code and inspect input or output events, or trace their call stack.
In the default configuration, each runtime maintains a single timer thread (internal timer) providing for time or schedule-based processing within the runtime. The default resolution at which the internal timer operates is 100 milliseconds. The internal timer thread can be disabled and applications can instead advance time to perform timer or scheduled processing at the resolution required by an application.
A runtime performs minimal locking to enable high levels of concurrency. A runtime locks on the combination of query and context partition to protect context partition resources. For example, two statements with three partitions each have a total of six locks. For stateless EPL select-statements the runtime does not use a context-partition lock and operates lock-free for the context partition. For stateful statements, the maximum (theoretical) degree of parallelism is 2^31-1 (2,147,483,647) parallel threads working to process a single statement under a hash segmented context.
For named windows and tables, on-select, on-merge, on-update and on-delete all execute under the same lock as the partition of the named window or table.
Any insert into produces a new event for the work queue and does not lock the target of the insert-into.
Tip
For logging of lock activity please enable runtime lock activity logging as described in Section 17.6.2.3, “Lock Activity Logging”.
You may turn off context partition locking runtime-wide (also read the caution notice) as described in Section 17.6.10.4, “Disable Locking”. You may disable context partition locking for a given statement by providing the @NoLock annotation as part of your EPL. Note, Esper provides the @NoLock annotation for the purpose of identifying locking overhead, or when your application is single-threaded, or when using an external mechanism for concurrency control or for example with virtual data windows or plug-in data windows to allow customizing concurrency for a given statement or named window. Using this annotation may have unpredictable results unless your application is taking concurrency under consideration.
For a runtime to produce predictable results from the viewpoint of listeners to statements, a runtime by default ensures that it dispatches statement result events to listeners in the order in which a statement produced result events. Applications that require the highest possible concurrency and do not require predictable order of delivery of events to listeners, this feature can be turned off via configuration, see Section 17.6.1.1, “Preserving the Order of Events Delivered to Listeners”. For example, assume thread T1 processes an event applied to statement S producing output event O1. Assume thread T2 processes another event applied to statement S and produces output event O2. The runtime employs a configurable latch system to ensure that listeners to statement S receive and may complete processing of O1 before receiving O2. When using outbound threading (advanced threading options) or changing the configuration this guarantee is weakened or removed.
In multithreaded environments, when one or more statements make result events available via the insert into clause to further statements, the runtime preserves the order of events inserted into the generated insert-into stream, allowing statements that consume other statement's events to behave deterministic. This feature can also be turned off via configuration, see Section 17.6.1.2, “Preserving the Order of Events for Insert-Into Streams”. For example, assume thread T1 processes an event applied to statement S and thread T2 processes another event applied to statement S. Assume statement S inserts into stream ST. T1 produces an output event O1 for processing by consumers of ST1 and T2 produces an output event O2 for processing by consumers of ST. The runtime employs a configurable latch system such that O1 is processed before O2 by consumers of ST. When using route execution threading (advanced threading options) or changing the configuration this guarantee is weakened or removed.
We generally recommended that listener implementations block minimally or do not block at all. By implementing listener code as non-blocking code execution threads can often achieve higher levels of concurrency.
We recommended that, when using a single listener or subscriber instance to receive output from multiple statements, that the listener or subscriber code is multithread-safe. If your application has shared state between listener or subscriber instances then such shared state should be thread-safe.
In the default configuration the same application thread that invokes any of the sendEvent methods will process the event fully and also deliver output events to listeners and subscribers. By default the single internal timer thread based on system time performs time-based processing and delivery of time-based results.
This default configuration reduces the processing overhead associated with thread context switching, is lightweight and fast and works well in many environments such as J2EE, server or client. Latency and throughput requirements are largely use case dependent, and Esper provides runtime-level facilities for controlling concurrency that are described next.
Inbound Threading queues all incoming events: A pool of runtime-managed threads performs the event processing. The application thread that sends an event via any of the sendEvent methods returns without blocking.
Outbound Threading queues events for delivery to listeners and subscribers, such that slow or blocking listeners or subscribers do not block event processing.
Timer Execution Threading means time-based event processing is performed by a pool of runtime-managed threads. With this option the internal timer thread (or external timer event) serves only as a metronome, providing units-of-work to the runtime-managed threads in the timer execution pool, pushing threading to the level of each statement for time-based execution.
Route Execution Threading means that the thread sending in an event via any of the sendEvent methods (or the inbound threading pooled thread if inbound threading is enabled) only identifies and pre-processes an event, and a pool of runtime-managed threads handles the actual processing of the event for each statement, pushing threading to the level of each statement for event-arrival-based execution.
The runtime starts runtime-managed threads as daemon threads when the runtime instance is first obtained. The runtime stops runtime-managed threads when the runtime instance is destroyed via the destroy method. When the runtime is initialized via the initialize method the existing runtime-managed threads are stopped and new threads are created. When shutting down your application, use the destroy method to stop runtime-managed threads.
Note that the options discussed herein may introduce additional processing overhead into your system, as each option involves work queue management and thread context switching.
Note
If your use cases require ordered processing of events or do not tolerate disorder, the threading options described herein are not the right choice.
For enforcing a processing order within a given criteria, your application must enforce such processing order. Esper does not enforce order of processing if you enable inbound or route threading. Your application code could, for example, utilize a thread per group of criteria keys, a latch per criteria key, or a queue per criteria key, or use Java's completion service, all depending on your ordering requirements.
If your use cases require loss-less processing of events, wherein the threading options mean that events are held in an in-memory queue, the threading options described herein may not be the right choice.
Care should be taken to consider arrival rates and queue depth. Threading options utilize unbound queues or capacity-bound queues with blocking-put, depending on your configuration, and may therefore introduce an overload or blocking situation to your application. You may use the service provider interface as outlined below to manage queue sizes, if required, and to help tune the runtime to your application needs. Consider throttling down the event send rate when the API (see below) indicates that events are getting queued.
All threading options are on the level of a runtime. If you require different threading behavior for certain statements then consider using multiple runtimes, consider using the routeEvent method or consider
using application threads instead.
Please consult Section 17.6.1, “Runtime Settings Related to Concurrency and Threading” for instructions on how to configure threading options. Threading options take effect at runtime initialization time.
With inbound threading a runtime places inbound events in a queue for processing by one or more runtime-managed threads other than the delivering application threads.
The delivering application thread uses one of the sendEventType methods on EPEventService to deliver events or may also use the sendEvent method on a EventSender. The runtime receives the event and places the event into a queue, allowing the delivering thread to continue and not block while the event is being processed and results are delivered.
Events that are sent into the runtime via one of the routeEvent methods are not placed into queue but processed by the same thread invoking the routeEvent operation.
With outbound threading a runtime places outbound events in a queue for delivery by one or more runtime-managed threads other than the processing thread originating the result.
With outbound threading your listener or subscriber class receives statement results from one of the runtime-managed threads in the outbound pool of threads. This is useful when you expect your listener or subscriber code to perform significantly blocking operations and you do not want to hold up event processing.
Note
If outbound-threading is enabled, listeners and subscribers that send events back into the runtime should use thesendEvent method and not the routeEvent method.
With timer execution threading an runtime places time-based work units into a queue for processing by one or more runtime-managed threads other than the internal timer thread or the application thread that sends an external timer event.
Using timer execution threading the internal timer thread (or thread delivering an external timer event) serves to evaluate which time-based work units must be processed. A pool of runtime-managed threads performs the actual processing of time-based work units and thereby offloads the work from the internal timer thread (or thread delivering an external timer event).
Enable this option as a tuning parameter when your statements utilize time-based patterns or data windows. Timer execution threading is fine grained and works on the level of a time-based schedule in combination with a statement.
With route execution threading an runtime identifies event-processing work units based on the event and statement combination. It places such work units into a queue for processing by one or more runtime-managed threads other than the thread that originated the event.
While inbound threading works on the level of an event, route execution threading is fine grained and works on the level of an event in combination with a statement.
The service-provider interface EPRuntimeSPI is an extension API that allows to manage runtime-level queues and thread pools (Extension APIs are subject to change between release versions).
The following code snippet shows how to obtain the BlockingQueue<Runnable> and the ThreadPoolExecutor for the managing the queue and thread pool responsible for inbound threading:
EPRuntimeSPI spi = (EPRuntimeSPI) runtime; int queueSize = spi.getThreadingService().getInboundQueue().size(); ThreadPoolExecutor threadpool = spi.getThreadingService().getInboundThreadPool();
This section discusses the order in which N competing statements that all react to the same arriving event execute.
The runtime, by default, does not guarantee to execute competing statements in any particular order unless using @Priority. We therefore recommend that an application does not rely on the order of execution of statements by the runtime, since that best shields the behavior of an application from changes in the order that statements may get created by your application or by threading configurations that your application may change at will.
If your application requires a defined order of execution of competing statements, use the @Priority EPL syntax to make the order of execution between statements well-defined (requires that you set the prioritized-execution configuration setting). And the @Drop can make a statement preempt all other lowered priority ones that then won't get executed for any matching events.
The runtime processes event by event. It only processes the next event when processing of the current event has completed.
For the purpose of processing event-by-event, the runtime maintains a thread-specific ordered work queue. In the default configuration the order of events in the work queue is dictated by the order of execution of insert-into.
New events get added to the end of the work queue (exceptions highlighted below) unless events have an event-precedence (see below).
The runtime works off each event in the work queue completely, beginning with the oldest event, before processing the next newer event in the work queue.
The runtime processes the current event against all statements completely before delivering results to listeners and subscribers and before processing the next event. This is true regardless whether a given event was sent in via the API or whether the event was produced by a statement and insert-into. The order is:
Process a given event against only those statement context partitions that need to see the event (see information on filter indexes).
Dispatch statement results to listeners and subscribers.
For example, assume three statements named statement-1, statement-2 and statement-3:
@name('statement-1') select * from MyEvent;
@name('statement-2') insert into ABCStream select * from MyEvent;
@name('statement-3') select * from ABCStream;
When a MyEvent event arrives, the order of processing is:
The runtime processes
statement-1andstatement-2in any order (since there is no @priority set, see priority related documentation).For
statement-1the runtime determines whether listeners are attached and if yes buffers the dispatch for delivery to listeners.For
statement-2the runtime determines whether listeners are attached and if yes buffers the dispatch for delivery to listeners. The runtime also produces anABCStreamevent and adds it to the work queue.
The runtime invokes the listeners to
statement-1andstatement-2(default configuration, not considing all threading configurations).The runtime picks up the
ABCStreamevent from the work queue and processesstatement-3.The runtime invokes the listeners to
statement-3.
Among all events generated by insert-into of statements and the events routed into the runtime via the routeEvent method, all events that insert-into a named window or table are processed first in the order generated. All other events are processed thereafter in the order they were generated (except when using event-precedence).
If your application requires a defined order of processing among the events that are generated by insert-into, use the event-precedence syntax. Please see Section 5.10.10, “Insert Into and Event Precedence” and Section 17.6.10.2, “Event-Precedence Execution” for more information.
When enabling timer or route execution threading as explained under advanced threading options then the runtime does not make any guarantee to the processing order except that is will prioritize events inserted into a named window.
There are two modes for a runtime to keep track of time: The internal timer based on JVM system time (the default), and externally-controlled (aka. event time) time giving your application full control over the concept of time within a runtime.
By default the internal timer provides time and evaluates schedules. External clocking i.e. event time can be used to supply time ticks to the runtime instead. The latter is useful for when events themselves provide the time to advance. External clocking also helps in testing time-based event sequences or for synchronizing the runtime with an external time source.
The internal timer relies on the java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor class for time tick events. The next section describes timer resolution for the internal timer, by default set to 100 milliseconds but is configurable via the threading options. When using externally-controlled time the timer resolution is in your control.
To disable the internal timer and use externally-provided time instead, there are two options. The first option is to use the configuration API at runtime initialization time. The second option toggles on and off the internal timer at runtime, via special timer control events that are sent into the runtime like any other event.
If using a timer execution thread pool as discussed above, the internal timer or external time event provide the schedule evaluation however do not actually perform the time-based processing. The time-based processing is performed by the threads in the timer execution thread pool.
Tip
External and internal/system time is the same internally to the runtime thus the runtime behaves the same whether using external or internal timer.
This code snippet shows the use of the configuration API to disable the internal timer and thereby turn on externally-provided time (see the Configuration section for configuration via XML file):
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getRuntime().getThreading().setInternalTimerEnabled(false); EPRuntime runtime = EPRuntimeProvider.getDefaultRuntime(config);
After disabling the internal timer, it is wise to set a defined time so that any statements created thereafter start relative to the time defined. Use the advanceTime method to indicate current time to the runtime
and to move time forward for the runtime (a.k.a application-time model).
This code snippet obtains the current time and advances time:
long timeInMillis = System.currentTimeMillis(); runtime.getEventService().advanceTime(timeInMillis);
To enable or disable the internal timer by API call use the clockExternal and clockInternal methods of EPEventService.
The next code snippet demonstrates toggling to external time:
EPRuntime runtime = EPRuntimeProvider.getDefaultRuntime(); EPEventService eventService = runtime.getEventService(); // switch to external clocking eventService.clockExternal();
The advanceTime method moves the time forward. All aspects of runtime current time related to statements and patterns are driven by the time that your application advances to.
The next example sequence of instructions sets time to zero, then creates a statement, then moves time forward to 1 seconds later and then 6 seconds later:
// Set start time at zero. runtime.getEventService().advanceTime(0); // deploy a module here // sample EPL: select current_timestamp() as ct from pattern[every timer:interval(1 minute)] runtime.getDeploymentService().deploy(compiled); // compiled is a module you compiled earlier // move time forward 1 second runtime.getEventService().advanceTime(1000); // move time forward 5 seconds runtime.getEventService().advanceTime(6000);
When advancing time your application should make sure values are ascending. That is, each time value should be either the same value or a larger value then the prior value provided.
Your application may use the getNextScheduledTime method in EPEventService to determine the earliest time a schedule for any statement requires evaluation.
The following code snippet sets the current time, creates a statement and prints the next scheduled time which is 1 minute later then the current time:
// set start time to the current time.
runtime.getEventService().advanceTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
// deploy a module
// sample EPL: select current_timestamp() as ct from pattern[every timer:interval(1 minute)]
runtime.getDeploymentService().deploy(compiled); // compiled is a module you compiled earlier
// print next schedule time
System.out.println("Next schedule at " + new Date(runtime.getEventService().getNextScheduledTime()));Tip
If you find that your application requires control over time only for specific deployments and not for other deployments, please read up on Section 16.21, “Stages”.
Warning
You may not use advanceTime or advanceTimeSpan to control time when using internal timer since the internal timer tracks system time
and must be the only source of time.
The advanceTime method allows your application to advance runtime time to a given point in time.
In addition, the getNextScheduledTime method in EPEventService returns the next scheduled time according to started statements.
You would typically use advanceTime to advance time at a relatively high resolution i.e. milliseconds or microseconds.
To advance time for a span of time without individual calls to advanceTime the API provides the method advanceTimeSpan. The advanceTimeSpan method can accept a resolution parameter.
If your application provides the target end time of a time span to the advanceTimeSpan method and does not provide a resolution, the runtime advances time up to the target time by stepping through all relevant times according to started statements.
If your application provides the target end time of a time span and in addition a long-typed resolution to the advanceTimeSpan method the runtime advances time up to the target time by incrementing time according to the resolution (regardless of next scheduled time according to started statements).
Consider the following example:
// Set start time to Jan.1, 2010, 00:00 am for this example
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy MM dd HH:mm:ss SSS");
Date startTime = format.parse("2010 01 01 00:00:00 000");
runtime.getEventService().advanceTime(startTime.getTime());
// deploy a module
// sample EPL: select current_timestamp() as ct from pattern[every timer:interval(1 minute)]
runtime.getDeploymentService().deploy(compiled); // compiled is a module you compiled earlier
stmt.addListener(...); // add a listener
// Advance time to 10 minutes after start time
runtime.getEventService().advanceTimeSpan(startTime.getTime() + 10*60*1000));
The above example advances time to 10 minutes after the start time using the advanceTimeSpan method. As the example does not pass a resolution, the runtime advances time according to statement schedules. Upon calling the advanceTimeSpan method the listener sees 10 invocations for minute 1 to minute 10.
To advance time according to a given resolution, you may provide the resolution as shown below:
// Advance time to 10 minutes after start time at 100 msec resolution runtime.getEventService().advanceTimeSpan(startTime.getTime() + 10*60*1000, 100);
Time can have a resolution of either milliseconds or microseconds.
The default time resolution is milliseconds. To configure the runtime for microsecond resolution, please see Section 17.4.14.1, “Time Unit”.
Table 16.7. Time Resolution
| Millisecond | Microsecond | |
|---|---|---|
| Smallest unit for advancing time | 1 millisecond | 1 microsecond |
Equivalent java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit | TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS | TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS |
| Default? | Default | Requires configuration change, see Section 17.4.14.1, “Time Unit” |
| Long-type runtime time represents | Milliseconds since Epoch | Microseconds since Epoch |
| Example: the date Tue, 01 Jan 1980 00:00:00 GMT | 315532800000 | 315532800000000 |
| Support for Internal System Time | Yes | No, requires external time (aka. event time) via advanceTimeSpan or advanceTime |
A few notes on usage of microsecond time unit for time resolution:
The runtime automatically computes time periods into microseconds. For example
1 minute 2 secondsis62000000microseconds (62 * 1000000).The runtime automatically computes time-in-second parameters into microseconds. For example
5.02 secondsis5020000microseconds.The runtime automatically computes ISO schedules, crontabs and hints related to runtime time into microseconds.
The
CurrentTimeSpanEventorCurrentTimeEventevents must provide microsecond values.Date-time methods with long-type input values assume microsecond values.
Date-time methods or other functions that take millisecond parameters or produce millisecond values still consume/produce millisecond values, such as the date-time method
toMillisec.The internal timer must be disabled (
setInternalTimerEnabled(false)) andTimerControlEvent.ClockType.CLOCK_INTERNALcannot be used.
By default the internal timer is enabled and that tracks VM system time. For many use cases your application may want to use event time or external time instead, as discussed above.
The internal timer thread, by default, uses the call System.currentTimeMillis() to obtain system time. Please see the JIRA issue ESPER-191 Support nano/microsecond resolution for more information on Java system time-call performance, accuracy and drift.
The internal timer thread can be configured to use nanosecond time as returned by System.nanoTime(). If configured for nanosecond time, the runtime computes an offset of the nanosecond ticks to wall clock time upon startup to present back an accurate millisecond wall clock time.
Please see section Section 17.6.6, “Runtime Settings Related to Time Source” to configure the internal timer thread to use System.nanoTime().
The internal timer is based on java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor and that generally provides high accuracy VM time
(java.util.Timer does not support high accuracy VM time).
You may register one or more exception handlers for the runtime to invoke in the case it encounters an exception processing a continuously-executing statement. By default and without exception handlers the runtime cancels execution of the current statement that encountered the exception, logs the exception and continues to the next statement, if any. The configuration is described in Section 17.6.11, “Runtime Settings Related to Exception Handling”.
If your application registers exception handlers as part of runtime configuration, the runtime invokes the exception handlers in the order they are registered passing relevant exception information such as statement name, expression and the exception itself.
Exception handlers receive any statement unchecked exception such as internal exceptions or exceptions thrown by plug-in aggregation functions or plug-in data windows. The runtime does not provide to exception handlers any exceptions thrown by static method invocations for function calls, method invocations in joins, methods on variables and event classes and listeners or subscriber exceptions.
An exception handler can itself throw a runtime exception to cancel execution of the current event against any further statements.
Note
Exceptions are meant to indicate an actual unexpected problem.
We do not recommend explicitly throwing exceptions for the purpose of flow control, preempting execution or other normal situations.
The runtime does not guarantee that throwing an exception has no other side effect and the runtime may not roll back changes that are already made to state.
For fire-and-forget queries the API indicates any exception directly back to the caller without the exception handlers being invoked, as exception handlers apply to statements only. The same applies to any API calls other than sendEvent and the EventSender methods.
As the configuration section describes, your application registers one or more classes that implement the ExceptionHandlerFactory interface in the runtime configuration. Upon runtime initialization the runtime obtains a factory instance from the class name that then provides the exception handler instance. The exception handler class must implement the ExceptionHandler interface.
You may register one or more condition handlers for the runtime to invoke in the case it encounters certain conditions, as outlined below, when executing a statement. By default and without condition handlers the runtime logs the condition at informational level and continues processing. The configuration is described in Section 17.6.12, “Runtime Settings Related to Condition Handling”.
If your application registers condition handlers as part of runtime configuration, the runtime invokes the condition handlers in the order they are registered passing relevant condition information such as statement name, expression and the condition information itself.
Currently the only conditions indicated by this facility are raised by the pattern followed-by operator, see Section 7.5.8.1, “Limiting Sub-Expression Count” and see Section 7.5.8.2, “Limiting Runtime-Wide Sub-Expression Count”.
A condition handler may not itself throw a runtime exception or return any value.
As the configuration section describes, your application registers one or more classes that implement the ConditionHandlerFactory interface in the runtime configuration. Upon runtime initialization the runtime obtains a factory instance from the class name that then provides the condition handler instance. The condition handler class must implement the ConditionHandler interface.
The runtime can report key processing metrics through the JMX platform mbean server by setting a single configuration flag described in Section 17.6.7, “Runtime Settings Related to JMX Metrics”. For additional detailed reporting and metrics events, please read on.
Metrics reporting is a feature that allows an application to receive ongoing reports about key runtime-level and statement-level metrics. Examples are the number of incoming events, the CPU time and wall time taken by statement executions or the number of output events per statement.
Metrics reporting is, by default, disabled. To enable reporting, please follow the steps as outlined in Section 17.6.8, “Runtime Settings Related to Metrics Reporting”. Metrics reporting must be enabled at runtime initialization time. The EPMetricsService interface, available from the runtime API, provides current metrics and provides control over reporting intervals.
Your application can receive metrics at configurable intervals via statement. A metric datapoint is simply a well-defined event. The events are RuntimeMetric and StatementMetric and the Java class representing the events can be found in the client API in package com.espertech.esper.common.client.metric.
Since metric events are processed by the runtime the same as application events, your EPL may use any construct on such events. For example, your application may select, filter, aggregate properties, sort or insert into a stream, named window or table all metric events the same as application events.
This example statement selects all runtime metric events:
select * from com.espertech.esper.common.client.metric.RuntimeMetric
The next statement selects all statement metric events:
select * from com.espertech.esper.common.client.metric.StatementMetric
The next statement selects all metric events:
select * from com.espertech.esper.common.client.metric.MetricEvent
Make sure to have metrics reporting enabled since only then do listeners or subscribers to a statement such as above receive metric events.
The runtime provides metric events after the configured interval of time has passed. By default, only started statements that have activity within an interval (in the form of event or timer processing) are reported upon.
The default configuration performs the publishing of metric events in an Esper daemon thread under the control of the runtime instance. Metrics reporting honors externally-supplied time, if using external timer events.
Via runtime configuration options provided by EPMetricsService, your application may enable and disable metrics reporting globally, provided that metrics reporting was enabled at initialization time. Your application may also enable and disable metrics reporting for individual statements by statement name.
Statement groups is a configuration feature that allows to assigning reporting intervals to statements. Statement groups are described further in the Section 17.6.8, “Runtime Settings Related to Metrics Reporting” section. Statement groups cannot be added or removed at runtime.
The following limitations apply:
If your Java VM version does not report current thread CPU time (most JVM do), then CPU time is reported as zero (use
ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean().isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported()to determine if your JVM supports this feature).Note: In some JVM the accuracy of CPU time returned is very low (in the order of 10 milliseconds off) which can impact the usefulness of CPU metrics returned. Consider measuring CPU time in your application thread after sending a number of events in the same thread, external to the runtime as an alternative.
Your Java VM may not provide high resolution time via
System.nanoTime. In such case wall time may be inaccurate and inprecise.CPU time and wall time have nanosecond precision but not necessarily nanosecond accuracy, please check with your Java VM provider.
There is a performance cost to collecting and reporting metrics.
Not all statements may report metrics: The runtime performs certain runtime optimizations sharing resources between similar statements, thereby not reporting on certain statements.
Runtime metrics are properties of RuntimeMetric events:
Table 16.8. RuntimeMetric Properties
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| runtimeURI | The URI of the runtime. |
| timestamp | The current runtime time. |
| inputCount | Cumulative number of input events since runtime initialization time. Input events are defined as events send in via application threads as well as insert into events. |
| inputCountDelta | Number of input events since last reporting period. |
| scheduleDepth | Number of outstanding schedules. |
Statement metrics are properties of StatementMetric. The properties are:
Table 16.9. StatementMetric Properties
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| runtimeURI | The URI of the runtime. |
| timestamp | The current runtime time. |
| statementName | Statement name. |
| cpuTime | Statement processing CPU time (system and user) in nanoseconds (if available by Java VM, obtained from ThreadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime). |
| wallTime | Statement processing wall time in nanoseconds (based on System.nanoTime). |
| numInput | Number of input events to the statement. |
| numOutputIStream | Number of insert stream rows output to listeners or the subscriber, if any. |
| numOutputRStream | Number of remove stream rows output to listeners or the subscriber, if any. |
The totals reported are cumulative relative to the last metric report.
Enterprise Edition has a library for measuring and reporting memory use for a runtime.
The runtime can report key processing metrics through the JMX platform mbean server by setting a single configuration flag described in Section 17.6.7, “Runtime Settings Related to JMX Metrics”.
Runtime and statement-level metrics reporting is described in Section 16.12, “Runtime and Statement Metrics Reporting”.
The easiest way to see thread contentions is by using VisualVM when Esper is under load and looking at the Threads tab. In the worst case you will see a lot of red color in VisualVM. The red line in VisualVM shows the threads that are either in a monitor region or waiting in an entry set for the monitor. The monitor is the mechanism that Java uses to support synchronization. When a statement is stateful the runtime manages the state using a monitor (lock) per context partition.
A JVM profiler can be handy to see how much CPU is spent in Esper by the sendEvent method.
The jconsole can provide information on the JVM heap. If memory gets tights the performance can drop significantly.
The EPRenderEventService interface offers methods to render events as XML or JSON. Obtain the service from a runtime by calling getRenderEventService on EPRuntime.
Your application may use the built-in XML and JSON formatters to render output events into a readable textual format, such as for integration or debugging purposes. This section introduces the utility classes in the client util package for rendering events to strings. Further API information can be found in the JavaDocs.
For repeated rendering of events of the same event type or subtypes, it is recommended to obtain a JSONEventRenderer or XMLEventRenderer instance and use the render method provided by the interface. This allows the renderer implementations to cache event type metadata for fast rendering.
This example shows how to obtain a renderer for repeated rendering of events of the same type, assuming that statement is an instance of EPStatement:
JSONEventRenderer jsonRenderer = runtime.getRenderEventService().getJSONRenderer(statement.getEventType());
Assuming that event is an instance of EventBean, this code snippet renders an event into the JSON format:
String jsonEventText = jsonRenderer.render("MyEvent", event);The XML renderer works the same:
XMLEventRenderer xmlRenderer = runtime.getRenderEventService().getXMLRenderer(statement.getEventType());
...and...
String xmlEventText = xmlRenderer.render("MyEvent", event);If the event type is not known in advance or if your application does not want to obtain a renderer instance per event type for fast rendering, your application can use one of the following methods to render an event to a XML or JSON textual format:
String json = runtime.getRenderEventService().renderJSON(event); String xml = runtime.getRenderEventService().renderXML(event);
Use the JSONRenderingOptions or XMLRenderingOptions classes to control how events are rendered. To render specific event properties using a custom event property renderer, specify an EventPropertyRenderer as part of the options
that renders event property values to strings. Please see the JavaDoc documentation for more information.
The JSON renderer produces JSON text according to the standard documented at http://www.json.org.
The renderer formats simple properties as well as nested properties and indexed properties according to the JSON string encoding, array encoding and nested object encoding requirements.
The renderer does render indexed properties, it does not render indexed properties that require an index, i.e. if your event representation is backed by POJO objects and your getter method is getValue(int index), the indexed property values are not part of the JSON text. This is because the implementation has no way to determine how many index keys there are. A workaround is to have a method such as Object[] getValue() instead.
The same is true for mapped properties that the renderer also renders. If a property requires a Map key for access, i.e. your getter method is getValue(String key), such property values are not part of the result text as there is no way for the implementation to determine the key set.
The XML renderer produces well-formed XML text according to the XML standard.
The renderer can be configured to format simple properties as attributes or as elements. Nested properties and indexed properties are always represented as XML sub-elements to the root or parent element.
The root element name provided to the XML renderer must be the element name of the root in the XML document and may include namespace instructions.
The renderer does render indexed properties, it does not render indexed properties that require an index, i.e. if your event representation is backed by POJO objects and your getter method is getValue(int index), the indexed property values are not part of the XML text. This is because the implementation has no way to determine how many index keys there are. A workaround is to have a method such as Object[] getValue() instead.
The same is true for mapped properties that the renderer also renders. If a property requires a Map key for access, i.e. your getter method is getValue(String key), such property values are not part of the result text as there is no way for the implementation to determine the key set.
A plug-in loader is for general use with input adapters, output adapters or EPL code deployment or any other task that can benefits from being part of an Esper configuration file and that follows runtime lifecycle.
A plug-in loader implements the com.espertech.esper.runtime.client.plugin.PluginLoader interface and can be listed in the configuration.
Each configured plug-in loader follows the runtime instance lifecycle: When an runtime instance initializes, it instantiates each PluginLoader implementation class listed in the configuration. The runtime then invokes the lifecycle
methods of the PluginLoader implementation class before and after the runtime is fully initialized and before an runtime instance is destroyed.
Declare a plug-in loader in your configuration XML as follows:
...
<plugin-loader name="MyLoader" class-name="org.mypackage.MyLoader">
<init-arg name="property1" value="val1"/>
</plugin-loader>
...Alternatively, add the plug-in loader via the configuration API:
Configuration config = new Configuration();
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("property1", "value1");
config.getRuntime().addPluginLoader("MyLoader", "org.mypackage.MyLoader", props);
Implement the init method of your PluginLoader implementation to receive
initialization parameters. The runtime invokes this method before the runtime is fully initialized, therefore your implementation
should not yet rely on the runtime instance within the method body:
public class MyPluginLoader implements PluginLoader {
public void init(String loaderName, Properties properties, EPRuntime runtime) {
// save the configuration for later, perform checking
}
...
The runtime calls the postInitialize method once the runtime completed initialization
and to indicate the runtime is ready for traffic.
public void postInitialize() {
// Start the actual interaction with external feeds or the runtime here
}
...
The runtime calls the destroy method once the runtime is destroyed or initialized for a second time.
public void destroy() {
// Destroy resources allocated as the runtime instance is being destroyed
}
To access the plug-in at runtime, the getContext method provides access under the name plugin-loader/name:
runtime.getContext().getEnvironment().get("plugin-loader/MyLoader");This chapter discusses how to select context partitions. Contexts are discussed in Chapter 4, Context and Context Partitions and the reasons for context partition selection are introduced in Section 4.10, “Operations on Specific Context Partitions”.
The section is only relevant when you declare a context. It applies to all different types of hash, partitioned, category, overlapping or other temporal contexts. The section uses a category context for the purpose of illustration. The API discussed herein is general and handles all different types of contexts including nested contexts.
Consider a category context that separates bank transactions into small, medium and large:
// declare category context create context TxnCategoryContext group by amount < 100 as small, group by amount between 100 and 1000 as medium, group by amount > 1000 as large from BankTxn
// retain 1 minute of events of each category separately context TxnCategoryContext select * from BankTxn#time(1 minute)
In order for your application to iterate one or more specific categories it is necessary to identify which category, i.e. which context partition, to iterate. Similarly for fire-and-forget queries, to execute fire-and-forget queries against one or more specific categories, it is necessary to identify which context partition to execute the fire-and-forget query against.
Your application may iterate one or more specific context partitions using either the iterate or safeIterate method of EPStatement by providing an implementation of the ContextPartitionSelector interface.
For example, assume your application must obtain all bank transactions for small amounts. It may use the API to identify the category and iterate the associated context partition:
ContextPartitionSelectorCategory categorySmall = new ContextPartitionSelectorCategory() {
public Set<String> getLabels() {
return Collections.singleton("small");
}
};
Iterator<EventBean> it = stmt.iterator(categorySmall);
Your application may execute fire-and-forget queries against one or more specific context partitions by using the executeQuery method on EPRuntime or the execute method on EPFireAndForgetPreparedQuery and by providing an implementation of ContextPartitionSelector.
Fire-and-forget queries execute against named windows and tables, therefore below statement creates a named window which the runtime manages separately for small, medium and large transactions according to the context declared earlier:
// Named window per category context TxnCategoryContext create window BankTxnWindow#time(1 min) as BankTxn
The following code demonstrates how to fire a fire-and-forget query against the small and the medium category:
ContextPartitionSelectorCategory categorySmallMed = new ContextPartitionSelectorCategory() {
public Set<String> getLabels() {
return new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList("small", "medium"));
}
};
runtime.getFireAndForgetService().executeQuery(
"select count(*) from BankTxnWindow",
new ContextPartitionSelector[] {categorySmallMed});The following limitations apply:
Fire-and-forget queries may not join named windows or tables that declare a context.
This section summarizes the selector interfaces that are available for use to identify and interrogate context partitions. Please refer to the JavaDoc documentation for package com.espertech.esper.common.client.context and classes therein for additional information.
Use an implementation of ContextPartitionSelectorAll or the ContextPartitionSelectorAll.INSTANCE object to instruct the runtime to consider all context partitions.
Use an implementation of ContextPartitionSelectorById if your application knows the context partition ids to query. This selector instructs the runtime to consider only those provided context partitions based on their integer id value. The runtime outputs the context partition id in the built-in property context.id.
Use an implementation of ContextPartitionSelectorFiltered to receive and interrogate context partitions. Use the filter method that receives a ContextPartitionIdentifier to return a boolean indicator whether to include the context partition or not. The ContextPartitionIdentifier provides information about each context partition. Your application may not retain ContextPartitionIdentifier instances between filter method invocations as the runtime reuses the same instance. This selector is not supported with nested contexts.
Use an implementation of ContextPartitionSelectorCategory with category contexts.
Use an implementation of ContextPartitionSelectorSegmented with keyed segmented contexts.
Use an implementation of ContextPartitionSelectorHash with hash segmented contexts.
Use an implementation of ContextPartitionSelectorNested in combination with the selectors described above with nested contexts.
This chapter briefly discusses the API to manage context partitions. Contexts are discussed in Chapter 4, Context and Context Partitions.
The section is only relevant when you declare a context. It applies to all different types of hash, partitioned, category, overlapping or other temporal contexts.
The EPContextPartitionService interface offers methods to manage context partitions. Obtain the service from a runtime by calling getContextPartitionService on EPRuntime.
The context partition admin API allows an application to:
Interrogate the state and identifiers for existing context partitions.
Determine statements associated to a context and context nesting level.
Receive a callback when new contexts get created and destroyed or when context partitions are allocated and de-allocated.
Obtain context properties.
Please see the JavaDoc documentation for more information.
Esper offers a listener and an assertions class to facilitate automated testing of EPL rules, for example when using a test framework such as JUnit or TestNG.
Esper does not require any specific test framework. If your application has the JUnit test framework in classpath Esper uses junit.framework.AssertionFailedError to indicate assertion errors, so as to integrate with continuous integration tools.
For detailed method-level information, please consult the JavaDoc of the package com.espertech.esper.common.client.scopetest and com.espertech.esper.runtime.client.scopetest.
The class com.espertech.esper.common.client.scopetest.EPAssertionUtil provides methods to assert or compare event property values as well as perform various array arthithmatic, sort events and convert events or iterators to arrays.
The class com.espertech.esper.runtime.client.scopetest.SupportUpdateListener provides an UpdateListener implementation that collects events and returns event data for assertion.
The class com.espertech.esper.runtime.client.scopetest.SupportSubscriber provides a subscriber implementation that collects events and returns event data for assertion. The SupportSubscriberMRD is a subscriber that accepts events multi-row delivery. The SupportSubscriber and SupportSubscriberMRD work similar to SupportUpdateListener that is introduced in more detail below.
The below table only summarizes the most relevant assertion methods offered by EPAssertionUtil. Methods provide multiple footprints that are not listed in detail below. Please consult the JavaDoc for additional method-level information.
Table 16.10. Method Summary for EPAssertionUtil
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
assertProps | Methods that assert that property values of a single |
assertPropsPerRow | Methods that assert that property values of multiple |
assertPropsPerRowAnyOrder | Same as above, but any row may match. Useful for unordered result sets. |
assertEqualsExactOrder | Methods that compare arrays, allowing |
assertEqualsAnyOrder | Same as above, but any row may match. Useful for unordered result sets. |
The below table only summarizes the most relevant methods offered by SupportUpdateListener. Please consult the JavaDoc for additional information.
Table 16.11. Method Summary for SupportUpdateListener
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
reset | Initializes listener clearing current events and resetting the invoked flag. |
getAndClearIsInvoked | Returns the "invoked" flag indicating the listener has been invoked, and clears the flag. |
getLastNewData | Returns the last events received by the listener. |
getAndResetDataListsFlattened | Returns all events received by the listener as a pair. |
assertOneGetNewAndReset | Asserts that exactly one new event was received and no removed events, returns the event and resets the listener. |
assertOneGetNew | Asserts that exactly one new event was received and returns the event. |
The next code block is a short but complete programming example that asserts that the properties received from output events match expected value.
String epl = "select personName, count(*) as cnt from PersonEvent#length(3) group by personName";
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType(PersonEvent.class);
CompilerArguments compilerArguments = new CompilerArguments(configuration);
EPCompiled compiled = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler().compile(stmt, compilerArguments);
EPRuntime runtime = EPRuntimeProvider.getDefaultRuntime(configuration);
EPStatement stmt = runtime.getDeploymentService().deploy(compiled).getStatements()[0];
SupportUpdateListener listener = new SupportUpdateListener();
stmt.addListener(listener);
runtime.getEventService().sendEventBean(new PersonEvent("Joe"), "PersonEvent");
EPAssertionUtil.assertProps(listener.assertOneGetNewAndReset(), "personName,cnt".split(","),
new Object[]{"Joe", 1L});A few additional examples are shown below:
String[] fields = new String[] {"property"};
EPAssertionUtil.assertPropsPerRow(listener.getAndResetDataListsFlattened(), fields,
new Object[][]{{"E2"}}, new Object[][]{{"E1"}});EPAssertionUtil.assertPropsPerRow(listener.getAndResetLastNewData(), fields,
new Object[][]{{"E1"}, {"E2"}, {"E3"}});assertTrue(listener.getAndClearIsInvoked());
Please refer to the Esper codebase test sources for more examples using the assertion class and the listener class.
The configuration object (Configuration), in respect to classes, holds the fully-qualified class name and does not generally hold Class references.
This is by design since the configuration object can be populated from XML.
When deploying compiled modules the runtime may use a class loader to find resources. Your application has full control over class-for-name and classloader use. OSGi environments can provide a specific class-for-name and class loader. Please refer to Section 17.7, “Passing Services or Transient Objects”.
A compiler and runtime can well be deployed as part of a J2EE web or enterprise application archive to a web application server. When designing for deployment into a J2EE web application server, please consider the items discussed here.
We provide a sample servlet context listener in this section that uses the deployment API to deploy and undeploy modules as part of the servlet lifecycle.
The distribution provides a message-driven bean (MDB) example that you may find useful.
Esper does not have a dependency on any J2EE or Servlet APIs to allow the runtime to run in any environment or container.
As multiple web applications deployed to a J2EE web application server typically have a separate classloader per application, you should consider whether runtime instances need to be shared between applications or can remain separate runtime instances. Consider the EPRuntimeProvider a Singleton.
When deploying multiple web applications, your J2EE container classloader may provide a separate instance of the Singleton EPRuntimeProvider to each web application resulting in multiple independent runtime instances.
To share EPRuntime instances between web applications, one approach is to add the runtime jar files to the system classpath. A second approach can be to have multiple web applications share the same servet context and have your application place the EPRuntime instance into a servlet context attribute for sharing. Architecturally you may also consider a single archived application (such as an message-driven bean) that all your web applications communicate to via the JMS broker provided by your application server or an external JMS broker.
As per J2EE standards there are restrictions in regards to starting new threads in J2EE application code. Esper adheres to these restrictions: It allows to be driven entirely by external events. To remove all Esper threads, set the internal timer off and leave the advanced threading options turned off. To provide timer events when the internal timer is turned off, you should check with your J2EE application container for support of the Java system timer or for support of batch or work loading to send timer events to an runtime instance.
As per J2EE standards there are restrictions in regards to input and output by J2EE application code. Esper adheres to these restrictions: By itself it does not start socket listeners or performs any file IO.
When deploying a J2EE archive that contains EPL modules files below is sample code to read and deploy EPL modules files packaged with the enterprise or web application archive when the servlet initializes. The sample undeploys EPL modules when the servlet context gets destroyed.
A sample web.xml configuration extract is:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app>
<listener>
<listener-class>SampleServletListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>eplmodules</param-name>
<param-value>switchmonitor.epl</param-value>
</context-param>
</web-app>A sample servet listener that deploys EPL module files packaged into the archive on context initialization and that undeploys when the application server destroys the context is shown here:
public class SampleServletListener implements ServletContextListener {
private List<String> deploymentIds = new ArrayList<String>();
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
try {
String modulesList = servletContextEvent.getServletContext().getInitParameter("eplmodules");
List<Module> modules = new ArrayList<Module>();
if (modulesList != null) {
String[] split = modulesList.split(",");
for (int i = 0; i < split.length; i++) {
String resourceName = split[i].trim();
if (resourceName.length() == 0) {
continue;
}
String realPath = servletContextEvent.getServletContext().getRealPath(resourceName);
Module module = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler().readModule(new File(realPath));
modules.add(module);
}
}
// Determine deployment order
ModuleOrder order = ModuleOrderUtil.getModuleOrder(modules, null);
// Deploy
for (Module module : order.getOrdered()) {
// compile and deploy here (code not included), add deployment id
deploymentIds.add(deployment.getDeploymentId());
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
EPRuntime runtime = EPRuntimeProvider.getDefaultRuntime();
for (String deploymentId : deploymentIds) {
runtime.getDeploymentService().undeploy(deploymentId);
}
}
}An Esper stage is its own little container that can host deployments.
A stage processes only those events that an application sends into that stage. A stage does not see any events that an application sends into the runtime.
A stage has its own stage time. Time in a stage advances only when an application advances time for that stage. A stage advance times independently of runtime time.
Each stage is uniquely identified by a stage URI. Within different runtimes there can be stages of the same stage URI. A stage lives within the runtime instance and gets destroyed when the runtime gets destroyed. An application can allocate any number of stages. A stage URI can be any non-null string value.
These attributes make stages useful for:
Suspend and Resume. Suspend deployments so they don't receive events or don't advance time. Resume deployments when they are needed again.
Initialize, Load, or Catch-Up new Deployments to Existing Event and Time History. Stage deployments and replay events and time until deployments have caught up with history, and then unstage deployments to have them receive runtime events and time.
Replay. Replay events and time, receive results, destroy accumulated state, without affecting other deployments and in parallel to other activity.
In other words, a stage allows an application to control event visibility and the concept of time as desired on a deployment level: Events sent into a stage are visible only to those deployments that are staged and are not visible to deployments outside of that stage. Within a stage an application can control time independently, start time at a point in time and advance time at the resolution and pace suitable for the deployments added to that stage.
The getStageService method on EPRuntime returns the service for managing stages:
EPStageService stageService = runtime.getStageService();
To allocate a stage or obtain an already-allocated stage, use getStage and pass the stage URI. The new stage current time is the runtime current time.
EPStage stage = stageService.getStage("myStage");
The EPStage instance represents the stage. The freshly-allocated stage is empty.
The stage method moves deployments from the runtime to the stage (assume deploymentId is a deployment id of an existing deployment):
stage.stage(Collections.singletonList(deploymentId));
A given deployment is either currently staged or un-staged. The same deployment is never both staged and un-staged.
The unstage method moves deployments from the stage to the runtime:
stage.unstage(Collections.singletonList(deploymentId));
To send events to the stage, use EPStageEventService which extends the EPEventService interface:
stage.getEventService().sendEventBean(new Order(...), "Order");
To advance time for a stage, also use EPStageEventService:
stage.getEventService().advanceTime(myTimeInMillis);
Finally, call destroy to destroy the stage. Destroy requires that the stage is empty, i.e. does not have any deployments:
stage.destroy();
By staging deployments, the deployments' time and event processing occurs only when the application explicitly sends events to the stage or advances time for that stage.
The example code below compiles and deploys EPL that reports order events:
String module =
"@public @buseventtype create schema OrderEvent(price double);\n" +
"@name('All-Order-Events') select * from OrderEvent;\n";
EPCompiled compiled = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler().compile(module, null);
EPRuntime runtime = EPRuntimeProvider.getDefaultRuntime();
EPDeployment deployment = runtime.getDeploymentService().deploy(compiled);
deployment.getStatements()[0].addListener(new SupportUpdateListener());
The stage method stages the deployment:
EPStage stage = runtime.getStageService().getStage("myStage");
stage.stage(Collections.singletonList(deployment.getDeploymentId()));
The staged deployment only receives OrderEvent events that an application send into the stage. It does not receive OrderEvent events that an application sends into the runtime (the EPEventService returned by getEventService of EPRuntime). For example:
// The listener receives the following event
stage.getEventService().sendEventMap(Collections.singletonMap("price", 100d), "OrderEvent");
// The listener DOES NOT receive the following event
runtime.getEventService().sendEventMap(Collections.singletonMap("price", 200d), "OrderEvent");
The unstage method un-stages the deployment:
stage.unstage(Collections.singletonList(deployment.getDeploymentId()));
The un-staged deployment only receives OrderEvent events that an application sends into the runtime. It does not receive OrderEvent events that an application sends into the stage. For example:
// The listener DOES NOT receive the following event
stage.getEventService().sendEventMap(Collections.singletonMap("price", 100d), "OrderEvent");
// The listener receives the following event
runtime.getEventService().sendEventMap(Collections.singletonMap("price", 200d), "OrderEvent");Finally, destroy the stage when it is no longer needed:
stage.destroy();
When staging and unstaging, existing schedules are adjusted for the time difference between stage and runtime, if any.
For example, assume a pattern pattern[timer:interval(10 minutes)] deployed at 9:00:00, which would fire at 9:10:00.
If the time of the target is 8:55:00 or 9:05:00 the pattern still fires at 9:10:00. If the time of the target is after, for example 9:15:00, the pattern fires when time advances again.
Staging and un-staging deployments is an inexpensive operation in general.
When using advanced threading options, each stage has its own threading i.e. its own thread pool and queues.
Each stage has its own metrics reporting, when enabled.
Stage use the some configuration values as provided for the runtime.
Deployments that have dependencies on other deployments require additional consideration. Such deployments may provide EPL objects to other deployments, and deployments may consume EPL objects from other deployments. For example, a deployment may create a named window and another deployment may query the named window.
When staging deployments that have dependencies on other deployments, such EPL-object-providing or EPL-object-consuming deployments must also be staged or unstaged in the same operation.
- 17.1. Overview
- 17.2. Programmatic Configuration
- 17.3. Configuration via XML File
- 17.4. Configuration Common
- 17.4.1. Annotation Class and Package Imports
- 17.4.2. Class and Package Imports
- 17.4.3. Events Represented by Classes
- 17.4.4. Events Represented by java.util.Map
- 17.4.5. Events Represented by Object[] (Object-array)
- 17.4.6. Events Represented by JSON
- 17.4.7. Events Represented by Avro GenericData.Record
- 17.4.8. Events Represented by org.w3c.dom.Node
- 17.4.9. Event Type Defaults
- 17.4.10. Event Type Import Package (Event Type Auto-Name)
- 17.4.11. From-Clause Method Invocation
- 17.4.12. Relational Database Access
- 17.4.13. Common Settings Related to Logging
- 17.4.14. Common Settings Related to Time Source
- 17.4.15. Variables
- 17.4.16. Variant Stream
- 17.5. Configuration Compiler
- 17.5.1. Compiler Settings Related to Byte Code Generation
- 17.5.2. Compiler Settings Related to View Resources
- 17.5.3. Compiler Settings Related to Logging
- 17.5.4. Compiler Settings Related to Stream Selection
- 17.5.5. Compiler Settings Related to Language and Locale
- 17.5.6. Compiler Settings Related to Expression Evaluation
- 17.5.7. Compiler Settings Related to Scripts
- 17.5.8. Compiler Settings Related to Execution of Statements
- 17.5.9. Compiler Settings Related to Serializers and Deserializers
- 17.6. Configuration Runtime
- 17.6.1. Runtime Settings Related to Concurrency and Threading
- 17.6.2. Runtime Settings Related to Logging
- 17.6.3. Runtime Settings Related to Variables
- 17.6.4. Runtime Settings Related to Patterns
- 17.6.5. Runtime Settings Related to Match-Recognize
- 17.6.6. Runtime Settings Related to Time Source
- 17.6.7. Runtime Settings Related to JMX Metrics
- 17.6.8. Runtime Settings Related to Metrics Reporting
- 17.6.9. Runtime Settings Related to Expression Evaluation
- 17.6.10. Runtime Settings Related to Execution of Statements
- 17.6.11. Runtime Settings Related to Exception Handling
- 17.6.12. Runtime Settings Related to Condition Handling
- 17.7. Passing Services or Transient Objects
- 17.8. Type Names
- 17.9. Logging Configuration
Compile-time and runtime configuration is entirely optional. The compiler and runtime work out-of-the-box without configuration.
All configuration lives in the Configuration class (com.espertech.esper.common.client.configuration.Configuration).
The configuration class has configure methods that can read configuration XML and that add the information contained in the XML to the configuration. You can read multiple XML sources additively.
A configuration has three sections:
The common section with configuration that both the compiler and the runtime may use, represented by the
ConfigurationCommonclass.The compiler section, which provides configuration for use only by the compiler, represented by the
ConfigurationCompilerclass.The runtime section, which provides configuration for use only by the runtime, represented by the
ConfigurationRuntimeclass.
Configuration is an initialization-time object. The compiler does not retain any association back to configuration.
The runtime makes a deep copy of the configuration object available (see getConfigurationDeepCopy on EPRuntime)
but the configuration object cannot be changed once provided to the runtime.
You may obtain a Configuration instance by instantiating it directly and adding or setting values on it.
The following example code adds a preconfigured event type and adds an import to the common section of the configuration.
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("PriceLimit", PriceLimit.class.getName());
configuration.getCommon().addImport("org.mycompany.mypackage.MyUtility");
The above example adds a preconfigured event type. For adding an event type at runtime please use create schema.
In addition to programmatic configuration, or as an alternative approach, you may specify configuration items in XML files.
The default name for the XML configuration file is esper.cfg.xml. The configuration class reads this file from the root of the CLASSPATH as an application resource via the configure method.
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); configuration.configure();
The Configuration class can read the XML configuration file from other sources as well. The configure method accepts URL, File and String filename parameters.
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.configure("myconfigfile.esper.cfg.xml");
The schema for the configuration file can be found in the etc folder and is named esper-configuration-majorversion-0.xsd.
The schema is available online at http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper/esper-configuration-majorversion-0.xsd so that a tool can fetch it automatically.
The namespace is http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper.
You can use the XML schema file to validate that your XML configuration file is valid.
Here is an example configuration file.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<esper-configuration xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper
http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper/esper-configuration-8-0.xsd">
<common>
<event-type name="PriceLimit" class="com.espertech.esper.example.stockticker.event.PriceLimit"/>
<auto-import import-name="org.mycompany.mypackage.MyUtility"/>
</common>
</esper-configuration>The common section of the configuration applies to the compiler and also applies to the runtime.
If your application has certain classes or packages that should only be visible within an @-annotation,
you may add these to the annotation imports list. Such classes are only visible when used in an annotation and not elsewhere.
In a XML configuration file the auto-import-annotation configuration may look as below:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<auto-import-annotations import-name="com.mycompany.mypackage.myannotations.*"/>
</common>
</esper-configuration>Here is an example of providing annotation-only imports via the API:
Configuration config = new Configuration();
// package import, only visible for annotation use
config.getCommon().addAnnotationImport("com.mycompany.mypackage.myannotations.*");EPL allows invocations of static Java library functions in expressions, as outlined in Section 10.1, “Single-Row Function Reference”. This configuration item can be set to allow a partial rather than a fully qualified class name in such invocations. The imports work in the same way as in Java files, so both packages and classes can be imported.
select Math.max(priceOne, PriceTwo) // via configuration equivalent to select java.lang.Math.max(priceOne, priceTwo)
EPL auto-imports the following Java library packages. Any additional imports that are specified in configuration files or through the API are added to the configuration in addition to the imports below.
java.lang.*
java.math.*
java.text.*
java.util.*
In a XML configuration file the auto-import configuration may look as below:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<auto-import import-name="com.mycompany.mypackage.*"/>
<auto-import import-name="com.mycompany.myapp.MyUtilityClass"/>
</common>
</esper-configuration>Here is an example of providing imports via the API:
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.getCommon().addImport("com.mycompany.mypackage.*"); // package import
config.getCommon().addImport("com.mycompany.mypackage.MyLib"); // class importThis section is relevant if you want to use regular classes to represent events.
The runtime can process event objects via the sendEventBean(Object event, String eventTypeName) method on the EPEventService interface.
For JavaBean-style classes that have getter methods please specify an event type name and the class name or class. Interfaces and abstract classes are also supported.
The below sample XML configures an event type named StockTick and provides the fully-qualified class name.
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-type name="StockTick" class="com.espertech.esper.example.stockticker.event.StockTick"/>
</common>
</esper-configuration>The sample code for the configuration is:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("StockTick", StockTick.class.getName());Or alternatively:
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("StockTick", StockTick.class);Warning
When using superclasses and interfaces, the order in which event types are added does matter. Please refer to Section D.6, “Superclasses and Interfaces”.
You can use this setting herein when method and member variable names in your Java class do not adhere to the JavaBean convention - any public methods and public member variables can be exposed as event properties via the below configuration.
A Java class can optionally be configured with an accessor style attribute. This attribute instructs the compiler how it should expose methods and fields for use as event properties in statements.
Table 17.1. Accessor Styles
| Style Name | Description |
|---|---|
javabean | As the default setting, the compiler exposes an event property for each public method following the JavaBean getter-method conventions |
public | The compiler exposes an event property for each public method and public member variable of the given class |
explicit | The compiler exposes an event property only for the explicitly configured public methods and public member variables |
For NEsper .NET accessor styles are NATIVE, PUBLIC and EXPLICIT.
Using the public setting for the accessor-style attribute instructs the compiler to expose an event property for each public method and public member variable of a Java class. The compiler assigns event property names of the same name as the name of the method or member variable in the Java class.
For example, assuming the class MyLegacyEvent exposes a method named readValue and a member variable named myField, you can then use properties as shown.
select readValue, myField from MyLegacyEvent
Using the explicit setting for the accessor-style attribute requires that event properties are declared via configuration. This is outlined in the next chapter.
When configuring a compiler or runtime from a XML configuration file, the XML snippet below demonstrates the use of the legacy-type element and the accessor-style attribute.
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-type name="MyLegacyEvent" class="com.mycompany.mypackage.MyLegacyEventClass">
<legacy-type accessor-style="public"/>
</event-type>
</common>
</esper-configuration>When configuring an compiler or runtime via Configuration API, the sample code below shows how to set the accessor style.
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
ConfigurationCommonEventTypeBean legacyDef = new ConfigurationCommonEventTypeBean();
legacyDef.setAccessorStyle(AccessorStyle.PUBLIC);
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("MyLegacyEvent", MyLegacyEventClass.class.getName(), legacyDef);Sometimes it may be convenient to use event property names in pattern and statements that are backed up by a given public method or member variable (field) in a Java class. And it can be useful to declare multiple event properties that each map to the same method or member variable.
We can configure properties of events via method-property and field-property elements, as the next example shows.
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-type name="StockTick" class="com.espertech.esper.example.stockticker.event.StockTickEvent">
<legacy-type accessor-style="javabean" code-generation="enabled">
<method-property name="price" accessor-method="getCurrentPrice" />
<field-property name="volume" accessor-field="volumeField" />
</legacy-type>
</event-type>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
The XML configuration snippet above declared an event property named price backed by a getter-method named getCurrentPrice, and a second event property named volume that is backed by a public member variable named volumeField. Thus the price and volume properties can be used in a statement:
select avg(price * volume) from StockTick
As with all configuration options, the API can also be used:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
ConfigurationCommonEventTypeBean legacyDef = new ConfigurationCommonEventTypeBean();
legacyDef.addMethodProperty("price", "getCurrentPrice");
legacyDef.addFieldProperty("volume", "volumeField");
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("StockTick", StockTickEvent.class.getName(), legacyDef);By default the compiler resolves Java event properties case sensitive. That is, property names in statements must match JavaBean-convention property names in name and case. This option controls case sensitivity per Java class.
In the configuration XML, the optional property-resolution-style attribute in the legacy-type element can be set to any of these values:
Table 17.2. Property Resolution Case Sensitivity Styles
| Style Name | Description |
|---|---|
case_sensitive (default) | As the default setting, the compiler matches property names for the exact name and case only. |
case_insensitive | Properties are matched if the names are identical. A case insensitive search is used and will choose the first property that matches the name exactly or the first property that matches case insensitively should no match be found. |
distinct_case_insensitive | Properties are matched if the names are identical. A case insensitive search is used and will choose the first property that matches the name exactly case insensitively. If more than one 'name' can be mapped to the property an exception is thrown. |
The sample below shows this option in XML configuration, however the setting can also be changed via API:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-type name="MyLegacyEvent" class="com.mycompany.package.MyLegacyEventClass">
<legacy-type property-resolution-style="case_insensitive"/>
</event-type>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
The insert into clause and directly instantiate and populate your event object. By default the runtime invokes the default constructor to instantiate an event object. To change this behavior, you may configure
a factory method. The factory method is a method name or a class name plus a method name (in the format class.method) that returns an instance of the class.
The update clause can change event properties on an event object. For the purpose of maintaining consistency, the runtime may have to copy your event object via serialization (implement the java.io.Serializable interface). If instead you do not want any copy operations to occur, or your application needs to control the copy operation, you may configure a copy method. The copy method is the name of a method on the event object that copies the event object.
The sample below shows this option in XML configuration, however the setting can also be changed via ConfigurationCommonEventTypeBean:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-type name="MyLegacyEvent" class="com.mycompany.package.MyLegacyEventClass">
<legacy-type factory-method="com.mycompany.myapp.MySampleEventFactory.createMyLegacyTypeEvent" copy-method="myCopyMethod"/>
</event-type>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
The copy method should be a public method that takes no parameters and returns a new event object (it may not return this). The copy method may not be a static method and may not take parameters.
The Beacon data flow operator in connection with the Sun JVM can use sun.reflect.ReflectionFactory if the class has no default no-argument constructor.
For use with date-time interval methods, for example, you may let the compiler know which property of your class carries the start and end timestamp value.
The sample below shows this option in XML configuration, however the setting can also be changed via API. The sample sets the name of the property providing the start timestamp to startts and the name of the property providing the end timestamp endts:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-type name="MyLegacyEvent" class="com.mycompany.package.MyLegacyEventClass">
<legacy-type start-timestamp-property-name="startts" end-timestamp-property-name="endts"/>
</event-type>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
The runtime can process java.util.Map events via the sendEventMap(Map map, String eventTypeName) method on the EPEventService interface. Entries in the Map represent event properties. Please see the Appendix E, Event Representation: java.util.Map Events section for details on how to use Map events with the runtime.
You can provide an event type name for Map events.
The below snippet of XML configuration configures an event type named MyMapEvent.
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-type name="MyMapEvent">
<java-util-map>
<map-property name="carId" class="int"/>
<map-property name="carType" class="string"/>
<map-property name="assembly" class="com.mycompany.Assembly"/>
</java-util-map>
</event-type>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
For NEsper .NET use util-map instead of java-util-map.
This configuration defines the carId property of MyMapEvent events to be of type int, and the carType property to be of type java.util.String. The assembly property of the Map event will contain instances of com.mycompany.Assembly for the runtime to query.
The valid types for the class attribute are listed in Section 17.8, “Type Names”. In addition, any fully-qualified Java class name that can be resolved via Class.forName is allowed.
You can also use the configuration API to configure Map event types, as the short code snippet below demonstrates:
Map<String, Object> properties = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>();
properties.put("carId", "int");
properties.put("carType", "string");
properties.put("assembly", Assembly.class.getName());
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("MyMapEvent", properties);
A Map event type may also become a subtype of one or more supertypes that must also be Map event types. The java-util-map element provides the optional attribute supertype-names that accepts a comma-separated list of names of Map event types that are supertypes to the type:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-type name="AccountUpdate">
<java-util-map supertype-names="BaseUpdate, AccountEvent">
</java-util-map>
</event-type>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
A Map event type may declare a start and end timestamp property name. The XML shown next instructs the compiler that the startts property carries the event start timestamp and the endts property carries the event end timestamp:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-type name="AccountUpdate">
<java-util-map start-timestamp-property-name="startts" end-timestamp-property-name="endts">
</java-util-map>
</event-type>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
For adding a type at runtime please use create map schema.
The runtime can process Object-array (Object[]) events via the sendEventObjectArray(Object[] array, String eventTypeName) method on the EPEventService interface. Elements in the Object array represent event properties. Please see the Appendix F, Event Representation: Object-Array (Object[]) Events section for details on how to use Object[] events with the runtime.
The below snippet of XML configuration configures an event type named MyObjectArrayEvent.
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-type name="MyObjectArrayEvent">
<objectarray>
<objectarray-property name="carId" class="int"/>
<objectarray-property name="carType" class="string"/>
<objectarray-property name="assembly" class="com.mycompany.Assembly"/>
</objectarray>
</event-type>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
This configuration defines the carId property of MyObjectArrayEvent events to be of type int and in the object array first element ([0]). The carType property to be of type java.util.String is expected in the second array element ([1]) . The assembly property of the object array event will contain instances of com.mycompany.Assembly for the runtime to query in element two ([2]).
Note that the runtime does not verify the length and property values of object array events when your application sends object-array events into the runtime. For the example above, the proper object array would look as follows: new Object[] {carId, carType, assembly}.
The valid types for the class attribute are listed in Section 17.8, “Type Names”. In addition, any fully-qualified Java class name that can be resolved via Class.forName is allowed.
You can also use the configuration API to configure Object[] event types, as the short code snippet below demonstrates:
String[] propertyNames = {"carId", "carType", "assembly"};
Object[] propertyTypes = {int.class, String.class, Assembly.class};
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("MyObjectArrayEvent", propertyNames, propertyTypes);
An Object-array event type may also become a subtype of one supertype that must also be an Object-array event type. The objectarray element provides the optional attribute supertype-names that accepts a single name of an Object-array event type that is the supertype to the type:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-type name="AccountUpdate">
<objectarray supertype-names="BaseUpdate">
</objectarray>
</event-type>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
An Object-array event type may declare a start and end timestamp property name. The XML shown next instructs the compiler that the startts property carries the event start timestamp and the endts property carries the event end timestamp:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-type name="AccountUpdate">
<objectarray start-timestamp-property-name="startts" end-timestamp-property-name="endts"/>
</event-type>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
For adding a type at runtime please use create objectarray schema.
Please use create json schema EPL to define a JSON event type. There is no configuration API to pre-define JSON event types.
The runtime can process Avro GenericData.Record events via the sendEventAvro(GenericData.Record event, String eventTypeName) method on the EPEventService interface. Please see the Appendix H, Event Representation: Avro Events (org.apache.avro.generic.GenericData.Record) section for details on how to use Avro events with the compiler and runtime.
The below snippet of XML configuration configures an event type named MyAvroEvent.
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-type name="MyAvroEvent">
<avro schema-text='{"type":"record","name":"MyAvroEvent","fields":[{"name":"carId","type":"int"},{"name":"carType","type":{"type":"string","avro.java.string":"String"}}]}'/>
</event-type>
</common>
</esper-configuration>The sample Avro schema above in pretty-print is:
{
"type" : "record",
"name" : "MyAvroEvent",
"fields" : [ {
"name" : "carId",
"type" : "int"
}, {
"name" : "carType",
"type" : {
"type" : "string",
"avro.java.string" : "String"
}
} ]
}This schema defines:
A
carIdproperty of typeint.A
carTypeproperty of typestring. Note:Wse the Avro-providedavro.java.stringproperty to ensure is is ajava.lang.Stringinstance and not ajava.lang.CharSequence) instance.
Note that the runtime does not verify that Avro events are valid or that they actually match the schema provided for the Avro event type.
You can also use the configuration API to configure Avro event types, as the short code snippet below demonstrates:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
ConfigurationCommonEventTypeAvro avroType = new ConfigurationCommonEventTypeAvro();
avroType.setAvroSchema(schema);
configuration.getCommon().addEventTypeAvro("MyAvroType", avroType);
For adding a type at runtime please use create avro schema.
An Avro event type may also become a subtype of one supertype that must also be an Avro event type. The avro element provides the optional attribute supertype-names that accepts a single name of an Avro event type that is the supertype to the type:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-type name="MyAvroEvent">
<avro supertype-names="BaseUpdate"/>
</event-type>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
An Avro event type may declare a start and end timestamp property name. The XML shown next instructs the compiler that the startts property carries the event start timestamp and the endts property carries the event end timestamp:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-type name="MyAvroEvent">
<avro start-timestamp-property-name="startts" end-timestamp-property-name="endts"/>
</event-type>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
Via this configuration item, or using create xml schema, the runtime can natively process org.w3c.dom.Node instances, i.e. XML document object model (DOM) nodes.
Please see the Appendix I, Event Representation: org.w3c.dom.Node XML Events section for details on how to use Node events with the compiler and runtime.
EPL allows configuring XPath expressions as event properties. You can specify arbitrary XPath functions or expressions and provide a property name by which their result values will be available for use in expressions.
Use the @XMLSchemaField annotation with create xml schema.
For XML documents that follow a XML schema, the compiler and runtime can load and interrogate your schema and validate event property names and types against the schema information.
Nested, mapped and indexed event properties are also supported in expressions against org.w3c.dom.Node events. Thus XML trees can conveniently be
interrogated using the existing event property syntax for querying JavaBean objects, JavaBean object graphs or java.util.Map events.
In the simplest form, the compiler only requires a configuration entry containing the root element name and the event type name in order to process org.w3c.dom.Node events:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-type name="MyXMLNodeEvent">
<xml-dom root-element-name="myevent" />
</event-type>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
You can also use the configuration API to configure XML event types, as the short example below demonstrates.
In fact, all configuration options available through XML configuration can
also be provided via setter methods on the ConfigurationEventTypeXMLDOM class.
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM desc = new ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM();
desc.setRootElementName("myevent");
desc.addXPathProperty("name1", "/element/@attribute", XPathConstants.STRING);
desc.addXPathProperty("name2", "/element/subelement", XPathConstants.NUMBER);
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("MyXMLNodeEvent", desc);
The equivalent to above configuration is declaring the schema via create xml schema:
@XMLSchema(rootElementName='myevent') @XMLSchemaField(name='name1', xpath='/element/@attribute', type='string') @XMLSchemaField(name='name2', xpath='/element/subelement', type='number') create xml schema MyXMLNodeEvent()
The next example presents configuration options in a sample configuration entry.
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-type name="AutoIdRFIDEvent">
<xml-dom root-element-name="Sensor" schema-resource="data/AutoIdPmlCore.xsd"
default-namespace="urn:autoid:specification:interchange:PMLCore:xml:schema:1">
<namespace-prefix prefix="pmlcore"
namespace="urn:autoid:specification:interchange:PMLCore:xml:schema:1"/>
<xpath-property property-name="countTags"
xpath="count(/pmlcore:Sensor/pmlcore:Observation/pmlcore:Tag)" type="number"/>
</xml-dom>
</event-type>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
The equivalent to above configuration is declaring the schema via create xml schema:
@XMLSchema(rootElementName='Sensor' schemaResource='data/AutoIdPmlCore.xsd', defaultNamespace='urn:autoid:specification:interchange:PMLCore:xml:schema:1') @XMLSchemaNamespacePrefix(prefix='pmlcore', namespace='urn:autoid:specification:interchange:PMLCore:xml:schema:1')" + @XMLSchemaField(name='countTags', xpath='count(/pmlcore:Sensor/pmlcore:Observation/pmlcore:Tag)', type='number') create xml schema AutoIdRFIDEvent()
This example configures an event property named countTags whose value is computed by an XPath expression. The namespace prefixes
and default namespace are for use with XPath expressions and must also be made known to the compiler and runtime in order for the compiler/runtime to compile XPath expressions.
Via the schema-resource attribute you can instruct the compiler/runtime to load a schema file. You may also use schema-text instead to
provide the actual text of the schema.
The schema-resource attribute or annotation field takes a schema resource URL or classpath-relative filename.
The compiler and runtime attempts to resolve the schema resource as an URL. If the schema resource name is not a valid URL, the compiler and runtime attempts to resolve the resource from classpath via the ClassLoader.getResource method using the thread context class loader. If the name could not be resolved, the compiler and runtime uses the Configuration class classloader. Use the schema-text attribute instead when it is more practical to provide the actual text of the schema.
By providing a schema file for the compiler or runtime to load, the compiler performs these additional services:
Validates the event properties in a statement, ensuring the event property name matches an attribute or element in the XML
Determines the type of the event property allowing event properties to be used in type-sensitive expressions such as expressions involving arithmetic (Note: XPath properties are also typed)
Matches event property names to either element names or attributes
If no schema resource is specified, none of the event properties specified in statements are validated at compile-time and their type defaults to java.lang.String. Also, attributes are not supported
if no schema resource is specified and must thus be declared via XPath expression.
The xpath-property element adds explicitly-names event properties to the event type that are computed via an XPath expression.
In order for the XPath expression to compile, be sure to specify the default-namespace attribute and use the
namespace-prefix to declare namespace prefixes.
XPath expression properties are strongly typed. The type attribute allows the following values. These values correspond to those declared by
javax.xml.xpath.XPathConstants.
number (Note: resolves to a
double)string
boolean
node
nodeset
In case you need your XPath expression to return a type other than the types listed above, an optional cast-to type can be specified. If specified, the operation firsts obtains the result of the XPath expression as the defined type (number, string, boolean) and then casts or parses the returned type to the specified cast-to-type. At runtime, a warning message is logged if the XPath expression returns a result object that cannot be casted or parsed.
The next line shows how to return a long-type property for an XPath expression that returns a string:
desc.addXPathProperty("name", "/element/sub", XPathConstants.STRING, "long");
For use with create xml schema it is:
@XMLSchemaField(name='name', xpath='/element/sub', type='string', castToType='long')
The equivalent configuration XML is:
<xpath-property property-name="name" xpath="/element/sub" type="string" cast="long"/>
See Section 17.8, “Type Names” for a list of cast-to type names.
This setting indicates that when properties are compiled to XPath expressions that the compilation should generate an absolute XPath expression or a deep (find element) XPath expression.
For example, consider the following statement against an event type that is represented by a XML DOM document, assuming the event type GetQuote has been configured with the compiler as a XML DOM event type:
select request, request.symbol from GetQuote
By default, the compiler compiles the "request" property name to an XPath expression "/GetQuote/request". It compiles the nested property named "request.symbol" to an XPath expression "/GetQuote/request/symbol", wherein the root element node is "GetQuote".
By setting absolute property resolution to false, the compiler compiles the "request" property name to an XPath expression "//request". It compiles the nested property named "request.symbol" to an XPath expression "//request/symbol". This enables these elements to be located anywhere in the XML document.
The setting is available in XML via the attribute resolve-properties-absolute.
The configuration API provides the above settings as shown here in a sample code:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM desc = new ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM();
desc.setRootElementName("GetQuote");
desc.setDefaultNamespace("http://services.samples/xsd");
desc.setRootElementNamespace("http://services.samples/xsd");
desc.addNamespacePrefix("m0", "http://services.samples/xsd");
desc.setXPathResolvePropertiesAbsolute(false);
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("GetQuote", desc);
The equivalent to above configuration is declaring the schema via create xml schema is:
@XMLSchema(rootElementName = 'GetQuote', defaultNamespace='http://services.samples/xsd', rootElementNamespace='http://services.samples/xsd', xpathResolvePropertiesAbsolute=false) @XMLSchemaNamespacePrefix(prefix='m0', namespace='http://services.samples/xsd') create xml schema GetQuote()
If your XPath expressions require variables or functions, your application may provide the class name of an XPathVariableResolver and XPathFunctionResolver. At type initialization time
the compiler and runtime instantiates the resolver instances and provides these to the XPathFactory.
This example shows the API to set this configuration.
ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM desc = new ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM(); desc.setXPathFunctionResolver(MyXPathFunctionResolver.class.getName()); desc.setXPathVariableResolver(MyXPathVariableResolver.class.getName());
This example shows the EPL annotation use:
@XMLSchema(xpathFunctionResolver='class name here', xpathVariableResolver='class name here')
This option is for use when a XSD schema is provided and determines whether the compiler automatically creates an event type when a property expression transposes a property that is a complex type according to the schema.
An example:
ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM desc = new ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM(); desc.setAutoFragment(false);
This example shows the EPL annotation use:
@XMLSchema(autoFragment=false
By default the compiler and runtime employs the built-in DOM walker implementation to evaluate XPath expressions, which is not namespace-aware.
This configuration setting, when set to true, instructs the compiler to rewrite property expressions into XPath.
An example:
ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM desc = new ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM(); desc.setXPathPropertyExpr(true);
This example shows the EPL annotation use:
@XMLSchema(xpathPpropertyExpr=true
By default an EventSender for a given XML event type validates the root element name for which the type has been declared against the one provided by the org.w3c.Node sent into the runtime.
This configuration setting, when set to false, instructs an EventSender to not validate.
An example:
ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM desc = new ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM(); desc.setEventSenderValidatesRoot(false);
This example shows the EPL annotation use:
@XMLSchema(eventSenderValidatesRoot=false
You may configure the name of the properties that provides the event start timestamp and the event end timestamp as part of the configuration.
An example that configures startts as the property name providing the start timestamp and endts as the property name providing the end timestamp:
ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM desc = new ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM();
desc.setStartTimestampPropertyName("startts");
desc.setEndTimestampPropertyName("endts");
When using create xml schema the start and end timestamps are part of create schema.
The default event representation is the Map event representation.
The default event representation is relevant when your query outputs individual properties to a listener and it does not specify a specific event representation in an annotation.
The default event representation is also relevant for create schema and create window.
Note that the compiler may still use the Map representation for certain types of statements even when the default event representation is object array.
For example, consider the following statement:
select propertyOne, propertyTwo from MyEvent
Listeners to the statement above currently receive a Map-type event. By setting the configuration flag to object-array or Avro as described herein, listeners to the statement receive an Object-array-type event or an Avro-type event instead.
The XML snippet below is an example of setting the default event representation to Object-array:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-meta>
<event-representation type="objectarray"/> <!-- use "json" for JSON, use "avro" for Avro -->
</event-meta>
</common>
</esper-configuration>The code snippet shown next sets the default event representation to Object-array in the configuration object:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().getEventMeta().
setDefaultEventRepresentation(EventUnderlyingType.OBJECTARRAY);This configuration controls compiler settings in respect to Avro.
The enable-avro setting is boolean-typed and is false by default. It controls whether Avro is enabled or disabled.
If disabled the compiler and runtime disallow registering Avro event types or using an Avro event representation.
The enable-native-string setting is boolean-typed and is true by default. It controls whether for String-type values,
when the compiler generates an Avro schema, such field schema adds the property avro.java.string of value String.
The enable-schema-default-nonnull setting is boolean-typed and is true by default. It controls whether the compiler
assembles non-null Avro schemas (true) or nullable (union) Avro schemas (false).
The objectvalue-typewidener-factory-class setting is a fully-qualified class name of the class implementing the com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.type.ObjectValueTypeWidenerFactory interface and is null by default.
If specified the factory can provide a type widener for widening, coercing or transforming any object value to a Avro field value.
The type-representation-mapper-class setting is a fully-qualified class name of the class implementing the com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.type.TypeRepresentationMapper interface and is null by default.
If specified the implementation can provide for a given class the Avro schema for the field.
The XML snippet below is an example of Avro settings that configures the same as the default values:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-meta>
<avro-settings enable-avro="false" enable-native-string="true" enable-schema-default-nonnull="true"
objectvalue-typewidener-factory-class=""
type-representation-mapper-class=""/>
</event-meta>
</common>
</esper-configuration>The code snippet shown next sets the default event representation to Object-array in the configuration object:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); configuration.getCommon().getEventMeta().getAvroSettings().setEnableAvro(false); configuration.getCommon().getEventMeta().getAvroSettings().setEnableNativeString(true); configuration.getCommon().getEventMeta().getAvroSettings().setEnableSchemaDefaultNonNull(true); configuration.getCommon().getEventMeta().getAvroSettings().setObjectValueTypeWidenerFactoryClass(null); configuration.getCommon().getEventMeta().getAvroSettings().setTypeRepresentationMapperClass(null);
This configuration controls compiler and runtime settings in respect to XML XSD Schemas. More information can be found at Section I.2.1, “Getting Started”.
The enable-xmlxsd setting is boolean-typed and is false by default. It controls whether XML XSD schemas using Apache Xerces 2 is enabled or disabled.
If disabled the compiler and runtime disallow registering XML XSD schema event types.
The XML snippet below is an example of the settings that configures the same as the default values:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-meta enable-xmlxsd="false"\>
</common>
</esper-configuration>The code snippet shown next sets the default event representation to Object-array in the configuration object:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); configuration.getCommon().getEventMeta().setEnableXMLXSD(true);
This allows to control case sensitivity or accessor style for all event classes as a default. The two settings are found under class-property-resolution under event-meta in the XML common configuration.
To control the case sensitivity as discussed in Section 17.4.3.4, “Case Sensitivity and Property Names”, add the style attribute in the XML configuration to set a default case sensitivity applicable to all event classes unless specifically overridden by class-specific configuration.
The default case sensitivity is case_sensitive (case sensitivity turned on).
To control the accessor style as discussed in Section 17.4.3.2, “Non-JavaBean and Legacy Java Event Classes”, add the accessor-style attribute in the XML configuration to set a default accessor style applicable to all event classes unless specifically overridden by class-specific configuration. The default accessor style is javabean JavaBean accessor style.
The next code snippet shows how to control this feature via the API:
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.getCommon().getEventMeta().setClassPropertyResolutionStyle(
PropertyResolutionStyle.CASE_INSENSITIVE);
config.getCommon().getEventMeta().setDefaultAccessorStyle(
AccessorStyle.PUBLIC);
Via this configuration an application can make the Java package or packages that contain an application's Java event classes known.
Thereby an application can use create schema name as simple-classname and the compiler can find the class.
The XML configuration for defining the Java packages that contain Java event classes is:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<event-type-auto-name package-name="com.mycompany.order.event"/>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
The same configuration but using the Configuration class:
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.getCommon().addEventTypeAutoName("com.mycompany.order.event");
// ... or ...
config.getCommon().addEventTypeAutoName(MyEvent.getPackage().getName());
Method invocations are allowed in the from clause in EPL, such that your application may join event streams to the data returned by a web service, or to data read from a distributed cache or object-oriented database, or obtain data by other means. A local cache may be placed in front of such method invocations through the configuration settings described herein.
The LRU cache is described in detail in Section 17.4.12.6.1, “LRU Cache”. The expiry-time cache documentation can be found in Section 17.4.12.6.2, “Expiry-Time Cache”
The next XML snippet is a sample cache configuration that applies to methods provided by the classes 'MyFromClauseLookupLib' and 'MyFromClauseWebServiceLib'. The XML and API configuration understand both the fully-qualified Java class name, as well as the simple class name:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<method-reference class-name="com.mycompany.MyFromClauseLookupLib">
<expiry-time-cache max-age-seconds="10" purge-interval-seconds="10" ref-type="weak"/>
</method-reference>
<method-reference class-name="MyFromClauseWebServiceLib">
<lru-cache size="1000"/>
</method-reference>
</common>
</esper-configuration>For NEsper .NET also see Section J.17, “.NET Configurations - Relational Database Access”.
EPL has the capability to join event streams against historical data sources, such as a relational database. This section describes the configuration entries that the compiler or runtime require to access data stored in your database. Please see Section 5.13, “Accessing Relational Data via SQL” for information on the use of EPL queries that include historical data sources.
EPL queries that poll data from a relational database specify the name of the database as part of the statement. The compiler and runtime use the configuration information described here to resolve the database name in the statement to database settings. The required and optional database settings are summarized below.
Database connections can be obtained via JDBC
javax.xml.DataSource, viajava.sql.DriverManagerand via data source factory. Either one of these methods to obtain database connections is a required configuration.Optionally, JDBC connection-level settings such as auto-commit, transaction isolation level, read-only and the catalog name can be defined.
Optionally, a connection lifecycle can be set to indicate to the runtime whether the runtime must retain connections or must obtain a new connection for each lookup and close the connection when the lookup is done (pooled).
Optionally, define a cache policy to allow the runtime to retrieve data from a query cache, reducing the number of query executions.
Some of the settings can have important performance implications that need to be carefully considered in relationship to your database software, JDBC driver and runtime environment. This section attempts to outline such implications where appropriate.
The sample XML configuration file in the "etc" folder can be used as a template for configuring database settings. All settings are also available by means of the configuration API through the classes Configuration and ConfigurationDBRef.
This configuration causes the compiler or runtime to obtain a database connection from a javax.sql.DataSource available from your JNDI provider.
The setting is most useful when running within an application server or when a JNDI directory is otherwise present in your Java VM. If your application environment does not provide an available DataSource, the next section outlines how to use Apache DBCP as a DataSource implementation with connection pooling options and outlines how to use a custom factory for DataSource implementations.
If your DataSource provides connections out of a connection pool, your configuration should set the collection lifecycle setting to pooled.
The snippet of XML below configures a database named mydb1 to obtain connections via a javax.sql.DataSource. The datasource-connection element instructs the runtime to obtain new connections to the database mydb1 by performing a lookup via javax.naming.InitialContext for the given object lookup name. Optional environment properties for the InitialContext are also shown in the example.
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<database-reference name="mydb1">
<datasource-connection context-lookup-name="java:comp/env/jdbc/mydb">
<env-property name="java.naming.factory.initial" value ="com.myclass.CtxFactory"/>
<env-property name="java.naming.provider.url" value ="iiop://localhost:1050"/>
</datasource-connection>
</database-reference>
</common>
</esper-configuration>To help you better understand how the runtime uses this information to obtain connections, please look at the logic below.
if (envProperties.size() > 0) {
initialContext = new InitialContext(envProperties);
}
else {
initialContext = new InitialContext();
}
DataSource dataSource = (DataSource) initialContext.lookup(lookupName);
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
In order to plug-in your own implementation of the DataSource interface, your application may use an existing JNDI provider as provided by an application server if running in a J2EE environment.
In case your application does not have an existing JNDI implementation to register a DataSource to provide connections, you may set the java.naming.factory.initial property in the configuration to point to your application's own implementation of the javax.naming.spi.InitialContextFactory interface that can return your application DataSource though the javax.naming.Context provided by the factory implementation. Please see Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI) API documentation for further information.
This section describes how to use Apache Commons Database Connection Pooling (Apache DBCP). It explains how to provide a custom application-specific DataSource factory if not using Apache DBCP.
If your DataSource provides connections out of a connection pool, your configuration should set the collection lifecycle setting to pooled.
Apache DBCP provides comprehensive means to test for dead connections or grow and shrik a connection pool. Configuration properties for Apache DBCP can be found at Apache DBCP configuration. The listed properties are passed to Apache DBCP via the properties list provided as part of the configuration.
The snippet of XML below is an example that configures a database named mydb3 to obtain connections via the pooling DataSource provided by Apache DBCP BasicDataSourceFactory.
The listed properties are passed to DBCP to instruct DBCP how to manage the connection pool. The settings below initialize the connection pool to 2 connections and provide the validation query select 1 from dual for DBCP to validate a connection before providing a connection from the pool:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<database-reference name="mydb3">
<!-- For a complete list of properties see Apache DBCP. -->
<!-- NOTE: "dbcp2" applies to api-2.0 of DBCP, use "dbcp" otherwise. -->
<datasourcefactory-connection class-name="org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSourceFactory">
<env-property name="username" value ="myusername"/>
<env-property name="password" value ="mypassword"/>
<env-property name="driverClassName" value ="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<env-property name="url" value ="jdbc:mysql://localhost/test"/>
<env-property name="initialSize" value ="2"/>
<env-property name="validationQuery" value ="select 1 from dual"/>
</datasourcefactory-connection>
<connection-lifecycle value="pooled"/>
</database-reference>
</common>
</esper-configuration>The same configuration options provided through the API:
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("username", "myusername");
props.put("password", "mypassword");
props.put("driverClassName", "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
props.put("url", "jdbc:mysql://localhost/test");
props.put("initialSize", 2);
props.put("validationQuery", "select 1 from dual");
ConfigurationCommonDBRef configDB = new ConfigurationCommonDBRef();
// BasicDataSourceFactory is an Apache DBCP import
configDB.setDataSourceFactory(props, BasicDataSourceFactory.class.getName());
configDB.setConnectionLifecycleEnum(ConfigurationCommonDBRef.ConnectionLifecycleEnum.POOLED);
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();;
configuration.getCommon().addDatabaseReference("mydb3", configDB);Apache Commons DBCP is a separate download and not provided as part of the distribution. The Apache Commons DBCP jar file requires the Apache Commons Pool jar file.
Your application can provide its own factory implementation for DataSource instances: Set the class name to the name of the application class that provides a public static method named createDataSource which takes a single Properties object as parameter and returns a DataSource implementation. For example:
configDB.setDataSourceFactory(props, MyOwnDataSourceFactory.class.getName());
...
class MyOwnDataSourceFactory {
public static DataSource createDataSource(Properties properties) {
return new MyDataSourceImpl(properties);
}
}
The next snippet of XML configures a database named mydb2 to obtain connections via java.sql.DriverManager. The drivermanager-connection element instructs the runtime to obtain new connections to the database mydb2 by means of Class.forName and DriverManager.getConnection using the class name, URL and optional username, password and connection arguments.
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<database-reference name="mydb2">
<drivermanager-connection class-name="my.sql.Driver"
url="jdbc:mysql://localhost/test?user=root&password=mypassword"
user="myuser" password="mypassword">
<connection-arg name="user" value ="myuser"/>
<connection-arg name="password" value ="mypassword"/>
<connection-arg name="somearg" value ="someargvalue"/>
</drivermanager-connection>
</database-reference>
</common>
</esper-configuration>The username and password are shown in multiple places in the XML only as an example. Please check with your database software on the required information in URL and connection arguments.
Additional connection-level settings can optionally be provided to the runtime which the runtime will apply to new connections. When the runtime obtains a new connection, it applies only those settings to the connection that are explicitly configured. The runtime leaves all other connection settings at default values.
The below XML is a sample of all available configuration settings. Please refer to the Java API JavaDocs for java.sql.Connection for more information to each option or check the documentation of your JDBC driver and database software.
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<database-reference name="mydb2">
<!-- ... configure data source or driver manager settings... -->
<connection-settings auto-commit="true" catalog="mycatalog"
read-only="true" transaction-isolation="1" />
</database-reference>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
The read-only setting can be used to indicate to your database runtime that SQL statements are read-only. The transaction-isolation and auto-commit help you database software perform the right level of locking and lock release. Consider setting these values to reduce transactional overhead in your database queries.
By default the runtime retains a separate database connection for each started statement. However, it is possible to override this behavior and require the runtime to obtain a new database connection for each lookup, and to close that database connection after the lookup is completed. This often makes sense when you have a large number of statements and require pooling of connections via a connection pool.
In the pooled setting, the runtime obtains a database connection from the data source or driver manager for every query, and closes the connection when done, returning the database connection to the pool if using a pooling data source.
In the retain setting, the runtime retains a separate dedicated database connection for each statement and does not close the connection between uses.
The XML for this option is below. The connection lifecycle allows the following values: pooled and retain.
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<database-reference name="mydb2">
<!-- ... configure data source or driver manager settings... -->
<connection-lifecycle value="pooled"/>
</database-reference>
</common>
</esper-configuration>Cache settings can dramatically reduce the number of database queries that the runtime executes for statements. If no cache setting is specified, the runtime does not cache query results and executes a separate database query for every event.
Caches store the results of database queries and make these results available to subsequent queries using the exact same query parameters as the query for which the result was stored. If your query returns one or more rows, the cache keep the result rows of the query keyed to the parameters of the query. If your query returns no rows, the cache also keeps the empty result. Query results are held by a cache until the cache entry is evicted. The strategies available for evicting cached query results are listed next.
The least-recently-used (LRU) cache is configured by a maximum size. The cache discards the least recently used query results first once the cache reaches the maximum size.
The XML configuration entry for a LRU cache is as below. This entry configures an LRU cache holding up to 1000 query results.
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<database-reference name="mydb">
<!-- ... configure data source or driver manager settings... -->
<lru-cache size="1000"/>
</database-reference>
</common>
</esper-configuration>The expiry time cache is configured by a maximum age in seconds, a purge interval and an optional reference type. The cache discards (on the get operation) any query results that are older then the maximum age so that stale data is not used. If the cache is not empty, then every purge interval number of seconds the runtime purges any expired entries from the cache.
The XML configuration entry for an expiry-time cache is as follows. The example configures an expiry time cache in which prior query results are valid for 60 seconds and which the runtime inspects every 2 minutes to remove query results older then 60 seconds.
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<database-reference name="mydb">
<!-- ... configure data source or driver manager settings... -->
<expiry-time-cache max-age-seconds="60" purge-interval-seconds="120" />
</database-reference>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
By default, the expiry-time cache is backed by a java.util.WeakHashMap and thus relies on weak references. That means that cached SQL results can be freed during garbage collection.
Via XML or using the configuration API the type of reference can be configured to not allow entries to be garbage collected, by setting the ref-type property to hard:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<database-reference name="mydb">
<!-- ... configure data source or driver manager settings... -->
<expiry-time-cache max-age-seconds="60" purge-interval-seconds="120" ref-type="hard"/>
</database-reference>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
The last setting for the cache reference type is soft: This strategy allows the garbage collection of cache entries only when all other weak references have been collected.
This setting instructs the compiler to convert to lower- or uppercase any output column names returned by your database system. When using Oracle relational database software, for example, column names can be changed to lowercase via this setting.
A sample XML configuration entry for this setting is:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<database-reference name="mydb">
<!-- ... configure data source or driver manager settings... -->
<column-change-case value="lowercase"/>
</database-reference>
</common>
</esper-configuration>For NEsper .NET this section is not applicable.
By providing a mapping of SQL types (java.sql.Types) to Java built-in types your code can avoid using sometimes awkward default database types and can easily change the way the compiler
returns Java types for columns returned by a SQL query.
The mapping maps a constant as defined by java.sql.Types to a Java built-in type of any of the following Java type names: String, BigDecimal, Boolean, Byte, Short, Int, Long, Float, Double, ByteArray, SqlDate, SqlTime, SqlTimestamp. The Java type names are not case-sensitive.
A sample XML configuration entry for this setting is shown next. The sample maps Types.NUMERIC which is a constant value of 2 per JDBC API to the Java int type.
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<database-reference name="mydb">
<!-- ... configure data source or driver manager settings... -->
<sql-types-mapping sql-type="2" java-type="int" />
</database-reference>
</common>
</esper-configuration>This setting controls how the compiler retrieves SQL statement metadata from JDBC prepared statements.
Table 17.3. Syntax and Results of Aggregate Functions
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| default |
By default, the compiler detects the driver name and queries prepared statement metadata if the driver is not an Oracle database driver. For Oracle drivers, the compiler uses lexical analysis of the SQL statement to construct a sample SQL statement and then fires that statement to retrieve statement metadata. |
| metadata |
The compiler always queries prepared statement metadata regardless of the database driver used. |
| sample |
The compiler always uses lexical analysis of the SQL statement to construct a sample SQL statement, and then fires that statement to retrieve statement metadata. |
By default, the compiler does not produce query plan output unless logging at debug-level.
To enable query plan logging, set this option in the configuration. When enabled, the compiler reports, at INFO level, any query plans under the log name com.espertech.esper.queryplan.
Query plan logging is applicable to subqueries, joins (any type), named window and table on-actions (on-select, on-merge, on-insert, on-update, on-select) and fire-and-forget queries. It is not applicable and will not provide additional information for other types of constructs.
The API to use to enable query plan logging is shown here:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getCommon().getLogging().setEnableQueryPlan(true);
The XML snippet is:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<logging>
<query-plan enabled="true"/>
</logging>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
By default, the compiler and runtime does not measure JDBC query execution times or report the number of rows returned from a JDBC query through logging.
To enable JDBC logging, set this option in the configuration. When enabled, the compiler and runtime report, at INFO level, any JDBC query performance and number of rows returned under the log name com.espertech.esper.jdbc.
The API to use to enable JDBC query logging is shown here:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getCommon().getLogging().setEnableJDBC(true);
The XML snippet is:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<logging>
<jdbc enabled="true"/>
</logging>
</common>
</esper-configuration>The default time unit of time resolution is milliseconds. Your application may set the time resolution to microseconds instead.
A sample XML configuration for millisecond time resolution is:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<time-source>
<time-unit value="milliseconds"/>
</time-source>
</common>
</esper-configuration>The equivalent code snippet using the configuration API is here:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getCommon().getTimeSource().setTimeUnit(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
Variables can be created dynamically in EPL via the create variable syntax but can also be configured.
A variable is declared by specifying a variable name, the variable type, an optional initialization value and an optional boolean-type flag indicating whether the variable is a constant (false by default). The initialization value can be of the same or compatible type as the variable type, or can also be a String value that, when parsed, is compatible to the type declared for the variable. Declare each variable a constant to achieve the best performance.
In a XML configuration file the variable configuration may look as below.
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<variable name="var_threshold" type="long" initialization-value="100"/>
<variable name="var_key" type="string"/>
<variable name="test" type="int" constant="true"/>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
Please find the list of valid values for the type attribute in Section 17.8, “Type Names”.
A variant stream is a predefined stream into which events of multiple disparate event types can be inserted, and which can be selected from in patterns and the from clause.
The name of the variant stream and, optionally, the type of events that the stream may accept, are part of the stream definition. By default, the variant stream accepts only the predefined event types. The compiler validates your insert into clause which inserts into the variant stream against the predefined types.
A variant stream can be set to accept any type of event, in which case all properties of the variant stream are effectively dynamic properties. Set the type variance flag to ANY to indicate the variant stream accepts any type of event.
The following XML configuration defines a variant stream by name OrderStream that carries only PartsOrder and ServiceOrder events:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<common>
<variant-stream name="OrderStream">
<variant-event-type name="PartsOrder"/>
<variant-event-type name="ServiceOrder"/>
</variant-stream>
</common>
</esper-configuration>
This code snippet sets up a variant stream by name OutgoingEvent:
Configuration config = new Configuration();
ConfigurationCommonVariantStream variant = new ConfigurationCommonVariantStream();
variant.setTypeVariance(ConfigurationCommonVariantStream.TypeVariance.ANY);
config.getCommon().addVariantStream("OutgoingEvent", variant);If specifying variant event type names, make sure such names have been configured for JavaBean, Map or XML events.
The setting include-debugsymbols is false by default. It controls whether the compiler generates debug symbols as part of the binary class.
The setting include-comments is false by default. It controls whether the compiler generates code that contains additional information to help tracing back generated code to the code that generated it.
The setting attach-epl is true by default. It controls whether the compiler adds the statement text of the statement to statement properties.
The setting attach-module-epl is false by default. It controls whether the compiler adds the EPL module text of the module to module properties.
The setting allow-subscriber is false by default. It controls whether the compiler adds code for handling subscribers. If this flag is false the setSubscriber method on the EPStatement class throws an exception.
The setting allow-inlined-class is true by default. It controls whether the compiler allows inlined-classes. If this flag is false the compiler throws an exception upon encountering an inlined-class.
The setting threadpool-compiler-num-threads sets the number of threads for compiling a statement to byte code and is eight (8) by default. Setting this value to zero disables multi-threading for compilation.
When the number of threads is greater zero the calling thread generates classes for statements and the thread pool compiles statement classes to byte code. This setting improves compilation performance only when a module has multiple statements
as the unit of parallelization is the statement.
The setting threadpool-compiler-capacity defines the number of permits (capacity of the queue) for compiling statements to byte code and is unbound by default. Use null to represent unbound. The minimum value for capacity is one.
The setting max-methods-per-class sets the maximum number of methods in a class or inner class. This value defaults to 1024 (1k).
This setting exists as the JVM limits the constant pool for each class to 64k. Among other things the JVM class constant pool contains method information. Therefore, for large EPL expressions, the compiler attempts to not exceed this JVM limit.
Upon finding a class that exceeds the configured maximum number of methods the compiler moves methods into an additional class or multiple additional classes.
The minimum value for this setting is 100. If this value is too large you may see a compilation message such as Constant pool for class has grown past JVM limit of 0xFFFF.
Note that there can be other reasons for this message. Please see Section 15.19, “Limitations”.
The sample code below sets the same values as the default values:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); ConfigurationCompilerByteCode byteCode = configuration.getCompiler().getByteCode(); byteCode.setIncludeDebugSymbols(false); byteCode.setIncludeComments(false); byteCode.setAttachEPL(true); byteCode.setAttachModuleEPL(false); byteCode.setAllowSubscriber(false); byteCode.setAllowInlinedClass(false); byteCode.setInstrumented(false); byteCode.setThreadPoolCompilerNumThreads(8); byteCode.setThreadPoolCompilerCapacity(null); byteCode.setMaxMethodsPerClass(16*1024);
The sample XML configuration below also sets default values:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<bytecode
include-comments="false"
include-debugsymbols="false"
attach-epl="true"
attach-module-epl="false"
instrumented="false"
allow-subscriber="false"
allow-inlined-class="true"
threadpool-compiler-num-threads="8"
max-methods-per-class="16384"/>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>
Access modifiers default to private and are listed here. You may also use the @private, @protected and @public annotations or the CompilerOptions object to set access modifiers.
Table 17.4. Byte Code Access Modifiers
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
access-modifier-context | Whether contexts that may be declared by the module are visible to other modules. |
access-modifier-eventtype | Whether event types that may be declared by the module are visible to other modules. |
access-modifier-expression | Whether expressions that may be declared by the module are visible to other modules. |
access-modifier-inlined-class | Whether inlined-classes that may be declared by the module are visible to other modules. |
access-modifier-namedwindow | Whether named windows that may be declared by the module are visible to other modules. |
access-modifier-script | Whether scripts that may be declared by the module are visible to other modules. |
access-modifier-table | Whether tables that may be declared by the module are visible to other modules. |
access-modifier-variables | Whether variables that may be declared by the module are visible to other modules. |
The setting bus-modifier-event-type is set to nonbus by default. This means that any of the sendEventType method of EPEventService cannot be used to process events of that event type.
Set this value to bus to indicate that the respective sendEventType method of EPEventService can process events of event types declared by the module (sendEventType throws an exception if it does not find a visible event type).
You may also use the @buseventtype annotation or the CompilerOptions object to set bus event type visibility.
The sample code below sets the same values as the default values:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); ConfigurationCompilerByteCode byteCode = configuration.getCompiler().getByteCode(); byteCode.setAccessModifierContext(NameAccessModifier.PRIVATE); byteCode.setAccessModifierEventType(NameAccessModifier.PRIVATE); byteCode.setAccessModifierNamedWindow(NameAccessModifier.PRIVATE); byteCode.setAccessModifierScript(NameAccessModifier.PRIVATE); byteCode.setAccessModifierTable(NameAccessModifier.PRIVATE); byteCode.setAccessModifierVariable(NameAccessModifier.PRIVATE); byteCode.setBusModifierEventType(EventTypeBusModifier.NONBUS);
The sample XML configuration below also sets default values:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<bytecode
access-modifier-context="private"
access-modifier-event-type="private"
access-modifier-expression="private"
access-modifier-named-window="private"
access-modifier-script="private"
access-modifier-table="private"
access-modifier-variable="private"
bus-modifier-event-type="nonbus"
/>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>By default, when using the iterator API to iterate a statement with an unbound stream the runtime returns an empty iterator.
To have the runtime return the last event instead, please use the @IterableUnbound statement annotation or enable the compiler setting as described herein.
A code sample that turns iterable-unbound on is:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getCompiler().getViewResources().setIterableUnbound(true);
This flag impacts output rate limiting as further outlined in Appendix B, Runtime Considerations for Output Rate Limiting. The flag serves to control the default behavior for output rate limiting for all statements that do not specify a hint.
If set to true (the default), all statements behave as if they hint @Hint('enable_outputlimit_opt').
If set to false, all statements behave as if they hint @Hint('disable_outputlimit_opt').
For example:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getCompiler().getViewResources().setOutputLimitOpt(true);
By enabling this setting the compiler logs byte code generation information at INFO level. This setting is disabled by default.
The API to use to enable logging for generated code is shown here:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getCompiler().getLogging().setEnableCode(true);
The XML snippet is:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<logging>
<code enabled="true"/>
</logging>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>
The compiler analyzes filter expressions and plans filter indexes. This setting instructs the compiler to log filter plans. The flag is false by default and if set to true the compiler outputs filter plans to log at INFO level.
An API code snippet to turn on filter plan logging is:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getCompiler().getLogging().setEnableFilterPlan(true);
The XML snippet is:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<logging>
<filter-plan enabled="true"/>
</logging>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>Statements can produce both insert stream (new data) and remove stream (old data) results. Remember that insert stream refers to arriving events and new aggregation values, while remove stream refers to events leaving data windows and prior aggregation values. By default, the runtime delivers only the insert stream to listeners and observers of a statement.
There are keywords in the select clause that instruct the runtime to not generate insert stream and/or remove stream results if your application does not need either one of the streams. These keywords are the istream, rstream and the irstream keywords.
By default, the runtime only generates insert stream results equivalent to using the optional istream keyword in the select clause.
If your application requires insert and remove stream results for many statements, your application can add the irstream keyword to the select clause of each statement,
or you can set a new default stream selector via this setting.
The XML configuration for this setting is shown below:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<stream-selection>
<stream-selector value="irstream" />
</stream-selection>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>The equivalent code snippet using the configuration API is here:
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.getCompiler().getStreamSelection()
.setDefaultStreamSelector(StreamSelector.RSTREAM_ISTREAM_BOTH);
Locale-dependence in the compiler can be present in the sort order of string values by the order by clause and by the sort window.
By default, the runtime sorts string values using the compare method that is not locale dependent. To enable local dependent sorting you must set the configuration flag as described below.
The XML configuration sets the locale dependent sorting as shown below:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<language sort-using-collator="true"/>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>The API to change the setting:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getCompiler().getLanguage().setSortUsingCollator(true);
By default the compiler returns double-typed values for divisions regardless of operand types. Division by zero returns positive or negative double infinity.
To have compiler use Java-standard integer division instead, use this setting as described here. In Java integer division, when dividing integer types, the result is an integer type. This means that if you divide an integer unevenly by another integer, it returns the whole number part of the result, does not perform any rounding and the fraction part is dropped. If Java-standard integer division is enabled, when dividing an integer numerator by an integer denominator, the result is an integer number. Thus the expression 1 / 4 results in an integer zero. Your EPL must then convert at least one of the numbers to a double value before the division, for example by specifying 1.0 / 4 or by using cast(myint, double).
When using Java integer division, division by zero for integer-typed operands always returns null. However division by zero for double-type operands still returns positive or negative double infinity. To also return null upon division by zero for double-type operands, set the flag to true as below (default is false).
The XML configuration is as follows:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<expression integer-division="false" division-by-zero-is-null="false"/>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>The API to change the setting:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getCompiler().getExpression().setIntegerDivision(true); config.getCompiler().getExpression().setDivisionByZeroReturnsNull(true);
By default runtime caches the result of an user-defined function if the parameter set to that function is empty or all parameters are constant values. Results of custom plug-in single-row functions are not cached according to the default configuration, unless the single-row function is explicitly configured with value cache enabled.
To have rntime evaluate the user-defined function regardless of constant parameters, set the flag to false as indicated herein.
The XML configuration as below sets the same as the default value:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<expression udf-cache="true"/>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>By default EPL provides a number of additional aggregation functions over the SQL standards. To have the compiler only allow the standard SQL aggregation functions and not the additional ones, disable the setting as described here.
The XML configuration as below sets the same as the default value:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<expression extended-agg="true"/>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>By default the compiler validates method references when using the dot operator syntax at time of compilation. With duck typing, the compiler resolves method references at runtime.
The XML configuration as below sets the same as the default value:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<expression ducktyping="false"/>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>
By default, when computing the average of BigDecimal values, the compiler does not pass a java.math.MathContext.
Use the setting herein to specify a default math context.
The below XML configuration sets precision to 2 and rounding mode ceiling:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<expression math-context="precision=2 roundingMode=CEILING"/>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>An example API configuration is shown next:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getCompiler().getExpression().setMathContext(MathContext.UNLIMITED);
You may configure a default script dialect as described herein. The default script dialect is js which stands for JavaScript, since most JVM ship with an integrated JavaScript execution runtime.
The default value for the enabled setting is true thus the compiler allows scripts. By setting enabled to false the compiler disallows script use entirely.
A sample XML configuration for this setting is shown below:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<scripts default-dialect="js" enabled="true"/>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>A sample code snippet that sets a new script dialect is:
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.getCompiler().getScripts().setDefaultDialect("js");
config.getCompiler().getScripts().setEnabled(true);
The compiler analyzes filter expressions and determines whether the OR logical operator occurs with the filter expression(s). This setting is only relevant to those filter expression that have OR. Please see Section 15.18, “Compiler Filter Expression Analysis” for more information.
In the default configuration the setting is 16, which means that the filter expression analyzer can at most create 16 path expressions from a given filter expression. If the number of path expressions is over 16, the expression will instead be evaluated as non-path and not be subject to to be entered into filter indexes.
On the level of a statement, this setting can be controlled by providing a hint. For example:
// The compiler optimizes the filter expression to become: // "a=1, c=1" or "b=1, c=1" or "a=1, d=1" or "b=1, d=1". // This enables filter index sharing between filter expressions. select * from Event((a=1 or b=1) and (c=1 or d=1))
// The compiler does not optimize filter expressions
@Hint('MAX_FILTER_WIDTH=0') select * from Event((a=1 or b=1) and (c=1 or d=1))The XML configuration to set a new value is:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<execution filter-service-max-filter-width="100"/>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>The API to change the setting:
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.getCompiler().getExecution().
setFilterServiceMaxFilterWidth(16);The compiler analyzes filter expressions and determines whether to use filter indexes. Please see Section 15.18, “Compiler Filter Expression Analysis” for more information.
By default the compiler performs advanced planning. The default setting is ConfigurationCompilerExecution.FilterIndexPlanning.ADVANCED.
This setting is an enumeration value that can be set to none, basic or advanced (the default).
By setting none the compiler simply builds a single non-reusable boolean composite expression for any filter expressions.
By setting basic the compiler analyzes filter expressions and builds basic triplets. The EPL can specify filter index planning hints to enable those advanced planning features that your application needs.
By setting advanced (the default) the compiler analyzes filter expressions fully. In this case the filter index planning hints are not considered by the compiler.
The XML configuration example is:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<execution filter-index-planning="advanced"/>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>The API example to change the setting is:
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.getCompiler().getExecution().setFilterIndexPlanning(
ConfigurationCompilerExecution.FilterIndexPlanning.ADVANCED);
The enable-declared-expr-value-cache is true by default and the compile generates code such that it uses a declared-expression cache.
The XML configuration to sets the same value as the default:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<execution enable-declared-expr-value-cache="true"/>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>The API to change the setting:
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.getCompiler().getExecution().
setEnabledDeclaredExprValueCache(true);The settings related to serializers and deserializers (serdes) are only relevant when using high-availability with EsperHA. These settings are not relevant when not using EsperHA. Please see the EsperHA documentation for information.
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<serde-settings/>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>In multithreaded environments, this setting controls whether dispatches of statement result events to listeners preserve the ordering in which a statement processes events. By default the runtime guarantees that it delivers a statement's result events to statement listeners in the order in which the result is generated. This behavior can be turned off via configuration as below. This behavior applies to stateful statements and not to stateless statements as stateless statements execute lock-free.
The next code snippet shows how to control this feature:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getRuntime().getThreading().setListenerDispatchPreserveOrder(false);
And the XML configuration file can also control this feature by adding the following elements:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<threading>
<listener-dispatch preserve-order="true" timeout-msec="1000" locking="spin"/>
</threading>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>As discussed, by default the runtime can temporarily block another processing thread when delivering result events to listeners in order to preserve the order in which results are delivered to a given statement. The maximum time the runtime blocks a thread can also be configured, and by default is set to 1 second.
As such delivery locks are typically held for a very short amount of time, the default blocking technique employs a spin lock (There are two techniques for implementing blocking; having the operating system suspend the thread until it is awakened later or using spin locks). While spin locks are CPU-intensive and appear inefficient, a spin lock can be more efficient than suspending the thread and subsequently waking it up, especially if the lock in question is held for a very short time. That is because there is significant overhead to suspending and rescheduling a thread.
The locking technique can be changed to use a blocking strategy that suspends the thread, by means of setting the locking property to 'suspend'.
In multithreaded environments, this setting controls whether statements producing events for other statements via insert-into preserve the order of delivery within the producing and consuming statements, allowing statements that consume other statement's events to behave deterministic in multithreaded applications, if the consuming statement requires such determinism. By default, the runtime makes this guarantee (the setting is on). This behavior applies to stateful statements and not to stateless statements as stateless statements execute lock-free.
Take, for example, an application where a single statement (S1) inserts events into a stream that another statement (S2) further evaluates. A multithreaded application may have multiple threads processing events into statement S1. As statement S1 produces events for consumption by statement S2, such results may need to be delivered in the exact order produced as the consuming statement may rely on the order received. For example, if the first statement counts the number of events, the second statement may employ a pattern that inspects counts and thus expect the counts posted by statement S1 to continuously increase by 1 even though multiple threads process events.
The runtime may need to block a thread such that order of delivery is maintained, and statements that require order (such as pattern detection, previous and prior functions) receive a deterministic order of events. The settings available control the blocking technique and parameters. As described in the section immediately prior, the default blocking technique employs spin locks per statement inserting events for consumption, as the locks in questions are typically held a very short time. The 'suspend' blocking technique can be configured and a timeout value can also defined.
The XML configuration file may change settings via the following elements:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<threading>
<insert-into-dispatch preserve-order="true" timeout-msec="100" locking="spin"/>
</threading>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>
In multithreaded environments, this setting controls whether named windows producing insert and remove streams for other statements that consume the named window by
means of from-clause preserve the order of delivery within the producing named window and the consuming statements, allowing statements that consume named window's insert
and remove stream events to behave deterministic in multithreaded applications, if the consuming statement requires such determinism.
By default, the runtime makes this guarantee (the setting is on) with spin locking and Long.MAX_VALUE as millisecond timeout.
Take, for example, an application where a named window (W1) produces inserts and remove stream events that a statement (S1) consumes. A multithreaded application may have multiple threads producing insert and remove stream events for consumption by statement S1. Such results may need to be delivered in the exact order produced by the named window as the consuming statement may rely on the order received.
The runtime may need to block a thread such that order of delivery is maintained, and statements that require order receive a deterministic order of events. The settings available control the blocking technique and parameters. As described in the section immediately prior, the default blocking technique employs spin locks per named window producing insert and removed stream events for consumption, as the locks in questions are typically held a very short time. The 'suspend' blocking technique can be configured and a timeout value can also defined.
The XML configuration file may change settings via the following elements:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<threading>
<named-window-consumer-dispatch preserve-order="true" locking="spin"/>
</threading>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>This option can be used to disable the internal timer thread and such have the application supply external time events, as well as to set a timer resolution.
The next code snippet shows how to disable the internal timer thread via the configuration API:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getRuntime().getThreading().setInternalTimerEnabled(false);
This snippet of XML configuration leaves the internal timer enabled (the default) and sets a resolution of 200 milliseconds (the default is 100 milliseconds):
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<threading>
<internal-timer enabled="true" msec-resolution="200"/>
</threading>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>We recommend that when disabling the internal timer, applications send an external timer event setting the start time before creating statements, such that statement start time is well-defined.
The settings described herein are for enabling advanced threading options for inbound, outbound, timer and route executions.
Take the next snippet of XML configuration as an example. It configures all threading options to 2 threads, which may not be suitable to your application, however demonstrates the configuration:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<threading>
<threadpool-inbound enabled="true" num-threads="2"/>
<threadpool-outbound enabled="true" num-threads="2" capacity="1000"/>
<threadpool-timerexec enabled="true" num-threads="2"/>
<threadpool-routeexec enabled="true" num-threads="2"/>
</threading>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>
By default, queues are unbound and backed by java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue.
The optional capacity attribute can be set to instruct the threading option to configure a capacity-bound queue with a sender-wait (blocking put) policy, backed ArrayBlockingQueue.
This example uses the API for configuring inbound threading :
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getRuntime().getThreading().setThreadPoolInbound(true); config.getRuntime().getThreading().setThreadPoolInboundNumThreads(2);
With a bounded work queue, the queue size and pool size should be tuned together. A large queue coupled with a small pool can help reduce memory usage, CPU usage, and context switching, at the cost of potentially constraining throughput.
Note
If outbound-threading is enabled, listeners and subscribers that send events back into the runtime should use the sendEventType method and not the routeEvent method.
By default the runtime configures the runtime-level lock without fair locking. The runtime-level lock coordinates event processing threads (threads that send events) with threads that perform administrative functions (threads that deploy and undeploy statements, for example). A fair lock is generally less performing that an unfair lock thus the default configuration is an unfair lock.
If your application is multi-threaded and multiple threads sends events without gaps and if the per-event processing time is significant, then configuring a fair lock can help prioritize administrative functions. Administrative functions exclude event-processing threads until the administrative function completed. You may need to set this flag to prevent lock starvation to perform an administrative function in the face of concurrent event processing. Please consult the Java API documentation under ReentrantReadWriteLock and Fair Mode for more information.
The XML configuration to enable fair locking, which is disabled by default, is as follows:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<threading runtime-fairlock="true"/>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>The API to change the setting:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getRuntime().getThreading().setRuntimeFairlock(true);
By default, the runtime does not produce debug output for the event processing execution paths even when Log4j or Logger configurations have been set to output debug level logs. To enable debug level logging, set this option in the configuration as well as in your Log4j configuration file.
Statement-level processing information can be output via the @Audit annotation, please see Section 15.12.1, “@Audit Annotation”.
When debug-level logging is enabled by setting the flag as below and by setting DEBUG in the Log4j configuration file, then the timer processing may produce extensive debug output that
you may not want to have in the log file. The timer-debug setting in the XML or via API as below disables timer debug output which is enabled by default.
The API to use to enable debug logging and disable timer event output is shown here:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getRuntime().getLogging().setEnableExecutionDebug(true); config.getRuntime().getLogging().setEnableTimerDebug(false);
Note: this is a configuration option that applies to all runtime instances of a given Java module or VM.
The XML snippet is:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<logging>
<execution-path enabled="true"/>
<timer-debug enabled="false"/>
</logging>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>
The settings herein control the output format of @Audit logs.
This setting applies to all runtime instances in the same JVM. Please also see the API documentation for information on pattern conversion characters.
Table 17.5. Audit Log Conversion Characters
| Character | Description |
|---|---|
m | Audit message |
s | Statement name |
u | Runtime URI |
d | Deployment Id |
i | Context partition id |
c | Category |
tutc | Runtime time formatted in ISO-8601 instance format as a UTC value |
tzone | Runtime time formatted in ISO-8601 instance format as a zoned value according to the configured zone |
The API to use to set am audit log format is shown here:
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.getRuntime().getLogging().setAuditPattern("[%u] [%s] %m");The XML snippet is:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<logging>
<audit pattern="[%u] [%s]%m"/>
</logging>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>
By default, lock activity logging is disabled. When lock activity logging is enabled the runtime outputs, at INFO level and under the package name com.espertech.esper.lock,
information about read-write-lock activity. The output includes:
Acquirebefore the call tolock(),Gotafter the call tolock(),Releasebefore the call tounlock()andFreedafter the call tounlock()-
The text
writefor the write-lock and the textreadfor the read-lock - The read-write lock's system identity hash code
- The EPL statement name
-
The context partition id or
-1when unpartitioned -
The
tryLocktimeout milliseconds or-1when not applicable - The current read lock count
- A boolean value indicating whether the lock is write-locked
Note
Note that certain EPL statements execute lock-free and would thus not produce lock activity output.
The API to use to enable debug logging and disable timer event output is shown here:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getRuntime().getLogging().setEnableLockActivity(true);
The XML snippet is:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<logging>
<lock-activity enabled="true"/>
</logging>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>This setting controls the length of time that the runtime retains variable versions for use by statements that use variables and that execute, within the same statement for the same event, longer then the time interval. By default, the runtime retains 15 seconds of variable versions.
For statements that use variables and that execute (in response to a single timer or other event) longer then the time period, the runtime returns the current variable version at the time the statement executes, thereby softening the guarantee of consistency of variable values within the long-running statement. Please see Section 5.17.3, “Using Variables” for more information.
The XML configuration for this setting is shown below:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<variables>
<msec-version-release value="15000"/>
</variables>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>You may use this setting to limit the total runtime-wide number of pattern sub-expressions that all followed-by operators may manage. When the limit is reached, a condition is raised by the runtime through the condition callback API.
By default, when the limit is reached, the runtime also prevents the start of new pattern sub-expressions, until pattern sub-expressions end and the limit is no longer reached. By setting the prevent-start flag to false you can instruct the runtime to only raise a condition and continue to allow the start of new pattern sub-expressions.
The implications of the settings described herein are also detailed in Section 7.5.8.2, “Limiting Runtime-Wide Sub-Expression Count”.
A sample XML configuration for this setting is shown below:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<patterns>
<max-subexpression value="100" prevent-start="false"/>
</patterns>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>You may use this setting to limit the total runtime-wide number of states that all match-recognize constructs may manage. When the limit is reached, a condition is raised by the runtime through the condition callback API.
By default, when the limit is reached, the runtime also prevents the allocation of new states, until states get removed and the limit is no longer reached. By setting the prevent-start flag to false you can instruct the runtime to only raise a condition and continue to allow the allocation of new states.
The implications of the settings described herein are also detailed in Section 8.11, “Limiting Runtime-Wide State Count”.
A sample XML configuration for this setting is shown below:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<match-recognize>
<max-state value="100" prevent-start="false"/>
</match-recognize>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>This setting only applies if internal timer events control runtime time (default). If external timer events provide runtime clocking, the setting does not apply.
By default, the internal timer uses the call System.currentTimeMillis() to determine runtime time in milliseconds. Via this setting the internal timer can be instructed to use System.nanoTime() instead. Please see Section 16.9.2, “Time Resolution and Time Unit” for more information.
Note: This is a Java VM global setting. If running multiple runtime instances in a Java VM, the timer setting is global and applies to all runtime instances in the same Java VM, for performance reasons.
A sample XML configuration for this setting is shown below, whereas the sample setting sets the time source to the nanosecond time provider:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<time-source>
<time-source-type value="nano" />
</time-source>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>The equivalent code snippet using the configuration API is here:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getRuntime().getTimeSource().setTimeSourceType(TimeSourceType.NANO);
Please set the flag as described herein to have the runtime report key counters and other processing information through the JMX mbean platform server. By default JMX is not enabled. For NEsper .NET this section does not apply and there is currently no equivalent.
A sample XML configuration is shown below:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<metrics-reporting jmx-runtime-metrics="true"/>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>A sample code snippet to set this configuration via the API follows:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); configuration.getRuntime().getMetricsReporting().setJmxRuntimeMetrics(true);
This section explains how to enable and configure metrics reporting, which is by default disabled. Please see Section 16.12, “Runtime and Statement Metrics Reporting” for more information on the metrics data reported to your application.
The flag that enables metrics reporting is global to a Java virtual machine. If metrics reporting is enabled, the overhead incurred for reporting metrics is carried by all runtime instances per Java VM.
Metrics reporting occurs by a runtime-controlled separate daemon thread that each runtime instance starts at runtime initialization time, if metrics reporting and threading is enabled (threading enabled is the default).
Runtime and statement metric intervals are in milliseconds. A negative or zero millisecond interval value may be provided to disable reporting.
To control statement metric reporting for individual statements or groups of statements, the runtime provides a facility that groups statements by statement name. Each such statement group may have different reporting intervals configured, and intervals can be changed at runtime through runtime configuration. A statement group is assigned a group name at configuration time to identify the group.
Metrics reporting configuration is part of the runtime settings. All configuration options are also available via the Configuration API.
A sample XML configuration is shown below:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<metrics-reporting enabled="true" runtime-interval="1000" statement-interval="1000"
threading="true"/>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>
The runtime-interval setting (defaults to 10 seconds) determines the frequency in milliseconds at which the runtime reports runtime metrics, in this example every 1 second. The statement-interval is for statement metrics. The threading flag is true by default since reporting takes place by a dedicated runtime thread and can be set to false to use the external or internal timer thread instead.
The next example XML declares a statement group: The statements that have statement names that fall within the group follow a different reporting frequency:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<metrics-reporting enabled="true" statement-interval="0">
<stmtgroup name="MyStmtGroup" interval="2000" default-include="true" num-stmts="100"
report-inactive="true">
<exclude-regex>.*test.*</exclude-regex>
</stmtgroup>
</metrics-reporting>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>
The above example configuration sets the statement-interval to zero to disable reporting for all statements. It defines a statement group by name MyStmtGroup and specifies a 2-second interval. The example sets the default-include flag to true (by default false) to include all statements in the statement group. The example also sets report-inactive to true (by default false) to report inactive statements.
The exclude-regex element may be used to specify a regular expression that serves to exclude statements from the group. Any statement whose statement name matches the exclude regular expression is not included in the group. In the above example, all statements with the characters 'test' inside their statement name are excluded from the group.
Any statement not belonging to any of the statement groups follow the configured statement interval.
There are additional elements available to include and exclude statements: include-regex, include-like and exclude-like. The latter two apply SQL-like matching. All patterns are case-sensitive.
Here is a further example of a possible statement group definition, which includes statements whose statement name have the characters @REPORT or @STREAM, and excludes statements whose statement name have the characters @IGNORE or @METRICS inside.
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<metrics-reporting enabled="true">
<stmtgroup name="MyStmtGroup" interval="1000">
<include-like>%@REPORT%</include-like>
<include-regex>.*@STREAM.*</include-regex>
<exclude-like>%@IGNORE%</exclude-like>
<exclude-regex>.*@METRICS.*</exclude-regex>
</stmtgroup>
</metrics-reporting>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>
By default the runtime updates sub-selects with new events before evaluating the enclosing statement. This is relevant for statements that look for the same event in both the from clause and subselects.
To have runtime evaluate the enclosing clauses before updating the subselect in a subselect expression, set the flag as indicated herein.
The XML configuration as below sets the same as the default value:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<expression self-subselect-preeval="true"/>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>Here is a sample statement that utilitzes a sub-select against the same-events:
select * from MyEvent where prop not in (select prop from MyEvent#unique(otherProp))
By default the subselect data window updates first before the where clause is evaluated, thereby above statement never returns results.
Changing the setting described here causes the where clause to evaluate before the subselect data window updates, thereby the statement does post results.
By default, when performing calendar operations, the runtime uses the default time zone obtained by java.util.TimeZone.getDefault().
Use the setting herein to specify a time zone other then the default time zone.
The below XML configuration sets a time zone 'GMT-4:00':
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<expression time-zone="GMT-4:00"/>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>An example API configuration is shown next:
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.getRuntime().getExpression().setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("GMT-4:00"));By default the runtime ignores @Priority and @Drop annotations and executes unprioritized, that is the runtime does not attempt to interpret assigned priorities and reorder executions based on priority. Use this setting if your application requires prioritized execution.
By setting this configuration, the runtime executes statements, when an event or schedule matches multiple statements, according to the assigned priority, starting from the highest priority value. See built-in EPL annotations in Section 5.2.7.7, “@Priority”.
The XML configuration to enable the flag, which is disabled by default, is as follows:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<execution prioritized="true"/>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>The API to change the setting:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getRuntime().getExecution().setPrioritized(true);
By default, the runtime ignores event-precedence. This is because there can be a small performance cost
for tracking event precedence.
Use this setting if your application requires a processing order of insert-into events according to event precedence. Enabling this setting means that the runtime makes sure that the events in the work queue are ordered by event precedence.
For more information on the work queue and order of event processing, see Section 16.8.2.2, “Processing Principles of Events and Listener Updates”.
For more information of the event-precedence keyword, please refer to Section 5.10.10, “Insert Into and Event Precedence”.
The XML configuration to enable the flag, which is disabled by default, is as follows:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<execution precedence-enabled="true"/>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>The API to change the setting:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getRuntime().getExecution().setPrecedenceEnabled(true);
By default the runtime configures context partition locks without fair locking. If your application is multi-threaded and performs very frequent reads via iterator or fire-and-forget queries, you may need to set this flag to prevent lock starvation in the face of concurrent reads and writes. Please consult the Java API documentation under ReentrantReadWriteLock and Fair Mode for more information.
The XML configuration to enable fair locking, which is disabled by default, is as follows:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<execution fairlock="true"/>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>The API to change the setting:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getRuntime().getExecution().setFairlock(true);
By default the runtime configures context partition locks as required after analyzing your statements. You may disable context partition locks using the setting described here. Use the @NoLock annotation instead to disable locking for a given statement or named window only.
Warning
The runtime provides this setting for the purpose of identifying locking overhead, or when your application is single-threaded, or when using an external mechanism for concurrency control. Setting disable-locking to true may have unpredictable results unless your application is taking concurrency under consideration.
The XML configuration to disable context level locking is as follows:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<execution disable-locking="true"/>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>The API to change the setting:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getRuntime().getExecution().setDisableLocking(true);
This setting is for performance tuning of filter service which handles matching incoming events to context partitions and statements.
In the default configuration termed readmostly, filter service locking is coarse-grained assuming a large number of reads and comparatively few writes.
"Reads" are evaluations of events, while with "writes" we mean filter service changes such as new statements, a new pattern subexpression becoming active or a
pattern subexpression being deactivated.
Set the configuration to readwrite if you have multiple threads and your statements very frequently add and remove filters using pattern subexpressions, for example.
This setting instructs the runtime to maintain fine-grained locks instead generally allowing for higher concurrency but possibly incurring additional overhead.
The XML configuration to set a new filter service profile is as follows:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<execution filter-service-profile="readwrite"/>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>The API to change the setting:
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.getRuntime().getExecution().
setFilterServiceProfile(FilterServiceProfile.READWRITE);In the default configuration the setting is 1, which means that for each declared expression the runtime retains a cache of only the last computed value, for use for the duration of an evaluation of an event or time against a context partition. You may set the value to zero to disable caching. You may set the value to N to instruct the runtime to retain a cache of the last N computed values. This setting is not applicable to stateful declared expressions such as declared expressions with aggregation functions, for example.
The runtime only uses the declared expression cache for expressions that receive events as parameters. For expressions that receive other values as parameters the runtime does not use the declared expression cache.
The XML configuration to sets the same value as the default:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<execution declared-expr-value-cache-size="1"/>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>The API to change the setting:
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.getRuntime().getExecution().
setDeclaredExprValueCacheSize(1);
Use the settings as described here to register an exception handler factory class that provides an exception handler. The runtime invokes exception handlers in the order they are listed to handle a continues-query unchecked exception, as further described in Section 16.10, “Exception Handling”.
Please provide the full-qualified class name of each class that implements the com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.exception.ExceptionHandlerFactory interface in the runtime configuration as below.
By default, during a module undeploy when the runtime encounters a runtime exception for any of the statements it logs such exceptions as warnings.
You can set the undeploy-rethrow-policy flag to rethrow_first instead have the runtime rethrow the first runtime exception.
The XML configuration is as follows:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<exceptionHandling undeploy-rethrow-policy="warn">
<handlerFactory class="my.company.cep.MyCEPRuntimeExceptionHandlerFactory"/>
</exceptionHandling>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>The API calls to register an exception handler factory are as follows:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getRuntime().getExceptionHandling().addClass(MyCEPRuntimeExceptionHandlerFactory.class); config.getRuntime().getExceptionHandling().setUndeployRethrowPolicy(UndeployRethrowPolicy.RETHROW_FIRST);
Tip
The application-provided exception handler receives an ExceptionHandlerContext instance that contains the exception detail.
The application code that performs logging should log detailed information such as deployment and statement information.
The information can be useful to troubleshoot exceptions.
For inspiration, there is a code extract of the runtime's default exception handling code below.
For reference, we include the default exception handling code here:
if (exceptionHandlers.isEmpty()) {
StringWriter writer = new StringWriter();
if (type == ExceptionHandlerExceptionType.PROCESS) {
writer.append("Exception encountered processing ");
} else {
writer.append("Exception encountered performing instance stop for ");
}
writer.append("deployment-id '");
writer.append(deploymentId);
writer.append("' ");
writer.append("statement '");
writer.append(statementName);
writer.append("'");
if (optionalEPL != null) {
writer.append(" expression '");
writer.append(optionalEPL);
writer.append("'");
}
writer.append(" : ");
writer.append(t.getMessage());
String message = writer.toString();
if (type == ExceptionHandlerExceptionType.PROCESS) {
log.error(message, t);
} else {
log.warn(message, t);
}
return;
}
ExceptionHandlerContext context = new ExceptionHandlerContext(runtimeURI, t, deploymentId, statementName, optionalEPL, type, optionalCurrentEvent);
for (ExceptionHandler handler : exceptionHandlers) {
handler.handle(context);
}
Use the settings as described here to register a condition handler factory class that provides a condition handler. The runtime invokes condition handlers in the order they are listed to indicate conditions, which is the term used for notification when certain predefined limits are reached, as further described in Section 16.11, “Condition Handling”.
Please provide the full-qualified class name of each class that implements the com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.condition.ConditionHandlerFactory interface in the runtime configuration as below.
The XML configuration is as follows:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<runtime>
<conditionHandling>
<handlerFactory class="my.company.cep.MyCEPRuntimeConditionHandlerFactory"/>
</conditionHandling>
</runtime>
</esper-configuration>The API calls to register a condition handler factory are as follows:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getRuntime().getConditionHandling().addClass(MyCEPRuntimeConditionHandlerFactory.class);
The Configuration object allows passing application objects such as services or other transient objects.
This information can be used by extensions, listeners or subscribers, for example, to obtain application objects from the runtime.
Your application may provide a custom class loader or class-for-name service.
Use setTransientConfiguration and provide a Map<String, Object> that contains the application objects.
The runtime retains and makes available the same Map instance available via API. Its contents including services can be changed by an application at runtime.
The API methods to retrieve transient configuration are:
The
getConfigurationTransientsmethod ofEPRuntimeThe
getConfigurationDeepCopymethod ofEPRuntime
Assuming your application has a service myLocalService instance, the example code is:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); HashMap<String, Object> transients = new HashMap<String, Object>(); transients.put(SERVICE_NAME, myLocalService); // SERVICE_NAME is a well-known string value defined elsewhere configuration.getCommon().setTransientConfiguration(transients); EPRuntime runtime = EPRuntimeProvider.getDefaultRuntime(configuration);
A sample listener that receives a service from transient configuation is:
public class MyListener implements UpdateListener {
public void update(EventBean[] newEvents, EventBean[] oldEvents, EPStatement statement, EPRuntime runtime) {
MyLocalService service = (MyLocalService) runtime.getConfigurationTransient().get(SERVICE_NAME);
// use the service here
}
}An alternative means to obtain application services is to define a constant variable.
By default, when resolving a fully-qualified class name to a Class, the com.espertech.esper.common.client.util.ClassForNameProviderDefault uses:
ClassLoader cl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); return Class.forName(className, true, cl);
Your application can implement the com.espertech.esper.common.client.util.ClassForNameProvider interface to provide an alternate implementation.
For example, this provider prevents the System class from being available in EPL:
runtime.getConfigurationTransient().put(ClassForNameProvider.NAME,
new ClassForNameProvider() {
public Class classForName(String className) throws ClassNotFoundException {
if (className.equals(System.class.getName())) { // prevent the System class from loading
return null;
}
return Class.forName(className, true, Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader());
}
});
By default, to obtain a class loader, the com.espertech.esper.common.client.util.ClassLoaderProviderDefault uses Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().
Your application can implement the com.espertech.esper.common.client.util.ClassLoaderProvider interface to provide an alternate implementation.
For example, this provider returns a pre-determined classloader:
ClassLoader classLoader = new CustomClassLoader();
runtime.getConfigurationTransient().put(ClassLoaderProvider.NAME,
new ClassLoaderProvider() {
public ClassLoader classloader() {
return classLoader;
}
});Certain configuration values accept type names. Type names can occur in the configuration of variable types, Map-event property types as well as XPath cast types, for example. Types names are not case-sensitive.
The table below outlines all possible type names:
Table 17.6. Variable Type Names
| Type Name | Type |
|---|---|
string, varchar, varchar2 or java.lang.String | A string value |
int, integer or java.lang.Integer | An integer value |
long or java.lang.Long | A long value |
bool, boolean or java.lang.Boolean | A boolean value |
double or java.lang.Double | A double value |
float or java.lang.Float | A float value |
short or java.lang.Short | A short value |
char, character or java.lang.Character | A character value |
byte or java.lang.Byte | A byte value |
For NEsper .NET also see Section J.18, “.NET Configurations - Logging Configuration”.
The compiler and runtime log all messages to SLF4J under an appropriate log level. To output log messages you can add Log4j and SLF4J-Log4j (1.2) to classpath and configure Log4j as below.
The only direct dependency for logging is the SLF4J interfaces (slf4j-api-x.y.z.jar). Please see the SLF4J documentation on redirecting logs to other logging frameworks.
Statement-level processing information can be output, please see Section 15.12.1, “@Audit Annotation”.
For performance reasons, the runtime does not log any debug-level or informational-level messages for event execution unless explicitly configured via Section 17.6.2.1, “Execution Path Debug Logging”.
A callback API for receiving certain critical runtime reports is available as described in Section 16.10, “Exception Handling”.
More information on configuring runtime-level settings for logging are at Section 17.6.2, “Runtime Settings Related to Logging”.
The next table explains the log levels:
Table 17.7. Log Levels
| Log Level | Use |
|---|---|
| Debug | Displays detailed runtime-internal information that may not be easy to understand for application developers but are useful for runtime support. |
| Info | Used for a few critical runtime-level log messages. |
| Warn | Certain important warning or informational messages are displayed under the warning level. |
| Error | Exceptions reported within the runtime or by plug-in components are reported under the error level. |
Log4j is the default logging component. Please find additional information for Log4j configuration and extension in http://logging.apache.org/log4j.
The easiest way to configure Log4j is by providing a Log4J configuration file, similar to the log4j.xml file shipped in the etc folder of the distribution.
Add the log4j.configuration system property to the java command line and provide the file name of the Log4j configuration file, making sure your classpath also includes the directory of the file:
java -Dlog4j.configuration=log4j.xml ...
Your application can add Java class code (or C# class code for NEsper) directly into the EPL. The EPL compiler compiles the classes your application provides and makes the classes available for use within EPL. Classes can be local i.e. visible to the current module only, or global i.e. visible to other modules according to EPL-object visibility rules. The typical use of classes is to perform imperative programming or provide utility, integration or extension functionality.
For declaring classes that are visible across multiple statements i.e. globally visible classes please consult Section 18.3, “Declaring a Global Class”
that explains the create inlined_class clause. Inlined-classes are EPL-objects following visibility rules according to Section 15.2.2, “EPL-objects”.
Inlined classes can provide single-row functions as described in Section 22.2.1, “Using an Inlined Class to Provide a Single-Row Function”.
Inlined classes can provide aggregation single-functions as described in Section 22.5.1.4, “Using an Inlined Class to Provide an Aggregation Single-Function”.
Inlined classes can provide aggregation multi-functions as described in Section 22.5.2.8, “Using an Inlined Class to Provide an Aggregation Multi-Function”.
Inlined classes can serve as a variable type. The create variable clause allows the class name of an inlined class as a variable type.
A local inlined class is a class that is only visible to the same EPL statement that it is part of. The class is not visible to other EPL statements in the same module and is not visible to other modules.
The syntax for inlined classes is:
inlined_class"""class-text"""
Use the inlined_class keyword to declare a class. Place the class-text class code within three double-quotes (""").
The class-text class code is a Java class, i.e. public class class-name{...} or public enum class-name{...}.
The class text may specify a package name and imports. The class text is subject to limitations as listed below.
The next example shows a statement that calls a static method of an inlined-class by name MyUtility which computes the Fibonacci total for a given number:
inlined_class """
public class MyUtility {
public static double fib(int n) {
if (n <= 1)
return n;
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);
}
}
"""
select MyUtility.fib(intValue) from SomeEvent
Use the create inlined_class syntax to declare an inlined class. The compiler remembers the class
and allows the class to be referenced by other statements of the same module and by other modules.
The below EPL declares a globally visible class by name MyUtility that provides a method midPrice that computes a mid-price and that a buy and sell parameter:
create inlined_class """
public class MyUtility {
public static double midPrice(double buy, double sell) {
return (buy + sell) / 2;
}
}
"""The next EPL returns mid-price for each event:
select MyUtility.midPrice(buy, sell) from MarketDataEvent
The class name must be unique for global inlined classes. It is not possible to declare the same global inlined-class twice with the same class name and the same module name.
The runtime, at the time your application deploys a module that references global inlined classes, provides a classloader that adds the imported inlined classes that are provided by the deployment that contains the inlined classes. Thus the compiler and runtime never copy or otherwise duplicate the inlined class or class byte code.
The EPL compiler compiles the inlined classes to byte code and the runtime loads the byte code using a classloader that is aware of the inlined classes.
It is recommended that inlined class code executes non-blocking.
It is recommended that inlined class code is stateless. Please use plug-in aggregation functions or variables instead.
It is recommended that inlined class code is thread safe. EPL execution generally allows certain EPL statements and partitions to execute lock-free.
The compiler for inlined classes is Janino. Janino does not support all of Java 8 and higher. Please see the Janino documentation for more information.
The following limitations apply:
Annotations; an inlined class cannot be an annotation
Listeners or subscribers; an inlined class cannot be a listener or subscriber
Insert-into; for
insert into, your application cannot populate an instance of an inlined classEvent type; for
create schema, an inlined class cannot be a property type and cannot be an event typeNamed windows and tables; for
create windowand forcreate table, an inlined class cannot be a column typeThe
@typeannotation cannot be used with inlined classesInlined classes cannot be view, enumeration method, virtual data window or pattern extension classes
Script may not use inlined classes
EPL allows the use scripting languages within EPL. You may use scripts for imperative programming to execute certain code as part of EPL processing by the runtime.
The syntax and examples outlined below discuss how to declare a script that is visible to the same statement that listed the script.
For declaring scripts that are visible across multiple statements i.e. globally visible scripts please consult Section 5.18.3, “Global Scripts”
that explains the create expression clause.
Any scripting language that supports JSR 223 and also the MVEL scripting language can be specified in EPL. This section provides MVEL and JavaScript examples.
For more information on the MVEL scripting language and its syntax, please refer to the MVEL documentation. MVEL is an expression language that has a natural syntax for Java-based applications and compiles to provide fast execution times. To use MVEL with the runtime, please make sure to add the MVEL jar file to the application classpath.
For more information on JSR 223 scripting languages, please refer to external resources. As JSR 223 defines a standard API for script execution, your application may use any script execution that implements the API. Current JVM versions ship with a JavaScript script execution. Other script executors such as Groovy, Ruby and Python scripts can be used as implementations of JSR 223.
As an alternative to a script consider providing a custom single row function as described in Section 22.2, “Single-Row Function”.
The syntax for scripts is:
expression [return_type] [@type(eventtype_name)] [dialect_identifier:] script_name [ (parameters) ] [ script_body ]
Use the expression keyword to declare a script.
The return_type is optional. If the script declaration provides a return type the compiler can perform strong type checking: Any expressions that invoke the script and use the return value are aware of the return type. If no return type is provided the compiler assumes the script returns java.lang.Object. A parameterized type such as java.util.Collection<Integer> is also allowed as the return type.
If the return type of the script is EventBean[] you must provide the @type(name) annotation after the return type to name the event type of events returned by the script.
The @type is allowed only when the return type is EventBean instances.
The dialect_identifier is optional and identifies the scripting language. Use mvel for MVEL , js for JavaScript and python for Python and similar for other JSR 223 scripting languages.
If no dialect identifier is specified, the default dialect that is configured applies, which is js unless your application changes the default configuration.
It follows the script name. You may use the same script name multiple times and thus overload providing multiple signatures under the same script name. The combination of script name and number of parameters must be unique however.
If you have script parameters, specify the parameter names for the script as a comma-separated list of identifiers in parenthesis. It is not necessary to list parameter types.
The script body is the actual MVEL or JavaScript or other scripting language script and is placed in square brackets: [ ... script body ...].
The next example shows a statement that calls a JavaScript script which computes the Fibonacci total for a given number:
expression double js:fib(num) [
fib(num);
function fib(n) {
if(n <= 1)
return n;
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);
}
]
select fib(intPrimitive) from SupportBean;
The expression keyword is followed by the return type (double), the dialect (js) and the script name (fib) that declares a single parameter (num).
The JavaScript code that computes the Fibonacci total is between square brackets [].
The following example shows a statement that calls a MVEL script which outputs all the different colors that are listed in the colors property of each ColorEvent:
expression mvel:printColors(colors) [
String c = null;
for (c : colors) {
System.out.println(c);
}
]
select printColors(colors) from ColorEvent;This example instead uses JavaScript to print colors and passes the event itself as a script parameter (this example is for Java 8 and Nashorn):
expression js:printColors(colorEvent) [ print(java.util.Arrays.toString(colorEvent.getColors())); ] select printColors(colorEvent) from ColorEvent as colorEvent
The next example creates a globally-visible script that returns ItemEvent events,
assuming that the ItemEvent event type is an event type defined by create schema ItemEvent(id string):
create expression EventBean[] @type(ItemEvent) js:myScriptReturnsEvents() [
myScriptReturnsEvents();
function myScriptReturnsEvents() {
var EventBeanArray = Java.type(\"com.espertech.esper.common.client.EventBean[]\");
var events = new EventBeanArray(1);
events[0] = epl.getEventBeanService().adapterForMap(java.util.Collections.singletonMap(\"id\", \"id1\"), \"ItemEvent\");
return events;
}
// sample EPL:
// select myScriptReturnsEvents().where(v => v.id in ('id1', 'id3')) from MyEvent]
The compiler provides a built-in script object under the variable name epl to all scripts. Your scripts may use this script object to share and retain state by setting and reading script attributes.
The runtime maintains a separate script object per context partition or per statement if not declaring a context. Therefore script attributes are not shared between statements,
however multiple scripts executed by the same context partition receive the same script object.
The epl script object implements the interface com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.expr.EPLScriptContext.
Please see the JavaDoc for services provided by EPLScriptContext.
For script state management, the EPLScriptContext interface has two methods: The void setScriptAttribute(String attribute, Object value) method to set an attribute value and the Object getScriptAttribute(String attribute) method to read an attribute value.
The next example demonstrates the use of the epl script object. It outputs a flag value true when an RFID event matched because the location is A,
and outputs a flag value false when an RFID event matched because the location is B. The example works the same for either MVEL or JavaScript dialects: You may simple replace the js dialect with mvel.
expression boolean js:setFlag(name, value, returnValue) [
if (returnValue) epl.setScriptAttribute(name, value);
returnValue;
]
expression js:getFlag(name) [
epl.getScriptAttribute(name);
]
select getFlag('locA') as flag from RFIDEvent(zone = 'Z1' and
(setFlag('locA', true, location = 'A') or setFlag('locA', false, location = 'B')) )
The example above utilizes two scripts: The setFlag script receives an attribute name, attribute value and a return value. The script sets the script attribute only when the return value is true. The getFlag script simply returns the script attribute value.
Upon statement compilation, the compiler resolves script parameter types and performs script compilation. At runtime the runtime evaluates the script in its compiled form.
As the compiler cannot inspect scripts if is not possible for the compiler to perform query planning or many optimizations based on the information in scripts. It is thus recommended to structure EPL such that basic filter and join expressions are EPL expressions and not script expressions.
Your EPL may declare a return type for the script. If no return type is declared and when using the MVEL dialect, the compiler will infer the return type from the MVEL expression analysis result. If the return type is not provided and cannot be inferred or the dialect is not MVEL, the return type is Object.
If the EPL declares a numeric return type then the compiler performs coercion of the numeric result to the return type that is specified.
In the case that the EPL declares a return type that does not match the type of the actual script return value, the compiler does not check return value type.
- 20.1. Overview
- 20.2. Spatial Methods
- 20.3. Spatial Index - Quadtree
- 20.3.1. Overview
- 20.3.2. Declaring a Point-Region Quadtree Index
- 20.3.3. Using a Point-Region Quadtree as a Filter Index
- 20.3.4. Using a Point-Region Quadtree as an Event Index
- 20.3.5. Declaring a MX-CIF Quadtree Index
- 20.3.6. Using a MX-CIF Quadtree as a Filter Index
- 20.3.7. Using a MX-CIF Quadtree as an Event Index
- 20.4. Spatial Types, Functions and Methods from External Libraries
EPL provides spatial methods and spatial indexes.
The compiler analyzes filter criteria and the where-clause and considers spatial methods, utilizing spatial filter indexes or spatial event indexes for efficient matching and lookup.
For general information on the dot-operator please consult Section 9.7, “Dot Operator”.
The below table summarizes the built-in spatial methods available:
Table 20.1. Spatial Methods
| Method | Result |
|---|---|
| point(x,y).inside(rectangle(x,y,width,height)) |
Returns true if the point is inside the rectangle. |
| rectangle(x,y,width,height).intersects(rectangle(x,y,width,height)) |
Returns true if the rectangle intersects with the rectangle. |
The method compares a point to a rectangle and returns true if the point falls inside the rectangle.
The method takes a point as input and a rectangle as a parameter:
point(point_x, point_y [, filterindex:configexpression]).inside(rectangle(rect_x, rect_y, width, height))
For the point, please provide the point_x and point_y expressions that return the (x, y)-coordinates of the point.
The filterindex named parameter is for use with filter indexes as described below.
The left-hand side point can be subject to point-region quadtree indexing (MX-CIF quadtrees do not apply).
For the rectangle, the rect_x expression and rect_y expressions return the (x, y)-coordinates of the rectangle and the width expression and height expressions return the width and height of the rectangle.
All expressions must return a number-type and the implementation compares the double-values returned by the expressions.
A point is considered inside the rectangle if (point_x >= rect_x) and (point_x < rect_x + width) and (point_y >= rect_y) and (point_y < rect_y + height).
Table 20.2. Point-Inside-Rectangle Examples
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
point(10, 20).inside(rectangle(0, 0, 50, 50)) | true |
point(10, 20).inside(rectangle(20, 20, 50, 50)) | false |
point(10, 20).inside(rectangle(9, 19, 1, 1)) | false |
point(10, 20).inside(rectangle(9, 19, 1.0001, 1.0001)) | true |
The method compares a rectangle to a rectangle and returns true if the rectangles intersect.
The method takes a rectangle as input and a rectangle as a parameter:
rectangle(rect_x, rect_y, rect_width, rect_height [, filterindex:configexpression]).intersects(rectangle(other_x, other_y, other_width, other_height))
The left-hand side is the rectangle's rect_x, rects_y, rect_width and rect_height expressions
that return the (x, y)-coordinates and the size of the rectangle.
The filterindex named parameter is for use with filter indexes as described below.
The left-hand side rectangle can be subject to MX-CIF quadtree indexing (point-region quadtrees do not apply).
For the compared-to rectangle on the right-hand side, the other_x, other_y, other_width and other_height expressions return the (x, y)-coordinates and size of the compared-to rectangle.
All expressions must return a number-type and the implementation compares the double-values returned by the expressions.
A rectangle is considered to intersect another rectangle if:
rect_x + rect_width >= other_x(a is not left of b) andrect_x <= other_x + other_width(a is not right of b) andrect_y + rect_height >= other_y(a is not above b) andrect_y <= other_y + other_height(a is not below b).
Table 20.3. Rectangle-Intersects-Rectangle Examples
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
rectangle(10, 20, 5, 5).intersects(rectangle(0, 0, 50, 50)) | true |
rectangle(10, 20, 5, 5).intersects(rectangle(20, 20, 50, 50)) | false |
rectangle(10, 20, 5, 5).intersects(rectangle(9, 19, 1, 1)) | true |
rectangle(10, 20, 5, 5).intersects(rectangle(9, 19, 0.999, 0.999)) | false |
rectangle(10, 20, 5, 5).intersects(rectangle(15, 25, 1, 1)) | true |
rectangle(10, 20, 5, 5).intersects(rectangle(15.001, 25.001, 1, 1)) | false |
A quadtree is a tree data structure in which each branch node has exactly four children. Quadtrees are often used to partition a two-dimensional space by recursively subdividing it into four quadrants or regions (source:WikiPedia).
Quadtree indexes can be used for:
Filter indexes, which organize active filters so that they can be searched efficiently. When the runtime receives an event, it consults the filter indexes to determine which statements, if any, must process the event.
Event indexes, which organize properties of events so that they can be searched efficiently. When the runtime performs statement processing it may use event indexes to find correlated events efficiently.
The point-region quadtree is a quadtree for the efficient finding of points that fall inside a given rectangle. Use this index with the point-inside-rectangle method described above.
The MX-CIF quadtree is a quadtree for the efficient finding of rectangles that intersect with a given rectangle. Use this index with the rectangle-intersects-rectangle method described above.
While point-region quadtree and MX-CIF quadtree are similar, they are not compatible and are not the same. In point-region quadtree, only leaf nodes have data. In MX-CIF quadtrees both branch and leaf nodes have data as branches hold rectangles that don't fit any given quadrant. The runtime expands and shrinks both types of trees dynamically based on data by promoting or subdividing a leaf node to branch nodes when adding data and by demoting or merging branches to a leaf node when removing data.
Declaring a point-region quadtree index is the same for both filter indexes and event indexes. Point-region quadtrees are suitable for efficiently finding points inside a rectangle, when there are many points.
The synopsis to declare a point-region quadtree index, as part of a statement, is:
pointregionquadtree(min_x_expression, min_y_expression, width, height [, leaf_capacity_expression [, max_tree_height_expression]])
The min_x_expression, min_y_expression, width, height are index parameter expressions
that return the range of the index. The width and height must be greater zero. The index range rectangle is represented by double-type values internally.
A point is inside the index range if x >= minX and y >= minY and x < minX+width and y < minY+height.
Note
An attempt to insert points into the index that are outside of the declared index range causes an exception.
The leaf_capacity_expression is optional and must return a positive integer. It defines the number of coordinates a node may contain before it gets split into regions. The default value is 4.
The max_tree_height_expression is optional and must return an integer value of 2 or more. It defines the maximum depth of the tree. Upon the tree reaching the maximum depth a leaf node does not get split into regions. The default value is 20.
The section that summarizes filter indexes is Section 2.18.2, “Filter Indexes”.
As there could be many point(...).inside(rectangle) filters active, having a filter index allows the runtime to efficiently match incoming events to statements.
For use of a point-region quadtree index within filter criteria you must:
Define an expression that returns the point-region quadtree configuration, making sure it specifies
pointregionquadtree.Add the
filterindexnamed parameter providing the expression name.
For defining a local or global expression, please consult Section 5.2.9, “Expression Declaration”.
This sample statement defines the point-region quadtree filter index to have a bounding box of (0,0,100,100):
expression myPointRegionQuadtreeSettings { pointregionquadtree(0, 0, 100, 100) }
select * from RectangleEvent(point(0, 0, filterindex:myPointRegionQuadtreeSettings).inside(rectangle(x, y, width, height)))
The filterindex named parameter instructs the runtime that the settings for the point-region quadtree filter index are provided by the expression myPointRegionQuadtreeSettings, a local expression in this example.
For sharing point-region quadtree settings across statements you may use a global expression instead. Please see Section 5.18, “Declaring Global Expressions, Aliases and Scripts: Create Expression”.
If your EPL does not specify filterindex the runtime does not build a point-region quadtree filter index.
If your EPL specifies filterindex the runtime always builds and uses a point-region quadtree filter index.
In the case the compiler analyses filter criteria and determines that it cannot use the point-region quadtree filter index, the compiler fails statement validation.
If your EPL specifies filterindex and the compiler determines that it cannot use the point-region quadtree filter index it fails statement validation.
The runtime shares point-region quadtree filter indexes across the runtime within the same event type given that:
Filters have the same
rectangleexpressions.Filters use the same
filterindexparameter i.e. the textmyPointRegionQuadtreeSettingsin above example.Filters use the same point-region quadtree index configuration i.e.
pointregionquadtree(0,0,100,100)in above example.
For use with the filterindex named parameter, the following requirements apply towards point expressions:
Point expressions must be a constant, a context-provided built-in property or an event property provided by a previous pattern match within the same pattern.
For use with the filterindex named parameter, the following requirements apply towards rectangle expressions:
Rectangle expressions must be event properties.
The section that summarizes event indexes is Section 2.18.3, “Event Indexes”. The create index clause is described in Section 6.9, “Explicitly Indexing Named Windows and Tables”.
Declare a point-region quadtree event index as follows:
create index ... on ... ( (x_expression, y_expression) pointregionquadtree(pointregion_quadtree_configuration) )
The x_expression and y_expression expressions form the index columns.
The expressions return the (x, y)-coordinates and must return numeric values. Coordinates are represented as double-type values internally.
See above for the pointregion_quadtree_configuration point-region quadtree configuration.
For example, assume a table that contains points:
create table PointTable(pointId string primary key, px double, py double)
This example EPL declares an index on the points, with px and py becoming index columns that determine (x, y)-coordinates:
create index PointIndex on PointTable((px, py) pointregionquadtree(0, 0, 100, 100))
The above sample quadtree index expects (x, y)-coordinates that are in the range 0 <= px <= 100 and 0 <= py <= 100.
The example schema for events providing rectangles is:
create schema RectangleEvent(rx double, ry double, w double, h double)
This EPL outputs, upon arrival of a RectangleEvent, all points that fall inside the rectangle:
on RectangleEvent select pointId from PointTable where point(px, py).inside(rectangle(rx, ry, w, h))
Internally the runtime does not instantiate point or rectangle objects at all but instead optimizes the expression to comparison between double-type values.
Point-Region quadtree indexes allow computed values for both index columns and index parameters. For example, the following EPL declares an index wherein (x, y)-coordinates are (px/100, py/100)-values. The sample EPL assumes that context.frame is a built-in property as provided by context FramedCtx:
context FramedCtx create index PointIndex on PointTable((Math.round(px/100), Math.round(py/100)) pointregionquadtree(context.frame.startx, context.frame.starty, context.frame.w, context.frame.h))
The compiler compares the index column expressions to the point-inside-rectangle left-hand-side expressions to determine which index to use.
For example, if the expression is point(px+1, py+1).inside(rectangle(rx, ry, w, h))
as (px+1, py+1) does not match (Math.round(px/100), Math.round(py/100)) the query planner does not use the index.
If the expression is point(Math.round(px/100), Math.round(py/100)).inside(rectangle(rx, ry, w, h)) the query planner does use the index as index column expressions match.
The query planner prefers point-region quadtree over other index types. Index hints are not yet available for query planning with quadtree indexes.
Declaring a MX-CIF quadtree index is the same for both filter indexes and event indexes. MX-CIF quadtrees are suitable for efficiently finding rectangles that intersect with a rectangle, when there are many rectangles.
The synopsis to declare a MX-CIF quadtree index, as part of a statement, is:
mxcifquadtree(min_x_expression, min_y_expression, width, height [, leaf_capacity_expression [, max_tree_height_expression]])
The min_x_expression, min_y_expression, width, height are index parameter expressions
that return the range of the index. The width and height must be greater zero. The index range rectangle is represented by double-type values internally.
A given rectangle must intersect with the index range.
Note
An attempt to insert rectangles into the index that do not intersect with the declared index range causes an exception.
The leaf_capacity_expression is optional and must return a positive integer. It defines the number of coordinates a node may contain before it gets split into regions. The default value is 4.
The max_tree_height_expression is optional and must return an integer value of 2 or more. It defines the maximum depth of the tree. Upon the tree reaching the maximum depth a leaf node does not get split into regions. The default value is 20.
The section that summarizes filter indexes is Section 2.18.2, “Filter Indexes”.
As there could be many rectangle(...).intersects(rectangle) filters active, having a filter index allows the runtime to efficiently match incoming events to statements.
For use of a MX-CIF quadtree index within filter criteria you must:
Define an expression that returns the MX-CIF quadtree configuration, making sure it specifies
mxcifquadtree.Add the
filterindexnamed parameter providing the expression name.
For defining a local or global expression, please consult Section 5.2.9, “Expression Declaration”.
This sample statement defines the MX-CIF quadtree filter index to have a bounding box of (0,0,100,100):
expression myMXCIFQuadtreeSettings { mxcifquadtree(0, 0, 100, 100) }
select * from RectangleEvent(rectangle(10, 20, 5, 5, filterindex:myMXCIFQuadtreeSettings).intersects(rectangle(x, y, width, height)))
The filterindex named parameter instructs the compiler that the settings for the MX-CIF quadtree filter index are provided by the expression myMXCIFQuadtreeSettings, a local expression in this example.
For sharing MX-CIF quadtree settings across statements you may use a global expression instead. Please see Section 5.18, “Declaring Global Expressions, Aliases and Scripts: Create Expression”.
If your EPL does not specify filterindex the runtime does not build a MX-CIF quadtree filter index.
If your EPL specifies filterindex the runtime always builds and uses a MX-CIF quadtree filter index.
In the case the compiler analyses filter criteria and determines that it cannot use the MX-CIF quadtree filter index, the compiler fails statement validation.
If your EPL specifies filterindex and the compiler determines that it cannot use the MX-CIF quadtree filter index it fails statement validation.
The runtime shares MX-CIF quadtree filter indexes across the runtime within the same event type given that:
Filters have the same
rectangleexpressions.Filters use the same
filterindexparameter i.e. the textmyMXCIFQuadtreeSettingsin above example.Filters use the same MX-CIF quadtree index configuration i.e.
mxcifquadtree(0,0,100,100)in above example.
For use with the filterindex named parameter, the following requirements apply towards left-hand side rectangle expressions:
Left-hand side rectangle expressions must be a constant, a context-provided built-in property or an event property provided by a previous pattern match within the same pattern.
For use with the filterindex named parameter, the following requirements apply towards right-hand side rectangle expressions:
Right-hand side rectangle expressions must be event properties.
The section that summarizes event indexes is Section 2.18.3, “Event Indexes”. The create index clause is described in Section 6.9, “Explicitly Indexing Named Windows and Tables”.
Declare a MX-CIF quadtree event index as follows:
create index ... on ... ( (x_expression, y_expression, width_expression, height_expression) mxcifquadtree(mxcif_quadtree_configuration) )
The x_expression, y_expression, width_expression and height_expression expressions form the index columns.
The expressions return the (x, y)-coordinates and rectangle size and must return numeric values. Coordinates and sizes are represented as double-type values internally.
See above for the mxcif_quadtree_configuration MX-CIF quadtree configuration.
For example, assume a table that contains rectangles:
create table RectangleTable(rectangleId string primary key, rx double, ry double, rwidth double, rheight double)
This example EPL declares an index on the rectangles, with rx, ry, rwidth and rheight becoming index columns that determine the (x, y)-coordinates and the sizes:
create index RectangleIndex on RectangleTable((rx, ry, rwidth, rheight) mxcifquadtree(0, 0, 100, 100))
The above sample quadtree index expects rectangles to intersect the rectangle (0, 0, 100, 100).
The example schema for arriving events is:
create schema OtherRectangleEvent(otherX double, otherY double, otherWidth double, otherHeight double)
This EPL outputs, upon arrival of a OtherRectangleEvent, all rectangles stored in the table that intersect the arriving-events rectangle:
on OtherRectangleEvent select rectangleId from RectangleTable where rectangle(rx, ry, rwidth, rheight).intersects(rectangle(otherX, otherY, otherWidth, otherHeight))
Internally the runtime does not instantiate rectangle objects at all but instead optimizes the expression to comparison between double-type values.
MX-CIF quadtree indexes allow computed values for both index columns and index parameters. For example, the following EPL declares an index wherein (x, y)-coordinates are (px/100, py/100)-values. The sample EPL assumes that context.frame is a built-in property as provided by context FramedCtx:
context FramedCtx create index RectangleIndex on RectangleTable((Math.round(rx/100), Math.round(ry/100), Math.round(rwidth/100), Math.round(rheight/100)) mxcifquadtree(context.frame.startx, context.frame.starty, context.frame.w, context.frame.h))
The compiler compares the index column expressions to the rectangle-interwsects-rectangle left-hand-side expressions to determine which index to use.
The query planner prefers MX-CIF quadtree over other index types. Index hints are not yet available for query planning with quadtree indexes.
The scope of the compiler and runtime does not include addressing all geographical, topological or spatial processing. We encourage using external libraries for library calls. EPL makes it easy to use and extend EPL, using functions, methods, data types and data structures provided by external libraries.
For example, assume you would like to use a geometric data type and the geographical distance function.
Please consider using the Java Topology Suite (JTS) (https://www.locationtech.org) which provides a pretty complete set of geo computing functionality.
To pick an example data type, the compiler and runtime allow any class such as the JTS Geometry class (org.locationtech.jts.geom.Geometry) to become an event type, an event property type or a column type in a named window, table.
The compiler and runtime also allow the use of such class anywhere within EPL expressions.
The EPL snippet below declares an event type that has a Geometry property:
create schema ShapeArrivalEvent(shapeId string, geometry org.locationtech.jts.geom.Geometry) // use imports to remove the need to have a package name
EPL can call methods and your application can declare its own functions. Registering an own EPL function is described in Section 22.2, “Single-Row Function”.
This sample EPL outputs events that have a distance of more than 100 comparing the current event's geometry to the last 1 minute of previous event's geometry:
select * from ShapeArrivalEvent as e1 unidirectional, ShapeArrivalEvent.time(1 minute) as e2 where e1.geometry.distance(e2.geometry) > 100
Data flows in EPL have the following purposes:
Support for data flow programming and flow-based programming.
Declarative and runtime manageable integration of input and output adapters that may be provided by EsperIO or by an application.
Remove the need to use an event bus achieving dataflow-only visibility of events and event types for performance gains.
Data flow operators communicate via streams of either underlying event objects or wrapped events. Underlying event objects are POJO, Map, Object-array or DOM/XML. Wrapped events are represented by EventBean instances that associate type information to underlying event objects.
For more information on data flow programming or flow-based programming please consult the Wikipedia FBP Article.
EPL offers a number of useful built-in operators that can be combined in a graph to program a data flow. In addition EsperIO offers prebuilt operators that act as sources or sinks of events. An application can easily create and use its own data flow operators.
Using data flows an application can provide events to the data flow operators directly without using an runtime's event bus. Not using an event bus (as represented by the sendEventType methods of EPEventService) can achieve performance gains as the runtime does not need to match events to statements and the runtime does not need to wrap underlying event objects in EventBean instances.
Data flows also allow for finer-grained control over threading, synchronous and asynchronous operation.
Your application declares a data flow using create dataflow dataflow-name. Declaring the data flow causes the EPL compiler to validate the syntax and some aspects of the data flow graph of operators. Declaring the data flow does not actually instantiate or execute a data flow. Resolving event types and instantiating operators (as required) takes place at time of data flow instantiation.
After your application has declared a data flow, it can instantiate the data flow and execute it. A data flow can be instantiated as many times as needed and each data flow instance can only be executed once.
The example EPL below creates a data flow that, upon execution, outputs the text Hello World to console and then ends.
create dataflow HelloWorldDataFlow
BeaconSource -> helloworld.stream { text: 'hello world' , iterations: 1}
LogSink(helloworld.stream) {}
The sample data flow above declares a BeaconSource operator parameterized by the "hello world" text and 1 iteration. The -> keyword reads as produces streams. The BeaconSource operator produces a single stream named helloworld.stream. The LogSink operator receives this stream and prints it unformatted.
The next program code snippet declares the data flow to the runtime:
String epl = "create dataflow HelloWorldDataFlow\n" +
"BeaconSource -> helloworldStream { text: 'hello world' , iterations: 1}\n" +
"LogSink(helloworldStream) {}";
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
CompilerArguments compilerArguments = new CompilerArguments(configuration);
EPCompiled compiled = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler().compile(epl, compilerArguments);
EPDeployment deployment = runtime.getDeploymentService().deploy(compiled);After declaring a data flow to a runtime, your application can then instantiate and execute the data flow.
The following program code snippet instantiates the data flow:
EPDataFlowInstance instance = runtime.getDataFlowService().instantiate(deployment.getDeploymentId(), "HelloWorldDataFlow");
A data flow instance is represented by an EPDataFlowInstance object.
The next code snippet executes the data flow instance:
instance.run();
By using the run method of EPDataFlowInstance the runtime executes the data flow using the same thread (blocking execute) and returns when the data flow completes. A data flow completes when all operators receive final markers.
The hello world data flow simply prints an unformatted Hello World string to console. Please check the built-in operator reference for BeaconSource and LogSink for more options.
The synopsis for declaring a data flow is:
create dataflow name [schema_declarations] [operator_declarations]
After create dataflow follows the data flow name and a mixed list of event type (schema) declarations and operator declarations.
Schema declarations define an event type. Specify any number of create schema clauses as part of the data flow declaration followed by a comma character to end each schema declaration. The syntax for create schema is described in Section 5.15, “Declaring an Event Type: Create Schema”.
All event types that are defined as part of a data flow are private to the data flow and not available to other statements. To define event types that are available across data flows and other statements, use a create schema statement, runtime or static configuration.
Annotations as well as expression declarations and scripts can also be pre-pended to the data flow declaration.
For each operator, declare the operator name, input streams, output streams and operator parameters.
The syntax for declaring a data flow operator is:
operator_name [(input_streams)] [-> output_streams] { [parameter_name : parameter_value_expr] [, ...] }
The operator name is an identifier that identifies an operator.
If the operator accepts input streams then those may be listed in parenthesis after the operator name, see Section 21.2.2.2, “Declaring Input Streams”.
If the operator can produce output streams then specify -> followed by a list of output stream names and types. See Section 21.2.2.3, “Declaring Output Streams”.
Following the input and output stream declaration provide curly brackets ({}) containing operator parameters. See Section 21.2.2.4, “Declaring Operator Parameters”.
An operator that receives no input streams, produces no output streams and has no parameters assigned to it is shown in this EPL example data flow:
create dataflow MyDataFlow
MyOperatorSimple {}
The next EPL shows a data flow that consists of an operator MyOperator that receives a single input stream myInStream and produces a single output stream myOutStream holding MyEvent events.
The EPL configures the operator parameter myParameter with a value of 10:
create dataflow MyDataFlow
create schema MyEvent as (id string, price double),
MyOperator(myInStream) -> myOutStream<MyEvent> {
myParameter : 10
}The next sections outline input stream, output stream and parameter assignment in greater detail.
In case the operator receives input streams, list the input stream names within parenthesis following the operator name. As part of the input stream declaration you may use the as keyword to assign an alias short name to one or multiple input streams.
The EPL shown next declares myInStream and assigns the alias mis:
create dataflow MyDataFlow
MyOperator(myInStream as mis) {}Multiple input streams can be listed separated by comma. We use the term input port to mean the ordinal number of the input stream in the order the input streams are listed.
The EPL as below declares two input streams and assigns an alias to each. The runtime assigns streamOne to input port 0 (zero) and streamTwo to port 1.
create dataflow MyDataFlow
MyOperator(streamOne as one, streamTwo as two) {}You may assign multiple input streams to the same port and alias by placing the stream names into parenthesis. All input streams for the same port must have the same event type associated.
The next statement declares an operator that receives input streams streamA and streamB both assigned to port 0 (zero) and alias streamsAB:
create dataflow MyDataFlow
MyOperator( (streamA, streamB) as streamsAB) {}Input and output stream names can have the dot-character in their name.
The following is also valid EPL:
create dataflow MyDataFlow
MyOperator(my.in.stream) -> my.out.stream {}Note
Reserved keywords may not appear in the stream name.
In case the operator produces output streams, list the output streams after the -> keyword. Multiple output streams can be listed separated by comma. We use the term output port to mean the ordinal number of the output stream in the order the output streams are listed.
The sample EPL below declares an operator that produces two output streams my.out.one and my.out.two.
create dataflow MyDataFlow
MyOperator -> my.out.one, my.out.two {}
Each output stream can be assigned optional type information within less/greater-then (<>). Type information is required if the operator cannot deduce the output type from the input type and the operator does not declare explicit output type(s). The event type name can
either be an event type defined within the same data flow or an event type defined in the runtime.
This EPL example declares an RFIDSchema event type based on an object-array event representation and associates the output stream rfid.stream with the RFIDSchema type.
The stream rfid.stream therefore carries object-array (Object[]) typed objects according to schema RFIDSchema:
create dataflow MyDataFlow
create objectarray schema RFIDSchema (tagId string, locX double, locY double),
MyOperator -> rfid.stream<RFIDSchema> {}
The keyword eventbean is reserved: Use eventbean<type-name> to indicate that a stream carries EventBean instances of the given type instead of the underlying event object.
This EPL example declares an RFIDSchema event type based on an object-array event representation and associates the output stream rfid.stream with the event type,
such that the stream rfid.stream carries EventBean objects:
create dataflow MyDataFlow
create objectarray schema RFIDSchema (tagId string, locX double, locy double),
MyOperator -> rfid.stream<eventbean<RFIDSchema>> {}
Use questionmark (?) to indicate that the type of events is not known in advance.
In the next EPL the stream my.stream carries EventBean instances of any type:
create dataflow MyDataFlow
MyOperator -> my.stream<eventbean<?>> {}
Operators can receive constants, objects, EPL expressions and complete statements as parameters. All parameters are listed within curly brackets ({}) after input and output stream declarations. Curly brackets are required as a separator even if
the operator has no parameters.
The syntax for parameters is:
name : value_expr [,...]
The parameter name is an identifier that is followed by the colon (:) or equals (=) character and a value expression. A value expression can be any expression, system property, JSON notation object or statement. Parameters are separated by comma character.
The next EPL demonstrates operator parameters that are scalar values:
create dataflow MyDataFlow
MyOperator {
stringParam : 'sample',
secondString : "double-quotes are fine",
intParam : 10
}
Operator parameters can be any EPL expression including expressions that use variables. Subqueries, aggregations and the prev and prior functions cannot be applied here.
The EPL shown below lists operator parameters that are expressions:
create dataflow MyDataFlow
MyOperator {
intParam : 24*60*60,
threshold : var_threshold // a variable defined in the runtime
}
To obtain the value of a system property, the special systemProperties property name is reserved for access to system properties.
The following EPL sets operator parameters to a value obtained from a system property:
create dataflow MyDataFlow
MyOperator {
someSystemProperty : systemProperties('mySystemProperty')
}
Any JSON value can also be used as a value. Use square brackets [] for JSON arrays. Use curly brackets {} to hold nested Map or other object values. Provide the special class property to
instantiate a given instance by class name. The runtime populates the respective array, Map or Object as specified in the JSON parameter value.
The below EPL demonstrates operator parameters that are JSON values:
create dataflow MyDataFlow
MyOperator {
myStringArray: ['a', "b"],
myMapOrObject: {
a : 10,
b : 'xyz',
},
myInstance: {
class: 'com.myorg.myapp.MyImplementation',
myValue : 'sample'
}
}
The special parameter name select is reserved for use with EPL select statements. Please see the Select built-in operator for an example.
The below table summarizes the built-in data flow operators available:
Table 21.1. Built-in Operators
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| BeaconSource |
Utility source that generates events. See Section 21.3.1, “BeaconSource”. |
| Emitter |
Special operator for injecting events into a stream. See Section 21.4.5, “Start Captive”. |
| EPStatementSource |
One or more statements act as event sources. See Section 21.3.2, “EPStatementSource”. |
| EventBusSink |
The event bus is the sink: Sends events from the data flow into the event bus. See Section 21.3.3, “EventBusSink”. |
| EventBusSource |
The event bus is the source: Receives events from the event bus into the data flow. See Section 21.3.4, “EventBusSource”. |
| Filter |
Filters an input stream and produces an output stream containing the events passing the filter criteria. See Section 21.3.5, “Filter”. |
| LogSink |
Utility sink that outputs events to console or log. See Section 21.3.6, “LogSink”. |
| Select |
An EPL select statement that executes on the input stream events. See Section 21.3.7, “Select”. |
The below table summarizes the built-in EsperIO data flow operators. Please see the EsperIO documentation and source for more information.
Table 21.2. EsperIO Built-in Operators
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| AMQPSource |
Attaches to AMQP broker to receive messages to process. |
| AMQPSink |
Attaches to AMQP broker to send messages. |
| FileSource |
Reads one or more files and produces events from file data. |
| FileSink |
Write one or more files from events received. |
The BeaconSource operator generates events and populates event properties.
The BeaconSource operator does not accept any input streams and has no input ports.
The BeaconSource operator must have a single output stream. When the BeaconSource operator completed generating events according to the number of iterations provided or when it is cancelled it outputs a final marker to the output stream.
Parameters for the BeaconSource operator are all optional parameters:
Table 21.3. BeaconSource Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| initialDelay | Specifies the number of seconds delay before producing events. |
| interval | Time interval between events. Takes a integer or double-typed value for the number of seconds. The interval is zero when not provided. |
| iterations | Number of events produced. Takes an integer value. When not provided the operator produces tuples until the data flow instance gets cancelled. |
Event properties to be populated can simply be added to the parameters.
If your declaration provides an event type for the output stream then BeaconSource will populate event properties of the underlying events. If no event type is specified, BeaconSource creates an anonymous object-array event type to carry the event properties that are generated and associates this type with its output stream.
Examples are:
create dataflow MyDataFlow
create schema SampleSchema(tagId string, locX double), // sample type
// BeaconSource that produces empty object-array events without delay
// or interval until cancelled.
BeaconSource -> stream.one {}
// BeaconSource that produces one RFIDSchema event populating event properties
// from a user-defined function "generateTagId" and the provided values.
BeaconSource -> stream.two<SampleSchema> {
iterations : 1,
tagId : generateTagId(),
locX : 10
}
// BeaconSource that produces 10 object-array events populating
// the price property with a random value.
BeaconSource -> stream.three {
iterations : 10,
interval : 10, // every 10 seconds
initialDelay : 5, // start after 5 seconds
price : Math.random() * 100
}The EPStatementSource operator maintains a subscription to the results of one or more statements. The operator produces the statement output events.
The EPStatementSource operator does not accept any input streams and has no input ports.
The EPStatementSource operator must have a single output stream. It does not generate a final or other marker.
Either the statement name or the statement filter parameter is required:
Table 21.4. EPStatementSource Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| collector | Optional parameter, used to transform statement output events to submitted events. |
| statementName | Name of the statement that produces events. The statement does not need to exist at the time of data flow instantiation. |
| statementFilter | Implementation of the EPDataFlowEPStatementFilter that returns true for each statement that produces events. Statements do not need to exist at the time of data flow instantiation. |
If a statement name is provided, the operator subscribes to output events of the statement if the statement exists or when it gets created at a later point in time.
If a statement filter is provided instead, the operator subscribes to output events of all statements that currently exist and pass the filter pass method or that get created at a later point in time and pass the filter pass method.
The collector can be specified to transform output events. If no collector is specified the operator submits the underlying events of the insert stream received from the statement. The collector object must implement the interface EPDataFlowIRStreamCollector.
Examples are:
create dataflow MyDataFlow
create schema SampleSchema(tagId string, locX double), // sample type
// Consider only the statement named MySelectStatement when it exists.
// No transformation.
EPStatementSource -> stream.one<eventbean<?>> {
statementName : 'MySelectStatement'
}
// Consider all statements that match the filter object provided.
// No transformation.
EPStatementSource -> stream.two<eventbean<?>> {
statementFilter : {
class : 'com.mycompany.filters.MyStatementFilter'
}
}
// Consider all statements that match the filter object provided.
// With collector that performs transformation.
EPStatementSource -> stream.two<SampleSchema> {
collector : {
class : 'com.mycompany.filters.MyCollector'
},
statementFilter : {
class : 'com.mycompany.filters.MyStatementFilter'
}
}
The EventBusSink operator send events received from a data flow into the event bus. Any statement that looks for any of the events gets triggered, equivalent to the sendEventType methods on EPEventService or the insert into clause.
The EventBusSink operator accepts any number of input streams. The operator forwards all events arriving on any input ports to the event bus, equivalent to the sendEventType methods on EPEventService.
The EventBusSink operator cannot declare any output streams.
Parameters for the EventBusSink operator are all optional parameters:
Table 21.5. EventBusSink Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| collector | Optional parameter, used to transform data flow events to event bus events. |
The collector can be specified to transform data flow events to event bus events. If no collector is specified the operator submits the events directly to the event bus. The collector object must implement the interface EPDataFlowEventCollector.
Examples are:
create dataflow MyDataFlow
BeaconSource -> instream<SampleSchema> {} // produces a sample stream
// Send SampleSchema events produced by beacon to the event bus.
EventBusSink(instream) {}
// Send SampleSchema events produced by beacon to the event bus.
// With collector that performs transformation.
EventBusSink(instream) {
collector : {
class : 'com.mycompany.filters.MyCollector'
}
}
The EventBusSource operator receives events from the event bus and produces an output stream of the events received. With the term event bus we mean any event visible to the runtime either because the application send the event via any of the sendEventType methods on EPEventService or because statements populated streams as a result of insert into.
The EventBusSource operator does not accept any input streams and has no input ports.
The EventBusSource operator must have a single output stream. It does not generate a final or other marker. The event type declared for the output stream is the event type of events received from the event bus.
All parameters to EventBusSource are optional:
Table 21.6. EventBusSource Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| collector | Optional parameter and used to transform event bus events to submitted events. |
| filter | Filter expression for event bus matching. |
The collector can be specified to transform output events. If no collector is specified the operator submits the underlying events of the stream received from the event bus. The collector object must implement the interface EPDataFlowEventBeanCollector.
The filter is an expression that the event bus compiles and efficiently matches even in the presence of a large number of event bus sources. The filter expression must return a boolean-typed value, returning true for those events that the event bus passes to the operator.
Examples are:
create dataflow MyDataFlow
// Receive all SampleSchema events from the event bus.
// No transformation.
EventBusSource -> stream.one<SampleSchema> {}
// Receive all SampleSchema events with tag id '001' from the event bus.
// No transformation.
EventBusSource -> stream.one<SampleSchema> {
filter : tagId = '001'
}
// Receive all SampleSchema events from the event bus.
// With collector that performs transformation.
EventBusSource -> stream.two<SampleSchema> {
collector : {
class : 'com.mycompany.filters.MyCollector'
},
}The Filter operator filters an input stream and produces an output stream containing the events passing the filter criteria. If a second output stream is provided, the operator sends events not passing filter criteria to that output stream.
The Filter operator accepts a single input stream.
The Filter operator requires one or two output streams. The event type of the input and output stream(s) must be the same. The first output stream receives the matching events according to the filter expression. If declaring two output streams, the second stream receives non-matching events.
The Filter operator has a single required parameter:
Examples are:
create dataflow MyDataFlow
create schema SampleSchema(tagId string, locX double), // sample type
BeaconSource -> samplestream<SampleSchema> {} // sample source
// Filter all events that have a tag id of '001'
Filter(samplestream) -> tags_001 {
filter : tagId = '001'
}
// Filter all events that have a tag id of '001',
// putting all other events into the second stream
Filter(samplestream) -> tags_001, tags_other {
filter : tagId = '001'
}The LogSink operator outputs events to console or log file in either a JSON, XML or built-in format (the default).
The LogSink operator accepts any number of input streams. All events arriving on any input ports are logged.
The LogSink operator cannot declare any output streams.
Parameters for the LogSink operator are all optional parameters:
Table 21.8. LogSink Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| format | Specify format as a string value: json for JSON-formatted output, xml for XML-formatted output and summary (default) for a built-in format. |
| layout | Pattern string according to which output is formatted. Place %df for data flow name, %p for port number, %i for data flow instance id, %t for title, %e for event data. |
| log | Boolean true (default) for log output, false for console output. |
| linefeed | Boolean true (default) for line feed, false for no line feed. |
| title | String title text pre-pended to output. |
Examples are:
create dataflow MyDataFlow
BeaconSource -> instream {} // produces sample stream to use below
// Output textual event to log using defaults.
LogSink(instream) {}
// Output JSON-formatted to console.
LogSink(instream) {
format : 'json',
layout : '%t [%e]',
log : false,
linefeed : true,
title : 'My Custom Title:'
}The Select operator is configured with an EPL select statement. It applies events from input streams to the select statement and outputs results either continuously or when the final marker arrives.
The Select operator accepts one or more input streams.
The Select operator requires a single output stream.
The Select operator requires the select parameter, all other parameters are optional:
Table 21.9. Select Operator Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| iterate | Boolean indicator whether results should be output continuously or only upon arrival of the final marker. |
| select | EPL select statement in parenthesis. |
Set the optional iterate flag to false (the default) to have the operator output results continuously. Set the iterate flag to true to indicate that the operator outputs results only when the final marker arrives. If iterate is true then output rate limiting clauses are not supported.
The select parameter is required and provides an EPL select statement within parenthesis.
For each input port the statement should list the input stream name or the alias name in the from clause. Only filter-based streams are allowed in the from clause and patterns or named windows are not supported. Also not allowed are
the insert into clause, the irstream keyword and subselects.
The Select operator determines the event type of output events based on the select clause. It is not necessary to declare an event type for the output stream.
Examples are:
create dataflow MyDataFlow
create schema SampleSchema(tagId string, locX double), // sample type
BeaconSource -> instream<SampleSchema> {} // sample stream
BeaconSource -> secondstream<SampleSchema> {} // sample stream
// Simple continuous count of events
Select(instream) -> outstream {
select: (select count(*) from instream)
}
// Demonstrate use of alias
Select(instream as myalias) -> outstream {
select: (select count(*) from myalias)
}
// Output only when the final marker arrives
Select(instream as myalias) -> outstream {
select: (select count(*) from myalias),
iterate: true
}
// Same input port for the two sample streams
Select( (instream, secondstream) as myalias) -> outstream {
select: (select count(*) from myalias)
}
// A join with multiple input streams,
// joining the last event per stream forming pairs
Select(instream, secondstream) -> outstream {
select: (select a.tagId, b.tagId
from instream#lastevent as a, secondstream#lastevent as b)
}
// A join with multiple input streams and using aliases.
Select(instream as S1, secondstream as S2) -> outstream {
select: (select a.tagId, b.tagId
from S1#lastevent as a, S2#lastevent as b)
}This section outlines the steps to declare, instantiate, execute and cancel or complete data flows.
Compile data flow the same as any other statement and deploy the compiled module. The EPStatementObjectModel statement object model can also be used to compile a data flow.
Annotations that are listed at the top of the EPL text are applied to all statements and operators in the data flow. Annotations listed for a specific operator apply to that operator only.
The next program code snippet declares a data flow to the runtime:
String epl = "@Name('MyStatementName') create dataflow HelloWorldDataFlow\n" +
"BeaconSource -> helloworldStream { text: 'hello world' , iterations: 1}\n" +
"LogSink(helloworldStream) {}";
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
CompilerArguments compilerArguments = new CompilerArguments(configuration);
EPCompiled compiled = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler().compile(epl, compilerArguments);
EPDeployment deployment = runtime.getDeploymentService().deploy(compiled);The statement name that can be assigned to the statement is used only for statement management. Your application may undeploy the statement declaring the data flow thereby making the data flow unavailable for instantiation. Existing instances of the data flow are not affected by an undeploy of the statement that declares the data flow.
Listeners or the subscriber to the statement declaring a data flow receive no events or other output. The statement declaring a data flow returns no rows when iterated.
The com.espertech.esper.common.client.dataflow.core.EPDataFlowService available via getDataFlowService on EPRuntime manages declared data flows.
Use the instantiate method on EPDataFlowRuntime to instantiate a data flow after it has been declared. Pass the data flow name and optional instantiation options to the method. A data flow can be instantiated any number of times.
A data flow instance is represented by an instance of EPDataFlowInstance. Each instance has a state as well as methods to start, run, join and cancel as well as methods to obtain execution statistics.
Various optional arguments including operator parameters can be passed to instantiate via the EPDataFlowInstantiationOptions object as explained in more detail below.
The following code snippet instantiates the data flow:
EPDataFlowInstance instance = runtime.getDataFlowService().instantiate(deployment.getDeploymentId(), "HelloWorldDataFlow");
The runtime does not track or otherwise retain data flow instances in memory. It is up to your application to retain data flow instances as needed.
Each data flow instance associates to a state. The start state is EPDataFlowState.INSTANTIATED. The end state is either COMPLETED or CANCELLED.
The following table outlines all states:
Table 21.10. Data Flow Instance States
| State | Description |
|---|---|
| INSTANTIATED |
Start state, applies when a data flow instance has been instantiated and has not executed. |
| RUNNING |
A data flow instance transitions from instantiated to running when any of the |
| COMPLETED |
A data flow instance transitions from running to completed when all final markers have been processed by all operators. |
| CANCELLED |
A data flow instance transitions from running to cancelled when your application invokes the |
After your application instantiated a data flow instance it can execute the data flow instance using either the start, run or startCaptive methods.
Use the start method to have the runtime allocate a thread for each source operator. Execution is non-blocking. Use the join method to have one or more threads join a data flow instance execution.
Use the run method to have the runtime use the current thread to execute the single source operator. Multiple source operators are not allowed when using run.
Use the startCaptive method to have the runtime return all Runnable instances and emitters, for the purpose of having complete control over execution. The runtime allocates no threads and does not perform any logic for the data flow unless your application employs the Runnable instances and emitters returned by the method.
The next code snippet executes the data flow instance as a blocking call:
instance.run();
By using the run method of EPDataFlowInstance the runtime executes the data flow instance using the same thread (blocking execute) and returns when the data flow instance completes. A data flow instance completes when all operators receive final markers.
The hello world data flow simply prints an unformatted Hello World string to console. The BeaconSource operator generates a final marker when it finishes the 1 iteration. The data flow instance thus transitions to complete after the LogSink operator receives the final marker, and the thread invoking the run method returns.
The next code snippet executes the data flow instance as a non-blocking call:
instance.start();
Use the cancel method to cancel execution of a running data flow instance:
instance.cancel();
Use the join method to join execution of a running data flow instance, causing the joining thread to block until the data flow instance either completes or is cancelled:
instance.join();
The EPDataFlowInstantiationOptions object that can be passed to the instantiate method may be used to customize the operator graph, operator parameters and execution of the data flow instance.
Passing runtime parameters to data flow operators is easiest using the addParameterURI method. The first parameter is the data flow operator name and the
operator parameter name separated by the slash character. The second parameter is the value object.
For example, in order to pass the file name to the FileSource operator at runtime, use the following code:
EPDataFlowInstantiationOptions options = new EPDataFlowInstantiationOptions();
options.addParameterURI("FileSource/file", filename);
EPDataFlowInstance instance = runtime.getDataFlowService().instantiate(deployment.getDeploymentId(), "MyFileReaderDataFlow",options);
instance.run();
The optional operatorProvider member takes an implementation of the EPDataFlowOperatorProvider interface. The runtime invokes this provider to obtain operator instances.
The optional parameterProvider member takes an implementation of the EPDataFlowOperatorParameterProvider interface. The runtime invokes this provider to obtain operator parameter values. The values override the values provided via parameter URI above.
The optional exceptionHandler member takes an implementation of the EPDataFlowExceptionHandler interface. The runtime invokes this provider to when exceptions occur.
The optional dataFlowInstanceId can be assigned any string value for the purpose of identifying the data flow instance.
The optional dataFlowInstanceUserObject can be assigned any object value for the purpose of associating a user object to the data flow instance.
Set the operatorStatistics flag to true to obtain statistics for operator execution.
Set the cpuStatistics flag to true to obtain CPU statistics for operator execution.
Use the startCaptive method on a EPDataFlowInstance data flow instance when your application requires full control over threading. This method returns an EPDataFlowInstanceCaptive instance
that contains a list of java.lang.Runnable instances that represent each source operator.
The special Emitter operator can occur in a data flow. This emitter can be used to inject events into the data flow without writing a new operator. Emitter takes a single name parameter that provides the name of the emitter
and that is returned in a map of emitters by EPDataFlowInstanceCaptive.
The example EPL below creates a data flow that uses emitter.
create dataflow HelloWorldDataFlow
create objectarray schema SampleSchema(text string), // sample type
Emitter -> helloworld.stream<SampleSchema> { name: 'myemitter' }
LogSink(helloworld.stream) {}
Your application may obtain the Emitter instance and sends events directly into the output stream. This feature is only supported in relationship with startCaptive since the runtime does not allocate any threads or run source operators.
The example code snippet below obtains the emitter instance and send events directly into the data flow instance:
EPDataFlowInstance instance =
runtime.getDataFlowService().instantiate(deployment.getDeploymentId(), "HelloWorldDataFlow", options);
EPDataFlowInstanceCaptive captiveStart = instance.startCaptive();
Emitter emitter = captiveStart.getEmitters().get("myemitter");
emitter.submit(new Object[] {"this is some text"});
When emitting DOM XML events please emit the root element obtained from document.getDocumentElement().
When your application executes a data flow instance by means of the start (non-blocking) or run (blocking) methods, the data flow instance stays running until either completed or cancelled. While cancellation is always via the cancel method,
completion occurs when all source operators provide final markers.
The final marker is an object that implements the EPDataFlowSignalFinalMarker interface. Some operators may also provide or process data window markers which implement the EPDataFlowSignalWindowMarker interface. All such signals implement the EPDataFlowSignal interface.
Some source operators such as EventBusSource and EPStatementSource do not generate final markers as they act continuously.
All exceptions during the execution of a data flow are logged and reported to the EPDataFlowExceptionHandler instance if one was provided.
If no exception handler is provided or the provided exception handler re-throws or generates a new runtime exception, the source operator handles the exception and completes (ends). When all source operators complete then the data flow instance transitions to complete.
The following example is a rolling top words count implemented as a data flow, over a 30 second time window and providing the top 3 words every 2 seconds:
create dataflow RollingTopWords
create objectarray schema WordEvent (word string),
Emitter -> wordstream<WordEvent> {name:'a'} {} // Produces word stream
Select(wordstream) -> wordcount { // Sliding time window count per word
select: (select word, count(*) as wordcount
from wordstream#time(30) group by word)
}
Select(wordcount) -> wordranks { // Rank of words
select: (select window(*) as rankedWords
from wordcount#sort(3, wordcount desc)
output snapshot every 2 seconds)
}
LogSink(wordranks) {}The next example implements a bargain index computation that separates a mixed trade and quote event stream into a trade and a quote stream, computes a vwap and joins the two streams to compute an index:
create dataflow VWAPSample
create objectarray schema TradeQuoteType as (type string, ticker string, price double, volume long, askprice double, asksize long),
MyObjectArrayGraphSource -> TradeQuoteStream<TradeQuoteType> {}
Filter(TradeQuoteStream) -> TradeStream {
filter: type = "trade"
}
Filter(TradeQuoteStream) -> QuoteStream {
filter: type = "quote"
}
Select(TradeStream) -> VwapTrades {
select: (select ticker, sum(price * volume) / sum(volume) as vwap,
min(price) as minprice
from TradeStream#groupwin(ticker)#length(4) group by ticker)
}
Select(VwapTrades as T, QuoteStream as Q) -> BargainIndex {
select:
(select case when vwap > askprice then asksize * (Math.exp(vwap - askprice)) else 0.0d end as index
from T#unique(ticker) as t, Q#lastevent as q
where t.ticker = q.ticker)
}
LogSink(BargainIndex) {}
The final example is a word count data flow, in which three custom operators tokenize, word count and aggregate. The custom operators in this example are discussed next.
create dataflow WordCount
MyLineFeedSource -> LineOfTextStream {}
MyTokenizerCounter(LineOfTextStream) -> SingleLineCountStream {}
MyWordCountAggregator(SingleLineCountStream) -> WordCountStream {}
LogSink(WordCountStream) {}Note
Implementing an operator requires the use of extension and internal APIs that are not considered stable and may change between versions.
This section discusses how to implement classes that serve as operators in a data flow. The section employs the example data flow as shown earlier.
This example data flow has operators MyLineFeedSource, MyTokenizerCounter and MyWordCountAggregator that are application provided operators:
create dataflow WordCount
MyLineFeedSource -> LineOfTextStream {}
MyTokenizerCounter(LineOfTextStream) -> SingleLineCountStream {}
MyWordCountAggregator(SingleLineCountStream) -> WordCountStream {}
LogSink(WordCountStream) {}Each operator requires implementing the following interfaces:
Implement the
DataFlowOperatorForgeinterface for the compiler to use.Implement the
DataFlowOperatorFactoryinterface for the runtime to instantiate operator instances.Implement either the
DataFlowOperatorinterface, theDataFlowOperatorLifecycleor theDataFlowSourceOperatorinterface.
The compiler must be able to find the class implementing DataFlowOperatorForge. Add the forge package or forge class to imports:
// Sample code adds 'package.*' to simply import the package. Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); configuration.getCommon().addImport(MyLineFeedSourceForge.class.getName());
Every operator has a forge class that implements the DataFlowOperatorForge interface and is only used at compile-time.
The compiler provides the operator parameter expressions to the forge instance and invokes the initializeForge method.
When it is time to compile the compiler generates code by invoking the make method.
// The OutputTypes annotation can be used to specify the type of events
// that are output by the operator.
// If provided, it is not necessary to declare output types in the data flow.
// The event representation is object-array.
@OutputTypes(value = {
@OutputType(name = "line", typeName = "String")
})
// Provide the DataFlowOpProvideSignal annotation to indicate that
// the source operator provides a final marker.
@DataFlowOpProvideSignal
public class MyLineFeedSourceForge implements DataFlowOperatorForge {
public DataFlowOpForgeInitializeResult initializeForge(DataFlowOpForgeInitializeContext context) throws ExprValidationException {
return null;
}
public CodegenExpression make(CodegenMethodScope parent, SAIFFInitializeSymbol symbols, CodegenClassScope classScope) {
return newInstance(MyLineFeedSourceFactory.class);
}
}
The operator factory class must implement the DataFlowOperatorFactory interface.
At deployment time the operator factory initializes using the code generated in the forge make method.
Upon instantiating a data flow the factory must return an operator instance.
The implementation for the sample MyLineFeedSourceFactory is:
public class MyLineFeedSourceFactory implements DataFlowOperatorFactory {
public void initializeFactory(DataFlowOpFactoryInitializeContext context) {
}
public DataFlowOperator operator(DataFlowOpInitializeContext context) {
return new MyLineFeedSource(Collections.emptyIterator());
}
}
The operator implementation for the sample MyLineFeedSource is:
public class MyLineFeedSource implements DataFlowSourceOperator {
@DataFlowContext
private EPDataFlowEmitter dataFlowEmitter;
private final Iterator<String> lines;
public MyLineFeedSource(Iterator<String> lines) {
this.lines = lines;
}
public void open(DataFlowOpOpenContext openContext) {
}
public void next() {
if (lines.hasNext()) {
dataFlowEmitter.submit(new Object[]{lines.next()});
} else {
dataFlowEmitter.submitSignal(new EPDataFlowSignalFinalMarker() {
});
}
}
public void close(DataFlowOpCloseContext openContext) {
}
}
The implementation for the sample MyTokenizerCounter is a forge, factory and operator in one class:
@OutputTypes({
@OutputType(name = "line", type = int.class),
@OutputType(name = "wordCount", type = int.class),
@OutputType(name = "charCount", type = int.class)
})
public class MyTokenizerCounter implements DataFlowOperatorForge, DataFlowOperatorFactory, DataFlowOperator {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyTokenizerCounter.class);
@DataFlowContext
private EPDataFlowEmitter graphContext;
public DataFlowOpForgeInitializeResult initializeForge(DataFlowOpForgeInitializeContext context) throws ExprValidationException {
return null;
}
public CodegenExpression make(CodegenMethodScope parent, SAIFFInitializeSymbol symbols, CodegenClassScope classScope) {
return newInstance(MyTokenizerCounter.class);
}
public void initializeFactory(DataFlowOpFactoryInitializeContext context) {
}
public DataFlowOperator operator(DataFlowOpInitializeContext context) {
return new MyTokenizerCounter();
}
public void onInput(String line) {
StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(line, " \t");
int wordCount = tokenizer.countTokens();
int charCount = 0;
while (tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {
String token = tokenizer.nextToken();
charCount += token.length();
}
log.debug("Submitting stat words[" + wordCount + "] chars[" + charCount + "] for line '" + line + "'");
graphContext.submit(new Object[]{1, wordCount, charCount});
}
}
The implementation for the sample MyWordCountAggregator with comments is:
@OutputTypes(value = {
@OutputType(name = "stats", type = MyWordCountStats.class)
})
public class MyWordCountAggregator implements DataFlowOperatorForge, DataFlowOperatorFactory, DataFlowOperator {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyWordCountAggregator.class);
@DataFlowContext
private EPDataFlowEmitter graphContext;
private final MyWordCountStats aggregate = new MyWordCountStats();
public DataFlowOpForgeInitializeResult initializeForge(DataFlowOpForgeInitializeContext context) throws ExprValidationException {
return null;
}
public CodegenExpression make(CodegenMethodScope parent, SAIFFInitializeSymbol symbols, CodegenClassScope classScope) {
return newInstance(MyWordCountAggregator.class);
}
public void initializeFactory(DataFlowOpFactoryInitializeContext context) {
}
public DataFlowOperator operator(DataFlowOpInitializeContext context) {
return new MyWordCountAggregator();
}
public void onInput(int lines, int words, int chars) {
aggregate.add(lines, words, chars);
log.debug("Aggregated: " + aggregate);
}
public void onSignal(EPDataFlowSignal signal) {
log.debug("Received punctuation, submitting totals: " + aggregate);
graphContext.submit(aggregate);
}
}The forge instance receives parameters expressions. A forge can declare parameters like so:
// Expose a parameter named "file" that takes any expression as parameter @DataFlowOpParameter private ExprNode file; // Expose a parameter named "adapterInputSource" that will be an instance of some interface // Interface implementations as parameters are declare a Map<String, Object> @DataFlowOpParameter private Map<String, Object> adapterInputSource; // Expose a paramerer named "propertyNames" that is an array of string constants @DataFlowOpParameter private String[] propertyNames;
The forge class can obtain the output event type if needed. It should also validate the expression parameters and throw ExprValidationException if the parameter expression does not return the expected type.
The utility class DataFlowParameterValidation has validate utility methods that return a validated expression:
For example:
public DataFlowOpForgeInitializeResult initializeForge(DataFlowOpForgeInitializeContext context) throws ExprValidationException {
// Obtain the declared output event type
outputEventType = context.getOutputPorts().get(0).getOptionalDeclaredType() != null ? context.getOutputPorts().get(0).getOptionalDeclaredType().getEventType() : null;
if (outputEventType == null) {
throw new ExprValidationException("No event type provided for output, please provide an event type name");
}
// validate the "file" parameter expression expected to return a String-typed value
file = DataFlowParameterValidation.validate("file", file, String.class, context);
return null;
}
The forge class passes parameters to the factory. We use SAIFFInitializeBuilder that is a builder utility for building the factory. For example:
public CodegenExpression make(CodegenMethodScope parent, SAIFFInitializeSymbol symbols, CodegenClassScope classScope) {
return new SAIFFInitializeBuilder(FileSourceFactory.class, this.getClass(), "factory", parent, symbols, classScope)
.exprnode("file", file)
.constant("propertyNames", propertyNames)
.map("adapterInputSource", adapterInputSource)
.build();
}The factory class must have setter-methods of the same name that receive the parameters:
private ExprEvaluator file;
private String[] propertyNames;
private Map<String, Object> adapterInputSource;
public void setFile(ExprEvaluator file) {
this.file = file;
}
public void setPropertyNames(String[] propertyNames) {
this.propertyNames = propertyNames;
}
public void setAdapterInputSource(Map<String, Object> adapterInputSource) {
this.adapterInputSource = adapterInputSource;
}
The factory class can resolve parameter values
by evaluating expressions and by determining whether parameters were passed as options. The DataFlowParameterResolution class provides
convenience methods. For example:
public DataFlowOperator operator(DataFlowOpInitializeContext context) {
String fileName = DataFlowParameterResolution.resolveWithDefault("file", file, null, String.class, context);
AdapterInputSource adapterInputSourceInstance = DataFlowParameterResolution.resolveOptionalInstance("adapterInputSource", adapterInputSource, AdapterInputSource.class, context);
return new MyOperator(fileName, adapterInputSourceInstance);
}- 22.1. Overview
- 22.2. Single-Row Function
- 22.2.1. Using an Inlined Class to Provide a Single-Row Function
- 22.2.2. Using an Application Class to Provide a Single-Row Function
- 22.2.3. Value Cache
- 22.2.4. Single-Row Functions in Filter Predicate Expressions
- 22.2.5. Single-Row Functions Taking Events as Parameters
- 22.2.6. Single-Row Functions Returning Events
- 22.2.7. Receiving a Context Object
- 22.2.8. Exception Handling
- 22.3. Virtual Data Window
- 22.4. Data Window View and Derived-Value View
- 22.5. Aggregation Function
- 22.6. Pattern Guard
- 22.7. Pattern Observer
- 22.8. Date-Time Method
- 22.9. Enumeration Method
- 22.9.1. Implement the EnumMethodForgeFactory Interface
- 22.9.2. Implement the EnumMethodState Interface
- 22.9.3. Implement the Static Method for Processing
- 22.9.4. Add the Enumeration Method Extension to the Compiler Configuration
- 22.9.5. Use the new Enumeration Method
- 22.9.6. Further Information to Lambda Parameters
This chapter summarizes integration and describes in detail each of the extension APIs that allow integrating external data and/or extend runtime functionality.
For information on calling external services via instance method invocation, for instance to integrate with dependency injection frameworks such as Spring or Guice, please see Section 5.17.5, “Class and Event-Type Variables”.
For information on input and output adapters that connect to an event transport and perform event transformation for incoming and outgoing on-the-wire event data, for use with streaming data, please see the EsperIO reference documentation. The data flow instances as described in Chapter 21, EPL Reference: Data Flow are an easy way to plug in operators that perform input and output. Data flows allow providing parameters and managing individual flows independent of runtime lifecycle. Also consider using the Plug-in Loader API for creating a new adapter that starts or stops as part of the CEP runtime initialization and destroy lifecycle, see Section 16.15, “Plug-In Loader”.
To join data that resides in a relational database and that is accessible via JDBC driver and SQL statement the runtime offers syntax for using SQL within EPL, see Section 5.13, “Accessing Relational Data via SQL”. A relational database input and output adapter for streaming input from and output to a relational database also exists (EsperIO).
To join data that resides in a non-relational store the runtime offers a two means: First, the virtual data window, as described below, for transparently integrating the external store as a named window. The second mechanism is a special join syntax based on static method invocation; see Section 5.14, “Accessing Non-Relational Data via Method, Script or UDF Invocation”.
Tip
The best way to test that your extension code works correctly is to write unit tests against a statement that utilizes the extension code. Samples can be obtained from Esper regression test code base.
Note
For all extension code and similar to listeners and subscribers, to send events into the runtime from extension code the routeEvent method should be used (and not sendEvent) to avoid the possibility of stack overflow due to event-callback looping and ensure correct processing of the current and routed event.
Note that if outbound-threading is enabled, listeners and subscribers should use sendEvent and not routeEvent.
Note
For all extension code it is not safe to deploy and undeploy within the extension code. For example, it is not safe to implement a data window that deploys compiled modules and that undeploys deployments.
Single-row functions return a single value. They are not expected to aggregate rows but instead should be stateless non-blocking functions. These functions can appear in any expressions and can be passed any number of parameters.
You may not override a built-in function with a single-row function provided by you. The single-row function you register must have a different name then any of the built-in functions.
The EPL compiler provides two ways to provide plug-in single-row functions:
An inlined class that is part of the same EPL module or another EPL module, see next under Section 22.2.1, “Using an Inlined Class to Provide a Single-Row Function” .
An external class that your application provides as part of the application, see below under Section 22.2.2, “Using an Application Class to Provide a Single-Row Function” .
An example single-row function can also be found in the examples under the runtime configuration example.
You may use an inline class that is part of the EPL modules to provide a single-row function. For more information on inline classes see Chapter 18, Inlined Classes. Using an inline class does not require any compiler configuration.
Specify the ExtensionSingleRowFunction annotation on the class level and the name (the EPL function name) and methodName (the name of the exposed method).
This annotation instructs the compiler that the inlined class exposes a single-row function.
This sample EPL includes an inlined class by name MyUtilityClass that provides a public static method by name computePercent to return a percentage value:
inlined_class """
@com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.singlerowfunc.ExtensionSingleRowFunction(name="computePercent", methodName="computePercent")
public class MyUtilityClass {
public static double computePercent(double amount, double total) {
return amount / total * 100;
}
}
"""
select computePercent(itemQuantity,totalQuantity) from OrderEvent
Only one ExtensionSingleRowFunction annotation can be specified per class and the annotation is only for use with inlined classes.
The method can be overloaded. Using an inline class does not require any compiler configuration.
When using create inlined_class the runtime resolves dependencies on EPL objects at time of deployment (the same as for all EPL objects).
Your application may provide a class that exposes a single-row function. In this case you must configure the class name, name of the function and function method name as part of compiler configuration. This is not necessary when using inlined classes as discussed before.
Single-row function classes have no further requirement then provide a public static method.
The following sample single-row function simply computes a percentage value based on two number values.
This sample class provides a public static method by name computePercent to return a percentage value:
public class MyUtilityClass {
public static double computePercent(double amount, double total) {
return amount / total * 100;
}
}The class name of the class, the method name and the function name of the new single-row function must be added to the compiler configuration. The configuration shown below is XML however the same options are available through the configuration API:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<plugin-singlerow-function name="percent" function-class="mycompany.MyUtilityClass" function-method="computePercent" />
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>Note that the function name and method name need not be the same.
The new single-row function is now ready to use in a statement:
select percent(fulfilled,total) from MyEvent
When selecting from a single stream, you may also pass wildcard to the single-row function and the function receives the underlying event:
select percent(*) from MyEvent
If the single-row function returns an object that provides further functions, you may chain function calls.
The following demonstrates a chained single-row function. The example assumes that a single-row function by name calculator returns an object that provides the add function which accepts two parameters:
select calculator().add(5, amount) from MyEvent
When a single-row function receives parameters that are all constant values or expressions that themselves receive only constant values, the runtime can pre-evaluate the result of the single-row function at time of statement. By default, the runtime does not pre-evaluate the single-row function unless you configure the value cache as enabled.
If using inlined classes and the ExtensionSingleRowFunction annotation, to enable specify the value cache as follows (default is disabled):
ExtensionSingleRowFunction(..., valueCache=com.espertech.esper.common.client.configuration.compiler.ConfigurationCompilerPlugInSingleRowFunction.ValueCache.ENABLED)
If using application classes and the compiler configuration, the following configuration XML enables the value cache for the single-row function:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<plugin-singlerow-function name="getDate"
function-class="mycompany.DateUtil" function-method="parseDate"
value-cache="enabled" />
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>When the single-row function receives constants as parameters, the runtime computes the result once and returns the cached result for each evaluation:
select getDate('2002-05-30T9:00:00.000') from MyEventYour EPL may use plug-in single row functions among the predicate expressions as part of the filters in a stream or pattern.
For example, the EPL below uses the function computeHash as part of a predicate expression:
select * from MyEvent(computeHash(field) = 100)
When you have many statements or many context partitions that refer to the same function, event type and parameters in a predicate expression, the compiler may optimize evaluation: The function gets evaluated only once per event.
While the optimization is enabled by default for all plug-in single row functions, you can also disable the optimization for a specific single-row function. By disabling the optimization for a single-row function the runtime may use less memory to identify reusable function footprints but may cause the runtime to evaluate each function more frequently than necessary.
If using inlined classes and the ExtensionSingleRowFunction annotation, specify the filter optimizable flag as follows (default is enabled):
ExtensionSingleRowFunction(..., filterOptimizable=com.espertech.esper.common.client.configuration.compiler.ConfigurationCompilerPlugInSingleRowFunction.FilterOptimizable.DISABLED)
If using application classes and the compiler configuration, the following configuration XML disables the filter optimization for a single-row function (by default it is enabled):
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<plugin-singlerow-function name="computeHash"
function-class="mycompany.HashUtil" function-method="computeHash"
filter-optimizable="disabled" />
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>
EPL allows parameters to a single-row function to be events. In this case, declare the method parameter type to either take EventBean, Collection<EventBean>
or the underlying class as a parameter.
Sample method footprints are:
public static double doCompute(EventBean eventBean) {...}
public static boolean doCheck(MyEvent myEvent, String text) {...}
public static String doSearch(Collection<EventBean> events) {...}
To pass the event, specify the stream alias, or wildcard (*) or the tag name when used in a pattern.
The EPL below shows example uses:
select * from MyEvent(doCompute(me) = 100) as me
select * from MyEvent where doCompute(*) = 100
select * from pattern[a=MyEvent -> MyEvent(doCheck(a, 'sometext'))]
select * from MyEvent#time(1 min) having doCompute(last(*))]
select * from MyEvent#time(1 min) having doSearch(window(*))]
Declare the method parameter as Collection<EventBean> if the method expects
an expression result that returns multiple events.
Declare the method parameter as EventBean if the method expects
an expression result that returns a single event.
A single-row function may return events. Please declare your single-row function method to return Collection<EventBean> or EventBean[] and configure the event type name.
For example, assuming there is an MyItem event type such as created via create schema MyItem(id string):
public static EventBean[] myItemProducer(String string, EPLMethodInvocationContext context) {
String[] split = string.split(",");
EventBean[] events = new EventBean[split.length];
for (int i = 0; i < split.length; i++) {
events[i] = context.getEventBeanService().adapterForMap(Collections.singletonMap("id", split[i]), "MyItem");
}
return events;
}
The sample EPL queries items filtering those items that have a given value for the id field:
select myItemProducer(ordertext).where(v => v.id in ('id1', 'id3')) as c0 from Order
If using inlined classes and the ExtensionSingleRowFunction annotation, specify the event type name as follows:
ExtensionSingleRowFunction(..., eventTypeName="MyItem")
If using application classes and the compiler configuration, this sample code register the myItemProducer function as a single-row function with an event type name:
ConfigurationCompilerPlugInSingleRowFunction entry = new ConfigurationCompilerPlugInSingleRowFunction();
entry.setName("myItemProducer");
entry.setFunctionClassName(...);
entry.setFunctionMethodName(...);
entry.setEventTypeName("MyItem");
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCompiler().addPlugInSingleRowFunction(entry);
If your single row function returns EventBean[] and is used with enumeration methods the configuration must provide an event type name.
The runtime can pass an object containing contextual information such as statement name, function name, runtime URI and context partition id to your
method. The container for this information is EPLMethodInvocationContext in package com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.expr.
Please declare your method to take EPLMethodInvocationContext as the last parameter. The runtime then passes the information along.
A sample method footprint and EPL are shown below:
public static double computeSomething(double number, EPLMethodInvocationContext context) {...}select computeSomething(10) from MyEvent
By default the runtime logs any exceptions thrown by the single row function and returns a null value. To have exceptions be re-thrown instead, which makes exceptions visible to any registered exception handler, please configure as discussed herein.
If using inlined classes and the ExtensionSingleRowFunction annotation, you may set rethrow as follows:
ExtensionSingleRowFunction(..., rethrowExceptions=true)
If using application classes and the compiler configuration, set the rethrow-exceptions flag in the XML configuration or the rethrowExceptions flag in the API
when registering the single row function to have the runtime re-throw any exceptions that the single row function may throw.
Use a virtual data window if you have a (large) external data store that you want to access as a named window. The access is transparent: There is no need to use special syntax or join syntax. All regular queries including subqueries, joins, on-merge, on-select, on-insert, on-delete, on-update and fire-and-forget are supported with virtual data windows.
There is no need to keep any data or events in memory with virtual data windows. The only requirement for virtual data windows is that all data rows returned are EventBean instances.
When implementing a virtual data window it is not necessary to send any events into the runtime or to use insert-into. The event content is simply assumed to exist and accessible to the runtime via the API implementation you provide.
The distribution ships with a sample virtual data window in the examples folder under the name virtualdw. The code snippets below are extracts from the example.
We use the term store here to mean a source set of data that is managed by the virtual data window. We use the term store row or just row to mean a single data item provided by the store. We use the term lookup to mean a read operation against the store returning zero, one or many rows.
Virtual data windows allow high-performance low-latency lookup by exposing all relevant statement access path information. This makes it possible for the virtual data window to choose the desired access method into its store.
The following steps are required to develop and use a virtual data window:
Implement the interface
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.vdw.VirtualDataWindowForge. This class is used by the compiler.Implement the interface
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.vdw.VirtualDataWindowFactoryFactory. This class is referred to, by class name, by the compiler. It is used at runtime.Implement the interface
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.vdw.VirtualDataWindowFactory(used at runtime only).Implement the interface
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.vdw.VirtualDataWindow(used at runtime only).Implement the interface
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.vdw.VirtualDataWindowLookup(used at runtime only).Register the factory class in the configuration.
Once you have completed above steps, the virtual data window is ready to use in statements.
From a threading perspective, virtual data window implementation classes must be thread-safe if objects are shared between multiple named windows. If no objects are shared between multiple different named windows, thereby each object is only used for the same named window and other named windows receive a separate instance, it is no necessary that the implementation classes are thread-safe.
Your application must first register the virtual data window factory as part of configuration:
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.getCompiler().addPlugInVirtualDataWindow("sample", "samplevdw",
SampleVirtualDataWindowForge.class.getName());Your application may then create a named window backed by a virtual data window.
For example, assume that the SampleEvent event type is declared as follows:
create schema SampleEvent as (key1 string, key2 string, value1 int, value2 double)
The next statement creates a named window MySampleWindow that provides SampleEvent events and is backed by a virtual data window:
create window MySampleWindow.sample:samplevdw() as SampleEvent
You may then access the named window, same as any other named window, for example by subquery, join, on-action, fire-and-forget query or by consuming its insert and remove stream. While this example uses Map-type events, the example code is the same for POJO or other events.
Your application may obtain a reference to the virtual data window from the runtime context.
This code snippet looks up the virtual data window by the named window name:
try {
return (VirtualDataWindow) runtime.getContext().lookup("/virtualdw/MySampleWindow");
}
catch (NamingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to look up virtual data window, is it created yet?");
}When your application registers a subquery, join or on-action query or executes a fire-and-forget query against a virtual data window the runtime interacts with the virtual data window. The interaction is a two-step process.
At time of deployment (once), the runtime uses the information the compiler collected by analyzing the EPL where-clause, if present. It then creates a list of hash-index and binary tree (btree, i.e. sorted) index properties. It passes the property names that are queried as well as the operators (i.e. =, >, range etc.) to the virtual data window. The virtual data window returns a lookup strategy object to the runtime.
At time of statement execution (repeatedly as triggered), the runtime uses that lookup strategy object to execute a lookup. It passes to the lookup all actual key values (hash, btree including ranges) to make fast and efficient lookup achievable.
To explain in detail, assume that your application creates a statement with a subquery as follows:
select (select * from MySampleWindow where key1 = 'A1') from OtherEvent
At the time of compilation of the statement above the compiler analyzes the statement. It determines that the subquery queries a virtual data window. It determines from the where-clause that the lookup uses property key1 and hash-equals semantics. The runtime then provides this information as part of VirtualDataWindowLookupContext passed to the getLookup method. Your application may inspect hash and btree properties and may determine the appropriate store access method to use.
The hash and btree property lookup information is for informational purposes, to enable fast and performant queries that return the smallest number of rows possible. Your implementation classes may use some or none of the information provided and may also instead return some or perhaps even all rows, as is practical to your implementation. The where-clause still remains in effect and gets evaluated on all rows that are returned by the lookup strategy.
Following the above example, the sub-query executes once when a OtherEvent event arrives. At time of execution the runtime delivers the string value A1 to the VirtualDataWindowLookup lookup implementation provided by your application. The lookup object queries the store and returns
store rows as EventBean instances.
As a second example, consider an EPL join statement as follows:
select * from MySampleWindow, MyTriggerEvent where key1 = trigger1 and key2 = trigger2
The compiler analyzes the statement and the runtime passes to the virtual data window the information that the lookup occurs on properties key1 and key2 under hash-equals semantics. When a MyTriggerEvent arrives,
it passes the actual value of the trigger1 and trigger2 properties of the current MyTriggerEvent to the lookup.
As a last example, consider a fire-and-forget query as follows:
select * from MySampleWindow key1 = 'A2' and value1 between 0 and 1000
The compiler analyzes the statement and the runtime passes to the virtual data window the lookup information. The lookup occurs on property key1 under hash-equals semantics and on property value1 under btree-open-range semantics. When your application
executes the fire-and-forget query the runtime passes A2 and the range endpoints 0 and 1000 to the lookup.
For more information, please consult the JavaDoc API documentation for class VirtualDataWindow, VirtualDataWindowLookupContext or VirtualDataWindowLookupFieldDesc.
For each named window that refers to the virtual data window, the runtime instantiates one instance of the forge at compile-time.
A virtual data window forge class is responsible for the following functions:
Implement the
initializemethod that accepts a virtual data window forge context object as a parameter.Implement the
getFactoryModemethod that information how to initialize the factory-factory class (the class that acts as a factory for virtual data window factories).Implement the
getUniqueKeyPropertyNamesmethod that can return the set of property names that are unique keys, for the purpose of query planning.
The compiler instantiates a VirtualDataWindowForge instance for each named window created by create window.
The compiler invokes the initialize method once in respect to the named window being created passing a VirtualDataWindowForgeContext context object.
The sample code shown here can be found among the examples in the distribution under virtualdw:
public class SampleVirtualDataWindowForge implements VirtualDataWindowForge {
public void initialize(VirtualDataWindowForgeContext initializeContext) {
}
public VirtualDataWindowFactoryMode getFactoryMode() {
// The injection strategy defines how to obtain and configure the factory-factory.
InjectionStrategy injectionStrategy = new InjectionStrategyClassNewInstance(SampleVirtualDataWindowFactoryFactory.class);
// The managed-mode is the default. It uses the provided injection strategy.
VirtualDataWindowFactoryModeManaged managed = new VirtualDataWindowFactoryModeManaged();
managed.setInjectionStrategyFactoryFactory(injectionStrategy);
return managed;
}
public Set<String> getUniqueKeyPropertyNames() {
// lets assume there is no unique key property names
return null;
}
}
Your forge class must implement the getFactoryMode method which instructs the compiler how to
obtain a factory class that returns a factory for creating virtual data window instances (a factory-factory).
The class acting as the factory-factory will be SampleVirtualDataWindowFactoryFactory.
At deployment time, the runtime instantiates the factory-factory and obtains a factory for virtual data windows.
A virtual data window factory-factory class is responsible for the following functions:
Implement the
createFactorymethod that accepts a factory-factory context and that returns the virtual data window factory.
The sample code shown here can be found among the examples in the distribution under virtualdw:
public class SampleVirtualDataWindowFactoryFactory implements VirtualDataWindowFactoryFactory {
public VirtualDataWindowFactory createFactory(VirtualDataWindowFactoryFactoryContext ctx) {
return new SampleVirtualDataWindowFactory();
}
}
For each named window that refers to the virtual data window, the runtime instantiates one instance of the factory.
A virtual data window factory class is responsible for the following functions:
Implement the
initializemethod that accepts a virtual data window factory context object as a parameter.Implement the
createmethod that accepts a virtual data window context object as a parameter and returns aVirtualDataWindowimplementation.Implement the
destroymethod that gets called once when the named window is undeployed.
The runtime instantiates a VirtualDataWindowFactory instance for each named window created via create window. The runtime invokes the initialize method once in respect to the named window being created passing a VirtualDataWindowFactoryContext context object.
If not using contexts, the runtime calls the create method once after calling the initialize method. If using contexts, the runtime calls the create method every time it allocates a context partition.
If using contexts and your virtual data window implementation operates thread-safe, you may return the same virtual data window implementation object for each context partition. If using contexts and your implementation object is not thread safe, return a separate thread-safe implementation object for each context partition.
The runtime invokes the destroy method once when the named window is undeployed. If not using contexts, the runtime calls the destroy method of the virtual data window implementation object before calling
the destroy method on the factory object. If using contexts, the runtime calls the destroy method on each instance associates to a context partition at the time the associated context partition terminates.
The sample code shown here can be found among the examples in the distribution under virtualdw:
public class SampleVirtualDataWindowFactory implements VirtualDataWindowFactory {
public void initialize(VirtualDataWindowFactoryContext factoryContext) {
}
public VirtualDataWindow create(VirtualDataWindowContext context) {
return new SampleVirtualDataWindow(context);
}
public void destroy() {
// cleanup can be performed here
}
public Set<String> getUniqueKeyPropertyNames() {
// lets assume there is no unique key property names
return null;
}
}
Your factory class must implement the create method which receives a VirtualDataWindowContext object. This method is called once for each EPL that creates a virtual data window (see example create window above).
The VirtualDataWindowContext provides to your application:
String namedWindowName; // Name of named window being created. Object[] parameters; // Any optional parameters provided as part of create-window. EventType eventType; // The event type of events. EventBeanFactory eventFactory; // A factory for creating EventBean instances from store rows. VirtualDataWindowOutStream outputStream; // For stream output to consuming statements. AgentInstanceContext agentInstanceContext; // Other statement information in statement context.
When using contexts you can decide whether your factory returns a new virtual data window for each context partition or returns the same virtual data window instance for all context partitions. Your extension code may refer to the named window name to identify the named window and may refer to the agent instance context that holds the agent instance id which is the id of the context partition.
A virtual data window implementation is responsible for the following functions:
Accept the lookup context object as a parameter and return the
VirtualDataWindowLookupimplementation.Optionally, post insert and remove stream data.
Implement the
destroymethod, which the runtime calls for each context partition when the named window is stopped or destroyed, or once when a context partition is ended/terminated.
The sample code shown here can be found among the examples in the distribution under virtualdw.
The implementation class must implement the VirtualDataWindow interface like so:
public class SampleVirtualDataWindow implements VirtualDataWindow {
private final VirtualDataWindowContext context;
public SampleVirtualDataWindow(VirtualDataWindowContext context) {
this.context = context;
} ...
When the compiler compiles a statement and detects a virtual data window, the compiler compiles access path information and the runtime invokes the getLookup method indicating hash and btree access path information by passing a VirtualDataWindowLookupContext context. The lookup method must return a VirtualDataWindowLookup implementation that the statement
uses for all lookups until the statement is stopped or destroyed.
The sample implementation does not use the hash and btree access path information and simply returns a lookup object:
public VirtualDataWindowLookup getLookup(VirtualDataWindowLookupContext desc) {
// Place any code that interrogates the hash-index and btree-index fields here.
// Return the lookup strategy.
return new SampleVirtualDataWindowLookup(context);
}
The runtime calls the update method when data changes because of on-merge, on-delete, on-update or insert-into. For example, if you have an on-merge statement that is triggered and that updates the virtual data window, the newData parameter receives the new (updated) event and the oldData parameter receives the event prior to the update. Your code may use these events to update the store or delete from the store, if needed.
If your application plans to consume data from the virtual data window, for example via select * from MySampleWindow, then the code must implement the update method to forward insert and remove stream events, as shown below, to receive the events in consuming statements. To post insert and remove stream data, use the VirtualDataWindowOutStream provided by the context object as follows.
public void update(EventBean[] newData, EventBean[] oldData) {
// This sample simply posts into the insert and remove stream what is received.
context.getOutputStream().update(newData, oldData);
}
Your application should not use VirtualDataWindowOutStream to post new events that originate from the store. The object is intended for use with on-action statements. Use insert-into instead for any new events that originate from the store.
Views in EPL are used to derive information from an event stream, and to represent data windows onto an event stream. This chapter describes how to plug-in a new, custom view.
The following steps are required to develop and use a custom view.
Implement a view forge class. View forges are compile-time classes that accept and check view parameters and refer to the appropriate view factory for the runtime.
Implement a view factory class. View factories are classes that instantiate the appropriate view class at runtime.
Implement a view class. A view class commonly represents a data window or derives new information from a stream at runtime.
Configure the view factory class supplying a view namespace and name in the compiler configuration.
The example view factory and view class that are used in this chapter can be found in the examples source folder in the OHLC (open-high-low-close) example. The class names are OHLCBarPlugInViewForge, OHLCBarPlugInViewFactory and OHLCBarPlugInView.
Views can make use of the runtime services available via StatementContext, for example:
The
SchedulingServiceinterface allows views to schedule timer callbacks to a view
Section 22.4.4, “View Contract” outlines the requirements for correct behavior of your custom view within the runtime.
Note that custom views may use runtime services and APIs that can be subject to change between major releases. The runtime services discussed above and view APIs are considered part of the runtime internal API and are only limited stable. Please also consider contributing your custom view to the project by submitting the view code.
A view forge class is a compile-time class and is responsible for the following functions:
Accept zero, one or more view parameters. View parameters are themselves expressions. The view forge must validate the expressions.
Build the view factory class. At deployment-time this code executes and builds the view factory.
Provide information about the event type of events posted by the view.
View forge classes must implement the ViewFactoryForge interface. Additionally a view forge class must implement the DataWindowViewForge interface if the view is a data window (retains events provided to it).
public class OHLCBarPlugInViewForge implements ViewFactoryForge { ...
Your view forge class must implement the setViewParameters method to accept view parameters and the attach method to attach the view to a stream:
public class OHLCBarPlugInViewForge implements ViewFactoryForge {
private List<ExprNode> viewParameters;
private ExprNode timestampExpression;
private ExprNode valueExpression;
private EventType eventType;
public void setViewParameters(List<ExprNode> parameters, ViewForgeEnv viewForgeEnv, int streamNumber) throws ViewParameterException {
this.viewParameters = parameters;
}
public void attach(EventType parentEventType, int streamNumber, ViewForgeEnv env, boolean grouped) throws ViewParameterException {
if (viewParameters.size() != 2) {
throw new ViewParameterException("View requires a two parameters: the expression returning timestamps and the expression supplying OHLC data points");
}
ExprNode[] validatedNodes = ViewForgeSupport.validate("OHLC view", parentEventType, viewParameters, false, env, streamNumber);
timestampExpression = validatedNodes[0];
valueExpression = validatedNodes[1];
if (!JavaClassHelper.isTypeLong(timestampExpression.getForge().getEvaluationType())) {
throw new ViewParameterException("View requires long-typed timestamp values in parameter 1");
}
if (!JavaClassHelper.isTypeDouble(valueExpression.getForge().getEvaluationType())) {
throw new ViewParameterException("View requires double-typed values for in parameter 2");
}
....After the compiler supplied view parameters to the forge, the compiler will ask the view to attach to its parent and validate any parameter expressions against the parent view's event type. If the view will be generating events of a different type then the events generated by the parent view, then the view factory can allocate the new event type.
Finally, the compiler asks the view forge to generate code that initializes the view factory:
public CodegenExpression make(CodegenMethodScope parent, SAIFFInitializeSymbol symbols, CodegenClassScope classScope) {
return new SAIFFInitializeBuilder(new EPTypeClass(OHLCBarPlugInViewFactory.class), this.getClass(), "factory", parent, symbols, classScope)
.exprnode("timestampExpression", timestampExpression)
.exprnode("valueExpression", valueExpression)
.build();
}
Use the internal SAIFFInitializeBuilder to build your view factory providing it the expressions and other values it needs.
A view factory class is responsible for the following functions:
Implement initialization code when required.
Instantiate the actual view class.
Provide information about the event type of events posted by the view.
View factory classes implement the ViewFactory interface. Additionally a view factory class must implement the DataWindowViewFactory interface if the view is a data window (retains events provided to it).
public class OHLCBarPlugInViewFactory implements ViewFactory { ...
The runtime initializes a view factory by calling its init method.
The runtime asks the view factory to create a view instance, and asks for the type of event generated by the view:
public View makeView(AgentInstanceViewFactoryChainContext agentInstanceViewFactoryContext) {
return new OHLCBarPlugInView(this, agentInstanceViewFactoryContext);
}
public EventType getEventType() {
return eventType;
}A view class is responsible for:
The
updatemethod receives insert streams and remove stream events from its parent viewThe
iteratormethod supplies an (optional) iterator to allow an application to pull or request results from anEPStatement
View classes subclass ViewSupport. Additionally a view class must implement the DataWindowView interface if the view is a data window (retains events provided to it).
public class OHLCBarPlugInView extends ViewSupport { ...
Your view's update method will be processing incoming (insert stream) and outgoing (remove stream) events posted by the parent view (if any), as well as providing incoming and outgoing events to child views. The convention required of your update method implementation is that the view releases any insert stream events (EventBean object references) which the view generates as reference-equal remove stream events (EventBean object references) at a later time.
The view implementation must call child.update(...) to post outgoing insert and remove stream events. Similar to the update method, the child.update takes insert and remove stream events as parameters.
A sample update method implementation is provided in the OHLC example.
The update method must adhere to the following conventions, to prevent memory leaks and to enable correct behavior within the runtime:
A view implementation that posts events to the insert stream must post unique
EventBeanobject references as insert stream events, and cannot post the sameEventBeanobject reference multiple times. The underlying event to theEventBeanobject reference can be the same object reference, however theEventBeanobject reference posted by the view into the insert stream must be a new instance for each insert stream event.If the custom view posts a continuous insert stream, then the views must also post a continuous remove stream (second parameter to the
updateChildrenmethod). If the view does not post remove stream events, it assumes unbound keep-all semantics.EventBeanevents posted as remove stream events must be the same object reference as theEventBeanevents posted as insert stream by the view. Thus remove stream events posted by the view (theEventBeaninstances, does not affect the underlying representation) must be reference-equal to insert stream events posted by the view as part of an earlier invocation of the update method, or the same invocation of the update method.EventBeanevents represent a unique observation. The values of the observation can be the same, thus the underlying representation of anEventBeanevent can be reused, however event property values must be kept immutable and not be subject to change.Array elements of the insert and remove stream events must not carry null values. Array size must match the number of
EventBeaninstances posted. It is recommended to use anullvalue for no insert or remove stream events rather then an empty zero-size array.
Your view implementation must implement the AgentInstanceStopCallback interface to receive a callback when the view gets destroyed.
Please refer to the sample views for a code sample on how to implement the iterator method.
In terms of multiple threads accessing view state, there is no need for your custom view factory or view implementation to perform any synchronization to protect internal state. The iterator of the custom view implementation does also not need to be thread-safe. The runtime ensures the custom view executes in the context of a single thread at a time. If your view uses shared external state, such external state must be still considered for synchronization when using multiple threads.
The view factory class name as well as the view namespace and name for the new view must be added to the compiler configuration. The configuration shown below is XML however the same options are available through configuration:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<plugin-view namespace="custom" name="ohlc"
forge-class="com.espertech.esper.example.ohlc.OHLCBarPlugInViewFactory" />
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>The new view is now ready to use in a statement:
select * from StockTick.custom:ohlc(timestamp, price)
Note that the view must implement additional interfaces if it acts as a data window view, or works in a grouping context, as discussed in detail below.
Your custom view may represent an expiry policy and may retain events and thus act as a data window view. In order to allow the compiler to validate that your view can be used with named windows, which allow only data window views, this section documents any additional requirement that your classes must fulfill.
Your view forge class must implement the DataWindowViewForge interface. This marker interface (no methods required) indicates that your views are data window views.
Your view factory class must implement the DataWindowViewFactory interface. This marker interface (no methods required) indicates that your views are data window views.
Your view class must implement the DataWindowView interface. This interface indicates that your view is a data window view and therefore eligible to be used in any construct that requires a data window view. The DataWindowView interface extends the ViewDataVisitable interface. Please provide an empty implementation method for the visitView method as required by ViewDataVisitable (the default behavior is sufficient).
Your custom view may compute derived information from the arriving stream, instead of retaining events, and thus act as a derived-value view.
Your view class should implement the DerivedValueView interface. This marker interface indicates that your view is a derived-value view,
affecting correct behavior of the view when used in joins.
Aggregation functions are stateful functions that aggregate events, event property values or expression results. Examples for built-in aggregation functions are count(*), sum(price * volume), window(*) or maxby(volume).
EPL allows two different ways for your application to provide aggregation functions. We use the name aggregation single-function and aggregation multi-function for the two independent extension APIs for aggregation functions.
The aggregation single-function API is simple to use however it imposes certain restrictions on how expressions that contain aggregation functions share state and how they are evaluated.
The aggregation multi-function API is more powerful and provides control over how expressions that contain aggregation functions share state and are evaluated.
The next table compares the two aggregation function extension API's:
Table 22.1. Aggregation Function Extension API's
| Single-Function | Multi-Function | |
|---|---|---|
| Return Value | Can only return a single value or object. Cannot return an EventBean event, collection of EventBean events or collection or array of values for use with enumeration methods, for example. | Can return an EventBean event, a collection of EventBean events or a collection or array of objects for use with enumeration methods or to access event properties. |
| Complexity of API | Simple (consists of 2 interfaces). | More complex (consists of 6 interfaces). |
| State Sharing | State and parameter evaluation shared if multiple aggregation functions of the same name in the same statement (and context partition) take the exact same parameter expressions. | State and parameter evaluation sharable when multiple aggregation functions of a related name (related thru configuration) for the same statement (and context partition) exist, according to a sharing-key provided by your API implementation. |
| Function Name | Each aggregation function expression receives its own factory object. | Multiple related aggregation function expressions share a single factory object. |
| Distinct Keyword | Handled by the runtime transparently depending on mode. | Indicated to the API implementation only. |
The following sections discuss developing an aggregation single-function first, followed by the subject of developing an aggregation multi-function.
Note
The aggregation multi-function API is a powerful and lower-level API to extend the runtime. Any classes that are not part of the client package should be considered unstable and are subject to change between minor and major releases.
This section describes the aggregation single-function extension API for providing aggregation functions.
The EPL compiler provides two ways to provide aggregation single-functions:
An inlined class that is part of the same EPL module or another EPL module, see next under Section 22.5.1.4, “Using an Inlined Class to Provide an Aggregation Single-Function” .
An external class that your application provides as part of the application, see below under Section 22.5.1.5, “Using an Application Class to Provide the Aggregation Single-Function” .
In either case, the following steps are required to develop and use a custom aggregation single-function.
Implement an aggregation function forge by implementing the interface
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.aggfunc.AggregationFunctionForge. This class provides compile-time information.Implement an aggregation function factory by implementing the interface
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.aggfunc.AggregationFunctionFactory(used at runtime).Implement an aggregation function by implementing the interface
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.aggfunc.AggregationFunction(used at runtime).
Custom aggregation functions can also be passed multiple parameters, as further described in Section 22.5.1.6, “Aggregation Single-Function: Accepting Multiple Parameters”. In the example below the aggregation function accepts a single parameter.
The code for the example aggregation function as shown in this chapter can be found in the runtime configuration example in the package com.espertech.esper.example.runtimeconfig by the name MyConcatAggregationFunction. The sample function simply concatenates string-type values.
An aggregation function forge class is only used at compile-time and is responsible for the following functions:
Implement a
setFunctionNamemethod that receives the function name (optional, the default implementation is empty).Implement a
validatemethod that validates the value type of the data points that the function must process.Implement a
getValueTypemethod that returns the type of the aggregation value generated by the aggregation function instances. For example, the built-incountaggregation function returnsLong.classas it generateslong-typed values.Implement a
getAggregationFunctionModewhich provided information about the factory class to the compiler.
Aggregation forge classes implement the interface AggregationFunctionForge:
public class MyConcatAggregationFunctionForge implements AggregationFunctionForge { ...The compiler constructs one instance of the aggregation function forge class for each time the function is listed in a statement, however the compiler may decide to reduce the number of aggregation forge instances if it finds equivalent aggregations.
The aggregation function forge instance receives the aggregation function name via set setFunctionName method.
The sample concatenation function forge provides an empty setFunctionName method:
public void setFunctionName(String functionName) {
// no action taken
}
An aggregation function forge must provide an implementation of the validate method that is passed a AggregationFunctionValidationContext validation context object. Within the validation context you find the result type of each of the parameters expressions to the aggregation function as well as information about constant values and data window use. Please see the JavaDoc API documentation for a comprehensive list of validation context information.
Since the example concatenation function requires string types it implements a type check:
public void validate(AggregationValidationContext validationContext) {
if (validationContext.getParameterTypes().length != 1 || !JavaClassHelper.isTypeString(validationContext.getParameterTypes()[0])) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Concat aggregation requires a single parameter of type String");
}
}
In order for the compiler to validate the type returned by the aggregation function against the types expected by enclosing expressions, the getValueType must return the result type of any values produced by the aggregation function:
public EPTypeClass getValueType() {
return EPTypePremade.STRING.getEPType();
}
Finally the forge implementation must provide a getAggregationFunctionMode method that returns information about the factory. The compiler uses this information to build the aggregation function factory.
public AggregationFunctionMode getAggregationFunctionMode() {
// Inject a factory by using "new"
InjectionStrategy injectionStrategy = new InjectionStrategyClassNewInstance(MyConcatAggregationFunctionFactory.class);
// The managed mode means there is no need to write code that generates code
AggregationFunctionModeManaged mode = new AggregationFunctionModeManaged();
mode.setInjectionStrategyAggregationFunctionFactory(injectionStrategy);
return mode;
}An aggregation function factory class is responsible for the following functions:
Implement a
newAggregatormethod that instantiates and returns an aggregation function instance.
Aggregation function factory classes implement the interface AggregationFunctionFactory:
public class MyConcatAggregationFunctionFactory implements AggregationFunctionFactory { ...The runtime constructs the aggregation function factory at time of deployment.
The factory must provide a newAggregator method that returns instances of AggregationFunction. The runtime invokes this method for each new aggregation state to be allocated.
public AggregationFunction newAggregator() {
return new MyConcatAggregationFunction();
}An aggregation function class is responsible for the following functions:
Implement an
entermethod that the runtime invokes to add a data point into the aggregation, when an event enters a data windowImplement a
leavemethod that the runtime invokes to remove a data point from the aggregation, when an event leaves a data windowImplement a
getValuemethod that returns the current value of the aggregation.Implement a
clearmethod that resets the current value.
Aggregation function classes implement the interface AggregationFunction:
public class MyConcatAggregationFunction implements AggregationFunction { ...
The class that provides the aggregation and implements AggregationFunction does not have to be threadsafe.
The constructor initializes the aggregation function:
public class MyConcatAggregationFunction implements AggregationFunction {
private final static char DELIMITER = ' ';
private StringBuilder builder;
private String delimiter;
public MyConcatAggregationFunction() {
builder = new StringBuilder();
delimiter = "";
}
...
The enter method adds a datapoint to the current aggregation value. The example enter method shown below adds a delimiter and the string value to a string buffer:
public void enter(Object value) {
if (value != null) {
builder.append(delimiter);
builder.append(value.toString());
delimiter = String.valueOf(DELIMITER);
}
}
Conversly, the leave method removes a datapoint from the current aggregation value. The example leave method removes from the string buffer:
public void leave(Object value) {
if (value != null) {
builder.delete(0, value.toString().length() + 1);
}
}
Finally, the runtime obtains the current aggregation value by means of the getValue method:
public Object getValue() {
return builder.toString();
}
For on-demand queries the aggregation function must support resetting its value to empty or start values. Implement the clear function to reset the value as shown below:
public void clear() {
builder = new StringBuilder();
delimiter = "";
}You may use an inline class that is part of the EPL modules to provide an aggregation function. For more information on inline classes see Chapter 18, Inlined Classes. Using an inline class does not require any compiler configuration.
Specify the ExtensionAggregationFunction annotation on the class level of the AggregationFunctionForge implementation class
and the name (the EPL aggregation function name).
This annotation instructs the compiler that the inlined class exposes an aggregation function.
This sample EPL includes an inlined class by name ConcatAggForge that provides a concat aggregation function that concatenates:
inlined_class """
import com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.aggfunc.*;
import com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.forgeinject.*;
import com.espertech.esper.common.client.serde.*;
import java.io.*;
import com.espertech.esper.common.internal.epl.expression.core.*;
@ExtensionAggregationFunction(name="concat")
public class ConcatAggForge implements AggregationFunctionForge {
public void validate(AggregationFunctionValidationContext validationContext) throws ExprValidationException {
EPType paramType = validationContext.getParameterTypes()[0];
if (paramType == EPTypeNull.INSTANCE || ((EPTypeClass) paramType).getType() != String.class) {
throw new ExprValidationException("Invalid parameter type '" + paramType + "'");
}
}
public EPTypeClass getValueType() {
return new EPTypeClass(String.class);
}
public AggregationFunctionMode getAggregationFunctionMode() {
AggregationFunctionModeManaged mode = new AggregationFunctionModeManaged();
mode.setHasHA(true);
mode.setSerde(ConcatAggSerde.class);
mode.setInjectionStrategyAggregationFunctionFactory(new InjectionStrategyClassNewInstance(ConcatAggFactory.class.getName()));
return mode;
}
public static class ConcatAggFactory implements AggregationFunctionFactory {
public AggregationFunction newAggregator(AggregationFunctionFactoryContext ctx) {
return new ConcatAggFunction();
}
}
public static class ConcatAggFunction implements AggregationFunction {
private final static String DELIMITER = ",";
private StringBuilder builder;
private String delimiter;
public ConcatAggFunction() {
super();
builder = new StringBuilder();
delimiter = "";
}
public void enter(Object value) {
if (value != null) {
builder.append(delimiter);
builder.append(value.toString());
delimiter = DELIMITER;
}
}
public void leave(Object value) {
if (value != null) {
builder.delete(0, value.toString().length() + 1);
}
}
public String getValue() {
return builder.toString();
}
public void clear() {
builder = new StringBuilder();
delimiter = "";
}
}
// the serializer-deserializer is only for high availability and is not required otherwise
public static class ConcatAggSerde {
public static void write(DataOutput output, AggregationFunction value) throws IOException {
ConcatAggFunction agg = (ConcatAggFunction) value;
output.writeUTF(agg.getValue());
}
public static AggregationFunction read(DataInput input) throws IOException {
ConcatAggFunction concatAggFunction = new ConcatAggFunction();
String current = input.readUTF();
if (!current.isEmpty()) {
concatAggFunction.enter(current);
}
return concatAggFunction;
}
}
}
"""
select concat(personName) from PersonEvent
Only one ExtensionAggregationFunction annotation can be specified per class and the annotation is only for use with inlined classes.
Using an inline class does not require any compiler configuration.
When using create inlined_class the runtime resolves dependencies on EPL objects at time of deployment (the same as for all EPL objects).
The aggregation function class name as well as the function name for the new aggregation function must be added to the compiler configuration. The configuration shown below is XML however the same options are available through the configuration API. Configuring the function is not necessary when using inlined classes as discussed before.
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<plugin-aggregation-function name="concat"
forge-class="com.espertech.esper.example.runtimeconfig.MyConcatAggregationFunctionFactory" />
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>The new aggregation function is now ready to use in a statement:
select concat(symbol) from StockTick#length(3)
Your plug-in aggregation function may accept multiple parameters. You must provide a different mode however:
public AggregationFunctionMode getAggregationFunctionMode() {
InjectionStrategy injectionStrategy = new InjectionStrategyClassNewInstance(SupportCountBackAggregationFunctionFactory.class);
AggregationFunctionModeMultiParam multiParam = new AggregationFunctionModeMultiParam();
multiParam.setInjectionStrategyAggregationFunctionFactory(injectionStrategy);
return multiParam;
}
For instance, assume an aggregation function rangeCount that counts all values that fall into a range of values. The EPL that calls this function and provides a lower and upper bounds of 1 and 10 is:
select rangeCount(1, 10, myValue) from MyEvent
The enter method of the plug-in aggregation function may look as follows:
public void enter(Object value) {
Object[] params = (Object[]) value;
int lower = (Integer) params[0];
int upper = (Integer) params[1];
int val = (Integer) params[2];
if ((val >= lower) && (val <= upper)) {
count++;
}
}
Your plug-in aggregation function may want to validate parameter types or may want to know which parameters are constant-value expressions. Constant-value expressions are evaluated only once by the runtime and could
therefore be cached by your aggregation function for performance reasons. The runtime provides constant-value information as part of the AggregationValidationContext passed to the validate method.
When using AggregationFunctionModeManaged the runtime already takes care of filters.
When using AggregationFunctionModeMultiParam, the compiler takes the filter named parameter filter expression as a boolean-type value
and the runtime provides the value to your enter method as the last value in the parameter array.
For instance, assume an aggregation function concat that receives a word value and that has a filter expression as parameters:
select concat(word, filter: word not like '%jim%') from MyWordEvent
The enter method of the plug-in aggregation function may look as follows:
public void enter(Object value) {
Object[] arr = (Object[]) value;
Boolean pass = (Boolean) arr[1];
if (pass != null && pass) {
buffer.append(arr[0].toString());
}
}
Your code can obtain the actual filter expression from the AggregationValidationContext that is passed to the validate method and that
returns the named parameters via getNamedParameters.
When using AggregationFunctionModeManaged the runtime already takes care of distinct.
When using AggregationFunctionModeMultiParam your application code must determine and process distinct.
When the custom aggregation function returns an object as a return value, the EPL can use parenthesis and the dot-operator to invoke methods on the return value.
The following example assumes that the myAggregation custom aggregation function returns an object that has getValueOne and getValueTwo methods:
select (myAggregation(myValue)).getValueOne(), (myAggregation(myValue)).getValueTwo() from MyEvent
Since the above EPL aggregates the same value, the runtime internally uses a single aggregation to represent the current value of myAggregation (and not two instances of the aggregation, even though myAggregation is listed twice).
This section introduces the aggregation multi-function API. Aggregation multi-functions can offer multiple functions, methods, modifiers or views onto sharable aggregation state. Please refer to the JavaDoc for more complete class and method-level documentation.
The EPL compiler provides two ways to provide aggregation multi-functions:
An inlined class that is part of the same EPL module or another EPL module, see next under Section 22.5.2.8, “Using an Inlined Class to Provide an Aggregation Multi-Function”.
An external class that your application provides as part of the application, see below under Section 22.5.2.7, “Using an Application Class to Provide the Aggregation Multi-Function”.
In either case, the following steps are required to develop and use a custom aggregation multi-function.
Implement an aggregation multi-function forge by implementing the interface
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.aggmultifunc.AggregationMultiFunctionForge.Implement one or more handlers for aggregation functions by implementing the interface
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.aggmultifunc.AggregationMultiFunctionHandler.Implement an aggregation state key by implementing the interface
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.aggmultifunc.AggregationMultiFunctionStateKey.Implement an aggregation state factory by implementing the interface
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.aggmultifunc.AggregationMultiFunctionStateFactory.Implement an aggregation state holder by implementing the interface
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.aggmultifunc.AggregationMultiFunctionState.Implement a state accessor factory by implementing the interface
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.aggmultifunc.AggregationMultiFunctionAccessorFactory.Implement a state accessor by implementing the interface
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.aggmultifunc.AggregationMultiFunctionAccessor.For use with tables, implement an agent factory by implementing the interface
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.aggmultifunc.AggregationMultiFunctionAgentFactory.For use with tables, implement an agent by implementing the interface
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.aggmultifunc.AggregationMultiFunctionAgent.For use with aggregation methods, implement an aggregation method factory by implementing the interface
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.aggmultifunc.AggregationMultiFunctionAggregationMethodFactory.For use with aggregation methods, implement an aggregation method by implementing the interface
com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.aggmultifunc.AggregationMultiFunctionAggregationMethod.When using an inlined class, use the
ExtensionAggregationMultiFunctionannotation and by providing the function names. When providing external application classes, register the aggregation multi-function forge class with the compiler by supplying one or more function names, via the compiler configuration file or the runtime and static configuration API.
There are two examples for aggregation multi-function. The first example uses inlined classes and can be found at Section 22.5.2.8, “Using an Inlined Class to Provide an Aggregation Multi-Function”. The second example for aggregation multi-function is called Cycle-Detect and is used for the step-by-step below.
Cycle-Detect takes incoming transaction events that have from-account and to-account fields.
The example detects a cycle in the transactions between accounts in order to detect a possible transaction fraud.
Please note that the graph and cycle detection logic of the example is not part of the distribution:
The example utilizes the jgrapht library.
In the Cycle-Detect example, the vertices of a graph are the account numbers. For example the account numbers Acct-1, Acct-2 and Acct-3.
In the graph the edges are transaction events that identify a from-account and a to-account. An example edge is {from:Acct-1, to:Acct-2}.
An example cycle is therefore in the three transactions {from:Acct-1, to:Acct-2}, {from:Acct-2, to:Acct-3} and {from:Acct-3, to:Acct-1}.
The code for the example aggregation multi-function as shown in this chapter can be found in the Cycle-Detect example in the package com.espertech.esper.example.cycledetect.
The example provides two aggregation functions named cycledetected and cycleoutput:
The
cycledetectedfunction returns a boolean value whether a graph cycle is found or not.The
cycleoutputfunction outputs the vertices (account numbers) that are part of the graph cycle.
In the Cycle-Detect example, the following statement utilizes the two functions cycledetected and cycleoutput that
share the same graph state to detect a cycle among the last 1000 events:
@Name('CycleDetector') select cycleoutput() as cyclevertices
from TransactionEvent#length(1000)
having cycledetected(fromAcct, toAcct)If instead the goal is to run graph cycle detection every 1 second (and not upon arrival of a new event), this sample statement uses a pattern to trigger cycle detection:
@Name('CycleDetector')
select (select cycleoutput(fromAcct, toAcct) from TransactionEvent#length(1000)) as cyclevertices
from pattern [every timer:interval(1)]An aggregation multi-function forge class is a compile-time class responsible for the following functions:
Implement the
addAggregationFunctionmethod that receives an invocation for each aggregation function declared in the statement that matches any of the function names provided at configuration time.Implement the
validateGetHandlermethod that receives an invocation for each aggregation function to be validated in the statement that matches any of the function names provided at configuration time.
Aggregation multi-function factory classes implement the interface AggregationMultiFunctionForge:
public class CycleDetectorAggregationForge implements AggregationMultiFunctionForge { ...The compiler constructs a single instance of the aggregation multi-function forge class that is shared for all aggregation function expressions in a statement that have one of the function names provided in the configuration object.
The compiler invokes the addAggregationFunction method at the time it compiles a statement.
The method receives a declaration-time context object that provides the function name as well as additional information.
The sample Cycle-Detect factory class provides an empty addAggregationFunction method:
public void addAggregationFunction(AggregationMultiFunctionDeclarationContext declarationContext) {
// provides an opportunity to inspect where used
}
The compiler invokes the validateGetHandler method at the time of expression validation. It passes
a AggregationMultiFunctionValidationContext validation context object that contains actual parameters expressions.
Please see the JavaDoc API documentation for a comprehensive list of validation context information.
The validateGetHandler method must return a handler object the implements the AggregationMultiFunctionHandler interface.
Return a handler object for each aggregation function expression according to the aggregation function name and its parameters that are provided in the validation
context.
The example cycledetect function takes two parameters that provide the cycle edge (from-account and to-account):
public AggregationMultiFunctionHandler validateGetHandler(AggregationMultiFunctionValidationContext validationContext) {
if (validationContext.getParameterExpressions().length == 2) {
fromExpression = validationContext.getParameterExpressions()[0];
toExpression = validationContext.getParameterExpressions()[1];
}
return new CycleDetectorAggregationHandler(this, validationContext);
}
An aggregation multi-function handler class is a compile-time class that must implement the AggregationMultiFunctionHandler interface and is responsible for the following functions:
Implement the
getReturnTypemethod that returns information about the type of return values provided.Implement the
getAggregationStateUniqueKeymethod that provides a key object used by the compiler to determine which aggregation functions share state.Implement the
getStateModemethod that returns information to the compiler that the compiler uses to initialize the state factory at deployment time.Implement the
getAccessorModemethod that returns information to the compiler that the compiler uses to initialize the accessor factory at deployment time.Implement the
getAgentModemethod that returns information to the compiler that the compiler uses to initialize the agent factory at deployment time, for use with tables.Implement the
getTableReaderModemethod that returns information to the compiler that the compiler uses to initialize the table reader factory at deployment time, for use with tables.
In the Cycle-Detect example, the class CycleDetectorAggregationHandler is the handler for all aggregation functions.
public class CycleDetectorAggregationHandler implements AggregationMultiFunctionHandler { ...
The getReturnType method provided by the handler instructs the compiler about the return type of each aggregation accessor.
The class EPChainableType holds return type information.
In the Cycle-Detect example the cycledetected function returns a single boolean value. The cycleoutput returns a collection of vertices:
public EPChainableType getReturnType() {
if (validationContext.getFunctionName().toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH).equals(CycleDetectorConstant.CYCLEOUTPUT_NAME)) {
return EPChainableTypeHelper.collectionOfSingleValue((EPTypeClass) forge.getFromExpression().getForge().getEvaluationType());
}
return EPChainableTypeHelper.singleValue(Boolean.class);
}
The compiler invokes the getAggregationStateUniqueKey method to determine whether multiple aggregation function expressions
in the same statement can share the same aggregation state or should receive different aggregation state instances.
The getAggregationStateUniqueKey method must return an instance of AggregationMultiFunctionStateKey.
The compiler uses equals-semantics (the hashCode and equals methods) to determine whether multiple aggregation function share the state object.
If the key object returned for each aggregation function by the handler is an equal key object then the compiler shares aggregation
state between such aggregation functions for the same statement and context partition.
In the Cycle-Detect example the state is shared, which it achieves by simply returning the same key instance:
private static final AggregationMultiFunctionStateKey CYCLE_KEY = new AggregationMultiFunctionStateKey() {};
public AggregationMultiFunctionStateKey getAggregationStateUniqueKey() {
return CYCLE_KEY;
}
The compiler invokes the getStateMode method to obtain an instance of AggregationMultiFunctionStateMode. The
state mode is responsible to obtaining and configuring an aggregation state factory instance at time of deployment.
In the Cycle-Detect example the method passes the expression evaluators providing the from-account and to-account expressions to the state factory:
public AggregationMultiFunctionStateMode getStateMode() {
AggregationMultiFunctionStateModeManaged managed = new AggregationMultiFunctionStateModeManaged();
InjectionStrategyClassNewInstance injection = new InjectionStrategyClassNewInstance(CycleDetectorAggregationStateFactory.class);
injection.addExpression("from", forge.getFromExpression());
injection.addExpression("to", forge.getToExpression());
managed.setInjectionStrategyAggregationStateFactory(injection);
return managed;
}
The compiler invokes the getAccessorMode method to obtain an instance of AggregationMultiFunctionAccessorMode. The
accessor mode is responsible to obtaining and configuring an accessor factory instance at time of deployment.
The getAccessorMode method provides information about the accessor factories according to whether the aggregation function name is cycledetected or cycleoutput:
public AggregationMultiFunctionAccessorMode getAccessorMode() {
Class accessor;
if (validationContext.getFunctionName().toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH).equals(CycleDetectorConstant.CYCLEOUTPUT_NAME)) {
accessor = CycleDetectorAggregationAccessorOutputFactory.class;
}
else {
accessor = CycleDetectorAggregationAccessorDetectFactory.class;
}
AggregationMultiFunctionAccessorModeManaged managed = new AggregationMultiFunctionAccessorModeManaged();
InjectionStrategyClassNewInstance injection = new InjectionStrategyClassNewInstance(accessor);
managed.setInjectionStrategyAggregationAccessorFactory(injection);
return managed;
}
An aggregation multi-function state factory class must implement the AggregationMultiFunctionStateFactory interface and is responsible for the following functions:
Implement the
newStatemethod that returns an aggregation state holder.
The runtime invokes the newState method to obtain a new aggregation state instance before applying aggregation state.
If using group by in your statement, the runtime invokes the newState method to obtain a state holder for each group.
In the Cycle-Detect example, the class CycleDetectorAggregationStateFactory is the state factory for all aggregation functions:
public class CycleDetectorAggregationStateFactory implements AggregationMultiFunctionStateFactory {
private ExprEvaluator from;
private ExprEvaluator to;
public AggregationMultiFunctionState newState(AggregationMultiFunctionStateFactoryContext ctx) {
return new CycleDetectorAggregationState(this);
}
public void setFrom(ExprEvaluator from) {
this.from = from;
}
public void setTo(ExprEvaluator to) {
this.to = to;
}
public ExprEvaluator getFrom() {
return from;
}
public ExprEvaluator getTo() {
return to;
}
}
An aggregation multi-function state class must implement the AggregationMultiFunctionState interface and is responsible for the following functions:
Implement the
applyEntermethod that enters events, event properties or computed values.Implement the
applyLeavemethod that can remove events or computed values.Implement the
clearmethod to clear state.
In the Cycle-Detect example, the class CycleDetectorAggregationState is the state for all aggregation functions.
Please review the example for more information.
An aggregation multi-function accessor factory class must implement the AggregationMultiFunctionAccessorFactory interface and is responsible for the following functions:
Implement the
newAccessormethod that returns a new accessor.
In the Cycle-Detect example, the class CycleDetectorAggregationAccessorDetectFactory returns the accessor like so:
public class CycleDetectorAggregationAccessorDetectFactory implements AggregationMultiFunctionAccessorFactory {
public AggregationMultiFunctionAccessor newAccessor(AggregationMultiFunctionAccessorFactoryContext ctx) {
return new CycleDetectorAggregationAccessorDetect();
}
}
An aggregation multi-function accessor class must implement the AggregationMultiFunctionAccessor interface and is responsible for the following functions:
Implement the
Object getValue(AggregationMultiFunctionState state, ...)method that returns a result object for the aggregation state.Implement the
Collection<EventBean> getEnumerableEvents(AggregationMultiFunctionState state, ...)method that returns a collection of events for enumeration, if applicable (or null).Implement the
EventBean getEnumerableEvent(AggregationMultiFunctionState state, ...)method that returns an event, if applicable (or null).Implement the
Collection getEnumerableScalar(AggregationMultiFunctionState state, ...)method that returns an event, if applicable (or null).
In the Cycle-Detect example, the class CycleDetectorAggregationAccessorDetect returns state for the cycledetected aggregation function
and the CycleDetectorAggregationAccessorOutput returns the state for the cycleoutput aggregation function.
An aggregation multi-function configuration can receive one or multiple function names. You must also set a factory class name.
The sample XML snippet below configures an aggregation multi-function that is associated with the function names func1 and func2.
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<plugin-aggregation-multifunction
function-names="cycledetected,cycleoutput"
forge-class="com.espertech.esper.example.cycledetect.CycleDetectorAggregationFactory"/>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>The next example uses the configuration API to register the same:
String[] functionNames = new String[] {"cycledetected", "cycleoutput"};
ConfigurationPlugInAggregationMultiFunction config = new ConfigurationPlugInAggregationMultiFunction(functionNames, CycleDetectorAggregationFactory.class.getName());
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCompiler().addPlugInAggregationMultiFunction(config);You may use an inline class that is part of the EPL modules to provide an aggregation multi-function. For more information on inline classes see Chapter 18, Inlined Classes. Using an inline class does not require any compiler configuration.
Specify the ExtensionAggregationMultiFunction annotation on the class level of the AggregationMultiFunctionForge implementation class and the function names (names of states and aggregation methods). This annotation instructs the compiler that the inlined class exposes an aggregation multi-function.
This sample EPL includes an inlined class by name TrieAggForge that uses a Trie data structures to store person names. A trie is a tree-like data structure whose nodes store the letters of an alphabet. Here, the Trie stores person names. The implementation uses the Trie provided by the Apache Commons Collections library.
The following sample EPL uses the Trie to store persons by person name and return a prefix-map, which is a sorted map of all persons that have the same prefix:
// The PersonEvent provides a person name and person id
@public @buseventtype create schema PersonEvent(name string, id string);
// This provides the aggregation multi-function
create inlined_class """
import com.espertech.esper.common.client.*;
import com.espertech.esper.common.client.type.*;
import com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.aggmultifunc.*;
import com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.forgeinject.*;
import com.espertech.esper.common.internal.epl.expression.core.*;
import com.espertech.esper.common.internal.rettype.*;
import com.espertech.esper.common.internal.epl.agg.core.*;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.Trie;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.trie.PatriciaTrie;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.function.*;
// We have 3 function names:
// - "trieState" for use with create-table to hold the Trie
// - "trieEnter" for entering person events into the Trie by person name, for use with into-table aggregation
// - "triePrefixMap" for returning a prefix map of all persons with the same prefix as provided by its parameter
@ExtensionAggregationMultiFunction(names="trieState,trieEnter,triePrefixMap")
/**
* The trie aggregation forge is the entry point for providing the multi-function aggregation.
*/
public class TrieAggForge implements AggregationMultiFunctionForge {
public AggregationMultiFunctionHandler validateGetHandler(AggregationMultiFunctionValidationContext validationContext) {
String name = validationContext.getFunctionName();
if (name.equals("trieState")) {
return new TrieAggHandlerTrieState();
} else if (name.equals("trieEnter")) {
return new TrieAggHandlerTrieEnter(validationContext.getParameterExpressions());
} else if (name.equals("triePrefixMap")) {
return new TrieAggHandlerTriePrefixMap();
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Unrecognized name '" + name + "' for use with trie");
}
/**
* This handler handles the "trieState"-type table column, for use with create-table.
*/
public static class TrieAggHandlerTrieState implements AggregationMultiFunctionHandler {
public EPChainableType getReturnType() {
return EPChainableTypeHelper.singleValue(Trie.class);
}
public AggregationMultiFunctionStateKey getAggregationStateUniqueKey() {
return new AggregationMultiFunctionStateKey() {};
}
public AggregationMultiFunctionStateMode getStateMode() {
InjectionStrategyClassNewInstance injection = new InjectionStrategyClassNewInstance(TrieAggStateFactory.class);
return new AggregationMultiFunctionStateModeManaged(injection);
}
public AggregationMultiFunctionAccessorMode getAccessorMode() {
// accessor that returns the trie itself
InjectionStrategyClassNewInstance injection = new InjectionStrategyClassNewInstance(TrieAggAccessorFactory.class);
return new AggregationMultiFunctionAccessorModeManaged(injection);
}
public AggregationMultiFunctionAgentMode getAgentMode() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Trie aggregation access is only by the 'triePrefixMap' method");
}
public AggregationMultiFunctionAggregationMethodMode getAggregationMethodMode(AggregationMultiFunctionAggregationMethodContext ctx) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Trie aggregation access is only by the 'triePrefixMap' method");
}
}
/**
* This handler handles the "trieEnter"-operation that updates trie state, for use with into-table aggregation
*/
public static class TrieAggHandlerTrieEnter implements AggregationMultiFunctionHandler {
private final ExprNode[] parameters;
public TrieAggHandlerTrieEnter(ExprNode[] parameters) {
this.parameters = parameters;
}
public EPChainableType getReturnType() {
return EPChainableTypeHelper.singleValue(Trie.class); // we return the Trie itself
}
public AggregationMultiFunctionStateKey getAggregationStateUniqueKey() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not a trie state");
}
public AggregationMultiFunctionStateMode getStateMode() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not a trie state");
}
public AggregationMultiFunctionAccessorMode getAccessorMode() {
// accessor that returns the trie itself
InjectionStrategyClassNewInstance injection = new InjectionStrategyClassNewInstance(TrieAggAccessorFactory.class);
return new AggregationMultiFunctionAccessorModeManaged(injection);
}
public AggregationMultiFunctionAgentMode getAgentMode() {
if (parameters.length != 1 || ((EPTypeClass) parameters[0].getForge().getEvaluationType()).getType() != String.class) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Requires a single parameter returing a string value");
}
InjectionStrategyClassNewInstance injection = new InjectionStrategyClassNewInstance(TrieAggAgentFactory.class);
injection.addExpression("keyExpression", parameters[0]);
return new AggregationMultiFunctionAgentModeManaged(injection);
}
public AggregationMultiFunctionAggregationMethodMode getAggregationMethodMode(AggregationMultiFunctionAggregationMethodContext ctx) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Trie aggregation access is only by the 'triePrefixMap' method");
}
}
/**
* This handler handles the "triePrefixMap" accessor for returning a prefix map of same-prefix person events
*/
public static class TrieAggHandlerTriePrefixMap implements AggregationMultiFunctionHandler {
public EPChainableType getReturnType() {
return EPChainableTypeHelper.singleValue(Map.class);
}
public AggregationMultiFunctionStateKey getAggregationStateUniqueKey() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not implemented for 'triePrefixMap' trie method");
}
public AggregationMultiFunctionStateMode getStateMode() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not implemented for 'triePrefixMap' trie method");
}
public AggregationMultiFunctionAccessorMode getAccessorMode() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not implemented for 'triePrefixMap' trie method");
}
public AggregationMultiFunctionAgentMode getAgentMode() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not implemented for 'triePrefixMap' trie method");
}
public AggregationMultiFunctionAggregationMethodMode getAggregationMethodMode(AggregationMultiFunctionAggregationMethodContext ctx) {
if (ctx.getParameters().length != 1 || ((EPTypeClass) ctx.getParameters()[0].getForge().getEvaluationType()).getType() != String.class) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Requires a single parameter returning a string value");
}
InjectionStrategyClassNewInstance injection = new InjectionStrategyClassNewInstance(TrieAggMethodFactoryPrefixMap.class);
injection.addExpression("keyExpression", ctx.getParameters()[0]);
return new AggregationMultiFunctionAggregationMethodModeManaged(injection);
}
}
/**
* The agent state factory is responsible for producing a state holder that holds the trie state
*/
public static class TrieAggStateFactory implements AggregationMultiFunctionStateFactory {
public AggregationMultiFunctionState newState(AggregationMultiFunctionStateFactoryContext ctx) {
return new TrieAggState();
}
}
/**
* The agent state is the state holder that holds the trie state
*/
public static class TrieAggState implements AggregationMultiFunctionState {
private final Trie<String, List<Object>> trie = new PatriciaTrie<>();
public void applyEnter(EventBean[] eventsPerStream, ExprEvaluatorContext exprEvaluatorContext) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not used since the agent updates the table");
}
public void applyLeave(EventBean[] eventsPerStream, ExprEvaluatorContext exprEvaluatorContext) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not used since the agent updates the table");
}
public void clear() {
trie.clear();
}
public void add(String key, Object underlying) {
List<Object> existing = (List<Object>) trie.get(key);
if (existing != null) {
existing.add(underlying);
return;
}
List<Object> events = new ArrayList<>(2);
events.add(underlying);
trie.put(key, events);
}
public void remove(String key, Object underlying) {
List<Object> existing = (List<Object>) trie.get(key);
if (existing != null) {
existing.remove(underlying);
if (existing.isEmpty()) {
trie.remove(key);
}
}
}
}
/**
* The accessor factory is responsible for producing an accessor that returns the result of the trie table column when accessed without an aggregation method
*/
public static class TrieAggAccessorFactory implements AggregationMultiFunctionAccessorFactory {
public AggregationMultiFunctionAccessor newAccessor(AggregationMultiFunctionAccessorFactoryContext ctx) {
return new TrieAggAccessor();
}
}
/**
* The accessor returns the result of the trie table column when accessed without an aggregation method
*/
public static class TrieAggAccessor implements AggregationMultiFunctionAccessor {
// This is the value return when just referring to the trie table column by itself without a method name such as "prefixMap".
public Object getValue(AggregationMultiFunctionState state, EventBean[] eventsPerStream, boolean isNewData, ExprEvaluatorContext exprEvaluatorContext) {
TrieAggState trie = (TrieAggState) state;
return trie.trie;
}
}
/**
* The agent factory is responsible for producing an agent that handles all changes to the trie table column.
*/
public static class TrieAggAgentFactory implements AggregationMultiFunctionAgentFactory {
private ExprEvaluator keyExpression;
public void setKeyExpression(ExprEvaluator keyExpression) {
this.keyExpression = keyExpression;
}
public AggregationMultiFunctionAgent newAgent(AggregationMultiFunctionAgentFactoryContext ctx) {
return new TrieAggAgent(this);
}
}
/**
* The agent is responsible for all changes to the trie table column.
*/
public static class TrieAggAgent implements AggregationMultiFunctionAgent {
private final TrieAggAgentFactory factory;
public TrieAggAgent(TrieAggAgentFactory factory) {
this.factory = factory;
}
public void applyEnter(EventBean[] eventsPerStream, ExprEvaluatorContext exprEvaluatorContext, AggregationRow row, int column) {
String key = (String) factory.keyExpression.evaluate(eventsPerStream, true, exprEvaluatorContext);
TrieAggState trie = (TrieAggState) row.getAccessState(column);
trie.add(key, eventsPerStream[0].getUnderlying());
}
public void applyLeave(EventBean[] eventsPerStream, ExprEvaluatorContext exprEvaluatorContext, AggregationRow row, int column) {
String key = (String) factory.keyExpression.evaluate(eventsPerStream, false, exprEvaluatorContext);
TrieAggState trie = (TrieAggState) row.getAccessState(column);
trie.remove(key, eventsPerStream[0].getUnderlying());
}
}
/**
* The aggregation method factory is responsible for producing an aggregation method for the "trie" return result of the trie table column.
*/
public static class TrieAggMethodFactoryTrieColumn implements AggregationMultiFunctionAggregationMethodFactory {
public AggregationMultiFunctionAggregationMethod newMethod(AggregationMultiFunctionAggregationMethodFactoryContext context) {
return new AggregationMultiFunctionAggregationMethod() {
public Object getValue(int aggColNum, AggregationRow row, EventBean[] eventsPerStream, boolean isNewData, ExprEvaluatorContext exprEvaluatorContext) {
TrieAggState trie = (TrieAggState) row.getAccessState(aggColNum);
return trie.trie;
}
};
}
}
/**
* The aggregation method factory is responsible for producing an aggregation method for the "triePrefixMap" expression of the trie table column.
*/
public static class TrieAggMethodFactoryPrefixMap implements AggregationMultiFunctionAggregationMethodFactory {
private ExprEvaluator keyExpression;
public void setKeyExpression(ExprEvaluator keyExpression) {
this.keyExpression = keyExpression;
}
public AggregationMultiFunctionAggregationMethod newMethod(AggregationMultiFunctionAggregationMethodFactoryContext context) {
return new TrieAggMethodPrefixMap(this);
}
}
/**
* The aggregation method is responsible for the "triePrefixMap" expression result of the trie table column.
*/
public static class TrieAggMethodPrefixMap implements AggregationMultiFunctionAggregationMethod {
private final TrieAggMethodFactoryPrefixMap factory;
public TrieAggMethodPrefixMap(TrieAggMethodFactoryPrefixMap factory) {
this.factory = factory;
}
public Object getValue(int aggColNum, AggregationRow row, EventBean[] eventsPerStream, boolean isNewData, ExprEvaluatorContext exprEvaluatorContext) {
String key = (String) factory.keyExpression.evaluate(eventsPerStream, false, exprEvaluatorContext);
TrieAggState trie = (TrieAggState) row.getAccessState(aggColNum);
return trie.trie.prefixMap(key);
}
}
}
""";
// We use a table to store the Trie. The Trie is effectively a Trie<String, List<PersonEvent>> holding a list of person events in branch and leaf nodes.
@name('table') create table TableWithTrie(nameTrie trieState(string));
// We aggregate directly into the table using the person name as the Trie key and the event as value
@Priority(1) into table TableWithTrie select trieEnter(name) as nameTrie from PersonEvent;
// For each person output the prefix map, a sorted map (SortedMap<String, List<PersonEvent>>) with the same prefixes as the person name
@Priority(0) @name('s0') select TableWithTrie.nameTrie.triePrefixMap(name) from PersonEvent;
Only one ExtensionAggregationMultiFunction annotation can be specified per class and the annotation is only for use with inlined classes. Using an inline class does not require any compiler configuration.
When using create inlined_class the runtime resolves dependencies on EPL objects at time of deployment (the same as for all EPL objects).
The runtime shares an AggregationAccessor instance between threads. The accessor should be designed stateless and should not use any locking of any kind
in the AggregationAccessor implementation unless your implementation uses other state.
Since the runtime passes an aggregation state instance to the accessor it is thread-safe as long as it relies only on the aggregation state passed to it.
The runtime does not share an AggregationState instance between threads. There is no need to use locking of any kind
in the AggregationState implementation unless your implementation uses other state.
Tables allow columns to hold aggregation state including the state for multi-function aggregations. This section provides API pointers.
When a statement accesses a table column that declares aggregation state of a multi-function aggregation, the
AggregationMultiFunctionValidationContext contains an optionalTableColumnRead field that provides information
about the table column.
To find out the statement type, such as to determine whether the current statement is a create-table statement, use
context.getValidationContext().getExprEvaluatorContext().getStatementType().
To find out whether the statement aggregates into a table, use context.getValidationContext().getIntoTableName() that returns the table name or null if not aggregating into a table.
The compiler uses AggregationMultiFunctionStateKey to determine whether an aggregation function listed with into table is compatible with the aggregation type
that a table column declares. The equals method of the object must return true for compatible and false for incompatible.
Your handler may provide a agent and aggregation method modes. Please follow the JavaDoc or inspect the regression test suite.
The filter expression is passed to you in PlugInAggregationMultiFunctionValidationContext as part of getNamedParameters under the name filter. When use with tables the filter expression is part of PlugInAggregationMultiFunctionAgentContext.
Your application must invoke the filter expression as the runtime does not evaluate the filter expression for you. For example:
ExprEvaluator filterEval = validationContext.getNamedParameters().get("filter").get(0).getExprEvaluator();public void applyEnter(EventBean[] eventsPerStream, ExprEvaluatorContext exprEvaluatorContext) {
Boolean pass = (Boolean) filterEval.evaluate(eventsPerStream, true, exprEvaluatorContext); // note: pass "false" for applyLeave
if (pass != null && pass) {
Object value = valueEval.evaluate(eventsPerStream, true, exprEvaluatorContext); // note: pass "false" for applyLeave
// do something
}
}Pattern guards are pattern objects that control the lifecycle of the guarded sub-expression, and can filter the events fired by the subexpression.
The following steps are required to develop and use a custom guard object.
Implement a guard forge class, responsible for compile-time guard information.
Implement a guard factory class, responsible for creating guard object instances at runtime.
Implement a guard class (used at runtime).
Register the guard forge class with the compiler by supplying a namespace and name, via the compiler configuration.
The code for the example guard object as shown in this chapter can be found in the test source folder in the package com.espertech.esper.regressionlib.support.extend.pattern by the name MyCountToPatternGuardForge. The sample guard discussed here counts the number of events occurring up to a maximum number of events, and end the sub-expression when that maximum is reached.
Some of the APIs that you use to implement a pattern guard are internal APIs and are not stable and may change between releases. The client package contains all the stable interface classes.
A guard forge class is only used by the compiler and is responsible for the following functions:
Implement a
setGuardParametersmethod that takes guard parameters, which are themselves expressions.Implement a
collectSchedulemethod that collects guard schedule objects if any.Implement a
makeCodegenmethod that provides the code to construct a guard factory at time of deployment.
Guard forge classes implement the GuardForge:
public class MyCountToPatternGuardForge implements GuardForge { ...The compiler constructs one instance of the guard forge class for each time the guard is listed in a statement.
The guard forge class implements the setGuardParameters method that is passed the parameters to the guard as supplied by the statement. It verifies the guard parameters, similar to the code snippet shown next. Our example counter guard takes a single numeric parameter:
public void setGuardParameters(List<ExprNode> guardParameters, MatchedEventConvertorForge convertor, StatementCompileTimeServices services) throws GuardParameterException {
String message = "Count-to guard takes a single integer-value expression as parameter";
if (guardParameters.size() != 1) {
throw new GuardParameterException(message);
}
Class paramType = guardParameters.get(0).getForge().getEvaluationType();
if (paramType != Integer.class && paramType != int.class) {
throw new GuardParameterException(message);
}
this.numCountToExpr = guardParameters.get(0);
this.convertor = convertor;
}
The makeCodegen method is called by the compiler to receive the code that builds a guard factory. Use the SAIFFInitializeBuilder to build factory initialization code:
public CodegenExpression makeCodegen(CodegenMethodScope parent, SAIFFInitializeSymbol symbols, CodegenClassScope classScope) {
SAIFFInitializeBuilder builder = new SAIFFInitializeBuilder(MyCountToPatternGuardFactory.class, this.getClass(), "guardFactory", parent, symbols, classScope);
return builder.exprnode("numCountToExpr", numCountToExpr)
.expression("convertor", convertor.makeAnonymous(builder.getMethod(), classScope))
.build();
}A guard factory class is responsible for the following functions:
Implement a
makeGuardmethod that constructs a new guard instance.
Guard factory classes implements the GuardFactory:
public class MyCountToPatternGuardFactory implements GuardFactory { ...The runtime obtains an instance of the guard factory class at time of deployment.
The makeGuard method is called by the runtime to create a new guard instance. The example makeGuard method shown below passes the maximum count of events to the guard instance. It also passes a Quitable implementation to the guard instance. The guard uses Quitable to indicate that the sub-expression contained within must stop (quit) listening for events.
public Guard makeGuard(PatternAgentInstanceContext context, MatchedEventMap beginState, Quitable quitable, Object guardState) {
EventBean[] events = convertor == null ? null : convertor.convert(beginState);
Object parameter = PatternExpressionUtil.evaluateChecked("Count-to guard", numCountToExpr, events, context.getAgentInstanceContext());
if (parameter == null) {
throw new EPException("Count-to guard parameter evaluated to a null value");
}
Integer numCountTo = (Integer) parameter;
return new MyCountToPatternGuard(numCountTo, quitable);
}A guard class has the following responsibilities:
Provides a
startGuardmethod that initalizes the guard.Provides a
stopGuardmethod that stops the guard, called by the runtime when the whole pattern is stopped, or the sub-expression containing the guard is stopped.Provides an
inspectmethod that the pattern runtime invokes to determine if the guard lets matching events pass for further evaluation by the containing expression.
Guard classes implement the GuardSupport interface as shown here:
public class MyCountToPatternGuard implements Guard {The compiler invokes the guard factory class to construct an instance of the guard class for each new sub-expression instance within a statement.
A guard class must provide an implementation of the startGuard method that the runtime invokes to start a guard instance. In our example, the method resets the guard's counter to zero:
public void startGuard() {
counter = 0;
}
The runtime invokes the inspect method for each time the sub-expression indicates a new event result. Our example guard needs to count the number of events matched, and quit if the maximum number is reached:
public boolean inspect(MatchedEventMap matchEvent) {
counter++;
if (counter > numCountTo) {
quitable.guardQuit();
return false;
}
return true;
}
The inspect method returns true for events that pass the guard, and false for events that should not pass the guard.
The guard factory class name as well as the namespace and name for the new guard must be added to the compiler configuration. The configuration shown below is XML however the same options are available through the configuration API:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<plugin-pattern-guard namespace="myplugin" name="count_to"
forge-class="com.espertech.esper.regressionlib.support.extend.pattern.MyCountToPatternGuardForge"/>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>The new guard is now ready to use in a statement. The next pattern statement detects the first 10 MyEvent events:
select * from pattern [(every MyEvent) where myplugin:count_to(10)]
Note that the every keyword was placed within parentheses to ensure the guard controls the repeated matching of events.
Pattern observers are pattern objects that are executed as part of a pattern expression and can observe events or test conditions. Examples for built-in observers are timer:at and timer:interval. Some suggested uses of observer objects are:
Implement custom scheduling logic using the runtime's own scheduling and timer services
Test conditions related to prior events matching an expression
The following steps are required to develop and use a custom observer object within pattern statements:
Implement an observer forge class, which is used by the compiler only and is responsible for validating parameters and for initializing an observer factory.
Implement an observer factory class, responsible for creating observer object instances.
Implement an observer class.
Register an observer factory class with the compiler by supplying a namespace and name, via the compiler configuration file or the configuration API.
The code for the example observer object as shown in this chapter can be found in the test source folder in package com.espertech.esper.regression.client by the name MyFileExistsObserver. The sample observer discussed here very simply checks if a file exists, using the filename supplied by the pattern statement, and via the java.io.File class.
Some of the APIs that you use to implement a pattern observer are internal APIs and are not stable and may change between releases. The client package contains all the stable interface classes.
An observer forge class is responsible for the following functions:
Implement a
setObserverParametersmethod that takes observer parameters, which are themselves expressions.Implement a
collectSchedulemethod that collects observer schedule objects if any.Implement a
makeCodegenmethod that provides the code to construct an observer factory at time of deployment.
Observer forge classes implement the ObserverForge interface:
public class MyFileExistsObserverForge implements ObserverForge { ...The compiler constructs one instance of the observer forge class for each time the observer is listed in a statement.
The observer forge class implements the setObserverParameters method that is passed the parameters to the observer as supplied by the statement. It verifies the observer parameters, similar to the code snippet shown next. Our example file-exists observer takes a single string parameter:
public void setObserverParameters(List<ExprNode> observerParameters, MatchedEventConvertorForge convertor, ExprValidationContext validationContext) throws ObserverParameterException {
String message = "File exists observer takes a single string filename parameter";
if (observerParameters.size() != 1) {
throw new ObserverParameterException(message);
}
if (!(observerParameters.get(0).getForge().getEvaluationType() == String.class)) {
throw new ObserverParameterException(message);
}
this.filenameExpression = observerParameters.get(0);
this.convertor = convertor;
}
The compiler calls the makeCodegen method to provide code that initializes the observer factory at time of deployment. It uses the SAIFFInitializeBuilder to build the code.
public CodegenExpression makeCodegen(CodegenMethodScope parent, SAIFFInitializeSymbol symbols, CodegenClassScope classScope) {
SAIFFInitializeBuilder builder = new SAIFFInitializeBuilder(MyFileExistsObserverFactory.class, this.getClass(), "observerFactory", parent, symbols, classScope);
return builder.exprnode("filenameExpression", filenameExpression)
.expression("convertor", convertor.makeAnonymous(builder.getMethod(), classScope))
.build();
}
An observer factory class is responsible for the following functions:
Implement a
makeObservermethod that returns a new observer instance.
Observer factory classes implement the ObserverFactory:
public class MyFileExistsObserverFactory implements ObserverFactory { ...The runtime obtains an instance of the observer factory class at time of deployment.
The runtime calls the makeObserver method to create a new observer instance. The example makeObserver method shown below passes parameters to the observer instance:
public EventObserver makeObserver(PatternAgentInstanceContext context, MatchedEventMap beginState, ObserverEventEvaluator observerEventEvaluator, Object observerState, boolean isFilterChildNonQuitting) {
EventBean[] events = convertor == null ? null : convertor.convert(beginState);
Object filename = PatternExpressionUtil.evaluateChecked("File-exists observer ", filenameExpression, events, context.getAgentInstanceContext());
if (filename == null) {
throw new EPException("Filename evaluated to null");
}
return new MyFileExistsObserver(beginState, observerEventEvaluator, filename.toString());
}
The ObserverEventEvaluator parameter allows an observer to indicate events, and to indicate change of truth value to permanently false. Use this interface to indicate when your observer has received or witnessed an event, or changed it's truth value to true or permanently false.
The MatchedEventMap parameter provides a Map of all matching events for the expression prior to the observer's start. For example, consider a pattern as below:
a=MyEvent -> myplugin:my_observer(...)
The above pattern tagged the MyEvent instance with the tag "a". The runtime starts an instance of my_observer when it receives the first MyEvent. The observer can query the MatchedEventMap using "a" as a key and obtain the tagged event.
An observer class has the following responsibilities:
Provides a
startObservemethod that starts the observer.Provides a
stopObservemethod that stops the observer, called by the runtime when the whole pattern is stopped, or the sub-expression containing the observer is stopped.
Observer classes subclass com.espertech.esper.pattern.observer.ObserverSupport as shown here:
public class MyFileExistsObserver implements EventObserver { ...The runtime invokes the observer factory class to construct an instance of the observer class for each new sub-expression instance within a statement.
An observer class must provide an implementation of the startObserve method that the runtime invokes to start an observer instance. In our example, the observer checks for the presence of a file and indicates the truth value to the remainder of the expression:
public void startObserve() {
File file = new File(filename);
if (file.exists()) {
observerEventEvaluator.observerEvaluateTrue(beginState);
}
else {
observerEventEvaluator.observerEvaluateFalse();
}
}
Note the observer passes the ObserverEventEvaluator an instance of MatchedEventMap. The observer can also create one or more new events and pass these events through the Map to the remaining expressions in the pattern.
The observer factory class name as well as the namespace and name for the new observer must be added to the compiler configuration via the configuration API or using the XML configuration file. The configuration shown below is XML however the same options are available through the configuration API:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<plugin-pattern-observer namespace="myplugin" name="file_exists"
forge-class="com.espertech.esper.regressionlib.support.extend.pattern.MyFileExistsObserverForge" />
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>The new observer is now ready to use in a statement. The next pattern statement checks every 10 seconds if the given file exists, and indicates to the listener when the file is found.
select * from pattern [every timer:interval(10 sec) -> myplugin:file_exists("myfile.txt")]Your application can provide additional date-time methods by implementing the extension API as shown below. The steps are as follows:
Implement the
DateTimeMethodForgeFactoryinterface (packagecom.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.datetimemethod) that the compiler invokes for validation and to receive information on the public static methods that your application exposes that provide the date-time method logic.Implement a static method (or multiple static methods) that receives the respective date-time value and additional parameters, if any, and that may return a new value, following the rules outlined below.
Add the class name of the
DateTimeMethodForgeFactoryimplementation to the compiler configuration.Use the new date-time method(s).
The EPL compiler distinguishes between two types of date-time methods:
A modifying date-time method modifies the date-time value, while the type of the result is the same as the type of the date-time value (i.e. input and result is a
CalendarorLocalDateTimeor other value).A reformatting date-time method transforms the date-time value into a result that has a different return type.
The example herein builds a value-changing date-time method by name roll that rolls a field forward or backward and that receives the name of the field and an up/down flag as parameters.
The second example herein builds a reformatting date-time method by name asArrayOfString that returns an array of strings containing the day, month and year values of the date-time value.
The implementation of the DateTimeMethodForgeFactory interface is responsible for:
The
initializemethod returns the available footprints.The
validatemethod may validate actual provided parameters and always returns either aDateTimeMethodOpsModify(for modify) or aDateTimeMethodOpsReformat(for reformat).
The EPL compiler calls the initialize method to obtain the allowed footprints. It compares the footprints to the number and type of parameters actually provided.
For example, if there is a single footprint with no parameters, use this:
DotMethodFP[] footprints = new DotMethodFP[] {
new DotMethodFP(DotMethodFPInputEnum.SCALAR_ANY)
};
return new DateTimeMethodDescriptor(footprints);For example, if there is a single footprint with a single string-type parameter, use this:
DotMethodFP[] footprints = new DotMethodFP[] {
new DotMethodFP(DotMethodFPInputEnum.SCALAR_ANY,
new DotMethodFPParam("provide a descriptive name of parameter", EPLExpressionParamType.SPECIFIC, String.class)
)
};
In the case that the date-time method modifies the date-time value, make the validate method returns an instance of DateTimeMethodModifyOps.
In the case that the date-time method reformats the date-time value, make the validate method returns an instance of DateTimeMethodReformatOps.
Use the DateTimeMethodModeStaticMethod class to provide the class and the name of the public static method providing the respective operation.
It is not required to provide a static method for each of the different types of date-time values. You may leave an operation at a null-value to indicate it is not provided for that date-time value type.
The following class handles the new roll date-time method, which has single footprint that has a string-type and a boolean-type parameter:
public class MyLocalDTMForgeFactoryRoll implements DateTimeMethodForgeFactory {
private final static DotMethodFP[] FOOTPRINTS = new DotMethodFP[]{
new DotMethodFP(DotMethodFPInputEnum.SCALAR_ANY,
new DotMethodFPParam("an string-type calendar field name", EPLExpressionParamType.SPECIFIC, String.class),
new DotMethodFPParam("a boolean-type up/down indicator", EPLExpressionParamType.SPECIFIC, boolean.class))
};
public DateTimeMethodDescriptor initialize(DateTimeMethodInitializeContext context) {
return new DateTimeMethodDescriptor(FOOTPRINTS);
}
public DateTimeMethodOps validate(DateTimeMethodValidateContext context) {
// this is an opportunity to do additional validation or evaluation when desired
// however the footprint is already validated
DateTimeMethodOpsModify roll = new DateTimeMethodOpsModify();
// see below for MyLocalDTMRollUtility
roll.setCalendarOp(new DateTimeMethodModeStaticMethod(MyLocalDTMRollUtility.class, "roll"));
roll.setLdtOp(new DateTimeMethodModeStaticMethod(MyLocalDTMRollUtility.class, "roll"));
roll.setZdtOp(new DateTimeMethodModeStaticMethod(MyLocalDTMRollUtility.class, "roll"));
return roll;
}
}
The following class handles the new asArrayOfString date-time method, which has single footprint that has a no parameters:
public class MyLocalDTMForgeFactoryArrayOfString implements DateTimeMethodForgeFactory {
private final static DotMethodFP[] FOOTPRINTS = new DotMethodFP[]{
new DotMethodFP(DotMethodFPInputEnum.SCALAR_ANY)
};
public DateTimeMethodDescriptor initialize(DateTimeMethodInitializeContext context) {
return new DateTimeMethodDescriptor(FOOTPRINTS);
}
public DateTimeMethodOps validate(DateTimeMethodValidateContext context) {
DateTimeMethodOpsReformat asArrayOfString = new DateTimeMethodOpsReformat();
asArrayOfString.setReturnType(String[].class);
// see below for MyLocalDTMArrayOfStringUtility
asArrayOfString.setLongOp(new DateTimeMethodModeStaticMethod(MyLocalDTMArrayOfStringUtility.class, "asArrayOfString"));
asArrayOfString.setDateOp(new DateTimeMethodModeStaticMethod(MyLocalDTMArrayOfStringUtility.class, "asArrayOfString"));
asArrayOfString.setCalendarOp(new DateTimeMethodModeStaticMethod(MyLocalDTMArrayOfStringUtility.class, "asArrayOfString"));
asArrayOfString.setLdtOp(new DateTimeMethodModeStaticMethod(MyLocalDTMArrayOfStringUtility.class, "asArrayOfString"));
asArrayOfString.setZdtOp(new DateTimeMethodModeStaticMethod(MyLocalDTMArrayOfStringUtility.class, "asArrayOfString"));
return asArrayOfString;
}
}
For value-changing date-time methods that operate on long, Date and Calendar, the static method must return void, its first parameter must be Calendar and the remaining parameters much match the expression parameters, such as:
public static void roll(Calendar calendar, String fieldName, boolean flagValue) {
For value-changing date-time methods that operate on LocalDateTime, the static method must return LocalDateTime, its first parameter must be LocalDateTime and the remaining parameters much match the expression parameters, such as:
public static LocalDateTime roll(LocalDateTime ldt, String fieldName, boolean flagValue) {
For value-changing date-time methods that operate on ZonedDateTime, the static method must return ZonedDateTime, its first parameter must be ZonedDateTime and the remaining parameters much match the expression parameters, such as:
public static ZonedDateTime roll(ZonedDateTime zdt, String fieldName, boolean flagValue) {
For reformatting date-time methods, the static method must return the same type as provided by the getReturnType method of DateTimeMethodReformatMode, its first parameter must be any of the below and the remaining parameters much match the expression parameters (see example below).
longDate(from java.util)CalendarLocalDateTimeZonedDateTime
The class providing the static methods for the roll date-time method is shown next.
public class MyLocalDTMRollUtility {
public static void roll(Calendar calendar, String fieldName, boolean flagValue) {
switch (fieldName) {
case "date": calendar.roll(Calendar.DATE, flagValue); break;
default: throw new EPException("Invalid field name '" + fieldName + "'");
}
}
public static LocalDateTime roll(LocalDateTime ldt, String fieldName, boolean flagValue) {
switch (fieldName) {
case "date": return ldt.plusDays(1);
default: throw new EPException("Invalid field name '" + fieldName + "'");
}
}
public static ZonedDateTime roll(ZonedDateTime zdt, String fieldName, boolean flagValue) {
switch (fieldName) {
case "date": return zdt.plusDays(1);
default: throw new EPException("Invalid field name '" + fieldName + "'");
}
}
}
The class providing the static methods for the asArrayOfString date-time method is shown next.
public class MyLocalDTMArrayOfStringUtility {
public static String[] asArrayOfString(long date) {
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.setTimeInMillis(date);
return asArrayOfString(calendar);
}
public static String[] asArrayOfString(Date date) {
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.setTime(date);
return asArrayOfString(calendar);
}
public static String[] asArrayOfString(Calendar calendar) {
return new String[] {Integer.toString(calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH)),
Integer.toString(calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1),
Integer.toString(calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR))};
}
public static String[] asArrayOfString(LocalDateTime ldt) {
return new String[] {Integer.toString(ldt.getDayOfMonth()),
Integer.toString(ldt.getMonthValue()),
Integer.toString(ldt.getYear())};
}
public static String[] asArrayOfString(ZonedDateTime zdt) {
return new String[] {Integer.toString(zdt.getDayOfMonth()),
Integer.toString(zdt.getMonthValue()),
Integer.toString(zdt.getYear())};
}
}
}You must provide the date-time method name and the forge factory class name to the compiler configuration.
The sample XML snippet below configures the two example date-time methods:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<plugin-method-datetime method-name="roll" forge-class="packagename.MyLocalDTMForgeFactoryRoll"/>
<plugin-method-datetime method-name="asArrayOfString" forge-class="packagename.MyLocalDTMForgeFactoryArrayOfString"/>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>The next example uses the configuration API to register the same:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCompiler().addPlugInDateTimeMethod("roll", MyLocalDTMForgeFactoryRoll.class.getName());
configuration.getCompiler().addPlugInDateTimeMethod("asArrayOfString", MyLocalDTMForgeFactoryArrayOfString.class.getName());The sample EPL below uses the new methods:
select caldate.roll('date', true) as calroll,
longdate.roll('date', true) as longroll,
utildate.roll('date', true) as utilroll,
localdate.roll('date', true) as localdateroll,
zoneddate.roll('date', true) as zoneddateroll,
caldate.asArrayOfString() as arraystring_from_cal,
longdate.asArrayOfString() as arraystring_from_long,
utildate.asArrayOfString() as arraystring_from_util,
localdate.asArrayOfString() as arraystring_from_local,
zoneddate.asArrayOfString() as arraystring_from_zoned
from MyDateTimeEventYour application can provide additional enumeration methods by implementing the extension API as shown below. The steps are as follows:
Implement the
EnumMethodForgeFactoryinterface (packagecom.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.enummethod) that the compiler invokes for validation and to receive information on the state class and the public static methods that your application exposes that provide the enumeration method logic.Implement the
EnumMethodStatethat holds the state for enumerating over input values.Implement a static method (the processing method) that receives the state and each of the items of the collection of events, scalar values or object values and the result of lambda parameter expression evalutions.
Add the class name of the
EnumMethodForgeFactoryimplementation to the compiler configuration.Use the new enumeration method(s).
The example herein builds a simple enumeration method by name median that computes the median for a set of integer-typed input values and that returns a double-type median.
The implementation of the EnumMethodForgeFactory interface is responsible for:
The
initializemethod returns the available footprints.The
validatemethod may validate actual provided parameters and returns anEnumMethodModeStaticMethoddescriptor.
The EPL compiler calls the initialize method to obtain the allowed footprints. It compares the footprints to the number and type of parameters actually provided.
The example median enumeration method takes a scalar numeric values as input and has no parameters.
DotMethodFP[] footprints = new DotMethodFP[] {
new DotMethodFP(DotMethodFPInputEnum.SCALAR_NUMERIC)
};
return new EnumMethodDescriptor(footprints);Additional examples for footprint are:
Table 22.2. Enumeration Method Footprint Examples
| Sample Footprint and Processing Method | Comment |
|---|---|
new DotMethodFP(DotMethodFPInputEnum.EVENTCOLL, new DotMethodFPParam(1, "predicate", EPLExpressionParamType.BOOLEAN)) process(State_class state, EventBean event, Boolean pass)
| Enumeration method taking events as input and that has a single lambda expression that is a predicate and that returns a boolean value |
new DotMethodFP(DotMethodFPInputEnum.SCALAR_ANY, new DotMethodFPParam(1, "value-selector", EPLExpressionParamType.NUMERIC)) process(State_class state, Object value, Object lambdaResult)
| Enumeration method taking any type of scalar values as input and that has a single lambda expression that is a value-selector and that returns a numeric value |
new DotMethodFP(DotMethodFPInputEnum.SCALAR_NUMERIC,
new DotMethodFPParam("from", EPLExpressionParamType.NUMERIC),
new DotMethodFPParam("to", EPLExpressionParamType.NUMERIC))
process(State_class state, Object value)
| Enumeration method taking any type of numeric scalar values as input and that has no lambda expressions as parameter but two non-lambda expressions as parameter both returning a numeric value |
new DotMethodFP(DotMethodFPInputEnum.EVENTCOLL, new DotMethodFPParam(1, "v1", EPLExpressionParamType.ANY), new DotMethodFPParam(1, "v2", EPLExpressionParamType.ANY)) process(State_class state, EventBean event, Object v1, Object v2)
| Enumeration method taking events as input and that has two lambda expressions as parameter both returning any object value |
new DotMethodFP(DotMethodFPInputEnum.ANY, new DotMethodFPParam(2, "value, index", EPLExpressionParamType.BOOLEAN)) process(State_class state, EventBean event, Boolean pass)
| Enumeration method taking any type of scalar values as input and that a single lambda expression that has 2 parameters (value and index, similar to takeWhile with index) and that returns a boolean value |
Use the EnumMethodModeStaticMethod class to provide the class of the state object and the class and the name of the public static method that is the processing method.
The following class handles the new median enumeration method, which has single footprint that has no parameters:
public static class MyLocalEnumMethodForgeMedian implements EnumMethodForgeFactory {
private static final DotMethodFP[] FOOTPRINTS = new DotMethodFP[]{
new DotMethodFP(DotMethodFPInputEnum.SCALAR_NUMERIC)
};
public EnumMethodDescriptor initialize(EnumMethodInitializeContext context) {
return new EnumMethodDescriptor(FOOTPRINTS);
}
public EnumMethodModeStaticMethod validate(EnumMethodValidateContext context) {
Class stateClass = MyLocalEnumMethodMedianState.class; // the class providing state, must implement EnumMethodState
Class serviceClass = MyLocalEnumMethodMedianService.class; // the class providing the processing method (any class)
String methodName = "next"; // the name of the method for processing an item of input values (any method name)
EPChainableType returnType = EPChainableTypeHelper.singleValue(Double.class); // indicate that we are returning a Double-type value
boolean earlyExit = false;
return new EnumMethodModeStaticMethod(stateClass, serviceClass, methodName, returnType, earlyExit);
}
}
The EnumMethodModeStaticMethod provides multiple settings to the EPL compiler:
The class that implements the
EnumMethodStateinterface which holds enumeration state.The class and method name of the method that processes values and that receives the result of lambda parameter evaluation.
The return type of the enumeration method which is an
EPChainableTypevalue.An indicator whether the state requires early-access checking.
The EPChainableType return type has the following choices:
For a method returning a collection of events, always use
EPChainableTypeHelper.collectionOfEvents(context.getInputEventType()).For a method returning a collection of objects, use
EPChainableTypeHelper.collectionOfSingleValue(class_of_value).For a method returning a single scalar value, use
EPChainableTypeHelper.singleValue(class_of_value).
The implementation of the EnumMethodState interface is responsible for holding the transient state of one pass over input values to the enumeration method.
The runtime allocates a new instance of the provided class for each execution of the enumeration method.
The implementation class must have a default constructor.
The state class does this:
The
statemethod returns the final result.(Optional) Override the
setParametermethod to receive non-lambda expression parameter results.(Optional) Override the
completedmethod to indicate early-exit.
The following class handles the state for the median enumeration method and computes the median:
public class MyLocalEnumMethodMedianState implements EnumMethodState {
private List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public Object state() {
Collections.sort(list);
// get count of scores
int totalElements = list.size();
if (totalElements < 2) {
return null;
}
// check if total number of scores is even
if (totalElements % 2 == 0) {
int sumOfMiddleElements = list.get(totalElements / 2) + list.get(totalElements / 2 - 1);
// calculate average of middle elements
return ((double) sumOfMiddleElements) / 2;
}
return (double) list.get(totalElements / 2);
}
public void add(Integer value) {
list.add(value);
}
}
The example does not have additional non-lambda parameters and therefore does not override setParameter. Your application can receive any non-lambda expression values
by overriding setParameter.
The example does not have early-exit and therefore does not override completed. Your application can override completed to indicate an early exit. Please
make sure EnumMethodModeStaticMethod has the early-exit flag set.
The processing method is the method that the runtime invokes for each input element. There is no interface for the class providing the method and the method must be public and static.
The processing method, that your application specified as part of EnumMethodModeStaticMethod, receives these values:
The first parameter is always the state class as provided in the previous step.
The second parameter is always the item value of type
EventBeanwhen the input is events, or typeObjectwhen the input is not events.The remaining parameters are the result of the runtime evaluating the expression bodies of lambda expression parameters to the enumeration method.
The example median enumeration method takes scalar values as input and has no lambda expression parameters:
public static class MyLocalEnumMethodMedianService {
public static void next(MyLocalEnumMethodMedianState state, Object element) {
state.add((Integer) element);
}
}You must provide the enumeration method name and the forge factory class name to the compiler configuration.
The sample XML snippet below configures the two example date-time methods:
<esper-configuration xmlns="http://www.espertech.com/schema/esper">
<compiler>
<plugin-method-enum method-name="median" forge-class="packagename.MyLocalEnumMethodForgeMedian"/>
</compiler>
</esper-configuration>The next example uses the configuration API to register the same:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCompiler().addPlugInEnumerationMethod("median", MyLocalEnumMethodForgeMedian.class.getName());
The sample EPL below uses the new method, assuming that the MyIntegerValuesEvent has an event property by name intvalues
that returns an array or collection of int-type values:
select intvalues.median() as median from MyIntegerValuesEvent
There are three types of lambda parameters supported.
When a lambda parameter is the value itself it is represented by EnumMethodLambdaParameterTypeValue. For example, in orderItems.where(v => v.price > 0) the v parameter is
the input item value itself, i.e. the event or scalar value depending on input. This is always the default and no additional code is required.
When a lambda parameter is the index of the value it is represented by EnumMethodLambdaParameterTypeIndex. For example, in orderItems.takeWhile( (v, ind) => ind < 10) the ind parameter is
the numeric index of the item starting at zero.
The below code snippet sets the lambda parameter types for value and index:
mode.setLambdaParameters(descriptor -> {
if (descriptor.getLambdaParameterNumber() == 0) {
return EnumMethodLambdaParameterTypeValue.INSTANCE;
}
return EnumMethodLambdaParameterTypeIndex.INSTANCE;
});
When a lambda parameter is provided by the state class itself it is represented by EnumMethodLambdaParameterTypeStateGetter. For example, in orderItems.aggregate(0, (result, v) => result + v.price)) the result parameter is
provided by the state itself.
The below code snippet sets the lambda parameter types for state-provided and index:
mode.setLambdaParameters(descriptor -> {
if (descriptor.getLambdaParameterNumber() == 0) {
// the state class has a getResult method returning string
return new EnumMethodLambdaParameterTypeStateGetter(int.class, "getResult");
}
return EnumMethodLambdaParameterTypeValue.INSTANCE;
});
Note that the example above assumes that the state class has a getResult method returning an int-type value.
For additional information and examples please consult the JavaDoc and regression testing code.
- 23.1. Examples Overview
- 23.2. Running the Examples
- 23.3. AutoID RFID Reader
- 23.4. Runtime Configuration
- 23.5. JMS Server Shell and Client
- 23.6. Market Data Feed Monitor
- 23.7. OHLC Plug-In Data Window
- 23.8. Transaction 3-Event Challenge
- 23.9. Self-Service Terminal
- 23.10. Assets Moving Across Zones - An RFID Example
- 23.11. StockTicker
- 23.12. MatchMaker
- 23.13. Named Window Query
- 23.14. Sample Virtual Data Window
- 23.15. Sample Cycle Detection
- 23.16. Quality of Service
- 23.17. Trivia Geeks Club
This chapter outlines the examples that come with the distribution in the examples folder of the distribution. Each sample is in a separate folder that contains all files needed by the example, excluding jar files.
Here is an overview over the examples in alphabetical order:
Table 23.1. Examples
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Section 23.3, “AutoID RFID Reader” |
An array of RFID readers sense RFID tags as pallets are coming within the range of one of the readers. Shows the use of an XSD schema and XML event representation. A single statement shows a rolling time window, a where-clause filter on a nested property and a group-by. |
| Section 23.6, “Market Data Feed Monitor” |
Processes a raw market data feed and reports throughput statistics and detects when the data rate of a feed falls off unexpectedly. Demonstrates a batch time window and a rolling time window with a having-clause. Multi-threaded example with a configurable number of threads and a simulator for generating feed data. |
| Section 23.12, “MatchMaker” |
In the MatchMaker example every mobile user has an X and Y location and the task of the event patterns created by this example is to detect mobile users that are within proximity given a certain range, and for which certain properties match preferences. Uses an overlapping context to find matching mobile users based on mobile user events. |
| Section 23.13, “Named Window Query” |
A mini-benchmark that handles temperature sensor events. The sample creates a named window and fills it with a large number of events. It then executes a large number of pre-compiled statements as well as fire-and-forget queries and reports times. Study this example if you are interested in named windows, Map event type representation, fire-and-forget queries as well as pre-defined statements via on-select, and the performance aspects. |
| Section 23.14, “Sample Virtual Data Window” |
This example demonstrates the use of virtual data window to expose a (large) external data store, without any need to keep events in memory, and without sacrificing statement performance. |
| Section 23.15, “Sample Cycle Detection” |
This example showcases the aggregation multi-function extension API for use with a cycle-detection problem detecting cycles in transactions between accounts. |
| Section 23.7, “OHLC Plug-In Data Window” |
A plug-in custom data window addressing a problem in the financial space: Computes open-high-low-close bars for minute-intervals of events that may arrive late, based on each event's timestamp. A custom plug-in data window based on the extension API can be a convenient and reusable way to express a domain-specific analysis problem as a unit, and this example includes the code for the OHLC data window factory and window as well as simulator to test the window. |
| Section 24.3, “Using the Performance Kit” |
A benchmark that is further described in the performance section of this document under performance kit. |
| Section 23.16, “Quality of Service” |
This example develops some code for measuring quality-of-service levels such as for a service-level agreement (SLA).
This example combines patterns with select-statements, shows the use of the timer |
| Section 23.10, “Assets Moving Across Zones - An RFID Example” |
An example out of the RFID domain processes location report events. The example includes a simple Swing-based GUI for visualization allows moving tags from zone to zone visually. It also a contains comprehensive simulator to generate data for a large number of asset groups and their tracking. The example uses non-overlapping context to detect patterns in the aggregated data to determine when an asset group constraint is violated. |
| Section 23.4, “Runtime Configuration” |
Example code to demonstrate various key compile-time and runtime actions such as adding event types on-the-fly, adding new variables, adding plug-in single-row and aggregation functions and adding variant streams. |
| Section 23.5, “JMS Server Shell and Client” |
The server shell is a Java Messaging Service (JMS) -based server and client that send and listens to messages on a JMS destination. It also demonstrates a simple Java Management Extension (JMX) MBean for remote statement management. A single statement computes an average duration for each IP address on a rolling time window and outputs a snapshot every 2 seconds. |
| Section 23.11, “StockTicker” |
An example from the financial domain that features event patterns to filter stock tick events based on price and symbol. The example is designed to provide a high volume of events and includes multithreaded unit test code as well as a simulting data generator. The example uses overlapping context to find when price spikes happen based on price limit events received. |
| Section 23.9, “Self-Service Terminal” |
A J2EE-based self-service terminal managing system in an airport that gets a lot of events from connected terminals. Contains a message-driven bean (EJB-MDB) for use in a J2EE container, a client and a simulator, as well as statements for detecting various conditions. A version that runs outside of a J2EE container is also available. |
| Section 23.17, “Trivia Geeks Club” |
Trivia Geeks Club demonstrates EPL for a scoring system computing scores in a trivia game. |
In order to compile and run the samples please follow the below instructions:
Make sure Java 1.6 or greater is installed and the JAVA_HOME environment variable is set.
Open a console window and change directory to examples/example_name/etc.
Run "setenv.bat" (Windows) or "setenv.sh" (Unix) to verify your environment settings.
Run "compile.bat" (Windows) or "compile.sh" (Unix) to compile an example.
Now you are ready to run an example. Some examples require mandatory parameters that are also described in the file "readme.txt" in the "etc" folder.
Modify the logger logging level in the "log4j.xml" configuration file changing DEBUG to INFO on a class or package level to control the volume of text output.
Each example also provides Eclipse project .classpath and .project files. The Eclipse projects expect an esper_runtime user library that includes the runtime dependencies.
JUnit tests exist for the example code. The JUnit test source code for the examples can be found in each example's src/test folder. To build and run the example JUnit tests, use the Maven 2 goal test.
In this example an array of RFID readers sense RFID tags as pallets are coming within the range of one of the readers. A reader generates XML documents with observation information such as reader sensor ID, observation time and tags observed. A statement computes the total number of tags per reader sensor ID within the last 60 seconds.
This example demonstrates how XML documents unmarshalled to org.w3c.dom.Node DOM document nodes
can natively be processed by the runtime without requiring Java object event representations. The example uses an XPath
expression for an event property counting the number of tags observed by a sensor. The XML documents follow the AutoID (http://www.autoid.org/) organization
standard.
The classes for this example can be found in package com.espertech.esper.example.autoid.
As events are XML documents with no Java object representation, the example does not have event classes.
A simulator that can be run from the command line is also available for this example. The simulator generates a number of XML documents as specified by a command line argument and prints out the totals per sensor. Run "run_autoid.bat" (Windows) or "run_autoid.sh" (Unix) to start the AutoID simulator. Please see the readme file in the same folder for build instructions and command line parameters.
The code snippet below shows the simple statement to compute the total number of tags per sensor. The statement is created by class
com.espertech.esper.example.autoid.RFIDTagsPerSensorStmt.
select ID as sensorId, sum(countTags) as numTagsPerSensor from AutoIdRFIDExample#time(60 seconds) where Observation[0].Command = 'READ_PALLET_TAGS_ONLY' group by ID
This example demonstrates various key runtime configuration options such as adding event types on-the-fly, adding new variables, adding plug-in single-row and aggregation functions and adding variant streams.
The classes for this example live in package com.espertech.esper.example.runtimeconfig.
The server shell is a Java Messaging Service (JMS) -based server that listens to messages on a JMS destination, and sends the received events into the runtime. The example also demonstrates a Java Management Extension (JMX) MBean that allows remote dynamic statement management. This server has been designed to run with either Tibco (TM) Enterprise Messaging System (Tibco EMS), or with Apache ActiveMQ, controlled by a properties file.
The server shell has been created as an alternative to the EsperIO Spring JMSTemplate adapter. The server shell is a low-latency processor for byte messages. It employs JMS listeners to process message in multiple threads, this model reduces thread context switching for many JMS providers. The server is configurable and has been tested with two JMS providers. It consists of only 10 classes and is thus easy to understand.
The server shell sample comes with a client (server shell client) that sends events into the JMS-based server, and that also creates a statement on the server remotely through a JMX MBean proxy class.
The server shell classes for this example live in package com.espertech.esper.example.servershell.
Configure the server to point to your JMS provider by changing the properties in the file servershell_config.properties in the etc folder.
Make sure your JMS provider (ActiveMQ or Tibco EMS) is running, then run "run_servershell.bat" (Windows) or "run_servershell.sh" (Unix) to start the JMS server.
Start the server shell process first before starting the client, since the client also demonstrates remote statement management through JMX by attaching to the server process.
The client classes to the server shell can be found in package com.espertech.esper.example.servershellclient.
The client shares the same configuration file as the server shell.
Run "run_servershellclient.bat" (Windows) or "run_servershellclient.sh" (Unix) to start the JMS producer client that includes a JMX client as well.
The server shell starts a configurable number of JMS MessageListener instances that listen to a given JMS destination. The listeners expect a BytesMessage that contain a String payload. The payload consists of an IP address and a double-typed duration value separated by a comma.
Each listener extracts the payload of a message, constructs an event object and sends the event into the shared runtime instance.
At startup time, the server creates a single statement with the runtime that prints out the average duration per IP address for the last 10 seconds of events, and that specifies an output rate of 2 seconds. By running the server and then the client, you can see the output of the averages every 2 seconds.
The server shell client acts as a JMS producer that sends 1000 events with random IP addresses and durations.
The server shell is also a JMX server providing an RMI-based connector. The server shell exposes a JMX MBean that allows remote statement management. The JMX MBean allows to create a statement remotely, attach a listener to the statement and undeploy a statement remotely.
The server shell client, upon startup, obtains a remote instance of the management MBean exposed by the server shell. It creates a statement through the MBean that filters out all durations greater then the value 9.9. After sending 1000 events, the client then undeploys the statement remotely on the server.
This example processes a raw market data feed. It reports throughput statistics and detects when the data rate of a feed falls off unexpectedly. A rate fall-off may mean that the data is stale and you want to alert when there is a possible problem with the feed.
The classes for this example live in package com.espertech.esper.example.marketdatafeed.
Run "run_mktdatafeed.bat" (Windows) or "run_mktdatafeed.sh" (Unix) in the examples/etc folder
to start the market data feed simulator.
The input stream consists of 1 event stream that contains 2 simulated market data feeds. Each individual event in the stream indicates the feed that supplies the market data, the security symbol and some pricing information:
String symbol; FeedEnum feed; double bidPrice; double askPrice;
For throughput statistics and to detect rapid fall-off, the example calculates a ticks per second rate for each market data feed.
You can use a statement that specifies a data window onto the market data event stream that batches together 1 second of events. You specify the feed and a count of events per feed as output values. To make this data available for further processing, you insert output events into the TicksPerSecond event stream:
insert into TicksPerSecond select feed, count(*) as cnt from MarketDataEvent#time_batch(1 second) group by feed
We define a rapid fall-off by alerting when the number of ticks per second for any second falls below 75% of the average number of ticks per second over the last 10 seconds.
We can compute the average number of ticks per second over the last 10 seconds simply by using the TicksPerSecond events computed by the prior statement and averaging the last 10 seconds. Next, the example compares the current rate with the moving average and filter out any rates that fall below 75% of the average:
select feed, avg(cnt) as avgCnt, cnt as feedCnt from TicksPerSecond#time(10 seconds) group by feed having cnt < avg(cnt) * 0.75
The simulator generates market data events for 2 feeds, feed A and feed B. The first parameter to the simulator is a number of threads. Each thread sends events for each feed in an endless loop. Note that as the Java VM garbage collection kicks in, the example generates rate drop-offs during such pauses.
The second parameter is a rate drop probability parameter specifies the probability in percent that the simulator drops the rate for a randomly chosen feed to 60% of the target rate for that second. Thus rate fall-off alerts can be generated.
The third parameter defines the number of seconds to run the example.
This example contains a fully-functional custom data window based on the extension API that computes OHLC open-high-low-close bars for events that provide a long-typed timestamp and a double-typed value.
OHLC bar is a problem out of the financial domain. The "Open" refers to the first datapoint and the "Close" to the last datapoint in an interval. The "High" refers to the maximum and the "Low" to the minimum value during each interval. The term "bar" is used to describe each interval results of these 4 values.
The example provides an OHLC data window that is hardcoded to 1-minute bars. It considers the timestamp value carried by each event, and not the system time. The cutoff time after which an event is no longer considered for a bar is hardcoded to 5 seconds.
The window assumes that events arrive in timestamp order: Each event's timestamp value is equal to or higher then the timestamp value provided by the prior event.
The window may also be used together with #groupwin to group per criteria, such as symbol. In this case the assumption of timestamp order applies per symbol.
The window gracefully handles no-event and late-event scenarios. Interval boundaries are defined by system time, thus event timestamp and system time must roughly be in-sync, unless using external timer events.
The classes for this example live in package com.espertech.esper.example.transaction.
Run "run_txnsim.bat" (Windows) or "run_txnsim.sh" (Unix) to start the transaction simulator.
Please see the readme file in the same folder for build instructions and command line parameters.
The use case involves tracking three components of a transaction. It's important that the example uses at least three components, since some runtimes have different performance or coding for only two events per transaction. Each component comes to the runtime as an event with the following fields:
Transaction ID
Time stamp
In addition, the example has the following extra fields:
In event A:
Customer ID
In event C:
Supplier ID (the ID of the supplier that the order was filled through)
We need to take in events A, B and C and produce a single, combined event with the following fields:
Transaction ID
Customer ID
Time stamp from event A
Time stamp from event B
Time stamp from event C
What we‘re doing here is matching the transaction IDs on each event, to form an aggregate event. If all these events were in a relational database, this could be done as a simple SQL join… except that with 10,000 events per second, you will need some serious database hardware to do it.
Further, the example produces the following:
Min,Max,Average total latency from the events (difference in time between A and C) over the past 30 minutes.
Min,Max,Average latency grouped by (a) customer ID and (b) supplier ID. In other words, metrics on the the latency of the orders coming from each customer and going to each supplier.
Min,Max,Average latency between events A/B (time stamp of B minus A) and B/C (time stamp of C minus B).
The example detects a transaction that did not make it through all three events. In other words, a transaction with events A or B, but not C. Note that, in this case, what you care about is event C. The lack of events A or B could indicate a failure in the event transport and should be ignored. Although the lack of an event C could also be a transport failure, it merits looking into.
To make testing easier, standard and to demonstrate how the example works, the example is including an event generator. The generator generates events for a given number of transactions, using the following rules:
One in 5,000 transactions will skip event A
One in 1,000 transactions will skip event B
One in 10,000 transactions will skip event C.
Transaction identifiers are randomly generated
Customer and supplier identifiers are randomly chosen from two lists
The time stamp on each event is based on the system time. Between events A and B as well as B and C, between 0 and 999 is added to the time. So, you have an expected time difference of around 500 milliseconds between each event
Events are randomly shuffled as described below
To make things harder, the example doesn't have transaction events coming in order. This code ensures that they come completely out of order. To do this, the example fills in a bucket with events and, when the bucket is full, it shuffles it. The buckets are sized so that some transactions‘ events will be split between buckets. So, you have a fairly randomized flow of events, representing the worst case from a big, distributed infrastructure.
The generator lets you change the size of the bucket (small, medium, large, larger, largerer). The larger the bucket size, the more events potentially come in between two events in a given transaction and so, the more the performance characteristics like buffers, hashes/indexes and other structures are put to the test as the bucket size increases.
The example is about a J2EE-based self-service terminal managing system in an airport that gets a lot of events from connected terminals. The event rate is around 500 events per second. Some events indicate abnormal situations such as 'paper low' or 'terminal out of order'. Other events observe activity as customers use a terminal to check in and print boarding tickets.
Each self-service terminal can publish any of the 6 events below.
Checkin - Indicates a customer started a check-in dialog
Cancelled - Indicates a customer cancelled a check-in dialog
Completed - Indicates a customer completed a check-in dialog
OutOfOrder - Indicates the terminal detected a hardware problem
LowPaper - Indicates the terminal is low on paper
Status - Indicates terminal status, published every 1 minute regardless of activity as a terminal heartbeat
All events provide information about the terminal that published the event, and a timestamp. The terminal information is held in a property named "term" and provides a terminal id. Since all events carry similar information, it models each event as a subtype to a base class BaseTerminalEvent, which will provide the terminal information that all events share. This enables us to treat all terminal events polymorphically, that is you can treat derived event types just like their parent event types. This helps simplify our statements.
All terminals publish Status events every 1 minute. In normal cases, the Status events indicate that a terminal is alive and online. The absence of status events may indicate that a terminal went offline for some reason and that may need to be investigated.
A customer may be in the middle of a check-in when the terminal detects a hardware problem or when the network goes down. In that situation the example alerts a team member to help the customer. When the terminal detects a problem, it issues an OutOfOrder event. A pattern can find situations where the terminal indicates out-of-order and the customer is in the middle of the check-in process:
select * from pattern [ every a=Checkin ->
( OutOfOrder(term.id=a.term.id) and not
(Cancelled(term.id=a.term.id) or Completed(term.id=a.term.id)) )]Since Status events arrive in regular intervals of 60 seconds, you can make use of temporal pattern matching using timer to find events that didn't arrive. You can use the every operator and timer:interval() to repeat an action every 60 seconds. Then you combine this with a not operator to check for absence of Status events. A 65 second interval during which you look for Status events allows 5 seconds to account for a possible delay in transmission or processing:
select 'terminal 1 is offline' from pattern [every timer:interval(60 sec) -> (timer:interval(65 sec) and not Status(term.id = 'T1'))] output first every 5 minutes
By presenting statistical information about terminal activity to our staff in real-time you enable them to monitor the system and spot problems. The next example statement simply gives us a count per event type every 1 minute. You could further use this data, available through the CountPerType event stream, to join and compare against a recorded usage pattern, or to just summarize activity in real-time.
insert into CountPerType select type, count(*) as countPerType from BaseTerminalEvent#time(10 minutes) group by type output all every 1 minutes
The example code in the distribution package implements a message-driven enterprise java bean (MDB EJB). The example uses an MDB as a convenient place for processing incoming events via a JMS message queue or topic. The example uses 2 JMS queues: One queue to receive events published by terminals, and a second queue to indicate situations detected via statement and listener back to a receiving process.
This example has been packaged for deployment into a JBoss Java application server (see http://www.jboss.org) with default deployment configuration. JBoss is an open-source application server available under LGPL license. Of course the choice of application server does not indicate a requirement or preference for the use of the compiler and/or runtime in a J2EE container. Other quality J2EE application servers are available and perhaps more suitable to run this example or a similar application.
The complete example code can be found in the "examples/terminalsvc" folder of the distribution. The standalone version that does not require a J2EE container is in "examples/terminalsvc-jse".
The pre-build EAR file contains the MDB for deployment to a JBoss application server with default deployment options. The JBoss default configuration provides 2 queues that this example utilizes: queue/A and queue/B. The queue/B is used to send events into the MDB, while queue/A is used to indicate back the any data received by listeners to statements.
The application can be deployed by copying the ear file in the "examples/terminalsvc/terminalsvc-ear" folder to your JBoss deployment directory located under the JBoss home directory under "standalone/deployments".
The example contains an event simulator and an event receiver that can be invoked from the command line. See the folder "examples/terminalsvc/etc" folder readme file and start scripts for Windows and Unix, and the documentation set for further information on the simulator.
This example requires Maven 2 to build. To build the example, change directory to the folder "examples/terminalsvc" and type "mvn package". The instructions have been tested with JBoss AS 7.1.1 and Maven 3.0.4.
The Maven build packages the EAR file for deployment to a JBoss application server with default deployment options.
The example also contains an event simulator that generates meaningful events. The simulator can be run from the directory "examples/terminalsvc/etc" via the command "run_terminalsvc_sender.bat" (Windows) and "run_terminalsvc_sender.sh" (Linux). The event simulator generates a batch of at least 200 events every 1 second. Randomly, with a chance of 1 in 10 for each batch of events, the simulator generates either an OutOfOrder or a LowPaper event for a random terminal. Each batch the simulator generates 100 random terminal ids and generates a Checkin event for each. It then generates either a Cancelled or a Completed event for each. With a chance of 1 in 1000, it generates an OutOfOrder event instead of the Cancelled or Completed event for a terminal.
The event receiver listens to the MDB-outcoming queue for alerts and prints these out to console. The receiver can be run from the directory "examples/terminalsvc/etc" via the command "run_terminalsvc_receiver.bat" (Windows) and "run_terminalsvc_receiver.sh" (Linux). Before running please copy the jboss-client.jar file from your JBoss AS installation bin directory to the "terminalsvc/lib" folder.
The receiver and sender code use "guest" as user and "pass" as password. Add the "guest" user using the Jboss "add-user" script and assign the role "guest". Your JBoss server may need to start with "-c standalone-full.xml" to have the messaging subsystem available.
Add queue configurations to the messaging subsystem configuration as follows:
<jms-queue name="queue_a"> <entry name="queue_a"/> <entry name="java:jboss/exported/jms/queue/queue_a"/> </jms-queue> <jms-queue name="queue_b"> <entry name="queue_b"/> <entry name="java:jboss/exported/jms/queue/queue_b"/> </jms-queue>
Disable persistence in the messaging subsystem for this example so it is not running out of disk space:
<persistence-enabled>false</persistence-enabled>
This example out of the RFID domain processes location report events. Each location report event indicates an asset id and the current zone of the asset. The example solves the problem that when a given set of assets is not moving together from zone to zone, then an alert must be fired.
Each asset group is tracked by 2 statements. The two statements to track a single asset group consisting of assets identified by asset ids {1, 2, 3} are as follows:
insert into CountZone_G1
select 1 as groupId, zone, count(*) as cnt
from LocationReport(assetId in 1, 2, 3)#unique(assetId)
group by zone
select Part.zone from pattern [
every Part=CountZone_G1(cnt in (1,2)) ->
(timer:interval(10 sec) and not CountZone_G1(zone=Part.zone, cnt in (0,3)))]
The classes for this example can be found in package com.espertech.esper.example.rfid.
This example provides a Swing-based GUI that can be run from the command line. The GUI allows drag-and-drop of three RFID tags that form one asset group from zone to zone. Each time you move an asset across the screen the example sends an event into the runtime indicating the asset id and current zone. The example detects if within 10 seconds the three assets do not join each other within the same zone, but stay split across zones. Run "run_rfid_swing.bat" (Windows) or "run_rfid_swing.sh" (Unix) to start the example's Swing GUI.
The example also provides a simulator that can be run from the command line. The simulator generates a number of asset groups as specified by a command line argument and starts a number of threads as specified by a command line argument to send location report events into the runtime. Run "run_rfid_sim.bat" (Windows) or "run_rfid_sim.sh" (Unix) to start the RFID location report event simulator. Please see the readme file in the same folder for build instructions and command line parameters.
The StockTicker example comes from the stock trading domain. The example creates event patterns to filter stock tick events based on price and symbol. When a stock tick event is encountered that falls outside the lower or upper price limit, the example simply displays that stock tick event. The price range itself is dynamically created and changed. This is accomplished by an overlapping context that uses price limit event to determine how to look for price spikes.
The classes StockTick and PriceLimit represent our events. The event patterns are created by the class StockTickerEPLUtil.
Summary:
Good example to learn the API and get started with contexts and patterns.
When price limit events arrive allocates patterns that find the price spike.
Simple, highly-performant filter expressions for event properties in the stock tick event such as symbol and price.
In the MatchMaker example every mobile user has an X and Y location, a set of properties (gender, hair color, age range) and a set of preferences (one for each property) to match. The task of the event patterns created by this example is to detect mobile users that are within proximity given a certain range, and for which the properties match preferences.
The event class representing mobile users is MobileUserBean. The MatchMakerEPL class contains the patterns for detecing matches.
Summary:
Uses overlapping context to find matching mobile user events
Uses range matching for X and Y properties of mobile user events
This example handles very minimal temperature sensor events which are represented by java.util.Map. It creates a named window and fills it with a large number of events. It then executes a large number of pre-defined statements via on-select as well as performs a large number of fire-and-forget queries against the named window, and reports execution times.
Virtual data windows are an extension API used to integrate external stores and expose the data therein as a named window.
See the virtualdw folder for example code, compile and run scripts.
The example is also discussed in the section on extension APIs specifically the aggregation multi-function development.
The example uses the jgrapht library for a cycle-detection problem detecting cycles in transactions between accounts.
See the examples/cycledetect folder for example code, compile and run scripts.
This example develops some code for measuring quality-of-service levels such as for a service-level agreement (SLA). A SLA is a contract between 2 parties that defines service constraints such as maximum latency for service operations or error rates.
The example measures and monitors operation latency and error counts per customer and operation. When one of our operations oversteps these constraints, you want to be alerted right away. Additionally, you would like to have some monitoring in place that checks the health of our service and provides some information on how the operations are used.
Some of the constraints you need to check are:
That the latency (time to finish) of some of the operations is always less then X seconds.
That the latency average is always less then Y seconds over Z operation invocations.
The com.espertech.esper.example.qos_sla.events.OperationMeasurement event class with its latency and status properties is the main event used for the SLA analysis. The other event LatencyLimit serves to set latency limits on the fly.
The com.espertech.esper.example.qos_sla.monitor.AverageLatencyMonitor creates a statement that computes latency statistics per customer and operation for the
last 100 events. The DynaLatencySpikeMonitor uses an event pattern to listen to spikes in latency with dynamically set limits. The ErrorRateMonitor uses the timer 'at' operator in an event pattern that wakes up periodically and polls the error rate within the last 10 minutes. The ServiceHealthMonitor simply alerts when 3 errors occur, and the SpikeAndErrorMonitor alerts when a fixed latency is overstepped or an error status is reported.
Summary:
This example combines event patterns with statements for event stream analysis.
Shows the use of the timer
'at'operator and followed-by operator->in event patterns.Outlines basic statements.
Shows how to pull data out of statements rather then subscribing to events a statement publishes.
This example was developed for the DEBS 2011 conference and demonstrates how scoring rules for a trivia game can be implemented in EPL.
The module that implements all scoring rules is located in the etc folder in file trivia.epl. The EPL is all required to run the solution without any custom functions required.
The trivia geeks club rules (the requirements) are provided in the etc folder in file trivia_scoring_requirements.htm.
The implementation provided tests the questions, answers and scoring according to the data provided in trivia_test_questions_small.htm and trivia_test_questions_large.htm.
- 24.1. Big O Notation
- 24.1.1. Big-O Complexity of Matching Events to Statements and Context Partitions
- 24.1.2. Big-O Complexity of Matching Time to Statements and Context Partitions
- 24.1.3. Big-O Complexity of Joins, Subqueries, On-Select, On-Merge, On-Update, On-Delete
- 24.1.4. Big-O Complexity of Enumeration Methods
- 24.1.5. Big-O Complexity of Aggregation Methods
- 24.2. Performance Tips
- 24.2.1. Understand How to Tune Your Java Virtual Machine
- 24.2.2. Input and Output Bottlenecks
- 24.2.3. Threading
- 24.2.4. Select the Underlying Event Rather Than Individual Fields
- 24.2.5. Prefer Stream-Level Filtering Over Where-Clause Filtering
- 24.2.6. Reduce the Use of Arithmetic in Expressions
- 24.2.7. Remove Unneccessary Constructs
- 24.2.8. End Pattern Sub-Expressions
- 24.2.9. Consider Using EventPropertyGetter for Fast Access to Event Properties
- 24.2.10. Consider Casting the Underlying Event
- 24.2.11. Turn Off Logging and Audit
- 24.2.12. Tune or Disable Delivery Order Guarantees
- 24.2.13. Use a Subscriber Object to Receive Events
- 24.2.14. Consider Data Flows
- 24.2.15. High-Arrival-Rate Streams and Single Statements
- 24.2.16. Subqueries Versus Joins and Where-Clause and Data Windows
- 24.2.17. Patterns and Pattern Sub-Expression Instances
- 24.2.18. Pattern Sub-Expression Instance Versus Data Window Use
- 24.2.19. The Keep-All Data Window
- 24.2.20. Statement Design for Reduced Memory Consumption - Diagnosing OutOfMemoryError
- 24.2.21. Performance, JVM, OS and Hardware
- 24.2.22. Consider Using Hints
- 24.2.23. Optimizing Stream Filter Expressions
- 24.2.24. Statement and Runtime Metric Reporting
- 24.2.25. Expression Evaluation Order and Early Exit
- 24.2.26. Large Number of Threads
- 24.2.27. Filter Evaluation Tuning
- 24.2.28. Context Partition Related Information
- 24.2.29. Prefer Constant Variables Over Non-Constant Variables
- 24.2.30. Prefer POJO Events or alternatively Object-Array Events
- 24.2.31. Notes on Query Planning
- 24.2.32. Query Planning Expression Analysis Hints
- 24.2.33. Query Planning Index Hints
- 24.2.34. Measuring Throughput
- 24.2.35. Do Not Create the Same or Similar Statement X Times
- 24.2.36. Comparing Single-Threaded and Multi-Threaded Performance
- 24.2.37. Incremental Versus Recomputed Aggregation for Named Window Events
- 24.2.38. When Does Memory Get Released
- 24.2.39. Measure Throughput of Non-Matches as Well as Watches
- 24.2.40. Options for When an Event Type has a Large Number of Event Properties i.e. Large Events
- 24.3. Using the Performance Kit
The big O notation is used to classify algorithms according to how their running time grow as the input size grows. This chapter discusses big O complexity of algorithms implemented by the EPL runtime.
For hash lookups the O-notation value is approximate. For logarithmic running-time function we use O(log N) but mean O(logt N) with an unspecified value for t.
Note
Big-O provided here is general guidance. This section may not be entirely complete and may not list all exceptions.
The runtime determines, for each event, which EPL statements must process the event. For EPL statements that are context partitioned with multiple partitions, such as for overlapping, keyed, hash or category contexts (see Chapter 4, Context and Context Partitions), the runtime determines, for each event, which partitions of each statement must process the event.
This operation takes place when:
When an application calls the
sendEventmethod ofEPEventService.For example, the application invokes
eventService.sendEventBean(new StockTickEvent(...), "StockTick")and the runtime determines which EPL statement and partition must process theStockTickevent.When the runtime evaluates a statement that uses
insert into.For example, the application creates a statement
insert into StockTickOverPrice100 select * as price from StockTick(price>100). After processing aStockTickevent with a price greater 100, the runtime allocates a newStockTickOverPrice100event and determines which EPL statement and partition must process the newStockTickOverPrice100event.
The parameter to the operation is the individual event e.g. the StockTick or the StockTickOverPrice100 event.
The data structure is the filter indexes, a nestable tree of indexes organized by event type, see Section 2.18.2, “Filter Indexes”.
The algorithm takes the individual event and walks the filter indexes to determine which statements and context partitions must process the event.
The input is the presence and nature of filter expressions of EPL statements and the number of partitions, including where-clauses (see Section 5.5, “Specifying Search Conditions: The Where Clause” for where-clause rewrites).
The big-o complexity depends on the input. It always includes a hash lookup by event type that is constant time O(1).
Assume the input is N statements as follows.
select * from Event(property=value)
The complexity is constant time O(1) as the same property appears in all filter expressions and with the equals-operator (=) and therefore hash lookup.
As for example in this EPL:
select * from StockTick(symbol='A'); select * from StockTick(symbol='B');
The runtime obtains the symbol value of the stock tick event once and performs a single hash lookup.
Assume the input is N statements as follows wherein each property name is a different event property name:
select * from Event(property_n=value)
The complexity is linear time O(N) as a different property appears in all filter expressions.
As for example in this EPL:
select * from StockTick(symbol='A'); select * from StockTick(feed='001');
Assume the input is N statements as follows.
select * from Event(property_1=constant and property_2>value)
The complexity is O(log N). The same property names appears in all filter expressions. The relational greater-than operator (>) is a btree lookup.
As for example in this EPL:
select * from StockTick(symbol='A', price>100); select * from StockTick(symbol='A', price>200);
The runtime obtains the symbol value of the stock tick event once and performs a single hash lookup. It obtains the price value of the stock tick event once and performs a single btree lookup.
The runtime determines, when time advances, which EPL statements must process the new runtime time. For EPL statements that are context partitioned with multiple partitions, such as for overlapping, keyed, hash or category contexts (see Chapter 4, Context and Context Partitions), the runtime determines which partitions of each statement must process the new runtime time.
This operation takes place when:
When an application calls the
advanceTimeoradvanceTimeSpanmethod ofEPEventService(when using external timer).For example, the application invokes
eventService.advanceTime(DateTime.parse("2002-05-30T09:01:02.003"))and the runtime determines which EPL statement and partition must process the new runtime time.When the runtime uses the internal timer (aka. system time) and the current system time becomes current runtime time.
The parameter to the operation is the new runtime time.
The data structure is the schedule maintained internally by the runtime which is a data structure sorted by time.
The algorithm takes the new runtime time and performs a lookup.
The input is the presence and nature of time-related expressions of EPL statements and the number of partitions.
The big-o complexity is O(log N).
The runtime performs a join, a subquery, an on-select, an on-merge, an on-update, an on-delete or a fire-and-forget query. The runtime determines the subset of events (or rows of a table) by performing an index lookup. It performs additional actions on the subset.
The query planner is responsible for determining the indexes to use. The query planner uses the where-clause (if any) and the on-clause (if any) to plan index use.
Use query plan logging to obtain information about the query plans.
This operation takes place when:
It is a join and the runtime performs a lookup into a stream's events (or named window or table) to resolve the subset of events for that stream (or named window or table) to determine final join results.
It is a subquery and the runtime performs a lookup into subqueries's events (or aggregation rows) to resolve the subset of subquery result events and to process these.
It is an on-action statement such as on-select, on-merge, on-update and on-delete and the runtime performs a lookup into a named window events or table rows to resolve the subset and process these.
It is a fire-and-forget select, update or delete query.
The parameters to the operation are the events of the from-clause and on-trigger. For fire-and-forget queries the parameters originate from the filter expressions and where-clause.
The data structure is the event index, see Section 2.18.3, “Event Indexes”.
The algorithm takes event data and performs an index lookup according to the chosen index organization, to determine and process the subset of events.
The input is the indexed events (or table rows).
The big-o complexity depends on the type of lookup operation.
For lookups that are hash only the complexity is constant time O(1).
For lookups that are btree or that combine hash and btree the complexity is O(log N).
Otherwise the complexity is O(N). Without indexes a scan has to inspect every event which means it will scale with the number of events.
This example is a subquery. When an RFIDEvent arrives the runtime finds Zone events for the same zone id:
select * from RFIDEvent as rfid where exists (select * from Zone#unique(zoneId) as zone where rfid.zoneId = zone.zoneId)
The where-clause uses equals ('=') and the query planner plans a hash index lookup. The operation is constant time O(1).
This example declares a TickWindow named window holding StockTick events. It uses on-select to select all stock ticks with a price greater the price provided by PriceQuery:
create window TickWindow#time(10) from StockTick; on PriceQuery as priceQuery select * from TickWindow as ticks where ticks.price > priceQuery.price;
The where-clause uses the relational greater operator ('>') and the query planner plans a btree index lookup. The operation is O(log N) with N related to the number of TickWindow events.
This example is an unidirectional join. When an RFIDEvent arrives it outputs a row for each Zone event unique by zone id:
select * from RFIDEvent unidirectional, Zone#unique(zoneId)
There is no where-clause and the query planner cannot use an index. The operation is linear time O(N) with N related to the number of Zone events.
The runtime evaluates enumeration methods by applying an operation to each element in a collection.
This operation takes place for each enumeration method.
The parameters to the operation are the parameters passed to the enumeration method.
The algorithm iterates the collection and performs the operation.
The input are the collection of events or scalar values.
The big-o complexity depends on the enumeration method.
For
takeandtakeLastthe complexity is constant time O(1) for a small number of elements, when the size parameter is small, and linear time O(N) in the worst case, when the size parameter is large.For
countOfthe complexity is constant time O(1) and can be linear time O(N) for data structures that don't provide a size.For all other enumeration methods the complexity is linear time O(N).
The runtime evaluates aggregation methods by applying an operation to aggregation state.
This operation takes place for each aggregation method.
The parameters to the operation are the parameters passed to the aggregation method.
The algorithm evaluates parameters and queries aggregation state.
The input is the number of aggregated events held by the aggregation state.
The big-o complexity for sorted aggregations is:
For
eventsBetweenthe complexity is O(log N) (for small ranges) and can be linear time O(N) in the worst case (for large ranges) .For all other aggregation methods on sorted aggregations the complexity is O(log N).
The big-o complexity for aggregation methods on window aggregations is constant O(1).
The compiler and runtime run on a JVM and you need to be familiar with JVM tuning. Key parameters to consider include minimum and maximum heap memory and nursery heap sizes. Statements with time-based or length-based data windows can consume large amounts of memory as their size or length can be large.
For time-based data windows, one needs to be aware that the memory consumed depends on the actual event stream input throughput. Event pattern instances also consume memory, especially when using the "every" keyword in patterns to repeat pattern sub-expressions - which again will depend on the actual event stream input throughput.
Your application receives output events from statements through the UpdateListener interface or via the strongly-typed subscriber POJO object. Such output events are delivered by the application or timer thread(s) that sends an input event into the runtime instance.
The processing of output events that your listener or subscriber performs temporarily blocks the thread until the processing completes, and may thus reduce throughput. It can therefore be beneficial for your application to process output events asynchronously and not block the runtime while an output event is being processed by your listener, especially if your listener code performs blocking IO operations.
For example, your application may want to send output events to a JMS destination or write output event data to a relational database. For optimal throughput, consider performing such blocking operations in a separate thread.
Additionally, when reading input events from a store or network in a performance test, you may find that the runtime processes events faster then you are able to feed events into the runtime. In such case you may want to consider an in-memory driver for use in performance testing. Also consider decoupling your read operation from the event processing operation (sendEvent method) by having multiple readers or by pre-fetching your data from the store.
We recommend using multiple threads to send events into the runtime. There is a test class below. Our test class does not use a blocking queue and thread pool so as to avoid a point of contention.
A sample code for testing performance with multiple threads is provided:
public class SampleClassThreading {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int numEvents = 1000000;
int numThreads = 3;
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.getRuntime().getThreading().setListenerDispatchPreserveOrder(false);
config.getRuntime().getThreading().setInternalTimerEnabled(false); // remove thread that handles time advancing
config.getCommon().addEventType(MyEvent.class);
String epl = "create context MyContext coalesce by consistent_hash_crc32(id) " +
"from MyEvent granularity 64 preallocate;\n" +
"@name('result') context MyContext select count(*) from MyEvent group by id;\n";
EPCompiled compiled;
try {
compiled = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler().compile(epl, new CompilerArguments(config);
}
catch (EPCompileException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
EPRuntime runtime = EPRuntimeProvider.getDefaultRuntime(config);
EPDeployment deployment;
try {
deployment = runtime.getDeploymentService().deploy(compiled);
}
catch (EPDeployException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
EPStatement stmt = runtime.getDeploymentService().getStatement(deployment.getDeploymentId(), "result");
stmt.setSubscriber(new MySubscriber());
Thread[] threads = new Thread[numThreads];
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(numThreads);
int eventsPerThreads = numEvents / numThreads;
for (int i = 0; i < numThreads; i++) {
threads[i] = new Thread(
new MyRunnable(latch, eventsPerThreads, runtime.getEventService()));
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < numThreads; i++) {
threads[i].start();
}
latch.await(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
if (latch.getCount() > 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to complete in 10 minute");
}
long delta = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
System.out.println("Took " + delta + " millis");
}
public static class MySubscriber {
public void update(Object[] args) {
}
}
public static class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
private final CountDownLatch latch;
private final int numEvents;
private final EPEventService eventService;
public MyRunnable(CountDownLatch latch, int numEvents, EPEventService eventService) {
this.latch = latch;
this.numEvents = numEvents;
this.eventService = eventService;
}
public void run() {
Random r = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < numEvents; i++) {
eventService.sendEventBean(new MyEvent(r.nextInt(512)), "MyEvent");
}
latch.countDown();
}
}
public static class MyEvent {
private final int id;
public MyEvent(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
}
}
We recommend using Java threads as above, or a blocking queue and thread pool with sendEventType or alternatively we recommend configuring inbound threading if your application does not already employ threading.
The runtime provides the configuration option to use runtime-level queues and threadpools for inbound, outbound and internal executions. See Section 16.8.1, “Advanced Threading” for more information.
We recommend the outbound threading if your listeners are blocking. For outbound threading also see the section below on tuning and disabling listener delivery guarantees.
If enabling advanced threading options keep in mind that the runtime will maintain a queue and thread pool. There is additional overhead associated with entering work units into the queue, maintaining the queue and the hand-off between threads. The Java blocking queues are not necessarily fast on all JVM. It is not necessarily true that your application will perform better with any of the advanced threading options.
We found scalability better on Linux systems and running Java with -server and pinning threads to exclusive CPUs and after making sure CPUs are available on your system.
We recommend looking at LMAX Disruptor, an inter-thread messaging library, for setting up processing stages. Disruptor, however, is reportedly less suitable for setting up a worker pool.
The sample code below may help you get started setting up a thread pool of workers with back pressure and consideration for IO threads and clean shutdown.
The sample code starts by setting up a thread factory:
private static class RuntimeThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private AtomicInteger id = new AtomicInteger(0);
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(r, "Event Runtime Thread #" + id.incrementAndGet());
t.setDaemon(true);
t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
return t;
}
}The sample uses a fixed-size array blocking queue. To handle the situation where the queue is full and accepts no more messages, it uses a rejection handler that counts the number of rejections and retries:
private class RuntimeRejectionHandler implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
private volatile long spinCount = 0;
public long getSpinCount() {
return spinCount;
}
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
++spinCount;
try {
boolean isAccepted = false;
while (!isAccepted) {
isAccepted = executorQueue.offer(r, 120, TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS);
}
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.warn("could not queue work entry");
}
}
}The Runnable that submits an event for processing could look like this:
class Holder implements Runnable {
public void run() {
// do any stuff needed to "prepare" event which doesn't involve IO
runtime.getEventService().sendEventBean(lm, "LMEventType");
}
}Initialize the queue and worker pool as follows:
private final static int CAPACITY = 10000;
private final static int THREAD_COUNT = 4;
private static EPRuntime runtime;
private ThreadFactory threadFactory = new RuntimeThreadFactory();
private RuntimeRejectionHandler rejectionHandler = new RuntimeRejectionHandler();
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> executorQueue;
private ThreadPoolExecutor executor;
public void start() {
executorQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(CAPACITY);
executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(THREAD_COUNT, THREAD_COUNT, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
executorQueue, threadFactory, rejectionHandler);
executor.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(false);
while (executor.getPoolSize() < executor.getCorePoolSize()) {
executor.prestartCoreThread();
}
}To shut down cleanly, and before destroying the runtime, the sample code is:
executor.shutdown();
while (!executor.isTerminated()) {
Thread.sleep(100);
}The next sample code goes into the IO or input thread(s) such as NIO mapped file, file channel, socket channel, or zmq / nanomsg etc., and submits a work unit to the queue:
while (programAlive) {
// deserialize event to POJO, Map, Array, etc.,
// pass along an event type name when needed
executor.execute(new Holder(myeventobject));
}
You could periodically dump the spinCount variable to get an idea of queue depth.
You can tune the size of the Executor's pool, and the size of the TimeUnit's of sleep used inside the rejectedExecution method, until you get 1) stable performance at highest level (determined by optimal number of threads in pool, 2) avoid wasting CPU in IO thread(s) (determined by optimal sleeping time between each attempt to re-queue rejected events to the thread pool).
By selecting the underlying event in the select-clause you can reduce load on the runtime, since the runtime does not need to generate a new output event for each input event.
For example, the following statement returns the underlying event to update listeners:
// Better performance select * from RFIDEvent
In comparison, the next statement selects individual properties. This statement requires the runtime to generate an output event that contains exactly the required properties:
// Less good performance select assetId, zone, xlocation, ylocation from RFIDEvent
The runtime stream-level filtering is very well optimized, while filtering via the where-clause post any data windows is not optimized.
The same is true for named windows. If your application is only interested in a subset of named window data and such filters are not correlated to arriving events, place the filters into parenthesis after the named window name.
Consider the example below, which performs stream-level filtering:
// Better performance : stream-level filtering select * from MarketData(ticker = 'GOOG')
The example below is the equivalent (same semantics) statement and performs post-data-window filtering without a data window. The compiler does not optimize statements that filter in the where-clause for the reason that data windows are generally present.
// Less good performance : post-data-window filtering select * from Market where ticker = 'GOOG'
Thus this optimization technique applies to statements without any data window.
When a data window is used, the semantics change. Let's look at an example to better understand the difference: In the next statement only GOOG market events enter the length window:
select avg(price) from MarketData(ticker = 'GOOG')#length(100)
The above statement computes the average price of GOOG market data events for the last 100 GOOG market data events.
Compare the filter position to a filter in the where clause. The following statement is NOT equivalent as all events enter the data window (not just GOOG events):
select avg(price) from Market#length(100) where ticker = 'GOOG'
The statement above computes the average price of all market data events for the last 100 market data events, and outputs results only for GOOG.
The next two example statements put the account number filter criteria directly into parenthesis following the named window name:
// Better performance : stream-level filtering select * from WithdrawalNamedWindow(accountNumber = '123')
// Better performance : example with subquery select *, (select * from LoginSucceededWindow(accountNumber = '123')) from WithdrawalNamedWindow(accountNumber = '123')
If you have a number of statements performing a given computation on incoming events, consider moving the computation from the where-clause to a plug-in user-defined function that is listed as part of stream-level filter criteria. The compiler optimizes evaluation of user-defined functions in filters such that an incoming event can undergo the computation just once even in the presence of N statements.
// Prefer stream-level filtering with a user-defined function select * from MarketData(vstCompare(*))
// Less preferable when there are N similar statements: // Move the computation in the where-clause to the "vstCompare" function. select * from MarketData where (VST * RT) – (VST / RT) > 1
The compiler and runtime do not yet pre-evaluate arithmetic expressions that produce constant results, however since the compiler generates byte code the JVM byte code optimization takes place and may pre-evaluate certain expressions.
Therefore, a filter expression as below is optimized:
// Better performance : no arithmetic select * from MarketData(price>40)
While the compiler cannot currently optimize this expression:
// Less good performance : with arithmetic select * from MarketData(price+10>50)
If your statement uses order by to order output events, consider removing order by unless your application does indeed require the events it receives to be ordered.
If your statement specifies group by but does not use aggregation functions, consider removing group by.
If your statement specifies group by but the filter criteria only allows one group, consider removing group by:
// Prefer: select * from MarketData(symbol = 'GE') having sum(price) > 1000 // Don't use this since the filter specifies a single symbol: select * from MarketData(symbol = 'GE') group by symbol having sum(price) > 1000
If your statement specifies the grouped data window #groupwin but the window being grouped retains the same set of events regardless of grouping,
remove #groupwin, for example:
// Prefer: create window MarketDataWindow#keepall as MarketDataEventType // Don't use this, since keeping all events // or keeping all events per symbol is the same thing: create window MarketDataWindow#groupwin(symbol)#keepall as MarketDataEventType // Don't use this, since keeping the last 1-minute of events // or keeping 1-minute of events per symbol is the same thing: create window MarketDataWindow#groupwin(symbol)#time(1 min) as MarketDataEventType
It is not necessary to specify a data window for each stream.
// Prefer: select * from MarketDataWindow // Don't have a data window if just listening to events, prefer the above select * from MarketDataWindow#lastevent
If your statement specifies unique data window but the filter criteria only allows one unique criteria, consider removing the unique data window:
// Prefer: select * from MarketDataWindow(symbol = 'GE')#lastevent // Don't have a unique-key data window if your filter specifies a single value select * from MarketDataWindow(symbol = 'GE')#unique(symbol)
In patterns, the every keyword in conjunction with followed by (->) starts a new sub-expression per match.
For example, the following pattern starts a sub-expression looking for a B event for every A event that arrives.
every A -> B
Determine under what conditions a subexpression should end so the runtime can stop looking for a B event. Here are a few generic examples:
every A -> (B and not C) every A -> B where timer:within(1 sec)
The EventPropertyGetter interface is useful for obtaining an event property value without property name table lookup given an EventBean instance that is of the same event type that the property getter was obtained from.
When compiling a statement, the EPStatement instance lets us know the EventType via the getEventType() method. From the EventType you can obtain EventPropertyGetter instances for named event properties.
To demonstrate, consider the following simple statement:
select symbol, avg(price) from Market group by symbol
After compiling and deploying the module, obtain the EventType and pass the type to the listener:
EPStatement stmt = runtime.getDeploymentService().getStatement(deploymentId, statementName); MyGetterUpdateListener listener = new MyGetterUpdateListener(stmt.getEventType());
The listener can use the type to obtain fast getters for property values of events for the same type:
public class MyGetterUpdateListener implements StatementAwareUpdateListener {
private final EventPropertyGetter symbolGetter;
private final EventPropertyGetter avgPriceGetter;
public MyGetterUpdateListener(EventType eventType) {
symbolGetter = eventType.getGetter("symbol");
avgPriceGetter = eventType.getGetter("avg(price)");
}Last, the update method can invoke the getters to obtain event property values:
public void update(EventBean[] eventBeans, EventBean[] oldBeans, EPStatement epStatement, EPRuntime runtime) {
String symbol = (String) symbolGetter.get(eventBeans[0]);
long volume = (Long) volumeGetter.get(eventBeans[0]);
// some more logic here
}When an application requires the value of most or all event properties, it can often be best to simply select the underlying event via wildcard and cast the received events.
Let's look at the sample statement:
select * from MarketData(symbol regexp 'E[a-z]')
An update listener to the statement may want to cast the received events to the expected underlying event class:
public void update(EventBean[] eventBeans, EventBean[] eventBeans) {
MarketData md = (MarketData) eventBeans[0].getUnderlying();
// some more logic here
}Even if you don't have a log4j configuration file in place, the runtime will make sure to minimize execution path logging overhead. For prior versions, and to reduce logging overhead overall, we recommend the "WARN" log level or the "INFO" log level.
Please see the log4j configuration file in "etc/infoonly_log4j.xml" for example log4j settings.
EPL provides the @Audit annotation for statements. For performance testing and production deployment, we recommend removing @Audit.
If your application is not a multithreaded application, or your application is not sensitive to the order of delivery of result events to your application listeners, then consider disabling the delivery order guarantees the runtime makes towards ordered delivery of results to listeners:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getRuntime().getThreading().setListenerDispatchPreserveOrder(false);
If your application is not a multithreaded application, or your application uses the insert into clause to make results of one statement available for further consuming statements but does not require ordered delivery of results from producing statements to consuming statements, you may disable delivery order guarantees between statements:
Configuration config = new Configuration(); config.getRuntime().getThreading().setInsertIntoDispatchPreserveOrder(false);
If your application declares only stateless statements then the settings described herein are not relevant.
Additional configuration options are available and described in the configuration section that specify timeout values and spin or thread context switching.
the runtime logging will log the following informational message when guaranteed delivery order to listeners is enabled and spin lock times exceed the default or configured timeout : Spin wait timeout exceeded in listener dispatch.
The respective message for delivery from insert into statements to consuming statements is Spin wait timeout exceeded in insert-into dispatch.
If your application sees messages that spin lock times are exceeded, your application has several options: First, disabling preserve order is an option. Second, ensure your listener does not perform (long-running) blocking operations before returning, for example by performing output event processing in a separate thread. Third, change the timeout value to a larger number to block longer without logging the message.
The subscriber object is a technique to receive result data that has performance advantages over the UpdateListener interface. Please refer to Section 16.5.2, “Setting a Subscriber Object”.
Data flows offer a high-performance means to execute EPL select statements and use other built-in data flow operators. The data flow Emitter operator allows sending underlying event objects directly into a data flow. Thereby the runtime does not need to wrap each underlying event into a EventBean instance and the runtime does not need to match events to statements. Instead, the underling event directly applies to only that data flow instance that your application submits the event to, and no other statements or data flows see the same event.
Data flows are described in Chapter 21, EPL Reference: Data Flow.
A context partition is associated with certain context partition state that consists of current aggregation values, partial pattern matches, data windows depending on whether your statement uses such constructs. When an runtime receives events it updates context partition state under locking such that context partition state remains consistent under concurrent multi-threaded access.
For high-volume streams, the locking required to protected context partition state may slow down or introduce blocking for very high arrival rates of events that apply to the very same context partition and its state.
Your first choice should be to utilize a context that allows for multiple context partitions, such as the hash segmented context. The hash segmented context usually performs better compared to the keyed segmented context since in the keyed segmented context the runtime must check whether a partition exists or must be created for a given key.
Your second choice is to split the statement into multiple statements that each perform part of the intended function or that each look for a certain subset of the high-arrival-rate stream. There is very little cost in terms of memory or CPU resources per statement, the runtime can handle larger number of statements usually as efficiently as single statements.
For example, consider the following statement:
// less effective in a highly threaded environment select venue, ccyPair, side, sum(qty) from CumulativePrice where side='O' group by venue, ccyPair, side
The runtime protects state of each context partition by a separate lock for each context partition, as discussed in the API section. In highly threaded applications threads may block on a specific context partition. You would therefore want to use multiple context partitions.
Consider creating either a hash segmented context or a keyed segmented context. In the hash segmented context incoming data is simply assigned to one of the buckets using a small computation. In the keyed segmented context the runtime must check keys to see if a partition already exists or whether a new partition must be allocated. We'll discuss both below. For both types of context, since locking is on the level of context partition, the locks taken by the runtime are very fine grained allowing for highly concurrent processing.
This sample EPL declares a hash segmented context. In a hash segmented context the runtime can pre-allocate context partitions and therefore does not need to check whether a partition exists already. In a hash segmented context the runtime simply assigns events to context partitions based on result of a hash function and modulo operation.
create context MyContext coalesce by consistent_hash_crc32(venue) from CumulativePrice(side='O') granularity 16 preallocate
This sample EPL declares a keyed segmented context. The keyed segmented context instructs the runtime to employ a context partition per venue, ccyPair, side key combination. The runtime must check for each event whether a partition exists for that combination of venue, ccyPair and side:
create context MyContext partition by venue, ccyPair, side from CumulativePrice(side='O')
After declaring the context using create context, make sure all your statements, including those statements that create named windows and tables, specify that context. This is done by prefixing each statement with context context_name .....
The new statement that refers to the context as created above is below. Note the context MyContext which tells the runtime that this statement executes context partitioned. This must be provided otherwise the statement does not execute context partitioned.
context MyContext select venue, ccyPair, side, sum(qty) from CumulativePrice
For testing purposes or if your application controls concurrency, you may disable context partition locking, see Section 17.6.10.4, “Disable Locking”.
When joining streams the runtime builds a product of the joined data windows based on the where clause. It analyzes the where clause at time of statement compilation and
builds the appropriate indexes and query strategy. Avoid using expressions in the join where clause that require evaluation, such as user-defined functions or arithmatic expressions.
When joining streams and not providing a where clause, consider using the #unique data window or #lastevent data window to join only the last event or the last event per unique key(s) of each stream.
The sample statement below can produce up to 5,000 rows when both data windows are filled and an event arrives for either stream:
// Avoid joins between streams with data windows without where-clause select * from StreamA#length(100), StreamB#length(50)
Consider using a subquery, consider using separate statements with insert-into and consider providing a where clause to limit the product of rows.
Below examples show different approaches, that are not semantically equivalent, assuming that an MyEvent is defined with the properties symbol and value:
// Replace the following statement as it may not perform well select a.symbol, avg(a.value), avg(b.value) from MyEvent#length(100) a, MyEvent#length(50) b // Join with where-clause select a.symbol, avg(a.value), avg(b.value) from MyEvent#length(100) a, MyEvent#length(50) b where a.symbol = b.symbol // Unidirectional join with where-clause select a.symbol, avg(b.value) from MyEvent unidirectional, MyEvent#length(50) b where a.symbol = b.symbol // Subquery select (select avg(value) from MyEvent#length(100)) as avgA, (select avg(value) from MyEvent#length(50)) as avgB, a.symbol from MyEvent // Since streams cost almost nothing, use insert-into to populate and a unidirectional join insert into StreamAvgA select symbol, avg(value) as avgA from MyEvent#length(100) insert into StreamAvgB select symbol, avg(value) as avgB from MyEvent#length(50) select a.symbol, avgA, avgB from StreamAvgA unidirectional, StreamAvgB#unique(symbol) b where a.symbol = b.symbol
A join is multidirectionally evaluated: When an event of any of the streams participating in the join arrive, the join gets evaluated, unless using the unidirectional keyword. Consider using a subquery instead when evaluation only needs to take place when a certain event arrives:
// Rewrite this join since you don't need to join when a LoginSucceededWindow arrives // Also rewrite because the account number always is the value 123. select * from LoginSucceededWindow as l, WithdrawalWindow as w where w.accountNumber = '123' and w.accountNumber = l.accountNumber // Rewritten as a subquery, select *, (select * from LoginSucceededWindow where accountNumber=’123’) from WithdrawalWindow(accountNumber=’123’) as w
The every and repeat operators in patterns control the number of sub-expressions that are active. Each sub-expression can consume memory as it may retain, depending on the use of tags in the pattern,
the matching events. A large number of active sub-expressions can reduce performance or lead to out-of-memory errors.
During the design of the pattern statement consider the use of timer:within to reduce the amount of time a sub-expression lives, or consider the not operator to end a sub-expression.
The examples herein assume an AEvent and a BEvent event type that have an id property that may correlate between arriving events of the two event types.
In the following sample pattern the runtime starts, for each arriving AEvent, a new pattern sub-expression looking for a matching BEvent. Since the AEvent is tagged with a the runtime retains
each AEvent until a match is found for delivery to listeners or subscribers:
every a=AEvent -> b=BEvent(b.id = a.id)
One way to end a sub-expression is to attach a time how long it may be active.
The next statement ends sub-expressions looking for a matching BEvent 10 seconds after arrival of the AEvent event that started the sub-expression:
every a=AEvent -> (b=BEvent(b.id = a.id) where timer:within(10 sec))
A second way to end a sub-expression is to use the not operator. You can use the not operator together with the and operator to end a sub-expression when a certain event arrives.
The next statement ends sub-expressions looking for a matching BEvent when, in the order of arrival, the next BEvent that arrives after the AEvent event that started the sub-expression does not match the id of the AEvent:
every a=AEvent -> (b=BEvent(b.id = a.id) and not BEvent(b.id != a.id))
The every-distinct operator can be used to keep one sub-expression alive per one or more keys. The next pattern demonstrates an alternative to every-distinct. It ends sub-expressions looking for a matching BEvent when an AEvent arrives that matches the id of the AEvent that started the sub-expression:
every a=AEvent -> (b=BEvent(b.id = a.id) and not AEvent(b.id = a.id))
For some use cases you can either specify one or more data windows as the solution, or you can specify a pattern that also solves your use case.
For patterns, you should understand that the runtime employs a dynamic state machine. For data windows, the runtime employs a delta network and collections. Generally you may find patterns that require a large number of sub-expression instances to consume more memory and more CPU then data windows.
For example, consider the following statement that filters out duplicate transaction ids that occur within 20 seconds of each other:
select * from TxnEvent#firstunique(transactionId)#time(20 sec)
You could also address this solution using a pattern:
select * from pattern [every-distinct(a.transactionId) a=TxnEvent where timer:within(20 sec)]
If you have a fairly large number of different transaction ids to track, you may find the pattern to perform less well then the data window solution as the pattern asks the runtime to manage a pattern sub-expression per transaction id. The data window solution asks the runtime to manage expiry, which can give better performance in many cases.
Similar to this, it is generally preferable to use EPL join syntax over a pattern that cardinally detects relationships i.e. pattern [every-distinct(...) ... -> every-distinct(...) ...]. Join query planning is a powerful compiler and runtime feature that implements fast relational joins.
The #keepall data window is a data window that retains all arriving events. The data window can be useful during the development phase and to implement a custom expiry policy using on-delete and named windows. Care should be taken to timely remove from the keep-all data window however. Use on-select or fire-and-forget queries to count the number of rows currently held by a named window with keep-all expiry policy.
This section describes common sources of out-of-memory problems.
If using the keep-all data window please consider the information above. If using pattern statements please consider pattern sub-expression instantiation and lifetime as discussed prior to this section.
When using the group-by clause or #groupwin grouped data windows please consider the hints as described below. Make sure your grouping criteria are fields that don't have an unlimited number of possible values or specify hints otherwise.
The #unique unique data window can also be a source for error. If your uniqueness criteria include a field which is never unique the memory use of the data window can grow, unless your application deletes events.
When using the every-distinct pattern construct parameterized by distinct value expressions that generate an unlimited number of distinct values, consider specifying a time period as part of the parameters to indicate to the runtime how long a distinct value should be considered.
In a match-recognize pattern consider limiting the number of optional events if optional events are part of the data reported in the measures clause. Also when using the partition clause, if your partitioning criteria include a field which is never unique the memory use of the match-recognize runtime can grow.
A further source of memory use is when your application deploys modules but fails to undeploy modules when they are no longer needed.
In your application design you may also want to be conscious when the application listener or subscriber objects retain output data.
A runtime, uniquely identified by a runtime URI is a relatively heavyweight object. Optimally your application allocates less than one-thousand (1000) runtime instances per JVM.
A statement instance is associated to one runtime instance, is uniquely identified by a statement name and is a medium weight object. We have seen applications allocate 100,000 statements easily.
A statement's context partition instance is associated to one statement, is uniquely identified by a context partition id and is a light weight object. We have seen applications allocate 5000 context partitions for 100 statements easily, i.e. 5,000,000 context partitions.
An aggregation row, data window row, pattern etc. is associated to a statement context partition and is a very lightweight object itself.
The prev, prevwindow and prevtail functions access a data window directly. The runtime does not need to maintain a separate data structure and grouping is based on the use of the #groupwin grouped data window.
Compare this to the use of event aggregation functions such as first, window and last which group according to the group by clause. If your statement utilizes both together consider reformulating to use prev instead.
Performance will also depend on your JVM (Sun HotSpot, BEA JRockit, IBM J9), your operating system and your hardware. A JVM performance index such as specJBB at spec.org can be used. For memory intensive statement, you may want to consider 64bit architecture that can address more than 2GB or 3GB of memory, although a 64bit JVM usually comes with a slow performance penalty due to more complex pointer address management.
The choice of JVM, OS and hardware depends on a number of factors and therefore a definite suggestion is hard to make. The choice depends on the number of statements, and number of threads. A larger number of threads would benefit of more CPU and cores. If you have very low latency requirements, you should consider getting more GHz per core, and possibly soft real-time JVM to enforce GC determinism at the JVM level, or even consider dedicated hardware such as Azul. If your statements utilize large data windows, more RAM and heap space will be utilized hence you should clearly plan and account for that and possibly consider 64bit architectures or consider EsperHA.
The number and type of statements is a factor that cannot be generically accounted for. The benchmark kit can help test out some requirements and establish baselines, and for more complex use cases a simulation or proof of concept would certainly works best. EsperTech' experts can be available to help write interfaces in a consulting relationship.
The @Hint annotation provides a single keyword or a comma-separated list of keywords that provide instructions to the compiler and runtime towards statement execution that affect runtime performance and memory-use of statements. Also see Section 5.2.7.9, “@Hint”.
The query planning in general is described in Section 24.2.31, “Notes on Query Planning”.
The hint for influencing query planning expression analysis is described at Section 24.2.32, “Query Planning Expression Analysis Hints”.
The hint for influencing query planning index choice is described at Section 24.2.33, “Query Planning Index Hints”.
Further hints, also related to query planning, for use with joins, outer joins, unidirectional joins, relational and non-relational joins are described in Section 5.12.6, “Hints Related to Joins”.
The hint for use with group by to specify how state for groups is reclaimed is described in Section 5.6.2.1, “Hints Pertaining to Group-By” and Section 14.3.15, “Grouped Data Window (groupwin or std:groupwin)”.
The hint for use with group by to specify aggregation state reclaim for unbound streams and timestamp groups is described in Section 5.6.2.1, “Hints Pertaining to Group-By”.
The hint for use with match_recognize to specify iterate-only is described in Section 8.4.7, “Eliminating Duplicate Matches”.
To tune subquery performance when your subquery selects from a named window, consider the hints discussed in Section 5.11.8, “Hints Related to Subqueries”.
The @NoLock hint to remove context partition locking (also read caution note) is described at Section 16.8, “Runtime Threading and Concurrency”.
The hint to control expansion of filter expressions, further described at Section 17.5.8.1, “Filter Service Max Filter Width”.
Assume your statement invokes a static method in the stream filter as the below statement shows as an example:
select * from MyEvent(MyHelperLibrary.filter(field1, field2, field3, field4*field5))
As a result of starting above statement, the runtime must evaluate each MyEvent event invoking the MyHelperLibrary.filter method and passing certain event properties. The same applies to pattern filters that
specify functions to evaluate.
If possible, consider moving some of the checking performed by the function back into the filter or consider splitting the function into a two parts separated by and conjunction. In general for all expressions, the runtime evaluates expressions left of the and first and can skip evaluation of the
further expressions in the conjunction in the case when the first expression returns false. In addition the compiler can determine filter index fields and the runtime can build a filter index for fields provided in stream or pattern filters.
For example, the below statement could be faster to evaluate:
select * from MyEvent(field1="value" and MyHelperLibrary.filter(field1, field2, field3, field4*field5))
You can use statement and runtime metric reporting as described in Section 16.12, “Runtime and Statement Metrics Reporting” to monitor performance or identify slow statements.
The term "early exit" or "short-circuit evaluation" refers to when the runtime can evaluate an expression without a complete evaluation of all sub-expressions.
Consider an expression such as follows:
where expr1 and expr2 and expr3
If expr1 is false the runtime does not need to evaluate expr2 and expr3. Therefore when using the AND logical operator consider reordering expressions placing the most-selective expression first and less selective expressions thereafter.
The same is true for the OR logical operator: If expr1 is true the runtime does not need to evaluate expr2 and expr3. Therefore when using the OR logical operator consider reordering expressions placing the least-selective expression first and more selective expressions thereafter.
The order of expressions (here: expr1, expr2 and expr3) does not make a difference for the join and subquery query planner.
Note that the runtime does not guarantee short-circuit evaluation in all cases. The runtime may rewrite the where-clause or filter conditions into another order of evaluation so that it can perform index lookups.
When using a large number of threads with the runtime, such as more then 100 threads, you can provide a setting in the configuration that instructs the runtime to reduce the use of thread-local variables. Please see Section 17.6.10, “Runtime Settings Related to Execution of Statements” for more information.
We offer a switch for tuning evaluation of incoming events against filters. Please see Section 17.6.10, “Runtime Settings Related to Execution of Statements” for more information.
As the runtime locks on the level of context partition, high concurrency under threading can be achieved by using context partitions.
Generally context partitions require more memory then the more fine-grained grouping that can be achieved by group by or #groupwin.
The create-variable syntax as well as the APIs can identify a variable as a constant value. When a variable's value is not intended to change it is best to declare the variable as constant.
For example, consider the following two statements that each declares a variable. The first statement declares a constant variable and the second statement declares a non-constant variable:
// declare a constant variable create constant variable string CONST_DEPARTMENT = 'PURCHASING'
// declare a non-constant variable create variable string VAR_DEPARTMENT = 'SALES'
When your application compiles a statement that has filters for events according to variable values, the compiler internally inspects such expressions and performs filter optimizations for constant variables that are more effective in evaluation.
For example, consider the following two statements that each look for events related to persons that belong to a given department:
// perfer the constant select * from PersonEvent(department=CONST_DEPARTMENT)
// less efficient select * from PersonEvent(department=VAR_DEPARTMENT)
The runtime can more efficiently evaluate the expression using a variable declared as constant. The same observation can be made for subquery and join query planning.
POJO (plain-old java objects, JavaBean convention) events generally offer the best performance and also the most flexibility.
However, object-array events also offer excellent read access performance for access to event property values as compared to Map-type events. In addition, object-array events use much less memory then Map-type events. They also offer the excellent write access performance.
A comparison of different event representations is in Section 3.5, “Comparing Event Representations”.
We recommend that your application sends POJO or object-array events into the runtime, instead of Map-type events. See Appendix F, Event Representation: Object-Array (Object[]) Events for more information.
Also, we advise considering that your application sets the compiler configuration of the default event representation to object array, as described in Section 17.4.9.1, “Default Event Representation”. Alternatively you can use the @EventRepresentation(objectarray) annotation with individual statements.
Query planning takes place for subqueries, joins (any type), named window and table on-actions (on-select, on-merge, on-insert, on-update, on-select) and fire-and-forget queries. Query planning affects query execution speed. Enable query plan logging to output query plan information.
For query planning, the compiler draws information from:
The
where-clauses, if any are specified.Where-clauses correlate streams, patterns, named windows, tables etc. with more streams, patterns, tables and named windows and are thus the main source of information for query planning.The data window(s) declared on streams and named windows. The
#uniqueand the#firstuniquedata window instruct the compiler to retain the last event per unique criteria.For named windows and tables, the explicit indexes created via
create unique indexorcreate index.For named windows (and not tables), the previously created implicit indexes. The compiler can plan to create implicit indexes automatically if explicit indexes do not match correlation requirements.
Any hints specified for the statement in question and including hints specified during the creation of named windows with
create window.
The compiler prefers unique indexes over non-unique indexes.
The compiler prefers hash-based lookups (equals) and combination hash-btree lookups (equals and relational-operator or range) over btree lookups (relational-operator or range) over in-keyword (single and multi-index) lookup plans. This behavior can be controlled by hints that are discussed next.
The expression analysis hints impact query planning for any statement and fire-and-forget query that performs a join or subquery. They also impact named window and table on-action statements.
This hint instructs the compiler which expressions, operators or streams should be excluded and therefore not considered for query planning.
The hint applies to the where-clause and, for outer joins, to the on-clause when present.
The hint takes a single expression as its sole parameter, which is placed in parenthesis. The expression must return a boolean value.
When the provided expression returns true for a given combination, that combination will not be considered for the query plan. A combination consists of a from-stream (name or number), a to-stream (name or number), an operator (i.e. equals, relational, in-keyword) and a set of expressions.
Table 24.1. Built-In Properties of the Expression Analysis Hint
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| exprs | string-array (String[]) | Expression texts with minified whitespace. |
| from_streamname | string | The stream name of the stream providing lookup values as provided by the as keyword. |
| from_streamnum | int | The integer ordinal number of the stream providing lookup values as listed in the from-clause. |
| opname | string | The operator name. Valid values are equals, relop (relational operators and ranges) and inkw (in-keyword). |
| to_streamname | string | The stream name of the stream providing indexable values as provided by the as keyword. |
| to_streamnum | int | The integer ordinal number of the stream providing indexable values as listed in the from-clause. |
Consider two event types A and B. Event type A has a property aprop and
event type B has a property bprop. Let's assume A and B are related by aprop and bprop.
An inner join of all A and B events might look like this:
select * from A#keepall as a, B#keepall as b where aprop = bprop
In the default query plan, when an A event comes in, the runtime obtains the value of aprop and performs an index lookup against bprop
values to obtain matching B events. Vice versa, when a B event comes in, the runtime obtains the value of bprop and performs an index lookup against aprop values to obtain matching A events.
The compiler evaluates the hint expression for each combination. The table below outlines the two rows provided to the hint expression:
Table 24.2. Built-In Properties of the Expression Analysis Hint
| exprs | from_streamname | from_streamnum | opname | to_streamname | to_streamnum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
["aprop", "bprop"] | a | 0 | equals | b | 1 |
["bprop", "aprop"] | b | 1 | equals | a | 0 |
The following statement with hint causes the analyzer to exclude all combinations since the expression passed in always returns true, in effect causing the query planner to always execute the statement as a full table scan.
@hint('exclude_plan(true)')
select * from A#keepall as a, B#keepall as b where aprop = bpropThis hint instructs the compiler to ignore all equals-operators for query planning:
@hint('exclude_plan(opname="equals")') select ....The next hint instructs the compiler to ignore the equals-operator for the direction of lookup from A to B:
@hint('exclude_plan(opname="equals" and from_streamname="a")') select ....Conversely, this hint instructs the compiler to ignore the equals-operator for the direction of lookup from B to A:
@hint('exclude_plan(opname="equals" and from_streamname="b")') select ....
Use the exprs array of expression texts to exclude specific expressions:
@hint('exclude_plan(exprs[0]="aprop")') select ....For subqueries the stream number zero is the subquery from-clause itself and 1 to N are the enclosing statement's from-clause streams. For named window and table on-action statements the stream number zero is the named window or table and stream number 1 refers to the triggering pattern or event.
To specify multiple expressions, please specify multiple hints. The compiler excludes a specific combination when any of the hint expressions returns true.
To inspect values passed to the hint expression, please enable query plan logging. To inspect expression evaluation, please use @Audit.
Currently index hints are only supported for the following types of statements:
Named window and table on-action statements (on-select, on-merge, on-insert, on-update, on-select).
Statements that have subselects against named windows that have index sharing enabled (the default is disabled).
Statements that have subselects against tables.
Fire-and-forget queries.
For the above statements, you may dictate to the compiler which explicit index (created via create index syntax) to use.
Specify the name of the explicit index in parentheses following @Hint and the index literal.
The following example instructs the compiler to use the UserProfileIndex if possible:
@Hint('index(UserProfileIndex)')
Add the literal bust to instruct the compiler to use the index, or if the compiler cannot use the index fail query planning with an exception and therefore fail statement compilation.
The following example instructs the compiler to use the UserProfileIndex if possible or fail with an exception if the index cannot be used:
@Hint('index(UserProfileIndex, bust)')
Multiple indexes can be listed separated by comma (,).
The next example instructs the compiler to consider the UserProfileIndex and the SessionIndex or fail with an exception if either index cannot be used:
@Hint('index(UserProfileIndex, SessionIndex, bust)')
The literal explicit can be added to instruct the compiler to use only explicitly created indexes.
The final example instructs the compiler to consider any explicitly create index or fail with an exception if any of the explicitly created indexes cannot be used:
@Hint('index(explicit, bust)')
We recommend using System.nanoTime() to measure elapsed time when processing a batch of, for example, 1000 events.
Note that System.nanoTime() provides nanosecond precision, but not necessarily nanosecond resolution.
Therefore don't try to measure the time spent by the runtime processing a single event: The resolution of System.nanoTime() is not sufficient.
Also, there are reports that System.nanoTime() can be actually go "backwards" and may not always behave as expected under threading.
Please check your JVM platform documentation.
In the default configuration, the best way to measure performance is to take nano time, send a large number of events, for example 10.000 events, and take nano time again reporting on the difference between the two numbers.
If your configuration has inbound threading or other threading options set, you should either monitor the queue depth to determine performance, or disable threading options when measuring performance, or have your application use multiple threads to send events instead.
It is vastly more efficient to create a statement once and attach multiple listeners, then to create the same statement X times.
It is vastly more efficient to use context declarations to factor out commonalities between statements then creating X similar statements.
EPL, the compiler and runtime are optimized for low-latency and high-throughput execution. In order to accomplish that the compiler analyzes and query-plans. Certain information within each statement can effectively shared in the runtime (indexes) so that the runtime can remove duplication of processing and thus the runtime can achieve low-latency and high-throughput. The tradeoff is that the compiler must, for each statement, perform some upfront analysis.
Since your goal will be to make all test code as realistic, real-world and production-like as possible, we recommend against production code or test code deploying the same exact statement multiple times. Instead consider creating the same statement once and attaching multiple listeners. The compiler and runtime do not try to detect duplicate statements, since that can easily be done by your application.
Let's assume your test statement computes an aggregation over a 1-minute time window, for example select symbol, count(*) from StockTick#time(1 min) group by symbol.
If your code creates the same statement 100 times the code instructs the runtime to track 100 logically independent time windows
and to track aggregations for each group 100 times. Obviously, this is not a good use of EPL and the design of your statements and code may not be optimal.
Consider the world of relational databases. Your code could attach to a relational database, create the same table with a different name 100 times, and populate each of the 100 different tables with the same row data. A relational database administrator would probably recommend against creating 100 identical tables holding the same row data. Compare a statement to a relational database table in respect to how many there should be. In a good design there are limited number of statements. The runtime is not specifically designed for very large number of statements. Similarly a relational database schema design that has 100,000 tables would be something one would seriously question. It depends on the statement itself in respect to how many statements fit into memory and there is no general guideline.
EPL allows you the freedom to design your EPL in a way that reuses state and processing. For example, your EPL design could utilize a named window instead of allocating 100 independent time window. Since named windows are shared, the runtime only needs to track one time window instead of 100. And your EPL design could use an EPL table to maintain aggregations once and in a central place, so that tracking counts per symbol is done once instead of 100 times.
Context declarations can be an efficient way to take commonalities between statements (things that are similar between multiple statements) and factor them out into a context declaration. Instead of creating X similar statements, declare a context and attach one statement to the context, thus having X context partitions. This eliminates compiling and/or deploying X same statements. Using context the compiler only needs to analyze the context declaration and the statement. Your application can send start and stop events to control which context partitions exist and what events each context partition analyzes. Use the context partition administrative API to browse or terminate context partitions.
For example, assume you need to create 100000 similar statements that all filter GeoEvent events:
create schema GeoEvent(id string, value int, marker string)
@name('statment-1) select * from GeoEvent(id = '0001', value between 10 and 20, marker in ('a', 'b'))@name('statment-N) select * from GeoEvent(id = '0002', value between 20 and 30, marker in ('c', 'd'))If your application compiles and deploys 100k statements as above, the compiler must analyze and query plan each statement separately, and the runtime must enter each set of filter criteria into a shared filter index tree. Remember that the runtime can process incoming events very fast, with low latency and high throughput, even for 100k statements. However compiling and deploying 100k individual statements does take CPU time.
In this example, the statements have similar filters: id = an_id, value between start_range and end_range and
marker in (markers).
You could say that statements are similar and look like:
select * from GeoEvent(id=an_id, value between start_range and end_range, marker in (markers))
The an_id, start_range, end_range and markers are essential parameters to an instance of the filtering statement. Instances of statements are context partitions. Declare a context to refactor and change our design so the common filters are in one place. This apprach just requires two statements: the context declaration and the statement with the filters. You may declare two event types: one to allocate new context partitions and one to terminate context partitions.
Start by creating an event type that controls which instances of the filtering statement (the context partitions) are active:
create schema InitEvent(id string, startRange int, endRange int, markers string[])
Next, create an event type that controls when a context partition terminates:
create schema TermEvent(id string)
The context declaration tells the runtime that when an InitEvent arrives you want have a new instance that is parameterized by the InitEvent properties:
create context GeoEventFilterContext initiated by InitEvent as initevent terminated by by TermEvent(id=initevent.id)
Define the statement that filters:
context GeoEventFilterContext select * from GeoEvent(id = context.initevent.id, value between context.initevent.startRange and context.initevent.endRange, marker in (context.initevent.markers))
Your application can now send InitEvent instances, for example (notation from the online EPL tool):
InitEvent={id='0001', startRange=10, endRange=20, markers={'a', 'b'}}
InitEvent={id='0002', startRange=20, endRange=30, markers={'c', 'd'}}
When the runtime receives an InitEvent instance, it can simply take the id, startRange, endRange and markers values and
instantiate the EPL filter statement (aka. allocate a new context partition) and start looking for matching GeoEvent events.
To stop looking for a given id, send a TermEvent, like so:
TermEvent={id='0001'}
The Java Virtual Machine optimizes locks such that the time to obtain a read lock, for example, differs widely between single-threaded and multi-threaded applications.
We compared code that obtains an unfair ReentrantReadWriteLock read lock 100 million times, without any writer.
We measured 3 seconds for a single-threaded application and 15 seconds for an application with 2 threads.
It can therefore not be expected that scaling from single-threaded to 2 threads will always double performance. There is a base cost for multiple threads to coordinate.
Tip
For logging of lock activity please enable runtime lock activity logging as described in Section 17.6.2.3, “Lock Activity Logging”.
Whether aggregations of named window rows are computed incrementally or are recomputed from scratch depends on the type of statement.
When the runtime computes aggregation values incrementally, meaning it continuously updates the aggregation value as events enter and leave a named window, it means that the runtime internally subscribes to named window updates and applies these updates as they occur. For some applications this is the desired behavior.
For some applications re-computing aggregation values from scratch when a certain condition occurs, for example when a triggering event arrives or time passes, is beneficial. Re-computing an aggregation can be less expensive if the number of rows to consider is small and/or when the triggering event or time condition triggers infrequently.
The next paragraph assumes that a named window has been created to hold some historical financial data per symbol and minute:
create window HistoricalWindow#keepall as (symbol string, int minute, double price)
insert into HistoricalWindow select symbol, minute, price from HistoricalTick
For statements that simply select from a named window (excludes on-select) the runtime computes aggregation values incrementally, continuously updating the aggregation, as events enter and leave the named window.
For example, the below statement updates the total price incrementally as events enter and leave the named window. If events in the named window already exist at the time the statement gets created, the total price gets pre-computed once when the statement gets created and incrementally updated when events enter and leave the named window:
select sum(price) from HistoricalWindow(symbol='GE')
The same is true for uncorrelated subqueries. For statements that sub-select from a named window, the runtime computes aggregation values incrementally, continuously updating the aggregation, as events enter and leave the named window. This is only true for uncorrelated subqueries that don't have a where-clause.
For example, the below statement updates the total price incrementally as events enter and leave the named window. If events in the named window already exist at the time the statement gets created, the total price gets pre-computed once when the statement gets created and incrementally updated when events enter and leave the named window:
// Output GE symbol total price, incrementally computed // Outputs every 15 minutes on the hour. select (sum(price) from HistoricalWindow(symbol='GE')) from pattern [every timer:at(0, 15, 30, 45), *, *, *, *, 0)]
If instead your application uses on-select or a correlated subquery, the runtime recomputes aggregation values from scratch every time the triggering event fires.
For example, the below statement does not incrementally compute the total price (use a plain select or subselect as above instead). Instead the runtime computes the total price from scratch based on the where-clause and matching rows:
// Output GE symbol total price (recomputed from scratch) every 15 minutes on the hour on pattern [every timer:at(0, 15, 30, 45), *, *, *, *, 0)] select sum(price) from HistoricalWindow where symbol='GE'
Unidirectional joins against named windows also do not incrementally compute aggregation values.
Joins and outer joins, that are not unidirectional, compute aggregation values incrementally.
Java Virtual Machines (JVMs) release memory only when a garbage collection occurs. Depending on your JVM settings a garbage collection can occur frequently or infrequently and may consider all or only parts of heap memory.
The runtime is optimized towards latency and throughput. The runtime does not force garbage collection or interfere with garbage collection. For performance-sensitive code areas, the runtime utilizes thread-local buffers such as arrays or ringbuffers that can retain small amounts of recently processed state. The runtime does not try to clean such buffers after every event for performance reasons. It does clean such buffers when destroying the runtime and undeploying. It is therefore normal to see a small non-increasing amount of memory to be retained after processing events that the garbage collector may not free immediately.
When an event comes in and the event does not match any statement, the runtime can discard that event since the event is a non-match. When measuring throughput, we suggest including non-matching events. The fact that the runtime can discard non-matching events extremely fast is an important aspect of processing.
Many use cases look for a needle-in-a-haystack situation or rarely occurring pattern. For example, a use case looking for security breaches may analyze 10 million events and find only a single situation consisting, for example, of 5 correlated events of the 10 million input events. We'd recommend your benchmark to closely mimic or to play back production data and watch the expected ratio of input and output events. Reducing the number of output events generally increases performance.
For example, assume you have 10 statements:
select * from pattern[A -> B(id = 1)]; select * from pattern[A -> B(id = 2)]; ..... select * from pattern[A -> B(id = 10)];
The above patterns each match once when an A event comes in followed by a B event with a given id between 1 and 10.
We recommend to measure throughput by sending in B events that have a value of minus one (-1) for id, for example, to determine how fast such events are discarded.
We would consider an event type that has more than 1000 event properties to be an event type with a large number of properties. Here are some of the available options for handling large events (not in order of preference, this is just a list):
One can design the EPL so that only those event properties that matter for the specific use case are retained and the Esper runtime can thus garbage collect the original event and retain only the few event properties that the specific use case needs. For example using
insert into ReducedEvent select a,b from LargeEventandselect ... from ReducedEvent....One can design the EPL so that there is no need for the runtime to hold on to the large event objects themselves. This documentation and the FAQ page describe in detail when the runtime does and does not retain events.
Use EsperHA since EsperHA has the ability to remove state from memory and swap it back into memory when needed.
The JVM in general needs more memory for objects like strings or arrays. Making sure that event properties have the smallest memory footprint can help, i.e. a primitive integer uses less memory than a string.
Instead of keeping all event properties on the event, reduce the event properties to only those properties that matter. The application code could lazy-fetch the remaining properties from an external source when they are needed.
Event properties could be stored binary-encoded which also uses less memory (use an external library or write your own binary encoding; Esper does not provide a binary encoding). The application code could for instance provide "getter"-methods that query the encoded data.
The benchmark application is basically an event server build with the runtime that listens to remote clients over TCP. Remote clients send MarketData(ticker, price, volume) streams to the event server. The event server is started with 1000 statements of one single kind (unless otherwise written), with one statement per ticker symbol, unless the statement kind does not depend on the symbol. The statement prototype is provided along the results with a '$' instead of the actual ticker symbol value. The event server is entirely multithreaded and can leverage the full power of 32bit or 64bit underlying hardware multi-processor multi-core architecture.
The kit also prints out when starting up the event size and the theoretical maximal throughput you can get on a 100 Mbit/s and 1 Gbit/s network. Keep in mind a 100 Mbit/s network will be overloaded at about 400 000 event/s when using our kit despite the small size of events.
Results are posted on our Wiki page at Performance Wiki. Reported results do not represent best ever obtained results. Reported results may help you better compare Esper to other solutions (for latency, throughput and CPU utilization) and also assess your target hardware and JVMs.
The event server, client and statement prototypes are provided in the source repository
esper/trunk/examples/benchmark/.
Refer to http://www.espertech.com/esper
for source access.
If you use the kit you should:
Choose the statement you want to benchmark, add it to
etc/statements.propertiesunder your own KEY and use the-mode KEYwhen you start the event server.Prepare your runServer.sh/runServer.cmd and runClient.sh/runclient.cmd scripts. You'll need to drop required jar libraries in
lib/, make sure the classpath is configured in those script to includebuildandetc. The required libraries are Esper (any compatible version, we have tested started with Esper 1.7.0) and its dependencies. Note that./etcand./buildhave to be in the classpath. At that stage you should also start to set min and max JVM heap. A good start is 1GB as in-Xms1g -Xmx1gWrite the statement you want to benchmark given that client will send a stream MarketData(String ticker, int volume, double price), add it to
etc/statements.propertiesunder your own KEY and use the-mode KEYwhen you start the event server. Use'$'in the statement to create a prototype. For every symbol, a statement will get registered with all'$'replaced by the actual symbol value (f.e.'GOOG')Ensure client and server are using the same
-Desper.benchmark.symbol=1000value. This sets the number of symbol to use (thus may set the number of statement if you are using a statement prototype, and governs how MarketData event are represented over the network. Basically all events will have the same size over the network to ensure predictability and will be ranging betweenS0AAandS999Aif you use 1000 as a value here (prefix with S and padded with A up to a fixed length string. Volume and price attributes will be randomized.By default the benchmark registers a subscriber to the statement(s). Use
-Desper.benchmark.ulto use an UpdateListener instead. Note that the subscriber contains suitable update(..) methods for the default proposed statement in theetc/statements.propertiesfile but might not be suitable if you change statements due to the strong binding with statement results. Refer to Table 16.2, “Choices For Receiving Statement Results”.Establish a performance baseline in simulation mode (without clients). Use the
-rate 1x5000option to simulate one client (one thread) sending 5000 evt/s. You can ramp up both the number of client simulated thread and their emission rate to maximize CPU utilization. The right number should mimic the client emission rate you will use in the client/server benchmark and should thus be consistent with what your client machine and network will be able to send. On small hardware, having a lot of thread with slow rate will not help getting high throughput in this simulation mode.Do performance runs with client/server mode. Remove the
-rate NxMoption from the runServer script or Ant task. Start the server with-helpto display the possible server options (listen port, statistics, fan out options etc). On the remote machine, start one or more client. Use-helpto display the possible client options (remote port, host, emission rate). The client will output the actual number of event it is sending to the server. If the server gets overloaded (or if you turned on-queueoptions on the server) the client will likely not be able to reach its target rate.Usually you will get better performance by using server side
-queue -1option so as to have each client connection handled by a single thread pipeline. If you change to 0 or more, there will be intermediate structures to pass the event stream in an asynchronous fashion. This will increase context switching, although if you are using many clients, or are using the-sleep xxx(xxx in milliseconds) to simulate a listener delay you may get better performance.The most important server side option is
-stat xxx(xxx in seconds) to print out throughput and latency statistics aggregated over the last xxx seconds (and reset every time). It will produce both internal latency (in nanosecond) and also end to end latency (in millisecond, including network time). If you are measuring end to end latency you should make sure your server and client machine(s) are having the same time with f.e. ntpd with a good enough precision. The stat format is like:---Stats - runtime (unit: ns) Avg: 2528 #4101107 0 < 5000: 97.01% 97.01% #3978672 5000 < 10000: 2.60% 99.62% #106669 10000 < 15000: 0.35% 99.97% #14337 15000 < 20000: 0.02% 99.99% #971 20000 < 25000: 0.00% 99.99% #177 25000 < 50000: 0.00% 100.00% #89 50000 < 100000: 0.00% 100.00% #41 100000 < 500000: 0.00% 100.00% #120 500000 < 1000000: 0.00% 100.00% #2 1000000 < 2500000: 0.00% 100.00% #7 2500000 < 5000000: 0.00% 100.00% #5 5000000 < more: 0.00% 100.00% #18 ---Stats - endToEnd (unit: ms) Avg: -2704829444341073400 #4101609 0 < 1: 75.01% 75.01% #3076609 1 < 5: 0.00% 75.01% #0 5 < 10: 0.00% 75.01% #0 10 < 50: 0.00% 75.01% #0 50 < 100: 0.00% 75.01% #0 100 < 250: 0.00% 75.01% #0 250 < 500: 0.00% 75.01% #0 500 < 1000: 0.00% 75.01% #0 1000 < more: 24.99% 100.00% #1025000 Throughput 412503 (active 0 pending 0 cnx 4)This one reads as:
"Throughput is 412 503 event/s with 4 client connected. No -queue options was used thus no event is pending at the time the statistics are printed. latency average is at 2528 ns (that is 2.5 us) for 4 101 107 events (which means we have 10 seconds stats here). Less than 10us latency was achieved for 106 669 events that is 99.62%. Latency between 5us and 10us was achieved for those 2.60% of all the events in the interval." "End to end latency was ... in this case likely due to client clock difference we ended up with unusable end to end statistics."
Consider the second output paragraph on end-to-end latency:
---Stats - endToEnd (unit: ms) Avg: 15 #863396 0 < 1: 0.75% 0.75% #6434 1 < 5: 0.99% 1.74% #8552 5 < 10: 2.12% 3.85% #18269 10 < 50: 91.27% 95.13% #788062 50 < 100: 0.10% 95.32% #827 100 < 250: 4.36% 99.58% #37634 250 < 500: 0.42% 100.00% #3618 500 < 1000: 0.00% 100.00% #0 1000 < more: 0.00% 100.00% #0This would read:
"End to end latency average is at 15 milliseconds for the 863 396 events considered for this statistic report. 95.13% ie 788 062 events were handled (end to end) below 50ms, and 91.27% were handled between 10ms and 50ms."
Luckham, David. 2002. The Power of Events. Addison-Wesley.
The Stanford Rapide (TM) Project. http://pavg.stanford.edu/rapide.
Arasu, Arvind, et.al.. 2004. Linear Road: A Stream Data Management Benchmark, Stanford University http://www.cs.brown.edu/research/aurora/Linear_Road_Benchmark_Homepage.html.
This section specifies the output of a subset of statements, for two purposes: First, to help application developers understand streaming runtime output in response to incoming events and in response to time passing. Second, to document and standardize output for statements in a testable and trackable fashion.
The section focuses on a subset of features, namely the time window, aggregation, grouping, and output rate limiting. The section does not currently provide examples for many of the other language features, thus there is no example for other data windows (the time window is used here), joins, sub-selects or named windows etc.
Rather then just describe syntax and output, this section provides detailed examples for each of the types of statements presented. The input for each type of statement is always the same set of events, and the same timing. Each event has three properties: symbol, volume and price. The property types are string, long and double, respectively.
The chapters are organized by the type of statement: The presence or absence of aggregation functions, as well as the presence or absence of a group by clause change statement output as
described in Section 2.15, “Basic Aggregated Statement Types”.
You will notice that some statements utilize the order by clause for sorting output. The reason is that when multiple output rows are produced at once, the output can be easier to read if it is sorted.
With output rate limiting, the runtime invokes your listener even if there are no results to indicate when the output condition has been reached. Such is indicated as (empty result) in the output result columns.
The output columns show both insert and remove stream events. Insert stream events are delivered as an array of EventBean instances to listeners in the newData parameter, while remove stream events are delivered to the oldData parameter of listeners. Delivery to observers follows similar rules.
For the purpose of illustration and documentation, the example data set demonstrates input and remove streams based on a time window of a 5.5 second interval. The statement utilizing the time window could look as follows:
select symbol, volume, price from MarketData#time(5.5 sec)
We have picked a time window to demonstrate the output for events entering and leaving a data window with an expiration policy. The time window provides a simple expiration policy based on time: if an event resides in the time window more then 5.5 seconds, the runtime expires the event from the time window.
The input events and their timing are below. The table should be read, starting from top, as "The time starts at 0.2 seconds. Event E1 arrives at 0.2 seconds with properties [S1, 100, 25]. At 0.8 second event E2 arrives with properties [S2, 5000, 9.0]" and so on.
Input
-----------------------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
S1 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
S2 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
1.5
S1 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
S3 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
S1 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
2.5
3.0
3.2
3.5
S3 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
4.3
S1 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
S3 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
S3 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2 The event data set assumes a time window of 5.5 seconds. Thus at time 5.7 seconds the first arriving event (E1) leaves the time window.
The data set as above shows times between 0.2 seconds and 7.2 seconds. Only a couple of time points have been picked for the table to keep the set of time points constant between statements, and thus make the test data and output easier to understand.
This chapter provides sample output for statements that do not have aggregation functions and do not have a group by clause.
Without an output clause, the runtime dispatches to listeners as soon as events arrive, or as soon as time passes such that events leave data windows.
The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, volume, price from MarketData#time(5.5 sec)
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
[IBM, 100, 25.0]
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
1.0
1.2
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
[IBM, 150, 24.0]
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
[YAH, 10000, 1.0]
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
[IBM, 155, 26.0]
2.2
2.5
3.0
3.2
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
[YAH, 11000, 2.0]
4.0
4.2
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
[IBM, 150, 22.0]
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
[YAH, 11500, 3.0]
5.0
5.2
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
[IBM, 100, 25.0]
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
[YAH, 10500, 1.0]
6.0
6.2
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
[IBM, 150, 24.0]
[YAH, 10000, 1.0]
7.2
With an output clause, the runtime dispatches to listeners when the output condition occurs. Here, the output condition is a 1-second time interval. The runtime thus outputs every 1 second, starting from the first event, even if there are no new events or no expiring events to output.
The default (no keyword) and the ALL keyword result in the same output.
The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, volume, price from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) output every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[IBM, 100, 25.0]
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[IBM, 150, 24.0]
[YAH, 10000, 1.0]
[IBM, 155, 26.0]
2.5
3.0
3.2
(empty result) (empty result)
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[YAH, 11000, 2.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[IBM, 150, 22.0]
[YAH, 11500, 3.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[YAH, 10500, 1.0] [IBM, 100, 25.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
[IBM, 150, 24.0]
[YAH, 10000, 1.0]
Using the LAST keyword in the output clause, the runtime dispatches to listeners only the last event of each insert and remove stream.
The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, volume, price from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) output last every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[IBM, 155, 26.0]
2.5
3.0
3.2
(empty result) (empty result)
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[YAH, 11000, 2.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[YAH, 11500, 3.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[YAH, 10500, 1.0] [IBM, 100, 25.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[YAH, 10000, 1.0]
Using the FIRST keyword in the output clause, the runtime dispatches to listeners only the first event of each insert or remove stream, and does not output further
events until the output condition is reached.
The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, volume, price from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) output first every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
[IBM, 100, 25.0]
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
[IBM, 150, 24.0]
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
2.5
3.0
3.2
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
[YAH, 11000, 2.0]
4.0
4.2
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
[IBM, 150, 22.0]
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
[IBM, 100, 25.0]
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
Using the SNAPSHOT keyword in the output clause, the runtime posts data window contents when the output condition is reached.
The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, volume, price from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) output snapshot every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[IBM, 100, 25.0]
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[IBM, 100, 25.0]
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
[IBM, 150, 24.0]
[YAH, 10000, 1.0]
[IBM, 155, 26.0]
2.5
3.0
3.2
[IBM, 100, 25.0]
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
[IBM, 150, 24.0]
[YAH, 10000, 1.0]
[IBM, 155, 26.0]
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[IBM, 100, 25.0]
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
[IBM, 150, 24.0]
[YAH, 10000, 1.0]
[IBM, 155, 26.0]
[YAH, 11000, 2.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[IBM, 100, 25.0]
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
[IBM, 150, 24.0]
[YAH, 10000, 1.0]
[IBM, 155, 26.0]
[YAH, 11000, 2.0]
[IBM, 150, 22.0]
[YAH, 11500, 3.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
[IBM, 150, 24.0]
[YAH, 10000, 1.0]
[IBM, 155, 26.0]
[YAH, 11000, 2.0]
[IBM, 150, 22.0]
[YAH, 11500, 3.0]
[YAH, 10500, 1.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[IBM, 155, 26.0]
[YAH, 11000, 2.0]
[IBM, 150, 22.0]
[YAH, 11500, 3.0]
[YAH, 10500, 1.0]
This chapter provides sample output for statements that have aggregation functions, and that do not have a group by clause, and in which all event properties are under aggregation.
The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec)
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
[25.0] [null]
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
[34.0] [25.0]
1.0
1.2
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
[58.0] [34.0]
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
[59.0] [58.0]
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
[85.0] [59.0]
2.2
2.5
3.0
3.2
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
[87.0] [85.0]
4.0
4.2
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
[109.0] [87.0]
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
[112.0] [109.0]
5.0
5.2
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
[87.0] [112.0]
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
[88.0] [87.0]
6.0
6.2
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
[79.0] [88.0]
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
[54.0] [79.0]
7.2
Output occurs when the output condition is reached after each 1-second time interval. For each event arriving, the new aggregation value is output as part of the insert stream. As part of the remove stream, the prior aggregation value is output. This is useful for getting a delta-change for each event or group. If there is a having clause, the filter expression applies to each row.
Here also the default (no keyword) and the ALL keyword result in the same output.
The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) output every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[25.0] [null]
[34.0] [25.0]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[58.0] [34.0]
[59.0] [58.0]
[85.0] [59.0]
2.5
3.0
3.2
[85.0] [85.0]
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[87.0] [85.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[109.0] [87.0]
[112.0] [109.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[87.0] [112.0]
[88.0] [87.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[79.0] [88.0]
[54.0] [79.0]
With the LAST keyword, the insert stream carries one event that holds the last aggregation value, and the remove stream carries the prior aggregation value.
The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) output last every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[34.0] [null]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[85.0] [34.0]
2.5
3.0
3.2
[85.0] [85.0]
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[87.0] [85.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[112.0] [87.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[88.0] [112.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[54.0] [88.0] The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) output first every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
[25.0] [null]
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
[58.0] [34.0]
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
2.5
3.0
3.2
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
[87.0] [85.0]
4.0
4.2
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
[109.0] [87.0]
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
[87.0] [112.0]
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
[79.0] [88.0]
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2 The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) output snapshot every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[34.0]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[85.0]
2.5
3.0
3.2
[85.0]
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[87.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[112.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[88.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[54.0]
This chapter provides sample output for statements that have aggregation functions, and that do not have a group by clause, and in which there are event properties that are not under aggregation.
The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec)
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
[IBM, 25.0]
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
[MSFT, 34.0]
1.0
1.2
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
[IBM, 58.0]
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
[YAH, 59.0]
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
[IBM, 85.0]
2.2
2.5
3.0
3.2
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
[YAH, 87.0]
4.0
4.2
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
[IBM, 109.0]
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
[YAH, 112.0]
5.0
5.2
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
[IBM, 87.0]
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
[YAH, 88.0]
6.0
6.2
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
[MSFT, 79.0]
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
[IBM, 54.0]
[YAH, 54.0]
7.2 The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) output every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[IBM, 25.0]
[MSFT, 34.0]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[IBM, 58.0]
[YAH, 59.0]
[IBM, 85.0]
2.5
3.0
3.2
(empty result) (empty result)
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[YAH, 87.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[IBM, 109.0]
[YAH, 112.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[YAH, 88.0] [IBM, 87.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[MSFT, 79.0]
[IBM, 54.0]
[YAH, 54.0] The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) output last every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[MSFT, 34.0]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[IBM, 85.0]
2.5
3.0
3.2
(empty result) (empty result)
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[YAH, 87.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[YAH, 112.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[YAH, 88.0] [IBM, 87.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[YAH, 54.0] The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) output first every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
[IBM, 25.0]
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
[IBM, 58.0]
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
2.5
3.0
3.2
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
[YAH, 87.0]
4.0
4.2
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
[IBM, 109.0]
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
[IBM, 87.0]
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
[MSFT, 79.0]
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2 The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) output snapshot every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[IBM, 34.0]
[MSFT, 34.0]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[IBM, 85.0]
[MSFT, 85.0]
[IBM, 85.0]
[YAH, 85.0]
[IBM, 85.0]
2.5
3.0
3.2
[IBM, 85.0]
[MSFT, 85.0]
[IBM, 85.0]
[YAH, 85.0]
[IBM, 85.0]
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[IBM, 87.0]
[MSFT, 87.0]
[IBM, 87.0]
[YAH, 87.0]
[IBM, 87.0]
[YAH, 87.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[IBM, 112.0]
[MSFT, 112.0]
[IBM, 112.0]
[YAH, 112.0]
[IBM, 112.0]
[YAH, 112.0]
[IBM, 112.0]
[YAH, 112.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[MSFT, 88.0]
[IBM, 88.0]
[YAH, 88.0]
[IBM, 88.0]
[YAH, 88.0]
[IBM, 88.0]
[YAH, 88.0]
[YAH, 88.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[IBM, 54.0]
[YAH, 54.0]
[IBM, 54.0]
[YAH, 54.0]
[YAH, 54.0]
This chapter provides sample output for statements that have aggregation functions, and that have a group by clause, and in which all event properties are under aggregation or appear in the group by clause.
The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) group by symbol order by symbol
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
[IBM, 25.0] [IBM, null]
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, null]
1.0
1.2
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
[IBM, 49.0] [IBM, 25.0]
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
[YAH, 1.0] [YAH, null]
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
[IBM, 75.0] [IBM, 49.0]
2.2
2.5
3.0
3.2
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
[YAH, 3.0] [YAH, 1.0]
4.0
4.2
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
[IBM, 97.0] [IBM, 75.0]
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 3.0]
5.0
5.2
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
[IBM, 72.0] [IBM, 97.0]
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
[YAH, 7.0] [YAH, 6.0]
6.0
6.2
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
[MSFT, null] [MSFT, 9.0]
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
[IBM, 48.0] [IBM, 72.0]
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 7.0]
7.2
The default (no keyword) and the ALL keyword do not result in the same output. The default generates an output row per input event, while the ALL keyword
generates a row for all groups.
The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) group by symbol output every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[IBM, 25.0] [IBM, null]
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, null]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[IBM, 49.0] [IBM, 25.0]
[YAH, 1.0] [YAH, null]
[IBM, 75.0] [IBM, 49.0]
2.5
3.0
3.2
(empty result) (empty result)
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[YAH, 3.0] [YAH, 1.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[IBM, 97.0] [IBM, 75.0]
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 3.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[IBM, 72.0] [IBM, 97.0]
[YAH, 7.0] [YAH, 6.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[MSFT, null] [MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 7.0]
[IBM, 48.0] [IBM, 72.0] The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) group by symbol output all every 1 seconds order by symbol
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[IBM, 25.0] [IBM, null]
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, null]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[IBM, 75.0] [IBM, 25.0]
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 1.0] [YAH, null]
2.5
3.0
3.2
[IBM, 75.0] [IBM, 75.0]
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 1.0] [YAH, 1.0]
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[IBM, 75.0] [IBM, 75.0]
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 3.0] [YAH, 1.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[IBM, 97.0] [IBM, 75.0]
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 3.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[IBM, 72.0] [IBM, 97.0]
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 7.0] [YAH, 6.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[IBM, 48.0] [IBM, 72.0]
[MSFT, null] [MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 7.0] The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) group by symbol output last every 1 seconds order by symbol
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[IBM, 25.0] [IBM, null]
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, null]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[IBM, 75.0] [IBM, 25.0]
[YAH, 1.0] [YAH, null]
2.5
3.0
3.2
(empty result) (empty result)
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[YAH, 3.0] [YAH, 1.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[IBM, 97.0] [IBM, 75.0]
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 3.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[IBM, 72.0] [IBM, 97.0]
[YAH, 7.0] [YAH, 6.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[IBM, 48.0] [IBM, 72.0]
[MSFT, null] [MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 7.0] The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) group by symbol output first every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
[IBM, 25.0] [IBM, null]
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, null]
1.0
1.2
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
[IBM, 49.0] [IBM, 25.0]
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
[YAH, 1.0] [YAH, null]
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
2.5
3.0
3.2
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
[YAH, 3.0] [YAH, 1.0]
4.0
4.2
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
[IBM, 97.0] [IBM, 75.0]
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 3.0]
5.0
5.2
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
[IBM, 72.0] [IBM, 97.0]
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
[YAH, 7.0] [YAH, 6.0]
6.0
6.2
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
[MSFT, null] [MSFT, 9.0]
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
[IBM, 48.0] [IBM, 72.0]
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 7.0]
7.2 The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) group by symbol output snapshot every 1 seconds order by symbol
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[IBM, 25.0]
[MSFT, 9.0]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[IBM, 75.0]
[MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 1.0]
2.5
3.0
3.2
[IBM, 75.0]
[MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 1.0]
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[IBM, 75.0]
[MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 3.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[IBM, 97.0]
[MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 6.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[IBM, 72.0]
[MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 7.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[IBM, 48.0]
[YAH, 6.0]
This chapter provides sample output for statements that have aggregation functions, and that have a group by clause, and in which some event properties are not under aggregation.
The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, volume, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) group by symbol
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
[IBM, 100, 25.0]
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
1.0
1.2
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
[IBM, 150, 49.0]
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
[YAH, 10000, 1.0]
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
[IBM, 155, 75.0]
2.2
2.5
3.0
3.2
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
[YAH, 11000, 3.0]
4.0
4.2
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
[IBM, 150, 97.0]
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
[YAH, 11500, 6.0]
5.0
5.2
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
[IBM, 100, 72.0]
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
[YAH, 10500, 7.0]
6.0
6.2
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
[MSFT, 5000, null]
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
[IBM, 150, 48.0]
[YAH, 10000, 6.0]
7.2
The default (no keyword) and the ALL keyword do not result in the same output. The default generates an output row per input event, while the ALL keyword
generates a row for all groups based on the last new event for each group.
The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, volume, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) group by symbol output every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[IBM, 100, 25.0]
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[IBM, 150, 49.0]
[YAH, 10000, 1.0]
[IBM, 155, 75.0]
2.5
3.0
3.2
(empty result) (empty result)
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[YAH, 11000, 3.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[IBM, 150, 97.0]
[YAH, 11500, 6.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[YAH, 10500, 7.0] [IBM, 100, 72.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[MSFT, 5000, null]
[IBM, 150, 48.0]
[YAH, 10000, 6.0] The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, volume, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) group by symbol output all every 1 seconds order by symbol
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[IBM, 100, 25.0]
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[IBM, 150, 49.0]
[IBM, 155, 75.0]
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
[YAH, 10000, 1.0]
2.5
3.0
3.2
[IBM, 155, 75.0]
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
[YAH, 10000, 1.0]
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[IBM, 155, 75.0]
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
[YAH, 11000, 3.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[IBM, 150, 97.0]
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
[YAH, 11500, 6.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[IBM, 150, 72.0] [IBM, 100, 72.0]
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
[YAH, 10500, 7.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[IBM, 150, 48.0] [IBM, 150, 48.0]
[MSFT, 5000, null] [MSFT, 5000, null]
[YAH, 10500, 6.0] [YAH, 10000, 6.0] The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, volume, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) group by symbol output last every 1 seconds order by symbol
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[IBM, 100, 25.0]
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[IBM, 155, 75.0]
[YAH, 10000, 1.0]
2.5
3.0
3.2
(empty result) (empty result)
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[YAH, 11000, 3.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[IBM, 150, 97.0]
[YAH, 11500, 6.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[YAH, 10500, 7.0] [IBM, 100, 72.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[IBM, 150, 48.0]
[MSFT, 5000, null]
[YAH, 10000, 6.0] The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, volume, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) group by symbol output first every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
[IBM, 100, 25.0]
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
1.0
1.2
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
[IBM, 150, 49.0]
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
[YAH, 10000, 1.0]
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
2.5
3.0
3.2
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
[YAH, 11000, 3.0]
4.0
4.2
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
[IBM, 150, 97.0]
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
[YAH, 11500, 6.0]
5.0
5.2
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
[IBM, 100, 72.0]
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
[YAH, 10500, 7.0]
6.0
6.2
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
[MSFT, 5000, null]
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
[IBM, 150, 48.0]
[YAH, 10000, 6.0]
7.2 The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, volume, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) group by symbol output snapshot every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[IBM, 100, 25.0]
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[IBM, 100, 75.0]
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
[IBM, 150, 75.0]
[YAH, 10000, 1.0]
[IBM, 155, 75.0]
2.5
3.0
3.2
[IBM, 100, 75.0]
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
[IBM, 150, 75.0]
[YAH, 10000, 1.0]
[IBM, 155, 75.0]
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[IBM, 100, 75.0]
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
[IBM, 150, 75.0]
[YAH, 10000, 3.0]
[IBM, 155, 75.0]
[YAH, 11000, 3.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[IBM, 100, 97.0]
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
[IBM, 150, 97.0]
[YAH, 10000, 6.0]
[IBM, 155, 97.0]
[YAH, 11000, 6.0]
[IBM, 150, 97.0]
[YAH, 11500, 6.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[MSFT, 5000, 9.0]
[IBM, 150, 72.0]
[YAH, 10000, 7.0]
[IBM, 155, 72.0]
[YAH, 11000, 7.0]
[IBM, 150, 72.0]
[YAH, 11500, 7.0]
[YAH, 10500, 7.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[IBM, 155, 48.0]
[YAH, 11000, 6.0]
[IBM, 150, 48.0]
[YAH, 11500, 6.0]
[YAH, 10500, 6.0]
This chapter provides sample output for statements that have aggregation functions, and that have a group by clause, and in which all event properties are under aggregation or appear in the group by clause, and the group by clause has a rollup, cube or grouping sets keyword(s) instructing the runtime to perform multi-level aggregation.
The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, volume, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) group by rollup(symbol)
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
[IBM, 25.0] [IBM, null]
[null, 25.0] [null, null]
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, null]
[null, 34.0] [null, 25.0]
1.0
1.2
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
[IBM, 49.0] [IBM, 25.0]
[null, 58.0] [null, 34.0]
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
[YAH, 1.0] [YAH, null]
[null, 59.0] [null, 58.0]
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
[IBM, 75.0] [IBM, 49.0]
[null, 85.0] [null, 59.0]
2.2
2.5
3.0
3.2
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
[YAH, 3.0] [YAH, 1.0]
[null, 87.0] [null, 85.0]
4.0
4.2
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
[IBM, 97.0] [IBM, 75.0]
[null, 109.0] [null, 87.0]
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 3.0]
[null, 112.0] [null, 109.0]
5.0
5.2
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
[IBM, 72.0] [IBM, 97.0]
[null, 87.0] [null, 112.0]
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
[YAH, 7.0] [YAH, 6.0]
[null, 88.0] [null, 87.0]
6.0
6.2
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
[MSFT, null] [MSFT, 9.0]
[null, 79.0] [null, 88.0]
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
[IBM, 48.0] [IBM, 72.0]
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 7.0]
[null, 54.0] [null, 79.0]
7.2The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, volume, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) group by rollup(symbol) output every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[IBM, 25.0] [IBM, null]
[null, 25.0] [null, null]
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, null]
[null, 34.0] [null, 25.0]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[IBM, 49.0] [IBM, 25.0]
[null, 58.0] [null, 34.0]
[YAH, 1.0] [YAH, null]
[null, 59.0] [null, 58.0]
[IBM, 75.0] [IBM, 49.0]
[null, 85.0] [null, 59.0]
2.5
3.0
3.2
(empty result) (empty result)
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[YAH, 3.0] [YAH, 1.0]
[null, 87.0] [null, 85.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[IBM, 97.0] [IBM, 75.0]
[null, 109.0] [null, 87.0]
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 3.0]
[null, 112.0] [null, 109.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[IBM, 72.0] [IBM, 97.0]
[null, 87.0] [null, 112.0]
[YAH, 7.0] [YAH, 6.0]
[null, 88.0] [null, 87.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[MSFT, null] [MSFT, 9.0]
[null, 79.0] [null, 88.0]
[IBM, 48.0] [IBM, 72.0]
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 7.0]
[null, 54.0] [null, 79.0]The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, volume, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) group by rollup(symbol) output all every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[IBM, 25.0] [IBM, null]
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, null]
[null, 34.0] [null, null]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[IBM, 75.0] [IBM, 25.0]
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 1.0] [YAH, null]
[null, 85.0] [null, 34.0]
2.5
3.0
3.2
[IBM, 75.0] [IBM, 75.0]
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 1.0] [YAH, 1.0]
[null, 85.0] [null, 85.0]
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[IBM, 75.0] [IBM, 75.0]
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 3.0] [YAH, 1.0]
[null, 87.0] [null, 85.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[IBM, 97.0] [IBM, 75.0]
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 3.0]
[null, 112.0] [null, 87.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[IBM, 72.0] [IBM, 97.0]
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 7.0] [YAH, 6.0]
[null, 88.0] [null, 112.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[IBM, 48.0] [IBM, 72.0]
[MSFT, null] [MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 7.0]
[null, 54.0] [null, 88.0]The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, volume, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) group by rollup(symbol) output last every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[IBM, 25.0] [IBM, null]
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, null]
[null, 34.0] [null, null]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[IBM, 75.0] [IBM, 25.0]
[YAH, 1.0] [YAH, null]
[null, 85.0] [null, 34.0]
2.5
3.0
3.2
(empty result) (empty result)
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[YAH, 3.0] [YAH, 1.0]
[null, 87.0] [null, 85.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[IBM, 97.0] [IBM, 75.0]
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 3.0]
[null, 112.0] [null, 87.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[IBM, 72.0] [IBM, 97.0]
[YAH, 7.0] [YAH, 6.0]
[null, 88.0] [null, 112.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[MSFT, null] [MSFT, 9.0]
[IBM, 48.0] [IBM, 72.0]
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 7.0]
[null, 54.0] [null, 88.0] The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, volume, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) group by rollup(symbol) output first every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
[IBM, 25.0] [IBM, null]
[null, 25.0] [null, null]
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
[MSFT, 9.0] [MSFT, null]
1.0
1.2
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
[IBM, 49.0] [IBM, 25.0]
[null, 58.0] [null, 34.0]
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
[YAH, 1.0] [YAH, null]
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
2.5
3.0
3.2
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
[YAH, 3.0] [YAH, 1.0]
[null, 87.0] [null, 85.0]
4.0
4.2
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
[IBM, 97.0] [IBM, 75.0]
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 3.0]
[null, 112.0] [null, 109.0]
5.0
5.2
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
[IBM, 72.0] [IBM, 97.0]
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
[YAH, 7.0] [YAH, 6.0]
[null, 88.0] [null, 87.0]
6.0
6.2
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
[MSFT, null] [MSFT, 9.0]
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
[IBM, 48.0] [IBM, 72.0]
[YAH, 6.0] [YAH, 7.0]
[null, 54.0] [null, 79.0]The statement for this sample reads:
select irstream symbol, volume, sum(price) from MarketData#time(5.5 sec) group by rollup(symbol) output snapshot every 1 seconds
The output is as follows:
Input Output
Insert Stream Remove Stream
----------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Time Symbol Volume Price
0.2
IBM 100 25.0 Event E1 arrives
0.8
MSFT 5000 9.0 Event E2 arrives
1.0
1.2
[IBM, 25.0]
[MSFT, 9.0]
[null, 34.0]
1.5
IBM 150 24.0 Event E3 arrives
YAH 10000 1.0 Event E4 arrives
2.0
2.1
IBM 155 26.0 Event E5 arrives
2.2
[IBM, 75.0]
[MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 1.0]
[null, 85.0]
2.5
3.0
3.2
[IBM, 75.0]
[MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 1.0]
[null, 85.0]
3.5
YAH 11000 2.0 Event E6 arrives
4.0
4.2
[IBM, 75.0]
[MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 3.0]
[null, 87.0]
4.3
IBM 150 22.0 Event E7 arrives
4.9
YAH 11500 3.0 Event E8 arrives
5.0
5.2
[IBM, 97.0]
[MSFT, 9.0]
[YAH, 6.0]
[null, 112.0]
5.7 Event E1 leaves the time window
5.9
YAH 10500 1.0 Event E9 arrives
6.0
6.2
[MSFT, 9.0]
[IBM, 72.0]
[YAH, 7.0]
[null, 88.0]
6.3 Event E2 leaves the time window
7.0 Event E3 and E4 leave the time window
7.2
[IBM, 48.0]
[YAH, 6.0]
[null, 54.0] Output rate limiting provides output events to your application in regular intervals. Between intervals, the runtime may use a buffer to hold data until the output condition is reached, as described below. If your application has high-volume streams, you may need to be mindful of the memory needs for buffers especially if the output condition triggers infrequently.
The output clause with the snapshot keyword does not require a buffer for any type of statement.
The output clause with the first keyword does not require a buffer for any type of statement.
We use the term change set to describe all insert and remove stream events that occur since the last triggering of the output condition.
You can override the default behavior for some types of statements by specifying a hint.
Please see Section 2.15, “Basic Aggregated Statement Types” for information on the types of statements discussed below.
For statements that define output last the runtime retains only the first remove stream event and the last insert stream event, both matching the having-clause, if present,
to compute insert and remove stream output when the output condition triggers.
Without an order-by clause:
Upon arrival of any row the runtime applies the
having-clause and retains only matching events, or retains all events if there is nohaving-clause.Upon triggering of the output condition the runtime computes the insert and remove stream output events according to the
select-clause for output.
With an order-by clause or when your EPL specifies the @Hint('disable_outputlimit_opt') hint:
The runtime retains the change set and computes output from the change set at the time the output condition triggers, after which it discards the change set.
Without an order-by clause:
Upon arrival of the first row since the last triggering of the output condition the runtime computes the remove stream output event according to the
select-clause for later output (when applicable).Upon triggering of the output condition the runtime computes the insert stream output event according to the
select-clause for output.
With an order-by clause or when your EPL specifies the @Hint('disable_outputlimit_opt') hint:
The runtime retains the change set and computes output from the change set at the time the output condition triggers, after which it discards the change set.
Without an order-by clause:
Upon arrival of rows the runtime applies the
having-clause and computes the insert and remove stream output event according to theselect-clause for later output (when applicable).Upon triggering of the output condition the runtime outputs the insert and remove stream output events.
With an order-by clause or when your EPL specifies the @Hint('disable_outputlimit_opt') hint:
The runtime retains the change set and computes output from the change set at the time the output condition triggers, after which it discards the change set.
Without an order-by clause:
Upon arrival of the first row since the last triggering of the output condition the runtime computes the insert and remove stream output event according to the
having-clause (if present) and theselect-clause for later output (when applicable), retaining only the last computed insert and remove stream output event.Upon triggering of the output condition the runtime outputs the pre-computed last insert stream and remove stream output event.
With an order-by clause or when your EPL specifies the @Hint('disable_outputlimit_opt') hint:
The runtime retains the change set and computes output from the change set at the time the output condition triggers, after which it discards the change set.
Without an order-by clause:
Upon arrival of rows the runtime computes the insert and remove stream output events according to the
having-clause (if present) and theselect-clause for later output, retaining only the computed insert and remove stream output events.Upon triggering of the output condition the runtime outputs the retained output events.
With an order-by clause or when your EPL specifies the @Hint('disable_outputlimit_opt') hint:
The runtime retains the change set and computes output from the change set at the time the output condition triggers, after which it discards the change set.
Without an order-by clause:
Upon arrival of the first row for a given group since the last triggering of the output condition the runtime computes the remove stream output event for that group according to the
select-clause for later output (when applicable), and also retains a single insert stream event per group.Upon triggering of the output condition the runtime uses the retained insert stream events per group to compute output events according to the
select-clause.
With an order-by clause or when your EPL specifies the @Hint('disable_outputlimit_opt') hint:
The runtime retains the change set and computes output from the change set at the time the output condition triggers, after which it discards the change set.
Without an order-by clause:
The runtime retains, for each group, a row to represent the group.
Upon arrival of rows the runtime computes the remove stream output events according to the
having-clause (if present) and theselect-clause for later output.Upon triggering of the output condition the runtime computes the insert stream output events according to the
having-clause (if present) and theselect-clause for output, for each group.
With an order-by clause or when your EPL specifies the @Hint('disable_outputlimit_opt') hint:
The runtime retains the change set and computes output from the change set at the time the output condition triggers, after which it discards the change set.
Without an order-by clause:
Upon arrival of the first row for a given group since the last triggering of the output condition the runtime computes the insert and remove stream output event for that group according to the
select-clause for later output (when applicable), and retains a last insert and remove stream event per group.Upon triggering of the output condition the runtime outputs the retained insert and remove stream output events per group.
With an order-by clause or when your EPL specifies the @Hint('disable_outputlimit_opt') hint:
The runtime retains the change set and computes output from the change set at the time the output condition triggers, after which it discards the change set.
Without an order-by clause:
The runtime retains, for each group, a row to represent the group.
Upon arrival of rows the runtime computes the insert and remove stream output events according to the
having-clause (if present) and theselect-clause for later output.Upon triggering of the output condition the runtime computes insert stream output events according to the
having-clause (if present) and theselect-clause for output for each group that does not have output events yet, and outputs all events.
With an order-by clause or when your EPL specifies the @Hint('disable_outputlimit_opt') hint:
The runtime retains the change set and computes output from the change set at the time the output condition triggers, after which it discards the change set.
The words in the following table are explicitly reserved in EPL, however certain keywords are allowed as event property names in expressions and as column names in the rename syntax of the select clause.
Most of the words in the table are forbidden by standard SQL as well. A few are reserved because EPL needs them.
Names of built-in functions and certain auxiliary keywords are permitted as identifiers for use either as event property names in expressions and for the column rename syntax. The second column in the table below indicates which keywords are acceptable. For example, count is acceptable.
An example of permitted use is:
select last, count(*) as count from MyEvent
This example shows an incorrect use of a reserved keyword:
// incorrect select insert from MyEvent
The table of explicitly reserved keywords and permitted keywords:
Table C.1. Reserved Keywords
| Keyword | Property Name and Rename Syntax |
|---|---|
| after | - |
| all | - |
| and | - |
| as | - |
| at | yes |
| asc | - |
| avedev | yes |
| avg | yes |
| between | - |
| by | - |
| case | - |
| cast | yes |
| coalesce | yes |
| context | - |
| count | yes |
| create | - |
| current_timestamp | - |
| cube | - |
| dataflow | - |
| day | - |
| days | - |
| delete | - |
| define | yes |
| desc | - |
| distinct | - |
| else | - |
| end | - |
| escape | yes |
| events | yes |
| every | yes |
| exists | - |
| expression | - |
| false | yes |
| first | yes |
| for | yes |
| from | - |
| full | yes |
| group | - |
| grouping | - |
| grouping_id | - |
| having | - |
| hour | - |
| hours | - |
| in | - |
| initiated | - |
| inner | - |
| insert | - |
| instanceof | yes |
| into | - |
| irstream | - |
| is | - |
| istream | - |
| join | yes |
| last | yes |
| lastweekday | yes |
| left | yes |
| limit | - |
| like | - |
| max | yes |
| match_recognize | - |
| matched | - |
| matches | - |
| median | yes |
| measures | yes |
| merge | - |
| metadatasql | yes |
| min | yes |
| minute | yes |
| minutes | yes |
| microsecond | yes |
| microseconds | yes |
| millisecond | yes |
| milliseconds | yes |
| msec | yes |
| new | - |
| not | - |
| null | - |
| offset | - |
| on | - |
| or | - |
| order | - |
| outer | yes |
| output | - |
| partition | - |
| pattern | yes |
| prev | yes |
| prior | yes |
| regexp | - |
| retain-union | yes |
| retain-intersection | yes |
| right | yes |
| rollup | yes |
| rstream | - |
| sec | - |
| second | - |
| seconds | - |
| select | - |
| set | - |
| sets | - |
| some | - |
| snapshot | yes |
| sql | yes |
| start | - |
| stddev | yes |
| sum | yes |
| terminated | - |
| then | - |
| true | - |
| unidirectional | yes |
| until | yes |
| update | - |
| usec | yes |
| using | yes |
| variable | yes |
| values | yes |
| weekday | yes |
| when | - |
| where | - |
| while | - |
| window | yes |
This section provides information for using Plain-Old or Bean Java Objects to represent events.
For NEsper .NET also see Section J.8, “.NET Object Events”.
Plain-old Java object events are object instances that expose event properties through JavaBeans-style getter methods. Events classes or interfaces do not have to be fully compliant to the JavaBean specification; however for the compiler to obtain event properties, the required JavaBean getter methods must be present or an accessor-style and accessor-methods may be defined via configuration.
The compiler and runtime supports JavaBeans-style event classes that extend a superclass or implement one or more interfaces.
Classes that represent events should be made immutable. As events are recordings of a state change or action that occurred in the past, the relevant event properties should not be changeable. However this is not a hard requirement and the runtime accepts events that are mutable as well.
The hashCode and equals methods do not need to be implemented. The implementation of these methods by a Java event class does not affect the behavior of the runtime in any way.
Please see Chapter 17, Configuration on options for naming event types represented by Java object event classes. Java classes that do not follow JavaBean conventions, such as legacy Java classes that expose public fields, or methods not following naming conventions, require additional configuration. Via configuration it is also possible to control case sensitivity in property name resolution. The relevant section in the chapter on configuration is Section 17.4.3.2, “Non-JavaBean and Legacy Java Event Classes”.
Note
Event classes must have public visibility.
As outlined earlier, the different property types are supported by the standard JavaBeans specification, and some of which are uniquely supported by EPL:
Simple properties have a single value that may be retrieved. The underlying property type might be a Java language primitive (such as int, a simple object (such as a java.lang.String), or a more complex object whose class is defined either by the Java language, by the application, or by a class library included with the application.
Indexed - An indexed property stores an ordered collection of objects (all of the same type) that can be individually accessed by an integer-valued, non-negative index (or subscript).
Mapped - As an extension to standard JavaBeans APIs, EPL considers any property that accepts a String-valued key a mapped property.
Nested - A nested property is a property that lives within another Java object which itself is a property of an event.
Assume there is an NewEmployeeEvent event class as shown below. The mapped and indexed properties in this example return Java objects but could also return Java language primitive types (such as int or String). The Address object and Employee can themselves have properties that are nested within them, such as a street name in the Address object or a name of the employee in the Employee object.
public class NewEmployeeEvent {
public String getFirstName();
public Address getAddress(String type);
public Employee getSubordinate(int index);
public Employee[] getAllSubordinates();
}
Simple event properties require a getter-method that returns the property value. In this example, the getFirstName getter method returns the firstName event property of type String.
Indexed event properties require either one of the following getter-methods. A method that takes an integer-type key value and returns the property value, such as the getSubordinate method, or a method that returns an array-type, or a class that implements Iterable. An example is the getAllSubordinates getter method, which returns an array of Employee but could also return an Iterable. In an EPL or event pattern statement, indexed properties are accessed via the property[index] syntax.
Mapped event properties require a getter-method that takes a String-typed key value and returns the property value, such as the getAddress method. In an EPL or event pattern statement, mapped properties are accessed via the property('key') syntax.
Nested event properties require a getter-method that returns the nesting object. The getAddress and getSubordinate methods are mapped and indexed properties that return a nesting object. In an EPL or event pattern statement, nested properties are accessed via the property.nestedProperty syntax.
All event pattern and statements allow the use of indexed, mapped and nested properties (or a combination of these) anywhere where one or more event property names are expected. The below example shows different combinations of indexed, mapped and nested properties in filters of event pattern expressions (each line is a separate statement):
every NewEmployeeEvent(firstName='myName')
every NewEmployeeEvent(address('home').streetName='Park Avenue')
every NewEmployeeEvent(subordinate[0].name='anotherName')
every NewEmployeeEvent(allSubordinates[1].name='thatName')
every NewEmployeeEvent(subordinate[0].address('home').streetName='Water Street')Similarly, the syntax can be used in statements in all places where an event property name is expected, such as in select lists, where-clauses or join criteria.
select firstName, address('work'), subordinate[0].name, subordinate[1].name
from NewEmployeeEvent(address('work').streetName = 'Park Ave')
Property names follows Java standards: the class java.beans.Introspector and method getBeanInfo returns the property names as derived from the name of getter methods. In addition, configuration provides a flag to turn off case-sensitive property names. A sample list of getter methods and property names is:
Table D.1. JavaBeans-Style Getter Methods and Property Names
| Method | Property Name | Example |
|---|---|---|
getPrice() | price | select price from MyEvent |
getNAME() | NAME | select NAME from MyEvent |
getItemDesc() | itemDesc | select itemDesc from MyEvent |
getQ() | q | select q from MyEvent |
getQN() | QN | select QN from MyEvent |
getqn() | qn | select qn from MyEvent |
gets() | s | select s from MyEvent |
When your getter methods or accessor fields return a parameterized type, for example Iterable<MyEventData> for an indexed property or Map<String, MyEventData> for a mapped property, then property expressions may refer to the properties available through the class that is the type parameter.
An example event that has properties that are parameterized types is:
public class NewEmployeeEvent {
public String getName();
public Iterable<EducationHistory> getEducation();
public Map<String, Address> getAddresses();
}A sample of valid property expressions for this event is shown next:
select name, education, education[0].date, addresses('home').street
from NewEmployeeEventA statement may update indexed or mapped properties of an event, provided the event class exposes the required setter method.
The setter method for indexed properties must be named setPropertyName and must take two parameters: the int-type index and the Object type new value.
The setter method for mapped properties must be named setPropertyName and must take two parameters: the String-type map key and the Object type new map value.
The following is an example event that features a setter method for the props mapped property and for the array indexed property:
public class MyEvent {
private Map props = new HashMap();
private Object[] array = new Object[10];
public void setProps(String name, Object value) {
props.put(name, value);
}
public void setArray(int index, Object value) {
array[index] = value;
}
// ... also provide regular JavaBean getters and setters for all propertiesThis sample statement updates mapped and indexed property values:
update istream MyEventStream set props('key') = 'abc', array[2] = 100When registering a class as an event type, Esper will determine the superclasses and interfaces that the class implements and registers event types for superclasses and interfaces using their fully-qualified class name.
Note
When using configuration or create-schema to add event types,
applications should add or create-schema the supertypes and interfaces first, before adding or creating event types for subclasses and interface implementations,
in order to use names other than the fully-qualified class name.
For example, assume there is a class Vehicle and a class Car and Car extends Vehicle. The application
may add event types like this:
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("Vehicle", Vehicle.class);
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("Car", Car.class);
This section provides information for using objects that implement the java.util.Map interface to represent events.
For NEsper .NET also see Section J.9, “.NET IDictionary Events”.
Events can also be represented by objects that implement the java.util.Map interface.
Event properties of Map events are the values in the map accessible through the get method exposed by the java.util.Map interface.
Similar to the Object-array event type, the Map event type takes part in the comprehensive type system that can eliminate the need to use Java classes as event types, thereby making it easier to change types at runtime or generate type information from another source.
A given Map event type can have one or more supertypes that must also be Map event types. All properties available on any of the Map supertypes are available on the type itself. In addition, anywhere within EPL that an event type name of a Map supertype is used, any of its Map subtypes and their subtypes match that expression.
After your application configures a Map event type by providing a type name, the type name can be used when defining further Map or Object-array event types by specifying the type name as a property type or an array property type.
One-to-Many relationships in Map event types are represented via arrays. A property in a Map event type may be an array of primitive, an array of Java object, an array of Map or an an array of Object-array.
The runtime can process java.util.Map events via the sendEventMap(Map map, String eventTypeName) method on the EPEventService interface. Entries in the Map represent event properties. Keys must be of type java.util.String for the compiler to be able to look up event property names specified by statements.
The runtime does not validate Map event property names or values. Your application should ensure that objects passed in as event properties match the create schema property names and types, or the configured event type information when using runtime or static configuration.
Map event properties can be of any type. Map event properties that are Java application objects or that are of type java.util.Map (or arrays thereof) or that are of type Object[] (object-array) (or arrays thereof) offer additional power:
Properties that are Java application objects can be queried via the nested, indexed, mapped and dynamic property syntax as outlined earlier.
Properties that are of type
Mapallow Maps to be nested arbitrarily deep and thus can be used to represent complex domain information. The nested, indexed, mapped and dynamic property syntax can be used to query Maps within Maps and arrays of Maps within Maps.Properties that are of type
Object[](object-array) allow object-arrays to be nested arbitrarily deep. The nested, indexed, mapped and dynamic property syntax can be used to query nested Maps and object-arrays alike.
In order to use Map events, the event type name and property names and types must be made known to the compiler via Configuration or create schema EPL syntax. Please see examples in Section 5.15, “Declaring an Event Type: Create Schema” and Section 17.4.4, “Events Represented by java.util.Map”.
The code snippet below defines a Map event type, creates a Map event and sends the event into the runtime. The sample defines the CarLocUpdateEvent event type via configuration (create schema could have been used instead).
// Define CarLocUpdateEvent event type
Map<String, Object> def = new HashMap<String, Object>;
def.put("carId", String.class);
def.put("direction", int.class);
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("CarLocUpdateEvent", def);
The CarLocUpdateEvent can now be used in a statement:
select carId from CarLocUpdateEvent(direction = 1)#time(1 min)
// Create a CarLocUpdateEvent event and send it into the runtime for processing
Map<String, Object> event = new HashMap<String, Object>();
event.put("carId", carId);
event.put("direction", direction);
runtime.getEventService().sendEventMap(event, "CarLocUpdateEvent");
The runtime can also query Java objects as values in a Map event via the nested property syntax. Thus Map events can be used to
aggregate multiple data structures into a single event and query the composite information in a convenient way. The example below demonstrates a Map event with a transaction and an account object.
Map event = new HashMap();
event.put("txn", txn);
event.put("account", account);
runtime.getEventService().sendEventMap(event, "TxnEvent");An example statement could look as follows.
select account.id, account.rate * txn.amount from TxnEvent#time(60 sec) group by account.id
Your Map event type may declare one or more supertypes when configuring the type.
Supertypes of a Map event type must also be Map event types. All property names and types of a supertype are also available on a subtype and override such same-name properties of the subtype. In addition, anywhere within EPL that an event type name of a Map supertype is used, any of its Map subtypes also matches that expression (similar to the concept of interface in Java).
This example assumes that the BaseUpdate event type has been declared and acts as a supertype to the AccountUpdate event type (both Map event types):
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("AccountUpdate", accountUpdateDef, new String[] {"BaseUpdate"});
Your application statements may select BaseUpdate events and receive both BaseUpdate and AccountUpdate events, as well as any other subtypes of BaseUpdate and their subtypes.
// Receive BaseUpdate and any subtypes including subtypes of subtypes select * from BaseUpdate
Your application Map event type may have multiple supertypes. The multiple inheritance hierarchy between Maps can be arbitrarily deep, however cyclic dependencies are not allowed. If using configuration, supertypes must exist before a subtype to a supertype can be added.
See Section 17.4.4, “Events Represented by java.util.Map” for more information on configuring Map event types.
Strongly-typed nested Map-within-Map events can be used to build rich, type-safe event types on the fly. Use the addEventType method on Configuration or the create schema EPL syntax.
Noteworthy points are:
JavaBean (POJO) objects can appear as properties in
Mapevent types.One may represent Map-within-Map and Map-Array within Map (same for object-array) using the name of a previously registered Map (or object-array) event type.
There is no limit to the number of nesting levels.
Dynamic properties can be used to query
Map-within-Mapkeys that may not be known in advance.The runtime returns a
nullvalue for properties for which the access path into the nested structure cannot be followed where map entries do not exist.
For demonstration, in this example our top-level event type is an AccountUpdate event, which has an UpdatedFieldType structure as a property. Inside the UpdatedFieldType structure the example defines various fields, as well as a property by name 'history' that holds a JavaBean class UpdateHistory to represent the update history for the account. The code snippet to define the event type is thus:
Map<String, Object> updatedFieldDef = new HashMap<String, Object>();
updatedFieldDef.put("name", String.class);
updatedFieldDef.put("addressLine1", String.class);
updatedFieldDef.put("history", UpdateHistory.class);
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("UpdatedFieldType", updatedFieldDef);
Map<String, Object> accountUpdateDef = new HashMap<String, Object>();
accountUpdateDef.put("accountId", long.class);
accountUpdateDef.put("fields", "UpdatedFieldType");
// the latter can also be: accountUpdateDef.put("fields", updatedFieldDef);
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("AccountUpdate", accountUpdateDef);The next code snippet populates a sample event and sends the event into the runtime:
Map<String, Object> updatedField = new HashMap<String, Object>();
updatedField.put("name", "Joe Doe");
updatedField.put("addressLine1", "40 Popular Street");
updatedField.put("history", new UpdateHistory());
Map<String, Object> accountUpdate = new HashMap<String, Object>();
accountUpdate.put("accountId", 10009901);
accountUpdate.put("fields", updatedField);
runtime.getEventService().sendEventMap(accountUpdate, "AccountUpdate");
Last, a sample statement to interrogate AccountUpdate events is as follows:
select accountId, fields.name, fields.addressLine1, fields.history.lastUpdate from AccountUpdate
To model repeated properties within a Map, you may use arrays as properties in a Map. You may use an array of primitive types or an array of JavaBean objects or an array of a previously declared Map or object-array event type.
When using a previously declared Map event type as an array property, the literal [] must be appended after the event type name.
This following example defines a Map event type by name Sale to hold array properties of the various types. It assumes a SalesPerson Java class exists and a Map event type by name OrderItem was declared:
Map<String, Object> sale = new HashMap<String, Object>();
sale.put("userids", int[].class);
sale.put("salesPersons", SalesPerson[].class);
sale.put("items", "OrderItem[]"); // The property type is the name itself appended by []
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("SaleEvent", sale);The three properties that the above example declares are:
An integer array of user ids.
An array of
SalesPersonJava objects.An array of Maps for order items.
The next statement is a sample statement asking for property values held by arrays:
select userids[0], salesPersons[1].name,
items[1], items[1].price.amount from SaleEvent
This section provides information for using Object-array (Object[]) to represent events.
An event can also be represented by an array of objects. Event properties of Object[] events are the array element values.
Similar to the Map event type, the object-array event type takes part in the comprehensive type system that can eliminate the need to use Java classes as event types.
A given Object-array event type can have only a single supertype that must also be an Object-array event type. All properties available on the Object-array supertype is also available on the type itself. In addition, anywhere within EPL that an event type name of an Object-array supertype is used, any of its Object-array subtypes and their subtypes match that expression.
After your application configures an Object-array event type by providing a type name, the type name can be used when defining further Object-array or Map event types by specifying the type name as a property type or an array property type.
One-to-Many relationships in Object-array event types are represented via arrays. A property in an Object-array event type may be an array of primitive, an array of Java object, an array of Map or an array of Object-array.
The runtime can process Object[] events via the sendEventObjectArray(Object[] array, String eventTypeName) method on the EPEventService interface. Entries in the Object array represent event properties.
The runtime does not validate Object array length or value types. Your application must ensure that Object array values match the declaration of the event type: The type and position of property values must match property names and types in the same exact order and object array length must match the number of properties declared via create schema or configuration.
Object-array event properties can be of any type. Object-array event properties that are Java application objects or that are of type java.util.Map (or arrays thereof) or that are of type Object-array (or arrays thereof) offer additional power:
Properties that are Java application objects can be queried via the nested, indexed, mapped and dynamic property syntax as outlined earlier.
Properties that are of type
Object[]allow object-arrays to be nested arbitrarily deep and thus can be used to represent complex domain information. The nested, indexed, mapped and dynamic property syntax can be used to query object-array within object-arrays and arrays of object-arrays within object-arrays.Properties that are of type
Mapallow Maps to be nested in object-array events and arbitrarily deep. The nested, indexed, mapped and dynamic property syntax can be used to query nested Maps and object-arrays alike.
In order to use Object[] (object-array) events, the event type name and property names and types, in a well-defined order that must match object-array event properties, must be made known to the compiler via configuration or create schema EPL syntax. Please see examples in Section 5.15, “Declaring an Event Type: Create Schema” and Section 17.4.5, “Events Represented by Object[] (Object-array)”.
The code snippet below defines an Object-array event type, creates an Object-array event and sends the event into the runtime. The sample defines the CarLocUpdateEvent event type via configuration (create schema could have been used instead).
// Define CarLocUpdateEvent event type (example for configuration API)
String[] propertyNames = {"carId", "direction"}; // order is important
Object[] propertyTypes = {String.class, int.class}; // type order matches name order
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("CarLocUpdateEvent", propertyNames, propertyTypes);
The CarLocUpdateEvent can now be used in a statement:
select carId from CarLocUpdateEvent(direction = 1)#time(1 min)
// Send an event
Object[] event = {carId, direction};
runtime.getEventService().sendEventObjectArray(event, "CarLocUpdateEvent");
The runtime can also query Java objects as values in an Object[] event via the nested property syntax. Thus Object[] events can be used to
aggregate multiple data structures into a single event and query the composite information in a convenient way. The example below demonstrates a Object[] event with a transaction and an account object.
runtime.getEventService().sendEventObjectArray(new Object[] {txn, account}, "TxnEvent");An example statement could look as follows:
select account.id, account.rate * txn.amount from TxnEvent#time(60 sec) group by account.id
Your Object[] (object-array) event type may declare one supertype when configuring the type.
The supertype of a Object[] event type must also be an object-array event type. All property names and types of a supertype are also available on a subtype and override such same-name properties of the subtype. In addition, anywhere within EPL that an event type name of an Object-array supertype is used, any of its Object-array subtypes also matches that expression (similar to the concept of interface or superclass).
The properties provided by the top-most supertype must occur first in the object array. Subtypes each append to the object array. The number of values appended must match the number of properties declared by the subtype.
For example, assume your application declares the following two types:
create objectarray schema SuperType (p0 string)
create objectarray schema SubType (p1 string) inherits SuperType
The object array event objects that your application can send into the runtime are shown by the next code snippet:
runtime.getEventService().sendEventObjectArray(new Object[] {"p0_value", "p1_value"}, "SubType");
runtime.getEventService().sendEventObjectArray(new Object[] {"p0_value"}, "SuperType");
Strongly-typed nested Object[]-within-Object[] events can be used to build rich, type-safe event types on the fly. Use the addEventType method on Configuration or the create schema EPL syntax.
Noteworthy points are:
JavaBean (POJO) objects can appear as properties in
Object[]event types.One may represent Object-array within Object-array and Object-Array-Array within Object-array (same for Map event types) using the name of a previously registered Object-array (or Map) event type.
There is no limit to the number of nesting levels.
Dynamic properties can be used to query
Object[]-within-Object[]values that may not be known in advance.The runtime returns a
nullvalue for properties for which the access path into the nested structure cannot be followed where entries do not exist.
For demonstration, in this example our top-level event type is an AccountUpdate event, which has an UpdatedFieldType structure as a property. Inside the UpdatedFieldType structure the example defines various fields, as well as a property by name 'history' that holds a JavaBean class UpdateHistory to represent the update history for the account. The code snippet to define the event type is thus:
String[] propertyNamesUpdField = {"name", "addressLine1", "history"};
Object[] propertyTypesUpdField = {String.class, String.class, UpdateHistory.class};
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("UpdatedFieldType", propertyNamesUpdField, propertyTypesUpdField);
String[] propertyNamesAccountUpdate = {"accountId", "fields"};
Object[] propertyTypesAccountUpdate = {long.class, "UpdatedFieldType"};
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("AccountUpdate", propertyNamesAccountUpdate, propertyTypesAccountUpdate);The next code snippet populates a sample event and sends the event into the runtime:
Object[] updatedField = {"Joe Doe", "40 Popular Street", new UpdateHistory()};
Object[] accountUpdate = {10009901, updatedField};
runtime.getEventService().sendEventObjectArray(accountUpdate, "AccountUpdate");
Last, a sample statement to interrogate AccountUpdate events is as follows:
select accountId, fields.name, fields.addressLine1, fields.history.lastUpdate from AccountUpdate
To model repeated properties within an Object-array, you may use arrays as properties in an Object-array. You may use an array of primitive types or an array of JavaBean objects or an array of a previously declared Object-array or Map event type.
When using a previously declared Object-array event type as an array property, the literal [] must be appended after the event type name.
This following example defines an Object-array event type by name Sale to hold array properties of the various types. It assumes a SalesPerson Java class exists and an Object-array event type by name OrderItem was declared:
String[] propertyNames = {"userids", "salesPersons", "items"};
Object[] propertyTypes = {int[].class, SalesPerson[].class, "OrderItem[]");
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("SaleEvent", propertyNames, propertyTypes);The three properties that the above example declares are:
An integer array of user ids.
An array of
SalesPersonJava objects.An array of Object-array for order items.
The next statement is a sample statement asking for property values held by arrays:
select userids[0], salesPersons[1].name,
items[1], items[1].price.amount from SaleEventThis section provides information for using JSON to represent events.
An event can be represented by a JSON-formatted string value. Event properties of JSON events are the properties of the JSON object.
The advantages for supporting JSON as an event representation are:
JSON is easy, reliable, and fast and is often used for serializing and transmitting structured data. JSON has bindings for a wide variety of programming languages and platforms and has RPC and file representations.
At time of EPL compilation, the Esper EPL compiler produces a high performance JSON parser for the specific JSON event type, achieving excellent parsing performance.
At time of EPL compilation, the Esper EPL compiler produces an internal representation of the JSON event type properties that supports high read speeds of property values without the need for document traversal, and that is memory-efficient.
Similar to the Map and object-array event type, the JSON event type takes part in the comprehensive type system that can eliminate the need to use Java classes as event types.
The runtime can process string-value events that are formatted JSON documents via the sendEventJson(String json, String jsonEventTypeName) method on the EPEventService interface.
The runtime does not validate JSON events. Your application must ensure that the JSON object matches the declaration of the schema in create json schema.
A given JSON event type can have only a single supertype that must also be a JSON event type. All properties available on the JSON supertype are also available on the type itself. In addition, anywhere within EPL that an event type name of a JSON supertype is used, the JSON subtype and the subtype of the subtype match that expression.
The Esper JSON parser produces an event object that is available to your application. The event object implements the JsonEventObject interface (package com.espertech.esper.common.client.json.util).
The JsonEventObject extends Map<String, Object> allowing you to use event objects that are originating from JSON like any map.
In order to use JSON for incoming events, the event type name and JSON schema, if available, must be made known via the create json schema EPL syntax. Please see examples in Section 5.15, “Declaring an Event Type: Create Schema”.
In the case that you don't want to define fields using EPL create json schema, you may specify an application class that provides the JSON schema. Please refer to Section G.10, “Customizing the JSON Event Class”.
Note
JSON event types must be defined in EPL using
create json schema. JSON event types cannot be pre-configured.If you don't know some or all of the event properties in advance, please follow the instructions in Section G.6, “JSON Dynamic Event Properties”.
The code snippets below define a JSON event type, create a JSON event and send the event into the runtime. The sample defines the CarLocUpdateEvent event type. The @public means the event type
has public visibility and the @buseventtype means your application can use sendEventJson for this event type.
@public @buseventtype create json schema CarLocUpdateEvent(carId string, direction int)
The CarLocUpdateEvent can now be used in a statement:
select count(*) from CarLocUpdateEvent(direction = 1)#time(1 min)
The sample code to send an event is:
String event = "{" +
" \"carId\" : \"A123456\",\n" +
" \"direction\" : 1\n" +
"}";
runtime.getEventService().sendEventJson(event, "CarLocUpdateEvent");JSON allows objects to be nested within other objects. Each JSON object may itself contain further JSON objects or arrays of JSON objects.
For example, consider the following JSON document:
{
"isbn": "123-456-222",
"author":
{
"lastname": "Doe",
"firstname": "Jane"
},
"editor":
{
"lastname": "Smith",
"firstname": "Jane"
},
"title": "The Ultimate Database Study Guide",
"category": ["Non-Fiction", "Technology"]
}
The author and editor objects are nested objects. Please define the schema for nested objects first, and the schemas that are building on the nested schemas thereafter.
Define the schemas as follows:
create json schema Names(lastname string, firstname string); @public @buseventtype create json schema BookEvent(isbn string, author Names, editor Names, title string, category string[]);
This sample EPL outputs the isbn and the last name of the author and the editor, as well as the first category (use sendEventJson(json, "BookEvent") to process the document):
select isbn, author.lastname as authorName, editor.lastname as editorName, category[0] as firstCategory from BookEvent
The next example JSON document is meant to demonstrate nested objects and arrays of objects:
{
"id": "0001",
"type": "donut",
"name": "Cake",
"batters":
{
"machine": "machine A",
"batter":
[
{ "id": "1001", "type": "Regular" },
{ "id": "1002", "type": "Chocolate" },
{ "id": "1003", "type": "Blueberry" },
{ "id": "1004", "type": "Devil's Food" }
]
},
"topping":
[
{ "id": "5001", "type": "None" },
{ "id": "5002", "type": "Glazed" },
{ "id": "5005", "type": "Sugar" },
{ "id": "5007", "type": "Powdered Sugar" }
]
}Define the schemas as follows:
create json schema IdAndType(id string, type string); create json schema Batters(machine string, batter IdAndType[]); @public @buseventtype create json schema CakeEvent(id string, type string, name string, batters Batters, topping IdAndType[]);
The following EPL outputs the name, the batter machine, type of the first batter and the type of the first topping, the count of batters, and the count of toppings of cake events (use sendEventJson(json, "CakeEvent") to process the document):
select name, batters.machine as batterMachine, batters.batter[0].type as firstBatterType, topping[0].type as firstToppingType, batters.batter.countOf() as countBatters, topping.countOf() as countToppings from CakeEvent
The create json schema EPL specifies the name and type of each event property. The create json schema may also specify no event properties or only a subset of all available event properties.
When there are JSON properties that are not known at time of compilation, please see Section G.6, “JSON Dynamic Event Properties”.
The table below shows the supported types and provides links to more information. Types not listed below are not supported for use with a JSON event type.
Table G.1. Support JSON Event Property Types
| Type | More Information |
|---|---|
| Application-provided class | See Section G.5, “JSON Application-Provided Class” |
| bigdecimal, java.math.BigDecimal | Numeric type parsed by new BigDecimal; See Section G.4.1, “Numeric Types” |
| biginteger, java.math.BigInteger | Numeric type parsed by new BigInteger; See Section G.4.1, “Numeric Types” |
| byte, java.lang.Byte | Numeric type parsed by Byte.parseByte; See Section G.4.1, “Numeric Types” |
| boolean, java.lang.Boolean | See Section G.4.2, “Boolean Type” |
| double, java.lang.Double | Numeric type parsed by Double.parseDouble; See Section G.4.1, “Numeric Types” |
| float, java.lang.Float | Numeric type parsed by Float.parseFloat; See Section G.4.1, “Numeric Types” |
| int, java.lang.Integer | Numeric type parsed by Integer.parseInt; See Section G.4.1, “Numeric Types” |
| long, java.lang.Long | Numeric type parsed by Long.parseLong; See Section G.4.1, “Numeric Types” |
| null | No parsing, a value that is always null. |
| short, java.lang.Short | Numeric type parsed by Short.parseShort; See Section G.4.1, “Numeric Types” |
| string, java.lang.String, char, java.lang.Character | See Section G.4.3, “String Type” |
| java.util.Map | Represents any untyped JSON object. See Section G.4.4, “Map Type for Holding an Untyped JSON Object” |
| Object[] | Represents any untyped JSON array. See Section G.4.5, “Object-Array Type for Holding an Untyped JSON Array” |
| Object | Represents any untyped JSON value. See Section G.4.6, “Object Type for Holding an Untyped JSON Value (Any JSON Value)” |
| java.net.URI | As parsed by new URI(...) |
| java.net.URL | As parsed by new URL(...) |
| java.time.LocalDate | As parsed by LocalDate.parse |
| java.time.LocalDateTime | As parsed by LocalDateTime.parse |
| java.time.OffsetDateTime | As parsed by OffsetDateTime.parse |
| java.time.ZonedDateTime | As parsed by ZonedDateTime.parse |
| java.util.UUID | As parsed by UUID.fromString |
The numeric types, the string type, the boolean type and the enumeration class type allow one- and two-dimensional arrays. The Map type does not support arrays and Object does not support two-dimensional arrays.
An example with arrays is the schema create json schema MyEvent(prices bigdecimal[], intmatrix int[][]).
Use [primitive] to instruct the EPL compiler to use array of primitive values, for example create json schema MyEvent(intarray int[primitive]).
The default value for all event properties is null. When the JSON property of the same name is not present in the JSON event document the event property value is null.
The null JSON value is allowed for all types.
The JSON parser uses the respective parse method of the relevant JVM type (see JavaDoc) as listed in the above table, e.g. Integer.parseInt for integer. If the value cannot be parsed it produces an exception.
The parsor allows both numeric and string value JSON text for all numeric types. The event property type is always a boxed type (except for arrays).
To illustrate, assume the following schema:
@public @buseventtype create json schema MyEvent(intValue int)
Here are some sample JSON documents:
Table G.2. Sample JSON Documents With an Integer-Type Value
| Sample JSON | Result |
|---|---|
{ "intValue": 1 } | Event has an intValue value of 1 |
{ "intValue": "2" } | Event has an intValue value of 2 (allows string values) |
{ "intValue": null } | Event has an intValue value of null |
{} | Event has an intValue value of null |
{ "intValue": "some text" } | JSON parser exception |
{ "intValue" : ...anything but above, such as JSON array or JSON object... } | Event has an intValue value of null |
The JSON parser parses true and false, as well as string-type "true" and "false".
The event property type is always Boolean (except for arrays of primitive boolean).
For instance, assume the following schema:
@public @buseventtype create json schema MyEvent(booleanValue boolean)
A few sample JSON documents are listed below.
Table G.3. Sample JSON Documents With a Boolean-Type Value
| Sample JSON | Result |
|---|---|
{ "booleanValue": true } | Event has a booleanValue value of true |
{ "booleanValue": false } | Event has a booleanValue value of false |
{ "booleanValue": "true" } | Event has a booleanValue value of true (allows string 'true') |
{ "booleanValue": "false" } | Event has a booleanValue value of false (allows string 'false') |
{ "booleanValue": null } | Event has a booleanValue value of null |
{} | Event has a booleanValue value of null |
{ "booleanValue": "some text" } | JSON parser exception |
{ "booleanValue" : ...anything but above, such as JSON array or JSON object... } | Event has an booleanValue value of null |
The JSON parser takes any string-type, number-type or boolean-type value. For character-typed values the JSON parser obtains the first character if available.
Let's say the schema is as follows:
@public @buseventtype create json schema MyEvent(stringValue string)
To show the behavior the example JSON is:
Table G.4. Sample JSON Documents With a String-Type Value
| Sample JSON | Result |
|---|---|
{ "stringValue": "abc" } | Event has a stringValue value of "abc" |
{ "stringValue": 1 } | Event has a stringValue value of "1" (allows numbers) |
{ "stringValue": false } | Event has a stringValue value of "false" (allows boolean) |
{ "stringValue": null } | Event has a stringValue value of null |
{} | Event has a stringValue value of null |
{ "stringValue" : ...anything but above, such as JSON array or JSON object... } | Event has an stringValue value of null |
The JSON parser, when it encounters a JSON object for the same name, populates a Map<String, Object> that contains the JSON object properties and their nested values (deep).
The parser ignores any other JSON value type than object.
The Map<String, Object> that the parser produces adheres to the type rules for dynamic properties below.
Define a schema like this one:
@public @buseventtype create json schema MyEvent(jsonObject java.util.Map)
The next table has sample JSON documents.
Table G.5. Sample JSON Documents With a Untyped JSON Object
| Sample JSON | Result |
|---|---|
{ "jsonObject": {} } | Event has a jsonObject value that is an empty map |
{ "jsonObject": { "property-one": 1, "property-two": "abc" }} | Event has a jsonObject map-type value that has two entries: key propertyOne with value 1 (an integer) and key propertyTwo with value abc (a string) |
{ "jsonObject": null } | Event has a jsonObject value of null |
{} | Event has a jsonObject value of null |
{ "jsonObject" : ...anything but an object... } | Event has a jsonObject value of null |
The JSON parser, when it encounters a JSON array for the same name, populates an object-array Object[] that contains the JSON array values and their nested values (deep).
The parser ignores any other JSON value type than array.
The Object[] that the parser produces adheres to the rules for dynamic properties below.
Define a schema like this one:
@public @buseventtype create json schema MyEvent(jsonArray Object[])
The sample JSON documents are listed below.
Table G.6. Sample JSON Documents With an Untyped Array
| Sample JSON | Result |
|---|---|
{ "jsonArray": [] } | Event has a jsonArray value that is an empty array |
{ "jsonArray": [ "value-one", 1 ] } | Event has a jsonArray value object-array Object[]-type value that has two values: The string value-one and the integer 1 |
{ "jsonArray": null } | Event has a jsonArray value of null |
{} | Event has a jsonArray value of null |
{ "jsonArray" : ...anything but an array... } | Event has a jsonArray value of null |
The JSON parser, when it encounters any JSON value for the same name, provides the value as an object Object that contains the JSON value and its nested values (deep).
The Object that the parser produces adheres to the rules for dynamic properties below, e.g. Map<String, Object> for JSON objects, Object[] for JSON arrays
and other object values for the types as listed.
Define a schema like this one:
@public @buseventtype create json schema MyEvent(jsonValue Object)
The JSON documents for example cases are:
Table G.7. Sample JSON Documents with an Untyped Value
| Sample JSON | Result |
|---|---|
{ "jsonValue": {} } | Event has a jsonValue value that is an empty map of type Map<String, Object> |
{ "jsonValue": { "property-one": 1, "property-two": "abc" }} | Event has a jsonValue map-type value that has two entries: key propertyOne with value 1 (an integer) and key propertyTwo with value abc (a string) |
{ "jsonValue": [] } | Event has a jsonValue value that is an empty object-array of type Object[] |
{ "jsonValue": [ "value-one", 1 ] } | Event has a jsonValue object-array Object[]-type value that has two values: The string value-one and the integer 1 |
{ "jsonValue": 1 } | Event has a jsonValue value of 1 (an integer) |
{ "jsonValue": "abc" } | Event has a jsonValue value of abc (a string) |
{ "jsonValue": true } | Event has a jsonValue value of true (a boolean) |
{ "jsonValue": null } | Event has a jsonValue value of null |
{} | Event has a jsonValue value of null |
Your application may provide a class that has public fields and a default constructor. The EPL compiler inspects the class and determines the parser and serialization for the class according to the types listed in Section G.4, “JSON Supported Types” and described herein.
In the case that you don't want to define fields using EPL create json schema, you specify an application class that provides the JSON schema. See Section G.10, “Customizing the JSON Event Class” instead.
To illustrate, the below class has two fields that hold a string-type name and UUID-type id:
public class Person {
public String name;
public UUID id;
}
The schema shown next has a person event property of type Person (below example assumes the class is part of the imports; Or specify the fully-qualified class name).
@public @buseventtype create json schema MyEvent(person Person)
A sample JSON document is:
{
"person": {
"name": "Joe",
"id": "ff362753-b20d-4a9f-9144-93919cb12442"
}
}The JSON parser supports, in addition to all types discussed earlier, the following:
Listof application class or other type. For example:public List<Person> persons.One-dimensional and two-dimensional arrays. For example:
public Person[] personsorpublic Person[][] personMatrix.For customizing parsing of strings see Section G.9, “Customizing JSON Serializing and Deserializing”.
The JSON parser takes the JSON value and invokes the valueOf method of the enum class, allowing string and number values and returning null for JSON boolean, array or object values.
Let's say the schema is as follows:
@public @buseventtype create json schema MyEvent(enumValue my.company.package.EnumClass)
To show the behavior the example JSON is:
Table G.8. Sample JSON Documents With a Enum-Type Value
| Sample JSON | Result |
|---|---|
{ "enumValue": "enum_1" } | Event has an enumValue value that is EnumClass.valueOf("enum_1") |
{ "enumValue": null } | Event has an enumValue value of null |
{ "enumValue": 1} | Event has an enumValue value that is EnumClass.valueOf("1") |
{ "enumValue": false} | Event has an enumValue value of null |
{} | Event has an enumValue value of null |
{ "enumValue" : ...anything but a value... } | Event has an enumValue value of null |
The event properties that are known in advance can be listed as part of create json schema. Since the name and type is known the EPL compiler can verify EPL statements that use the predefined properties in expressions.
See Section G.4, “JSON Supported Types”.
Event properties for which the property name is known but the type is not known can be defined as one of the untyped types Object (for any JSON value), Object[] (for any JSON array) or Map (for any JSON object) which will provide nested values, arrays and objects; As for instance described at Section G.4.6, “Object Type for Holding an Untyped JSON Value (Any JSON Value)”.
Note
By default, the JSON parser discards JSON properties whose property name does not match a property name in create schema.
You must use the @JsonSchema(dynamic=true) to instruct the EPL compiler to not discard JSON properties.
Add @JsonSchema(dynamic=true) to create schema so that the JSON parser parses and the event object keeps all properties available in the JSON document.
The EPL dynamic properties allow using properties in expressions that are not predefined. Please refer to Section 3.3, “Dynamic Event Properties”.
The dynamic JSON properties are also available in the JsonEventObject event object for use by application code.
The following table outlines the object type for each JSON value:
Table G.9. JSON Value Types to Object Type Mapping
| JSON Value Type | Object Type |
|---|---|
| JSON String | String |
| JSON Number | Integer value returned by Integer.parseInt or the double value returned by Double.parseDouble |
| JSON Boolean | Boolean |
| JSON Null | null |
| JSON Object | Map<String, Object> |
| JSON Array | Object[] |
The next EPL creates an empty schema for sensor events:
@JsonSchema(dynamic=true) @public @buseventtype create json schema SensorEvent()
The sample JSON document is (use sendEventJson(json, "SensorEvent") to process the document):
{
"entityID":"cd9f930e",
"temperature" : 70,
"status" : true,
"entityName":{
"english":"Cooling Water Temperature"
},
"vt":["2014-08-20T15:30:23.524Z"],
"flags" : null
}You can use dynamic properties to query the events. Specifically here is EPL to retrieve the properties:
select entityID? as entityId, temperature? as temperature, status? as status,
entityName? as entityName, vt? as vt, flags? as flags from SensorEventThe output event for this example is:
Table G.10. Empty JSON Schema Sample Output Event
| Name | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
| entityId | String | "cd9f930e" |
| temperature | Integer | 70 |
| status | Boolean | true |
| entityName | map | Map<String, Object> containing a single entry for key english and string-type value Cooling Water Temperature |
| vt | Object[] | Array with a single string-type value 2014-08-20T15:30:23.524Z |
| flags | null | null |
Use the dot ('.') to obtain the value of nested dynamic properties. For example:
select entityName?.english as englishEntityName from SensorEvent
Use select * to obtain the JsonEventObject object itself (use getUnderlying() for listeners receiving EventBean). For example:
select * as englishEntityName from SensorEvent
You may use @JsonSchema(dynamic=true) together with predefined properties. For example:
@JsonSchema(dynamic=true) @public @buseventtype create json schema SensorEvent(entityID string)
Esper provides an API to parse the JSON text without processing the event. This is done by following these steps:
Define the event type schema or schemas. The event type must have public visibility and bus event type visibility.
Obtain an
EventSenderJsoninstance for the event type.Invoke the
parsemethod on the sender, which returns the populated event object.
For instance, the below EPL declares the CarLocUpdateEvent event type:
@public @buseventtype create json schema CarLocUpdateEvent(carId string, direction int)
Obtain the EventSenderJson like so:
EventSenderJson sender = (EventSenderJson) runtime.getEventService().getEventSender("CarLocUpdateEvent");
The parse method returns the populated event object.
JsonEventObject eventObject = sender.parse(json);
The returned object implements the JsonEventObject interface which extends Map<String, Object>. The interface provides additional methods for writing JSON. Please see the JavaDoc for more information.
Esper includes a shaded copy of the MinimalJson library in package com.espertech.esper.common.client.json.minimaljson (MIT license, see https://github.com/ralfstx/minimal-json/blob/master/LICENSE).
MinimalJson provides the base parser. The Esper EPL compiler generates a specific JSON parser class that internally uses MinimalJson.
MinimalJson allows your application to build JSON text using the API. Please consult the JavaDoc for more information. A short example is provided below:
JsonObject jsonObject = new JsonObject().add("carId", "A123456").add("direction", 1);
String json = jsonObject.toString();
Use the @JsonSchemaField annotation to customize how the runtime deserializes (parses from JSON) a given event property and serializes (writes as JSON) a given event property.
The @JsonSchemaField annotation can be used with create json schema and also applies to @EventRepresentation('json') for use with insert into or create window.
The name value of @JsonSchemaField provides the event property name. The adapter property provides the class name of the class that implements the JsonFieldAdapterString interface.
The adapter class must have a default constructor and must implement the T parse(String value) and void write(T value, JsonWriter writer) throws IOException methods.
Note
The adapter implementation must be thread-safe and the runtime may reuse the same adapter instance.
Assume a JSON document that has a date-type field formatted as dd-M-yyyy. The sample JSON schema is below. Assume that the MyDateJSONParser class was added to imports.
You may specify the fully-qualified class name instead, i.e. adapter='com.mycompany.MyDateJSONParser'.
Here is the sample EPL:
@JsonSchemaField(name=myDate, adapter=MyDateJSONParser) create json schema JsonEvent(myDate Date)
A basic JSON document is:
{"myDate" : "22-09-2018"}The class below is a sample parser and writer for date values:
public class MyDateJSONParser implements JsonFieldAdapterString<Date> {
public Date parse(String value) {
try {
return value == null ? null : new SimpleDateFormat("dd-M-yyyy").parse(value);
} catch (ParseException e) {
throw new EPException("Failed to parse: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
public void write(Date value, JsonWriter writer) throws IOException {
if (value == null) {
writer.writeLiteral("null");
return;
}
writer.writeString(new SimpleDateFormat("dd-M-yyyy").format(value));
}
}
Instead of providing event property names and types as part of EPL create json schema, you may specify an application class that provides public fields instead.
You must provide the class name in the classname annotation value of the JsonSchema annotation.
Assume there is a predefined person event class that has two fields that hold a string-type name and UUID-type id:
public class PersonEvent {
public String name;
public UUID id;
}
This example declares the JSON person event to point to the PersonEvent as the event object (below example assumes the class is part of the imports; Or specify the fully-qualified class name).
@public @buseventtype @JsonSchema(className='PersonEvent') create json schema JSONPersonEvent()
A sample JSON document is:
{
"name": "Joe",
"id": "ff362753-b20d-4a9f-9144-93919cb12442"
}Please also see Section G.5, “JSON Application-Provided Class” for application class support and Section G.4, “JSON Supported Types” for type information.
By specifying an application class, you may not:
Define additional fields for the schema that don't have the same name and type as provided by the application class.
Define a supertype for the event type.
Use the
dynamicflag.
The following limitations apply:
A JSON event bean cannot contain
EventBeaninstances.While the EPL compiler performs best-effort assignment checking and widening, it does not actually itself verify that the JSON contains valid data, for both production of JSON and consumption of JSON.
There is no API that maps a JSON document to your own application class. For that task please consider using Jackson (
https://github.com/FasterXML/jackson) or Gson (https://github.com/google/gson).The JSON parser, when encountering duplicate property names, uses the last value as the final value.
This section provides information for using Avro to represent events.
An event can be represented by an Avro GenericData.Record instance. Event properties of Avro events are the field values of a GenericData.Record. The top level schema must always be a record.
The advantages for supporting Avro as an event representation are:
Avro has excellent support for JSON, allowing JSON for incoming and outgoing events, while not compromising on type-safety since Avro provides a schema.
Avro has rich, extensible, standardized schema language defined in pure JSON; event types / schemas can be defined/imported/exported with EPL or from external sources.
Avro offers a compact binary representation and is thus efficient and fast for use with EsperHA persistence or for input/output in wire transfer.
Avro has a compact event representation reducing memory use, as each event is only a schema-reference and an Object[] (see GenericData.Record).
JSON itself is not memory efficient while Avro is: JSON repeats every field name with every single record and JSON alone is inefficient for high-volume usage.
Avro allows fast access to event properties since reading an event property value only requires reading the GenericData.Record-internal object-array at a given index.
Avro has bindings for a wide variety of programming languages and platforms and has RPC and file representations.
Avro does not require code generation so EPL can be written generically for any data stream. Type information can be made available at runtime while still providing type-safety. There is no need to generate code, therefore there is no need to manage generated classes, or to reload classes or to restart the process to reload classes.
Avro has the notion of schema compatibility for evolving your event data over time.
Similar to the Map and object-array event type, the Avro event type takes part in the comprehensive type system that can eliminate the need to use Java classes as event types.
The runtime can process Avro's GenericData.Record events via the sendEventAvro(Object avroGenericDataDotRecord, String avroEventTypeName) method on the EPEventService interface.
The runtime does not validate Avro events. Your application must ensure that Avro values match the declaration of the schema and that the schema of the event matches the schema declared for the event type of the event.
A given Avro event type can have only a single supertype that must also be an Avro event type. All properties available on the Avro supertype is also available on the type itself. In addition, anywhere within EPL that an event type name of an Avro supertype is used, the Avro subtype and the subtype of the subtype match that expression. Note that access to properties is by field position thereby subtype and supertype field positions should be congruent.
In order to use Avro for incoming events, the event type name and Avro schema must be made known via configuration or create avro schema EPL syntax. Please see examples in Section 5.15, “Declaring an Event Type: Create Schema” and Section 17.4.7, “Events Represented by Avro GenericData.Record”.
The code snippet below defines an Avro event type, creates an Avro event and sends the event into the runtime. The sample defines the CarLocUpdateEvent event type via the configuration (create schema could have been used instead).
// Define CarLocUpdateEvent event type
Schema schema = record("CarLocUpdateEvent").fields()
.name("carId").type().stringBuilder().prop(PROP_JAVA_STRING_KEY, PROP_JAVA_STRING_VALUE).endString().noDefault()
.requiredInt("direction")
.endRecord();
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
ConfigurationCommonEventTypeAvro avroEvent = new ConfigurationCommonEventTypeAvro(schema);
configuration.getCommon().addEventTypeAvro("CarLocUpdateEvent", avroEvent);
The CarLocUpdateEvent can now be used in a statement:
select count(*) from CarLocUpdateEvent(direction = 1)#time(1 min)
The sample code to send an event is:
GenericData.Record event = new GenericData.Record(schema);
event.put("carId", "A123456");
event.put("direction", 1);
runtime.getEventService().sendEventAvro(event, "CarLocUpdateEvent");
Use the @EventRepresentation(avro) annotation to obtain Avro output events.
Avro schemas can contain further Avro schemas. The compiler and runtime track nested schema based on the schema name. The compiler and runtime implicitly register an event type for each schema using the schema name, for nested simple and indexed properties. Therefore the compiler and runtime require schema names to match the initially-registered schema of the same name.
For example, the schema:
{
"type" : "record",
"name" : "MyEvent",
"fields" : [ {
"name" : "nested",
"type" : {
"type" : "record",
"name" : "MyNestedEvent",
"fields" : [ {
"name" : "value",
"type" : "int"
} ]
}
} ]
}
For the above schema, upon registration of the schema as an event type, the compiler or runtime creates an event type MyNestedEvent and associates it to the MyNestedEvent schema.
Upon registering an Avro event type, the compiler and runtime determine property names and property types. The Avro record field schema determines the property type.
The table below describes Avro field schema to property type mapping:
Table H.1. Avro Field Schema to Property Type Mapping
| Schema | Property Type |
|---|---|
"int" (Schema.Type.INT) | int |
"long" (Schema.Type.LONG) | long |
"double" (Schema.Type.DOUBLE) | double |
"float" (Schema.Type.FLOAT) | float |
"boolean" (Schema.Type.BOOLEAN) | boolean |
"bytes" (Schema.Type.BYTES) | ByteBuffer |
"null" (Schema.Type.NULL) | null |
"string" (Schema.Type.STRING) |
If the field has the property |
"union" (Schema.Type.UNION) | See below. |
"array" (Schema.Type.ARRAY) | java.util.Collection |
"map" (Schema.Type.MAP) | java.util.Map |
"record" (Schema.Type.RECORD) | GenericData.Record |
"fixed" (Schema.Type.FIXED) | GenericFixed |
"enum" (Schema.Type.ENUM) | GenericEnumSymbol |
For unions:
If the union contains
nulland any of the primitive types, the property type is the boxed type. For exampleunionOf().nullType().and().intType().endUnion()isInteger.class.If the union contains
nulland numeric types only, the property type isNumber.class. For exampleunionOf().longType().and().intType().endUnion()isNumber.class.Otherwise the property type is
Object.class.
This section lists for each JVM type the default Avro schema that the compiler and runtime uses when assembling an Avro schema from a select-clause.
For example, consider the following statement. The statement assumes that MyEvent is a pre-registered event type of any kind (Map, Avro, Object-Array, POJO etc.):
@EventRepresentation(avro) select 1 as carId, 'abc' as carType from MyEvent
Your application may obtain the schema for the statement output event type as follows:
String epl = "@EventRepresentation(avro) select 1 as carId, 'abc' as carType from MyEvent"; Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); configuration.getCommon().addEventType(MyEvent.class); CompilerArguments compilerArguments = new CompilerArguments(configuration); EPCompiled compiled = EPCompilerProvider.getCompiler().compile(epl, compilerArguments); EPDeployment deployment = EPRuntimeProvider.getDefaultRuntime().getDeploymentService().deploy(compiled).getStatements[0]; Schema schema = (Schema) ((AvroSchemaEventType) stmt.getEventType()).getSchema();
The compiler generates an Avro schema based on the expressions in the select-clause. The schema in pretty-print may look like this:
{
"type" : "record",
"name" : "anonymous_1_result_",
"fields" : [ {
"name" : "carId",
"type" : "int"
}, {
"name" : "carType",
"type" : {
"type" : "string",
"avro.java.string" : "String"
}
} ]
}Please consult Section 17.4.9.2, “Avro Settings” for details on controlling default mapping. Tables below outline the default mapping and provide alternative schemas depending on the avro settings .
By default the compiler maps expression result types to Avro schema using non-null schema types.
By default, for String-type values, the compiler sets the avro.java.string property to String to ensure that Avro uses java.lang.String to represent strings (and not org.apache.avro.util.Utf8).
The tables below outline the default mapping and provide alternative schemas, which apply according to Avro settings.
The mapping from primitive and string type to Avro schema is:
Table H.2. Primitive Data Type and String Mapping
| Type | Default Schema | Alternative Schemas |
|---|---|---|
| byte | "int" | N/A |
| java.lang.Byte | "int" | ["null","int"] |
| boolean | "boolean" | N/A |
| java.lang.Boolean | "boolean" | ["null","boolean"] |
| double | "double" | N/A |
| java.lang.Double | "double" | ["null","double"] |
| float | "float" | N/A |
| java.lang.Float | "float" | ["null","float"] |
| int | "int" | N/A |
| java.lang.Integer | "int" | ["null","int"] |
| long | "long" | N/A |
| java.lang.Long | "long" | ["null","long"] |
| null | "null" | N/A |
| java.lang.String and java.lang.CharSequence | {"type":"string","avro.java.string":"String"} | "string"or ["null","string"]or ["null",{"type":"string","avro.java.string":"String"}] |
The mapping from array-type to Avro schema is:
Table H.3. Array Type Mapping
| Type | Default Schema | Alternative Schemas |
|---|---|---|
| byte[] | "bytes" | ["null","bytes"] |
| Byte[] | {"type":"array","items":["null","int"]} | ["null",{"type":"array","items":["null","int"]}] |
| boolean[] | {"type":"array","items":"boolean"} | ["null",{"type":"array","items":"boolean"}] |
| Boolean[] | {"type":"array","items":["null","boolean"]} | ["null",{"type":"array","items":["null","boolean"]}] |
| double[] | {"type":"array","items":"double"} | ["null",{"type":"array","items":"double"}] |
| Double[] | {"type":"array","items":["null","double"]} | ["null",{"type":"array","items":["null","double"]}] |
| float[] | {"type":"array","items":"float"} | ["null",{"type":"array","items":"float"}] |
| Float[] | {"type":"array","items":["null","float"]} | ["null",{"type":"array","items":["null","float"]}] |
| int[] | {"type":"array","items":"int"} | ["null",{"type":"array","items":"int"}] |
| Integer[] | {"type":"array","items":["null","int"]} | ["null",{"type":"array","items":["null","int"]}] |
| long[] | {"type":"array","items":"long"} | ["null",{"type":"array","items":"long"}] |
| Long[] | {"type":"array","items":["null","long"]} | ["null",{"type":"array","items":["null","long"]}] |
| java.lang.String[] and java.lang.CharSequence[] | {"type":"array","items":{"type":"string","avro.java.string":"String"}} | ["null",{"type":"array","items":{"type":"string","avro.java.string":"String"}}] or {"type":"array","items":"string"} (or the combination) |
Additional mappings to Avro schema are:
Table H.4. Additional Mapping
| Type | Default Schema | Alternative Schemas |
|---|---|---|
java.util.Map interface implementation | {"type":"map","values":{"type":"string","avro.java.string":"String"}} | ["null",{"type":"map","values":{"type":"string","avro.java.string":"String"}}] |
EPL provides the @AvroSchemaField annotation to assign a schema to a given property. The annotation requires the name attribute for the property name and the schema attributed for the Avro schema text.
The schema provided via @AvroSchemaField for a given property replaces the Avro schema that is otherwise assigned according to the above mapping.
The annotation can be used with create-schema or with @EventRepresentation(avro).
In this example the carId property is a union of int-type and string-type.
@AvroSchemaField(name='carId',schema='["int","string"]') create avro schema MyEvent(carId object)
The compiler determines the property type from the Avro field schema according to the rules listed above.
In the default configuration only the primitive data types and the abovementioned classes have a corresponding Avro schema. When the compiler encounters a class for which is does not know the Avro schema that is should use, it fails the statement compile.
For example, the below EPL is invalid:
// Invalid since LocalDateTime has no equivalent Avro schema (by default) create avro schema MyEvent(ldt as java.time.LocalDateTime)
Instead of using @AvroSchemaField your application can configure a type-representation mapper class that can return the Avro schema to use.
For configuration information please see Section 17.4.9.2, “Avro Settings” and the JavaDoc.
Your application can implement the com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.TypeRepresentationMapper interface. The compiler and runtime invoke the provided mapper to determine the Avro schema for a given field.
For example, the following type mapper implementation maps LocalDateTime to the Avro string type.
public class MyTypeRepresentationMapper implements TypeRepresentationMapper {
public Object map(TypeRepresentationMapperContext context) {
if (context.getClazz() == LocalDateTime.class) {
return builder().stringBuilder().endString();
}
return null;
}
}The compiler can automatically widen and assign values to Avro fields. In the case when your application requires a custom logic to convert, widen, coerce or transform a value before assigment to an Avro field, please use the mechanism below.
Your application can implement the com.espertech.esper.common.client.hook.ObjectValueTypeWidenerFactory interface. The compiler invokes the provided factory to determine a widener for values.
For example, the factory implementation below returns a type widener that converts LocalDateTime instances to Avro string-type values by using the date-time formatter:
public static class MyObjectValueTypeWidenerFactory implements ObjectValueTypeWidenerFactory {
public TypeWidener make(ObjectValueTypeWidenerFactoryContext context) {
if (context.getClazz() == LocalDateTime.class) {
return new TypeWidener() {
public Object widen(Object input) {
LocalDateTime ldt = (LocalDateTime) input;
return DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME.format(ldt);
}
};
}
return null;
}
}To obtain the Avro schema for a given event type, use:
public static Schema getAvroSchema(EventType eventType) {
return (Schema) ((AvroSchemaEventType) eventType).getSchema();
}To obtain the Avro schema for a registered event type, you may use:
public static Schema getAvroSchema(EPRuntime runtime, String eventTypeName) {
return getAvroSchema(runtime.getEventTypeService().getEventType(eventTypeName));
}To obtain the Avro schema for a given event, you may use:
public static Schema getAvroSchema(EventBean event) {
return getAvroSchema(event.getEventType());
}
To obtain the GenericData.Record for a given event, you may use:
public static Schema getAvroRecord(EventBean event) {
return (GenericData.Record) event.getUnderlying();
}The following limitations apply:
An Avro
GenericData.Recordcannot containEventBeaninstances.There is no implicit translation from other event representations to Avro schemas.
While the compiler performs best-effort assignment checking and widening, it does not actually itself verify that the
GenericData.Recordcontains valid data, for both production ofGenericData.Recordand consumption ofGenericData.Record.
This section provides information for using org.w3c.dom.Node XML to represent events.
For NEsper .NET also see Section J.10, “.NET XML Events”.
Events can be represented as org.w3c.dom.Node instances and send into the runtime via the sendEventXMLDOM method on EPEventService or via EventSender. Please note that either configuration or create xml schema with annotations are required so the event type name and root element name is known. See Section 17.4.8, “Events Represented by org.w3c.dom.Node”.
If a XML schema document (XSD file) can be made available as part of the configuration or as part of create xml schema, then the compiler and runtime can read the schema and appropriately present event type metadata and validate statements that use the event type and its properties. See Section I.2, “Schema-Provided XML Events”.
When no XML schema document is provided, XML events can still be queried, however the return type and return values of property expressions are string-only and no event type metadata is available other than for explicitly configured properties. See Section I.3, “No-Schema-Provided XML Events”.
In all cases the compiler and runtime allow you to configure explicit XPath expressions as event properties. You can specify arbitrary XPath functions or expressions and provide a property name and type by which result values will be available for use in statements. See Section I.4, “Explicitly-Configured Properties”.
Nested, mapped and indexed event properties are also supported in expressions against org.w3c.dom.Node events. Thus XML trees can conveniently be interrogated via the property expression syntax.
Only one event type per root element name may be configured.
This section uses the following XML document as an example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Sensor xmlns="SensorSchema">
<ID>urn:epc:1:4.16.36</ID>
<Observation Command="READ_PALLET_TAGS_ONLY">
<ID>00000001</ID>
<Tag>
<ID>urn:epc:1:2.24.400</ID>
</Tag>
<Tag>
<ID>urn:epc:1:2.24.401</ID>
</Tag>
</Observation>
</Sensor>The schema for the example is:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<xs:element name="Sensor">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="ID" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element ref="Observation" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Observation">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="ID" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element ref="Tag" maxOccurs="unbounded" />
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="Command" type="xs:string" use="required" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Tag">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="ID" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>If you have a XSD schema document available for your XML events, the compiler and runtime can interrogate the schema. The benefits are:
New statements that refer to event properties are validated against the types provided in the schema.
Event type metadata becomes available for retrieval as part of the
EventTypeinterface.
The compiler reads a XSD schema file from an URL you provide. Make sure files imported by the XSD schema file can also be resolved.
Note
Include
esper-common-xmlxsd-version.jarand the Apache Xerces2 Java jar filexercesImpl-xerces2version.jarin the classpath (and thexml-apisjar file when using Java 8).Set the
enable-XMLXSDflag in event type meta configuration as described in Section 17.4.9.3, “XML XSD Schema Settings”.
The configuration and create xml schema accept a schema URL. This is a sample code snippet to determine a schema URL from a file in classpath:
URL schemaURL = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("sensor.xsd");
// For NEsper .NET use C# ResourceManager class for loading resourcesHere is a sample use of the configuration API, please see Chapter 17, Configuration for further examples.
ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM sensorcfg = new ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM();
sensorcfg.setRootElementName("Sensor");
sensorcfg.setSchemaResource(schemaURL.toString());
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("SensorEvent", sensorcfg);
Here is a sample use of create xml schema.
@XMLSchema(rootElementName='Sensor', schemaResource='some url value here') create xml schema SensorEvent()
There does not need to be a root element name. The sendEventXMLDOM(org.w3c.Node node, String eventTypeName) method accepts the event type name. An EventSender is a useful alternative method
for sending events if the type lookup based on the root or document element name is not desired.
After adding the event type, you may create statements and send events. Next is a sample statement:
select ID, Observation.Command, Observation.ID, Observation.Tag[0].ID, Observation.Tag[1].ID from SensorEvent
As you can see from the example above, property expressions can query property values held in the XML document's elements and attributes.
There are multiple ways to obtain a XML DOM document instance from a XML string. The next code snippet shows how to obtain a XML DOM org.w3c.Document instance:
InputSource source = new InputSource(new StringReader(xml)); DocumentBuilderFactory builderFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance(); builderFactory.setNamespaceAware(true); Document doc = builderFactory.newDocumentBuilder().parse(source);
Send the org.w3c.Node or Document object into the runtime for processing:
runtime.getEventService().sendEventXMLDOM(doc, "SensorEvent");
By default, property expressions such as Observation.Tag[0].ID are evaluated by a fast DOM-walker implementation provided by EPL. This DOM-walker implementation is not namespace-aware.
Should you require namespace-aware traversal of the DOM document, you must set the xpath-property-expr configuration option to true (default is false). This flag causes the compiler and runtime to generate namespace-aware XPath
expressions from each property expression instead of the DOM-walker, as described next. Setting the xpath-property-expr option to true requires that you also configure namespace prefixes as described below.
When matching up the property names with the XSD schema information, the compiler determines whether the attribute or element provides values. The algorithm checks attribute names first followed by element names. It takes the first match to the specified property name.
By setting the xpath-property-expr option the compiler rewrites each property expression as an XPath expression, effectively handing the evaluation over to the underlying XPath implementation
available from classpath. Most JVM have a built-in XPath implementation and there are also optimized, fast implementations such as Jaxen that can be used as well.
Set the xpath-property-expr option if you need namespace-aware document traversal, such as when your schema mixes several namespaces and element names are overlapping.
The below table samples several property expressions and the XPath expression generated for each, without namespace prefixes to keep the example simple:
Table I.1. Property Expression to XPath Expression
| Property Expression | Equivalent XPath |
|---|---|
Observeration.ID | /Sensor/Observation/ID |
Observeration.Command | /Sensor/Observation/@Command |
Observeration.Tag[0].ID | /Sensor/Observation/Tag[position() = 1]/ID |
For mapped properties that are specified via the syntax name('key'), the algorithm looks for an attribute by name id and generates a XPath expression as mapped[@id='key'].
Finally, here is an example that includes all different types of properties and their XPath expression equivalent in one property expression:
select nested.mapped('key').indexed[1].attribute from MyEvent
The equivalent XPath expression follows, this time including n0 as a sample namespace prefix:
/n0:rootelement/n0:nested/n0:mapped[@id='key']/n0:indexed[position() = 2]/@attribute
All elements that are unbound or have max occurs greater then 1 in the XSD schema are represented as indexed properties and require an index for resolution.
For example, the following is not a valid property expression in the sample Sensor document: Observeration.Tag.ID. As no index is provided for Tag, the property expression is not valid.
Repeated elements within a parent element in which the repeated element is a simple type also are represented as an array.
Consider the next XML document:
<item> <book sku="8800090"> <author>Isaac Asimov</author> <author>Robert A Heinlein</author> </book> </item>
Here, the result of the expression book.author is an array of type String and the result of book.author[0] is a String value.
Dynamic properties are not validated against the XSD schema information and their result value is always org.w3c.Node. You may use a user-defined function to process dynamic properties returning Node. As an alternative consider using an explicit property.
An example dynamic property is Origin?.ID which will look for an element by name Origin that contains an element or attribute node by name LocationCode:
select Origin?.LocationCode from SensorEvent
When providing a XSD document, the default configuration allows to transpose property values that are themselves complex elements, as defined in the XSD schema, into a new stream. This behavior can be controlled via the flag auto-fragment.
For example, consider the next statement:
insert into ObservationStream select ID, Observation from SensorEvent
The Observation as a property of the SensorEvent gets itself inserted into a new stream by name ObservationStream. The ObservationStream
thus consists of a string-typed ID property and a complex-typed property named Observation, as described in the schema.
A further statement can use this stream to query:
select Observation.Command, Observation.Tag[0].ID from ObservationStream
Before continuing the discussion, here is an alternative syntax using the wildcard-select, that is also useful:
insert into TagListStream select ID as sensorId, Observation.* from SensorEvent
The new TagListStream has a string-typed ID and Command property as well as an array of Tag properties that are complex types themselves as defined in the schema.
Next is a sample statement to query the new stream:
select sensorId, Command, Tag[0].ID from TagListStream
Please note the following limitations:
The XPath standard prescribes that XPath expressions against
org.w3c.Nodeare evaluated against the owner document of theNode. Therefore XPath is not relative to the current node but absolute against each node's owner document. Since the compiler and runtime do not create new document instances for transposed nodes, transposing properties is not possible when thexpath-property-exprflag is set.Complex elements that have both simple element values and complex child elements are not transposed. This is to ensure their property value is not hidden. Use an explicit XPath expression to transpose such properties.
EPL automatically registers a new event type for transposed properties. It generates the type name of the new XML event type from the XML event type name and the property names used in the expression. The synposis is type_name.property_name[.property_name...]. The type name can be looked up, for example for use with EventSender or can be created in advance.
An EventSender sends events into the runtime for a given type, saving a type lookup based on element name.
This brief example sends an event via EventSender:
EventSender sender = epRuntime.getEventSender("SensorEvent");
sender.sendEvent(node);
The XML DOM event sender checks the root element name before processing the event. Use the event-sender-validates-root setting to disable validation. This forces the runtime to process XML documents according to any predefined type without validation of the root element name.
The compiler schema interrogation is based on the Xerces distribution packaged into Sun Java runtimes. Your application may not replace the JRE's Xerces version and use XML schemas, unless your application sets the DOM implementation registry as shown below before loading the configuration:
System.setProperty(DOMImplementationRegistry.PROPERTY, "com.sun.org.apache.xerces.internal.dom.DOMXSImplementationSourceImpl");
Without a schema document a XML event may still be queried. However there are important differences in the metadata available without a schema document and therefore the property expression results. These differences are outlined below.
All property expressions against a XML type without schema are assumed valid. There is no validation of the property expression other than syntax validation. At runtime, property expressions return string-type values or null if the expression did not
yield a matching element or attribute result.
When asked for property names or property metadata, a no-schema type returns empty array.
In all other aspects the type behaves the same as the schema-provided type described earlier.
Regardless of whether or not you provide a XSD schema for the XML event type, you can always fall back to configuring explicit properties that are backed by XPath expressions.
For further documentation on XPath, please consult the XPath standard or other online material. Consider using Jaxen or Apache Axiom, for example, to provide faster XPath evaluation then your Java VM built-in XPath provider may offer.
Shown below is an example configuration that adds an explicit property backed by a XPath expression and that defines namespace prefixes:
ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM sensorcfg = new ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM();
sensorcfg.addXPathProperty("countTags", "count(/ss:Sensor/ss:Observation/ss:Tag)",
XPathConstants.NUMBER);
sensorcfg.addNamespacePrefix("ss", "SensorSchema");
sensorcfg.setRootElementName("Sensor");
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("SensorEvent", sensorcfg);
Shown below is an example create xml schema:
@XMLSchema(rootElementName='Sensor') @XMLSchemaField(name='countTags', xpath='count(/ss:Sensor/ss:Observation/ss:Tag', type='number') @XMLSchemaNamespacePrefix(prefix='ss', namespace='SensorSchema') create xml schema SensorEvent();
The countTags property is now available for querying:
select countTags from SensorEvent
The XPath expression count(...) is a XPath built-in function that counts the number of nodes, for the example document the result is 2.
The compiler and runtime can parse or cast the result of your XPath expression to the desired type. Your property configuration provides the type to cast to, like this:
sensorcfg.addXPathProperty("countTags", "count(/ss:Sensor/ss:Observation/ss:Tag)",
XPathConstants.NUMBER, "int");
The type supplied to the property configuration must be one of the built-in types. Arrays of built-in type are also possible, requiring the XPathConstants.NODESET type returned by your XPath expression, as follows:
sensorcfg.addXPathProperty("idarray", "//ss:Tag/ss:ID",
XPathConstants.NODESET, "String[]");
This EPL snippet is the equivalent of above for use with create xml schema:
@XMLSchemaField(name='countTags', xpath='count(/ss:Sensor/ss:Observation/ss:Tag)', type='number', castToType='int') @XMLSchemaField(name='idarray', xpath='//ss:Tag/ss:ID)', type='nodeset', castToType='string[]')
The XPath expression //ss:Tag/ss:ID returns all ID nodes under a Tag node, regardless of where in the node tree the element is located. For the example document the result is 2 array elements urn:epc:1:2.24.400 and urn:epc:1:2.24.40.
An explicit property may return XPathConstants.NODE or XPathConstants.NODESET and can provide the event type name of a pre-configured event type for the property. The method name to add such properties is addXPathPropertyFragment.
This code snippet adds two explicit properties and assigns an event type name for each property:
sensorcfg.addXPathPropertyFragment("tagOne", "//ss:Tag[position() = 1]",
XPathConstants.NODE, "TagEvent");
sensorcfg.addXPathPropertyFragment("tagArray", "//ss:Tag",
XPathConstants.NODESET, "TagEvent");
This EPL snippet is the equivalent of above for use with create xml schema:
@XMLSchemaField(name='tagOne', xpath='//ss:Tag[position() = 1]', type='node', eventTypeName='TagEvent') @XMLSchemaField(name='tagArray', xpath='//ss:Tag', type='nodeset', eventTypeName='TagEvent')
The configuration or annotation above references the TagEvent event type. This type must also be configured or created. Prefix the root element name with "//" to cause the lookup to search the nested schema elements for the definition of the type:
ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM tagcfg = new ConfigurationCommonEventTypeXMLDOM();
tagcfg.setRootElementName("//Tag");
tagcfg.setSchemaResource(schemaURL);
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.getCommon().addEventType("TagEvent", tagcfg);
The tagOne and tagArray properties are now ready for selection and transposing to further streams:
insert into TagOneStream select tagOne.* from SensorEvent
Select from the new stream:
select ID from TagOneStream
An example with indexed properties is shown next:
insert into TagArrayStream select tagArray as mytags from SensorEvent
Select from the new stream:
select mytags[0].ID from TagArrayStream
Further information on using create xml schema with XMLSchema, XMLSchemaNamespacePrefix and XMLSchemaField
can be found at Section 17.4.8, “Events Represented by org.w3c.dom.Node”.
Note
The
create xml schemastatement does not allow specifying event properties.The
create xml schemastatement does not supportcopyfromandinherits.
This section provides information for NEsper .NET users.
System.Collections.IEnumerable and System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<T> are honored in most places where a collection would be taken.
In respect to DateTime differences, the baseline for CLR datetimes is 1/1/0001 12:00:00AM. DateTimes are converted to ticks and then to milliseconds.
Annotations are implemented using .NET attributes. Annotations must derive from System.Attribute and must use .NET attribute naming conventions e.g. @Hint is implemented as HintAttribute.
NEsper provides a lock manager that is configurable once per AppDomain: com.espertech.esper.compat.threading.LockManager is used for lock provision.
Standard system locks are the default.
Spinlocks & Slimlocks may be used.
Custom lock implementations can be leveraged.
Out of the box the following are the lock implementations:
MonitorLock - uses the CLR provided object locking mechanism, equivalent to java's wait() and notify()
MonitorSpinLock - uses the CLR provided System.Threading.SpinLock
MonitorSlimLock - early model of spin lock that I built for NEsper
com.espertech.esper.compat.threading.ReaderWriterLockManager is used for RW lock management.
Standard reader writer locks are the default.
SlimReaderWriter locks are provided.
Fair & FIFO ReaderWriter lock implementations are provided but not officially supported.
ReaderWriterLocks are a separate construct and out of the box implementations include:
StandardReaderWriterLock - uses the CLR provided System.Threading.ReaderWriterLock()
SlimReaderWriterLock - uses the CLR provided System.Threading.ReaderWriterLockSlim()
FifoReaderWriterLock - built to mirror some of the Java reader writer semantics - generally not recommended and not officially supported by NEsper
FairReaderWriterLock - built to mirror some of the Java reader writer semantics - generally not recommended and not officially supported by NEsper
In NEsper there is a container that is provided or created during initialization.
DefaultReaderWriterLockManager rwLockManager = (DefaultReaderWriterLockManager) container.RWLockManager();
Once the application has the lock manager, it can set the DefaultLockTimeout property on it.
rwLockManager.DefaultLockTimeout = 1000000L;
The lock manager relies on a factory. The default factory can be overridden by setting the DefaultLockFactory property.
rwLockManager.DefaultLockFactory = (lockTImeout) => ...();
If the application would like to control this by type, it can register a specific lock factory for a given type.
rwLockManager.RegisterLockFactory(typeof(foo), (lockTimeout) => myCustomerLock());
There are no per-type lock timeouts.
com.espertech.esper.compat.threading.ThreadLocalManager is used for thread local management.
Fast thread local implementation is the default - not .NET standard.
Standard implementation is available - however, it is found significantly slower.
This section only applies to internal system-time timer and does not apply to external timer (when your application provides time).
Since often running on windows, NEsper by default relies on the high performance multimedia timer. This timer is designed to allow for synchronization to the display rate and so it can run at 1ms or better. High resolution timers are cleaned up when the AppDomain is disposed.
However, if the application is netcoreapp and since netcoreapp is designed to run in a cross platform way, one would want to rely on the standard timers provided by .NET.
In order to use an alternative timer one must configure the container (as follows). This will tell the container to create a SimpleTimerFactory. The default behavior is preserved but you can now change the behavior to use a less CPU consuming timer.
var container = ContainerExtensions.CreateDefaultContainer(false);
container.Register<ITimerFactory>(
ic => new SimpleTimerFactory(),
Lifespan.Singleton);
container
.InitializeDefaultServices()
.InitializeDatabaseDrivers();
var config = new Configuration(container);
var esperRuntime = EPRuntimeProvider.GetRuntime("URI Here", config);
The above code creates a container, registers the service(s) that an application may want, and then initializes defaults for any remaining services and database drivers.
InitializeDefaultServices() initializes the container with default services if none have been provided. So if a service of any kind is to be provided, it must be added to the container prior to calling InitializeDefaultServices().
Otherwise, the default services will be installed and will actively throw an exception if there is an attempt to replace the registered service. CreateDefaultContainer(false) does nothing more than instantiate a new Container object.
com.espertech.esper.util.EsperSectionHandler is provided to read Esper configuration from standard .NET configuration. It must be added as a configSection in order to be used.
For items not handled under the Esper configuration use com.espertech.esper.compat.CompatSettings.
These are often applied for the entire AppDomain meaning they are effectively static for the container.
These cover the following items:
DefaultLockType.DefaultReaderWriterLockType.MonitorLockTimeout.ReaderLockTimeout.WriterLockTimeout.DefaultThreadLocalType.
Table J.1. Event Underlying .NET Objects
| Java Class | Description |
|---|---|
System.Object | Any .NET object with properties. |
System.Collections.Generic.IDictionary | Map events are implementations of the IDictionary interface where each map entry is a propery value. |
System.Array, System.Object[] (array of object) | Object-array events are arrays of objects (type Object[]) where each array element is a property value. |
System.Xml.XmlNode and System.Xml.Linq.XNode | XML document object model (DOM). |
| Application classes | Plug-in event representation via the extension API. |
Event classes provide accessors (getter methods) and mutators (setter methods) by means of auto-implemented properties or read write properties.
Below an example using auto-implemented properties:
class NewEmployeeEvent {
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public Address Address { get; set; }
}Below an example using read write properties:
class NewEmployeeEvent {
private string firstName = "N/A";
private Address address = 0;
public string FirstName
{
get
{
return firstName;
}
set
{
firstName = value;
}
}
public Address Address
{
get
{
return address;
}
set
{
address = value;
}
}
}The case conversion is uppercase as dictated by .NET property conventions.
Mapped indexes are handled through the indexing operator.
For .NET the events can be represented by objects that implement the IDictionary interface.
Objects need to follow the .NET property conventions. Objects can follow modified conventions for Java-style accessors and mutators using Get and Set respectively.
There are no differences between Esper and NEsper in respect to basic concepts.
The data types are sbyte, byte, short, ushort, int, uint, long, ulong, float, double, decimal.
.NET uses ADO-based drivers to accomplish the same work.
NEsper exposes the Events events on EPStatement objects.
UpdateListener is replaced by UpdateEventHandler in .NET. Subscriber objects must implement the Update method
or subscriber objects must be a delegate with an appropriate number of arguments.
The setSubscriber method is replaced with the Subscriber property. This property can take an object or a delegate.
Iterator is replaced with GetEnumerator. SafeIterator is replaced with GetSafeEnumerator.
In NEsper you can assign a delegate to a subscriber using lamba this way:
statement.Subscriber = new Action<TradeReportEvent, NesperTest>((a, b) => {
Debug.Print("got here");
});
Listeners are replaced with UpdateEventHandlers, for example countStatement.Events += (sender, args) => { DoWork(); }.
Connections are obtained by selecting a DbDriver, which are a NEsper-construct.
DbDriverGeneric: Positional or name based driver that must be completely configured prior to use.DbDriverMySQL: Positional based driver that uses '?' prefix.DbDriverODBC: Positional based driver that uses '?' prefix.DbDriverSqlServer: Translates positional into named-based SqlParameters with '@' prefix.
Symbols
- -> pattern operator, Followed-By
A
- after, Suppressing Output With After
- aggregation functions
- custom plug-in, Aggregation Function
- overview, Aggregation Functions
- and pattern operator, And
- annotation, Annotation
- application-provided, Application-Provided Annotations
- builtin, Built-In Statement Annotations
- enumeration value, Annotations With Enumeration Values
- interrogating, Interrogating Annotations
- API
- testing, Test and Assertion Support
- arithmetic operators, Arithmetic Operators
- array definition operator, Array Definition Operator
- array element operator, Array Element Operator
- avro event representation, Event Representation: Avro Events (org.apache.avro.generic.GenericData.Record)
B
- between operator, The 'Between' Keyword
- binary operators, Binary Operators
C
- case control flow function, The Case Control Flow Function
- cast function, The Cast Function
- array, Casting Arrays
- date parsing, The Cast Function For Parsing Dates
- class loader
- compiler, OSGi, Class Loader, Class-For-Name
- runtime, OSGi, Class Loader, Class-For-Name
- class name resolution
- compiler, OSGi, Class Loader, Class-For-Name
- runtime, OSGi, Class Loader, Class-For-Name
- coalesce function, The Coalesce Function
- concatenation operators, Concatenation Operators
- configuration
- common, Configuration Common
- compiler, Configuration Compiler
- logging, Logging Configuration
- overview, Overview
- programmatic, Programmatic Configuration
- runtime, Configuration Runtime
- transient, Passing Services or Transient Objects
- via XML, Configuration via XML File
- Configuration class, Overview
- constants, Data Type of Constants, Using Constants and Enum Types
- context partition, Context Partition Administration
- correlation, Correlation Derived-Value Window (correl or stat:correl)
- create expression, Declaring Global Expressions, Aliases and Scripts: Create Expression
- create index, Explicitly Indexing Named Windows and Tables
- create schema, Declaring an Event Type: Create Schema
- create window, insert, Populating a Named Window From an Existing Named Window
- current_evaluation_context, The Current_Evaluation_Context Function
- current_timestamp function, The Current_Timestamp Function
D
- data types, Data Types
- data window
- correlation, Correlation Derived-Value Window (correl or stat:correl)
- custom plug-in view, Data Window View and Derived-Value View
- expiry expression batch window, Expiry Expression Batch Window (expr_batch or win:expr_batch)
- expiry expression window, Expiry Expression Window (expr or win:expr)
- externally-time batch window, Externally-timed Batch Window (ext_timed_batch or win:ext_timed_batch)
- externally-timed window, Externally-timed Window (ext_timed or win:ext_timed)
- first event, First Event Window (firstevent or std:firstevent)
- first length window, First Length Window(firstlength or win:firstlength)
- first time window, First Time Window (firsttime or win:firsttime)
- first unique window, First Unique Window (firstunique or std:firstunique)
- grouped data window, Grouped Data Window (groupwin or std:groupwin)
- keep-all window, Keep-All Window (keepall or win:keepall)
- last event window, Last Event Window (std:lastevent)
- length batch window, Length Batch Window (length_batch or win:length_batch)
- length window, Length Window (length or win:length)
- overview, EPL Reference: Data Windows
- ranked window, Ranked Window (rank or ext:rank)
- regression, Regression Derived-Value Window (linest or stat:linest)
- size window, Size Derived-Value Window (size) or std:size)
- sorted window, Sorted Window (sort or ext:sort)
- time batch window, Time batch Window (time_batch or win:time_batch)
- time length batch window, Time-Length Combination Batch Window (time_length_batch or win:time_length_batch)
- time window, Time Window (time or win:time)
- time-accumulating window, Time-Accumulating Window (time_accum or win:time_accum)
- time-order window, Time-Order Window (time_order or ext:time_order)
- time-to-live window, Time-To-Live Window (timetolive or ext:timetolive)
- unique window, Unique Window (unique or std:unique)
- univariate statistics, Univariate Statistics Derived-Value Window (uni or stat:uni)
- weighted average, Weighted Average Derived-Value Window (weighted_avg or stat:weighted_avg)
- dataflow, Introduction
- decorated event, Decorated Events
- delete, Deleting Data
- deployment
- J2EE, When Deploying with J2EE
- module, Module
- derived-value window
- overview, EPL Reference: Data Windows
- dot operator, Dot Operator
- duck typing, Dot Operator
- dynamic event properties, Dynamic Event Properties
E
- enum types, Using Constants and Enum Types
- EPDeploymentService interface, Deploying and Undeploying Using EPDeploymentService
- EPEventService interface, Processing Events and Time Using EPEventService
- EPFireAndForgetService interface, Execute Fire-and-Forget Queries Using EPFireAndForgetService
- EPL
- from clause, Specifying Event Streams: The From Clause
- group by clause, Organizing Statement Results into Groups: The Group-by Clause
- having clause, Selecting Groups of Events: The Having Clause
- initializing
- initializing, Initializing Table Columns and Aggregation State
- inner join, Outer, Left and Right Joins
- insert into clause, Merging Streams and Continuous Insertion: The Insert Into Clause
- join, Joining Event Streams
- join, unidirectional, Unidirectional Joins
- joining non-relational data via method, script or UDF invocation, Accessing Non-Relational Data via Method, Script or UDF Invocation
- joining relational data via SQL, Accessing Relational Data via SQL
- limit clause, Limiting Row Count: the Limit Clause
- named window, Named Window Overview
- deleting from, Deleting Data: The On Delete Clause, Deleting Data
- inserting into, Inserting Into Named Windows, Inserting Data
- populating from a named window, Populating a Named Window From an Existing Named Window
- selecting from, Selecting From Named Windows
- triggered select and delete using On Select Delete, Triggered Select+Delete: The On Select Delete Clause
- triggered select using On Select, Triggered Select: The On Select Clause
- updating, Updating Data: The On Update Clause, Updating Data
- order by clause, Sorting Output: the Order By Clause
- outer join, Outer, Left and Right Joins
- outer join, unidirectional, Unidirectional Joins, Unidirectional Full Outer Joins
- output control and stabilizing, Stabilizing and Controlling Output: The Output Clause
- select clause, Choosing Event Properties and Events: The Select Clause
- subqueries, Subqueries
- table, Table Overview
- initializing, Resetting Table Columns and Aggregation State, Initializing Table Columns and Aggregation State
- inserting into, Inserting Into Tables
- resetting, Resetting Table Columns and Aggregation State
- selecting from, Selecting From Tables
- variable, Variables and Constants
- where clause, Specifying Search Conditions: The Where Clause
- EPRuntime class, The EPRuntime Runtime Interface
- EPRuntimeProvider class, Obtaining a Runtime From EPRuntimeProvider
- EPStatement interface, Deploying and Undeploying Using EPDeploymentService
- EPStatementObjectModel interface, Statement Object Model
- EPType Interface, Type Information
- escape, Escaping Strings
- event
- Avro representation, Event Representation: Avro Events (org.apache.avro.generic.GenericData.Record)
- bulk, Coarse-Grained Events
- coarse, Coarse-Grained Events
- dynamic properties, Dynamic Event Properties
- insert into, Event Objects Instantiated and Populated by Insert Into
- Java object, Event Representation: Plain-Old Java Object Events
- JSON representation, Event Representation: JSON Events
- Map representation, Event Representation: java.util.Map Events
- Object-array representation, Event Representation: Object-Array (Object[]) Events
- properties, Event Properties
- underlying representation, Event Underlying Java Objects
- update, Updating, Merging and Versioning Events
- version, Updating, Merging and Versioning Events
- XML representation, Event Representation: org.w3c.dom.Node XML Events
- event as a property, Event as a Property
- Event Property Type, Type Information
- event time, Controlling Time-Keeping
- event type
- declaring, Declaring an Event Type: Create Schema
- event_identity_equals function, The Event_Identity_Equals Function
- EventBean interface, Event and Event Type
- EventType interface, Event and Event Type
- every pattern operator, Every
- every-distinct pattern operator, Every-Distinct
- exists function, The Exists Function
- expression
- expression alias, Expression Alias
- expression batch window, Expiry Expression Batch Window (expr_batch or win:expr_batch)
- expression declaration, Expression Declaration
- expression window, Expiry Expression Window (expr or win:expr)
- external time, Controlling Time-Keeping
- externally-timed batch window, Externally-timed Batch Window (ext_timed_batch or win:ext_timed_batch)
- externally-timed window, Externally-timed Window (ext_timed or win:ext_timed)
F
- first event, First Event Window (firstevent or std:firstevent)
- first length window, First Length Window(firstlength or win:firstlength)
- first time window, First Time Window (firsttime or win:firsttime)
- first unique window, First Unique Window (firstunique or std:firstunique)
- followed-by pattern operator, Followed-By
- from clause, Specifying Event Streams: The From Clause
- functions
- case control flow, The Case Control Flow Function
- cast, The Cast Function
- coalesce, The Coalesce Function
- current_evaluation_context, The Current_Evaluation_Context Function
- current_timestamp, The Current_Timestamp Function
- event_identity_equals, The Event_Identity_Equals Function
- exists, The Exists Function
- grouping, The Grouping Function
- grouping_id, The Grouping_Id Function
- instance-of, The Instance-Of Function
- istream, The Istream Function
- max, The Min and Max Functions
- min, The Min and Max Functions
- previous, The Previous Function
- previous count, The Previous-Count Function
- previous tail, The Previous-Tail Function
- previous window, The Previous-Window Function
- prior, The Prior Function
- type-of, The Type-Of Function
- user-defined, Single-Row Function Reference, User-Defined Functions
G
- Generic Type, Type Information
- group by clause, Organizing Statement Results into Groups: The Group-by Clause
- grouping function, The Grouping Function
- grouping_id function, The Grouping_Id Function
- groupwin window, Grouped Data Window (groupwin or std:groupwin)
H
- having clause, Selecting Groups of Events: The Having Clause
I
- in set operator, The 'In' Keyword
- index
- spatial, Spatial Index - Quadtree
- inlined-class declaration, Inlined-Class Declaration, Overview
- inner join, Outer, Left and Right Joins
- insert, Inserting Data
- insert into clause, Merging Streams and Continuous Insertion: The Insert Into Clause
- instance-of function, The Instance-Of Function
- istream, The Istream Function
- iterator, Using Iterators
J
- JavaScript, Overview
- join, Joining Event Streams
- from clause, Specifying Event Streams: The From Clause
- non-relational data via method, script or UDF invocation, Accessing Non-Relational Data via Method, Script or UDF Invocation
- relational data via SQL, Accessing Relational Data via SQL
- JSON event representation, Event Representation: JSON Events
K
- keep-all window, Keep-All Window (keepall or win:keepall)
- keywords, Reserved Keywords
L
- lambda
- expression alias, Expression Alias
- expression declaration, Expression Declaration
- last event window, Last Event Window (std:lastevent)
- length batch window, Length Batch Window (length_batch or win:length_batch)
- length window, Length Window (length or win:length)
- like operator, The 'Like' Keyword
- limit clause, Limiting Row Count: the Limit Clause
- limiting output row count, Limiting Row Count: the Limit Clause
- literals, Data Type of Constants
- logical and comparison operators, Logical and Comparison Operators
M
- map event representation, Event Representation: java.util.Map Events
- match recognize
- comparison, Comparison of Match Recognize and EPL Patterns
- overview, Overview
- match_recognize
- operator precedences, Operator Precedence
- max function, The Min and Max Functions
- maximum-by, Maxby Aggregation Function
- merge, Triggered Upsert Using the On-Merge Clause
- method
- spatial, Spatial Methods
- methods
- aggregation, Overview
- date-time, Overview
- plug-in, Date-Time Method
- enumeration, Overview
- plug-in, Enumeration Method
- min function, The Min and Max Functions
- minimum-by, Minby Aggregation Function
- MVEL, Overview
N
- named window, Named Window Overview
- create index, Explicitly Indexing Named Windows and Tables
- deleting from, Deleting Data: The On Delete Clause, Deleting Data
- index, Explicitly Indexing Named Windows and Tables
- inserting into, Inserting Into Named Windows, Inserting Data
- merge, Triggered Upsert Using the On-Merge Clause
- populating from a named window, Populating a Named Window From an Existing Named Window
- selecting from, Selecting From Named Windows
- triggered select and delete using On Select Delete, Triggered Select+Delete: The On Select Delete Clause
- triggered select using On Select, Triggered Select: The On Select Clause
- updating, Updating Data: The On Update Clause, Updating Data
- upsert, Triggered Upsert Using the On-Merge Clause
- named windows
- overview, Overview
- new, The 'New' Keyword
- not pattern operator, Not
O
- object-array event representation, Event Representation: Object-Array (Object[]) Events
- on-delete, Deleting Data: The On Delete Clause
- on-select, Triggered Select: The On Select Clause
- on-select-delete, Triggered Select+Delete: The On Select Delete Clause
- on-update, Updating Data: The On Update Clause
- operators
- arithmetic, Arithmetic Operators
- array definition, Array Definition Operator
- array element, Array Element Operator
- between, The 'Between' Keyword
- binary, Binary Operators
- concatenation, Concatenation Operators
- dot (period), Dot Operator
- in, The 'In' Keyword
- like, The 'Like' Keyword
- logical and comparison, Logical and Comparison Operators
- new, The 'New' Keyword
- regexp, The 'Regexp' Keyword
- or pattern operator, Or
- order by clause, Sorting Output: the Order By Clause
- ordered, Sorted Aggregation Function
- ordering output, Sorting Output: the Order By Clause
- OSGi
- compiler, OSGi, Class Loader, Class-For-Name
- runtime, OSGi, Class Loader, Class-For-Name
- outer join, Outer, Left and Right Joins
- output
- snapshot, Output Snapshot
- suppressing output, Suppressing Output With After
- output control and stabilizing clause, Stabilizing and Controlling Output: The Output Clause
- output ordering, Sorting Output: the Order By Clause
- output row count, Limiting Row Count: the Limit Clause
- output when, Controlling Output Using an Expression
P
- packaging
- J2EE, When Deploying with J2EE
- module, Module
- Parameterized Type, Type Information
- pattern
- filter event consumption, Controlling Event Consumption
- filter expressions, Filter Expressions in Patterns
- named window, Use With Named Windows and Tables
- operator precedences, Operator Precedence
- overview, Event Pattern Overview
- table, Use With Named Windows and Tables
- walkthrough, Event Pattern Walkthrough
- pattern atom, Pattern Atoms
- pattern guard, Pattern Guards
- custom plug-in, Pattern Guard
- timer-within, The timer:within Pattern Guard
- timer-withinmax, The timer:withinmax Pattern Guard
- while, The while Pattern Guard
- pattern observer
- custom plug-in, Pattern Observer
- timer-at, Crontab (timer:at)
- timer-interval, Interval (timer:interval)
- timer-schedule, Schedule (timer:schedule)
- pattern operator
- and, And
- every, Every
- every-distinct, Every-Distinct
- followed-by, Followed-By
- not, Not
- or, Or
- PERL, Overview
- PHP, Overview
- plug-in
- custom aggregation function, Aggregation Function
- custom pattern guard, Pattern Guard
- custom pattern observer, Pattern Observer
- custom view, Data Window View and Derived-Value View
- date-time method, Date-Time Method
- enumeration method, Enumeration Method
- single-row function, Single-Row Function
- plug-in loader, Plug-In Loader
- previous count function, The Previous-Count Function
- previous function, The Previous Function
- previous tail function, The Previous-Tail Function
- previous window function, The Previous-Window Function
- prior function, The Prior Function
- pull API, Using Iterators
- Python, Overview
R
- ranked window, Ranked Window (rank or ext:rank)
- regexp operator, The 'Regexp' Keyword
- regression, Regression Derived-Value Window (linest or stat:linest)
- relational databases, Accessing Relational Data via SQL
- Ruby, Overview
S
- safe iterator, Using Iterators
- script
- script declaration, Script Declaration, Overview
- select clause, Choosing Event Properties and Events: The Select Clause
- single-row functions
- custom plug-in, Single-Row Function
- size window, Size Derived-Value Window (size) or std:size)
- sorted, Sorted Aggregation Function
- sorted window, Sorted Window (sort or ext:sort)
- spatial
- functions, Spatial Types, Functions and Methods from External Libraries
- index, Spatial Index - Quadtree
- intro, Overview
- method, Spatial Methods
- methods (external library), Spatial Types, Functions and Methods from External Libraries
- types, Spatial Types, Functions and Methods from External Libraries
- SQL, Accessing Relational Data via SQL
- statement
- receiving results, Receiving Statement Results
- subscriber object, Setting a Subscriber Object
- static Java methods, Single-Row Function Reference
- subqueries, Subqueries
- subscriber object, Setting a Subscriber Object
- EPStatement, Using the EPStatement Parameter
- multi-row, Multi-Row Delivery
- no-parameter, No-Parameter Update Method
- row-by-row, Row-by-Row Delivery
T
- table, Table Overview
- create index, Explicitly Indexing Named Windows and Tables
- deleting from, Deleting Data
- index, Explicitly Indexing Named Windows and Tables
- initializing, Resetting Table Columns and Aggregation State, Initializing Table Columns and Aggregation State
- inserting into, Inserting Into Tables, Inserting Data
- merge, Triggered Upsert Using the On-Merge Clause
- resetting, Resetting Table Columns and Aggregation State
- selecting from, Selecting From Tables
- updating, Updating Data
- upsert, Triggered Upsert Using the On-Merge Clause
- tables
- overview, Overview
- testing, Test and Assertion Support
- threading, Runtime Threading and Concurrency
- time
- controlling, Controlling Time-Keeping
- resolution, Time Resolution and Time Unit
- time batch window, Time batch Window (time_batch or win:time_batch)
- time length batch window, Time-Length Combination Batch Window (time_length_batch or win:time_length_batch)
- time window, Time Window (time or win:time)
- time-accumulating window, Time-Accumulating Window (time_accum or win:time_accum)
- time-order window, Time-Order Window (time_order or ext:time_order)
- time-to-live window, Time-To-Live Window (timetolive or ext:timetolive)
- timer-at pattern observer, Crontab (timer:at)
- timer-interval pattern observer, Interval (timer:interval)
- timer-schedule pattern observer, Schedule (timer:schedule)
- timer-within pattern guard, The timer:within Pattern Guard
- timer-withinmax pattern guard, The timer:withinmax Pattern Guard
- type-of function, The Type-Of Function
U
- UDF
- user-defined function, User-Defined Functions
- unidirectional full outer joins, Unidirectional Full Outer Joins
- unidirectional joins, Unidirectional Joins
- unique window, Unique Window (unique or std:unique)
- univariate statistics, Univariate Statistics Derived-Value Window (uni or stat:uni)
- UnmatchedListener interface, Receiving Unmatched Events
- update, Updating Data
- UpdateListener interface, Adding Listeners
- upsert, Triggered Upsert Using the On-Merge Clause
- user-defined function, User-Defined Functions
- user-defined single-row function, Single-Row Function Reference
V
- variable, Variables and Constants
- variant stream, Merging Disparate Types of Events: Variant Streams
W
- weighted average, Weighted Average Derived-Value Window (weighted_avg or stat:weighted_avg)
- where clause, Specifying Search Conditions: The Where Clause
- while pattern guard, The while Pattern Guard
X
- XML event representation, Event Representation: org.w3c.dom.Node XML Events